Most Significant Bit First on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
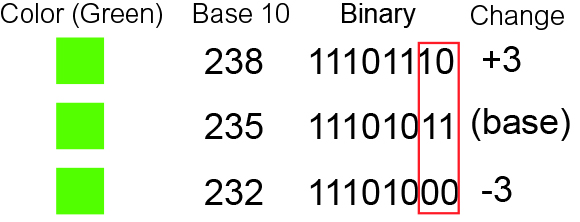 In digital steganography, sensitive messages may be concealed by manipulating and storing information in the least significant bits of an image or a sound file. The user may later recover this information by extracting the least significant bits of the manipulated pixels to recover the original message. This allows the storage or transfer of digital information to remain concealed.
In digital steganography, sensitive messages may be concealed by manipulating and storing information in the least significant bits of an image or a sound file. The user may later recover this information by extracting the least significant bits of the manipulated pixels to recover the original message. This allows the storage or transfer of digital information to remain concealed.
computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, e ...
, bit numbering is the convention used to identify the bit positions in a binary number
A binary number is a number expressed in the base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method of mathematical expression which uses only two symbols: typically "0" (zero) and "1" ( one).
The base-2 numeral system is a positional notatio ...
.
Bit significance and indexing
Incomputing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, e ...
, the least significant bit (LSB) is the bit position in a binary
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1)
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical operation that t ...
integer
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign (−1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the language ...
representing the binary 1s place of the integer. Similarly, the most significant bit (MSB) represents the highest-order place of the binary integer. The LSB is sometimes referred to as the ''low-order bit'' or ''right-most bit'', due to the convention in positional notation
Positional notation (or place-value notation, or positional numeral system) usually denotes the extension to any base of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system (or decimal system). More generally, a positional system is a numeral system in which the ...
of writing less significant digits further to the right. The MSB is similarly referred to as the ''high-order bit'' or ''left-most bit''. In both cases, the LSB and MSB correlate directly to the least significant digit
Digit may refer to:
Mathematics and science
* Numerical digit, as used in mathematics or computer science
** Hindu-Arabic numerals, the most common modern representation of numerical digits
* Digit (anatomy), the most distal part of a limb, such ...
and most significant digit of a decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers of the Hindu–Arabic numeral ...
integer.
Bit indexing correlates to the positional notation of the value in base 2. For this reason, bit index is not affected by how the value is stored on the device, such as the value's byte order
In computing, endianness, also known as byte sex, is the order or sequence of bytes of a word of digital data in computer memory. Endianness is primarily expressed as big-endian (BE) or little-endian (LE). A big-endian system stores the most sig ...
. Rather, it is a property of the numeric value in binary itself. This is often utilized in programming via bit shifting: A value of 1 << ''n'' corresponds to the ''n''th bit of a binary integer (with a value of 2n).
Least significant bit in digital steganography
 In digital steganography, sensitive messages may be concealed by manipulating and storing information in the least significant bits of an image or a sound file. The user may later recover this information by extracting the least significant bits of the manipulated pixels to recover the original message. This allows the storage or transfer of digital information to remain concealed.
In digital steganography, sensitive messages may be concealed by manipulating and storing information in the least significant bits of an image or a sound file. The user may later recover this information by extracting the least significant bits of the manipulated pixels to recover the original message. This allows the storage or transfer of digital information to remain concealed.
Unsigned integer example
This table illustrates an example of decimal value of 149 and the location of LSB. In this particular example, the position of unit value (decimal 1 or 0) is located in bit position 0 (n = 0). MSB stands for ''most significant bit'', while LSB stands for ''least significant bit''.Most- vs least-significant bit first
The expressions ''most significant bit first'' and ''least significant bit at last'' are indications on the ordering of the sequence of the bits in the bytes sent over a wire in a serial transmission protocol or in a stream (e.g. an audio stream). ''Most significant bit first'' means that the most significant bit will arrive first: hence e.g. the hexadecimal number0x12, 00010010 in binary representation, will arrive as the sequence 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 .
''Least significant bit first'' means that the least significant bit
In computing, bit numbering is the convention used to identify the bit positions in a binary number.
Bit significance and indexing
In computing, the least significant bit (LSB) is the bit position in a binary integer representing the binary 1 ...
will arrive first: hence e.g. the same hexadecimal number 0x12, again 00010010 in binary representation, will arrive as the (reversed) sequence 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0.
LSB 0 bit numbering
When the bit numbering starts at zero for theleast significant bit
In computing, bit numbering is the convention used to identify the bit positions in a binary number.
Bit significance and indexing
In computing, the least significant bit (LSB) is the bit position in a binary integer representing the binary 1 ...
(LSB) the numbering scheme is called ''LSB 0''. This bit numbering method has the advantage that for any unsigned number In computing, signedness is a property of data types representing numbers in computer programs. A numeric variable is ''signed'' if it can represent both positive and negative numbers, and ''unsigned'' if it can only represent non-negative numbers ...
the value of the number can be calculated by using exponentiation
Exponentiation is a mathematical operation, written as , involving two numbers, the '' base'' and the ''exponent'' or ''power'' , and pronounced as " (raised) to the (power of) ". When is a positive integer, exponentiation corresponds to re ...
with the bit number and a base of 2. The value of an unsigned binary integer
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign (−1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the language ...
is therefore
:
where ''bi'' denotes the value of the bit with number ''i'', and ''N'' denotes the number of bits in total.
MSB 0 bit numbering
When the bit numbering starts at zero for the most significant bit (MSB) the numbering scheme is called ''MSB 0''. The value of an unsigned binary integer is therefore :Other
ALGOL 68's elem operator is effectively "MSB 1 bit numbering" as the bits are numbered from left to right, with the first bit (bits elem 1) being the "most significant bit", and the expression (bits elem bits width) giving the "least significant bit". Similarly, when bits are coerced (typecast) to an array ofBoolean
Any kind of logic, function, expression, or theory based on the work of George Boole is considered Boolean.
Related to this, "Boolean" may refer to:
* Boolean data type, a form of data with only two possible values (usually "true" and "false" ...
(nbsp;
In word processing and digital typesetting, a non-breaking space, , also called NBSP, required space, hard space, or fixed space (though it is not of fixed width), is a space character that prevents an automatic line break at its position. In ...
''bool bits), the first element of this array (bits ''lwb bits is again the "most significant bit".
For MSB 1 numbering, the value of an unsigned binary integer is
:
PL/I numbers strings starting with 1 for the leftmost bit.
The Fortran function uses LSB 0 numbering.
See also
* ARINC 429 *Binary numeral system
A binary number is a number expressed in the base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method of mathematical expression which uses only two symbols: typically "0" (zero) and "1" ( one).
The base-2 numeral system is a positional notatio ...
* Signed number representations
* Two's complement
*Endianness
In computing, endianness, also known as byte sex, is the order or sequence of bytes of a word of digital data in computer memory. Endianness is primarily expressed as big-endian (BE) or little-endian (LE). A big-endian system stores the most sig ...
*Binary logarithm
In mathematics, the binary logarithm () is the power to which the number must be raised to obtain the value . That is, for any real number ,
:x=\log_2 n \quad\Longleftrightarrow\quad 2^x=n.
For example, the binary logarithm of is , the b ...
* Unit in the last place (ULP)
*Find first set
In computer software and hardware, find first set (ffs) or find first one is a bit operation that, given an unsigned machine word, designates the index or position of the least significant bit set to one in the word counting from the least signific ...
* MAC address: Bit-reversed notation
References
{{reflist Binary arithmetic Assembly languages