mortar shells on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
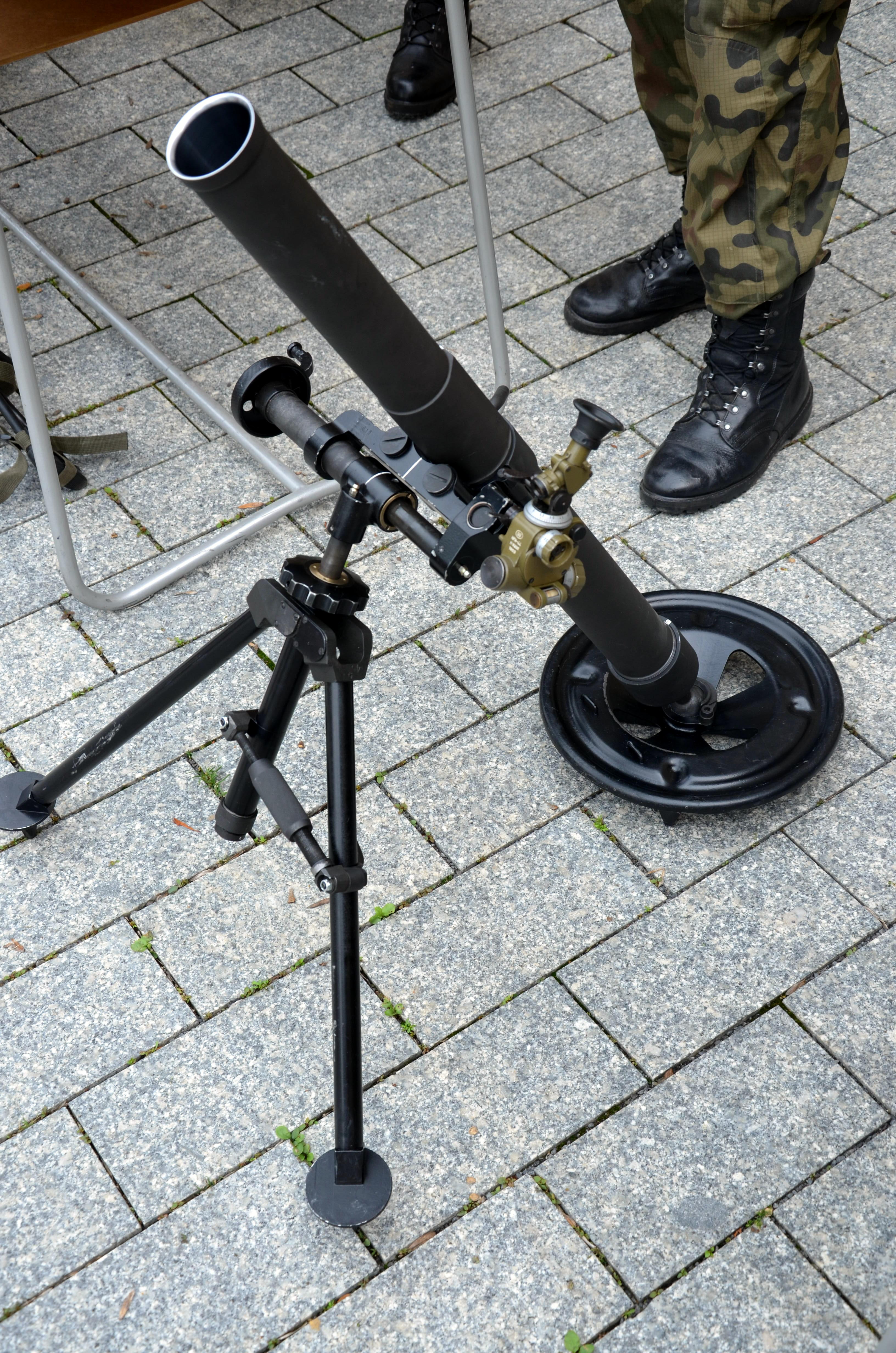 A mortar is usually a simple, lightweight, man-portable,
A mortar is usually a simple, lightweight, man-portable,
 Early mortars, such as the
Early mortars, such as the
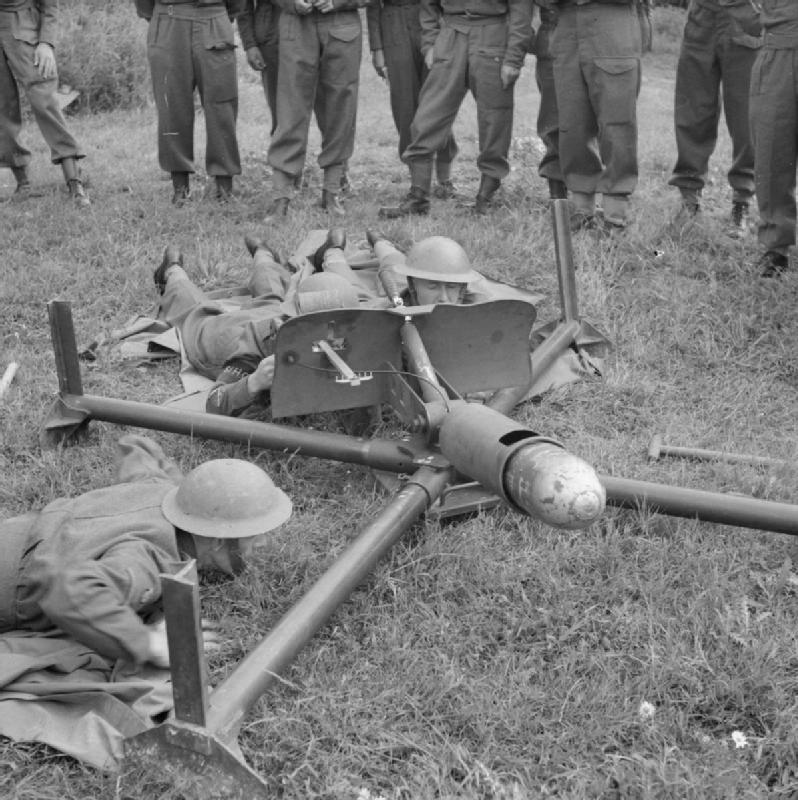
 It was not until the Stokes mortar was devised by Sir
It was not until the Stokes mortar was devised by Sir

 Gun-mortars are breech-loaded mortars usually equipped with a
Gun-mortars are breech-loaded mortars usually equipped with a
 A spigot mortar consists mainly of a solid rod or
A spigot mortar consists mainly of a solid rod or  Spigot mortars are generally out of favour in modern usage, replaced by small conventional mortars. Military applications of spigot mortars include:
* The 230 mm petard mortar used on the
Spigot mortars are generally out of favour in modern usage, replaced by small conventional mortars. Military applications of spigot mortars include:
* The 230 mm petard mortar used on the 

 Most modern mortar systems consist of four main components: a barrel, a base plate, a bipod and a sight. Modern mortars normally range in
Most modern mortar systems consist of four main components: a barrel, a base plate, a bipod and a sight. Modern mortars normally range in

- Army.mil, 29 March 2011 The Strix mortar round is a Swedish endphase-guided projectile fired from a 120 mm mortar currently manufactured by
File:RoaringMegFront.jpg, Roaring Meg on display at Goodrich Castle
File:LittleDavid.ogv, World War II US Army propaganda movie footage of the 914 mm "Little David" mortar
A Guide to Modern Mortar Systems
* * *
How does a Mortar work? - Visualization (Video)
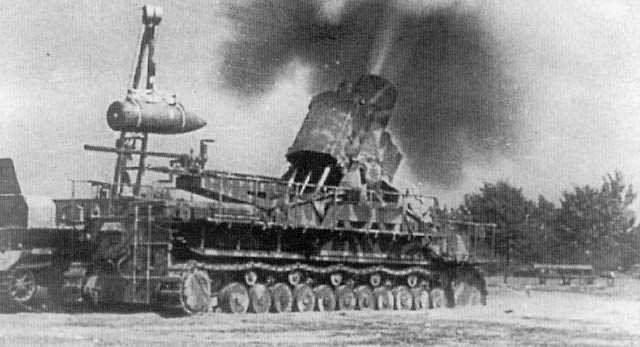
WW II-era German 60 cm self-propelled mortar.
Video
(streaming wmv) {{DEFAULTSORT:Mortar (Weapon) *Mortar Korean inventions
muzzle-loaded
A muzzleloader is any firearm into which the projectile and the propellant charge is loaded from the muzzle of the gun (i.e., from the forward, open end of the gun's barrel). This is distinct from the modern (higher tech and harder to make) desig ...
weapon, consisting of a smooth-bore
A smoothbore weapon is one that has a barrel without rifling. Smoothbores range from handheld firearms to powerful tank guns and large artillery mortars.
History
Early firearms had smoothly bored barrels that fired projectiles without signi ...
(although some models use a rifled barrel
In firearms, rifling is machining helical grooves into the internal (bore) surface of a gun's barrel for the purpose of exerting torque and thus imparting a spin to a projectile around its longitudinal axis during shooting to stabilize the pro ...
) metal tube fixed to a base plate (to spread out the recoil
Recoil (often called knockback, kickback or simply kick) is the rearward thrust generated when a gun is being discharged. In technical terms, the recoil is a result of conservation of momentum, as according to Newton's third law the force requ ...
) with a lightweight bipod
A bipod is a V-shaped portable attachment that helps support and steady a device, usually a weapon such as a long gun or a mortar. The term comes from the Latin prefix ''bi-'' and Greek root ''pod'', meaning "two" and "foot" respectively.
Bipod ...
mount and a sight
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding Biophysical environment, environment through photopic vision (daytime vision), color vision, scotopic vision (night vision), and mesopic vision (twilight vision), using light in the ...
. They launch explosive shells (technically called bombs) in high-arcing ballistic trajectories. Mortars are typically used as indirect fire
Indirect fire is aiming and firing a projectile without relying on a direct line of sight between the gun and its target, as in the case of direct fire. Aiming is performed by calculating azimuth and inclination, and may include correcting aim by ...
weapons for close fire support
Fire support is defined by the United States Department of Defense as " Fires that directly support land, maritime, amphibious, and special operations forces to engage enemy forces, combat formations, and facilities in pursuit of tactical and ope ...
with a variety of ammunition.
History
Mortars have been used for hundreds of years. The earliest mortars were used in Korea in a 1413 naval battle when Korean gunsmiths developed the ''wan'gu'' (gourd-shaped mortar) (완구, 碗口). The earliest version of the ''wan'gu'' dates back to 1407. Choi Hae-san (최해산, 崔海山) (1380–1443), the son ofChoe Mu-seon
Choe Mu-Seon (1325–1395) was a medieval Korean scientist, inventor, and military commander during the late Goryeo Dynasty and early Joseon Dynasty. He is best known for enabling Korea to domestically produce gunpowder by obtaining a recipe ...
(최무선, 崔茂宣) (1325–1395), is generally credited with inventing the ''wan'gu''. In the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
, general Qi Jiguang
Qi Jiguang (, November 12, 1528 – January 17, 1588), courtesy name Yuanjing, art names Nantang and Mengzhu, posthumous name Wuyi, was a Chinese military general and writer of the Ming dynasty. He is best known for leading the defense on the ...
recorded the use of a mini cannon called the Hu dun pao
''Hu dun pao'' (虎蹲砲) is the name of two different missile weapons in Chinese history. In the Song dynasty (960–1279), it was a trebuchet and its name is translated into English as Crouching Tiger Trebuchet; in the Ming dynasty (1368–1644 ...
that was similar to the mortar.
The first use in siege warfare
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized ...
was at the 1453 siege of Constantinople by Mehmed the Conqueror
Mehmed II ( ota, محمد ثانى, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ānī; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, ابو الفتح, Ebū'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Su ...
. An Italian account of the 1456 siege of Belgrade by Giovanni da Tagliacozzo states that the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
used seven mortars that fired "stone shots one Italian mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 English ...
high". The time of flight of these was apparently long enough that casualties could be avoided by posting observers to give warning of their trajectories.
 Early mortars, such as the
Early mortars, such as the Pumhart von Steyr
The Pumhart von Steyr is a medieval large-calibre cannon from Styria, Austria, and the largest known wrought-iron bombard by caliber. It weighs around 8 tons and has a length of more than 2.5 meters. It was produced in the early 15th century and ...
, were large and heavy and could not be easily transported. Simply made, these weapons were no more than iron bowls reminiscent of the kitchen and apothecary mortars
Mortar may refer to:
* Mortar (weapon), an indirect-fire infantry weapon
* Mortar (masonry), a material used to fill the gaps between blocks and bind them together
* Mortar and pestle, a tool pair used to crush or grind
* Mortar, Bihar, a villag ...
whence they drew their name. An early transportable mortar was invented by Baron Menno van Coehoorn
Menno, Baron van Coehoorn (; March 1641 – 17 March 1704) was a Dutch soldier and engineer, regarded as one of the most significant figures in Dutch military history. In an era when siege warfare dominated military campaigns, he and his French ...
in 1701. This mortar fired an exploding shell, which had a fuse
Fuse or FUSE may refer to:
Devices
* Fuse (electrical), a device used in electrical systems to protect against excessive current
** Fuse (automotive), a class of fuses for vehicles
* Fuse (hydraulic), a device used in hydraulic systems to protect ...
that was lit by the hot gases when fired. The Coehorn
A Coehorn (also spelled ''cohorn'') is a lightweight mortar originally designed by Dutch military engineer Menno van Coehoorn.
Concept and design
Van Coehoorn came to prominence during the 1688–97 Nine Years War, whose tactics have been su ...
mortar gained quick popularity, necessitating a new form of naval ship, the bomb vessel
A bomb vessel, bomb ship, bomb ketch, or simply bomb was a type of wooden sailing naval ship. Its primary armament was not cannons ( long guns or carronades) – although bomb vessels carried a few cannons for self-defence – but mortars mounte ...
. Mortars played a significant role in the Venetian conquest of Morea
The Morea ( el, Μορέας or ) was the name of the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The name was used for the Byzantine province known as the Despotate of the Morea, by the Ottoman ...
, and in the course of this campaign an ammunition depot in the Parthenon
The Parthenon (; grc, Παρθενών, , ; ell, Παρθενώνας, , ) is a former temple on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the goddess Athena during the fifth century BC. Its decorative sculptures are considere ...
was blown up. An early use of these more mobile mortars as field artillery
Field artillery is a category of mobile artillery used to support armies in the field. These weapons are specialized for mobility, tactical proficiency, short range, long range, and extremely long range target engagement.
Until the early 20t ...
(rather than siege artillery
Siege artillery (also siege guns or siege cannons) are heavy guns designed to bombard fortifications, cities, and other fixed targets. They are distinct from field artillery and are a class of siege weapon capable of firing heavy cannonballs o ...
) was by British forces in the suppression of the Jacobite rising of 1719
The Jacobite Rising of 1719 was a failed attempt to restore the exiled James Francis Edward Stuart to the throne of Great Britain. Part of a series of Jacobite risings between 1689 to 1745, it was the only one to be supported by Spain, then at wa ...
at the Battle of Glen Shiel
The Battle of Glen Shiel ( gd, Blàr Ghleann Seile) took place on 10 June 1719 in the West Scottish Highlands, during the 1719 Jacobite Rising. A Jacobite army composed of Highland levies and Spanish marines, was defeated by British troops, rei ...
. High angle trajectory mortars held a great advantage over standard field gun
A field gun is a field artillery piece. Originally the term referred to smaller guns that could accompany a field army on the march, that when in combat could be moved about the battlefield in response to changing circumstances ( field artille ...
s in the rough terrain of the West Highlands
The Highlands ( sco, the Hielands; gd, a’ Ghàidhealtachd , 'the place of the Gaels') is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland ...
of Scotland.
The mortar had fallen out of general use in Europe by the Napoleonic era
The Napoleonic era is a period in the history of France and Europe. It is generally classified as including the fourth and final stage of the French Revolution, the first being the National Assembly, the second being the Legislative ...
, although Manby Mortars were widely used on the coast to launch lines to ships in distress, and interest in their use as a weapon was not revived until the beginning of the 20th century. Mortars were heavily used by both sides during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
. At the Siege of Vicksburg
The siege of Vicksburg (May 18 – July 4, 1863) was the final major military action in the Vicksburg campaign of the American Civil War. In a series of maneuvers, Union Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant and his Army of the Tennessee crossed the Missis ...
, General Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union Ar ...
reported making mortars "by taking logs of the toughest wood that could be found, boring them out for six- or twelve-pound shells and binding them with strong iron bands. These answered as Coehorns, and shells were successfully thrown from them into the trenches of the enemy".
During the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
, Lieutenant General Leonid Gobyato
Leonid Nikolaevich Gobyato (russian: Леонид Николаевич Гобято; 6 February 1875 – 21 May 1915) was a lieutenant-general (awarded posthumously in 1915) in the Imperial Russian Army and designer of the modern, man-porta ...
of the Imperial Russian Army
The Imperial Russian Army (russian: Ру́сская импера́торская а́рмия, tr. ) was the armed land force of the Russian Empire, active from around 1721 to the Russian Revolution of 1917. In the early 1850s, the Russian Ar ...
applied the principles of indirect fire
Indirect fire is aiming and firing a projectile without relying on a direct line of sight between the gun and its target, as in the case of direct fire. Aiming is performed by calculating azimuth and inclination, and may include correcting aim by ...
from closed firing positions in the field and, with the collaboration of General Roman Kondratenko
Roman Isidorovich Kondratenko (russian: Роман Исидорович Кондратенко; October 12, 1857 – December 15, 1904) was a general in the Imperial Russian Army famous for his devout service in the defense of Port Arthur during ...
, he designed the first mortar that fired navy shells.
The German Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwaf ...
studied the Siege of Port Arthur
The siege of Port Arthur ( ja, 旅順攻囲戦, ''Ryojun Kōisen''; russian: link=no, Оборона Порт-Артура, ''Oborona Port-Artura'', August 1, 1904 – January 2, 1905) was the longest and most violent land battle of the Russ ...
, where heavy artillery had been unable to destroy defensive structures like barbed wire and bunkers. As a result, they developed a short-barreled rifled muzzle-loading mortar called the ''Minenwerfer
''Minenwerfer'' ("mine launcher" or "mine thrower") is the German name for a class of short range mine shell launching mortars used extensively during the First World War by the Imperial German Army. The weapons were intended to be used by engine ...
''. Heavily used during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, they were made in three sizes; , and .
Types
Stokes mortar
 It was not until the Stokes mortar was devised by Sir
It was not until the Stokes mortar was devised by Sir Wilfred Stokes
Sir Frederick Wilfrid Scott Stokes, (9 April 1860 – 7 February 1927) was the inventor in 1915 of the Stokes Mortar, which saw extensive use in the latter half of the First World War and was one of the first truly portable mortars.
Stokes wa ...
in 1915 during the First World War that the modern mortar transportable by one person was born. In the conditions of trench warfare
Trench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied lines largely comprising military trenches, in which troops are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artillery. Trench warfare became a ...
, there was a great need for a versatile and easily portable weapon that could be manned by troops under cover in the trenches. Stokes' design was initially rejected in June 1915 because it was unable to use existing stocks of British mortar ammunition, and it took the intervention of David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor, (17 January 1863 – 26 March 1945) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. He was a Liberal Party politician from Wales, known for leading the United Kingdom during t ...
(at that time Minister of Munitions
The Minister of Munitions was a British government position created during the First World War to oversee and co-ordinate the production and distribution of munitions for the war effort. The position was created in response to the Shell Crisis of ...
) and Lieutenant Colonel J. C. Matheson of the Trench Warfare Supply Department (who reported to Lloyd George) to expedite manufacture of the Stokes mortar. The weapon proved to be extremely useful in the muddy trenches of the Western Front, as a mortar round could be aimed to fall directly into trench
A trench is a type of excavation or in the ground that is generally deeper than it is wide (as opposed to a wider gully, or ditch), and narrow compared with its length (as opposed to a simple hole or pit).
In geology, trenches result from ero ...
es, where artillery shells, because of their low angle of flight, could not possibly go.
The Stokes mortar was a simple muzzle-loaded weapon, consisting of a smoothbore metal tube fixed to a base plate (to absorb recoil) with a lightweight bipod
A bipod is a V-shaped portable attachment that helps support and steady a device, usually a weapon such as a long gun or a mortar. The term comes from the Latin prefix ''bi-'' and Greek root ''pod'', meaning "two" and "foot" respectively.
Bipod ...
mount. When a mortar bomb was dropped into the tube, an impact sensitive primer
Primer may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Primer'' (film), a 2004 feature film written and directed by Shane Carruth
* ''Primer'' (video), a documentary about the funk band Living Colour
Literature
* Primer (textbook), a t ...
in the base of the bomb would make contact with a firing pin at the base of the tube, and detonate, firing the bomb towards the target. The Stokes mortar could fire as many as 25 bombs per minute and had a maximum range of , firing the original cylindrical unstabilised projectile.
A modified version of the mortar, which fired a modern fin-stabilised streamlined projectile
A projectile is an object that is propelled by the application of an external force and then moves freely under the influence of gravity and air resistance. Although any objects in motion through space are projectiles, they are commonly found in ...
and had a booster charge for longer range, was developed after World War I; this was in effect a new weapon. By World War II, it could fire as many as 30 bombs per minute and had a range of over with some shell types. The French developed an improved version of the Stokes mortar as the Brandt Mle 27, further refined as the Brandt Mle 31; this design was widely copied with and without license. These weapons were the prototypes for all subsequent light mortar developments around the world.
Mortar carrier


Mortar carrier
A mortar carrier, or self-propelled mortar, is a self-propelled artillery piece in which a mortar is the primary weapon. Simpler vehicles carry a standard infantry mortar while in more complex vehicles the mortar is fully integrated into the ...
s are vehicles which carry a mortar as a primary weapon. Numerous vehicles have been used to mount mortars, from improvised civilian trucks used by insurgents
An insurgency is a violent, armed rebellion against authority waged by small, lightly armed bands who practice guerrilla warfare from primarily rural base areas. The key descriptive feature of insurgency is its asymmetric nature: small irreg ...
, to modified Infantry fighting vehicle
An infantry fighting vehicle (IFV), also known as a mechanized infantry combat vehicle (MICV), is a type of armoured fighting vehicle used to carry infantry into battle and provide direct-fire support. The 1990 Treaty on Conventional Armed Forc ...
s, such as variants of the M3 half-track
The M3 half-track was an American armored personnel carrier half-track widely used by the Allies during World War II and in the Cold War. Derived from the M2 half-track car, the M3 was extensively produced, with about 15,000 standard M3s and mo ...
and M113 armored personnel carrier, to vehicles specifically intended to carry a mortar. Simpler vehicles carry a standard infantry mortar while in more complex vehicles the mortar is fully integrated into the vehicle and cannot be dismounted from the vehicle. Mortar carriers cannot be fired while on the move, and some must be dismounted to fire.
There are numerous armoured fighting vehicle
An armoured fighting vehicle (AFV) is an armed combat vehicle protected by armour, generally combining operational mobility with offensive and defensive capabilities. AFVs can be wheeled or tracked. Examples of AFVs are tanks, armoured car ...
s and even main battle tank
A main battle tank (MBT), also known as a battle tank or universal tank, is a tank that fills the role of armor-protected direct fire and maneuver in many modern armies. Cold War-era development of more powerful engines, better suspension sys ...
s that can be equipped with a mortar, either outside or inside of the cabin. The Israeli Merkava
The Merkava ( he, מרכבה, , "chariot") is a series of main battle tanks used by the Israel Defense Forces and the backbone of the IDF's armored corps. The tank began development in 1970, and its first generation, the Merkava mark 1, entere ...
tank uses a 60 mm mortar as a secondary armament. The Russian army
The Russian Ground Forces (russian: Сухопутные войска �В Sukhoputnyye voyska V, also known as the Russian Army (, ), are the Army, land forces of the Russian Armed Forces.
The primary responsibilities of the Russian Gro ...
uses the '' 2S4 Tyulpan'' self-propelled 240 mm heavy mortar which is one of the largest mortars in current use.
Gun-mortars
hydraulic recoil mechanism
A hydraulic recoil mechanism is a way of limiting the effects of recoil and adding to the accuracy and firepower of an artillery piece.
Description
The usual recoil system in modern quick-firing guns is the hydro-pneumatic recoil system. I ...
, and sometimes equipped with an autoloader
An autoloader or auto-loader is a mechanical aid or replacement for the personnel that load ordnance into crew-served weapons without being an integrated part of the gun itself. The term is generally only applied to larger weapons, such as nava ...
. They are usually mounted on an armored vehicle and are capable of direct fire
Direct fire or line-of-sight fire refers to firing of a ranged weapon whose projectile is launched directly at a target within the line-of-sight of the user. The firing weapon must have a sighting device and an unobstructed view to the target, w ...
. The archetypes are the Brandt Mle CM60A1
The Brandt Mle CM60A1, also known as the ''Brandt HB 60LP'', ''MCB-60 HB'', or simply as the Brandt 60mm LP Gun-Mortar,Interconair Armies & Weapons, Collected Issues 40-49'. Interconair Media Group, 1978 p. 45-60. is a 60 mm (2.36 in.) gun-mortar ...
and Brandt 60 mm LR, which combine features of modern infantry mortars together with those of modern cannon. Such weapons are most commonly smoothbore, firing fin-stabilised rounds, using relatively small propellant charges in comparison to projectile weight. They have short barrels in comparison to guns and are much more lightly built than guns of a similar calibre – all characteristics of infantry mortars. This produces a hybrid weapon capable of engaging area targets with indirect high-angle fire, and also specific targets such as vehicles and bunkers with direct fire. Such hybrids are much heavier and more complicated than infantry mortars, superior to rocket-propelled grenades in the anti-armour and bunker-busting role, but have a reduced range compared to modern gun-howitzer
A howitzer () is a long- ranged weapon, falling between a cannon (also known as an artillery gun in the United States), which fires shells at flat trajectories, and a mortar, which fires at high angles of ascent and descent. Howitzers, like ot ...
s and inferior anti-tank capability compared to modern anti-tank guided weapons. However, they do have a niche in, for example, providing a multi-role anti-personnel, anti-armour capability in light mobile formations. Such systems, like the Soviet 120 mm 2S9 Nona S9 may refer to:
Transportation
* SIAI S.9, a 1918 Italian flying boat
* Aircraft registration prefix of São Tomé and Príncipe
* USS ''S-9'' (SS-114), a 1920 S-class submarine of the United States Navy
* County Route S9 (California)
* Ran ...
, are mostly self-propelled (although a towed variant exists). The AMOS
Amos or AMOS may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Amos Records, an independent record label established in Los Angeles, California, in 1968
* Amos (band), an American Christian rock band
* ''Amos'' (album), an album by Michael Ray
* ''Amos' ...
(Advanced Mortar System) is an example of an even more advanced gun mortar system. It uses a 120 mm automatic twin-barrelled, breech-loaded mortar turret, which can be mounted on a variety of armored vehicles and attack boats. A modern example of a gun-mortar is the 2B9 Vasilek.
Spigot mortar
 A spigot mortar consists mainly of a solid rod or
A spigot mortar consists mainly of a solid rod or spigot
A tap (also spigot or faucet: see usage variations) is a valve controlling the release of a liquid or gas.
Nomenclature
United Kingdom
* Tap is used in the United Kingdom and most of the Commonwealth for any everyday type of valve, parti ...
, onto which a hollow tube in the projectile fits—inverting the normal tube-mortar arrangement. At the top of the tube in the projectile, a cavity contains propellant
A propellant (or propellent) is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or other motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the e ...
, such as cordite
Cordite is a family of smokeless propellants developed and produced in the United Kingdom since 1889 to replace black powder as a military propellant. Like modern gunpowder, cordite is classified as a low explosive because of its slow burn ...
. There is usually a trigger mechanism built into the base of the spigot, with a long firing pin running up the length of the spigot activating a primer
Primer may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Primer'' (film), a 2004 feature film written and directed by Shane Carruth
* ''Primer'' (video), a documentary about the funk band Living Colour
Literature
* Primer (textbook), a t ...
inside the projectile and firing the propellant charge. The advantage of a spigot mortar is that the firing unit (baseplate and spigot) is smaller and lighter than a conventional tube mortar of equivalent payload and range. It is also somewhat simpler to manufacture. Further, most spigot mortars have no barrel in the conventional sense, which means ammunition of almost any weight and diameter can be fired from the same mortar.
The disadvantage is that while most mortar bombs have a streamlined shape towards the back that fits a spigot mortar application well, using that space for the spigot mortar tube takes volume and mass away from the payload of the projectile. If a soldier is carrying only a few projectiles, the projectile weight disadvantage is not significant. However, the weight of a large quantity of the heavier and more complex spigot projectiles offsets the weight saved.
A near-silent mortar can operate using the spigot principle. Each round has a close-fitting sliding plug in the tube that fits over the spigot. When the round is fired, the projectile is pushed off the spigot, but before the plug clears the spigot it is caught by a constriction at the base of the tube. This traps the gases from the propelling charge and hence the sound of the firing. After World War II the Belgium Fly-K silent spigot mortar was accepted into French service as the TN-8111.
 Spigot mortars are generally out of favour in modern usage, replaced by small conventional mortars. Military applications of spigot mortars include:
* The 230 mm petard mortar used on the
Spigot mortars are generally out of favour in modern usage, replaced by small conventional mortars. Military applications of spigot mortars include:
* The 230 mm petard mortar used on the Churchill AVRE
This is a list of specialist variants of the Churchill tank which were used for purposes other than frontline combat.
Churchill Oke
A Churchill II or III with a flamethrower. The Oke flamethrowing tank was named after its designer, Major J.M. ...
by Britain in World War II.
* The 320 mm Type 98 mortar used by Japan in World War II to some psychological effect in the battles of Iwo Jima and Okinawa
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest city ...
* The Blacker Bombard
The Blacker Bombard, also known as the 29-mm Spigot Mortar, was an infantry anti-tank weapon devised by Lieutenant-Colonel Stewart Blacker in the early years of the Second World War.
Intended as a means to equip Home Guard units with an anti-tan ...
and PIAT
The Projector, Infantry, Anti Tank (PIAT) Mk I was a British man-portable anti-tank weapon developed during the Second World War. The PIAT was designed in 1942 in response to the British Army's need for a more effective infantry anti-tank weapon ...
anti-tank launchers used by Britain in World War II.
* The Hedgehog
A hedgehog is a spiny mammal of the subfamily Erinaceinae, in the eulipotyphlan family Erinaceidae. There are seventeen species of hedgehog in five genera found throughout parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, and in New Zealand by introducti ...
launcher, used from the deck of a ship, used 24 spigot mortars which fired a diamond pattern of anti-submarine projectiles into the sea ahead of the ship. A sinking projectile detonated if it struck a submarine, and the pattern was such that any submarine partly in the landing zone of the projectiles would be struck one or more times.
Non-military applications include the use of small-calibre spigot mortars to launch lightweight, low-velocity foam dummy targets used for training retriever
A retriever is a type of gun dog that retrieves game for a hunter. Generally gun dogs are divided into three major classifications: retrievers, flushing spaniels, and pointing breeds. Retrievers were bred primarily to retrieve birds or other ...
dogs for bird hunting. Simple launchers use a separate small primer cap as the sole propellant (similar or identical to the cartridges used in industrial nail gun
A nail gun, nailgun or nailer is a form of hammer used to drive nails into wood or other materials. It is usually driven by compressed air (pneumatic), electromagnetism, highly flammable gases such as butane or propane, or, for powder-actuate ...
s).

Improvised
Insurgent groups often use improvised, or "homemade" mortars to attack fortified military installations or terrorize civilians. They are usually constructed from heavy steel piping mounted on a steel frame. These weapons may fire standard mortar rounds, purpose-made shells, re-purposed gas cylinders filled with explosives and shrapnel, or any other type of improvised explosive, incendiary or chemical munitions. These were called "Barrack Busters" by the Provisional Irish Republican Army (PIRA).Syrian civil war
Improvised mortars used in the Syrian civil war are known as '' hell cannons''. Observers have noted that they are "wildly inaccurate" and responsible for hundreds of civilian deaths.Sri Lankan civil war
Improvised mortars used in the Sri Lankan civil war by the rebelTamil Tigers
The Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE; ta, தமிழீழ விடுதலைப் புலிகள், translit=Tamiḻīḻa viṭutalaip pulikaḷ, si, දෙමළ ඊළාම් විමුක්ති කොටි, t ...
are known as '' 'Pasilan 2000' '', has also been known as a "Rocket mortar or Arti-mortar" like the 122mm cannon, successor to the Baba Mortar used by the LTTE for ground operations since the 1980s. As "Baba" mortar rounds contained tar, they caused a fire when they hit the ground. The "Baba Mortar", the prototype mortar, were crude. But with time the weapon has improved.
The ''Pasilan 2000'', the improved version, has been developed with characteristics similar to a rocket launcher. The Pasilan 2000 was a heavy mortar fired from a mobile launcher mounted on a tractor. The shell does not emit constant muzzle flares like Artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
or MBRL. This is ideal for LTTE's camouflage and conceals attacking style. Once a round is fired, forward observers/spies/civilian spotters can correct the fire. The way the tube is installed is similar to the positioning of rocket pods. The length and calibre of the barrel indicate Pasilan 2000 system has common features to the Chinese made Type 82 130mm 30-tube MLRS (introduced by the Palestinian Liberation Army (PLA) in the early 1980s) rather than rail-guided Katyusha variants such as the Qassam Rocket. The warhead weight is 70kg and it is filled with TNT. It had a range of 15-25km. The rocket has since then undergone some modifications. The Pasilan 2000 was more lethal than Baba mortar. But it was not heavily used for ground attacks during the Eelam war 4
Eelam War IV is the name given to the fourth phase of armed conflict between the Sri Lankan military and the separatist Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE). Renewed hostilities began on the 26 July 2006, when Sri Lanka Air Force fighter jet ...
.
Modern
Design

 Most modern mortar systems consist of four main components: a barrel, a base plate, a bipod and a sight. Modern mortars normally range in
Most modern mortar systems consist of four main components: a barrel, a base plate, a bipod and a sight. Modern mortars normally range in calibre
In guns, particularly firearms, caliber (or calibre; sometimes abbreviated as "cal") is the specified nominal internal diameter of the gun barrel bore – regardless of how or where the bore is measured and whether the finished bore match ...
from 60 mm (2.36 in) to 120 mm (4.72 in). However, both larger and smaller mortars have been produced. The modern mortar is a muzzle-loaded weapon and relatively simple to operate. It consists of a barrel into which the gunners drop a mortar round. When the round reaches the base of the barrel it hits a fixed firing pin
A firing pin or striker is a part of the firing mechanism of a firearm that impacts the primer in the base of a cartridge and causes it to fire. In firearms terminology, a striker is a particular type of firing pin where a compressed spring ...
that fires the round. The barrel is generally set at an angle of between 45 and 85 degrees (800 to 1500 mils), with the higher angle producing a shorter horizontal trajectory. Some mortars have a moving firing pin, operated by a lanyard
A lanyard is a cord, length of webbing, or strap that may serve any of various functions, which include a means of attachment, restraint, retrieval, and activation and deactivation. A lanyard is also a piece of rigging used to secure or lowe ...
or trigger mechanism.
Ammunition

Ammunition
Ammunition (informally ammo) is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. Ammunition is both expendable weapons (e.g., bombs, missiles, grenades, land mines) and the component parts of other weap ...
for mortars generally comes in two main varieties: fin-stabilized and spin-stabilized. Examples of the former have short fins on their posterior portion, which control the path of the bomb in flight. Spin-stabilized mortar bombs rotate as they travel along and leave the mortar tube, which stabilizes them in much the same way as a rifle bullet. Both types of rounds can be either illumination (infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
or visible illumination), smoke
Smoke is a suspension of airborne particulates and gases emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-product ...
, high explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An exp ...
, and training rounds. Mortar bombs are often referred to, incorrectly, as "mortars".
Operators may fire spin-stabilized rounds from either a smoothbore or a rifled barrel. Rifled mortars are more accurate but slower to load. Since mortars are generally muzzle-loaded, mortar bombs for rifled barrels usually have a pre-engraved band, called an obturator, that engages with the rifling of the barrel. Exceptions to this were the U.S. M2 4.2-inch mortar
The M2 4.2-inch mortar was a U.S. rifled 4.2-inch (107 mm) mortar used during the Second World War, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War. It entered service in 1943. It was nicknamed the "Goon Gun" (from its large bullet-shaped shells, mono ...
and M30 mortar, whose ammunition had a sub-caliber expandable ring that enlarged when fired. This allows the projectile to slide down the barrel freely but grip the rifling when fired. The system resembles the Minié ball
The Minié ball or Minie ball, is a type of hollow-based bullet designed by Claude-Étienne Minié, inventor of the French Minié rifle, for muzzle-loading rifled muskets. It was invented in 1847 and came to prominence in the Crimean War and ...
for muzzle-loading rifles. For extra range, propellant rings (augmentation charges) are attached to the bomb's fins. The rings are usually easy to remove, because they have a major influence on the speed and thus the range of the bomb. Some mortar rounds can be fired without any augmentation charges, e.g., the 81 mm L16 mortar.
Precision guided
The XM395 Precision Guided Mortar Munition (PGMM) is a 120 mm guided mortar round developed by Alliant Techsystems. Based on Orbital ATK's Precision Guidance Kit for 155 mm artillery projectiles, XM395 combinesGPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
guidance and directional control surfaces into a package that replaces standard fuses, transforming existing 120 mm mortar bodies into precision-guided munitions. The XM395 munition consists of a GPS-guided kit fitted to standard 120 mm smoothbore mortar rounds that includes the fitting of a nose and tail subsystem containing the maneuvering parts.Picatinny fields first precision-guided mortars to troops in Afghanistan- Army.mil, 29 March 2011 The Strix mortar round is a Swedish endphase-guided projectile fired from a 120 mm mortar currently manufactured by
Saab Bofors Dynamics
Saab Bofors Dynamics, located in Karlskoga and Linköping, Sweden, is a subsidiary of the Saab Group that specializes in military materiel such as missile systems and anti-tank systems.
Its corporate heritage goes back to Bofors, a hammer mill, w ...
. STRIX is fired like a conventional mortar round. The round contains an infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
imaging sensor that it uses to guide itself onto any tank or armoured fighting vehicle in the vicinity where it lands. The seeker is designed to ignore targets that are already burning. Launched from any 120 mm mortar, STRIX has a normal range of up to 4.5 km. The addition of a special sustainer motor increases the range to 7.5 km.
The GMM 120
GMM 120 (''Guided Mortar Munition 120''; known as Patzmi; also referred to as Morty) is a GPS and/or laser-guided mortar munition, which was developed by Israel Military Industries
, former_name = Israel Military Industries
, type = State ...
(''Guided Mortar Munition 120''; known as Patzmi; also referred to as Morty) is a GPS and/or laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The fir ...
-guided mortar munition, which was developed by Israel Military Industries
, former_name = Israel Military Industries
, type = State-owned enterprise
, industry = Arms industry
, fate = Acquired by Elbit Systems
, successor = Elbit Systems Land
, founded =
, founder =
, defunct =
, hq_location_city = Ramat ...
. The Russian KM-8 Gran
KM-8 Gran is a Russian 120mm guided mortar weapon system with Malakhit fire control system using semi-active laser guidance to perform a top attack and able to attack moving and stationary targets.artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
such as guns and howitzer
A howitzer () is a long- ranged weapon, falling between a cannon (also known as an artillery gun in the United States), which fires shells at flat trajectories, and a mortar, which fires at high angles of ascent and descent. Howitzers, like ot ...
s, which allows light and medium (typically, 60 mm and 81 mm/82 mm) mortars to be considered light weapons; i.e. capable of transport by personnel without vehicle assistance. They are short-range weapons and often more effective than long range artillery for many purposes within their shorter range. In particular, because of its high, parabolic trajectory with a near vertical descent, the mortar can land bombs on nearby targets, including those behind obstacles or in fortification
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
s, such as light vehicles behind hills or structures, or infantry in trench
A trench is a type of excavation or in the ground that is generally deeper than it is wide (as opposed to a wider gully, or ditch), and narrow compared with its length (as opposed to a simple hole or pit).
In geology, trenches result from ero ...
es or spider hole
Illustration of a spider hole
In military slang, a spider hole is a type of camouflaged one-man foxhole, used for observation.
Etymology
The term is usually understood to be an allusion to the camouflaged hole constructed by the trapdoor ...
s. This also makes it possible to launch attacks from positions lower than the target of the attack. (For example, long-range artillery could not shell a target 1 km away and 30 metres (100 ft) higher, a target easily accessible to a mortar.)
In trench warfare
Trench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied lines largely comprising military trenches, in which troops are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artillery. Trench warfare became a ...
, mortars can fire directly into the enemy trench
A trench is a type of excavation or in the ground that is generally deeper than it is wide (as opposed to a wider gully, or ditch), and narrow compared with its length (as opposed to a simple hole or pit).
In geology, trenches result from ero ...
es, which is very hard or impossible to accomplish with long range artillery because of its much flatter trajectory. Mortars are also highly effective when used from concealed positions, such as the natural escarpments on hillsides or from woods, especially if forward observers are being employed in strategic positions to direct fire, an arrangement where the mortar is in relatively close proximity both to its forward observer and its target, allowing for fire to be quickly and accurately delivered with lethal effect. Mortars suffer from instability when used on snow or soft ground, because the recoil pushes them into the ground or snow unevenly. A Raschen bag addresses this problem.
Fin-stabilised mortar bombs do not have to withstand the rotational forces placed upon them by rifling or greater pressures, and can therefore carry a higher payload
Payload is the object or the entity which is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of ...
in a thinner skin than rifled artillery ammunition. Because of the difference in available volume, a smooth-bore mortar of a given diameter will have a greater explosive yield than a similarly sized artillery shell of a gun or howitzer. For example, a 120 mm mortar bomb has approximately the same explosive capability as a 152mm/155 mm artillery shell. Also, fin-stabilised munitions fired from a smooth-bore, which do not rely on the spin imparted by a rifled bore for greater accuracy, do not have the drawback of veering in the direction of the spin.
Largest mortars
From the 17th to the mid 20th century, very heavy, relatively immobile siege mortars were used, of up to one metre calibre, often made of cast iron and with an outside barrel diameter many times that of the bore diameter. An early example was Roaring Meg, with a 15.5-inch (390 mm) barrel diameter and firing a 220 lb (100 kg) hollow ball filled with gunpowder and used during theEnglish Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
in 1646.
The largest mortars ever developed were the Belgian "Monster Mortar
The Monster Mortar (french: Mortier Monstre, links=no) was one of the largest mortars ever developed. Also called Leopold or the Liège mortar, the caliber mortar was conceived by the French artillery officer Henri-Joseph Paixhans. The mortar was ...
" (24 inches; 610 mm; developed by Henri-Joseph Paixhans
Henri-Joseph Paixhans (; January 22, 1783, Metz – August 22, 1854, Jouy-aux-Arches) was a French artillery officer of the beginning of the 19th century.
Henri-Joseph Paixhans graduated from the École Polytechnique. He fought in the Napoleonic ...
in 1832), Mallet's Mortar
Mallet's Mortar was a British shell-firing mortar built for the Crimean War, but never used in combat.
The mortar was designed by Robert Mallet and was constructed in separate sections so that it could be transported.
Robert Mallet first made h ...
(36 inches; 914.4 mm; developed by Robert Mallet
Robert Mallet (3 June 1810 – 5 November 1881) was an Irish geophysicist, civil engineer, and inventor who distinguished himself in research on earthquakes and is sometimes called the father of seismology. His son, Frederick Richard Mallet was ...
in 1857), and the "Little David
Little David was the nickname of an American 36-inch (914 mm) caliber mortar designed to breach the Siegfried Line and then used for test-firing aerial bombs during World War II. With the same calibre as the British Mallet's Mortar, constructe ...
" (36 inches; 914.4 mm; developed in the United States for use in World War II). Although the latter two had a caliber of 36 inches, only the "Monster Mortar" was used in combat (at the Battle of Antwerp in 1832). The World War II German Karl-Gerät
"''Karl-Gerät''" (040/041) (German literally "Karl-device"), also known as ''Mörser Karl'', was a World War II German self-propelled siege mortar (''Mörser'') designed and built by Rheinmetall. Its heaviest munition was a diameter, shel ...
was a 60 cm (23.6 inch) mortar and the largest to see combat in modern warfare.
See also
*Carcass (projectile)
A carcass was an early form of Incendiary ammunition, incendiary bomb or shell (projectile), shell, intended to set targets on fire. It comprised an external casing, usually of cast iron, filled with a highly flammable mixture, and having three to ...
, used in mortars before the modern age
* Chemical mortar battalion The United States chemical mortar battalions were army units attached to U.S. infantry divisions during World War II. They were armed with 4.2-inch (107 mm) chemical mortars. For this reason they were also called the "Four-deucers".
Chemical morta ...
* ''Eprouvette As used by ordnance departments and armories, an Eprouvette is a one piece, fixed elevation mortar used to test the strength of gunpowder. It went out of general use by the middle of the 19th century. In use, a carefully weighed quantity of pow ...
'', a mortar used to test the strength of gunpowder
* Coehorn
A Coehorn (also spelled ''cohorn'') is a lightweight mortar originally designed by Dutch military engineer Menno van Coehoorn.
Concept and design
Van Coehoorn came to prominence during the 1688–97 Nine Years War, whose tactics have been su ...
a lightweight mortar, sometimes improvised
* List of heavy mortars
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
* List of infantry mortars
The list of infantry mortars catalogues weapons which are issued to infantry units to provide close range, rapid response, indirect fire capability of an infantry unit in tactical combat. In this sense the mortar has been called "infantryman's ...
* Livens Projector
The Livens Projector was a simple mortar-like weapon that could throw large drums filled with flammable or toxic chemicals.
In the First World War, the Livens Projector became the standard means of delivering gas attacks by the British Army a ...
References
External links
A Guide to Modern Mortar Systems
* * *
How does a Mortar work? - Visualization (Video)
WW II-era German 60 cm self-propelled mortar.
Video
(streaming wmv) {{DEFAULTSORT:Mortar (Weapon) *Mortar Korean inventions