Mississippi Mr on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mississippi () is a
 Descendant Native American tribes of the Mississippian culture in the Southeast include the
Descendant Native American tribes of the Mississippian culture in the Southeast include the
 During the colonial era, European settlers imported
During the colonial era, European settlers imported

 On January 9, 1861, Mississippi became the second state to declare its secession from the
On January 9, 1861, Mississippi became the second state to declare its secession from the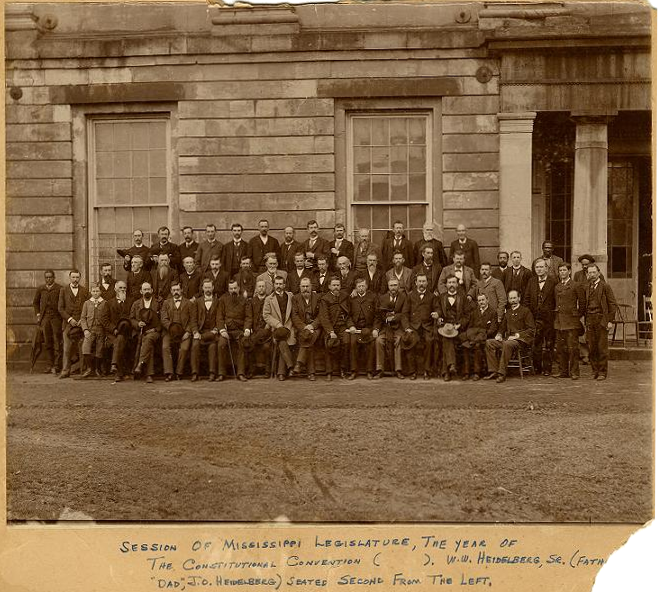  Around the start of the 20th century, two-thirds of the Mississippi farmers who owned land in the Delta were
Around the start of the 20th century, two-thirds of the Mississippi farmers who owned land in the Delta were  The loss of political influence contributed to the difficulties of African Americans in their attempts to obtain extended credit in the late 19th century. Together with imposition of
The loss of political influence contributed to the difficulties of African Americans in their attempts to obtain extended credit in the late 19th century. Together with imposition of
The Morris W. H. (Bill) Collins Speaker Series, Mississippi State University, accessed June 10, 2015 In 1966, the state was the last to repeal officially statewide Prohibition in the United States, prohibition of alcohol. Before that, Mississippi had taxed the illegal alcohol brought in by Rum-running, bootleggers. Governor Paul B. Johnson, Jr., Paul Johnson urged repeal and the sheriff "raided the annual Junior League Mardi Gras ball at the Jackson Country Club, breaking open the liquor cabinet and carting off the Champagne before a startled crowd of nobility and high-ranking state officials". On August 17, 1969, Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale, Category 5 Hurricane Camille hit the Mississippi coast, killing 248 people and causing US$1.5 billion in damage (1969 dollars). Mississippi ratified the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, in March 1984, which had already entered into force by August 1920; granting women the right to vote. In 1987, 20 years after the United States Supreme Court, U.S. Supreme Court had ruled in 1967's ''Loving v. Virginia'' that a similar Virginian law was unconstitutional, Mississippi repealed its ban on interracial marriage (also known as miscegenation), which had been enacted in 1890. It also repealed the Racial segregation in the United States, segregationist-era Poll tax (United States), poll tax in 1989. In 1995, the state symbolically ratified the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Thirteenth Amendment, which had abolished slavery in 1865. Though ratified in 1995, the state never officially notified the Archivist of the United States, Federal Archivist, which kept the ratification unofficial until 2013, when Ken Sullivan contacted the office of Secretary of State of Mississippi, Delbert Hosemann, who agreed to file the paperwork and make it official. In 2009, the legislature passed a bill to repeal other discriminatory civil rights laws, which had been enacted in 1964, the same year as the federal Civil Rights Act of 1964, Civil Rights Act, but ruled unconstitutional in 1967 by federal courts. Republican Governor Haley Barbour signed the bill into law. The end of legal segregation and The previous flag of Mississippi, used until June 30, 2020, featured the Flags of the Confederate States of America#Battle flag, Confederate battle flag. Mississippi became the last state to remove the Confederate battle flag as an official state symbol on June 30, 2020, when Governor Tate Reeves signed a law officially retiring the Flag of Mississippi#Second flag, second state flag. The current flag, The "New Magnolia" flag, was selected via referendum as part of the general election on November 3, 2020. It officially became the state flag on January 11, 2021, after being signed into law by the state legislature and governor.
The previous flag of Mississippi, used until June 30, 2020, featured the Flags of the Confederate States of America#Battle flag, Confederate battle flag. Mississippi became the last state to remove the Confederate battle flag as an official state symbol on June 30, 2020, when Governor Tate Reeves signed a law officially retiring the Flag of Mississippi#Second flag, second state flag. The current flag, The "New Magnolia" flag, was selected via referendum as part of the general election on November 3, 2020. It officially became the state flag on January 11, 2021, after being signed into law by the state legislature and governor.


 Mississippi is bordered to the north by
Mississippi is bordered to the north by
 Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 50,000 (United States Census Bureau as of 2017): Retrieved September 20, 2013
Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 20,000 but fewer than 50,000 (United States Census Bureau as of 2017):
Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 10,000 but fewer than 20,000 (United States Census Bureau as of 2017):
''(See: Lists of List of cities in Mississippi, cities, List of towns and villages in Mississippi, towns and villages, List of census-designated places in Mississippi, census-designated places, List of metropolitan areas in Mississippi, metropolitan areas, List of micropolitan areas in Mississippi, micropolitan areas, and List of counties in Mississippi, counties in Mississippi)''
Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 50,000 (United States Census Bureau as of 2017): Retrieved September 20, 2013
Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 20,000 but fewer than 50,000 (United States Census Bureau as of 2017):
Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 10,000 but fewer than 20,000 (United States Census Bureau as of 2017):
''(See: Lists of List of cities in Mississippi, cities, List of towns and villages in Mississippi, towns and villages, List of census-designated places in Mississippi, census-designated places, List of metropolitan areas in Mississippi, metropolitan areas, List of micropolitan areas in Mississippi, micropolitan areas, and List of counties in Mississippi, counties in Mississippi)''
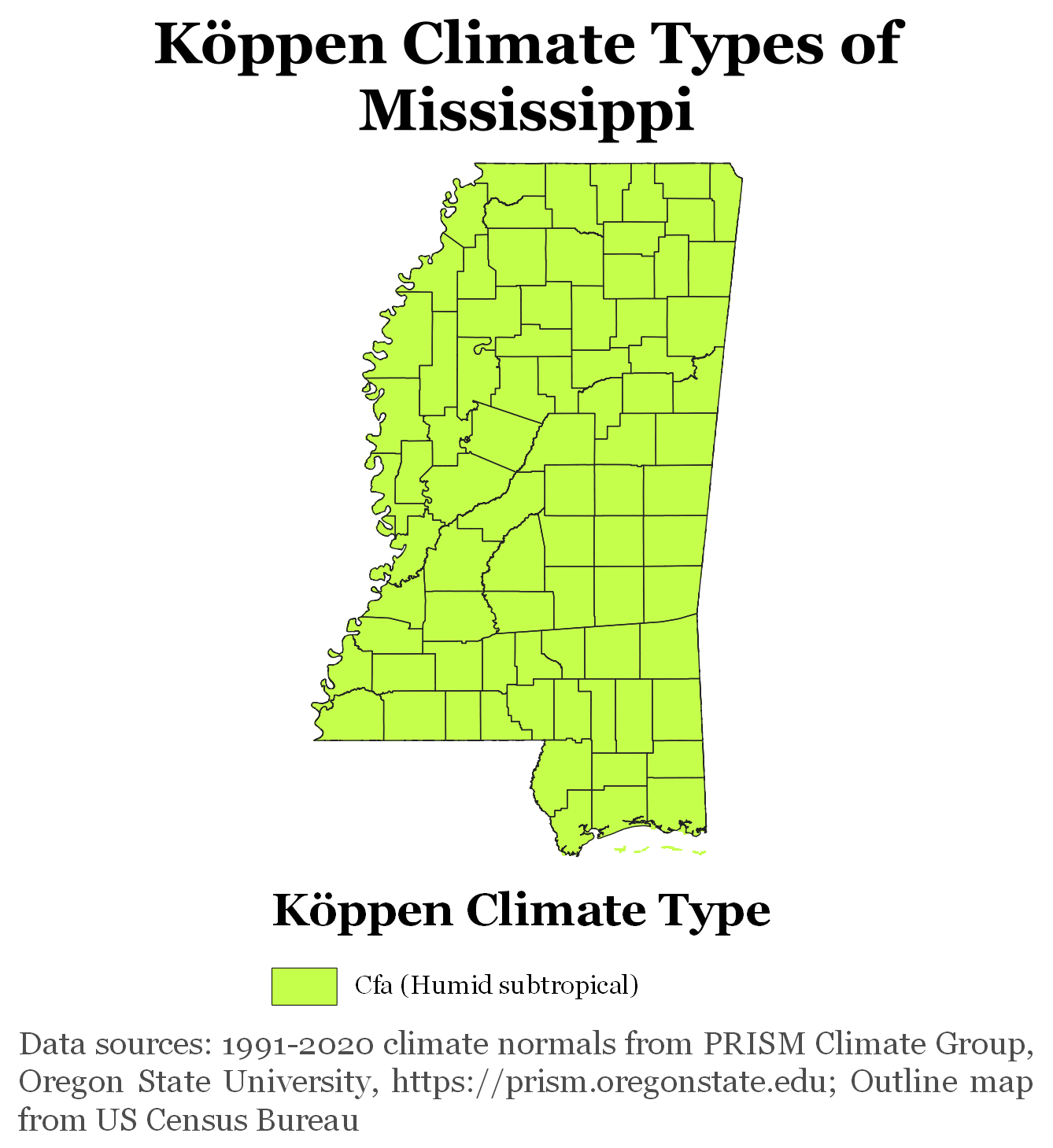 Mississippi has a
Mississippi has a  The late summer and fall is the seasonal period of risk for Tropical cyclone, hurricanes moving inland from the Gulf of Mexico, especially in the southern part of the state. Hurricane Camille in 1969 and Hurricane Katrina in 2005, which killed 238 people in the state, were the most devastating hurricanes to hit the state. Both caused nearly total storm surge destruction of structures in and around Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport, Biloxi, Mississippi, Biloxi, and Pascagoula, Mississippi, Pascagoula.
As in the rest of the
The late summer and fall is the seasonal period of risk for Tropical cyclone, hurricanes moving inland from the Gulf of Mexico, especially in the southern part of the state. Hurricane Camille in 1969 and Hurricane Katrina in 2005, which killed 238 people in the state, were the most devastating hurricanes to hit the state. Both caused nearly total storm surge destruction of structures in and around Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport, Biloxi, Mississippi, Biloxi, and Pascagoula, Mississippi, Pascagoula.
As in the rest of the

 Mississippi is heavily forested, with over half of the state's area covered by wild or cultivated trees. The southeastern part of the state is dominated by longleaf pine, in both uplands and lowland flatwoods and pitcher plant, Sarracenia bogs. The Mississippi Alluvial Plain, or Mississippi Delta, Delta, is primarily farmland and aquaculture ponds but also has sizeable tracts of Populus deltoides, cottonwood, Salix nigra, willows, bald cypress, and oaks. A belt of loess extends north to south in the western part of the state, where the Mississippi Alluvial Plain reaches the first hills; this region is characterized by rich, mesic mixed hardwood forests, with some species disjunct distribution, disjunct from Appalachian forests. Two bands of historical prairie, the Jackson Prairie and the Black Belt in the American South, Black Belt, run northwest to southeast in the middle and northeastern part of the state. Although these areas have been highly degraded by conversion to agriculture, a few areas remain, consisting of grassland with interspersed woodland of Juniperus virginiana, eastern redcedar, oaks, hickory, hickories, Maclura pomifera, osage-orange, and Celtis, sugarberry. The rest of the state, primarily north of Interstate 20 not including the prairie regions, consists of mixed pine-hardwood forest, common species being Pinus taeda, loblolly pine, oaks (e.g., Quercus nigra, water oak), hickory, hickories, Liquidambar styraciflua, sweetgum, and elm. Areas along large rivers are commonly inhabited by bald cypress, Nyssa aquatica, water tupelo, Planera aquatica, water elm, and Carya aquatica, bitter pecan. Commonly cultivated trees include loblolly pine, longleaf pine, Quercus pagoda, cherrybark oak, and cottonwood.
There are approximately 3000 species of vascular plants known from Mississippi. As of 2018, a project funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation aims to update that checklist of plants with museum (herbarium) plant collecting, vouchers and create an online atlas of each species's distribution.
About 420 species of List of birds of Mississippi, birds are known to inhabit Mississippi.
Mississippi has one of the richest fish faunas in the United States, with 204 native fish species.
Mississippi also has a rich freshwater mussel fauna, with about 90 species in the primary family of native mussels (Unionidae). Several of these species were extirpated during the construction of the Tennessee-Tombigbee Waterway.
Mississippi is home to 63 crayfish species, including at least 17 endemic species.
Mississippi is home to eight Capniidae, winter stonefly species.
Mississippi is heavily forested, with over half of the state's area covered by wild or cultivated trees. The southeastern part of the state is dominated by longleaf pine, in both uplands and lowland flatwoods and pitcher plant, Sarracenia bogs. The Mississippi Alluvial Plain, or Mississippi Delta, Delta, is primarily farmland and aquaculture ponds but also has sizeable tracts of Populus deltoides, cottonwood, Salix nigra, willows, bald cypress, and oaks. A belt of loess extends north to south in the western part of the state, where the Mississippi Alluvial Plain reaches the first hills; this region is characterized by rich, mesic mixed hardwood forests, with some species disjunct distribution, disjunct from Appalachian forests. Two bands of historical prairie, the Jackson Prairie and the Black Belt in the American South, Black Belt, run northwest to southeast in the middle and northeastern part of the state. Although these areas have been highly degraded by conversion to agriculture, a few areas remain, consisting of grassland with interspersed woodland of Juniperus virginiana, eastern redcedar, oaks, hickory, hickories, Maclura pomifera, osage-orange, and Celtis, sugarberry. The rest of the state, primarily north of Interstate 20 not including the prairie regions, consists of mixed pine-hardwood forest, common species being Pinus taeda, loblolly pine, oaks (e.g., Quercus nigra, water oak), hickory, hickories, Liquidambar styraciflua, sweetgum, and elm. Areas along large rivers are commonly inhabited by bald cypress, Nyssa aquatica, water tupelo, Planera aquatica, water elm, and Carya aquatica, bitter pecan. Commonly cultivated trees include loblolly pine, longleaf pine, Quercus pagoda, cherrybark oak, and cottonwood.
There are approximately 3000 species of vascular plants known from Mississippi. As of 2018, a project funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation aims to update that checklist of plants with museum (herbarium) plant collecting, vouchers and create an online atlas of each species's distribution.
About 420 species of List of birds of Mississippi, birds are known to inhabit Mississippi.
Mississippi has one of the richest fish faunas in the United States, with 204 native fish species.
Mississippi also has a rich freshwater mussel fauna, with about 90 species in the primary family of native mussels (Unionidae). Several of these species were extirpated during the construction of the Tennessee-Tombigbee Waterway.
Mississippi is home to 63 crayfish species, including at least 17 endemic species.
Mississippi is home to eight Capniidae, winter stonefly species.
 Mississippi's population has remained from 2 million people at the 1930 United States census, 1930 U.S. census, to 2.9 million at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. In contrast with
Mississippi's population has remained from 2 million people at the 1930 United States census, 1930 U.S. census, to 2.9 million at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. In contrast with
''The New York Times'', March 20, 2011, accessed October 25, 2012 In addition, Mississippi led the nation for most of the last decade in the growth of mixed marriages among its population. The total population has not increased significantly, but is young. Some of the above change in identification as mixed-race is due to new births. But, it appears mostly to reflect those residents who have chosen to identify as more than one race, who in earlier years may have identified by just one race and/or ethnicity. A binary racial system had been in place since slavery times and the days of official government racial segregation. In the civil rights era, people of African descent banded together in an inclusive community to achieve political power and gain restoration of their civil rights. As the demographer William H. Frey noted, "In Mississippi, I think it's [identifying as mixed race] changed from within." Historically in Mississippi, after Indian removal in the 1830s, the major groups were designated as black (African American), who were then mostly enslaved, and white (primarily European American). Matthew Snipp, also a demographer, commented on the increase in the 21st century in the number of people identifying as being of more than one race: "In a sense, they're rendering a more accurate portrait of their racial heritage that in the past would have been suppressed." After having accounted for a majority of the state's population since well before the American Civil War and through the 1930s, today
 Americans of Scots-Irish Americans, Scots-Irish, English Americans, English and Scottish Americans, Scottish ancestry are present throughout the state. It is believed that there are more people with such ancestry than identify as such on the census, in part because their immigrant ancestors are more distant in their family histories. English Americans, English, Scottish Americans, Scottish and Scots-Irish Americans, Scots-Irish are generally the most under-reported ancestry groups in both the South Atlantic states and the East South Central states. The historian David Hackett Fischer estimated that a minimum 20% of Mississippi's population is of English ancestry, though the figure is probably much higher, and another large percentage is of Scottish ancestry. Many Mississippians of such ancestry identify simply as American ancestry, American on questionnaires, because their families have been in North America for centuries. In the 1980 U.S. census, 656,371 Mississippians of a total of 1,946,775 identified as being of English ancestry, making them 38% of the state at the time.
The state in 2010 had the highest proportion of African Americans in the nation. The African American percentage of population has begun to increase due mainly to a younger population than the whites (the total fertility rates of the two races are approximately equal). Due to patterns of settlement and whites putting their children in private schools, in almost all of Mississippi's public school districts, a majority of students are African American. African Americans are the majority ethnic group in the northwestern Mississippi Delta, Yazoo Delta, and the southwestern and the central parts of the state. These are areas where, historically, African Americans owned land as farmers in the 19th century following the Civil War, or worked on cotton plantations and farms.
People of French American, French Creole ancestry form the largest demographic group in Hancock County, Mississippi, Hancock County on the Gulf Coast. The African American,
Americans of Scots-Irish Americans, Scots-Irish, English Americans, English and Scottish Americans, Scottish ancestry are present throughout the state. It is believed that there are more people with such ancestry than identify as such on the census, in part because their immigrant ancestors are more distant in their family histories. English Americans, English, Scottish Americans, Scottish and Scots-Irish Americans, Scots-Irish are generally the most under-reported ancestry groups in both the South Atlantic states and the East South Central states. The historian David Hackett Fischer estimated that a minimum 20% of Mississippi's population is of English ancestry, though the figure is probably much higher, and another large percentage is of Scottish ancestry. Many Mississippians of such ancestry identify simply as American ancestry, American on questionnaires, because their families have been in North America for centuries. In the 1980 U.S. census, 656,371 Mississippians of a total of 1,946,775 identified as being of English ancestry, making them 38% of the state at the time.
The state in 2010 had the highest proportion of African Americans in the nation. The African American percentage of population has begun to increase due mainly to a younger population than the whites (the total fertility rates of the two races are approximately equal). Due to patterns of settlement and whites putting their children in private schools, in almost all of Mississippi's public school districts, a majority of students are African American. African Americans are the majority ethnic group in the northwestern Mississippi Delta, Yazoo Delta, and the southwestern and the central parts of the state. These are areas where, historically, African Americans owned land as farmers in the 19th century following the Civil War, or worked on cotton plantations and farms.
People of French American, French Creole ancestry form the largest demographic group in Hancock County, Mississippi, Hancock County on the Gulf Coast. The African American,
 The revivals of the Great Awakening in the late 18th and early 19th centuries initially attracted the Plain Folk of the Old South, "plain folk" by reaching out to all members of society, including women and blacks. Both slaves and free blacks were welcomed into Methodist and Baptist churches. Independent black Baptist churches were established before 1800 in Virginia, Kentucky, South Carolina and Georgia, and later developed in Mississippi as well.
In the post-Civil War years, religion became more influential as the South became known as the "Bible Belt". By 2014, the Pew Research Center determined 83% of its population was Christian. In a separate study by the Public Religion Research Institute in 2020, 80% of the population was Christian.
Since the 1970s, fundamentalist conservative churches have grown rapidly, fueling Mississippi's conservative political trends among whites. In 1973 the Presbyterian Church in America attracted numerous conservative congregations. As of 2010, Mississippi remained a stronghold of the denomination, which originally was brought by Scots immigrants. The state has the highest adherence rate of the PCA in 2010, with 121 congregations and 18,500 members. It is among the few states where the PCA has higher membership than the PC(USA).
According to the Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA), in 2010 the
The revivals of the Great Awakening in the late 18th and early 19th centuries initially attracted the Plain Folk of the Old South, "plain folk" by reaching out to all members of society, including women and blacks. Both slaves and free blacks were welcomed into Methodist and Baptist churches. Independent black Baptist churches were established before 1800 in Virginia, Kentucky, South Carolina and Georgia, and later developed in Mississippi as well.
In the post-Civil War years, religion became more influential as the South became known as the "Bible Belt". By 2014, the Pew Research Center determined 83% of its population was Christian. In a separate study by the Public Religion Research Institute in 2020, 80% of the population was Christian.
Since the 1970s, fundamentalist conservative churches have grown rapidly, fueling Mississippi's conservative political trends among whites. In 1973 the Presbyterian Church in America attracted numerous conservative congregations. As of 2010, Mississippi remained a stronghold of the denomination, which originally was brought by Scots immigrants. The state has the highest adherence rate of the PCA in 2010, with 121 congregations and 18,500 members. It is among the few states where the PCA has higher membership than the PC(USA).
According to the Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA), in 2010 the
 The Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates that Mississippi's total state product in 2010 was $98 billion. GDP growth was .5 percent in 2015 and is estimated to be 2.4 in 2016 according to Dr. Darrin Webb, the state's chief economist, who noted it would make two consecutive years of positive growth since the recession.Pender, 2017. Per capita personal income in 2006 was $26,908, the lowest per capita personal income of any state, but the state also has the nation's lowest living costs. 2015 data records the adjusted per capita personal income at $40,105. Mississippians consistently rank as one of the highest per capita in charitable contributions.
At 56 percent, the state has one of the lowest workforce participation rates in the country. Approximately 70,000 adults are disabled, which is 10 percent of the workforce.
Mississippi's rank as one of the poorest states is related to its dependence on cotton agriculture before and after the Civil War, late development of its frontier bottomlands in the Mississippi Delta, repeated natural disasters of flooding in the late 19th and early 20th century that required massive capital investment in levees, and ditching and draining the bottomlands, and slow development of railroads to link bottomland towns and river cities.John Otto Solomon,''The Final Frontiers, 1880–1930: Settling the Southern Bottomlands''. Westport: Greenwood Press, 1999, pp.10–11, 42–43, 50–51, and 70 In addition, when Democrats regained control of the state legislature, they passed the 1890 constitution that discouraged corporate industrial development in favor of rural agriculture, a legacy that would slow the state's progress for years.
Before the Civil War, Mississippi was the fifth-wealthiest state in the nation, its wealth generated by the labor of slaves in cotton plantations along the rivers.
Slaves were counted as property and the rise in the cotton markets since the 1840s had increased their value. By 1860, a majority—55 percent—of the population of Mississippi was enslaved. Ninety percent of the Delta bottomlands were undeveloped and the state had low overall density of population.
The Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates that Mississippi's total state product in 2010 was $98 billion. GDP growth was .5 percent in 2015 and is estimated to be 2.4 in 2016 according to Dr. Darrin Webb, the state's chief economist, who noted it would make two consecutive years of positive growth since the recession.Pender, 2017. Per capita personal income in 2006 was $26,908, the lowest per capita personal income of any state, but the state also has the nation's lowest living costs. 2015 data records the adjusted per capita personal income at $40,105. Mississippians consistently rank as one of the highest per capita in charitable contributions.
At 56 percent, the state has one of the lowest workforce participation rates in the country. Approximately 70,000 adults are disabled, which is 10 percent of the workforce.
Mississippi's rank as one of the poorest states is related to its dependence on cotton agriculture before and after the Civil War, late development of its frontier bottomlands in the Mississippi Delta, repeated natural disasters of flooding in the late 19th and early 20th century that required massive capital investment in levees, and ditching and draining the bottomlands, and slow development of railroads to link bottomland towns and river cities.John Otto Solomon,''The Final Frontiers, 1880–1930: Settling the Southern Bottomlands''. Westport: Greenwood Press, 1999, pp.10–11, 42–43, 50–51, and 70 In addition, when Democrats regained control of the state legislature, they passed the 1890 constitution that discouraged corporate industrial development in favor of rural agriculture, a legacy that would slow the state's progress for years.
Before the Civil War, Mississippi was the fifth-wealthiest state in the nation, its wealth generated by the labor of slaves in cotton plantations along the rivers.
Slaves were counted as property and the rise in the cotton markets since the 1840s had increased their value. By 1860, a majority—55 percent—of the population of Mississippi was enslaved. Ninety percent of the Delta bottomlands were undeveloped and the state had low overall density of population.
 Largely due to the domination of the plantations in the American South, plantation economy, focused on the production of agriculture, agricultural
Largely due to the domination of the plantations in the American South, plantation economy, focused on the production of agriculture, agricultural
 Mississippi, like the rest of its southern neighbors, is a Right-to-work law#U.S. states with right-to-work laws, right-to-work state. It has some major automotive factories, such as the Toyota Motor Manufacturing Mississippi, Toyota Mississippi Plant in Blue Springs, Mississippi, Blue Springs and a Nissan Automotive plant in Canton, Mississippi, Canton. The latter produces the Nissan Titan.
Mississippi, like the rest of its southern neighbors, is a Right-to-work law#U.S. states with right-to-work laws, right-to-work state. It has some major automotive factories, such as the Toyota Motor Manufacturing Mississippi, Toyota Mississippi Plant in Blue Springs, Mississippi, Blue Springs and a Nissan Automotive plant in Canton, Mississippi, Canton. The latter produces the Nissan Titan.
 As with all other U.S. states and the federal government, Mississippi's government is based on the separation of legislative, executive and judicial power. Executive authority in the state rests with the Governor, currently Tate Reeves (Republican Party (United States), R). The lieutenant governor, currently Delbert Hosemann (Republican Party (United States), R), is elected on a separate ballot. Both the governor and lieutenant governor are elected to four-year terms of office. Unlike the federal government, but like many other U.S. states, most of the heads of major executive departments are elected by the citizens of Mississippi rather than appointed by the governor.
Mississippi is one of five states that elects its state officials in odd-numbered years (the others are Kentucky,
As with all other U.S. states and the federal government, Mississippi's government is based on the separation of legislative, executive and judicial power. Executive authority in the state rests with the Governor, currently Tate Reeves (Republican Party (United States), R). The lieutenant governor, currently Delbert Hosemann (Republican Party (United States), R), is elected on a separate ballot. Both the governor and lieutenant governor are elected to four-year terms of office. Unlike the federal government, but like many other U.S. states, most of the heads of major executive departments are elected by the citizens of Mississippi rather than appointed by the governor.
Mississippi is one of five states that elects its state officials in odd-numbered years (the others are Kentucky,
 Mississippi led the South in developing a Disfranchisement after Reconstruction era, disenfranchising constitution, passing it in 1890. By raising barriers to voter registration, the state legislature disenfranchised most blacks and many poor whites, excluding them from politics until the late 1960s. It established a one-party state dominated by white Democrats, particularly those politicians who supported poor whites and farmers. Although the state was dominated by one party, there were a small number of Democrats who fought against most legislative measures that disenfranchised most blacks. They also side with the small group of Mississippi Republicans that still existed in the state and Republicans at the federal level on legislative measures that benefited them.
Most blacks were still disenfranchised under the state's 1890 constitution and discriminatory practices, until passage of the
Mississippi led the South in developing a Disfranchisement after Reconstruction era, disenfranchising constitution, passing it in 1890. By raising barriers to voter registration, the state legislature disenfranchised most blacks and many poor whites, excluding them from politics until the late 1960s. It established a one-party state dominated by white Democrats, particularly those politicians who supported poor whites and farmers. Although the state was dominated by one party, there were a small number of Democrats who fought against most legislative measures that disenfranchised most blacks. They also side with the small group of Mississippi Republicans that still existed in the state and Republicans at the federal level on legislative measures that benefited them.
Most blacks were still disenfranchised under the state's 1890 constitution and discriminatory practices, until passage of the
 Mississippi is served by nine Interstate Highway System, interstate highways:
*
**
*
**
*
*
*
*
**
and fourteen main United States Numbered Highways, U.S. Routes:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
*
*
*
*
as well as a system of List of state highways in Mississippi, State Highways.
Mississippi is served by nine Interstate Highway System, interstate highways:
*
**
*
**
*
*
*
*
**
and fourteen main United States Numbered Highways, U.S. Routes:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
*
*
*
*
as well as a system of List of state highways in Mississippi, State Highways.
 *Arkabutla Lake of water; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
*Bay Springs Lake of water and of shoreline; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
*Grenada Lake of water; became operational in 1954; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
*Ross Barnett Reservoir of water; named for Ross Barnett, the 52nd List of Governors of Mississippi, Governor of Mississippi; became operational in 1966; constructed and managed by The Pearl River Valley Water Supply District, a state agency; provides water supply for the City of Jackson.
*Sardis Lake (Mississippi), Sardis Lake of water; became operational in October 1940; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
*Enid Lake of water; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army
*Arkabutla Lake of water; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
*Bay Springs Lake of water and of shoreline; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
*Grenada Lake of water; became operational in 1954; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
*Ross Barnett Reservoir of water; named for Ross Barnett, the 52nd List of Governors of Mississippi, Governor of Mississippi; became operational in 1966; constructed and managed by The Pearl River Valley Water Supply District, a state agency; provides water supply for the City of Jackson.
*Sardis Lake (Mississippi), Sardis Lake of water; became operational in October 1940; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
*Enid Lake of water; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army
 While Mississippi has been especially known for its music and literature, it has embraced other forms of art. Its strong religious traditions have inspired striking works by outsider artists who have been shown nationally.
Jackson established the USA International Ballet Competition, which is held every four years. This ballet competition attracts the most talented young dancers from around the world.
The Magnolia Independent Film Festival, still held annually in Starkville, Mississippi, Starkville, is the first and oldest in the state.
George Ohr, known as the "Mad Potter of Biloxi" and the father of abstract expressionism in pottery, lived and worked in Biloxi, MS.
While Mississippi has been especially known for its music and literature, it has embraced other forms of art. Its strong religious traditions have inspired striking works by outsider artists who have been shown nationally.
Jackson established the USA International Ballet Competition, which is held every four years. This ballet competition attracts the most talented young dancers from around the world.
The Magnolia Independent Film Festival, still held annually in Starkville, Mississippi, Starkville, is the first and oldest in the state.
George Ohr, known as the "Mad Potter of Biloxi" and the father of abstract expressionism in pottery, lived and worked in Biloxi, MS.
online edition
* Swain, Martha H. ed. ''Mississippi Women: Their Histories, Their Lives'' (2003). 17 short biographies
Mississippi Travel and TourismMississippi Development AuthorityThe "Mississippi Believe It" CampaignUSDA Mississippi State FactsUniversity Press of Mississippi
*[ftp://newftp.epa.gov/EPADataCommons/ORD/Ecoregions/ms/ms_eco_pg.pdf Ecoregions of Mississippi] *
Mississippi as Metaphor State, Region, and Nation in Historical Imagination
, ''Southern Spaces'', October 23, 2006. *
Mississippi State Databases
an annotated list of searchable databases compiled by the Government Documents Roundtable of the American Library Association. {{coord, 33, -90, dim:300000_region:US-MS_type:adm1st, name=State of Mississippi, display=title Mississippi, 1817 establishments in the United States Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Former French colonies Southern United States States and territories established in 1817 States of the Confederate States of America States of the Gulf Coast of the United States States of the United States Contiguous United States
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in the Southeastern
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each se ...
region of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, bordered to the north by Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
; to the east by Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
; to the southwest by Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
; and to the northwest by Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage ...
. Mississippi's western boundary is largely defined by the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
. Mississippi is the 32nd largest and 35th-most populous of the 50 U.S. states and has the lowest per-capita income in the United States. Jackson
Jackson may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Jackson (name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the surname or given name
Places
Australia
* Jackson, Queensland, a town in the Maranoa Region
* Jackson North, Qu ...
is both the state's capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and largest city. Greater Jackson is the state's most populous metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
, with a population of 591,978 in 2020.
On December 10, 1817, Mississippi became the 20th state admitted to the Union. By 1860, Mississippi was the nation's top cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
-producing state and slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
accounted for 55% of the state population. Mississippi declared its secession
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics le ...
from the Union
The Union may refer to:
Politics
* The Union (Germany) or CDU/CSU, the partnership of the German political parties the Christian Democratic Union and the Christian Social Union
* The Union (Italy), a former coalition of political parties in Ital ...
on January 9, 1861, and was one of the seven original Confederate States
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
, which constituted the largest slaveholding states in the nation. Following the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, it was restored to the Union on February 23, 1870.
Until the Great Migration of the 1930s, African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
were a majority of Mississippi's population. In 2020, 37.6% of Mississippi's population was African American, the highest percentage of any state. Mississippi was the site of many prominent events during the civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination ...
, including the Ole Miss riot of 1962
The Ole Miss riot of 1962 (September 30 – October 1, 1962), also known as the Battle of Oxford, was a violent disturbance that occurred at the University of Mississippi—commonly called Ole Miss—in Oxford, Mississippi. Segregationist r ...
by white students objecting to desegregation, the 1963 assassination of Medgar Evers
Medgar Wiley Evers (; July 2, 1925June 12, 1963) was an American civil rights activist and the NAACP's first field secretary in Mississippi, who was murdered by Byron De La Beckwith. Evers, a decorated U.S. Army combat veteran who had served i ...
, and the 1964 Freedom Summer murders of three activists working on voting rights.
Mississippi frequently ranks low among U.S. states
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
in measures of health, education, and development, while ranking high in measures of poverty. Top economic industries in Mississippi today are agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
and forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests, woodlands, and associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. Th ...
. Mississippi produces more than half of the country's farm-raised catfish, and is also a top producer of sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the Convolvulus, bindweed or morning glory family (biology), family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a r ...
es, cotton and pulpwood
Pulpwood is timber with the principal use of making wood pulp for paper production.
Applications
* Trees raised specifically for pulp production account for 15% of world pulp production, old growth forests 9% and second- and third- and more gener ...
. Other main industries in Mississippi include advanced manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing is the use of innovative technology to improve products or processes, with the relevant technology being described as advanced, innovative or cutting edge. Advanced manufacturing industries increasingly integrate new innov ...
, utilities
A public utility company (usually just utility) is an organization that maintains the infrastructure for a public service (often also providing a service using that infrastructure). Public utilities are subject to forms of public control and r ...
, transport
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, an ...
ation, and health services
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the preventive healthcare, prevention, diagnosis, therapy, treatment, wiktionary:amelioration, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other disability, physical and menta ...
.
Mississippi is almost entirely within the Gulf coastal plain
The Gulf Coastal Plain extends around the Gulf of Mexico in the Southern United States and eastern Mexico.
This coastal plain reaches from the Florida Panhandle, southwest Georgia, the southern two-thirds of Alabama, over most of Mississippi, wes ...
, and generally consists of lowland plains and low hills. The northwest remainder of the state consists of the Mississippi Delta
The Mississippi Delta, also known as the Yazoo–Mississippi Delta, or simply the Delta, is the distinctive northwest section of the U.S. state of Mississippi (and portions of Arkansas and Louisiana) that lies between the Mississippi and Yazoo ...
, a section of the Mississippi Alluvial Plain
The Mississippi River Alluvial Plain is an alluvial plain created by the Mississippi River on which lie parts of seven U.S. states, from southern Louisiana to southern Illinois (Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, Lou ...
. Mississippi's highest point is Woodall Mountain
Woodall Mountain is the highest natural point in the U.S. state of Mississippi at 806 feet (246 m). It is located just off Mississippi Highway 25, south of Iuka in Tishomingo County in the northeast part of the state.
Description
Located in th ...
at 807 feet (246 m) above sea level adjacent to the Cumberland Plateau
The Cumberland Plateau is the southern part of the Appalachian Plateau in the Appalachian Mountains of the United States. It includes much of eastern Kentucky and Tennessee, and portions of northern Alabama and northwest Georgia. The terms "Alle ...
; the lowest is the Gulf of Mexico. Mississippi has a humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
classification.
Etymology
The state's name is derived from theMississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
, which flows along and defines its western boundary. European-American settlers named it after the Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
word ᒥᓯ-ᓰᐱ ''misi-ziibi'' ().
History
Near 10,000 BC Native Americans or Paleo-Indians arrived in what today is referred to as theAmerican South
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
.
Paleo-Indians in the South were hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
s who pursued the megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, the megafauna (from Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and New Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") comprises the large or giant animals of an area, habitat, or geological period, extinct and/or extant. The most common threshold ...
that became extinct following the end of the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
age. In the Mississippi Delta
The Mississippi Delta, also known as the Yazoo–Mississippi Delta, or simply the Delta, is the distinctive northwest section of the U.S. state of Mississippi (and portions of Arkansas and Louisiana) that lies between the Mississippi and Yazoo ...
, Native American settlements and agricultural fields were developed on the natural levees, higher ground in the proximity of rivers. The Native Americans developed extensive fields near their permanent villages. Together with other practices, they created some localized deforestation but did not alter the ecology of the Mississippi Delta as a whole.
After thousands of years, succeeding cultures of the Woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the ''plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see ...
and Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a Native Americans in the United States, Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern United States, Midwestern, Eastern United States, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from appr ...
eras developed rich and complex agricultural societies, in which surplus supported the development of specialized trades. Both were mound builder cultures. Those of the Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a Native Americans in the United States, Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern United States, Midwestern, Eastern United States, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from appr ...
were the largest and most complex, constructed beginning about 950 AD. The peoples had a trading network spanning the continent from the Great Lakes to the Gulf Coast. Their large earthworks, which expressed their cosmology of political and religious concepts, still stand throughout the Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
and Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
valleys.
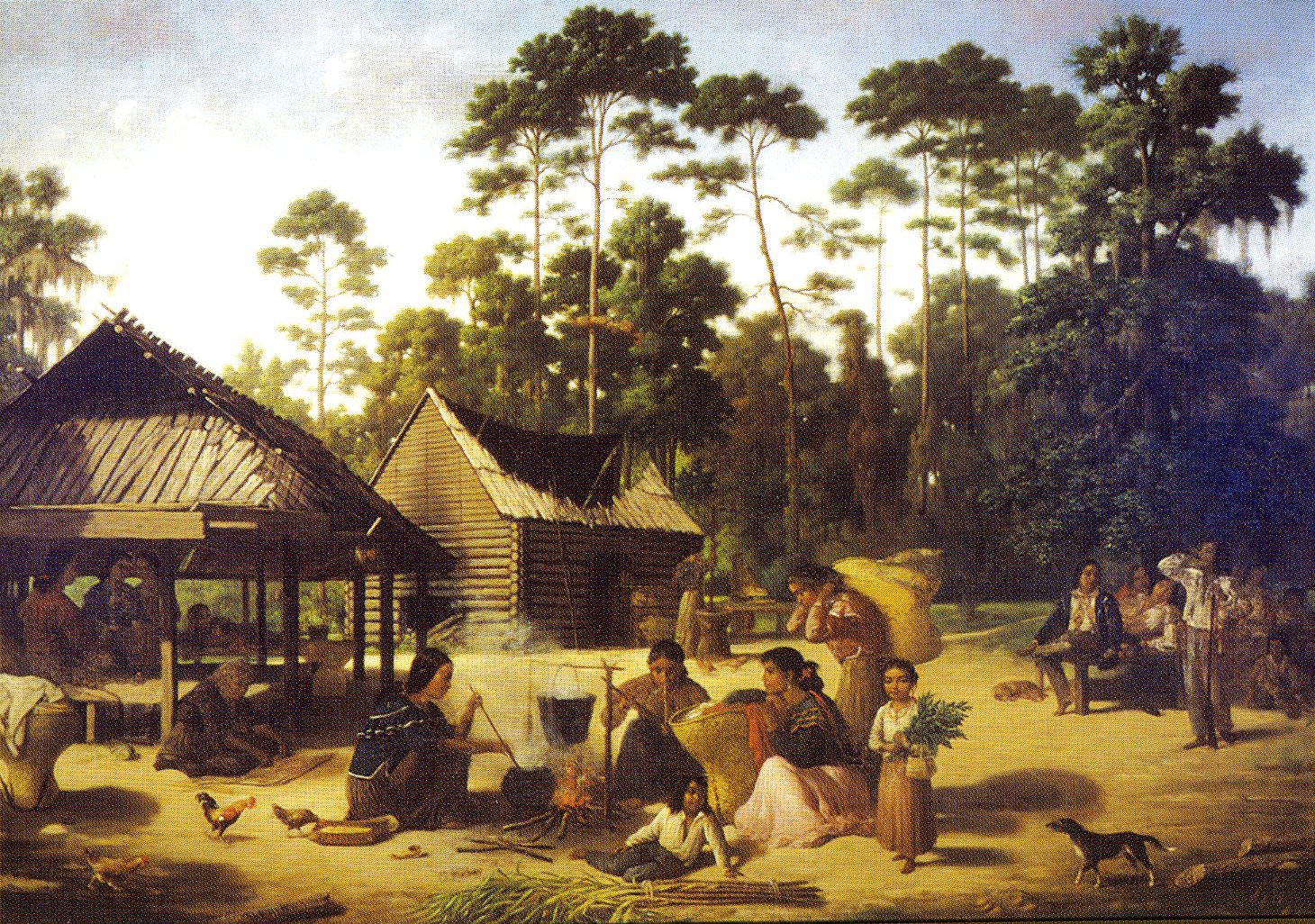
 Descendant Native American tribes of the Mississippian culture in the Southeast include the
Descendant Native American tribes of the Mississippian culture in the Southeast include the Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands. Their traditional territory was in the Southeastern United States of Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee as well in southwestern Kentucky. Their language is classified as ...
and Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
. Other tribes who inhabited the territory of Mississippi (and whose names were honored by colonists in local towns) include the Natchez Natchez may refer to:
Places
* Natchez, Alabama, United States
* Natchez, Indiana, United States
* Natchez, Louisiana, United States
* Natchez, Mississippi, a city in southwestern Mississippi, United States
* Grand Village of the Natchez, a site o ...
, the Yazoo, and the Biloxi
Biloxi ( ; ) is a city in and one of two county seats of Harrison County, Mississippi, United States (the other being the adjacent city of Gulfport). The 2010 United States Census recorded the population as 44,054 and in 2019 the estimated popu ...
.
The first major European expedition into the territory that became Mississippi was that of the Spanish explorer, Hernando de Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1500 – 21 May, 1542) was a Spanish explorer and '' conquistador'' who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire ...
, who passed through the northeast part of the state in 1540, in his second expedition to the New World.
Colonial era
In April 1699, French colonists established the first European settlement at ''Fort Maurepas
Fort Maurepas, later known as Old Biloxi,
"Pierre Le Moyne, Sieur d'Iberville" (biography),
''Catholic Encyclopedia'', 1907, webpage:
gives dates: 13 Feb. 1699, went to the mainland Biloxi,
with fort completion May 1, 1699; sailed f ...
'' (also known as Old Biloxi), built in the vicinity of present-day Ocean Springs
Ocean Springs is a city in Jackson County, Mississippi, United States, approximately east of Biloxi and west of Gautier. It is part of the Pascagoula, Mississippi Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 17,225 at the 2000 U.S. Census ...
on the Gulf Coast. It was settled by Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville
Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville (16 July 1661 – 9 July 1706) or Sieur d'Iberville was a French soldier, explorer, colonial administrator, and trader. He is noted for founding the colony of Louisiana in New France. He was born in Montreal to French ...
. In 1716, the French founded Natchez Natchez may refer to:
Places
* Natchez, Alabama, United States
* Natchez, Indiana, United States
* Natchez, Louisiana, United States
* Natchez, Mississippi, a city in southwestern Mississippi, United States
* Grand Village of the Natchez, a site o ...
on the Mississippi River (as ''Fort Rosalie
Fort Rosalie was built by the French in 1716 within the territory of the Natchez Native Americans and it was part of the French colonial empire in the present-day city of Natchez, Mississippi.
Early history
As part of the peace terms tha ...
''); it became the dominant town and trading post of the area. The French called the greater territory "New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spai ...
"; the Spanish continued to claim part of the Gulf coast
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Texas, Louisiana, Mississ ...
area (east of Mobile Bay
Mobile Bay ( ) is a shallow inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, lying within the state of Alabama in the United States. Its mouth is formed by the Fort Morgan Peninsula on the eastern side and Dauphin Island, a barrier island on the western side. The ...
) of present-day southern Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
, in addition to the entire area of present-day Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
. The British assumed control of the French territory after the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
.
 During the colonial era, European settlers imported
During the colonial era, European settlers imported enslaved Africans
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
to work on cash crop plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. The ...
s. Under French and Spanish rule, there developed a class of free people of color
In the context of the history of slavery in the Americas, free people of color (French: ''gens de couleur libres''; Spanish: ''gente de color libre'') were primarily people of mixed African, European, and Native American descent who were not ...
(''gens de couleur libres''), mostly multiracial
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-ethn ...
descendants of European men and enslaved or free black women, and their mixed-race
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-ethn ...
children. In the early days the French and Spanish colonists were chiefly men. Even as more European women joined the settlements, the men had interracial unions among women of African descent (and increasingly, multiracial descent), both before and after marriages to European women. Often the European men would help their multiracial children get educated or gain apprenticeships for trades, and sometimes they settled property on them; they often freed the mothers and their children if enslaved, as part of contracts of ''plaçage
Plaçage was a recognized extralegal system in French and Spanish slave colonies of North America (including the Caribbean) by which ethnic European men entered into civil unions with non-Europeans of African, Native American and mixed-race descen ...
''. With this social capital
Social capital is "the networks of relationships among people who live and work in a particular society, enabling that society to function effectively". It involves the effective functioning of social groups through interpersonal relationships ...
, the free people of color became artisans, and sometimes educated merchants and property owners, forming a third class between the Europeans and most enslaved Africans in the French and Spanish settlements, although not so large a free community as in the city of New Orleans
New Orleans ( , ,New Orleans
Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nuev ...
, Louisiana.
After Great Britain's victory in the Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nuev ...
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
(Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
), the French surrendered the Mississippi area to them under the terms of the Treaty of Paris (1763)
The Treaty of Paris, also known as the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Kingdom of France, France and Spanish Empire, Spain, with Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal in agree ...
. They also ceded their areas to the north that were east of the Mississippi River, including the Illinois Country and Quebec. After the Peace of Paris (1783)
The Peace of Paris of 1783 was the set of treaties that ended the American Revolutionary War. On 3 September 1783, representatives of King George III of Great Britain signed a treaty in Paris with representatives of the United States of America� ...
, the lower third of Mississippi came under Spanish rule as part of West Florida
West Florida ( es, Florida Occidental) was a region on the northern coast of the Gulf of Mexico that underwent several boundary and sovereignty changes during its history. As its name suggests, it was formed out of the western part of former S ...
. In 1819 the United States completed the purchase of West Florida and all of East Florida
East Florida ( es, Florida Oriental) was a colony of Great Britain from 1763 to 1783 and a province of Spanish Florida from 1783 to 1821. Great Britain gained control of the long-established Spanish colony of ''La Florida'' in 1763 as part of ...
in the Adams–Onís Treaty
The Adams–Onís Treaty () of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty,Weeks, p.168. was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to the U.S. and defined t ...
, and in 1822 both were merged into the Florida Territory
The Territory of Florida was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 30, 1822, until March 3, 1845, when it was admitted to the Union as the state of Florida. Originally the major portion of the Spanish te ...
.
United States territory
After theAmerican Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
(1775–83), Britain ceded this area to the new United States of America. The Mississippi Territory
The Territory of Mississippi was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from April 7, 1798, until December 10, 1817, when the western half of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Mississippi. T ...
was organized on April 7, 1798, from territory ceded by Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
and South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
to the United States. Their original colonial charters theoretically extended west to the Pacific Ocean. The Mississippi Territory was later twice expanded to include disputed territory claimed by both the United States and Spain.
From 1800 to about 1830, the United States purchased some lands (Treaty of Doak's Stand
The Treaty of Doak's Stand (7 Stat. 210, also known as Treaty with the Choctaw) was signed on October 18, 1820 (proclaimed on January 8, 1821) between the United States and the Choctaw Indian tribe. Based on the terms of the accord, the Choctaw ...
) from Native American tribes for new settlements of European Americans. The latter were mostly migrants from other Southern states, particularly Virginia and North Carolina, where soils were exhausted. New settlers kept encroaching on Choctaw land, and they pressed the federal government to expel the Native Americans. On September 27, 1830, the Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek
The Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek was a treaty which was signed on September 27, 1830, and proclaimed on February 24, 1831, between the Choctaw American Indian tribe and the United States Government. This treaty was the first removal treaty wh ...
was signed between the U.S. Government and the Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
. The Choctaw agreed to sell their traditional homelands in Mississippi and Alabama, for compensation and removal to reservations in Indian Territory
The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United St ...
(now Oklahoma). This opened up land for sale to European-American
European Americans (also referred to as Euro-Americans) are Americans of European ancestry. This term includes people who are descended from the first European settlers in the United States as well as people who are descended from more recent Eu ...
migrant settlement.
Article 14 in the treaty allowed those Choctaw who chose to remain in the states to become U.S. citizens, as they were considered to be giving up their tribal membership. They were the second major Native American ethnic group to do so (some Cherokee were the first, who chose to stay in North Carolina and other areas during rather than join the removal).
Today their descendants include approximately 9,500 persons identifying as Choctaw, who live in Neshoba, Newton, Leake, and Jones counties. The Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians
The Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians ( cho, Mississippi Chahta) is one of three federally recognized tribes of Choctaw Native Americans, and the only one in the state of Mississippi. On April 20, 1945, this tribe organized under the Indian Re ...
reorganized in the 20th century and is a Federally recognized tribe.
Many slaveholders brought enslaved African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
with them or purchased them through the domestic slave trade, especially in New Orleans
New Orleans ( , ,New Orleans
Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nuev ...
. Through the trade, an estimated nearly one million slaves were forcibly transported to the Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nuev ...
Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion in the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states most dependent on plantations and slavery prior to the American Civil War. Following the war ...
, including Mississippi, in an internal migration that broke up many slave families of the Upper South, where planters were selling excess slaves. The Southerners imposed slave laws in the Deep South and restricted the rights of free blacks.
Beginning in 1822, slaves in Mississippi were protected by law from cruel and unusual punishment by their owners. The Southern slave codes made the willful killing of a slave illegal in most cases. For example, the 1860 Mississippi case of ''Oliver v. State'' charged the defendant with murdering his own slave.

Statehood to Civil War
Mississippi became the 20th state on December 10, 1817. David Holmes was the first governor. The state was still occupied as ancestral land by several Native American tribes, including Choctaw, Natchez, Houma, Creek, and Chickasaw. Plantations were developed primarily along the major rivers, where the waterfront provided access to the major transportation routes. This is also where early towns developed, linked by thesteamboats
A steamboat is a boat that is marine propulsion, propelled primarily by marine steam engine, steam power, typically driving propellers or Paddle steamer, paddlewheels. Steamboats sometimes use the ship prefix, prefix designation SS, S.S. or S/S ...
that carried commercial products and crops to markets. The remainder of Native American ancestral land remained largely undeveloped but was sold through treaties until 1826, when the Choctaws and Chickasaws refused to sell more land. The combination of the Mississippi state legislature's abolition of Choctaw Tribal Government in 1829, President Andrew Jackson's Indian Removal Act
The Indian Removal Act was signed into law on May 28, 1830, by United States President Andrew Jackson. The law, as described by Congress, provided "for an exchange of lands with the Indians residing in any of the states or territories, and for ...
and the Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek
The Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek was a treaty which was signed on September 27, 1830, and proclaimed on February 24, 1831, between the Choctaw American Indian tribe and the United States Government. This treaty was the first removal treaty wh ...
of 1830, the Choctaw were effectively forced to sell their land and were transported to Oklahoma Territory. The forced migration of the Choctaw, together with other southeastern tribes removed as a result of the Act, became known as the Trail of Tears
The Trail of Tears was an ethnic cleansing and forced displacement of approximately 60,000 people of the "Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850 by the United States government. As part of the Indian removal, members of the Cherokee, ...
.
When cotton was king during the 1850s, Mississippi plantation owners—especially those of the Delta and Black Belt central regions—became wealthy due to the high fertility of the soil, the high price of cotton on the international market, and free labor gained through their holding enslaved African Americans. They used some of their profits to buy more cotton land and more slaves. The planters' dependence on hundreds of thousands of slaves for labor and the severe wealth imbalances among whites, played strong roles both in state politics and in planters' support for secession
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics le ...
. Mississippi was a slave society, with the economy dependent on slavery. The state was thinly settled, with population concentrated in the riverfront areas and towns.
By 1860, the enslaved African-American population numbered 436,631 or 55% of the state's total of 791,305 persons. Fewer than 1000 were free people of color
In the context of the history of slavery in the Americas, free people of color (French: ''gens de couleur libres''; Spanish: ''gente de color libre'') were primarily people of mixed African, European, and Native American descent who were not ...
. The relatively low population of the state before the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
reflected the fact that land and villages were developed only along the riverfronts, which formed the main transportation corridors. Ninety percent of the Delta bottomlands were still frontier and undeveloped.John C. Willis, ''Forgotten Time: The Yazoo-Mississippi Delta after the Civil War''. Charlottesville: University of Virginia Press, 2000, . The state needed many more settlers for development. The land further away from the rivers was cleared by freedmen and white migrants during Reconstruction and later.
Civil War to 20th century
 On January 9, 1861, Mississippi became the second state to declare its secession from the
On January 9, 1861, Mississippi became the second state to declare its secession from the Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
, and it was one of the founding members of the Confederate States
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
. The first six states to secede were those with the highest number of slaves. During the war, Union and Confederate forces struggled for dominance on the Mississippi River, critical to supply routes and commerce. More than 80,000 Mississippians fought in the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
for the Confederate Army
The Confederate States Army, also called the Confederate Army or the Southern Army, was the military land force of the Confederate States of America (commonly referred to as the Confederacy) during the American Civil War (1861–1865), fighting ...
. Around 17,000 black and 545 white Mississippians would serve in the Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union (American Civil War), Union of the collective U.S. st ...
. Pockets of Unionism in Mississippi were in places such as the northeastern corner of the state and Jones County, where Newton Knight
Newton Knight (November 10, 1829 – February 16, 1922) was an American farmer, soldier and Southern Unionist in Mississippi, best known as the leader of the Knight Company, a band of Confederate Army deserters who resisted the Confederacy du ...
, formed a revolt with Unionist leanings, known as the "Free State of Jones." Union General Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union Ar ...
's long siege of Vicksburg Vicksburg most commonly refers to:
* Vicksburg, Mississippi, a city in western Mississippi, United States
* The Vicksburg Campaign, an American Civil War campaign
* The Siege of Vicksburg, an American Civil War battle
Vicksburg is also the name of ...
finally gained the Union control of the river in 1863.
In the postwar period, freedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a formerly enslaved person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, enslaved people were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their captor-owners), abolitionism, emancipation (gra ...
withdrew from white-run churches to set up independent congregations. The majority of blacks left the Southern Baptist Convention
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC) is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist denomination, and the largest Protestant and second-largest Christian denomination in the United States. The wor ...
, sharply reducing its membership. They created independent black Baptist congregations. By 1895 they had established numerous black Baptist state associations and the National Baptist Convention of black churches.
In addition, independent black denominations, such as the African Methodist Episcopal Church
The African Methodist Episcopal Church, usually called the AME Church or AME, is a Black church, predominantly African American Methodist Religious denomination, denomination. It adheres to Wesleyan-Arminian theology and has a connexionalism, c ...
(established in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
in the early 19th century) and the African Methodist Episcopal Zion Church
African or Africans may refer to:
* Anything from or pertaining to the continent of Africa:
** People who are native to Africa, descendants of natives of Africa, or individuals who trace their ancestry to indigenous inhabitants of Africa
*** Ethn ...
(established in New York City), sent missionaries
A missionary is a member of a religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Mi ...
to the South in the postwar years. They quickly attracted hundreds of thousands of converts and founded new churches across the South. Southern congregations brought their own influences to those denominations as well.
During Reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
*Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*'' Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Unio ...
, the first Mississippi constitutional convention in 1868, with delegates both black and white, framed a constitution whose major elements would be maintained for 22 years. The convention was the first political organization in the state to include African-American representatives, 17 among the 100 members (32 counties had black majorities at the time). Some among the black delegates were freedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a formerly enslaved person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, enslaved people were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their captor-owners), abolitionism, emancipation (gra ...
, but others were educated free blacks who had migrated from the North. The convention adopted universal suffrage; did away with property qualifications for suffrage
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise, is the right to vote in representative democracy, public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally i ...
or for office, a change that also benefited both blacks and poor whites; provided for the state's first public school system; forbade race distinctions in the possession and inheritance of property; and prohibited limiting civil rights in travel. Under the terms of Reconstruction, Mississippi was restored to the Union on February 23, 1870.
Because the Mississippi Delta contained so much fertile bottomland that had not been developed before the American Civil War, 90 percent of the land was still frontier. After the Civil War, tens of thousands of migrants were attracted to the area by higher wages offered by planters trying to develop land. In addition, black and white workers could earn money by clearing the land and selling timber, and eventually advance to ownership. The new farmers included many freedmen, who by the late 19th century achieved unusually high rates of land ownership in the Mississippi bottomlands. In the 1870s and 1880s, many black farmers succeeded in gaining land ownership.
 Around the start of the 20th century, two-thirds of the Mississippi farmers who owned land in the Delta were
Around the start of the 20th century, two-thirds of the Mississippi farmers who owned land in the Delta were African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
. But many had become overextended with debt during the falling cotton prices of the difficult years of the late 19th century. Cotton prices fell throughout the decades following the Civil War. As another agricultural depression lowered cotton prices into the 1890s, numerous African-American farmers finally had to sell their land to pay off debts, thus losing the land which they had developed by hard, personal labor.
Democrats had regained control of the state legislature in 1875, after a year of expanded violence against blacks and intimidation of whites in what was called the "white line" campaign, based on asserting white supremacy
White supremacy or white supremacism is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races and thus should dominate them. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White su ...
. Democratic whites were well armed and formed paramilitary
A paramilitary is an organization whose structure, tactics, training, subculture, and (often) function are similar to those of a professional military, but is not part of a country's official or legitimate armed forces. Paramilitary units carr ...
organizations such as the Red Shirts to suppress black voting. From 1874 to the elections of 1875, they pressured whites to join the Democrats, and conducted violence against blacks in at least 15 known "riots" in cities around the state to intimidate blacks. They killed a total of 150 blacks, although other estimates place the death toll at twice as many. A total of three white Republicans and five white Democrats were reported killed. In rural areas, deaths of blacks could be covered up. Riots (better described as massacres of blacks) took place in Vicksburg, Clinton, Macon, and in their counties, as well-armed whites broke up black meetings and lynched
Lynching is an extrajudicial killing by a group. It is most often used to characterize informal public executions by a mob in order to punish an alleged transgressor, punish a convicted transgressor, or intimidate people. It can also be an ex ...
known black leaders, destroying local political organizations. Seeing the success of this deliberate "Mississippi Plan
The Mississippi Plan of 1875 was developed by white Southern Democrats as part of the white insurgency during the Reconstruction Era in the Southern United States. It was devised by the Democratic Party in that state to overthrow the Republican Pa ...
", South Carolina and other states followed it and also achieved white Democratic dominance. In 1877 by a national compromise, the last of federal troops were withdrawn from the region.
Even in this environment, black Mississippians continued to be elected to local office. However, black residents were deprived of all political power after white legislators passed a new state constitution in 1890 specifically to "eliminate the nigger from politics", according to the state's Democratic governor, James K. Vardaman
James Kimble Vardaman (July 26, 1861 – June 25, 1930) was an American politician from the U.S. state of Mississippi and was the Governor of Mississippi from 1904 to 1908. A Democrat, Vardaman was elected in 1912 to the United States Senate in ...
. It erected barriers to voter registration and instituted electoral provisions that effectively disenfranchised
Disfranchisement, also called disenfranchisement, or voter disqualification is the restriction of suffrage (the right to vote) of a person or group of people, or a practice that has the effect of preventing a person exercising the right to vote. D ...
most black Mississippians and many poor whites. Estimates are that 100,000 black and 50,000 white men were removed from voter registration rolls in the state over the next few years.
 The loss of political influence contributed to the difficulties of African Americans in their attempts to obtain extended credit in the late 19th century. Together with imposition of
The loss of political influence contributed to the difficulties of African Americans in their attempts to obtain extended credit in the late 19th century. Together with imposition of Jim Crow
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws enforcing racial segregation in the Southern United States. Other areas of the United States were affected by formal and informal policies of segregation as well, but many states outside the Sout ...
and racial segregation laws, whites increased violence against blacks, lynching mostly men, through the period of the 1890s and extending to 1930. Cotton crops failed due to boll weevil
The boll weevil (''Anthonomus grandis'') is a beetle that feeds on cotton buds and flowers. Thought to be native to Central Mexico, it migrated into the United States from Mexico in the late 19th century and had infested all U.S. cotton-growing ...
infestation and successive severe flooding in 1912 and 1913, creating crisis conditions for many African Americans. With control of the ballot box and more access to credit, white planters bought out such farmers, expanding their ownership of Delta bottomlands. They also took advantage of new railroads sponsored by the state.
20th century to present
In 1900, blacks made up more than half of the state's population. By 1910, a majority of black farmers in the Delta had lost their land and becomesharecropper
Sharecropping is a legal arrangement with regard to agricultural land in which a landowner allows a tenant to use the land in return for a share of the crops produced on that land.
Sharecropping has a long history and there are a wide range ...
s. By 1920, the third generation after freedom, most African Americans in Mississippi were landless laborers again facing poverty. Starting about 1913, tens of thousands of black Americans left Mississippi for the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
in the Great Migration to industrial cities such as St. Louis
St. Louis () is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578, while the bi-state metropolitan area, which e ...
, Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
, Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at th ...
, Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along the southern shore of Lake Erie, across the U.S. ...
, Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
and New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
. They sought jobs, better education for their children, the right to vote, relative freedom from discrimination, and better living. In the migration of 1910–1940, they left a society that had been steadily closing off opportunity. Most migrants from Mississippi took trains directly north to Chicago and often settled near former neighbors.
Blacks also faced violence in the form of lynching, shooting, and the burning of churches. In 1923, the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People
The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) is a civil rights organization in the United States, formed in 1909 as an interracial endeavor to advance justice for African Americans by a group including W. E. ...
stated "the Negro feels that life is not safe in Mississippi and his life may be taken with impunity at any time upon the slightest pretext or provocation by a white man".
In the early 20th century, some industries were established in Mississippi, but jobs were generally restricted to whites, including child workers. The lack of jobs also drove some southern whites north to cities such as Chicago and Detroit, seeking employment, where they also competed with European immigrants. The state depended on agriculture, but mechanization put many farm laborers out of work.
By 1900, many white ministers, especially in the towns, subscribed to the Social Gospel
The Social Gospel is a social movement within Protestantism that aims to apply Christian ethics to social problems, especially issues of social justice such as economic inequality, poverty, alcoholism, crime, racial tensions, slums, unclean envir ...
movement, which attempted to apply Christian ethics to social and economic needs of the day. Many strongly supported Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic ...
, believing it would help alleviate and prevent many sins. Mississippi became a dry state
A dry state was a state in the United States in which the manufacture, distribution, importation, and sale of alcoholic beverages was prohibited or tightly restricted. Some states, such as North Dakota, entered the United States as dry states, and ...
in 1908 by an act of the state legislature. It remained dry until the legislature passed a local option bill in 1966.
African-American Baptist churches grew to include more than twice the number of members as their white Baptist counterparts. The African-American call for social equality resonated throughout the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
in the 1930s and World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
in the 1940s.
The Second Great Migration
In the context of the 20th-century history of the United States, the Second Great Migration was the migration of more than 5 million African Americans from the South to the Northeast, Midwest and West. It began in 1940, through World War II, and ...
from the South started in the 1940s, lasting until 1970. Almost half a million people left Mississippi in the second migration, three-quarters of them black. Nationwide during the first half of the 20th century, African Americans became rapidly urbanized and many worked in industrial jobs. The Second Great Migration included destinations in the West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sunset, Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic languages, German ...
, especially California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
, where the buildup of the defense industry offered higher-paying jobs to both African Americans and whites.
Blacks and whites in Mississippi generated rich, quintessentially American music traditions: gospel music
Gospel music is a traditional genre of Christian music, and a cornerstone of Christian media. The creation, performance, significance, and even the definition of gospel music varies according to culture and social context. Gospel music is com ...
, country music
Country (also called country and western) is a genre of popular music that originated in the Southern and Southwestern United States in the early 1920s. It primarily derives from blues, church music such as Southern gospel and spirituals, ...
, jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a major ...
, blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form which originated in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues incorporated spirituals, work songs, field hollers, shouts, chants, and rhymed simple narrative ballads from the Afr ...
and rock and roll
Rock and roll (often written as rock & roll, rock 'n' roll, or rock 'n roll) is a Genre (music), genre of popular music that evolved in the United States during the late 1940s and early 1950s. It Origins of rock and roll, originated from Africa ...
. All were invented, promulgated or heavily developed by Mississippi musicians, many of them African American, and most came from the Mississippi Delta
The Mississippi Delta, also known as the Yazoo–Mississippi Delta, or simply the Delta, is the distinctive northwest section of the U.S. state of Mississippi (and portions of Arkansas and Louisiana) that lies between the Mississippi and Yazoo ...
. Many musicians carried their music north to Chicago, where they made it the heart of that city's jazz and blues.
So many African Americans left in the Great Migration that after the 1930s, they became a minority in Mississippi. In 1960 they made up 42% of the state's population. The whites maintained their discriminatory voter registration processes established in 1890, preventing most blacks from voting, even if they were well educated. Court challenges were not successful until later in the century. After World War II, African-American veterans returned with renewed commitment to be treated as full citizens of the United States and increasingly organized to gain enforcement of their constitutional rights.
The Civil Rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination ...
had many roots in religion, and the strong community of churches helped supply volunteers and moral purpose for their activism. Mississippi was a center of activity, based in black churches, to educate and register black voters, and to work for integration. In 1954 the state had created the Mississippi State Sovereignty Commission
The Mississippi State Sovereignty Commission (also called the Sov-Com) was a state agency in Mississippi from 1956 to 1977 tasked with fighting desegregation and controlling civil rights activism. It was overseen by the Governor of Mississippi. T ...
, a tax-supported agency, chaired by the Governor, that claimed to work for the state's image but effectively spied on activists and passed information to the local White Citizens' Councils to suppress black activism. White Citizens Councils
The Citizens' Councils (commonly referred to as the White Citizens' Councils) were an associated network of White supremacy, white supremacist, Racial segregation in the United States, segregationist organizations in the United States, concentra ...
had been formed in many cities and towns to resist integration of schools following the unanimous 1954 United States Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
ruling (''Brown v. Board of Education
''Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka'', 347 U.S. 483 (1954), was a landmark decision by the U.S. Supreme Court, which ruled that U.S. state laws establishing racial segregation in public schools are unconstitutional, even if the segregat ...
'') that segregation of public schools was unconstitutional. They used intimidation and economic blackmail against activists and suspected activists, including teachers and other professionals. Techniques included loss of jobs and eviction from rental housing.
In the summer of 1964 students and community organizers from across the country came to help register black voters in Mississippi and establish Freedom Schools Freedom Schools were temporary, alternative, and free schools for African Americans mostly in the South. They were originally part of a nationwide effort during the Civil Rights Movement to organize African Americans to achieve social, political and ...
. The Mississippi Freedom Democratic Party
The Mississippi Freedom Democratic Party (MFDP), also referred to as the Freedom Democratic Party, was an American political party created in 1964 as a branch of the populist Freedom Democratic organization in the state of Mississippi during the ...
was established to challenge the all-white Democratic Party of the Solid South
The Solid South or Southern bloc was the electoral voting bloc of the states of the Southern United States for issues that were regarded as particularly important to the interests of Democrats in those states. The Southern bloc existed especial ...
. Most white politicians resisted such changes. Chapters of the Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to the KKK or the Klan, is an American white supremacist, right-wing terrorist, and hate group whose primary targets are African Americans, Jews, Latinos, Asian Americans, Native Americans, and ...
and its sympathizers used violence against activists, most notably the murders of Chaney, Goodman, and Schwerner
The murders of Chaney, Goodman, and Schwerner, also known as the Freedom Summer murders, the Mississippi civil rights workers' murders, or the Mississippi Burning murders, refers to events in which three activists were abducted and murdered in ...
in 1964 during the Freedom Summer
Freedom Summer, also known as the Freedom Summer Project or the Mississippi Summer Project, was a volunteer campaign in the United States launched in June 1964 to attempt to register as many African-American voters as possible in Mississippi. ...
campaign. This was a catalyst for Congressional passage the following year of the Voting Rights Act of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights movement ...
. Mississippi earned a reputation in the 1960s as a reactionary state.
After decades of disenfranchisement, African Americans in the state gradually began to exercise their right to vote again for the first time since the 19th century, following the passage of federal civil rights legislation in 1964 and 1965, which ended ''de jure'' segregation and enforced constitutional voting rights. Registration of African-American voters increased and black candidates ran in the 1967 elections for state and local offices. The Mississippi Freedom Democratic Party fielded some candidates. Teacher Robert G. Clark, Jr., Robert G. Clark of Holmes County was the first African American to be elected to the State House since Reconstruction. He continued as the only African American in the state legislature until 1976 and was repeatedly elected into the 21st century, including three terms as Speaker of the House."Robert G. Clark, 26 October 2000 (video)"The Morris W. H. (Bill) Collins Speaker Series, Mississippi State University, accessed June 10, 2015 In 1966, the state was the last to repeal officially statewide Prohibition in the United States, prohibition of alcohol. Before that, Mississippi had taxed the illegal alcohol brought in by Rum-running, bootleggers. Governor Paul B. Johnson, Jr., Paul Johnson urged repeal and the sheriff "raided the annual Junior League Mardi Gras ball at the Jackson Country Club, breaking open the liquor cabinet and carting off the Champagne before a startled crowd of nobility and high-ranking state officials". On August 17, 1969, Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale, Category 5 Hurricane Camille hit the Mississippi coast, killing 248 people and causing US$1.5 billion in damage (1969 dollars). Mississippi ratified the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, in March 1984, which had already entered into force by August 1920; granting women the right to vote. In 1987, 20 years after the United States Supreme Court, U.S. Supreme Court had ruled in 1967's ''Loving v. Virginia'' that a similar Virginian law was unconstitutional, Mississippi repealed its ban on interracial marriage (also known as miscegenation), which had been enacted in 1890. It also repealed the Racial segregation in the United States, segregationist-era Poll tax (United States), poll tax in 1989. In 1995, the state symbolically ratified the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Thirteenth Amendment, which had abolished slavery in 1865. Though ratified in 1995, the state never officially notified the Archivist of the United States, Federal Archivist, which kept the ratification unofficial until 2013, when Ken Sullivan contacted the office of Secretary of State of Mississippi, Delbert Hosemann, who agreed to file the paperwork and make it official. In 2009, the legislature passed a bill to repeal other discriminatory civil rights laws, which had been enacted in 1964, the same year as the federal Civil Rights Act of 1964, Civil Rights Act, but ruled unconstitutional in 1967 by federal courts. Republican Governor Haley Barbour signed the bill into law. The end of legal segregation and
Jim Crow
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws enforcing racial segregation in the Southern United States. Other areas of the United States were affected by formal and informal policies of segregation as well, but many states outside the Sout ...
led to the integration of some churches, but most today remain divided along racial and cultural lines, having developed different traditions. After the Civil War, most African Americans left white churches to establish their own independent congregations, particularly Baptist churches, establishing state associations and a national association by the end of the century. They wanted to express their own traditions of worship and practice. In more diverse communities, such as Hattiesburg, Mississippi, Hattiesburg, some churches have multiracial congregations.
On August 29, 2005, Hurricane Katrina, though a Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale, Category 3 storm upon final landfall, caused even greater destruction across the entire of the Mississippi Gulf Coast from Louisiana to Alabama.
Geography


Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
, to the east by Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
, to the south by Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
and a narrow coast on the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
; and to the west, across the Mississippi River, by Louisiana and Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage ...
.
In addition to its namesake, major rivers in Mississippi include the Big Black River (Mississippi), Big Black River, the Pearl River (Mississippi-Louisiana), Pearl River, the Yazoo River, the Pascagoula River, and the Tombigbee River. Major lakes include Ross Barnett Reservoir, Arkabutla Lake, Arkabutla, Sardis Lake (Mississippi), Sardis, and Grenada Lake, Grenada, with the largest being Sardis Lake.
Mississippi is entirely composed of lowlands, the highest point being Woodall Mountain
Woodall Mountain is the highest natural point in the U.S. state of Mississippi at 806 feet (246 m). It is located just off Mississippi Highway 25, south of Iuka in Tishomingo County in the northeast part of the state.
Description
Located in th ...
, at above sea level, in the northeastern part of the state. The lowest point is sea level at the Gulf Coast. The state's mean elevation is above sea level.
Most of Mississippi is part of the East Gulf Coastal Plain. The coastal plain is generally composed of low hills, such as the Pine Hills in the south and the North Central Hills. The Pontotoc Ridge and the Fall Line Hills in the northeast have somewhat higher elevations. Yellow-brown loess soil is found in the western parts of the state. The northeast is a region of fertile black earth uplands, a geology that extend into the Black Belt (region of Alabama), Alabama Black Belt.
The coastline includes large bays at Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, Bay St. Louis, Biloxi, Mississippi, Biloxi, and Pascagoula, Mississippi, Pascagoula. It is separated from the Gulf of Mexico proper by the shallow Mississippi Sound, which is partially sheltered by Petit Bois Island (Mississippi), Petit Bois Island, Horn Island (Mississippi), Horn Island, Ship Island (Mississippi), East and West Ship Islands, Deer Island (Mississippi), Deer Island, Round Island (Mississippi), Round Island, and Cat Island (Mississippi), Cat Island.
The northwest remainder of the state consists of the Mississippi Delta
The Mississippi Delta, also known as the Yazoo–Mississippi Delta, or simply the Delta, is the distinctive northwest section of the U.S. state of Mississippi (and portions of Arkansas and Louisiana) that lies between the Mississippi and Yazoo ...
, a section of the Mississippi Alluvial Plain
The Mississippi River Alluvial Plain is an alluvial plain created by the Mississippi River on which lie parts of seven U.S. states, from southern Louisiana to southern Illinois (Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, Lou ...
. The plain is narrow in the south and widens north of Vicksburg, Mississippi, Vicksburg. The region has rich soil, partly made up of silt which had been regularly deposited by the Flood plain, flood waters of the Mississippi River.
Areas under the management of the National Park Service include:
* Brices Cross Roads National Battlefield Site near Baldwyn, Mississippi, Baldwyn
* Gulf Islands National Seashore
* Natchez National Historical Park in Natchez Natchez may refer to:
Places
* Natchez, Alabama, United States
* Natchez, Indiana, United States
* Natchez, Louisiana, United States
* Natchez, Mississippi, a city in southwestern Mississippi, United States
* Grand Village of the Natchez, a site o ...
* Natchez Trace National Scenic Trail in Tupelo, Mississippi, Tupelo
* Natchez Trace Parkway
* Tupelo National Battlefield in Tupelo
* Vicksburg National Military Park, Vicksburg National Military Park and Cemetery in Vicksburg, Mississippi, Vicksburg
Major cities and towns
 Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 50,000 (United States Census Bureau as of 2017): Retrieved September 20, 2013
Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 20,000 but fewer than 50,000 (United States Census Bureau as of 2017):
Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 10,000 but fewer than 20,000 (United States Census Bureau as of 2017):
''(See: Lists of List of cities in Mississippi, cities, List of towns and villages in Mississippi, towns and villages, List of census-designated places in Mississippi, census-designated places, List of metropolitan areas in Mississippi, metropolitan areas, List of micropolitan areas in Mississippi, micropolitan areas, and List of counties in Mississippi, counties in Mississippi)''
Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 50,000 (United States Census Bureau as of 2017): Retrieved September 20, 2013
Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 20,000 but fewer than 50,000 (United States Census Bureau as of 2017):
Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 10,000 but fewer than 20,000 (United States Census Bureau as of 2017):
''(See: Lists of List of cities in Mississippi, cities, List of towns and villages in Mississippi, towns and villages, List of census-designated places in Mississippi, census-designated places, List of metropolitan areas in Mississippi, metropolitan areas, List of micropolitan areas in Mississippi, micropolitan areas, and List of counties in Mississippi, counties in Mississippi)''
Climate
 Mississippi has a
Mississippi has a humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
with long, hot and humid summers, and short, mild winters. Temperatures average about in July and about in January. The temperature varies little statewide in the summer; however, in winter, the region near Mississippi Sound is significantly warmer than the inland portion of the state. The recorded temperature in Mississippi has ranged from , in 1966, at Corinth, Mississippi, Corinth in the northeast, to , in 1930, at Holly Springs, Mississippi, Holly Springs in the north. Heavy snowfall rarely occurs, but isn't unheard of, such as during the New Year's Eve 1963 snowstorm. Yearly Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation generally increases from north to south, with the regions closer to the Gulf being the most humid. Thus, Clarksdale, Mississippi, Clarksdale, in the northwest, gets about of precipitation annually and Biloxi, Mississippi, Biloxi, in the south, about . Small amounts of snow fall in northern and central Mississippi; snow is occasional in the southern part of the state.
 The late summer and fall is the seasonal period of risk for Tropical cyclone, hurricanes moving inland from the Gulf of Mexico, especially in the southern part of the state. Hurricane Camille in 1969 and Hurricane Katrina in 2005, which killed 238 people in the state, were the most devastating hurricanes to hit the state. Both caused nearly total storm surge destruction of structures in and around Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport, Biloxi, Mississippi, Biloxi, and Pascagoula, Mississippi, Pascagoula.
As in the rest of the
The late summer and fall is the seasonal period of risk for Tropical cyclone, hurricanes moving inland from the Gulf of Mexico, especially in the southern part of the state. Hurricane Camille in 1969 and Hurricane Katrina in 2005, which killed 238 people in the state, were the most devastating hurricanes to hit the state. Both caused nearly total storm surge destruction of structures in and around Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport, Biloxi, Mississippi, Biloxi, and Pascagoula, Mississippi, Pascagoula.
As in the rest of the Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion in the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states most dependent on plantations and slavery prior to the American Civil War. Following the war ...
, thunderstorms are common in Mississippi, especially in the southern part of the state. On average, Mississippi has around 27 tornadoes annually; the northern part of the state has more tornadoes earlier in the year and the southern part a higher frequency later in the year. Two of the five deadliest tornadoes in United States history have occurred in the state. These storms struck Natchez Natchez may refer to:
Places
* Natchez, Alabama, United States
* Natchez, Indiana, United States
* Natchez, Louisiana, United States
* Natchez, Mississippi, a city in southwestern Mississippi, United States
* Grand Village of the Natchez, a site o ...
, in southwest Mississippi (see The Great Natchez Tornado) and Tupelo, Mississippi, Tupelo, in the northeast corner of the state. About seven F5 tornadoes have been recorded in the state.
Climate change
Ecology, flora, and fauna

 Mississippi is heavily forested, with over half of the state's area covered by wild or cultivated trees. The southeastern part of the state is dominated by longleaf pine, in both uplands and lowland flatwoods and pitcher plant, Sarracenia bogs. The Mississippi Alluvial Plain, or Mississippi Delta, Delta, is primarily farmland and aquaculture ponds but also has sizeable tracts of Populus deltoides, cottonwood, Salix nigra, willows, bald cypress, and oaks. A belt of loess extends north to south in the western part of the state, where the Mississippi Alluvial Plain reaches the first hills; this region is characterized by rich, mesic mixed hardwood forests, with some species disjunct distribution, disjunct from Appalachian forests. Two bands of historical prairie, the Jackson Prairie and the Black Belt in the American South, Black Belt, run northwest to southeast in the middle and northeastern part of the state. Although these areas have been highly degraded by conversion to agriculture, a few areas remain, consisting of grassland with interspersed woodland of Juniperus virginiana, eastern redcedar, oaks, hickory, hickories, Maclura pomifera, osage-orange, and Celtis, sugarberry. The rest of the state, primarily north of Interstate 20 not including the prairie regions, consists of mixed pine-hardwood forest, common species being Pinus taeda, loblolly pine, oaks (e.g., Quercus nigra, water oak), hickory, hickories, Liquidambar styraciflua, sweetgum, and elm. Areas along large rivers are commonly inhabited by bald cypress, Nyssa aquatica, water tupelo, Planera aquatica, water elm, and Carya aquatica, bitter pecan. Commonly cultivated trees include loblolly pine, longleaf pine, Quercus pagoda, cherrybark oak, and cottonwood.
There are approximately 3000 species of vascular plants known from Mississippi. As of 2018, a project funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation aims to update that checklist of plants with museum (herbarium) plant collecting, vouchers and create an online atlas of each species's distribution.
About 420 species of List of birds of Mississippi, birds are known to inhabit Mississippi.
Mississippi has one of the richest fish faunas in the United States, with 204 native fish species.
Mississippi also has a rich freshwater mussel fauna, with about 90 species in the primary family of native mussels (Unionidae). Several of these species were extirpated during the construction of the Tennessee-Tombigbee Waterway.
Mississippi is home to 63 crayfish species, including at least 17 endemic species.
Mississippi is home to eight Capniidae, winter stonefly species.
Mississippi is heavily forested, with over half of the state's area covered by wild or cultivated trees. The southeastern part of the state is dominated by longleaf pine, in both uplands and lowland flatwoods and pitcher plant, Sarracenia bogs. The Mississippi Alluvial Plain, or Mississippi Delta, Delta, is primarily farmland and aquaculture ponds but also has sizeable tracts of Populus deltoides, cottonwood, Salix nigra, willows, bald cypress, and oaks. A belt of loess extends north to south in the western part of the state, where the Mississippi Alluvial Plain reaches the first hills; this region is characterized by rich, mesic mixed hardwood forests, with some species disjunct distribution, disjunct from Appalachian forests. Two bands of historical prairie, the Jackson Prairie and the Black Belt in the American South, Black Belt, run northwest to southeast in the middle and northeastern part of the state. Although these areas have been highly degraded by conversion to agriculture, a few areas remain, consisting of grassland with interspersed woodland of Juniperus virginiana, eastern redcedar, oaks, hickory, hickories, Maclura pomifera, osage-orange, and Celtis, sugarberry. The rest of the state, primarily north of Interstate 20 not including the prairie regions, consists of mixed pine-hardwood forest, common species being Pinus taeda, loblolly pine, oaks (e.g., Quercus nigra, water oak), hickory, hickories, Liquidambar styraciflua, sweetgum, and elm. Areas along large rivers are commonly inhabited by bald cypress, Nyssa aquatica, water tupelo, Planera aquatica, water elm, and Carya aquatica, bitter pecan. Commonly cultivated trees include loblolly pine, longleaf pine, Quercus pagoda, cherrybark oak, and cottonwood.
There are approximately 3000 species of vascular plants known from Mississippi. As of 2018, a project funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation aims to update that checklist of plants with museum (herbarium) plant collecting, vouchers and create an online atlas of each species's distribution.
About 420 species of List of birds of Mississippi, birds are known to inhabit Mississippi.
Mississippi has one of the richest fish faunas in the United States, with 204 native fish species.
Mississippi also has a rich freshwater mussel fauna, with about 90 species in the primary family of native mussels (Unionidae). Several of these species were extirpated during the construction of the Tennessee-Tombigbee Waterway.
Mississippi is home to 63 crayfish species, including at least 17 endemic species.
Mississippi is home to eight Capniidae, winter stonefly species.
Ecological problems
Flooding
Due to seasonal flooding, possible from December to June, the Mississippi River, Mississippi and Yazoo River, Yazoo rivers and their tributaries created a fertile floodplain in the Mississippi Delta. The river's flooding created natural levees, which planters had built higher to try to prevent flooding of land cultivated for cotton crops. Temporary workers built levees along the Mississippi River on top of the natural levees that formed from dirt deposited after the river flooded. From 1858 to 1861, the state took over levee building, accomplishing it through contractors and hired labor. In those years, planters considered their slaves too valuable to hire out for such dangerous work. Contractors hired gangs of Irish immigrant laborers to build levees and sometimes clear land. Many of the Irish were relatively recent immigrants from the famine years who were struggling to get established. Before theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, the earthwork levees averaged six feet in height, although in some areas they reached twenty feet.
Flooding has been an integral part of Mississippi history, but clearing of the land for cultivation and to supply wood fuel for steamboats took away the absorption of trees and undergrowth. The banks of the river were denuded, becoming unstable and changing the character of the river. After the Civil War, major floods swept down the valley in 1865, 1867, 1874 and 1882. Such floods regularly overwhelmed levees damaged by Confederate and Union fighting during the war, as well as those constructed after the war. In 1877, the state created the Mississippi Levee District for southern counties.
In 1879, the United States Congress created the Mississippi River Commission, whose responsibilities included aiding state levee boards in the construction of levees. Both white and black transient workers were hired to build the levees in the late 19th century. By 1882, levees averaged seven feet in height, but many in the southern Delta were severely tested by the flood that year. After the 1882 flood, the levee system was expanded. In 1884, the Yazoo-Mississippi Delta Levee District was established to oversee levee construction and maintenance in the northern Delta counties; also included were some counties in Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage ...
which were part of the Delta.
Flooding overwhelmed northwestern Mississippi in 1912–1913, causing heavy damage to the levee districts. Regional losses and the Mississippi River Levee Association's lobbying for a flood control bill helped gain passage of national bills in 1917 and 1923 to provide federal matching funds for local levee districts, on a scale of 2:1. Although U.S. participation in World War I interrupted funding of levees, the second round of funding helped raise the average height of levees in the Mississippi-Yazoo Delta to in the 1920s. Scientists now understand the levees have increased the severity of flooding by increasing the flow speed of the river and reducing the area of the floodplains. The region was severely damaged due to the Great Mississippi Flood of 1927, which broke through the levees. There were losses of millions of dollars in property, stock and crops. The most damage occurred in the lower Delta, including Washington County, Mississippi, Washington and Bolivar County, Mississippi, Bolivar counties.
Even as scientific knowledge about the Mississippi River has grown, upstream development and the consequences of the levees have caused more severe flooding in some years. Scientists now understand that the widespread clearing of land and building of the levees have changed the nature of the river. Such work removed the natural protection and absorption of wetlands and forest cover, strengthening the river's current. The state and federal governments have been struggling for the best approaches to restore some natural habitats in order to best interact with the original riverine ecology.
Demographics
 Mississippi's population has remained from 2 million people at the 1930 United States census, 1930 U.S. census, to 2.9 million at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. In contrast with
Mississippi's population has remained from 2 million people at the 1930 United States census, 1930 U.S. census, to 2.9 million at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. In contrast with Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
to its east, and Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
to its west, Mississippi has been the slowest growing of the three Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf coast states by population. According to the United States Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau, Mississippi's center of population is located in Leake County, Mississippi, Leake County, in the town of Lena, Mississippi, Lena.
From 2000 to 2010, the United States Census Bureau reported that Mississippi had the highest rate of increase in people identifying as mixed-race, up 70 percent in the decade; it amounts to a total of 1.1 percent of the population.Susan Saulny, "Black and White and Married in the Deep South: A Shifting Image"''The New York Times'', March 20, 2011, accessed October 25, 2012 In addition, Mississippi led the nation for most of the last decade in the growth of mixed marriages among its population. The total population has not increased significantly, but is young. Some of the above change in identification as mixed-race is due to new births. But, it appears mostly to reflect those residents who have chosen to identify as more than one race, who in earlier years may have identified by just one race and/or ethnicity. A binary racial system had been in place since slavery times and the days of official government racial segregation. In the civil rights era, people of African descent banded together in an inclusive community to achieve political power and gain restoration of their civil rights. As the demographer William H. Frey noted, "In Mississippi, I think it's [identifying as mixed race] changed from within." Historically in Mississippi, after Indian removal in the 1830s, the major groups were designated as black (African American), who were then mostly enslaved, and white (primarily European American). Matthew Snipp, also a demographer, commented on the increase in the 21st century in the number of people identifying as being of more than one race: "In a sense, they're rendering a more accurate portrait of their racial heritage that in the past would have been suppressed." After having accounted for a majority of the state's population since well before the American Civil War and through the 1930s, today
African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
s constitute approximately 37.8 percent of the state's population. Most have ancestors who were Slavery in the United States, enslaved, with many forcibly transported from the Upper South in the 19th century to work on the area's new plantations. Many of these slaves were mixed race, with European ancestors, as there were many children born into slavery with white fathers. Some also have Native American ancestry. During the first half of the 20th century, a total of nearly 400,000 African Americans left the state during the Great Migration, for opportunities in the North, Midwest and West. They became a minority in the state for the first time since early in its development.
Race and ethnicity
Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
(mostly in Neshoba County), and Chinese American portions of the population are also almost entirely native born.
The Chinese first came to Mississippi as indentured, contract workers from Cuba and History of Chinese Americans#California Gold Rush, California in the 1870s, and they originally worked as laborers on the cotton plantations. However, most Chinese families came later between 1910 and 1930 from other states, and most operated small family-owned groceries stores in the many small towns of the Delta. In these roles, the ethnic Chinese carved out a niche in the state between black and white, where they were concentrated in the Delta. These small towns have declined since the late 20th century, and many ethnic Chinese have joined the exodus to larger cities, including Jackson. Their population in the state overall has increased in the 21st century.
In the early 1980s many Vietnamese American, Vietnamese immigrated to Mississippi and other states along the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
, where they became employed in fishing-related work.
As of 2011, 53.8% of Mississippi's population younger than age 1 were minorities, meaning that they had at least one parent who was not non-Hispanic white.
Birth data
''Note: Births in table don't add up, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.'' *Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic and Latino Americans, White Hispanic origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.LGBT community
The 2010 United States census counted 6,286 same-sex unmarried-partner households in Mississippi, an increase of 1,512 since the 2000 United States census. Of those same-sex couples roughly 33% contained at least one child, giving Mississippi the distinction of leading the nation in the percentage of same-sex couples raising children. Mississippi has the largest percentage of LGBT African Americans, African American same-sex couples among total households. The state capital, Jackson, ranks tenth in the nation in concentration of African American same-sex couples. The state ranks fifth in the nation in the percentage of Hispanic Americans, Hispanic same-sex couples among all Hispanic households and ninth in the highest concentration of same-sex couples who are old age, seniors.Language
In 2000, 96.4% of Mississippi residents five years old and older spoke only English in the home, a decrease from 97.2% in 1990. English is largely Southern American English, with some South Midland speech in northern and eastern Mississippi. There is a common absence of final /r/, particularly in the elderly natives and African Americans, and the lengthening and weakening of the diphthongs /aɪ/ and /ɔɪ/ as in 'ride' and 'oil'. South Midland terms in northern Mississippi include: tow sack (burlap bag), dog irons (andirons), plum peach (clingstone peach), snake doctor (dragonfly), and stone wall (rock fence).Religion
Under French and Spanish rule beginning in the 17th century, European colonists were mostly Roman Catholics. The growth of the cotton culture after 1815 brought in tens of thousands of Anglo-American settlers each year, most of whom were Protestants from Southeastern states. Due to such migration, there was rapid growth in the number of Protestant denominations and churches, especially among the Methodist, Methodists, Presbyterian, Presbyterians and Baptist, Baptists. The revivals of the Great Awakening in the late 18th and early 19th centuries initially attracted the Plain Folk of the Old South, "plain folk" by reaching out to all members of society, including women and blacks. Both slaves and free blacks were welcomed into Methodist and Baptist churches. Independent black Baptist churches were established before 1800 in Virginia, Kentucky, South Carolina and Georgia, and later developed in Mississippi as well.
In the post-Civil War years, religion became more influential as the South became known as the "Bible Belt". By 2014, the Pew Research Center determined 83% of its population was Christian. In a separate study by the Public Religion Research Institute in 2020, 80% of the population was Christian.
Since the 1970s, fundamentalist conservative churches have grown rapidly, fueling Mississippi's conservative political trends among whites. In 1973 the Presbyterian Church in America attracted numerous conservative congregations. As of 2010, Mississippi remained a stronghold of the denomination, which originally was brought by Scots immigrants. The state has the highest adherence rate of the PCA in 2010, with 121 congregations and 18,500 members. It is among the few states where the PCA has higher membership than the PC(USA).
According to the Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA), in 2010 the
The revivals of the Great Awakening in the late 18th and early 19th centuries initially attracted the Plain Folk of the Old South, "plain folk" by reaching out to all members of society, including women and blacks. Both slaves and free blacks were welcomed into Methodist and Baptist churches. Independent black Baptist churches were established before 1800 in Virginia, Kentucky, South Carolina and Georgia, and later developed in Mississippi as well.
In the post-Civil War years, religion became more influential as the South became known as the "Bible Belt". By 2014, the Pew Research Center determined 83% of its population was Christian. In a separate study by the Public Religion Research Institute in 2020, 80% of the population was Christian.
Since the 1970s, fundamentalist conservative churches have grown rapidly, fueling Mississippi's conservative political trends among whites. In 1973 the Presbyterian Church in America attracted numerous conservative congregations. As of 2010, Mississippi remained a stronghold of the denomination, which originally was brought by Scots immigrants. The state has the highest adherence rate of the PCA in 2010, with 121 congregations and 18,500 members. It is among the few states where the PCA has higher membership than the PC(USA).
According to the Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA), in 2010 the Southern Baptist Convention
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC) is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist denomination, and the largest Protestant and second-largest Christian denomination in the United States. The wor ...
had 907,384 adherents and was the largest religious denomination in the state, followed by the United Methodist Church with 204,165, and the Roman Catholic Church with 112,488. Other religions have a small presence in Mississippi; as of 2010, there were 5,012 Islam in the United States, Muslims; 4,389 Hinduism, Hindus; and 816 of the Baháʼí Faith.
According to the Pew Research Center in 2014, with evangelical Protestantism as the predominant Christian affiliation, the Southern Baptist Convention remained the largest denomination in the state. Non-denominational Evangelicals were the second-largest, followed by Black church, historically African American denominations such as the National Baptist Convention, USA, Inc., National Baptist Convention, USA and Progressive National Baptist Convention.
Public opinion polls have consistently ranked Mississippi as the most religious state in the United States, with 59% of Mississippians considering themselves "very religious". The same survey also found that 11% of the population were non-Religious. In a 2009 Gallup poll, 63% of Mississippians said that they attended church weekly or almost weekly—the highest percentage of all states (U.S. average was 42%, and the lowest percentage was in Vermont at 23%). Another 2008 Gallup poll found that 85% of Mississippians considered religion an important part of their daily lives, the highest figure among all states (U.S. average 65%).
Health
The state is ranked 50th or last place among all the states for health care, according to the Commonwealth Fund, a nonprofit foundation working to advance performance of the health care system. Mississippi has the highest rate of infant and neonatal deaths of any U.S. state. Age-adjusted data also shows Mississippi has the highest overall death rate, and the highest death rate from heart disease, hypertension and hypertensive renal disease, influenza and pneumonia. In 2011, Mississippi (and Arkansas) had the fewest dentists per capita in the United States. For three years in a row, more than 30 percent of Mississippi's residents have been classified as obese. In a 2006 study, 22.8 percent of the state's children were classified as such. Mississippi had the Obesity in the United States, highest rate of obesity of any U.S. state from 2005 to 2008, and also ranks first in the nation for high blood pressure, diabetes, and Sedentary lifestyle, adult inactivity. In a 2008 study of African-American women, contributing risk factors were shown to be: lack of knowledge about body mass index (BMI), dietary behavior, physical inactivity and lack of social support, defined as motivation and encouragement by friends. A 2002 report on African-American adolescents noted a 1999 survey which suggests that a third of children were obese, with higher ratios for those in the Delta. The study stressed that "obesity starts in early childhood extending into the adolescent years and then possibly into adulthood". It noted impediments to needed behavioral modification, including the Delta likely being "the most disadvantaged, underserved region in the state" with African Americans the major ethnic group; lack of accessibility and availability of medical care; and an estimated 60% of residents living below the poverty level. Additional risk factors were that most schools had no physical education curriculum and nutrition education is not emphasized. Previous intervention strategies may have been largely ineffective due to not being culturally sensitive or practical. A 2006 survey found nearly 95 percent of Mississippi adults considered childhood obesity to be a serious problem. A 2017 study found that Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Mississippi was the leading health insurer with 53% followed by UnitedHealth Group at 13%.Economy
 The Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates that Mississippi's total state product in 2010 was $98 billion. GDP growth was .5 percent in 2015 and is estimated to be 2.4 in 2016 according to Dr. Darrin Webb, the state's chief economist, who noted it would make two consecutive years of positive growth since the recession.Pender, 2017. Per capita personal income in 2006 was $26,908, the lowest per capita personal income of any state, but the state also has the nation's lowest living costs. 2015 data records the adjusted per capita personal income at $40,105. Mississippians consistently rank as one of the highest per capita in charitable contributions.
At 56 percent, the state has one of the lowest workforce participation rates in the country. Approximately 70,000 adults are disabled, which is 10 percent of the workforce.
Mississippi's rank as one of the poorest states is related to its dependence on cotton agriculture before and after the Civil War, late development of its frontier bottomlands in the Mississippi Delta, repeated natural disasters of flooding in the late 19th and early 20th century that required massive capital investment in levees, and ditching and draining the bottomlands, and slow development of railroads to link bottomland towns and river cities.John Otto Solomon,''The Final Frontiers, 1880–1930: Settling the Southern Bottomlands''. Westport: Greenwood Press, 1999, pp.10–11, 42–43, 50–51, and 70 In addition, when Democrats regained control of the state legislature, they passed the 1890 constitution that discouraged corporate industrial development in favor of rural agriculture, a legacy that would slow the state's progress for years.
Before the Civil War, Mississippi was the fifth-wealthiest state in the nation, its wealth generated by the labor of slaves in cotton plantations along the rivers.
Slaves were counted as property and the rise in the cotton markets since the 1840s had increased their value. By 1860, a majority—55 percent—of the population of Mississippi was enslaved. Ninety percent of the Delta bottomlands were undeveloped and the state had low overall density of population.
The Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates that Mississippi's total state product in 2010 was $98 billion. GDP growth was .5 percent in 2015 and is estimated to be 2.4 in 2016 according to Dr. Darrin Webb, the state's chief economist, who noted it would make two consecutive years of positive growth since the recession.Pender, 2017. Per capita personal income in 2006 was $26,908, the lowest per capita personal income of any state, but the state also has the nation's lowest living costs. 2015 data records the adjusted per capita personal income at $40,105. Mississippians consistently rank as one of the highest per capita in charitable contributions.
At 56 percent, the state has one of the lowest workforce participation rates in the country. Approximately 70,000 adults are disabled, which is 10 percent of the workforce.
Mississippi's rank as one of the poorest states is related to its dependence on cotton agriculture before and after the Civil War, late development of its frontier bottomlands in the Mississippi Delta, repeated natural disasters of flooding in the late 19th and early 20th century that required massive capital investment in levees, and ditching and draining the bottomlands, and slow development of railroads to link bottomland towns and river cities.John Otto Solomon,''The Final Frontiers, 1880–1930: Settling the Southern Bottomlands''. Westport: Greenwood Press, 1999, pp.10–11, 42–43, 50–51, and 70 In addition, when Democrats regained control of the state legislature, they passed the 1890 constitution that discouraged corporate industrial development in favor of rural agriculture, a legacy that would slow the state's progress for years.
Before the Civil War, Mississippi was the fifth-wealthiest state in the nation, its wealth generated by the labor of slaves in cotton plantations along the rivers.
Slaves were counted as property and the rise in the cotton markets since the 1840s had increased their value. By 1860, a majority—55 percent—of the population of Mississippi was enslaved. Ninety percent of the Delta bottomlands were undeveloped and the state had low overall density of population.
 Largely due to the domination of the plantations in the American South, plantation economy, focused on the production of agriculture, agricultural
Largely due to the domination of the plantations in the American South, plantation economy, focused on the production of agriculture, agricultural cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
, the state's elite was reluctant to invest in infrastructure such as roads and railroads. They educated their children privately. Industrialization did not reach many areas until the late 20th century. The planter aristocracy, the elite of Antebellum era, antebellum Mississippi, kept the tax structure low for their own benefit, making only private improvements. Before the war the most successful planters, such as Confederate States of America, Confederate President Jefferson Davis, owned riverside properties along the Mississippi and Yazoo rivers in the Mississippi Delta. Away from the riverfronts, most of the Delta was undeveloped frontier.
During the Civil War, 30,000 Mississippi soldiers, mostly white, died from wounds and disease, and many more were left crippled and wounded. Changes to the labor structure and an agricultural depression throughout the South caused severe losses in wealth. In 1860 assessed valuation of property in Mississippi had been more than $500 million, of which $218 million (43 percent) was estimated as the value of slaves. By 1870, total assets had decreased in value to roughly $177 million.
Poor whites and landless former slaves suffered the most from the postwar economic depression. The constitutional convention of early 1868 appointed a committee to recommend what was needed for relief of the state and its citizens. The committee found severe destitution among the laboring classes. It took years for the state to rebuild levees damaged in battles. The upset of the commodity system impoverished the state after the war. By 1868 an increased cotton crop began to show possibilities for free labor in the state, but the crop of 565,000 bales produced in 1870 was still less than half of prewar figures.
Blacks cleared land, selling timber and developing bottomland to achieve ownership. In 1900, two-thirds of farm owners in Mississippi were blacks, a major achievement for them and their families. Due to the poor economy, low cotton prices and difficulty of getting credit, many of these farmers could not make it through the extended financial difficulties. Two decades later, the majority of African Americans were sharecroppers. The low prices of cotton into the 1890s meant that more than a generation of African Americans lost the result of their labor when they had to sell their farms to pay off accumulated debts.
After the Civil War, the state refused for years to build human capital by fully educating all its citizens. In addition, the reliance on agriculture grew increasingly costly as the state suffered loss of cotton crops due to the devastation of the boll weevil
The boll weevil (''Anthonomus grandis'') is a beetle that feeds on cotton buds and flowers. Thought to be native to Central Mexico, it migrated into the United States from Mexico in the late 19th century and had infested all U.S. cotton-growing ...
in the early 20th century, devastating floods in 1912–1913 and 1927, collapse of cotton prices after 1920, and drought in 1930.
It was not until 1884, after the flood of 1882, that the state created the Mississippi-Yazoo Delta District Levee Board and started successfully achieving longer-term plans for levees in the upper Delta. Despite the state's building and reinforcing levees for years, the Great Mississippi Flood of 1927 broke through and caused massive flooding of throughout the Delta, homelessness for hundreds of thousands, and millions of dollars in property damages. With the Depression coming so soon after the flood, the state suffered badly during those years. In the Great Migration, hundreds of thousands of African Americans migrated North and West for jobs and chances to live as full citizens.
Entertainment and tourism
The legislature's 1990 decision to legalize casino gambling along the Mississippi River and the Gulf Coast has led to increased revenues and economic gains for the state. Gambling towns in Mississippi have attracted increased tourism: they include the Gulf Coast resort towns of Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, Bay St. Louis, Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport and Biloxi, Mississippi, Biloxi, and the Mississippi River towns of Tunica Resorts, Mississippi, Tunica (the third largest gaming area in the United States), Greenville, Mississippi, Greenville, Vicksburg, Mississippi, Vicksburg andNatchez Natchez may refer to:
Places
* Natchez, Alabama, United States
* Natchez, Indiana, United States
* Natchez, Louisiana, United States
* Natchez, Mississippi, a city in southwestern Mississippi, United States
* Grand Village of the Natchez, a site o ...
.
Before Hurricane Katrina struck the Gulf Coast, Mississippi was the second-largest gambling state in the Union, after Nevada and ahead of New Jersey. An estimated $500,000 per day in tax revenue was lost following Hurricane Katrina's severe damage to several coastal casinos in Biloxi in August 2005. Because of the destruction from this hurricane, on October 17, 2005, Governor Haley Barbour signed a bill into law that allows casinos in Hancock and Harrison counties to rebuild on land (but within of the water). The only exception is in Harrison County, Mississippi, Harrison County, where the new law states that casinos can be built to the southern boundary of U.S. Route 90.
In 2012, Mississippi had the sixth largest gambling revenue of any state, with $2.25 billion. The federally recognized Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians
The Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians ( cho, Mississippi Chahta) is one of three federally recognized tribes of Choctaw Native Americans, and the only one in the state of Mississippi. On April 20, 1945, this tribe organized under the Indian Re ...
has established a gaming casino on its reservation, which yields revenue to support education and economic development.
Momentum Mississippi, a statewide, public–private partnership dedicated to the development of economic and employment opportunities in Mississippi, was adopted in 2005.
Manufacturing
 Mississippi, like the rest of its southern neighbors, is a Right-to-work law#U.S. states with right-to-work laws, right-to-work state. It has some major automotive factories, such as the Toyota Motor Manufacturing Mississippi, Toyota Mississippi Plant in Blue Springs, Mississippi, Blue Springs and a Nissan Automotive plant in Canton, Mississippi, Canton. The latter produces the Nissan Titan.
Mississippi, like the rest of its southern neighbors, is a Right-to-work law#U.S. states with right-to-work laws, right-to-work state. It has some major automotive factories, such as the Toyota Motor Manufacturing Mississippi, Toyota Mississippi Plant in Blue Springs, Mississippi, Blue Springs and a Nissan Automotive plant in Canton, Mississippi, Canton. The latter produces the Nissan Titan.
Taxation
Mississippi collects personal income tax in three tax brackets, ranging from 3% to 5%. The retail sales tax rate in Mississippi is 7%. Tupelo levies a local sales tax of 2.5%. State sales tax growth was 1.4 percent in 2016 and estimated to be slightly less in 2017. For purposes of assessment for ad valorem taxes, taxable property tax, property is divided into five classes. On August 30, 2007, a report by the United States Census Bureau indicated that Mississippi was the poorest state in the country. Major cotton farmers in the Delta have large, mechanized plantations, and they receive the majority of extensive federal subsidies going to the state, yet many other residents still live as poor, rural, landless laborers. The state's sizable poultry industry has faced similar challenges in its transition from family-run farms to large mechanized operations. Of $1.2 billion from 2002 to 2005 in federal subsidies to farmers in the Bolivar County area of the Delta, only 5% went to small farmers. There has been little money apportioned for rural development. Small towns are struggling. More than 100,000 people have left the region in search of work elsewhere. The state had a median household income of $34,473.Employment
As of December 2018, the state's unemployment rate was 4.7%, the seventh highest in the country after Arizona (4.9%),Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
(4.9%), New Mexico (5.0%), West Virginia (5.1%), Washington, D.C., District of Columbia (5.4%) and Alaska (6.5%).
Federal subsidies and spending
With Mississippi's fiscal conservatism, in which Medicaid, American welfare state, welfare, Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, food stamps, and other social programs are often cut, eligibility requirements are tightened, and stricter employment criteria are imposed, Mississippi ranks as having the second-highest ratio of spending to tax receipts of any state. In 2005, Mississippi citizens received approximately $2.02 per dollar of taxes in the way of federal spending. This ranks the state second-highest nationally, and represents an increase from 1995, when Mississippi received $1.54 per dollar of taxes in federal spending and was 3rd highest nationally. This figure is based on federal spending after large portions of the state were devastated by Hurricane Katrina, requiring large amounts of federal aid from the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). However, from 1981 to 2005, it was at least number four in the nation for federal spending vs. taxes received. A proportion of federal spending in Mississippi is directed toward large federal installations such as Camp Shelby, John C. Stennis Space Center, Naval Air Station Meridian, Meridian Naval Air Station, Columbus Air Force Base, and Keesler Air Force Base. Three of these installations are located in the area affected by Hurricane Katrina.Politics and government
 As with all other U.S. states and the federal government, Mississippi's government is based on the separation of legislative, executive and judicial power. Executive authority in the state rests with the Governor, currently Tate Reeves (Republican Party (United States), R). The lieutenant governor, currently Delbert Hosemann (Republican Party (United States), R), is elected on a separate ballot. Both the governor and lieutenant governor are elected to four-year terms of office. Unlike the federal government, but like many other U.S. states, most of the heads of major executive departments are elected by the citizens of Mississippi rather than appointed by the governor.
Mississippi is one of five states that elects its state officials in odd-numbered years (the others are Kentucky,
As with all other U.S. states and the federal government, Mississippi's government is based on the separation of legislative, executive and judicial power. Executive authority in the state rests with the Governor, currently Tate Reeves (Republican Party (United States), R). The lieutenant governor, currently Delbert Hosemann (Republican Party (United States), R), is elected on a separate ballot. Both the governor and lieutenant governor are elected to four-year terms of office. Unlike the federal government, but like many other U.S. states, most of the heads of major executive departments are elected by the citizens of Mississippi rather than appointed by the governor.
Mississippi is one of five states that elects its state officials in odd-numbered years (the others are Kentucky, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
, New Jersey and Virginia). Mississippi holds elections for these offices every four years, always in the year preceding presidential elections.
In a 2020 study, Mississippi was ranked as the 4th hardest state for citizens to vote in.
Laws
In 2004, Mississippi voters approved a state constitutional amendment banning same-sex marriage and prohibiting Mississippi from recognizing same-sex marriages performed elsewhere. The amendment passed 86% to 14%, the largest margin in any state. Same-sex marriage became legal in Mississippi on June 26, 2015, when the United States Supreme Court invalidated all state-level bans on same-sex marriage as unconstitutional in the landmark case ''Obergefell v. Hodges''. With the passing of HB 1523 in April 2016, from July it became legal in Mississippi to refuse service to same-sex couples, based on one's religious beliefs. The bill has become the subject of controversy. A federal judge blocked the law in July of that year; however, it was challenged, and a federal appeals court ruled in favor of the law in October 2017. Mississippi is one of the most anti-abortion states in the United States. A 2014 poll by Pew Research Center found that 59% of the state's population thinks abortion should be illegal in all/most cases, while only 36% of the state's population thinks abortion should be legal in all/most cases. Mississippi has banned Sanctuary city, sanctuary cities. Mississippi is one of thirty-one states which practice Capital punishment in the United States, capital punishment (see also: capital punishment in Mississippi). Section 265 of the Constitution of the State of Mississippi declares that "No person who denies the existence of a Supreme Being shall hold any office in this state." However, this religious test restriction was held to be unconstitutional by the U.S. Supreme Court in ''Torcaso v. Watkins'' (1961). Gun laws in Mississippi are among the most permissive in the country, with no license or background check required to openly carry handguns in most places in the state. In 2021, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in a 6−3 decision in ''Jones v. Mississippi'' that a Mississippi law allowing mandatory sentencing of children to life imprisonment without parole is valid and that states and judges can impose such sentences without separately deciding if the child can be rehabilitated.Political alignment
Voting Rights Act of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights movement ...
and concerted grassroots efforts to achieve registration and encourage voting. In the 1980s, whites divided evenly between the parties. In the 1990s, those voters largely shifted their allegiance to the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, first for national and then for state offices.
In 2019, a lawsuit was filed against an 1890 election law known as The Mississippi Plan, which requires that candidates must win the popular vote and a majority of districts. In 2020 Mississippi elections, the following year, 79% of Mississippians voted to remove the requirement of doing so.
Transportation
Air
Mississippi has six airports with commercial passenger service, the busiest in Jackson (Jackson-Evers International Airport).Roads
Mississippi is the only American state where people in cars may legally consume beer. Some localities have laws restricting the practice. In 2018, the state was ranked number eight in the Union in terms of impaired driving deaths. Mississippi is served by nine Interstate Highway System, interstate highways:
*
**
*
**
*
*
*
*
**
and fourteen main United States Numbered Highways, U.S. Routes:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
*
*
*
*
as well as a system of List of state highways in Mississippi, State Highways.
Mississippi is served by nine Interstate Highway System, interstate highways:
*
**
*
**
*
*
*
*
**
and fourteen main United States Numbered Highways, U.S. Routes:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
*
*
*
*
as well as a system of List of state highways in Mississippi, State Highways.
Rail
Passenger
Amtrak provides scheduled passenger service along two routes, the ''Crescent (Amtrak), Crescent'' and ''City of New Orleans (train), City of New Orleans''. Prior to severe damage from Hurricane Katrina, the ''Sunset Limited'' traversed the far south of the state; the route originated in Los Angeles, California and it terminated inFlorida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
.
Freight
All but two of the United States Class I railroads serve Mississippi (the exceptions are the Union Pacific and Canadian Pacific): *Canadian National Railway's Illinois Central Railroad subsidiary provides north–south service. *BNSF Railway has a northwest–southeast line across northern Mississippi. *Kansas City Southern Railway provides east–west service in the middle of the state and north–south service along theAlabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
state line.
*Norfolk Southern Railway provides service in the extreme north and southeast.
*CSX Transportation, CSX has a line along the Gulf Coast.
Water
Major rivers
*Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
*Big Black River (Mississippi), Big Black River
*Pascagoula River
*Pearl River (Mississippi-Louisiana), Pearl River
*Tennessee-Tombigbee Waterway
*Yazoo River
Major bodies of water
 *Arkabutla Lake of water; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
*Bay Springs Lake of water and of shoreline; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
*Grenada Lake of water; became operational in 1954; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
*Ross Barnett Reservoir of water; named for Ross Barnett, the 52nd List of Governors of Mississippi, Governor of Mississippi; became operational in 1966; constructed and managed by The Pearl River Valley Water Supply District, a state agency; provides water supply for the City of Jackson.
*Sardis Lake (Mississippi), Sardis Lake of water; became operational in October 1940; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
*Enid Lake of water; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army
*Arkabutla Lake of water; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
*Bay Springs Lake of water and of shoreline; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
*Grenada Lake of water; became operational in 1954; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
*Ross Barnett Reservoir of water; named for Ross Barnett, the 52nd List of Governors of Mississippi, Governor of Mississippi; became operational in 1966; constructed and managed by The Pearl River Valley Water Supply District, a state agency; provides water supply for the City of Jackson.
*Sardis Lake (Mississippi), Sardis Lake of water; became operational in October 1940; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
*Enid Lake of water; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army
Education
Until theCivil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
era, Mississippi had a small number of schools and no educational institutions for African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
. The first school for black students was not established until 1862.
During Reconstruction in 1871, black and white Republicans drafted a constitution that was the first to provide for a system of free public education in the state. The state's dependence on agriculture and resistance to taxation limited the funds it had available to spend on any schools. In the early 20th century, there were still few schools in rural areas, particularly for black children. With seed money from the Julius Rosenwald Fund, many rural black communities across Mississippi raised matching funds and contributed public funds to build new schools for their children. Essentially, many black adults taxed themselves twice and made significant sacrifices to raise money for the education of children in their communities, in many cases donating land and/or labor to build such schools.
Blacks and whites attended separate, Racial segregation in the United States, segregated Public school (government funded), public schools in Mississippi until the late 1960s, although such segregation had been declared unconstitutional by the United States Supreme Court in its 1954 ruling in ''Brown v. Board of Education
''Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka'', 347 U.S. 483 (1954), was a landmark decision by the U.S. Supreme Court, which ruled that U.S. state laws establishing racial segregation in public schools are unconstitutional, even if the segregat ...
''. In the majority-black Mississippi Delta counties, white parents worked through Citizens' Councils, White Citizens' Councils to set up private segregation academies, where they enrolled their children. Often funding declined for the public schools. But in the state as a whole, only a small minority of white children were withdrawn from public schools. State officials believed they needed to maintain public education to attract new businesses. Many black parents complained that they had little representation in school administration, and that many of their former administrators and teachers had been pushed out. They have had to work to have their interests and children represented.Bolton, Charles C. ''The Hardest Deal of All: The Battle Over School Integration in Mississippi, 1870–1980''. University Press of Mississippi, 2005, pp. 136, 178–179. , 9781604730609.
In the late 1980s, Mississippi's 954 public schools enrolled about 369,500 elementary and 132,500 secondary school, secondary students. Some 45,700 students attended private schools.
In the 21st century, 91% of white children and most of the black children in the state attend public schools. In 2008, Mississippi was ranked last among the fifty states in academic achievement by the American Legislative Exchange Council's ''Report Card on Education'', with the lowest average ACT (examination), ACT scores and sixth-lowest spending per pupil in the nation. In contrast, Mississippi had the 17th-highest average SAT (examination), SAT scores in the nation. As an explanation, the Report noted that 92% of Mississippi high school graduates took the ACT, but only 3% of graduates took the SAT, apparently a self-selection of higher achievers. This breakdown compares to the national average of high school graduates taking the ACT and SAT, of 43% and 45%, respectively.
Generally prohibited in the Western world, West at large, school corporal punishment is not unusual in Mississippi, with 31,236 public school students paddled at least one time circa 2016. A greater percentage of students were paddle (spanking), paddled in Mississippi than in any other state, according to government data for the 2011–2012 school year.
In 2007, Mississippi students scored the lowest of any state on the National Assessments of Educational Progress in both math and science.
Jackson, MS, Jackson, the state's capital city, is the site of the state residential school for deaf and hard of hearing students. Mississippi School for the Deaf, The Mississippi School for the Deaf was established by the state legislature in 1854 before the civil war.
Culture
 While Mississippi has been especially known for its music and literature, it has embraced other forms of art. Its strong religious traditions have inspired striking works by outsider artists who have been shown nationally.
Jackson established the USA International Ballet Competition, which is held every four years. This ballet competition attracts the most talented young dancers from around the world.
The Magnolia Independent Film Festival, still held annually in Starkville, Mississippi, Starkville, is the first and oldest in the state.
George Ohr, known as the "Mad Potter of Biloxi" and the father of abstract expressionism in pottery, lived and worked in Biloxi, MS.
While Mississippi has been especially known for its music and literature, it has embraced other forms of art. Its strong religious traditions have inspired striking works by outsider artists who have been shown nationally.
Jackson established the USA International Ballet Competition, which is held every four years. This ballet competition attracts the most talented young dancers from around the world.
The Magnolia Independent Film Festival, still held annually in Starkville, Mississippi, Starkville, is the first and oldest in the state.
George Ohr, known as the "Mad Potter of Biloxi" and the father of abstract expressionism in pottery, lived and worked in Biloxi, MS.
Music
Musicians of the state's Delta region were historically significant to the development of theblues
Blues is a music genre and musical form which originated in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues incorporated spirituals, work songs, field hollers, shouts, chants, and rhymed simple narrative ballads from the Afr ...
. Although by the end of the 19th century, two-thirds of the farm owners were black, continued low prices for cotton and national financial pressures resulted in most of them losing their land. More problems built up with the boll weevil infestation, when thousands of agricultural jobs were lost.
Jimmie Rodgers (country singer), Jimmie Rodgers, a native of Meridian and guitarist/singer/songwriter known as the "Father of Country Music", played a significant role in the development of the blues. He and Chester Arthur Burnett were friends and admirers of each other's music. Their friendship and respect is an important example of Mississippi's musical legacy. While the state has had a reputation for being racist, Mississippi musicians created new forms by combining and creating variations on musical traditions from African American traditions, and the musical traditions of white Southerners strongly shaped by Scots-Irish and other styles.
The state is creating a Mississippi Blues Trail, with dedicated markers explaining historic sites significant to the history of blues music, such as Clarksdale, Mississippi, Clarksdale's Riverside Hotel, where Bessie Smith died after her auto accident on U.S. Route 61, Highway 61. The Riverside Hotel is just one of many historical blues sites in Clarksdale. The Delta Blues Museum there is visited by tourists from all over the world. Close by is "Ground Zero", a contemporary blues club and restaurant co-owned by actor Morgan Freeman.
Elvis Presley, who created a sensation in the 1950s as a crossover artist and contributed to rock 'n' roll, was a native of Tupelo, Mississippi, Tupelo. From opera star Leontyne Price to the alternative rock band 3 Doors Down, to Gulf and western (music genre), gulf and western singer Jimmy Buffett, modern rock/jazz/world music guitarist-producer Clifton Hyde, to rappers David Banner, Big K.R.I.T. and Afroman, Mississippi musicians have been significant in all genres.
Sports
*Biloxi, Mississippi, Biloxi is home to the Biloxi Shuckers baseball team, a AA minor league affiliate of the Milwaukee Brewers and member of the Double-A South playing at MGM Park *Clinton, Mississippi, Clinton is home to the Mississippi Brilla FC, a USL League Two soccer team. *Pearl, Mississippi, Pearl is home to the Mississippi Braves baseball team, a AA minor league affiliate of the Atlanta Braves and member of the Double-A South playing at Trustmark Park. *Southaven, Mississippi, Southaven is home to the Memphis Hustle basketball team. The Hustle are an affiliate of the Memphis Grizzlies. They play in the NBA G League.See also
*Index of Mississippi-related articles *Outline of Mississippi *List of people from Mississippi *Mississippi literatureNotes
References
Further reading
* Busbee, Westley F. ''Mississippi: A History'' (2005). * Gonzales, Edmond, ed. ''A Mississippi Reader: Selected Articles from the Journal of Mississippi History'' (1980) * Krane, Dale and Stephen D. Shaffer. ''Mississippi Government & Politics: Modernizers versus Traditionalists'' (1992), government textbook * Loewen, James W. and Charles Sallis, eds. ''Mississippi: Conflict and Change'' (2nd ed. 1980), high school textbook * McLemore, Richard, ed. ''A History of Mississippi'' 2 vols. (1973), thorough coverage by scholars * Mitchell, Dennis J., ''A New History of Mississippi'' (2014) * Ownby, ted et al. eds. ''The Mississippi Encyclopedia'' (2017) * Skates, John Ray. ''Mississippi: A Bicentennial History'' (1979), popular * Sparks, Randy J. ''Religion in Mississippi'' (2001) 374 ponline edition
* Swain, Martha H. ed. ''Mississippi Women: Their Histories, Their Lives'' (2003). 17 short biographies
External links
*Mississippi Travel and Tourism
*[ftp://newftp.epa.gov/EPADataCommons/ORD/Ecoregions/ms/ms_eco_pg.pdf Ecoregions of Mississippi] *
Mississippi as Metaphor State, Region, and Nation in Historical Imagination
, ''Southern Spaces'', October 23, 2006. *
Mississippi State Databases
an annotated list of searchable databases compiled by the Government Documents Roundtable of the American Library Association. {{coord, 33, -90, dim:300000_region:US-MS_type:adm1st, name=State of Mississippi, display=title Mississippi, 1817 establishments in the United States Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Former French colonies Southern United States States and territories established in 1817 States of the Confederate States of America States of the Gulf Coast of the United States States of the United States Contiguous United States