Molecular Diagnostics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
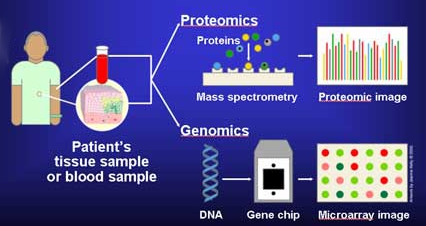
 Molecular diagnostics is a collection of techniques used to analyze biological markers in the
Molecular diagnostics is a collection of techniques used to analyze biological markers in the
 The field of molecular biology grew in the late twentieth century, as did its clinical application. In 1980, Yuet Wai Kan ''et al''. suggested a prenatal genetic test for
The field of molecular biology grew in the late twentieth century, as did its clinical application. In 1980, Yuet Wai Kan ''et al''. suggested a prenatal genetic test for


 Molecular diagnostics is a collection of techniques used to analyze biological markers in the
Molecular diagnostics is a collection of techniques used to analyze biological markers in the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
and proteome, and how their cells express their genes as protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s, applying molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and phys ...
to medical testing
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practice ...
. In medicine the technique is used to diagnose and monitor disease, detect risk, and decide which therapies will work best for individual patients, and in agricultural biosecurity
Biosecurity refers to measures aimed at preventing the introduction and/or spread of harmful organisms (e.g. viruses, bacteria, etc.) to animals and plants in order to minimize the risk of transmission of infectious disease. In agriculture, thes ...
similarly to monitor crop- and livestock disease, estimate risk
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environme ...
, and decide what quarantine
A quarantine is a restriction on the movement of people, animals and goods which is intended to prevent the spread of disease or pests. It is often used in connection to disease and illness, preventing the movement of those who may have been ...
measures must be taken.
By analysing the specifics of the patient and their disease, molecular diagnostics offers the prospect of personalised medicine.
These tests are useful in a range of medical specialties, including infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable d ...
, oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ó ...
, human leucocyte antigen typing (which investigates and predicts immune function), coagulation, and pharmacogenomicsthe genetic prediction of which drugs will work best. They overlap with clinical chemistry
Clinical chemistry (also known as chemical pathology, clinical biochemistry or medical biochemistry) is the area of chemistry that is generally concerned with analysis of bodily fluids for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. It is an appli ...
(medical tests on bodily fluids).
History
 The field of molecular biology grew in the late twentieth century, as did its clinical application. In 1980, Yuet Wai Kan ''et al''. suggested a prenatal genetic test for
The field of molecular biology grew in the late twentieth century, as did its clinical application. In 1980, Yuet Wai Kan ''et al''. suggested a prenatal genetic test for Thalassemia
Thalassemias are inherited blood disorders characterized by decreased hemoglobin production. Symptoms depend on the type and can vary from none to severe. Often there is mild to severe anemia (low red blood cells or hemoglobin). Anemia can resul ...
that did not rely upon DNA sequencingthen in its infancybut on restriction enzymes that cut DNA where they recognised specific short sequences, creating different lengths of DNA strand depending on which allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
(genetic variation) the fetus possessed. In the 1980s, the phrase was used in the names of companies such as ''Molecular Diagnostics Incorporated'' and ''Bethseda Research Laboraties Molecular Diagnostics''.
During the 1990s, the identification of newly discovered genes and new techniques for DNA sequencing led to the appearance of a distinct field of molecular and genomic laboratory medicine; in 1995, the ''Association for Molecular Pathology'' (AMP) was formed to give it structure. In 1999, the AMP co-founded ''The Journal of Medical Diagnostics''. Informa Healthcare launched ''Expert Reviews in Medical Diagnostics'' in 2001. From 2002 onwards, the HapMap Project aggregated information on the one-letter genetic differences that recur in the human populationthe single nucleotide polymorphismsand their relationship with disease. In 2012, molecular diagnostic techniques for Thalassemia use genetic hybridization tests to identify the specific single nucleotide polymorphism causing an individual's disease.
As the commercial application of molecular diagnostics has become more important, so has the debate about patenting of the genetic discoveries at its heart. In 1998, the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
's Directive 98/44/ECclarified that patents on DNA sequences were allowable. In 2010 in the US, AMP sued Myriad Genetics to challenge the latter's patents regarding two genes, BRCA1
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a ...
, BRCA2
''BRCA2'' and BRCA2 () are a human gene and its protein product, respectively. The official symbol (BRCA2, italic for the gene, nonitalic for the protein) and the official name (originally breast cancer 2; currently BRCA2, DNA repair associated) ...
, which are associated with breast cancer. In 2013, the U.S. Supreme Court partially agreed, ruling that a naturally occurring gene sequence could not be patented.
Techniques

Development from research tools
The industrialisation of molecular biology assay tools has made it practical to use them in clinics. Miniaturisation into a single handheld device can bring medical diagnostics into the clinic and into the office or home. The clinical laboratory requires high standards of reliability; diagnostics may require accreditation or fall under medical device regulations. , some US clinical laboratories nevertheless used assays sold for "research use only". Laboratory processes need to adhere to regulations, such as theClinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments
The Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) of 1988 are United States federal regulatory standards that apply to all clinical laboratory testing performed on humans in the United States, except clinical trials and basic research.
CLI ...
, Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA or the Kennedy– Kassebaum Act) is a United States Act of Congress enacted by the 104th United States Congress and signed into law by President Bill Clinton on August 21, 19 ...
, Good Laboratory Practice
In the experimental (non-clinical) research arena, good laboratory practice or GLP is a quality system of management controls for research laboratories and organizations to ensure the uniformity, consistency, reliability, reproducibility, qualit ...
, and Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
specifications in the United States. Laboratory Information Management Systems help by tracking these processes. Regulation applies to both staff and supplies. , twelve US states require molecular pathologists to be licensed; several boards such as the American Board of Medical Genetics
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the " United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, ...
and the American Board of Pathology certify technologists, supervisors, and laboratory directors.
Automation and sample barcoding maximise throughput and reduce the possibility of error or contamination during manual handling and results reporting. Single devices to do the assay from beginning to end are now available.
Assays
Molecular diagnostics uses ''in vitro'' biological assays such as PCR-ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence ...
or Fluorescence in situ hybridization. The assay detects a molecule, often in low concentrations, that is a marker
The term Marker may refer to:
Common uses
* Marker (linguistics), a morpheme that indicates some grammatical function
* Marker (telecommunications), a special-purpose computer
* Boundary marker, an object that identifies a land boundary
* Marke ...
of disease or risk in a sample taken from a patient. Preservation of the sample before analysis is critical. Manual handling should be minimised. The fragile RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
molecule poses certain challenges. As part of the cellular process of expressing genes as proteins, it offers a measure of gene expression but it is vulnerable to hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
and breakdown by ever-present RNAse enzymes. Samples can be snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen or incubated in preservation agents.
Because molecular diagnostics methods can detect sensitive markers, these tests are less intrusive than a traditional biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a d ...
. For example, because cell-free nucleic acids exist in human plasma, a simple blood sample can be enough to sample genetic information from tumours, transplants or an unborn fetus. Many, but not all, molecular diagnostics methods based on nucleic acids detection use polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) ...
(PCR) to vastly increase the number of nucleic acid molecules, thereby amplifying the target sequence(s) in the patient sample. PCR is a method that a template DNA is amplified using synthetic primers, a DNA polymerase, and dNTPs. The mixture is cycled between at least 2 temperatures: a high temperature for denaturing double-stranded DNA into single-stranded molecules and a low temperature for the primer to hybridize to the template and for the polymerase to extend the primer. Each temperature cycle theoretically doubles the quantity of target sequence. Detection of sequence variations using PCR typically involves the design and use oligonucleotide reagents that amplify the variant of interest more efficiently than wildtype sequence. PCR is currently the most widely used method for detection of DNA sequences. The detection of the marker might use real time PCR, direct sequencing, microarray chip
A microarray is a multiplex lab-on-a-chip. Its purpose is to simultaneously detect the expression of thousands of genes from a sample (e.g. from a tissue). It is a two-dimensional array on a solid substrate—usually a glass slide or silicon ...
sprefabricated chips that test many markers at once, or MALDI-TOF The same principle applies to the proteome and the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
. High-throughput protein arrays can use complementary DNA
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA synthesized from a single-stranded RNA (e.g., messenger RNA ( mRNA) or microRNA (miRNA)) template in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. cDNA is often used to express a sp ...
or antibodies to bind and hence can detect many different proteins in parallel. Molecular diagnostic tests vary widely in sensitivity, turn around time, cost, coverage and regulatory approval. They also vary in the level of validation applied in the laboratories using them. Hence, robust local validation in accordance with the regulatory requirements and use of appropriate controls is required especially where the result may be used to inform a patient treatment decision.
Benefits

Prenatal
Conventional prenatal tests for chromosomal abnormalities such asDown Syndrome
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with child development, physical growth delays, mild to moderate ...
rely on analysing the number and appearance of the chromosomesthe karyotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of metaphase chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is disce ...
. Molecular diagnostics tests such as microarray comparative genomic hybridisation test a sample of DNA instead, and because of cell-free DNA in plasma, could be less invasive, but as of 2013 it is still an adjunct to the conventional tests.
Treatment
Some of a patient's single nucleotide polymorphismsslight differences in their DNAcan help predict how quickly they will metabolise particular drugs; this is called pharmacogenomics. For example, the enzyme CYP2C19 metabolises several drugs, such as the anti-clotting agent Clopidogrel, into their active forms. Some patients possess polymorphisms in specific places on the 2C19 gene that makepoor metaboliser
Pharmacogenomics is the study of the role of the genome in drug response. Its name (''wikt:pharmaco-#Prefix, pharmaco-'' + ''genomics'') reflects its combining of pharmacology and genomics. Pharmacogenomics analyzes how the genetic makeup of an ...
s of those drugs; physicians can test for these polymorphisms and find out whether the drugs will be fully effective for that patient. Advances in molecular biology have helped show that some syndromes that were previously classed as a single disease are actually multiple subtypes with entirely different causes and treatments. Molecular diagnostics can help diagnose the subtypefor example of infections and cancersor the genetic analysis of a disease with an inherited component, such as Silver-Russell syndrome.
Infectious disease
Molecular diagnostics are used to identify infectious diseases such aschlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several w ...
, influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptom ...
virus and tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in w ...
; or specific strains such as H1N1 virus or SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a No ...
. Genetic identification can be swift; for example a loop-mediated isothermal amplification test diagnoses the malaria parasite and is rugged enough for developing countries. But despite these advances in genome analysis, in 2013 infections are still more often identified by other meanstheir proteome, bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bact ...
, or chromatographic profile. Molecular diagnostics are also used to understand the specific strain of the pathogenfor example by detecting which drug resistance
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, ...
genes it possessesand hence which therapies to avoid. In addition, assays based on metagenomic next generation sequencing can be implemented to identify pathogenic organisms without bias.
Disease risk management
A patient's genome may include an inherited or random mutation which affects the probability of developing a disease in the future. For example, Lynch syndrome is a genetic disease that predisposes patients tocolorectal
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being rem ...
and other cancers; early detection can lead to close monitoring that improves the patient's chances of a good outcome. Cardiovascular risk is indicated by biological markers and screening can measure the risk that a child will be born with a genetic disease such as Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. ...
. Genetic testing is ethically complex: patients may not want the stress of knowing their risk. In countries without universal healthcare, a known risk may raise insurance premiums.
Cancer
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bl ...
is a change in the cellular processes that cause a tumour to grow out of control. Cancerous cells sometimes have mutations in oncogenes, such as KRAS and CTNNB1
Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
Beta-catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcript ...
(β-catenin). Analysing the molecular signature of cancerous cellsthe DNA and its levels of expression via messenger RNAenables physicians to characterise the cancer and to choose the best therapy for their patients. As of 2010, assays that incorporate an array of antibodies against specific protein marker molecules are an emerging technology; there are hopes for these multiplex assays that could measure many markers at once. Other potential future biomarkers include micro RNA molecules, which cancerous cells express more of than healthy ones.
Cancer is a disease with excessive molecular causes and constant evolution. There's also heterogeneity of disease even in an individual. Molecular studies of cancer have proved the significance of driver mutations in the growth and metastasis of tumors. Many technologies for detection of sequence variations have been developed for cancer research. These technologies generally can be grouped into three approaches: polymerase chain reaction (PCR), hybridization, and next-generation sequencing (NGS). Currently, a lot of PCR and hybridization assays have been approved by FDA as in vitro diagnostics. NGS assays, however, are still at an early stage in clinical diagnostics.
To do the molecular diagnostic test for cancer, one of the significant issue is the DNA sequence variation detection. Tumor biopsy samples used for diagnostics always contain as little as 5% of the target variant as compared to wildtype sequence. Also, for noninvasive applications from peripheral blood or urine, the DNA test must be specific enough to detect mutations at variant allele frequencies of less than 0.1%.
Currently, by optimizing the traditional PCR, there's a new invention, amplification-refractory mutation system (ARMS) is a method for detecting DNA sequence variants in cancer. The principle behind ARMS is that the enzymatic extension activity of DNA polymerases is highly sensitive to mismatches near the 3' end of primer. Many different companies have developed diagnostics tests based on ARMS PCR primers. For instance, Qiagen therascreen, Roche cobas and Biomerieux THxID have developed FDA approved PCR tests for detecting lung, colon cancer and metastatic melanoma mutations in the KRAS, EGFR and BRAF genes. Their IVD kits were basically validated on genomic DNA extracted from FFPE tissue.
There's also microarrays that utilize hybridization mechanism to do diagnostics of cancer. More than a million of different probes can be synthesized on an array with Affymetrix's Genechip technology with a detection limit of one to ten copies of mRNA per well. Optimized microarrays are typically considered to produce repeatable relative quantitation of different targets. Currently, FDA have already approved a number of diagnostics assays utilizing microarrays: Agendia's MammaPrint assays can inform the breast cancer recurrence risk by profiling the expression of 70 genes related to breast cancer; Autogenomics INFNITI CYP2C19 assay can profile genetic polymorphisms, whose impacts on therapeutic response to antidepressants are great; and Affymetrix's CytoScan Dx can evaluate intellectual disabilities and congenital disorders by analyzing chromosomal mutation.
In the future, the diagnostic tools for cancer will likely to focus on the Next Generation Sequencing (NGS). By utilizing DNA and RNA sequencing to do cancer diagnostics, technology in the field of molecular diagnostics tools will develop better. Although NGS throughput and price have dramatically been reduced over the past 10 years by roughly 100-fold, we remain at least 6 orders of magnitude away from performing deep sequencing at a whole genome level. Currently, Ion Torrent developed some NGS panels based on translational AmpliSeq, for example, the Oncomine Comprehensive Assay. They are focusing on utilizing deep sequencing of cancer-related genes to detect rare sequence variants.
Molecular diagnostics tool can be used for cancer risk assessment. For example, the BRCA1/2 test by Myriad Genetics assesses women for lifetime risk of breast cancer. Also, some cancers are not always employed with clear symptoms. It is useful to analyze people when they do not show obvious symptoms and thus can detect cancer at early stages. For example, the ColoGuard test may be used to screen people over 55 years old for colorectal cancer. Cancer is a longtime-scale disease with various progression steps, molecular diagnostics tools can be used for prognosis of cancer progression. For example, the OncoType Dx test by Genomic Health can estimate risk of breast cancer. Their technology can inform patients to seek chemotherapy when necessary by examining the RNA expression levels in breast cancer biopsy tissue.
With rising government support in DNA molecular diagnostics, it is expected that an increasing number of clinical DNA detection assays for cancers will become available soon. Currently, research in cancer diagnostics are developing fast with goals for lower cost, less time consumption and simpler methods for doctors and patients.
See also
* Molecular medicine (the broader field of the molecular understanding of disease) * Molecular pathology * Laboratory Developed Test * Pathogenesis * Pathogenomics *Pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in ...
* Precision medicine
* Personalized medicine
Personalized medicine, also referred to as precision medicine, is a medical model that separates people into different groups—with medical decisions, practices, interventions and/or products being tailored to the individual patient based on the ...
References
{{Reflist Biotechnology Medical tests Medical genetics Pathogen genomics