Mokken Scale on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Mokken scale is a
Minimum Sample Size Requirements for Mokken Scale Analysis
in ''Educational and Psychological Measurement'
Volume: 74 issue: 5, page(s): 809-822
/ref>Palmgren, P.J., Brodin, U., Nilsson G.H., Watson, R., Stenfors, T. (2018) Investigating psychometric properties and dimensional structure of an educational environment measure (DREEM) using Mokken scale analysis – a pragmatic approach ''BMC Medical Education'' volume = 18, issue = 1, article 235
doi: 10.1111/jocn.14341
/ref>Aleo, G., Bagnasco, A., Watson, R., Dyson, J., Cowdell, F., Catania, G., Zanini, M.P., Cozani, E., Parodi, A., Saso, L. (2019) Comparing questionnaires across cultures: Using Mokken scaling to compare the Italian and English versions of the MOLES index ''Nursing Open'
doi: 10.1002/nop2.297
/ref>

 Mokken scaling belongs to
Mokken scaling belongs to
doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2009.11.004
/ref> The latter implies that all respondents to a series of questions all respond to them in the same order across the whole range of the latent trait. For dichotomously scored items, the Double Monotonicity model can mean invariant item ordering; however, for polytomously scored items this does not necessarily hold.Ligtvoet, R., van der Ark, L.A., te Marvelde J.M., and Sijtsma, K. (2010) Investigating an Invariant Item Ordering for Polytomously Scored Items in Educational and Psychological Measuremen
Volume: 70 issue: 4, page(s): 578-595
/ref> For invariant item ordering to hold not only should the item response functions not intersect, also, the item step response function between one level and the next within each item must not intersect.Sijtsma, K., Meijer R.R., van der Ark, L.A. (2011) Mokken scale analysis as time goes by: An update for scaling practitioners Personality and Individual Differences (2011
Volume: 50, page(s): 31–37
/ref>
stata
for use on
PerFit
Meijer, R.R., Niessen, A.S.M., and Tendeiro, J.N. (2015)
A practical guide to check the consistency of item response patterns in clinical research through person-fit statistics: examples and an computer programme
''Assessment'' 23, 56-62 Two guides on how to conduct a Mokken scale analysis have been published.
psychometric
Psychometrics is a field of study within psychology concerned with the theory and technique of measurement. Psychometrics generally refers to specialized fields within psychology and education devoted to testing, measurement, assessment, and ...
method of data reduction. A Mokken scale is a unidimensional scale that consists of hierarchically-ordered items that measure the same underlying, latent concept. This method is named after the political scientist Rob Mokken
Robert Jan (Rob) Mokken (born 28 April 1929) is a Dutch political scientist and Emeritus Professor of Political Science and Methodology at the University of Amsterdam.
Biography
Born in Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Mokken began his studies at the ...
who suggested it in 1971.
Mokken Scales have been used in psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries betwe ...
, education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Va ...
,Straat, J.H., Van Ark, L.A. and Sijtsma, K. (2014Minimum Sample Size Requirements for Mokken Scale Analysis
in ''Educational and Psychological Measurement'
Volume: 74 issue: 5, page(s): 809-822
/ref>Palmgren, P.J., Brodin, U., Nilsson G.H., Watson, R., Stenfors, T. (2018) Investigating psychometric properties and dimensional structure of an educational environment measure (DREEM) using Mokken scale analysis – a pragmatic approach ''BMC Medical Education'' volume = 18, issue = 1, article 235
political science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and power, and the analysis of political activities, political thought, political behavior, and associated constitutions and la ...
, public opinion
Public opinion is the collective opinion on a specific topic or voting intention relevant to a society. It is the people's views on matters affecting them.
Etymology
The term "public opinion" was derived from the French ', which was first use ...
, medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
and nursing
Nursing is a profession within the health care sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other health ...
.Cook, N.F., McCance, T., McCormack, B., Barr, O., Slater, P. (2018) Perceived caring attributes and priorities of pre‐registration nursing students throughout a nursing curriculum underpinned by person‐centredness ''Journal of Clinical Nursing'doi: 10.1111/jocn.14341
/ref>Aleo, G., Bagnasco, A., Watson, R., Dyson, J., Cowdell, F., Catania, G., Zanini, M.P., Cozani, E., Parodi, A., Saso, L. (2019) Comparing questionnaires across cultures: Using Mokken scaling to compare the Italian and English versions of the MOLES index ''Nursing Open'
doi: 10.1002/nop2.297
/ref>
Overview


 Mokken scaling belongs to
Mokken scaling belongs to item response theory
In psychometrics, item response theory (IRT) (also known as latent trait theory, strong true score theory, or modern mental test theory) is a paradigm for the design, analysis, and scoring of tests, questionnaires, and similar instruments measuring ...
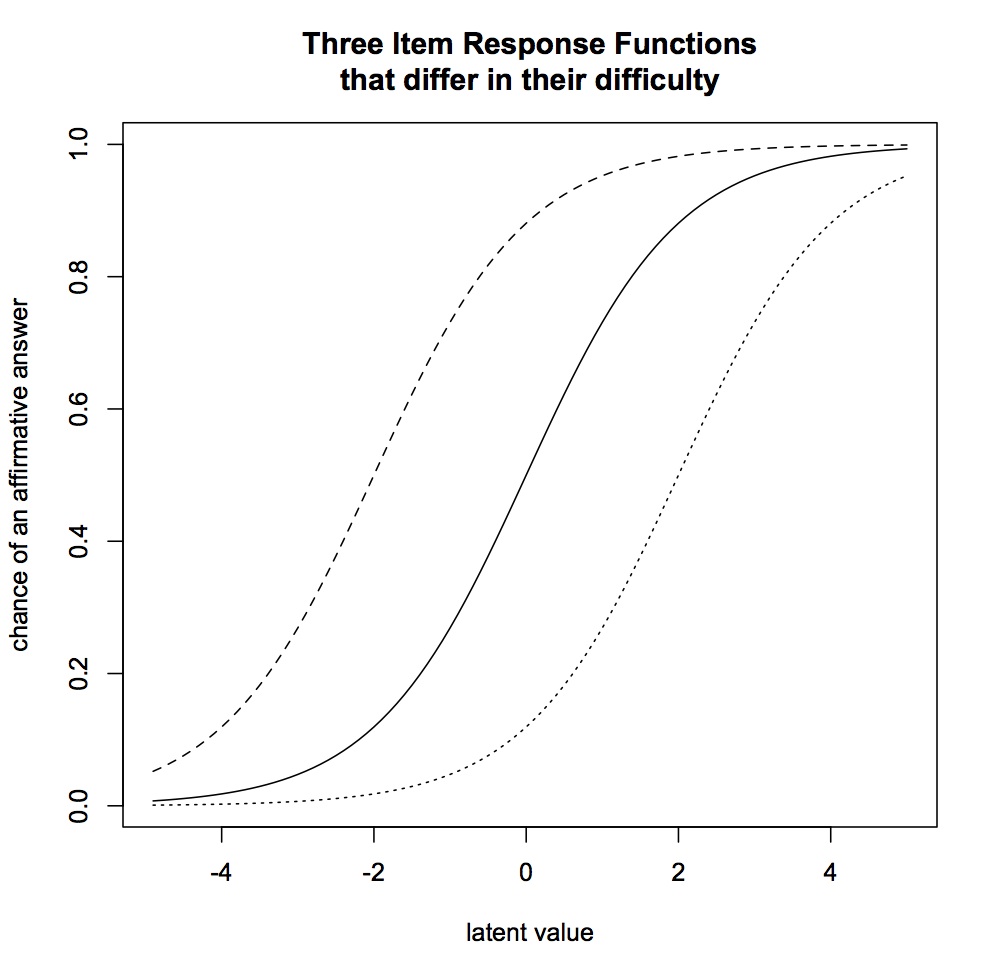
. In essence, a Mokken scale is a non-parametric, probabilistic version of Guttman scale. Both Guttman and Mokken scaling can be used to assess whether a number of items measure the same underlying concept. Both Guttman and Mokken scaling are based on the assumption that the items are hierarchically ordered: this means that they are ordered by degree of "difficulty". Difficulty here means the percentage of respondents that answers the question affirmatively. The hierarchical order means that a respondent who answered a difficult question correctly is assumed to answer an easy question correctly.Crichton, N. (1999) "Mokken Scale Analysis" ''Journal of Clinical Nursing 8, 388
The key difference between a Guttman and Mokken scale is that Mokken scaling is probabilistic in nature. The assumption is not that ''every'' respondent who answered a difficult question affirmatively will ''necessarily'' answer an easy question affirmatively. Violations of this are called Guttman errors. Instead, the assumption is that respondents who answered a difficult question affirmatively are more ''likely'' to answer an easy question affirmatively. The scalability of the scale is measured by Loevinger's coefficient H. H compares the actual Guttman errors to the expected number of errors if the items would be unrelated.
The chance that a respondent will answer an item correctly is described by an item response function. Mokken scales are similar to Rasch scales, in that they both adapted Guttman scales to a probabilistic model. However, Mokken scaling is described as 'non-parametric' because it makes no assumptions about the precise shape of the item response function, only that it is monotone and non-decreasing. The key difference between Mokken scales and Rasch scales is that the latter assumes that all items have the same item response function. In Mokken scaling the Item Response Functions differ for different items.
Mokken scales can come in two forms: first as the Double Monotonicity model, where the items can differ in their difficulty. It is essentially an ordinal version of Rasch scale; and second, as the Monotone Homogeneity model, where items differ in their discrimination parameter, which means that there can be a weaker relationship between some items and the latent variable and other items and the latent variable. Double Monotonicity models are used most often.
Monotone Homogeneity
Monotone Homogeneity models are based on three assumptions. # There is a unidimensional latent trait on which subject and items can be ordered. # The item response function is monotonically nondecreasing. This means that as one moves from one side of the latent variable to the other, the chance of giving a positive response should never decrease. # The items are locally stochastically independent: this means that responses to any two items by the same respondent should not be the function any other aspect of the respondent or the item, but his or her position on the latent trait.Double monotonicity and invariant item ordering
The Double Monotonicity model adds a fourth assumption, namely non-intersecting Item response functions, resulting in items that remain invariant rank-ordering. There has been some confusion in Mokken scaling between the concepts of Double Monotonicity model and invariant item ordering.Meijer, R.R. (2010) A comment on Watson, Deary, and Austin (2007) and Watson, Roberts, Gow, and Deary (2008): How to investigate whether personality items form a hierarchical scale? ''Personality and Individual Differences'doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2009.11.004
/ref> The latter implies that all respondents to a series of questions all respond to them in the same order across the whole range of the latent trait. For dichotomously scored items, the Double Monotonicity model can mean invariant item ordering; however, for polytomously scored items this does not necessarily hold.Ligtvoet, R., van der Ark, L.A., te Marvelde J.M., and Sijtsma, K. (2010) Investigating an Invariant Item Ordering for Polytomously Scored Items in Educational and Psychological Measuremen
Volume: 70 issue: 4, page(s): 578-595
/ref> For invariant item ordering to hold not only should the item response functions not intersect, also, the item step response function between one level and the next within each item must not intersect.Sijtsma, K., Meijer R.R., van der Ark, L.A. (2011) Mokken scale analysis as time goes by: An update for scaling practitioners Personality and Individual Differences (2011
Volume: 50, page(s): 31–37
/ref>
Sample size
The issue of sample size for Mokken scaling is largely unresolved. Work using simulated samples and varying the item quality in the scales (Loevinger's coefficient and the correlation between scales) suggests that, where the quality of the items is high that lower samples sizes in the region of 250-500 are required compared with sample sizes of 1250-1750 where the item quality is low. Using real data from the Warwick Edinburgh Mental Well Being Scale (WEMWBS) suggests that the required sample size depends on the Mokken scaling parameters of interest as they do not all respond in the same way to varying sample size.Extensions
While Mokken scaling analysis was originally developed to measure the extent to which individualdichotomous
A dichotomy is a partition of a whole (or a set) into two parts (subsets). In other words, this couple of parts must be
* jointly exhaustive: everything must belong to one part or the other, and
* mutually exclusive: nothing can belong simultan ...
items form a scale, it has since been extended for polytomous items. Moreover, while Mokken scaling analysis is a confirmatory method, meant to test whether a number of items form a coherent scale (like confirmatory factor analysis
In statistics, confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) is a special form of factor analysis, most commonly used in social science research.Kline, R. B. (2010). ''Principles and practice of structural equation modeling (3rd ed.).'' New York, New York: Gu ...
), an Automatic Item Selection Procedure has been developed to explore which latent dimensions structure responses on a number of observable items (like factor analysis
Factor analysis is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors. For example, it is possible that variations in six observed ...
).
AnalysisMokken scaling software
is available within the public domain statistical software
R (programming language)
R is a programming language for statistical computing and graphics supported by the R Core Team and the R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Created by statisticians Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman, R is used among data miners, bioinform ...
and also within the data analysis and statistical softwarstata
for use on
personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or tec ...
s is no longer compatible with current versions of Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for serv ...
. Also within the R (programming language)
R is a programming language for statistical computing and graphics supported by the R Core Team and the R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Created by statisticians Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman, R is used among data miners, bioinform ...
, unusual response patterns in Mokken Scales can be checked using the packagPerFit
Meijer, R.R., Niessen, A.S.M., and Tendeiro, J.N. (2015)
A practical guide to check the consistency of item response patterns in clinical research through person-fit statistics: examples and an computer programme
''Assessment'' 23, 56-62 Two guides on how to conduct a Mokken scale analysis have been published.
References
{{reflist, 2 Psychometrics Latent variable models Personality theories Market research