Mount Price (British Columbia) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mount Price is a small stratovolcano in the
 The Pacific Ranges Ecoregion is subdivided into seven
The Pacific Ranges Ecoregion is subdivided into seven
 Mount Price is one of the three principal volcanoes in the southern segment of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, the other two being Mount Garibaldi and The Black Tusk. Mount Price is also part of the Garibaldi Lake
Mount Price is one of the three principal volcanoes in the southern segment of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, the other two being Mount Garibaldi and The Black Tusk. Mount Price is also part of the Garibaldi Lake
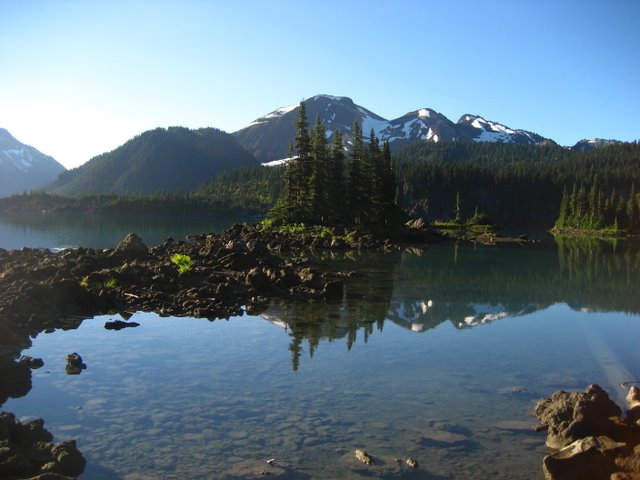
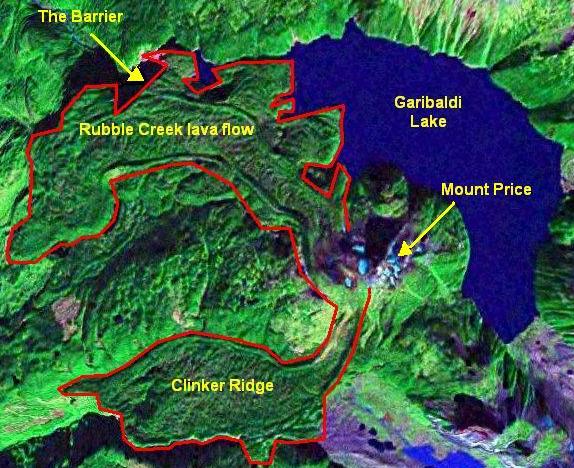 Mount Price attains an elevation of and is one of several Garibaldi Belt volcanoes that have been volcanically active throughout the Quaternary. In contrast to most stratovolcanoes in Canada, Mount Price has a nearly symmetrical structure. Its western slope is flanked by Clinker Peak, a
Mount Price attains an elevation of and is one of several Garibaldi Belt volcanoes that have been volcanically active throughout the Quaternary. In contrast to most stratovolcanoes in Canada, Mount Price has a nearly symmetrical structure. Its western slope is flanked by Clinker Peak, a
 After the Cordilleran Ice Sheet retreated from higher elevations less than 15,000 years ago, andesite eruptions of the third eruptive phase occurred from a satellite vent at Price Bay. These eruptions resulted in the creation of a small lava dome or scoria cone on Mount Price's northern flank with an elevation of . Possibly contemporaneous volcanism occurred at Clinker Peak with the eruption of two hornblende- biotite andesite lava flows. They are both at least thick and long, extending to the northwest and southwest. Their unusually large thickness is due to them ponding and cooling against the Cordilleran Ice Sheet when it still filled valleys at lower elevations. Age estimates for this final volcanic phase have varied from 15,000 years ago to as recently as 8,000 years ago.
A prominent feature of the Clinker Peak lava flows are the levees that demarcate the
After the Cordilleran Ice Sheet retreated from higher elevations less than 15,000 years ago, andesite eruptions of the third eruptive phase occurred from a satellite vent at Price Bay. These eruptions resulted in the creation of a small lava dome or scoria cone on Mount Price's northern flank with an elevation of . Possibly contemporaneous volcanism occurred at Clinker Peak with the eruption of two hornblende- biotite andesite lava flows. They are both at least thick and long, extending to the northwest and southwest. Their unusually large thickness is due to them ponding and cooling against the Cordilleran Ice Sheet when it still filled valleys at lower elevations. Age estimates for this final volcanic phase have varied from 15,000 years ago to as recently as 8,000 years ago.
A prominent feature of the Clinker Peak lava flows are the levees that demarcate the
 Mount Price is one of the four highest threat volcanoes in Canada situated within close proximity to major populations with critical civil and economic infrastructure, the other three being Mount Meager, Mount Garibaldi and Mount Cayley. Although Plinian eruptions have not been identified at Mount Price, Peléan eruptions can also produce large amounts of
Mount Price is one of the four highest threat volcanoes in Canada situated within close proximity to major populations with critical civil and economic infrastructure, the other three being Mount Meager, Mount Garibaldi and Mount Cayley. Although Plinian eruptions have not been identified at Mount Price, Peléan eruptions can also produce large amounts of  Because andesite is the main type of lava erupted from Mount Price, lava flows are a low to moderate hazard. Andesite is intermediate in
Because andesite is the main type of lava erupted from Mount Price, lava flows are a low to moderate hazard. Andesite is intermediate in
 Mount Price and its eruptive products lie within a conservation area called Garibaldi Provincial Park. Founded in 1927 as a Class A provincial park, this wilderness park covers an area of . Lying within its boundaries are a number of other volcanoes, such as Mount Garibaldi and The Black Tusk. Located north of Vancouver in the glaciated Coast Mountains, Garibaldi Provincial Park contains diverse vegetation, iridescent waters and a rich geological history. The park also has abundant wildlife, such as squirrels, chipmunks,
Mount Price and its eruptive products lie within a conservation area called Garibaldi Provincial Park. Founded in 1927 as a Class A provincial park, this wilderness park covers an area of . Lying within its boundaries are a number of other volcanoes, such as Mount Garibaldi and The Black Tusk. Located north of Vancouver in the glaciated Coast Mountains, Garibaldi Provincial Park contains diverse vegetation, iridescent waters and a rich geological history. The park also has abundant wildlife, such as squirrels, chipmunks,
Garibaldi Ranges
The Garibaldi Ranges are the next-to-southwesternmost subdivision of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains; only the North Shore Mountains are farther southwest. They lie between the valley formed by the pass between the Cheakamus River and G ...
of the Pacific Ranges
, photo = Mount Garibaldi (50997016501).jpg
, photo_size = 280px
, photo_caption = Mount Garibaldi massif as seen from Squamish
, map =
, map_image = South BC-NW USA-relief PacificRanges.png
, ...
in southwestern British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
, Canada. It has an elevation of and rises above the surrounding landscape on the western side of Garibaldi Lake
Garibaldi Lake is a turquoise-coloured alpine lake in British Columbia, Canada, located 37 km (23 mi) north of Squamish and 19 km (12 mi) south of Whistler. The lake lies within Garibaldi Provincial Park, which features mount ...
in New Westminster Land District
The New Westminster Land District is one of 59 land districts of British Columbia, Canada, which are the underlying cadastral divisions of that province, created with rest of those on Mainland British Columbia via the ''Lands Act'' of the Colony ...
. The mountain contains a number of subfeatures, including Clinker Peak on its western flank, which was the source of two thick lava flows between 15,000 and 8,000 years ago that ponded against glacial ice. These lava flows are structurally unstable, having produced large landslides
Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of environments, ...
as recently as the 1850s. A large provincial park
Ischigualasto Provincial Park
A provincial park (or territorial park) is a park administered by one of the provinces of a country, as opposed to a national park. They are similar to state parks in other countries. They are typically open to t ...
surrounds Mount Price and other volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the Crust (geology), crust of a Planet#Planetary-mass objects, planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Ear ...
es in its vicinity. It lies within an ecological region that surrounds much of the Pacific Ranges.
Mount Price is associated with a small group of volcanoes called the Garibaldi Lake volcanic field
The Garibaldi Lake volcanic field is a volcanic field, located in British Columbia, Canada. It was formed by a group of nine small andesitic stratovolcanoes and basaltic andesite vents in the scenic Garibaldi Lake area immediately north of Mo ...
. This forms part of the larger Garibaldi Volcanic Belt
The Garibaldi Volcanic Belt is a northwest–southeast trending volcanic chain in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains that extends from Watts Point in the south to the Ha-Iltzuk Icefield in the north. This chain of volcanoes is located in ...
, a north−south trending volcanic zone that represents a portion of the Canadian Cascade Arc. Mount Price began its formation 1.2million years ago and continued intermittently until sometime in the last 15,000 years. Although the mountain is not known to have been volcanically active for thousands of years, it could erupt again, which would potentially endanger the nearby populace. If this were to happen, relief efforts could be organized by teams such as the Interagency Volcanic Event Notification Plan
The Interagency Volcanic Event Notification Plan (IVENP) is a program in Canada established to outline the notification procedure of some of the main agencies that would be involved in response to a volcanic eruption in Canada, an eruption close to ...
who are prepared to notify people threatened by volcanic eruptions in Canada.
Geography
Mount Price is located south of Whistler on the western side of Garibaldi Lake in New Westminster Land District. It lies within the Pacific Ranges Ecoregion, a mountainous region of the southern Coast Mountains characterized by high, steep and rugged mountains made ofgranitic
A granitoid is a generic term for a diverse category of coarse-grained igneous rocks that consist predominantly of quartz, plagioclase, and alkali feldspar. Granitoids range from plagioclase-rich tonalites to alkali-rich syenites and from quartz- ...
rocks. Much of this ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of ...
encompasses the Pacific Ranges in southwestern British Columbia, although it also includes the northwesternmost portion of the Cascade Range in Washington state
Washington (), officially the State of Washington, is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. Named for George Washington—the first U.S. president—the state was formed from the western part of the Washington ...
. Several coastal islands, channels
Channel, channels, channeling, etc., may refer to:
Geography
* Channel (geography), in physical geography, a landform consisting of the outline (banks) of the path of a narrow body of water.
Australia
* Channel Country, region of outback Austral ...
and fjord
In physical geography, a fjord or fiord () is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Alaska, Antarctica, British Columbia, Chile, Denmark, Förden and East Jutland Fjorde, Germany, ...
s occur along the western margin of the Pacific Ranges Ecoregion. The Pacific Ranges Ecoregion is part of the Coast and Mountains Ecoprovince which forms part of the Humid Maritime and Highlands Ecodivision.
 The Pacific Ranges Ecoregion is subdivided into seven
The Pacific Ranges Ecoregion is subdivided into seven ecosection An ecosection is a biogeographic unit smaller than an ecoregion that contains minor physiographic, macroclimatic or oceanographic variations. They are a virtual ecological zone in the Canadian province of British Columbia, which contains 139 ecosec ...
s, the Eastern Pacific Ranges Ecosection being the main ecosection at Mount Price. This ecosection is characterized by a rugged landscape of mountains that increase in elevation from south to north; the northern summits contain large icefield
An ice field (also spelled icefield) is a mass of interconnected valley glaciers (also called mountain glaciers or alpine glaciers) on a mountain mass with protruding rock ridges or summits. They are often found in the colder climates and highe ...
s. A transitional climate between coastal maritime
Maritime may refer to:
Geography
* Maritime Alps, a mountain range in the southwestern part of the Alps
* Maritime Region, a region in Togo
* Maritime Southeast Asia
* The Maritimes, the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prin ...
and interior continental climates dominates the Eastern Pacific Ranges Ecosection. It is characterized by little precipitation and mild temperatures due to Pacific air often passing over this area. During winter, cold Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
air invades from the Central Interior, resulting in extreme cloud cover and snow. A number of other volcanoes are situated within the Eastern Pacific Ranges Ecosection. This includes Mount Meager, which lies near the headwaters of the Lillooet River
The Lillooet River is a major river of the southern Coast Mountains of British Columbia. It begins at Silt Lake, on the southern edge of the Lillooet Crown Icecap about 80 kilometres northwest of Pemberton and about 85 kilometres northwest of W ...
, and Mount Garibaldi
Mount Garibaldi (known as Nch'kaý to the indigenous Squamish people) is a dormant stratovolcano in the Garibaldi Ranges of the Pacific Ranges in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It has a maximum elevation of and rises above the surroun ...
and Mount Cayley
Mount Cayley is an eroded but potentially active stratovolcano in the Pacific Ranges of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. Located north of Squamish and west of Whistler, the volcano resides on the edge of the Powder Mountain Icefield. ...
, which lie in the Squamish River
The Squamish River is a short but very large river in the Canadian province of British Columbia. Its drainage basin is in size. The total length of the Squamish River is approximately .
Course
The Squamish River drains a complex of basins in the ...
watershed.
Several rivers flow through the Eastern Pacific Ranges Ecosection, including the Fraser Fraser may refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Fraser Point, South Orkney Islands
Australia
* Fraser, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb in the Canberra district of Belconnen
* Division of Fraser (Australian Capital Territory), a former federal e ...
and Coquihalla rivers on its eastern side, the Cheakamus, Squamish and Elaho rivers on its western side and the Lillooet River in the middle. Coastal western hemlock
''Tsuga heterophylla'', the western hemlock or western hemlock-spruce, is a species of hemlock native to the west coast of North America, with its northwestern limit on the Kenai Peninsula, Alaska, and its southeastern limit in northern Sonoma ...
forests dominate nearly all the valleys and lower slopes of this ecosection, the upper slopes containing subalpine
Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial f ...
mountain hemlock
''Tsuga mertensiana'', known as mountain hemlock, is a species of hemlock native to the west coast of North America, found between Southcentral Alaska and south-central California.
Description
''Tsuga mertensiana'' is a large evergreen conifer ...
forests and, to a lesser extent, Engelmann spruce
''Picea engelmannii'', with the common names Engelmann spruce, white spruce, mountain spruce, and silver spruce, is a species of spruce native to western North America. It is mostly a high-altitude mountain tree but also appears in watered canyon ...
and subalpine fir
''Abies lasiocarpa'', the subalpine fir or Rocky Mountain fir, is a western North American fir tree.
Description
''Abies lasiocarpa'' is a medium-sized evergreen conifer with a very narrow conic crown, growing to tall, exceptionally , with a t ...
forests. Alpine vegetation
Alpine plants are plants that grow in an alpine climate, which occurs at high elevation and above the tree line. There are many different plant species and taxa that grow as a plant community in these alpine tundra. These include perennial grasses, ...
lies just above the subalpine forests, which is normally overlain by barren rock. Wildlife such as grey jays, chipmunk
Chipmunks are small, striped rodents of the family Sciuridae. Chipmunks are found in North America, with the exception of the Siberian chipmunk which is found primarily in Asia.
Taxonomy and systematics
Chipmunks may be classified either as ...
s, squirrels, flickers, deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the re ...
, mountain goat
The mountain goat (''Oreamnos americanus''), also known as the Rocky Mountain goat, is a hoofed mammal endemic to mountainous areas of western North America. A subalpine to alpine species, it is a sure-footed climber commonly seen on cliffs an ...
s, wolverine
The wolverine (), (''Gulo gulo''; ''Gulo'' is Latin for " glutton"), also referred to as the glutton, carcajou, or quickhatch (from East Cree, ''kwiihkwahaacheew''), is the largest land-dwelling species of the family Mustelidae. It is a muscul ...
s, cougars and grizzly
The grizzly bear (''Ursus arctos horribilis''), also known as the North American brown bear or simply grizzly, is a population or subspecies of the brown bear inhabiting North America.
In addition to the mainland grizzly (''Ursus arctos horri ...
and black bear
Black bear or Blackbear may refer to:
Animals
* American black bear (''Ursus americanus''), a North American bear species
* Asian black bear (''Ursus thibetanus''), an Asian bear species
Music
* Black Bear (band), a Canadian First Nations group ...
s are locally present. The communities of Whistler, Pemberton, Mount Currie, Hope and Yale
Yale University is a private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. Established in 1701 as the Collegiate School, it is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and among the most prestigious in the wor ...
are situated within the Eastern Pacific Ranges Ecosection, all of which are connected to the Lower Mainland by a network of highways.
Geology
 Mount Price is one of the three principal volcanoes in the southern segment of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, the other two being Mount Garibaldi and The Black Tusk. Mount Price is also part of the Garibaldi Lake
Mount Price is one of the three principal volcanoes in the southern segment of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, the other two being Mount Garibaldi and The Black Tusk. Mount Price is also part of the Garibaldi Lake volcanic field
A volcanic field is an area of Earth's crust that is prone to localized volcanic activity. The type and number of volcanoes required to be called a "field" is not well-defined. Volcanic fields usually consist of clusters of up to 100 volcanoes ...
. This consists of several volcanoes and lava flows that formed in the last 1.3million years; the oldest volcanic rocks are found at Mount Price and The Black Tusk. Several volcanic rocks with differing compositions are present in the Garibaldi Lake volcanic field. This includes andesite
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predo ...
, dacite
Dacite () is a volcanic rock formed by rapid solidification of lava that is high in silica and low in alkali metal oxides. It has a fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic texture and is intermediate in composition between andesite and rhyolite ...
, basaltic andesite
Basaltic andesite is a volcanic rock that is intermediate in composition between basalt and andesite. It is composed predominantly of augite and plagioclase. Basaltic andesite can be found in volcanoes around the world, including in Central Amer ...
and basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
. It is unknown when the last eruption occurred but it may have been in the early Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
. Although no hot spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by c ...
s are known in the Garibaldi area, there is evidence of anomalously high heat flow in Table Meadows just south of Mount Price and elsewhere.
Like other volcanoes in the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, Mount Price formed as a result of subduction zone volcanism. As the Juan de Fuca Plate thrusts under the North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacif ...
at the Cascadia subduction zone
The Cascadia subduction zone is a convergent plate boundary that stretches from northern Vancouver Island in Canada to Northern California in the United States. It is a very long, sloping subduction zone where the Explorer, Juan de Fuca, a ...
, it forms volcanoes and volcanic eruptions. Unlike most subduction zones worldwide, there is no deep oceanic trench
Oceanic trenches are prominent long, narrow topographic depressions of the ocean floor. They are typically wide and below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor, but can be thousands of kilometers in length. There are about of oceanic tren ...
along the continental margin
A continental margin is the outer edge of continental crust abutting oceanic crust under coastal waters. It is one of the three major zones of the ocean floor, the other two being deep-ocean basins and mid-ocean ridges. The continental margi ...
of Cascadia. There is also very little seismic evidence that the Juan de Fuca Plate is actively subducting. The probable explanation lies in the rate of convergence
Convergence may refer to:
Arts and media Literature
*''Convergence'' (book series), edited by Ruth Nanda Anshen
*Convergence (comics), "Convergence" (comics), two separate story lines published by DC Comics:
**A four-part crossover storyline that ...
between the Juan de Fuca and North American plates. These two tectonic plate
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large te ...
s currently converge at a rate of per year, only about half the rate of convergence from seven million years ago. This slowed convergence likely accounts for reduced seismicity
Seismicity is a measure encompassing earthquake occurrences, mechanisms, and magnitude at a given geographical location. As such, it summarizes a region's seismic activity. The term was coined by Beno Gutenberg and Charles Francis Richter in 19 ...
and the lack of an oceanic trench. The best evidence for ongoing subduction is the existence of active volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a ...
in the Cascade Volcanic Arc
The Cascade Volcanoes (also known as the Cascade Volcanic Arc or the Cascade Arc) are a number of volcanoes in a volcanic arc in western North America, extending from southwestern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern Calif ...
.
Structure
 Mount Price attains an elevation of and is one of several Garibaldi Belt volcanoes that have been volcanically active throughout the Quaternary. In contrast to most stratovolcanoes in Canada, Mount Price has a nearly symmetrical structure. Its western slope is flanked by Clinker Peak, a
Mount Price attains an elevation of and is one of several Garibaldi Belt volcanoes that have been volcanically active throughout the Quaternary. In contrast to most stratovolcanoes in Canada, Mount Price has a nearly symmetrical structure. Its western slope is flanked by Clinker Peak, a parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
stratovolcano containing a breached volcanic crater
A volcanic crater is an approximately circular depression in the ground caused by volcanic activity. It is typically a bowl-shaped feature containing one or more vents. During volcanic eruptions, molten magma and volcanic gases rise from an und ...
. Oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a ...
of Mount Price's volcanic rock
Volcanic rock (often shortened to volcanics in scientific contexts) is a rock formed from lava erupted from a volcano. In other words, it differs from other igneous rock by being of volcanic origin. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic ...
s has given the mountain a red colour.
Mount Price stands within a cirque-like basin cut into the plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
on the south side of the valley of Garibaldi Lake. This basin consists of a wall of granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies under ...
, inclosing the volcano on its west and southwest sides. It is now almost completely filled up by Mount Price, but some small areas of its floor are exposed on the north side. The basin likely formed as a result of glacial action as its north side appears to have been almost certainly glaciated. It might otherwise have been attributed to explosive volcanism, but there are no fragmental materials around its margin which would confirm this.
Volcanic history
At least three phases of eruptive activity have been identified at Mount Price. The first eruptive phase 1.2million years ago depositedhornblende
Hornblende is a complex inosilicate series of minerals. It is not a recognized mineral in its own right, but the name is used as a general or field term, to refer to a dark amphibole. Hornblende minerals are common in igneous and metamorphic rock ...
andesite lava and pyroclastic rock
Pyroclastic rocks (derived from the el, πῦρ, links=no, meaning fire; and , meaning broken) are clastic rocks composed of rock fragments produced and ejected by explosive volcanic eruptions. The individual rock fragments are known as pyroc ...
s on the floor of the cirque-like basin after an Early Pleistocene glacial event. During the Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, widely known by its previous designation of Middle Pleistocene, is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. Th ...
about 300,000 years ago, volcanism of the second phase shifted westward and constructed the nearly symmetrical stratovolcano of Mount Price. Episodic eruptions during this phase of activity produced andesite and dacite lavas, as well as pyroclastic flow
A pyroclastic flow (also known as a pyroclastic density current or a pyroclastic cloud) is a fast-moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter (collectively known as tephra) that flows along the ground away from a volcano at average speeds of b ...
s from Peléan activity. Later, the volcano was overridden by the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which covered a large portion of western North America during glacial period
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betwe ...
s of the Quaternary.
 After the Cordilleran Ice Sheet retreated from higher elevations less than 15,000 years ago, andesite eruptions of the third eruptive phase occurred from a satellite vent at Price Bay. These eruptions resulted in the creation of a small lava dome or scoria cone on Mount Price's northern flank with an elevation of . Possibly contemporaneous volcanism occurred at Clinker Peak with the eruption of two hornblende- biotite andesite lava flows. They are both at least thick and long, extending to the northwest and southwest. Their unusually large thickness is due to them ponding and cooling against the Cordilleran Ice Sheet when it still filled valleys at lower elevations. Age estimates for this final volcanic phase have varied from 15,000 years ago to as recently as 8,000 years ago.
A prominent feature of the Clinker Peak lava flows are the levees that demarcate the
After the Cordilleran Ice Sheet retreated from higher elevations less than 15,000 years ago, andesite eruptions of the third eruptive phase occurred from a satellite vent at Price Bay. These eruptions resulted in the creation of a small lava dome or scoria cone on Mount Price's northern flank with an elevation of . Possibly contemporaneous volcanism occurred at Clinker Peak with the eruption of two hornblende- biotite andesite lava flows. They are both at least thick and long, extending to the northwest and southwest. Their unusually large thickness is due to them ponding and cooling against the Cordilleran Ice Sheet when it still filled valleys at lower elevations. Age estimates for this final volcanic phase have varied from 15,000 years ago to as recently as 8,000 years ago.
A prominent feature of the Clinker Peak lava flows are the levees that demarcate the lava channel A lava channel is a stream of fluid lava contained within zones of static (i.e., solid and stationary) lava or lava levees. The initial channel may not contain levees per se, until the parental flow solidifies over what develops into the channel and ...
s. The northwest lava flow forms a volcanic dam
A volcanic dam is a type of natural dam produced directly or indirectly by volcanism, which holds or temporarily restricts the flow of surface water in existing streams, like a man-made dam. There are two main types of volcanic dams, those create ...
known as The Barrier
The Barrier is a lava dam retaining the Garibaldi Lake system in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is over thick and about long where it impounds the lake.
The area below and adjacent to The Barrier is considered hazardous due to the u ...
. This retains the Garibaldi Lake system and has been the source of two large landslides in the past. The most recent major landslide in 1855–1856 resulted from failure along vertical rock fractures. It travelled down Rubble Creek
Rubble Creek is a creek in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It flows northwest from Garibaldi Lake into the Cheakamus River near the abandoned settlement of Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he ...
to the Cheakamus River valley, depositing of rock. The southwest lava flow is in the upper reaches of the Culliton Creek valley and forms Clinker Ridge. Both lava flows form steep cliffs; the current face of The Barrier is a result of the mid-19th century landslide.
Volcanic hazards
 Mount Price is one of the four highest threat volcanoes in Canada situated within close proximity to major populations with critical civil and economic infrastructure, the other three being Mount Meager, Mount Garibaldi and Mount Cayley. Although Plinian eruptions have not been identified at Mount Price, Peléan eruptions can also produce large amounts of
Mount Price is one of the four highest threat volcanoes in Canada situated within close proximity to major populations with critical civil and economic infrastructure, the other three being Mount Meager, Mount Garibaldi and Mount Cayley. Although Plinian eruptions have not been identified at Mount Price, Peléan eruptions can also produce large amounts of volcanic ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, created during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to refer ...
that could significantly affect the nearby communities of Whistler and Squamish. Peléan eruptions might cause short and long term water supply problems for the city of Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the ...
and most of the Lower Mainland. The catchment area
In human geography, a catchment area is the area from which a location, such as a city, service or institution, attracts a population that uses its services and economic opportunities. Catchment areas may be defined based on from where people are ...
for the Greater Vancouver watershed is downwind from Mount Price. An eruption producing floods and lahars could destroy parts of Highway 99, threaten communities such as Brackendale and endanger water supplies from Pitt Lake
Pitt Lake is the second-largest lake in the Lower Mainland of British Columbia. About in area, it is about long and about wide at its widest. It is one of the world's relatively few tidal lakes, and among the largest. In Pitt Lake, there is o ...
. Fisheries on the Pitt River
The Pitt River in British Columbia, Canada is a large tributary of the Fraser River, entering it a few miles upstream from New Westminster and about 25 km ESE of Downtown Vancouver. The river, which begins in the Garibaldi Ranges of the Co ...
would also be at risk. Mount Price is also close to a major air traffic route; volcanic ash reduces visibility and can cause jet engine failure, as well as damage to other aircraft systems. These volcanic hazards
A volcanic hazard is the probability a volcanic eruption or related geophysical event will occur in a given geographic area and within a specified window of time. The risk that can be associated with a volcanic hazard depends on the proximity and ...
become more serious as the Lower Mainland grows in population.
 Because andesite is the main type of lava erupted from Mount Price, lava flows are a low to moderate hazard. Andesite is intermediate in
Because andesite is the main type of lava erupted from Mount Price, lava flows are a low to moderate hazard. Andesite is intermediate in silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
content, indicating that it has a higher viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
than basaltic lava but is less viscous than dacite or rhyolite lava. As a result, andesite lava flows typically move slower than basaltic lava flows and are less likely to travel as far from their source. Dacite and rhyolite lavas are normally too viscous to flow away from a volcanic vent, resulting in the formation of lava domes. An exception is the Ring Creek dacite lava flow from Opal Cone
Opal Cone is a cinder cone located on the southeast flank of Mount Garibaldi in the Coast Mountains of British Columbia, Canada. It is the source of a long broad dacite lava flow with prominent wrinkled ridges. The lava flow is unusually long fo ...
on the southeastern flank of Mount Garibaldi, a length that is normally attained by basaltic lava flows.
Concerns about The Barrier's instability due to volcanic, tectonic
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents ...
or heavy rainfall activity prompted the provincial government
A state government is the government that controls a subdivision of a country in a federal form of government, which shares political power with the federal or national government. A state government may have some level of political autonomy, ...
to declare the area immediately below it unsafe for human habitation in 1980. This led to the evacuation of the small resort village of Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as ''Gioxeppe Gaibado''. In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as ''Jousé'' or ''Josep''. 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, pat ...
nearby and the relocation of residents to new recreational subdivisions away from the hazard zone. The area below and adjacent to The Barrier has since been referred to as the Barrier Civil Defence Zone by BC Parks. Although landslides are unlikely to happen in the near future, warning sign
A warning sign is a type of sign which indicates a potential hazard, obstacle, or condition requiring special attention. Some are traffic signs that indicate hazards on roads that may not be readily apparent to a driver.
While warning traffi ...
s are posted at the zone to make visitors aware of the potential danger and to minimize the chance of fatalities in the event of a slide. For safety reasons, BC Parks recommends visitors not to camp
Camp may refer to:
Outdoor accommodation and recreation
* Campsite or campground, a recreational outdoor sleeping and eating site
* a temporary settlement for nomads
* Camp, a term used in New England, Northern Ontario and New Brunswick to descri ...
, stop or linger in the Barrier Civil Defence Zone.
Monitoring
Like other volcanoes in the Garibaldi Lake volcanic field, Mount Price is not monitored closely enough by theGeological Survey of Canada
The Geological Survey of Canada (GSC; french: Commission géologique du Canada (CGC)) is a Canadian federal government agency responsible for performing geological surveys of the country, developing Canada's natural resources and protecting the e ...
to ascertain its activity level. The Canadian National Seismograph Network has been established to monitor earthquakes throughout Canada, but it is too far away to provide an accurate indication of activity under the mountain. It may sense an increase in seismic activity if Mount Price becomes highly restless, but this may only provide a warning for a large eruption; the system might detect activity only once the volcano has started erupting. If Mount Price were to erupt, mechanisms exist to orchestrate relief efforts. The Interagency Volcanic Event Notification Plan was created to outline the notification procedure of some of the main agencies that would respond to an erupting volcano in Canada, an eruption close to the Canada–United States border or any eruption that would affect Canada.
Human history
Protection
 Mount Price and its eruptive products lie within a conservation area called Garibaldi Provincial Park. Founded in 1927 as a Class A provincial park, this wilderness park covers an area of . Lying within its boundaries are a number of other volcanoes, such as Mount Garibaldi and The Black Tusk. Located north of Vancouver in the glaciated Coast Mountains, Garibaldi Provincial Park contains diverse vegetation, iridescent waters and a rich geological history. The park also has abundant wildlife, such as squirrels, chipmunks,
Mount Price and its eruptive products lie within a conservation area called Garibaldi Provincial Park. Founded in 1927 as a Class A provincial park, this wilderness park covers an area of . Lying within its boundaries are a number of other volcanoes, such as Mount Garibaldi and The Black Tusk. Located north of Vancouver in the glaciated Coast Mountains, Garibaldi Provincial Park contains diverse vegetation, iridescent waters and a rich geological history. The park also has abundant wildlife, such as squirrels, chipmunks, Canada jay
The Canada jay (''Perisoreus canadensis''), also known as the gray jay, grey jay, camp robber, or whisky jack, is a passerine bird of the family Corvidae. It is found in boreal forests of North America north to the tree line, and in the Rock ...
s and flickers. Garibaldi Provincial Park is named after Mount Garibaldi, which is in turn named after the Italian patriot and soldier Giuseppe Garibaldi.
Naming
Mount Price has had at least three names throughout its history. It was originally named Red Mountain for its red appearance, but the date when this name was adopted has not been cited. Another peak west ofOverlord Mountain
Overlord Mountain is a glacier-clad peak located in the Garibaldi Ranges of the Coast Mountains, in Garibaldi Provincial Park of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is the highest point of the Fitzsimmons Range, which is a subset of the Gar ...
was identified as Red Mountain on a 1923 sketch by Canadian mountaineer Neal M. Carter. To avoid confusion, the name of that mountain was changed to Fissile Peak on September 2, 1930, for its fissility. In 1952, Canadian volcanologist William Henry Mathews identified Mount Price as Clinker Mountain in the American Journal of Science. Clinker is a geological term used to describe rough lava fragments associated with 'a'a flows. The fragments are characterized by several sharp, jagged spines and are normally less than wide.
The name Mount Price appeared on a topographic map
In modern mapping, a topographic map or topographic sheet is a type of map characterized by large- scale detail and quantitative representation of relief features, usually using contour lines (connecting points of equal elevation), but histori ...
of Garibaldi Provincial Park
Garibaldi Provincial Park, also called Garibaldi Park, is a wilderness park located on the coastal mainland of British Columbia, Canada, 70 kilometres (43.5 mi) north of Vancouver. It was established in 1920 and named a Class A Provincial ...
in 1928. It later appeared on National Topographic System maps 92G and 92J in 1930 after a committee of the Garibaldi Park Board was set up to deal with nomenclature
Nomenclature (, ) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. The principles of naming vary from the relatively informal conventions of everyday speech to the internationally ag ...
. The committee requested that the Geographic Board of Canada
The Geographical Names Board of Canada (GNBC) is a national committee with a secretariat in Natural Resources Canada, part of the Government of Canada, which authorizes the names used and name changes on official federal government maps of Canada ...
adopt the name Mount Price for this mountain after Thomas E. Price, a former mountaineer and engineer of the Canadian Pacific Railway who was a member of the Garibaldi Park Board at the time of the park's formation in 1927. Price was born at Vancouver in 1887 and was a member of a mountaineering party that had climbed Mount Garibaldi by a new route in 1908. Clinker Peak and Clinker Ridge were both officially named on September 12, 1972, to retain Mount Price's earlier name, Clinker Mountain.
Geological studies
The Clinker Peak lava flows were one of the first described occurrences of lava having been impounded by glacial ice. They were the subject of significant study by William Henry Mathews, a pioneer in the study of subglacial eruptions and volcano-ice interactions in North America. In 1952, Mathews cited substantial evidence supporting the conclusion that the Clinker Peak lava flows ponded against glacial ice. This included the existence of glacially striated boulders in the lava flows,conformable
In mathematics, a matrix is conformable if its dimensions are suitable for defining some operation (''e.g.'' addition, multiplication, etc.).
Examples
* If two matrices have the same dimensions (number of rows and number of columns), they are ...
relations with glacial till
image:Geschiebemergel.JPG, Closeup of glacial till. Note that the larger grains (pebbles and gravel) in the till are completely surrounded by the matrix of finer material (silt and sand), and this characteristic, known as ''matrix support'', is d ...
, abnormal structures indicative of extrusion into standing meltwater or against ice, and widespread breccia
Breccia () is a rock composed of large angular broken fragments of minerals or rocks cemented together by a fine-grained matrix.
The word has its origins in the Italian language, in which it means "rubble". A breccia may have a variety of ...
and pillows
A pillow is a support of the body at rest for comfort, therapy, or decoration. Pillows are used in different variations by many species, including humans. Some types of pillows include throw pillows, body pillows, decorative pillows, and man ...
indicative of rapid quenching in meltwater or in water-soaked pyroclastic rocks under the ice.
Accessibility
Daisy Lake Road, north of Squamish, provides access to Garibaldi Provincial Park from Highway 99. At the end of this road is the Rubble Creek parking lot from which the Garibaldi Lake Trail extends to the Garibaldi Lake campground and ranger station. Ahiking trail
A trail, also known as a path or track, is an unpaved lane or small road usually passing through a natural area. In the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland, a path or footpath is the preferred term for a pedestrian or hiking trail. The ...
, known as the Mount Price Trail or the Mount Price Route, commences past the ranger station. This poorly marked path ascends to the shore of Garibaldi Lake and then returns inland where it traverses south along the lava flow forming The Barrier. The terrain of this part of the route is relatively rough, involving substantial scrambling
Scrambling is a mountaineering term for ascending steep terrain using one's hands to assist in holds and balance.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. It is also used to describe terrain that falls between hiking and rock climbing (as a “scrambl ...
over boulders of the lava flow. Eventually the trail reaches open terrain north of Mount Price and approaches the base of the volcano. Climbing Mount Price or Clinker Peak involves scree and snow plodding; both peaks do not require scrambling.
See also
*List of mountains of British Columbia *List of volcanoes in Canada *List of Cascade volcanoes *Volcanism of Western CanadaNotes
References
External links
* * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Price, Mount Two-thousanders of British Columbia Garibaldi Ranges Garibaldi Lake volcanic field Volcanoes of British Columbia Subduction volcanoes Quaternary volcanoes Stratovolcanoes of Canada Pleistocene North America