Milia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A milium (''plural'' milia), also called a milk spot or an oil seed, is a clog of the
A milium (''plural'' milia), also called a milk spot or an oil seed, is a clog of the
 A milium (''plural'' milia), also called a milk spot or an oil seed, is a clog of the
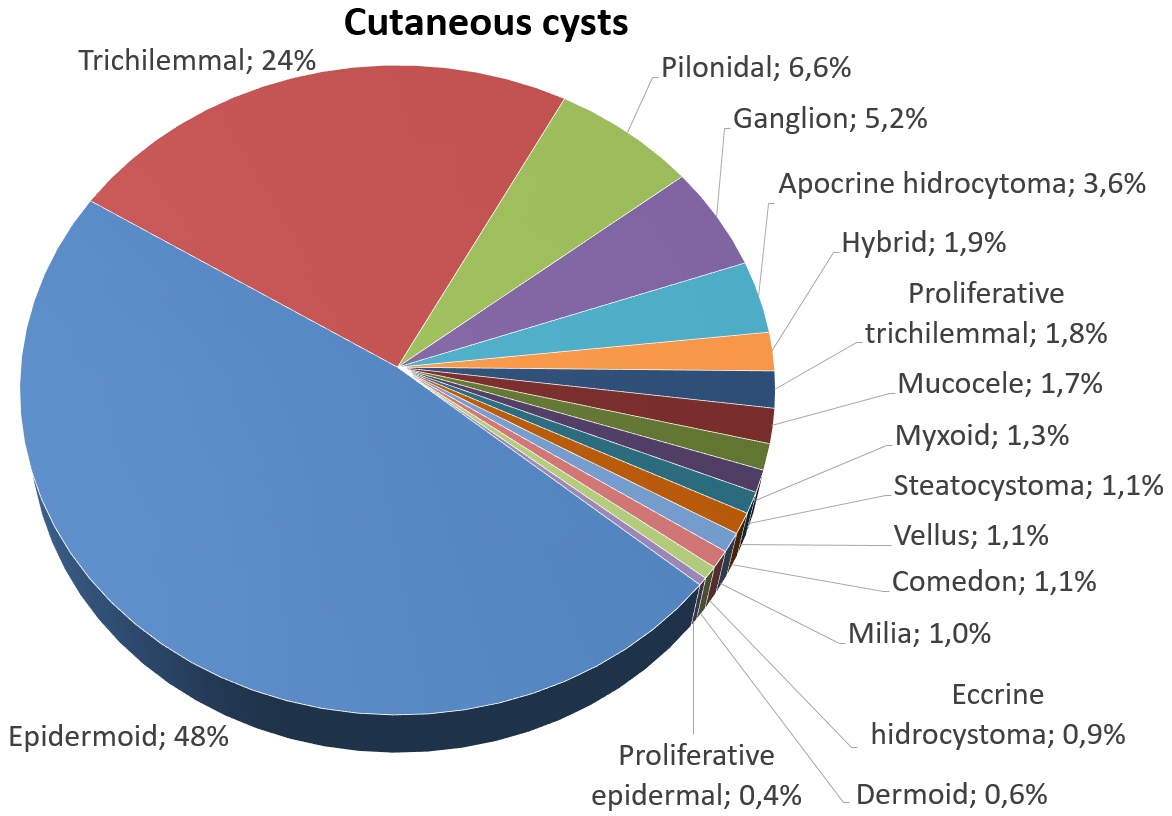
A milium (''plural'' milia), also called a milk spot or an oil seed, is a clog of the eccrine sweat gland
Eccrine sweat glands (; from Greek ''ekkrinein'' 'secrete'; sometimes called merocrine glands) are the major sweat glands of the human body, found in virtually all skin, with the highest density in palm and soles, then on the head, but much less ...
. It is a keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
-filled cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and cell division, division compared with the nearby Biological tissue, tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of Cell (biology), cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which ...
that can appear just under the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rele ...
or on the roof of the mouth.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . Milia are commonly associated with newborn babies
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to ...
, but can appear on people of all ages. They are usually found around the nose and eyes, and sometimes on the genitalia, often mistaken by those affected as warts or other sexually transmitted diseases
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, and oral sex ...
. Milia can also be confused with stubborn whiteheads.
In children, milia often disappear within two to four weeks. For adults, they can be removed by a physician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...
(a dermatologist
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical ...
has specialist knowledge in this area). A common method that a dermatologist uses to remove a milium is to nick the skin with a #11 surgical blade and then use a comedone extractor to press the cyst out.
See also
*Eruptive vellus hair cyst Eruptive vellus hair cysts (or EVHC) are small lesions that occur most often in the chest wall, abdomen and extremities, often with a crusted surface. EVHC may occur randomly, or it can be inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. The condition af ...
*Sebaceous hyperplasia
Sebaceous hyperplasia is a disorder of the sebaceous glands in which they become enlarged, producing flesh-colored or yellowish, shiny, often umbilicated bumps on the face. Newly formed nodules often swell with sweating (which is pathognomonic for ...
*Seborrheic keratosis
A seborrheic keratosis is a non-cancerous (benign) skin tumour that originates from cells, namely keratinocytes, in the outer layer of the skin called the epidermis. Like liver spots, seborrheic keratoses are seen more often as people age.
The tum ...
References
Epidermal nevi, neoplasms, and cysts Conditions of the skin appendages {{Epidermal-growth-stub