Montane Cloud Forests on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
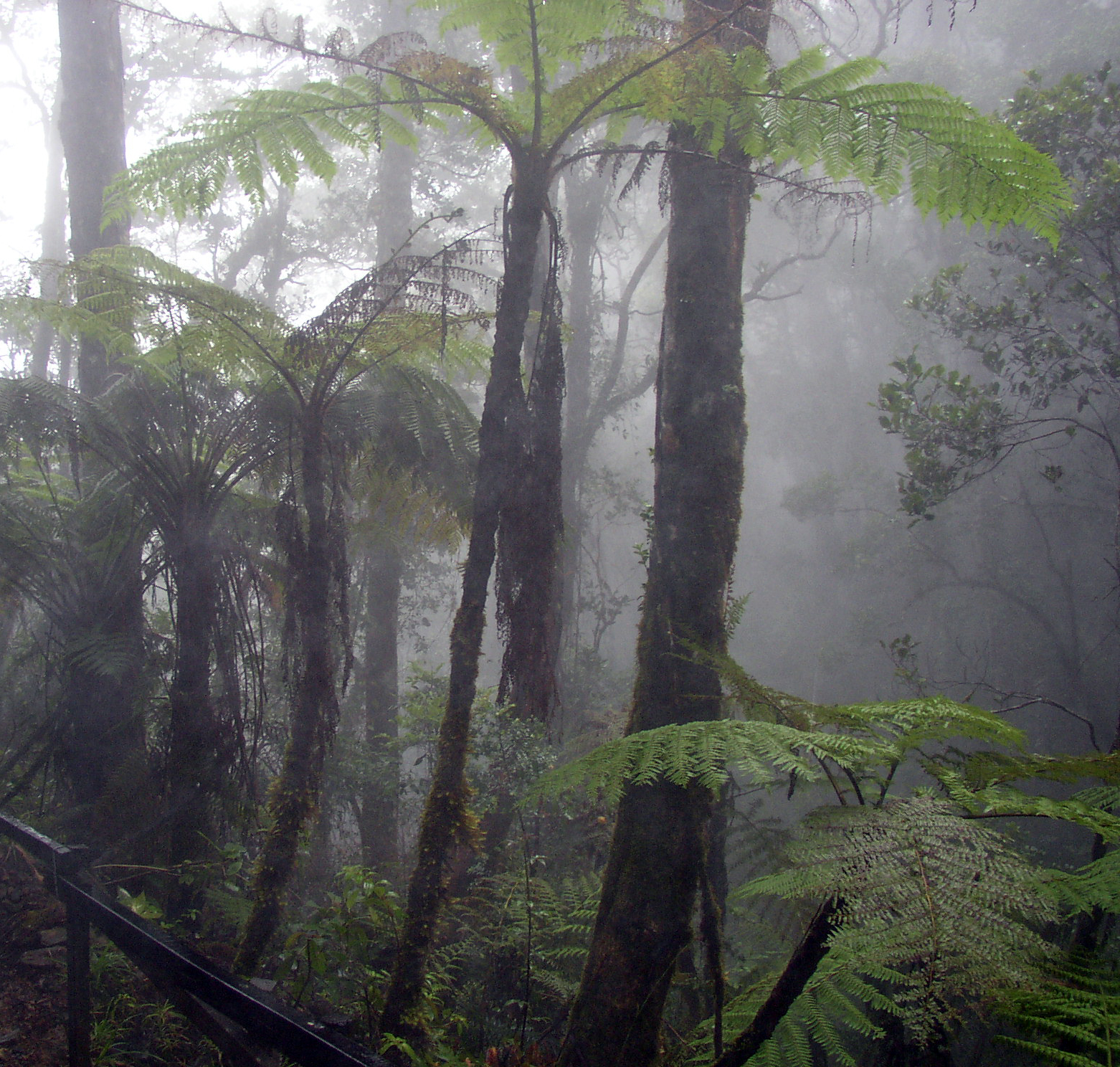

 A cloud forest, also called a water forest, primas forest, or tropical montane cloud forest (TMCF), is a generally tropical or
A cloud forest, also called a water forest, primas forest, or tropical montane cloud forest (TMCF), is a generally tropical or
 The presence of cloud forests is dependent on local climate (which is affected by the distance to the sea), the exposition and the latitude (from 23°N to 25°S), and the elevation (which varies from 500 m to 4000 m above sea level). Typically, there is a relatively small band of elevation in which the atmospheric environment is suitable for cloud forest development. This is characterized by persistent fog at the vegetation level, resulting in the reduction of direct sunlight and thus of evapotranspiration. Within cloud forests, much of the moisture available to plants arrives in the form of fog drip, where
The presence of cloud forests is dependent on local climate (which is affected by the distance to the sea), the exposition and the latitude (from 23°N to 25°S), and the elevation (which varies from 500 m to 4000 m above sea level). Typically, there is a relatively small band of elevation in which the atmospheric environment is suitable for cloud forest development. This is characterized by persistent fog at the vegetation level, resulting in the reduction of direct sunlight and thus of evapotranspiration. Within cloud forests, much of the moisture available to plants arrives in the form of fog drip, where
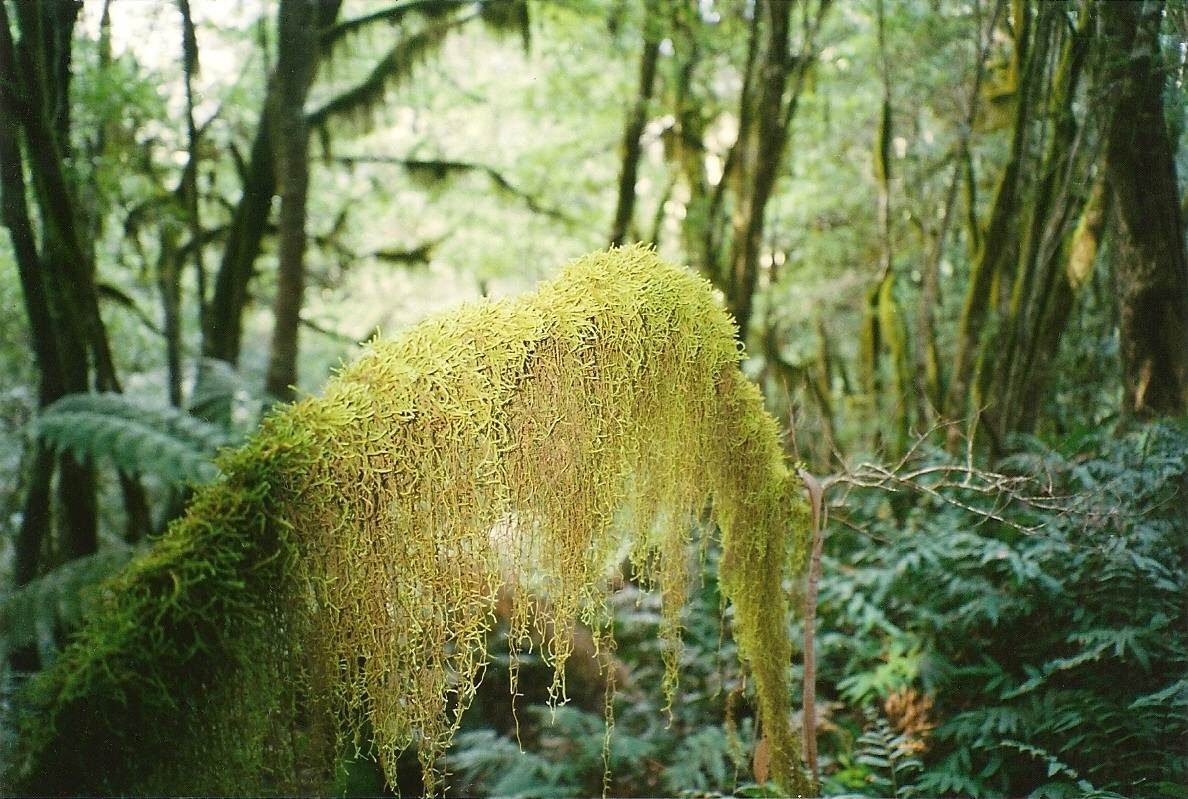
 In comparison with lower-altitude tropical moist forests, cloud forests show a reduced tree stature combined with increased stem density and generally, a lower diversity of woody plants. Trees in these regions are generally shorter and more heavily stemmed than in lower-altitude forests in the same regions, often with gnarled trunks and branches, forming dense, compact crowns. Their leaves become smaller, thicker and harder with increasing altitude. The high moisture promotes the development of a high
In comparison with lower-altitude tropical moist forests, cloud forests show a reduced tree stature combined with increased stem density and generally, a lower diversity of woody plants. Trees in these regions are generally shorter and more heavily stemmed than in lower-altitude forests in the same regions, often with gnarled trunks and branches, forming dense, compact crowns. Their leaves become smaller, thicker and harder with increasing altitude. The high moisture promotes the development of a high

 A cloud forest, also called a water forest, primas forest, or tropical montane cloud forest (TMCF), is a generally tropical or
A cloud forest, also called a water forest, primas forest, or tropical montane cloud forest (TMCF), is a generally tropical or subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Geographical z ...
, evergreen, montane, moist forest characterized by a persistent, frequent or seasonal low-level cloud cover, usually at the canopy level, formally described in the '' International Cloud Atlas'' (2017) as silvagenitus. Cloud forests often exhibit an abundance of moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hor ...
es covering the ground and vegetation, in which case they are also referred to as mossy forests. Mossy forests usually develop on the saddles of mountains, where moisture introduced by settling clouds is more effectively retained.
Cloud forests are among the most biodiversity rich ecosystems in the world with a large amount of species directly or indirectly depending on them.
Other moss forests include black spruce
''Picea mariana'', the black spruce, is a North American species of spruce tree in the pine family. It is widespread across Canada, found in all 10 provinces and all 3 territories. It is the official tree of the province of Newfoundland and Labra ...
/ feathermoss climax forest, with a moderately dense canopy and a forest floor of feathermosses including '' Hylocomium splendens'', '' Pleurozium schreberi'' and '' Ptilium crista-castrensis''. These weft-form mosses grow in boreal moss forests.
Climate
 The presence of cloud forests is dependent on local climate (which is affected by the distance to the sea), the exposition and the latitude (from 23°N to 25°S), and the elevation (which varies from 500 m to 4000 m above sea level). Typically, there is a relatively small band of elevation in which the atmospheric environment is suitable for cloud forest development. This is characterized by persistent fog at the vegetation level, resulting in the reduction of direct sunlight and thus of evapotranspiration. Within cloud forests, much of the moisture available to plants arrives in the form of fog drip, where
The presence of cloud forests is dependent on local climate (which is affected by the distance to the sea), the exposition and the latitude (from 23°N to 25°S), and the elevation (which varies from 500 m to 4000 m above sea level). Typically, there is a relatively small band of elevation in which the atmospheric environment is suitable for cloud forest development. This is characterized by persistent fog at the vegetation level, resulting in the reduction of direct sunlight and thus of evapotranspiration. Within cloud forests, much of the moisture available to plants arrives in the form of fog drip, where fog
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Reprint from Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influ ...
condenses on tree leaves and then drips onto the ground below.
Annual rainfall can range from 500 to 10,000 mm/year and mean temperature between 8 and 20 °C (46.4 and 68 °F).
While cloud forest today is the most widely used term, in some regions, these ecosystems or special types of cloud forests are called mossy forest, elfin forest, montane thicket, and dwarf cloud forest.
The definition of cloud forest can be ambiguous, with many countries not using the term (preferring such terms as Afromontane
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions ...
forest and upper montane rain forest, montane laurel forest
Laurel forest, also called laurisilva or laurissilva, is a type of subtropical forest found in areas with high humidity and relatively stable, mild temperatures. The forest is characterized by broadleaf tree species with evergreen, glossy and elo ...
, or more localised terms such as the Bolivian '' yungas'', and the '' laurisilva'' of the Atlantic Islands), and occasionally subtropical and even temperate forests in which similar meteorological conditions occur are considered to be cloud forests.
Characteristics

 In comparison with lower-altitude tropical moist forests, cloud forests show a reduced tree stature combined with increased stem density and generally, a lower diversity of woody plants. Trees in these regions are generally shorter and more heavily stemmed than in lower-altitude forests in the same regions, often with gnarled trunks and branches, forming dense, compact crowns. Their leaves become smaller, thicker and harder with increasing altitude. The high moisture promotes the development of a high
In comparison with lower-altitude tropical moist forests, cloud forests show a reduced tree stature combined with increased stem density and generally, a lower diversity of woody plants. Trees in these regions are generally shorter and more heavily stemmed than in lower-altitude forests in the same regions, often with gnarled trunks and branches, forming dense, compact crowns. Their leaves become smaller, thicker and harder with increasing altitude. The high moisture promotes the development of a high biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
and biodiversity of epiphyte
An epiphyte is an organism that grows on the surface of a plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, water (in marine environments) or from debris accumulating around it. The plants on which epiphytes grow are called phoroph ...
, particularly bryophytes, lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.ferns (including
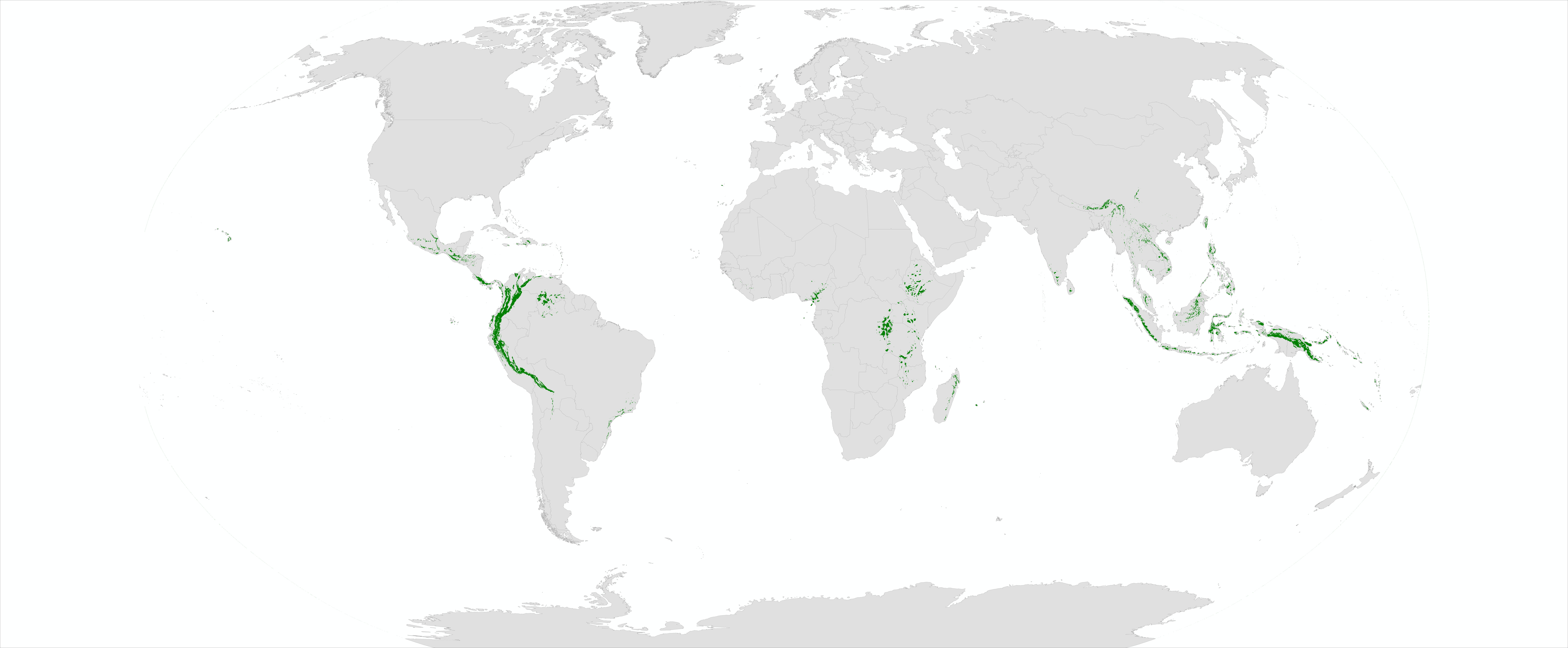 Only 1% of the global woodland consists of cloud forests. They previously comprised an estimated 11% of all tropical forests in the 1970s. A total of around 736 cloud forest sites have been identified in 59 countries by the World Conservation Monitoring Centre, with 327 of them legally
Only 1% of the global woodland consists of cloud forests. They previously comprised an estimated 11% of all tropical forests in the 1970s. A total of around 736 cloud forest sites have been identified in 59 countries by the World Conservation Monitoring Centre, with 327 of them legally

 * Watershed function: Because of the cloud-stripping strategy, the effective rainfall can be doubled in dry seasons and increase the wet season rainfall by about 10%. Experiments of Costin and Wimbush (1961) showed that the tree canopies of non-cloud forests intercept and evaporate 20 percent more of the precipitation than cloud forests, which means a loss to the land component of the hydrological cycle.
* Vegetation: Tropical montane cloud forests are not as species-rich as tropical lowland forests, but they provide the habitats for many species found nowhere else. For example, the Cerro de la Neblina, a cloud-covered mountain in the south of Venezuela, accommodates many shrubs, orchids, and
* Watershed function: Because of the cloud-stripping strategy, the effective rainfall can be doubled in dry seasons and increase the wet season rainfall by about 10%. Experiments of Costin and Wimbush (1961) showed that the tree canopies of non-cloud forests intercept and evaporate 20 percent more of the precipitation than cloud forests, which means a loss to the land component of the hydrological cycle.
* Vegetation: Tropical montane cloud forests are not as species-rich as tropical lowland forests, but they provide the habitats for many species found nowhere else. For example, the Cerro de la Neblina, a cloud-covered mountain in the south of Venezuela, accommodates many shrubs, orchids, and
 In 1970, the original extent of cloud forests on the Earth was around 50 million hectares.
In 1970, the original extent of cloud forests on the Earth was around 50 million hectares.
Tropical Montane Cloud Forest Initiative
* Roach, John (August 13, 2001)
National Geographic News
Cloud Forests United
Tropical hydrology and cloud forests project
Hydrology of tropical cloud forests project
Cloud Forest Video – Rara Avis CR
* ttp://www.andesconservation.org/ Andes Biodiversity and Ecosystem Research Group* * {{Authority control Habitats Montane forests Temperate rainforests Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests Tropical and subtropical coniferous forests Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests
filmy ferns
The Hymenophyllaceae, the filmy ferns and bristle ferns, are a family of two to nine genera (depending on classification system) and about 650 known species of ferns, with a subcosmopolitan distribution, but generally restricted to very damp pla ...
), bromeliads and orchids. The number of endemic plants can be very high.
An important feature of cloud forests is the tree crowns that intercept the wind-driven cloud moisture, part of which drips to the ground. This fog drip occurs when water droplets from the fog adhere to the needles or leaves of trees or other objects, coalesce into larger drops and then drop to the ground. It can be an important contribution to the hydrologic cycle.
Cloud forests are often peatlands, showcasing many classic peatland attributes. Due to the high water content of the soil, the reduced solar radiation and the low rates of decomposition and mineralization
Mineralization may refer to:
* Mineralization (biology), when an inorganic substance precipitates in an organic matrix
** Biomineralization, a form of mineralization
** Mineralization of bone, an example of mineralization
** Mineralized tissues are ...
, the soil acidity is very high, with more humus and peat often forming the upper soil layer.
Stadtmüller (1987) distinguishes two general types of tropical montane cloud forests:
* Areas with a high annual precipitation due to a frequent cloud cover in combination with heavy and sometimes persistent orographic rainfall; such forests have a perceptible canopy strata, a high number of epiphytes, and a thick peat layer which has a high storage capacity for water and controls the runoff;
* In drier areas with mainly seasonal rainfall, cloud stripping can amount to a large proportion of the moisture available to plants.
Distribution of tropical montane cloud forests
 Only 1% of the global woodland consists of cloud forests. They previously comprised an estimated 11% of all tropical forests in the 1970s. A total of around 736 cloud forest sites have been identified in 59 countries by the World Conservation Monitoring Centre, with 327 of them legally
Only 1% of the global woodland consists of cloud forests. They previously comprised an estimated 11% of all tropical forests in the 1970s. A total of around 736 cloud forest sites have been identified in 59 countries by the World Conservation Monitoring Centre, with 327 of them legally protected area
Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural, ecological or cultural values. There are several kinds of protected areas, which vary by level of protection depending on the ena ...
s as of 2002. Important areas of cloud forest are in Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and South America (mainly Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the no ...
, Venezuela, Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Oce ...
, Mexico, Ecuador, and Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
), East and Central Africa, India, Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
, Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Hawaii, Papua New Guinea, and in the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
.
The 1997 version of the World Conservation Monitoring Centre's database of cloud forests found a total of 605 tropical montane cloud forest sites in 41 countries. 280 sites, or 46% of the total, were located in Latin America, known in biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, ...
as the Neotropical realm. Twelve countries had tropical montane cloud forest sites, with the majority in Venezuela (64 sites), Mexico (64), Ecuador (35) and Colombia (28). Southeast Asia and Australasia had 228 sites in 14 countries – 66 in Indonesia, 54 in Malaysia, 33 in Sri Lanka, 32 in the Philippines, and 28 in Papua New Guinea. 97 sites were recorded in 21 African countries, mostly scattered on isolated mountains. Of the 605 sites, 264 were in protected areas.
Conservation status
Cloud forests occupied 0.4% of the global land surface in 2001 and harboured ~3,700 species of birds, mammal, amphibians and tree ferns (~15% of the global diversity of those groups), with half of those species entirely restricted to cloud forests. Worldwide, ~2.4% of cloud forests (in some regions, more than 8%) were lost between 2001 and 2018, especially in readily accessible places. While protected areas have slowed this decline, a large proportion of loss in TCF cover is still occurring despite formal protection.Temperate cloud forests
Although far from being universally accepted as true cloud forests, several forests in temperate regions have strong similarities with tropical cloud forests. The term is further confused by occasional reference to cloud forests in tropical countries as "temperate" due to the cooler climate associated with these misty forests.
Distribution of temperate cloud forests
* Argentina – Salta, Jujuy, Catamarca and Tucumán ( Southern Andean Yungas) *Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
– Lamington National Park, Springbrook National Park, Mount Bartle Frere
Mount Bartle Frere (pronunciation �mæɔnt̥ ˈbɐːɾəɫ ˈfɹɪə Ngajanji: Choorechillum) is the highest mountain in Queensland at an elevation of . The mountain was named after Sir Henry Bartle Frere, 1st Baronet, Sir Henry Bartle Frere ...
and Mount Bellenden Ker
Mount Bellenden Ker is the second-highest mountain in Queensland, Australia, with a height of . It is named after the botanist John Bellenden Ker Gawler. Located south of Cairns near Babinda, it is adjacent to Mount Bartle Frere, the state's ...
( Queensland) and Mount Gower ( Lord Howe Island)
* Brazil – Serra do Mar coastal forests
* Canada – Coastal British Columbia
* Chile – Bosque de Fray Jorge National Park
* People's Republic of China – Yunnan Plateau, mountains of southern and eastern China
* Ethiopia – Harenna Forest, Bale Mountains National Park and Kafa Biosphere Reserve in South West Ethiopia Peoples' Region
*Fiji Islands- Tropical Montane cloud forests of Taveuni sh, J., 1987. Stunted cloud-forest in Taveuni, Fiji. Gau Island eppel, G. and Thomas, N.T., 2009. Composition and structure of the cloud forest on Mt Delaco, Gau, Fiji. The South Pacific Journal of Natural and Applied Sciences, 27(1), pp.28-34.*Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
(Taiwan) – Yuanyang Lake Nature Reserve Yuanyang may refer to:
*Mandarin duck, also known as yuanyang ()
*Yuenyeung (), a popular beverage in Hong Kong, named after the mandarin duck
*Yuanyang County, Henan ()
*Yuanyang County, Yunnan (), well known for its spectacular rice-paddy terraci ...
, Chatianshan Nature Reserve, and Fuxing District in Taoyuan
* Iran – Eastern part of Alborz mountains, north of Iran, Golestan Province
*Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
– parts of Yakushima Island
* New Zealand – parts of Fiordland, Mount Taranaki, and Mount Cargill
* Pakistan – Shoghran Forest in the Kaghan Valley, and regions of Upper Swat
In the United States, a SWAT team (special weapons and tactics, originally special weapons assault team) is a police tactical unit that uses specialized or military equipment and tactics. Although they were first created in the 1960s to ...
in the northwest of Pakistan
* Peru – Peruvian Cloud Forest
* Portugal – Azores and Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
(often refers to the wetter, higher altitude expanse of '' laurisilva'')
* Spain – Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
('' laurisilva'') and very locally in Los Llanos del Juncal ( Alcornocales Natural Park) in the Province of Cádiz
Cádiz is a Provinces of Spain, province of southern Spain, in the southwestern part of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia. It is the southernmost part of mainland Spain, as well as the southernmost part of conti ...
.
* United States – Pacific Northwest and in the Southern Appalachians.
Importance
 * Watershed function: Because of the cloud-stripping strategy, the effective rainfall can be doubled in dry seasons and increase the wet season rainfall by about 10%. Experiments of Costin and Wimbush (1961) showed that the tree canopies of non-cloud forests intercept and evaporate 20 percent more of the precipitation than cloud forests, which means a loss to the land component of the hydrological cycle.
* Vegetation: Tropical montane cloud forests are not as species-rich as tropical lowland forests, but they provide the habitats for many species found nowhere else. For example, the Cerro de la Neblina, a cloud-covered mountain in the south of Venezuela, accommodates many shrubs, orchids, and
* Watershed function: Because of the cloud-stripping strategy, the effective rainfall can be doubled in dry seasons and increase the wet season rainfall by about 10%. Experiments of Costin and Wimbush (1961) showed that the tree canopies of non-cloud forests intercept and evaporate 20 percent more of the precipitation than cloud forests, which means a loss to the land component of the hydrological cycle.
* Vegetation: Tropical montane cloud forests are not as species-rich as tropical lowland forests, but they provide the habitats for many species found nowhere else. For example, the Cerro de la Neblina, a cloud-covered mountain in the south of Venezuela, accommodates many shrubs, orchids, and insectivorous
A robber fly eating a hoverfly
An insectivore is a carnivorous animal or plant that eats insects. An alternative term is entomophage, which can also refer to the human practice of eating insects.
The first vertebrate insectivores were ...
plants which are restricted to this mountain only.
* Fauna: The endemism in animals is also very high. In Peru, more than one-third of the 270 endemic birds, mammals, and frogs are found in cloud forests. One of the best-known cloud forest mammals is the Spectacled Bear (Tremarctos ornatus). Many of those endemic animals have important functions, such as seed dispersal and forest dynamics in these ecosystems.
Current situation
 In 1970, the original extent of cloud forests on the Earth was around 50 million hectares.
In 1970, the original extent of cloud forests on the Earth was around 50 million hectares. Population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to ...
, poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...
and uncontrolled land use have contributed to the loss of cloud forests. The 1990 Global Forest Survey found that 1.1% of tropical mountain and highland forests were lost each year, which was higher than in any other tropical forests. In Colombia, one of the countries with the largest area of cloud forests, only 10–20% of the initial cloud forest cover remains. Significant areas have been converted to plantations, or for use in agriculture and pasture. Significant crops in montane forest zones include tea and coffee, and the logging
Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or logs onto trucks or skeleton cars.
Logging is the beginning of a supply chain ...
of unique species causes changes to the forest structure.
In 2004, an estimated one-third of all cloud forests on the planet were protected at that time.
Impact of climate change
Because of their delicate dependency on local climates, cloud forests will be strongly affected by global climate change. Results show that the extent of environmentally suitable areas for cloud forest in Mexico will sharply decline in the next 70 years. A number of climate models suggest low-altitude cloudiness will be reduced, which means the optimum climate for many cloud forest habitats will increase in altitude. Linked to the reduction of cloud moisture immersion and increasing temperature, the hydrological cycle will change, so the system will dry out. This would lead to the wilting and the death of epiphytes, which rely on high humidity. Frogs and lizards are expected to suffer from increased drought. Calculations suggest the loss of cloud forest in Mexico would lead to extinction of up to 37 vertebrates specific to that region. In addition, climate changes can result in a higher number of hurricanes, which may increase damage to tropical montane cloud forests. All in all, the results of climate change will be a loss in biodiversity, altitude shifts in species ranges and community reshuffling, and, in some areas, complete loss of cloud forests.In botanical gardens
Cloud-forest conditions are hard and expensive to replicate in a glasshouse because it is necessary to maintain very high humidity. Day temperatures have to be between 70-75F while night temperatures have to be maintained between 55-60F. In most cases, sophisticated refrigeration equipment has to be used to provide night temperatures below 60F. Such displays are usually quite small, but there are some notable exceptions. In the United States, The Atlanta Botanical Garden has a large tropical cloud forest greenhouse with a large collection of cloud forest epiphytes from around the world. It implements a refrigeration system to decrease the temperature at night. For many years, the Singapore Botanic Gardens had a so-called coolhouse. The Gardens by the Bay features a coolhouse that is simply named "Cloud Forest
A cloud forest, also called a water forest, primas forest, or tropical montane cloud forest (TMCF), is a generally tropical or subtropical, evergreen, montane, moist forest characterized by a persistent, frequent or seasonal low-level cloud c ...
". The latter features a -high artificial mountain clad in epiphyte
An epiphyte is an organism that grows on the surface of a plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, water (in marine environments) or from debris accumulating around it. The plants on which epiphytes grow are called phoroph ...
s such as orchids, ferns, clubmosses, bromeliad
The Bromeliaceae (the bromeliads) are a family of monocot flowering plants of about 80 genera and 3700 known species, native mainly to the tropical Americas, with several species found in the American subtropics and one in tropical west Africa, ...
s and others. Due to a relatively mild climate and summer fog, the San Francisco Botanical Garden
The San Francisco Botanical Garden at Strybing Arboretum (formerly Strybing Arboretum) is located in San Francisco's Golden Gate Park. Its 55 acres (22.3 ha) represents nearly 9,000 different kinds of plants from around the world, with p ...
has three outdoor cloud forest collections, including a 2-acre Mesoamerican Cloud Forest established in 1985. The Buffalo and Erie County Botanical Gardens contains a " Panama Cloud Forest" garden in House 11.
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Tropical Montane Cloud Forest Initiative
* Roach, John (August 13, 2001)
National Geographic News
Cloud Forests United
Tropical hydrology and cloud forests project
Hydrology of tropical cloud forests project
Cloud Forest Video – Rara Avis CR
* ttp://www.andesconservation.org/ Andes Biodiversity and Ecosystem Research Group* * {{Authority control Habitats Montane forests Temperate rainforests Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests Tropical and subtropical coniferous forests Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests