Mind–body problem on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The mind–body problem is a philosophical debate concerning the relationship between thought and
The mind–body problem is a philosophical debate concerning the relationship between thought and
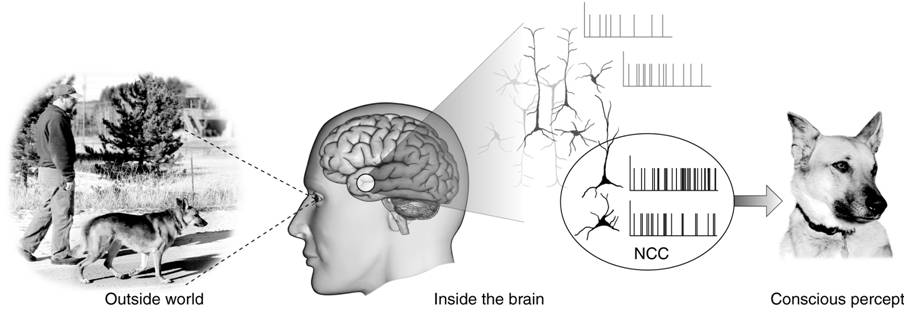 The ''neural correlates of consciousness'' "are the smallest set of brain mechanisms and events sufficient for some specific conscious feeling, as elemental as the color red or as complex as the sensual, mysterious, and primeval sensation evoked when looking at jungle scene..." Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena.
The ''neural correlates of consciousness'' "are the smallest set of brain mechanisms and events sufficient for some specific conscious feeling, as elemental as the color red or as complex as the sensual, mysterious, and primeval sensation evoked when looking at jungle scene..." Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena.
 There are two common but distinct dimensions of the term ''consciousness'', one involving ''arousal'' and ''states of consciousness'' and the other involving ''content of consciousness'' and ''conscious states''. To be conscious ''of'' something, the brain must be in a relatively high state of arousal (sometimes called ''vigilance''), whether awake or in
There are two common but distinct dimensions of the term ''consciousness'', one involving ''arousal'' and ''states of consciousness'' and the other involving ''content of consciousness'' and ''conscious states''. To be conscious ''of'' something, the brain must be in a relatively high state of arousal (sometimes called ''vigilance''), whether awake or in
The Body and Society: Exploration in Social Theory
'.
Plato's Middle Period Metaphysics and Epistemology - The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
*
The Mind/Body Problem
BBC Radio 4 discussion with Anthony Grayling, Julian Baggini & Sue James (''In Our Time'', Jan. 13, 2005) {{DEFAULTSORT:Mind-body problem Arguments in philosophy of mind Baruch Spinoza Cognition Concepts in epistemology Concepts in metaphysics Concepts in the philosophy of mind Concepts in the philosophy of science Consciousness studies Dichotomies Enactive cognition Epistemological theories History of psychology Metaphysical theories Metaphysics of mind Neuroscience Ontology Philosophical problems Philosophy and thought in the Dutch Republic René Descartes Thought
 The mind–body problem is a philosophical debate concerning the relationship between thought and
The mind–body problem is a philosophical debate concerning the relationship between thought and consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scien ...
in the human mind
The mind is the set of faculties responsible for all mental phenomena. Often the term is also identified with the phenomena themselves. These faculties include thought, imagination, memory, will, and sensation. They are responsible for vario ...
, and the brain as part of the physical body. The debate goes beyond addressing the mere question of how mind and body function chemically and physiologically. Interactionism arises when mind and body are considered as distinct, based on the premise that the mind and the body are fundamentally different in nature.
The problem was popularized by René Descartes
René Descartes ( or ; ; Latinized: Renatus Cartesius; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Mathe ...
in the 17th century, resulting in Cartesian dualism, and by pre- Aristotelian philosophers, in Avicennian philosophy, and in earlier Asian traditions. A variety of approaches have been proposed. Most are either dualist or monist. Dualism maintains a rigid distinction between the realms of mind and matter. Monism
Monism attributes oneness or singleness (Greek: μόνος) to a concept e.g., existence. Various kinds of monism can be distinguished:
* Priority monism states that all existing things go back to a source that is distinct from them; e.g., i ...
maintains that there is only one unifying reality as in neutral or substance or essence, in terms of which everything can be explained.
Each of these categories contains numerous variants. The two main forms of dualism are substance dualism, which holds that the mind is formed of a distinct type of substance not governed by the laws of physics, and property dualism, which holds that mental properties involving conscious experience are fundamental properties, alongside the fundamental properties identified by a completed physics. The three main forms of monism are physicalism, which holds that the mind consists of matter organized in a particular way; idealism
In philosophy, the term idealism identifies and describes metaphysics, metaphysical perspectives which assert that reality is indistinguishable and inseparable from perception and understanding; that reality is a mental construct closely con ...
, which holds that only thought truly exists and matter is merely a representation of mental processes; and neutral monism
Neutral monism is an umbrella term for a class of metaphysical theories in the philosophy of mind. These theories reject the dichotomy of mind and matter, believing the fundamental nature of reality to be neither mental nor physical; in other word ...
, which holds that both mind and matter are aspects of a distinct essence that is itself identical to neither of them. Psychophysical parallelism is a third possible alternative regarding the relation between mind and body, between interaction (dualism) and one-sided action (monism).
Several philosophical perspectives have been developed which reject the mind–body dichotomy. The historical materialism
Historical materialism is the term used to describe Karl Marx's theory of history. Marx locates historical change in the rise of class societies and the way humans labor together to make their livelihoods. For Marx and his lifetime collaborat ...
of Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
and subsequent writers, itself a form of physicalism, held that consciousness was engendered by the material contingencies of one's environment. An explicit rejection of the dichotomy is found in French structuralism, and is a position that generally characterized post-war Continental philosophy.
The absence of an empirically identifiable meeting point between the non-physical mind (if there is such a thing) and its physical extension (if there is such a thing) has been raised as a criticism of dualism, and many modern philosophers of mind maintain that the mind is not something separate from the body. These approaches have been particularly influential in the sciences, particularly in the fields of sociobiology
Sociobiology is a field of biology that aims to examine and explain social behavior in terms of evolution. It draws from disciplines including psychology, ethology, anthropology, evolution, zoology, archaeology, and population genetics. Within t ...
, computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, automation, and information. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, information theory, and automation) to practical disciplines (includin ...
, evolutionary psychology
Evolutionary psychology is a theoretical approach in psychology that examines cognition and behavior from a modern evolutionary perspective. It seeks to identify human psychological adaptations with regards to the ancestral problems they evol ...
, and the neuroscience
Neuroscience is the science, scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions and disorders. It is a Multidisciplinary approach, multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, an ...
s.
An ancient model of the mind known as the Five-Aggregate Model, described in the Buddhist teachings, explains the mind as continuously changing sense impressions and mental phenomena. Considering this model, it is possible to understand that it is the constantly changing sense impressions and mental phenomena (i.e., the mind) that experiences/analyzes all external phenomena in the world as well as all internal phenomena including the body anatomy, the nervous system as well as the organ brain. This conceptualization leads to two levels of analyses: (i) analyses conducted from a third-person perspective on how the brain works, and (ii) analyzing the moment-to-moment manifestation of an individual's mind-stream (analyses conducted from a first-person perspective). Considering the latter, the manifestation of the mind-stream is described as happening in every person all the time, even in a scientist who analyses various phenomena in the world, including analyzing and hypothesizing about the organ brain.
Mind–body interaction and mental causation
Philosophers David L. Robb and John F. Heil introduce mental causation in terms of the mind–body problem of interaction: Contemporary neurophilosopher Georg Northoff suggests that mental causation is compatible with classical formal and final causality. Biologist, theoretical neuroscientist and philosopher, Walter J. Freeman, suggests that explaining mind–body interaction in terms of "circular causation" is more relevant than linear causation. Inneuroscience
Neuroscience is the science, scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions and disorders. It is a Multidisciplinary approach, multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, an ...
, much has been learned about correlations between brain activity and subjective, conscious experiences. Many suggest that neuroscience will ultimately explain consciousness:
"...consciousness is a biological process that will eventually be explained in terms of molecular signaling pathways used by interacting populations of nerve cells..." However, this view has been criticized because ''consciousness'' has yet to be shown to be a ''process'', and the "hard problem" of relating consciousness directly to brain activity remains elusive.A term attributed to David Chalmers by
Since 1927, at the Solvay Conference in Austria, European physicists of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, realized that the interpretations of their experiments with light and electricity required a different theory to explain why light behaves both as a wave and particle. The implications were profound. The usual empirical model of explaining natural phenomena could not account for this duality of matter and non-matter. In a significant way, this has brought back the conversation on the mind-body duality.
Neural correlates
 The ''neural correlates of consciousness'' "are the smallest set of brain mechanisms and events sufficient for some specific conscious feeling, as elemental as the color red or as complex as the sensual, mysterious, and primeval sensation evoked when looking at jungle scene..." Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena.
The ''neural correlates of consciousness'' "are the smallest set of brain mechanisms and events sufficient for some specific conscious feeling, as elemental as the color red or as complex as the sensual, mysterious, and primeval sensation evoked when looking at jungle scene..." Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena.
Neurobiology and neurophilosophy
A science ofconsciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scien ...
must explain the exact relationship between subjective conscious mental states and brain states formed by electrochemical interactions in the body, the so-called hard problem of consciousness. Neurobiology studies the connection scientifically, as do neuropsychology and neuropsychiatry. ''Neurophilosophy'' is the interdisciplinary study of neuroscience
Neuroscience is the science, scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions and disorders. It is a Multidisciplinary approach, multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, an ...
and philosophy of mind
Philosophy of mind is a branch of philosophy that studies the ontology and nature of the mind and its relationship with the body. The mind–body problem is a paradigmatic issue in philosophy of mind, although a number of other issues are ad ...
. In this pursuit, neurophilosophers, such as Patricia Churchland, Paul Churchland and Daniel Dennett
Daniel Clement Dennett III (born March 28, 1942) is an American philosopher, writer, and cognitive scientist whose research centers on the philosophy of mind, philosophy of science, and philosophy of biology, particularly as those fields rel ...
, have focused primarily on the body rather than the mind. In this context, neuronal correlates may be viewed as causing consciousness, where consciousness can be thought of as an undefined property that depends upon this complex, adaptive, and highly interconnected biological system. However, it's unknown if discovering and characterizing neural correlates may eventually provide a theory of consciousness that can explain the first-person experience of these "systems", and determine whether other systems of equal complexity lack such features.
The massive parallelism of neural networks allows redundant populations of neurons to mediate the same or similar percepts. Nonetheless, it is assumed that every subjective state will have associated neural correlates, which can be manipulated to artificially inhibit or induce the subject's experience of that conscious state. The growing ability of neuroscientists to manipulate neurons using methods from molecular biology in combination with optical tools was achieved by the development of behavioral and organic models that are amenable to large-scale genomic analysis and manipulation. Non-human analysis such as this, in combination with imaging of the human brain, have contributed to a robust and increasingly predictive theoretical framework.
Arousal and content
 There are two common but distinct dimensions of the term ''consciousness'', one involving ''arousal'' and ''states of consciousness'' and the other involving ''content of consciousness'' and ''conscious states''. To be conscious ''of'' something, the brain must be in a relatively high state of arousal (sometimes called ''vigilance''), whether awake or in
There are two common but distinct dimensions of the term ''consciousness'', one involving ''arousal'' and ''states of consciousness'' and the other involving ''content of consciousness'' and ''conscious states''. To be conscious ''of'' something, the brain must be in a relatively high state of arousal (sometimes called ''vigilance''), whether awake or in REM sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream vi ...
. Brain arousal level fluctuates in a circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., endogenous) and responds to ...
but these natural cycles may be influenced by lack of sleep, alcohol and other drugs, physical exertion, etc. Arousal can be measured behaviorally by the signal amplitude required to trigger a given reaction (for example, the sound level that causes a subject to turn and look toward the source). High arousal states involve conscious states that feature specific perceptual content, planning and recollection or even fantasy. Clinicians use scoring systems such as the Glasgow Coma Scale to assess the level of arousal in patients with ''impaired states of consciousness'' such as the comatose state, the persistent vegetative state, and the minimally conscious state
A minimally conscious state (MCS) is a disorder of consciousness distinct from persistent vegetative state and locked-in syndrome. Unlike persistent vegetative state, patients with MCS have partial preservation of conscious awareness. MCS is a ...
. Here, "state" refers to different amounts of externalized, physical consciousness: ranging from a total absence in coma, persistent vegetative state and general anesthesia, to a fluctuating, minimally conscious state, such as sleep walking and epileptic seizure.
Many nuclei with distinct chemical signatures in the thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all direction ...
, midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal ( alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', " ...
and pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of ...
must function for a subject to be in a sufficient state of brain arousal to experience anything at all. These nuclei therefore belong to the enabling factors for consciousness. Conversely it is likely that the specific content of any particular conscious sensation is mediated by particular neurons in the cortex and their associated satellite structures, including the amygdala
The amygdala (; plural: amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nuclei located deep and medially within the temporal lobes of the brain's cerebrum in complex v ...
, thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all direction ...
, claustrum and the basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG), or basal nuclei, are a group of subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates. In humans, and some primates, there are some differences, mainly in the division of the globus pallidus into an extern ...
.
Types of dualism
The following is a very brief account of some contributions to the mind–body problem.Interactionism
The viewpoint of interactionism suggests that the mind and body are two separate substances, but that each can affect the other. This interaction between the mind and body was first put forward by the philosopherRené Descartes
René Descartes ( or ; ; Latinized: Renatus Cartesius; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Mathe ...
. Descartes believed that the mind was non-physical and permeated the entire body, but that the mind and body interacted via the pineal gland. This theory has changed throughout the years, and in the 20th century its main adherents were the philosopher of science Karl Popper and the neurophysiologist John Carew Eccles. A more recent and popular version of Interactionism is the viewpoint of emergentism. This perspective states that mental states are a result of the brain states, and that the mental events can then influence the brain, resulting in a two way communication between the mind and body.
Epiphenomenalism
The viewpoint of epiphenomenalism suggests that the physical brain can cause mental events in the mind, but that the mind cannot interact with the brain at all; stating that mental occurrences are simply a side effect of the brain's processes. This viewpoint explains that while one's body may react to them feeling joy, fear, or sadness, that the emotion does not cause the physical response. Rather, it explains that joy, fear, sadness, and all bodily reactions are caused by chemicals and their interaction with the body.Psychophysical parallelism
The viewpoint of psychophysical parallelism suggests that the mind and body are entirely independent from one another. Furthermore, this viewpoint states that both mental and physical stimuli and reactions are experienced simultaneously by both the mind and body, however, there is no interaction nor communication between the two.Double aspectism
Double aspectism is an extension of psychophysical parallelism which also suggests that the mind and body cannot interact, nor can they be separated.Baruch Spinoza
Baruch (de) Spinoza (born Bento de Espinosa; later as an author and a correspondent ''Benedictus de Spinoza'', anglicized to ''Benedict de Spinoza''; 24 November 1632 – 21 February 1677) was a Dutch philosopher of Portuguese-Jewish origin, b ...
and Gustav Fechner were two of the notable users of double aspectism, however, Fechner later expanded upon it to form the branch of psychophysics in an attempt to prove the relationship of the mind and body.
Pre-established harmony
The viewpoint of pre-established harmony is another offshoot of psychophysical parallelism which suggests that mental events and bodily events are separate and distinct, but that they are both coordinated by an external agent, an example of such an agent could be God or another deity. A notable adherent to the idea of pre-established harmony is Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz in his theory of Monadology. His explanation of pre-established harmony relied heavily upon God as the external agent who coordinated the mental and bodily events of all things in the beginning.Occasionalism
The viewpoint of Occasionalism is another offshoot of psychophysical parallelism, however, the major difference is that the mind and body have some indirect interaction. Occasionalism suggests that the mind and body are separate and distinct, but that they interact through divine intervention.Nicolas de Malebranche
Nicolas Malebranche ( , ; 6 August 1638 – 13 October 1715) was a French Oratorian Catholic priest and rationalist philosopher. In his works, he sought to synthesize the thought of St. Augustine and Descartes, in order to demonstrate the a ...
was one of the main contributors to this idea, using it as a way to address his disagreements with Descartes' view of the mind-body problem. In Malebranche's occasionalism, he viewed thoughts as a wish for the body to move, which was then fulfilled by God causing the body to act.
Historical background
The Buddha
The Buddha (480–400 B.C.E), founder ofBuddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
, described the mind and the body as depending on each other in a way that two sheaves of reeds were to stand leaning against one another and taught that the world consists of mind and matter which work together, interdependently. Buddhist teachings describe the mind as manifesting from moment to moment, one thought moment at a time as a fast flowing stream. The components that make up the mind are known as the five aggregates (i.e., material form, feelings, perception, volition, and sensory consciousness), which arise and pass away continuously. The arising and passing of these aggregates in the present moment is described as being influenced by five causal laws: biological laws, psychological laws, physical laws, volitional laws, and universal laws. The Buddhist practice of mindfulness
Mindfulness is the practice of purposely bringing one's attention to the present-moment experience without evaluation, a skill one develops through meditation or other training. Mindfulness derives from Sati (Buddhism), ''sati'', a significant ...
involves attending to this constantly changing mind-stream.
Ultimately, the Buddha's philosophy is that both mind and forms are conditionally arising qualities of an ever-changing universe in which, when nirvāna
( , , ; sa, निर्वाण} ''nirvāṇa'' ; Pali: ''nibbāna''; Prakrit: ''ṇivvāṇa''; literally, "blown out", as in an oil lampRichard Gombrich, ''Theravada Buddhism: A Social History from Ancient Benāres to Modern Colombo.' ...
is attained, all phenomenal experience ceases to exist. According to the anattā doctrine of the Buddha, the conceptual self is a mere mental construct of an individual entity and is basically an impermanent illusion, sustained by form, sensation, perception, thought and consciousness. The Buddha argued that mentally clinging to any views will result in delusion and stress, since, according to the Buddha, a real self (conceptual self, being the basis of standpoints and views) cannot be found when the mind has clarity.
Plato
Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institutio ...
(429–347 B.C.E.) believed that the material world is a shadow of a higher reality that consists of concepts he called Forms. According to Plato, objects in our everyday world "participate in" these Forms, which confer identity and meaning to material objects. For example, a circle drawn in the sand would be a circle only because it participates in the concept of an ideal circle that exists somewhere in the world of Forms. He argued that, as the body is from the material world, the soul is from the world of Forms and is thus immortal. He believed the soul was temporarily united with the body and would only be separated at death, when it, if pure, would return to the world of Forms; otherwise, reincarnation follows. Since the soul does not exist in time and space, as the body does, it can access universal truths. For Plato, ideas (or Forms) are the true reality, and are experienced by the soul. The body is for Plato empty in that it can not access the abstract reality of the world; it can only experience shadows. This is determined by Plato's essentially rationalistic
In philosophy, rationalism is the epistemological view that "regards reason as the chief source and test of knowledge" or "any view appealing to reason as a source of knowledge or justification".Lacey, A.R. (1996), ''A Dictionary of Philosophy'' ...
epistemology
Epistemology (; ), or the theory of knowledge, is the branch of philosophy concerned with knowledge. Epistemology is considered a major subfield of philosophy, along with other major subfields such as ethics, logic, and metaphysics.
Episte ...
.
Aristotle
ForAristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical Greece, Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatet ...
(384–322 BC) ''mind'' is a faculty of the ''soul''. Regarding the soul, he said:
In the end, Aristotle saw the relation between soul and body as uncomplicated, in the same way that it is uncomplicated that a cubical shape is a property of a toy building block. The soul is a property exhibited by the body, one among many. Moreover, Aristotle proposed that when the body perishes, so does the soul, just as the shape of a building block disappears with destruction of the block.
Medieval Aristotelianism
Working in the Aristotelian-influenced tradition ofThomism
Thomism is the philosophical and theological school that arose as a legacy of the work and thought of Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274), the Dominican philosopher, theologian, and Doctor of the Church. In philosophy, Aquinas' disputed question ...
, Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas, OP (; it, Tommaso d'Aquino, lit=Thomas of Aquino; 1225 – 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican friar and priest who was an influential philosopher, theologian and jurist in the tradition of scholasticism; he is known wi ...
(1225–1274), like Aristotle, believed that the mind and the body are one, like a seal and wax; therefore, it is pointless to ask whether or not they are one. However, (referring to "mind" as "the soul") he asserted that the soul persists after the death of the body in spite of their unity, calling the soul "this particular thing". Since his view was primarily theological rather than philosophical, it is impossible to fit it neatly within either the category of physicalism or dualism
Dualism most commonly refers to:
* Mind–body dualism, a philosophical view which holds that mental phenomena are, at least in certain respects, not physical phenomena, or that the mind and the body are distinct and separable from one another
** ...
.
Influences of Eastern monotheistic religions
In religious philosophy of Eastern monotheism, dualism denotes abinary opposition
A binary opposition (also binary system) is a pair of related terms or concepts that are opposite in meaning. Binary opposition is the system of language and/or thought by which two theoretical opposites are strictly defined and set off against one ...
of an idea that contains two essential parts. The first formal concept of a "mind-body" split may be found in the divinity– secularity dualism of the ancient Persian religion of Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ont ...
around the mid-fifth century BC. Gnosticism
Gnosticism (from grc, γνωστικός, gnōstikós, , 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems which coalesced in the late 1st century AD among Judaism, Jewish and Early Christianity, early Christian sects. These ...
is a modern name for a variety of ancient dualistic ideas inspired by Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
popular in the first and second century AD. These ideas later seem to have been incorporated into Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be on ...
's ''"tripartite soul"'' that led into both the Christian sentiments expressed in the later Augustinian theodicy and Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islam ...
's Platonism in Islamic Philosophy.
Descartes
René Descartes
René Descartes ( or ; ; Latinized: Renatus Cartesius; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Mathe ...
(1596–1650) believed that mind exerted control over the brain ''via'' the pineal gland:
His posited relation between mind and body is called Cartesian dualism or substance dualism. He held that ''mind'' was distinct from ''matter'', but could influence matter. How such an interaction could be exerted remains a contentious issue.
Kant
For Kant (1724–1804) beyond ''mind'' and ''matter'' there exists a world of ''a priori'' forms, which are seen as necessary preconditions for understanding. Some of these forms, space and time being examples, today seem to be pre-programmed in the brain. Kant views the mind–body interaction as taking place through forces that may be of different kinds for mind and body.Huxley
ForHuxley
Huxley may refer to:
People
* Huxley (surname)
* The British Huxley family
* Thomas Henry Huxley (1825–1895), British biologist known as "Darwin's Bulldog"
* Aldous Huxley (1894–1963), British writer, author of ''Brave New World'', grandson ...
(1825–1895) the conscious mind was a by-product of the brain that has no influence upon the brain, a so-called epiphenomenon.
Whitehead
A. N. Whitehead
Alfred North Whitehead (15 February 1861 – 30 December 1947) was an English mathematician and philosopher. He is best known as the defining figure of the philosophical school known as process philosophy, which today has found applicat ...
advocated a sophisticated form of panpsychism that has been called by David Ray Griffin ''panexperientialism
In the philosophy of mind, panpsychism () is the view that the mind or a mindlike aspect is a fundamental and ubiquitous feature of reality. It is also described as a theory that "the mind is a fundamental feature of the world which exists thro ...
''.
Popper
For Popper (1902–1994) there are ''three'' aspects of the mind–body problem: the worlds of matter, mind, and of the creations of the mind, such as mathematics. In his view, the third-world creations of the mind could be interpreted by the second-world mind and used to affect the first-world of matter. An example might beradio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transm ...
, an example of the interpretation of the third-world (Maxwell's electromagnetic theory
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions ...
) by the second-world mind to suggest modifications of the external first world.
Searle
For Searle (b. 1932) the mind–body problem is a false dichotomy; that is, mind is a perfectly ordinary aspect of the brain. Searle proposed Biological naturalism in 1980.Ryle
With his book, '' The Concept of Mind'', Gilbert Ryle "was seen to have put the final nail in the coffin of Cartesian dualism". In the chapter "Descartes' Myth," Ryle introduces "the dogma of the Ghost in the machine" to describe the philosophical concept of the mind as an entity separate from the body:I hope to prove that it is entirely false, and false not in detail but in principle. It is not merely an assemblage of particular mistakes. It is one big mistake and a mistake of a special kind. It is, namely, a category mistake.
See also
General
*Bodymind
Bodymind is an approach to understand the relationship between the human body and mind where they are seen as a single integrated unit. It attempts to address the mind–body problem and resists the Western traditions of mind–body dualism. The t ...
* Chinese room
* Cognitive closure (philosophy)
In philosophy of science and philosophy of mind, cognitive closure is the proposition that human minds are constitutionally incapable of solving certain perennial philosophical problems. Owen Flanagan calls this position anti-constructive natural ...
* Cognitive neuroscience
Cognitive neuroscience is the scientific field that is concerned with the study of the biological processes and aspects that underlie cognition, with a specific focus on the neural connections in the brain which are involved in mental process ...
* Connectionism
Connectionism refers to both an approach in the field of cognitive science that hopes to explain mind, mental phenomena using artificial neural networks (ANN) and to a wide range of techniques and algorithms using ANNs in the context of artificial ...
* Consciousness in animals
Animal consciousness, or animal awareness, is the quality or state of self-awareness within a non-human animal, or of being aware of an external object or something within itself. In humans, consciousness has been defined as: sentience, awaren ...
* Downward causation In philosophy, downward causation is a causal relationship from higher levels of a system to lower-level parts of that system: for example, mental events acting to cause physical events. The term was originally coined in 1974 by the philosopher and ...
* ''Descartes' Error
''Descartes' Error: Emotion, Reason, and the Human Brain'' is a 1994 book by neuroscientist António Damásio describing the physiology of rational thought and decision, and how the faculties could have evolved through Darwinian natural selection ...
''
* Embodied cognition
Embodied cognition is the theory that many features of cognition, whether human or otherwise, are shaped by aspects of an organism's entire body. Sensory and motor systems are seen as fundamentally integrated with cognitive processing. The cogni ...
* Existentialism
Existentialism ( ) is a form of philosophical inquiry that explores the problem of human existence and centers on human thinking, feeling, and acting. Existentialist thinkers frequently explore issues related to the meaning
Meaning most comm ...
* Explanatory gap
* Free will
Free will is the capacity of agents to choose between different possible courses of action unimpeded.
Free will is closely linked to the concepts of moral responsibility, praise, culpability, sin, and other judgements which apply only to a ...
* Ideasthesia
* Namarupa (Buddhist concept)
* Neuroscience of free will
* Philosophical zombie
* Philosophy of artificial intelligence
* Pluralism
Pluralism denotes a diversity of views or stands rather than a single approach or method.
Pluralism or pluralist may refer to:
Politics and law
* Pluralism (political philosophy), the acknowledgement of a diversity of political systems
* Plur ...
* Problem of other minds
* Reductionism
Reductionism is any of several related philosophical ideas regarding the associations between phenomena which can be described in terms of other simpler or more fundamental phenomena. It is also described as an intellectual and philosophical pos ...
* Sacred–profane dichotomy
* Sentience
Sentience is the capacity to experience feelings and sensations. The word was first coined by philosophers in the 1630s for the concept of an ability to feel, derived from Latin '' sentientem'' (a feeling), to distinguish it from the ability to ...
* Strange loop (self-reflective thoughts)
* ''The Mind's I
''The Mind's I: Fantasies and Reflections on Self and Soul'' is a 1981 collection of essays and other texts about the nature of the mind and the self, edited with commentary by philosophers Douglas R. Hofstadter and Daniel C. Dennett. The tex ...
'' (book on the subject)
* Turing test
The Turing test, originally called the imitation game by Alan Turing in 1950, is a test of a machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behaviour equivalent to, or indistinguishable from, that of a human. Turing proposed that a human evaluato ...
* William H. Poteat
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * Kim, J. (1995). "Mind–Body Problem", ''Oxford Companion to Philosophy''. Ted Honderich (ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. * * Massimini, M.; Tononi, G. (2018). Sizing up Consciousness: Towards an Objective Measure of the Capacity for Experience. Oxford University Press. * Turner, Bryan S. (1996).The Body and Society: Exploration in Social Theory
'.
External links
*Plato's Middle Period Metaphysics and Epistemology - The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
*
The Mind/Body Problem
BBC Radio 4 discussion with Anthony Grayling, Julian Baggini & Sue James (''In Our Time'', Jan. 13, 2005) {{DEFAULTSORT:Mind-body problem Arguments in philosophy of mind Baruch Spinoza Cognition Concepts in epistemology Concepts in metaphysics Concepts in the philosophy of mind Concepts in the philosophy of science Consciousness studies Dichotomies Enactive cognition Epistemological theories History of psychology Metaphysical theories Metaphysics of mind Neuroscience Ontology Philosophical problems Philosophy and thought in the Dutch Republic René Descartes Thought