Micronesia Heatwave on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 Micronesia (, ) is a
Micronesia (, ) is a

 Micronesia (, ) is a
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion
A subregion is a part of a larger region or continent and is usually based on location. Cardinal directions, such as south are commonly used to define a subregion.
United Nations subregions
The Statistics Division of the United Nations (UN) ...
of Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
to the west, Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
to the east, and Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
to the south—as well as with the wider community of Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austro ...
.
The region has a tropical marine climate
A tropical marine climate is a tropical climate that is primarily influenced by the ocean. It is usually experienced by islands and coastal areas 10° to 20° north and south of the equator. There are two main seasons in a tropical marine climate: ...
and is part of the Oceanian realm
The Oceanian realm is one of the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) biogeographic realms, and is unique in not including any continental land mass. It has the smallest land area of any of the WWF realms.
This realm includes the islands of the Pacific Oc ...
. It includes four main archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arc ...
s—the Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the ce ...
, the Gilbert Islands, the Mariana Islands, and the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
—as well as numerous islands that are not part of any archipelago.
Political control of areas within Micronesia varies depending on the island, and is distributed among six sovereign nations. Some of the Caroline Islands are part of the Republic of Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the Caro ...
and some are part of the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
(often shortened to "FSM" or "Micronesia"—not to be confused with the identical name for the overall region). The Gilbert Islands (along with the Phoenix Islands
The Phoenix Islands, or Rawaki, are a group of eight atolls and two submerged coral reefs that lie east of the Gilbert Islands and west of the Line Islands in the central Pacific Ocean, north of Samoa. They are part of the Republic of Kiri ...
and the Line Islands in Polynesia) comprise the Republic of Kiribati
Kiribati (), officially the Republic of Kiribati ( gil, ibaberikiKiribati),Kiribati
''The Wor ...
. The Mariana Islands are affiliated with the United States; some of them belong to the U.S. Territory of ''The Wor ...
Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
and the rest belong to the U.S. Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mariånas; cal, Commonwealth Téél Falúw kka Efáng llól Marianas), is an unincorporated territory and commonw ...
. The island of Nauru is its own sovereign nation. The Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
all belong to the Republic of the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
. The sovereignty of Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of T ...
is contested: it is claimed both by the United States and by the Republic of the Marshall Islands. The United States has actual possession of Wake Island, which is under the immediate administration of the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part ...
.
Human settlement of Micronesia began several millennia ago. The Micronesian people are considered, by linguistic, archaeological, and human genetic evidence, a subset of the sea-migrating Austronesian people, who include the Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
n people and the Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
n people. Based on the current scientific consensus, the Austronesian peoples originated from a prehistoric seaborne migration, known as the Austronesian expansion
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austron ...
, from pre-Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, at around 3000 to 1500 BCE. Austronesians reached the northernmost Philippines, specifically the Batanes Islands
Batanes, officially the Province of Batanes ( ivv, Provinsiya nu Batanes; Ilocano: ''Probinsia ti Batanes''; fil, Lalawigan ng Batanes, ), is an archipelagic province in the Philippines, administratively part of the Cagayan Valley region. It i ...
, by around 2200 BCE. Austronesians were the first people to invent oceangoing sailing technologies (notably catamarans, outrigger boat
Outrigger boats are various watercraft featuring one or more lateral support floats known as outriggers, which are fastened to one or both sides of the main hull. They can range from small dugout canoes to large plank-built vessels. Outrigger ...
s, lashed-lug
Lashed-lug boats are ancient boat-building techniques of the Austronesian peoples. It is characterized by the use of sewn holes and later dowels ("treenails") to stitch planks edge-to-edge onto a dugout keel and solid carved wood pieces that form ...
boat building
Boat building is the design and construction of boats and their systems. This includes at a minimum a hull, with propulsion, mechanical, navigation, safety and other systems as a craft requires.
Construction materials and methods
Wood
Wo ...
, and the crab claw sail
The crab claw sail is a fore-and-aft triangular sail with spars along upper and lower edges. The crab claw sail was first developed by the Austronesian peoples some time around 1500 BC. It is used in many traditional Austronesian cultures in Islan ...
), which enabled their rapid dispersal into the islands of the Indo-Pacific. From 2000 BCE they assimilated (or were assimilated by) the earlier populations on the islands in their migration pathway.
The earliest known contact of Europeans with Micronesia was in 1521, when Spanish ships landed in the Marianas. Jules Dumont d'Urville
Jules Sébastien César Dumont d'Urville (; 23 May 1790 – 8 May 1842) was a French explorer and naval officer who explored the south and western Pacific, Australia, New Zealand, and Antarctica. As a botanist and cartographer, he gave his nam ...
is usually credited with coining the term "Micronesia" in 1832, but in fact, Domeny de Rienzi used the term a year earlier.
Geography
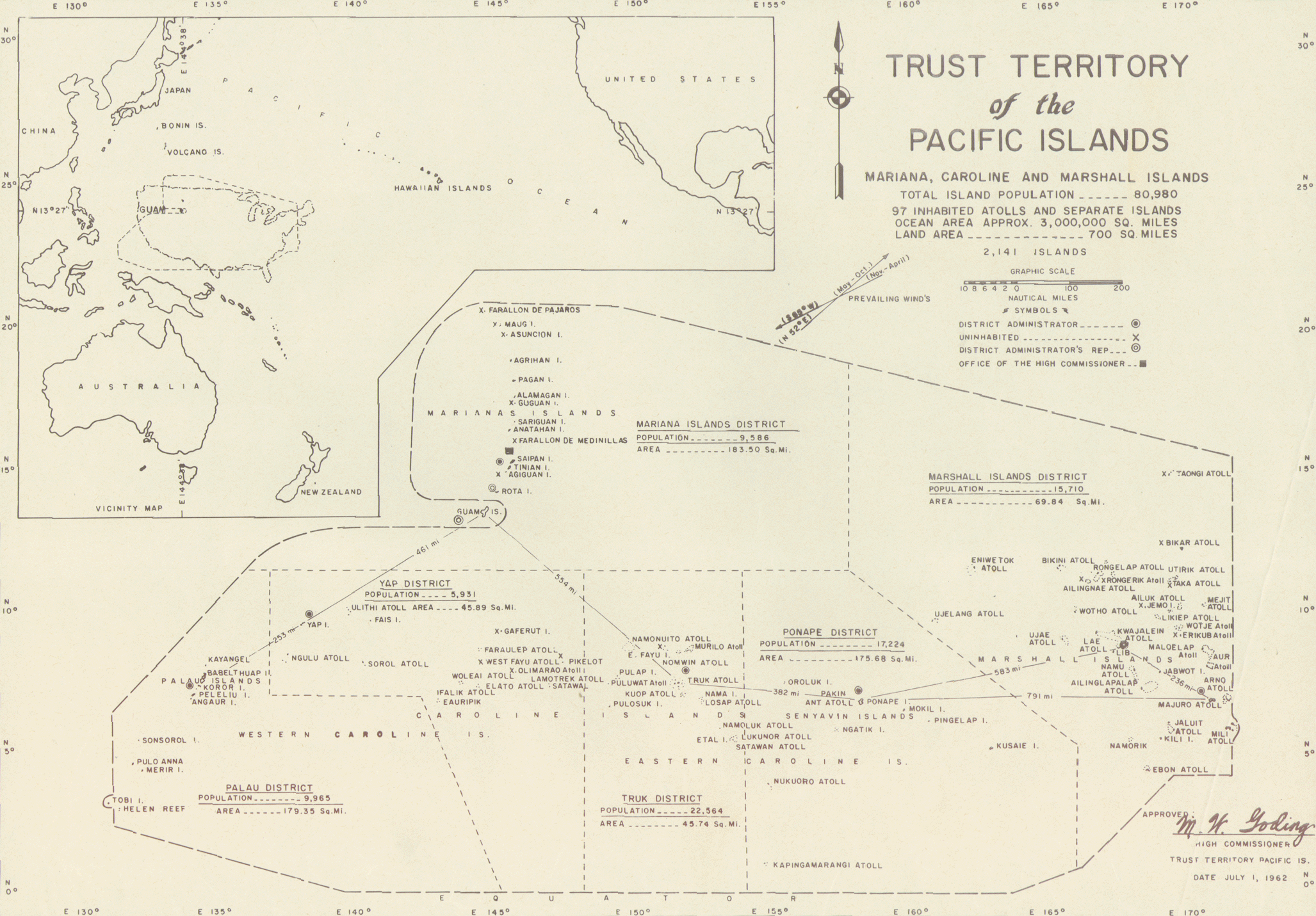
Micronesia is a region in Oceania that includes approximately 2100 islands, with a total land area of , the largest of which isGuam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
, which covers . The total ocean area within the perimeter of the islands is .
There are four main island groups in Micronesia:
* the Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the ce ...
(Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
and Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the ...
)
* the Gilbert Islands (Kiribati
Kiribati (), officially the Republic of Kiribati ( gil, ibaberikiKiribati),Kiribati
''The Wor ...
)
* the Mariana Islands (''The Wor ...
Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mariånas; cal, Commonwealth Téél Falúw kka Efáng llól Marianas), is an unincorporated territory and commonw ...
and Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
, US)
* the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
This does not include the separate island nation of Nauru, along with other distinctly separate islands and smaller island groups.
Caroline Islands
TheCaroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the ce ...
are a widely scattered archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arc ...
consisting of about 500 small coral island
A coral island is a type of island formed from coral detritus and associated organic material. It occurs in tropical and sub-tropical areas, typically as part of a coral reef which has grown to cover a far larger area under the sea.
Ecosystem
...
s, north of New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
and east of the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
. The Carolines consist of two republics: the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
, consisting of approximately 600 islands on the eastern side of the chain with Kosrae
Kosrae ( ), formerly known as Kusaie or Strong's Island, is an island in the Federated States of Micronesia. The State of Kosrae is one of the four states of the Federated States of Micronesia, and includes the main island of Kosrae and a few near ...
being the most eastern; and Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the ...
consisting of 250 islands on the western side.
Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands are a chain of sixteenatoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can gr ...
s and coral islands, arranged in an approximate north-to-south line. In a geographical sense, the equator serves as the dividing line between the northern Gilbert Islands and the southern Gilbert Islands. The Republic of Kiribati
Kiribati (), officially the Republic of Kiribati ( gil, ibaberikiKiribati),Kiribati
''The Wor ...
contains all of the Gilberts, including the island of ''The Wor ...
Tarawa
Tarawa is an atoll and the capital of the Republic of Kiribati,Kiribati
''
''
The Mariana Islands are an arc-shaped
 The
The
File:Castle Bravo Blast.jpg, Image of the
File:Aerial view of Nauru.jpg, Aerial view of Nauru
File:Nauru Denigomodu-Nibok.jpg, Nauruan districts of
File:Wake Island by Agate.jpg, Wake Island as depicted by the

 The
The
File:Map FM-Nan Madol.PNG, Central Nan Madol (map)
File:Nan Madol 5.jpg,
 The earliest known contact with Europeans occurred in 1521, when a Spanish expedition under
The earliest known contact with Europeans occurred in 1521, when a Spanish expedition under
 In the
In the
 In the early 20th century, the islands of Micronesia were divided between three foreign powers:
* the
In the early 20th century, the islands of Micronesia were divided between three foreign powers:
* the
 Nationally, the primary income is the sale of fishing rights to foreign nations that harvest tuna using huge purse seiners. A few Japanese Longline fishing, long liners still ply the waters. The crews aboard fishing fleets contribute little to the local economy since their ships typically set sail loaded with stores and provisions that are cheaper than local goods. Additional money comes in from government grants, mostly from the United States and the $150 million the US paid into a trust fund for reparations of residents of Bikini Atoll that had to move after nuclear testing. Few mineral deposits worth exploiting exist, except for some high-grade phosphate, Phosphate mining in Nauru, especially on Nauru.
Most residents of Micronesia can freely move to and work within, the United States. Relatives working in the US that send money home to relatives represent the primary source of individual income. Additional individual income comes mainly from government jobs and work within shops and restaurants.
The tourist industry consists mainly of scuba divers that come to see the coral reefs, do wall dives and visit sunken ships from WWII. Major stops for scuba divers in approximate order are Palau, Chuuk, Yap and Pohnpei. Some private yacht owners visit the area for months or years at a time. However, they tend to stay mainly at ports of entry and are too few in number to be counted as a major source of income.
Copra production used to be a more significant source of income, however, world prices have dropped in part to large palm plantations that are now planted in places like Borneo.
Nationally, the primary income is the sale of fishing rights to foreign nations that harvest tuna using huge purse seiners. A few Japanese Longline fishing, long liners still ply the waters. The crews aboard fishing fleets contribute little to the local economy since their ships typically set sail loaded with stores and provisions that are cheaper than local goods. Additional money comes in from government grants, mostly from the United States and the $150 million the US paid into a trust fund for reparations of residents of Bikini Atoll that had to move after nuclear testing. Few mineral deposits worth exploiting exist, except for some high-grade phosphate, Phosphate mining in Nauru, especially on Nauru.
Most residents of Micronesia can freely move to and work within, the United States. Relatives working in the US that send money home to relatives represent the primary source of individual income. Additional individual income comes mainly from government jobs and work within shops and restaurants.
The tourist industry consists mainly of scuba divers that come to see the coral reefs, do wall dives and visit sunken ships from WWII. Major stops for scuba divers in approximate order are Palau, Chuuk, Yap and Pohnpei. Some private yacht owners visit the area for months or years at a time. However, they tend to stay mainly at ports of entry and are too few in number to be counted as a major source of income.
Copra production used to be a more significant source of income, however, world prices have dropped in part to large palm plantations that are now planted in places like Borneo.
 The Chamorro people are the indigenous peoples of the Mariana Islands, which are politically divided between the Territories of the United States, United States territory of
The Chamorro people are the indigenous peoples of the Mariana Islands, which are politically divided between the Territories of the United States, United States territory of

History of Micronesia
{{Authority control Micronesia, Asia-Pacific Islands of Oceania Regions of Oceania
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arc ...
made up by the summits of fifteen volcanic mountains. The island chain arises as a result of the western edge of the Pacific Plate moving westward and plunging downward below the Mariana plate, a region that is the most volcanically active convergent plate boundary on Earth. The Marianas were politically divided in 1898, when the United States acquired title to Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
under the Treaty of Paris, 1898, which ended the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (cloc ...
. Spain then sold the remaining northerly islands to Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
in 1899. Germany lost all of her colonies at the end of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mariånas; cal, Commonwealth Téél Falúw kka Efáng llól Marianas), is an unincorporated territory and commonw ...
became a League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
Mandate, with Japan as the mandatory. After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, the islands were transferred into the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
Trust Territory
United Nations trust territories were the successors of the remaining League of Nations mandates and came into being when the League of Nations ceased to exist in 1946. All of the trust territories were administered through the United Nati ...
System, with the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
as Trustee. In 1976, the Northern Mariana Islands and the United States entered into a covenant of political union under which commonwealth status was granted the Northern Mariana Islands and its residents received United States citizenship.
Marshall Islands
 The
The Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
are located north of Nauru and Kiribati
Kiribati (), officially the Republic of Kiribati ( gil, ibaberikiKiribati),Kiribati
''The Wor ...
, east of the ''The Wor ...
Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
, and south of the U.S. territory of Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of T ...
. The islands consist of 29 low-lying atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can gr ...
s and 5 isolated islands, comprising 1,156 individual islands and islet
An islet is a very small, often unnamed island. Most definitions are not precise, but some suggest that an islet has little or no vegetation and cannot support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/or hard coral; may be permanen ...
s. The atolls and islands form two groups: the Ratak Chain
The Ratak Chain ( Marshallese: , ) is a chain of islands within the island nation of the Marshall Islands. Ratak means "sunrise". It lies to the east of the country's other island chain, the Ralik Chain. In 1999 the total population of the Rata ...
and the Ralik Chain
The Ralik Chain ( Marshallese: , ) is a chain of islands within the island nation of the Marshall Islands. Ralik means "sunset". It is west of the Ratak Chain. In 1999 the total population of the Ralik islands was 19,915. Christopher Loeak, who b ...
(meaning "sunrise" and "sunset" chains). All the islands in the chain are part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
, a presidential republic in free association with the United States. Having few natural resources, the islands' wealth is based on a service economy
Service economy can refer to one or both of two recent economic developments:
* The increased importance of the service sector in industrialized economies. The current list of Fortune 500 companies contains more service companies and fewer manu ...
, as well as some fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
and agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
. Of the 29 atolls, 24 of them are inhabited.
Bikini Atoll
Bikini Atoll ( or ; Marshallese: , , meaning "coconut place"), sometimes known as Eschscholtz Atoll between the 1800s and 1946 is a coral reef in the Marshall Islands consisting of 23 islands surrounding a central lagoon. After the Seco ...
is an atoll in the Marshall Islands. There are 23 islands in the Bikini Atoll. The islands of Bokonijien, Aerokojlol and Nam were vaporized during nuclear tests that occurred there. The islands are composed of low coral limestone and sand. The average elevation is only about above low tide level.
Castle Bravo
Castle Bravo was the first in a series of high-yield thermonuclear weapon design tests conducted by the United States at Bikini Atoll, Marshall Islands, as part of '' Operation Castle''. Detonated on March 1, 1954, the device was the most powerful ...
nuclear test, detonated on 1 March 1954, at Bikini Atoll
Bikini Atoll ( or ; Marshallese: , , meaning "coconut place"), sometimes known as Eschscholtz Atoll between the 1800s and 1946 is a coral reef in the Marshall Islands consisting of 23 islands surrounding a central lagoon. After the Seco ...
File:Cross spikes club.jpg, An illustration of the Cross Spikes Club of the US Navy on Bikini Atoll
Bikini Atoll ( or ; Marshallese: , , meaning "coconut place"), sometimes known as Eschscholtz Atoll between the 1800s and 1946 is a coral reef in the Marshall Islands consisting of 23 islands surrounding a central lagoon. After the Seco ...
, one of several Marshall Islands used for atomic bomb tests.
File:Kili Island - NASA Astronaut Photography.png, Kili Island
Kili Island or Kili Atoll ( Marshallese: , ) is a small, () island located in the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. It is the temporary home of 548 inhabitants who are descended from islanders who originally lived on Bikini Atoll. They were ...
is one of the smallest islands in the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
.
Nauru
Nauru is an oval-shapedisland country
An island country, island state or an island nation is a country whose primary territory consists of one or more islands or parts of islands. Approximately 25% of all independent countries are island countries. Island countries are historically ...
in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, south of the Equator, listed as the world's smallest republic, covering just . With residents, it is the third least-populated country, after Vatican City
Vatican City (), officially the Vatican City State ( it, Stato della Città del Vaticano; la, Status Civitatis Vaticanae),—'
* german: Vatikanstadt, cf. '—' (in Austria: ')
* pl, Miasto Watykańskie, cf. '—'
* pt, Cidade do Vati ...
and Tuvalu
Tuvalu ( or ; formerly known as the Ellice Islands) is an island country and microstate in the Polynesian subregion of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. Its islands are situated about midway between Hawaii and Australia. They lie east-nor ...
. The island is surrounded by a coral reef, which is exposed at low tide and dotted with pinnacles. The presence of the reef has prevented the establishment of a seaport
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as H ...
, although channels
Channel, channels, channeling, etc., may refer to:
Geography
* Channel (geography), in physical geography, a landform consisting of the outline (banks) of the path of a narrow body of water.
Australia
* Channel Country, region of outback Austral ...
in the reef allow small boats access to the island. A fertile coastal strip wide lies inland from the beach.
Denigomodu
Denigomodu is a district in the western part of the island of Nauru. It is the most populous district in Nauru.
It houses the expatriate housing compound "The Location". This makes it Nauru's largest settlement by population. 25.7% of the people ...
and Nibok
Wake Island
Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of T ...
is a coral atoll with a coastline of just north of the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
. It is an unorganized, unincorporated territory
Territories of the United States are sub-national administrative divisions overseen by the federal government of the United States. The various American territories differ from the U.S. states and tribal reservations as they are not sove ...
of the United States. Access to the island is restricted and all activities on the island are managed by the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part ...
. While geographically adjacent, it is not ethnoculturally part of Micronesia, due to its historical lack of human inhabitation. Micronesians may have possibly visited Wake Island in prehistoric times to harvest fish, but there is nothing to suggest any kind of settlement.https://www.sprep.org/attachments/15.pdf
United States Exploring Expedition
The United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–1842 was an exploring and surveying expedition of the Pacific Ocean and surrounding lands conducted by the United States. The original appointed commanding officer was Commodore Thomas ap Catesby ...
, drawn by Alfred Thomas Agate
Alfred Thomas Agate (February 14, 1812 – January 5, 1846) was a noted American artist, painter and miniaturist.
Agate lived in New York from 1831 to 1838. He studied with his brother, Frederick Styles Agate, a portrait and historical painter ...
File:Wake Island air.JPG, Aerial view Wake Island, looking westward
Geology
The majority of the islands in the area are part of acoral atoll
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secre ...
. Coral atolls begin as coral reefs
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
that grow on the slopes of a central volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the Crust (geology), crust of a Planet#Planetary-mass objects, planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Ear ...
. When the volcano sinks back down into the sea, the coral continues to grow, keeping the reef at or above water level. One exception is Pohnpei in the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
, which still has the central volcano and coral reefs around it.
Fauna
The Yap Islands host a number of endemic bird species, including the Yap monarch and the Olive white-eye, in addition to four other restricted-range bird species. The endangered Yap flying-fox, though often considered a subspecies of the Pelew flying fox or theMariana fruit bat
The Mariana fruit bat (''Pteropus mariannus''), also known as the Mariana flying fox, and the ''fanihi'' in Chamorro, is a megabat found only in the Mariana Islands and Ulithi (an atoll in the Caroline Islands). Habitat loss has driven it to enda ...
, is also endemic to Yap. 
Climate
The region has atropical marine climate
A tropical marine climate is a tropical climate that is primarily influenced by the ocean. It is usually experienced by islands and coastal areas 10° to 20° north and south of the equator. There are two main seasons in a tropical marine climate: ...
moderated by seasonal northeast trade winds
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisp ...
. There is little seasonal temperature variation. The dry season runs from December or January to June and the rainy season from July to November or December. Because of the location of some islands, the rainy season can sometimes include typhoon
A typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere. This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, and is the most active tropical cyclone basin on Earth, accounting for a ...
s.
History
Prehistory
Northern Marianas
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mariånas; cal, Commonwealth Téél Falúw kka Efáng llól Marianas), is an unincorporated territories of the Unit ...
were the first islands in Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
colonized by the Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austro ...
. They were settled by the voyagers who sailed eastwards from the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
in approximately 1500 BCE. These populations gradually moved southwards until they reached the Bismarck Archipelago and the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
by 1300 BCE and reconnected with the Lapita culture
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian people and their material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. They are believed to have originated from the northern Philipp ...
of the southeast migration branch of Austronesians moving through coastal New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
and Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
. By 1200 BCE, they again began crossing open seas beyond inter-island visibility, reaching Vanuatu
Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (french: link=no, République de Vanuatu; bi, Ripablik blong Vanuatu), is an island country located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of no ...
, Fiji, and New Caledonia; before continuing eastwards to become the ancestors of the Polynesian people
Polynesians form an ethnolinguistic group of closely related people who are native to Polynesia (islands in the Polynesian Triangle), an expansive region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island South ...
.
Further migrations by other Austronesians also followed, likely from Sulawesi, settling Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the ...
and Yap
Yap ( yap, Waqaab) traditionally refers to an island group located in the Caroline Islands of the western Pacific Ocean, a part of Yap State. The name "Yap" in recent years has come to also refer to the state within the Federated States of Micr ...
by around 1000 BCE. The details of this colonization, however, are not very well known. In 200 BCE, a loosely connected group of Lapita colonists from Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
also migrated back northwards, settling the islands of eastern Micronesia almost simultaneously. This region became the center of another wave of migrations radiating outwards, reconnecting them with other settled islands in western Micronesia.
Around 800 CE, a second wave of migrants from Southeast Asia arrived in the Marianas, beginning what is now known as the Latte period
Caffè latte (), often shortened to just latte () in English, is a coffee beverage of Italian origin made with espresso and steamed milk. Variants include the chocolate-flavored mocha or replacing the coffee with another beverage base such as ma ...
. These new settlers built large structures with distinctive capped stone pillars known as ''haligi''. They also reintroduced rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
(which did not survive earlier voyages), making the Northern Marianas the only islands in Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
where rice was grown prior to European contact. However, it was considered a high-status crop and only used in rituals. It did not become a staple until after Spanish colonization
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
.
Construction of Nan Madol
Nan Madol is an archaeological site adjacent to the eastern shore of the island of Pohnpei, now part of the Madolenihmw district of Pohnpei state in the Federated States of Micronesia in the western Pacific Ocean. Nan Madol was the capital of t ...
, a megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
ic complex made from basalt lava logs in Pohnpei, began in around 1180 CE. This was followed by the construction of the Leluh complex in Kosrae
Kosrae ( ), formerly known as Kusaie or Strong's Island, is an island in the Federated States of Micronesia. The State of Kosrae is one of the four states of the Federated States of Micronesia, and includes the main island of Kosrae and a few near ...
in around 1200 CE.
Nan Madol
Nan Madol is an archaeological site adjacent to the eastern shore of the island of Pohnpei, now part of the Madolenihmw district of Pohnpei state in the Federated States of Micronesia in the western Pacific Ocean. Nan Madol was the capital of t ...
File:Lelu Ruins, Kosrae, Micronesia.jpg, Leluh
File:Latte stones in Hagatna.jpg, Latte stone
A latte stone, or simply latte (also latde, latti, or latdi), is a Column, pillar (Chamorro language: ''haligi'') capped by a Sphere, hemispherical stone capital (architecture), capital (''tasa'') with the flat side facing up. Used as building sup ...
s
File:Yap Stone Money.jpg, Rai stone
Early European contact
 The earliest known contact with Europeans occurred in 1521, when a Spanish expedition under
The earliest known contact with Europeans occurred in 1521, when a Spanish expedition under Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the Eas ...
reached the Marianas. This contact is recorded in Antonio Pigafetta
Antonio Pigafetta (; – c. 1531) was an Venetian scholar and explorer. He joined the expedition to the Spice Islands led by explorer Ferdinand Magellan under the flag of the emperor Charles V and after Magellan's death in the Philippine Islands, ...
's chronicle of Magellan's voyage, in which he recounts that the Chamorro people had no apparent knowledge of people outside of their island group. A Portuguese account of the same voyage suggests that the Chamorro people who greeted the travellers did so "without any shyness as if they were good acquaintances".
Further contact was made during the sixteenth century, although often initial encounters were very brief. Documents relating to the 1525 voyage of Diogo da Rocha Diogo da Rocha was a captain who sailed for the Portuguese in 1525. He is credited as being the first to encounter the islands "to the Eastwards of Mindanao, and the islands of St. Lazarus" ( possibly Ulithi in the Caroline Islands
The Caro ...
suggest that he made the first European contact with inhabitants of the Caroline Islands, possibly staying on the Ulithi
Ulithi ( yap, Wulthiy, , or ) is an atoll in the Caroline Islands of the western Pacific Ocean, about east of Yap.
Overview
Ulithi consists of 40 islets totaling , surrounding a lagoon about long and up to wide—at one of the larges ...
atoll for four months and encountering Yap
Yap ( yap, Waqaab) traditionally refers to an island group located in the Caroline Islands of the western Pacific Ocean, a part of Yap State. The name "Yap" in recent years has come to also refer to the state within the Federated States of Micr ...
. Marshall Islanders were encountered by the expedition of Spanish navigator Álvaro de Saavedra Cerón
Álvaro de Saavedra Cerón (often written as Álvaro de Saavedra) (d. 1529) was one of the Spanish explorers in the Pacific Ocean. The exact date and place of his birth are unknown, but he was born in the late 15th century or early 16th century in ...
in 1529. Other contact with the Yap islands occurred in 1625.
Colonisation and conversion
In the early 17th centurySpain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
colonized Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
, the Northern Marianas
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mariånas; cal, Commonwealth Téél Falúw kka Efáng llól Marianas), is an unincorporated territories of the Unit ...
and the Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the ce ...
(what would later become the Federated States of Micronesia and the Republic of Palau), creating the Spanish East Indies
The Spanish East Indies ( es , Indias orientales españolas ; fil, Silangang Indiyas ng Espanya) were the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia and Oceania from 1565 to 1898, governed for the Spanish Crown from Mexico City and Madri ...
, which was governed from the Spanish Philippines
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
.
In 1819, the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions
The American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions (ABCFM) was among the first American Christian missionary organizations. It was created in 1810 by recent graduates of Williams College. In the 19th century it was the largest and most imp ...
—a Protestant group—brought their Puritan ways to Polynesia. Soon after, the Hawaiian Missionary Society was founded and sent missionaries into Micronesia. Conversion was not met with as much opposition, as the local religions were less developed (at least according to Western ethnographic accounts). In contrast, it took until the end of the 19th to the beginning of the 20th centuries for missionaries to fully convert the inhabitants of Melanesia; however, a comparison of the cultural contrast must take into account the fact that Melanesia has always had deadly strains of malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
present in various degrees and distributions throughout its history (see De Rays Expedition
The Third de Rays Expedition, or simply the de Rays Expedition, was the third New Guinea expedition of Marquis de Rays, a French nobleman who attempted to start a colony in the South Pacific. The expedition attempted to establish a colony in a ...
) and up to the present; conversely, Micronesia does not have—and never seems to have had—any malarial mosquitos nor pathogens on any of its islands in the past.
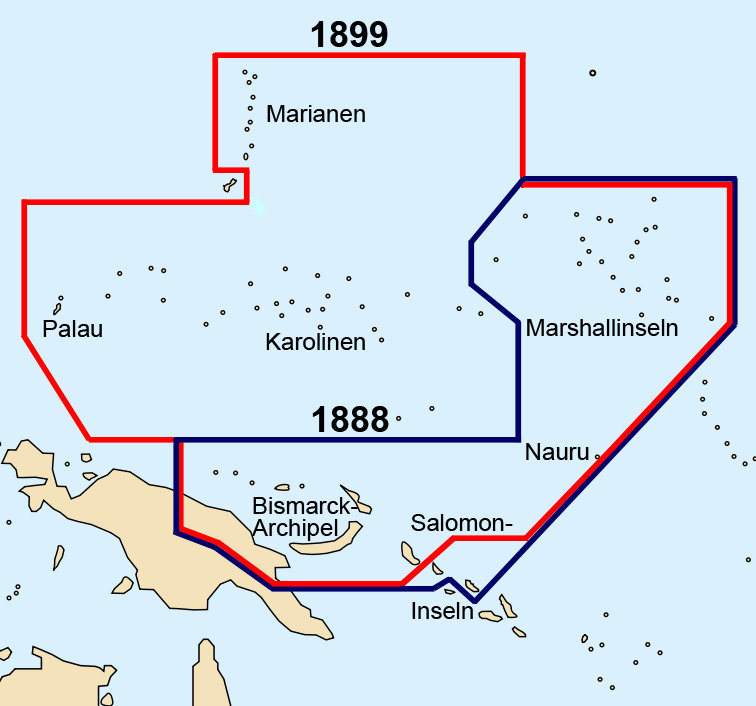
German–Spanish Treaty of 1899
 In the
In the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (cloc ...
, Spain lost many of its remaining colonies. In the Pacific, the United States took possession of the Spanish Philippines
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
and Guam. On 17 January 1899, the United States also took possession of unclaimed and uninhabited Wake Island. This left Spain with the remainder of the Spanish East Indies, about 6,000 tiny islands that were sparsely populated and not very productive. These islands were ungovernable after the loss of the administrative center of Manila and indefensible after the loss of two Spanish fleets in the war. The Spanish government therefore decided to sell the remaining islands to a new colonial power: the German Empire.
The treaty, which was signed by Spanish Prime Minister Francisco Silvela
Francisco Silvela y Le Vielleuze (15 December 1843, in Madrid – 29 May 1905, in Madrid) was a Spanish politician who became Prime Minister of Spain on 3 May 1899, succeeding Práxedes Mateo Sagasta. He served in this capacity until 22 October ...
on 12 February 1899, transferred the Caroline Islands, the Mariana Islands, Palau and other possessions to Germany. Under German control, the islands became a protectorate and were administered from German New Guinea
German New Guinea (german: Deutsch-Neu-Guinea) consisted of the northeastern part of the island of New Guinea and several nearby island groups and was the first part of the German colonial empire. The mainland part of the territory, called , ...
. Nauru had already been annexed and claimed as a colony by Germany in 1888.
20th century
 In the early 20th century, the islands of Micronesia were divided between three foreign powers:
* the
In the early 20th century, the islands of Micronesia were divided between three foreign powers:
* the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, which took control of Guam following the Spanish–American War of 1898 and claimed Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of T ...
;
* Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, which took Nauru and bought the Marshall, Caroline and Northern Mariana Islands from Spain; and
* the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
, which took the Gilbert Islands (Kiribati).
During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Germany's Pacific island territories were seized and became League of Nations mandates in 1923. Nauru became an Australian mandate, while Germany's other territories in Micronesia were given as a mandate to Japan and were named the South Seas Mandate. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, Nauru and Banaba, Ocean Island were occupied by Empire of Japan, Japanese troops, with also an Japanese occupation of the Gilbert Islands, occupation of some of the Gilbert Islands and were bypassed by the Allied advance across the Pacific. Following Japan's defeat in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
its mandate became a United Nations Trusteeship administered by the United States as the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands. Nauru became independent in 1968.
21st century
Today, most of Micronesia are independent states, except for the U.S. Commonwealth of theNorthern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mariånas; cal, Commonwealth Téél Falúw kka Efáng llól Marianas), is an unincorporated territory and commonw ...
, Guam and Wake Island, which are U.S. territories.
States and dependencies
Politics
The Pacific Community (SPC) is a regional intergovernmental organisation whose membership includes both nations and territories in the Pacific Ocean and their metropolitan powers.Economy
Demographics
The people today form many ethnicities, but all are descended from and belong to the Micronesian culture. The Micronesian culture was one of the last native cultures of the region to develop. It developed from a mixture of Melanesians and Filipino people, Filipinos. Because of this mixture of descent, many of the ethnicities of Micronesia feel closer to some groups inMelanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
, or the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
. A good example of this are the Yapese people who are related to Austronesian peoples, Austronesian tribes in the northern Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
. A 2011 survey found that 93.1% of Micronesian are Christians. Genetics also show a significant number of Micronesian have Japanese paternal ancestry: 9.5% of males from Micronesia as well as 0.2% in East Timor carry the Haplogroup D-M55.
There are also substantial Asian communities found across the region, most notably in the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mariånas; cal, Commonwealth Téél Falúw kka Efáng llól Marianas), is an unincorporated territory and commonw ...
where they form the majority and smaller communities of Europeans who have migrated from the United States or are descendants of settlers during European colonial rule in Micronesia.
Though they are all geographically part of the same region, they all have very different colonial histories. The US-administered areas of Micronesia have a unique experience that sets them apart from the rest of the Pacific. Micronesia has great economic dependency on its former or current motherlands, something only comparable to the French Pacific. Sometimes, the term ''American Micronesia'' is used to acknowledge the difference in cultural heritage.
Indigenous groups
Micronesians
=Carolinian people
= It is thought that ancestors of the Carolinian people may have originally immigrated from the Asian mainland and Indonesia to Micronesia around 2,000 years ago. Their primary language is Carolinian language, Carolinian, called ''Refaluwasch'' by native speakers, which has a total of about 5,700 speakers. The Carolinians have a matriarchy, matriarchal society in which respect is a very important factor in their daily lives, especially toward the matriarchs. Most Carolinians are of the Roman Catholic faith. The immigration of Carolinians to Saipan began in the early 19th century, after the Spain, Spanish reduced the local population of Chamorro people, Chamorro natives to just 3,700. They began to immigrate mostly sailing from small canoes from other islands, which atyphoon
A typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere. This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, and is the most active tropical cyclone basin on Earth, accounting for a ...
previously devastated. The Carolinians have a much darker complexion than the native Chamorro people, Chamorros.
=Chamorro people
= The Chamorro people are the indigenous peoples of the Mariana Islands, which are politically divided between the Territories of the United States, United States territory of
The Chamorro people are the indigenous peoples of the Mariana Islands, which are politically divided between the Territories of the United States, United States territory of Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
and the United States Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands in Micronesia. The Chamorro are commonly believed to have come from Southeast Asia at around 2000 Common Era, BC. They are most closely related to other Austronesian peoples, Austronesian natives to the west in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
and Taiwanese aborigines, Taiwan, as well as the Caroline Islands, Carolines to the south.
The Chamorro language is included in the Malayo-Polynesian languages, Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian languages, Austronesian family. Because Guam was colonized by Spain for over 300 years, many words derive from the Spanish language. The traditional Chamorro number system was replaced by Spanish numbers.
=Chuukese people
= The Chuukese people are an ethnic group inOceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
. They constitute 48% of the population of the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
. Their language is Chuukese language, Chuukese. The home atoll of Chuuk is also known by the former name Truk.
=Nauruan people
= The Nauruan people are an ethnicity inhabiting the Pacific Ocean, Pacific island of Nauru. They are most likely a blend of Indigenous peoples of Oceania, other Pacific peoples. The origin of the Nauruan people has not yet been finally determined. It can possibly be explained by the last Malayo-Pacific human migration (c. 1200). It was probably seafaring or shipwrecked Polynesians or Melanesians that established themselves in Nauru because there was not already an indigenous people present, whereas the Micronesians were already crossed with the Melanesians in this area.Kaping people
The roughly 3000 residents of the Federated States of Micronesia that reside in Kapingamarangi, nicknamed 'Kapings', live in one of the most remote locations in both Micronesia and the world at large. Their home atoll is almost from the nearest point of immigration. There are no regular flights; the only reliable way to legally visit is to travel on a high-speed sailboat to the atoll. Owing to this difficulty, few sailors travelling the Pacific attempt to visit. The local language is the Kapingamarangi language. The children typically attend high school on Pohnpei where they stay with relatives in an enclave that is almost exclusively made up of Kapings.Immigrant groups
East, South, and Southeast Asian people
There are large East Asia, East, South Asia, South and Southeast Asia, Southeast Asian communities found across certain Micronesian countries that are either immigrants, foreign workers or descendants of either one, most migrated to the islands during the 1800s and 1900s. According to the 2010 census results Guam was 26.3% Overseas Filipino, Filipino, 2.2% Korean diaspora, Korean, 1.6% Overseas Chinese, Chinese and 2% other Asian. The 2010 census showed the Northern Mariana Islands was 50% Asian of which 35.3% were Filipino, 6.8% Chinese, 4.2% Korean and 3.7% other Asian (mainly Japanese diaspora, Japanese, Bangladeshi diaspora, Bangladeshi and Thai people, Thai). The 2010 census for the Federated States of Micronesia showed 1.4% were Asian while statistics for Nauru showed 8% of Nauruans were Chinese. The 2005 census results for Palau showed 16.3% were Filipino, 1.6% Chinese, 1.6% Vietnamese and 3.4% other Asian (mostly Bangladeshi, Japanese and Korean). Japanese rule in Micronesia also led to Japanese people settling the islands and marrying native spouses. Kessai Note, the former president of theMarshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
has partial Japanese ancestry by way of his paternal grandfather, and Manny Mori, Emanuel Mori, the former president of the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
, is descended from one of the first settlers from Japan, Mori Koben, Koben Mori.
A significant number of Micronesians were shown to have paternal genetic relations with Japanese Haplogroup D-M55. Genetic testing found that 9.5% of males from Micronesia as well as 0.2% in East Timor carry what is believed to reflect recent admixture from Japan. That is, D-M116.1 (D1b1) is generally believed to be a primary subclade of D-M64.1 (D1b), possibly as a result of the Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies, Japanese military occupation of Southeast Asia during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
.
European people
The 2010 census results of Guam showed 7.1% were white while the 2005 census for Palau showed 8% were European. Smaller numbers at 1.9% in Palau and 1.8% in the Northern Mariana Islands were recorded as "white". In conjunction to the European communities there are large amounts of mixed Micronesians, some of which have European ancestry.Languages
The largest group of languages spoken in Micronesia are the Micronesian languages. They are in the family of Oceanic languages, part of the Austronesian languages, Austronesian language group. They descended from the Proto-Oceanic language, Proto-Oceanic, which in turn descended via Proto-Malayo-Polynesian language, Proto-Malayo-Polynesian from Proto-Austronesian language, Proto-Austronesian. The languages in the Micronesian family are Marshallese language, Marshallese, Gilbertese language, Gilbertese, Kosraean language, Kosraean, Nauruan language, Nauruan, as well as a large sub-family called the Chuukic–Pohnpeic languages containing 11 languages. On the eastern edge of the Federated States of Micronesia, the languages Nukuoro language, Nukuoro and Kapingamarangi language, Kapingamarangi represent an extreme westward extension of the Polynesian languages, Polynesian branch of Oceanic. Finally, there are two Malayo-Polynesian languages spoken in Micronesia that do not belong to the Oceanic languages: Chamorro language, Chamorro in the Mariana Islands and Palauan language, Palauan inPalau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the ...
.
Culture
Animals and food
By the time Western contact occurred, although Palau did not have dogs, they did have fowls and possibly pigs. Pigs are not native to Micronesia. Fruit bats are native to Palau, but other mammals are rare. Reptiles are numerous and both mollusks and fish are an important food source. The people of Palau, the Marianas and Yap often chew Areca nut, betel nuts seasoned with lime and pepper leaf. Western Micronesia was unaware of the ceremonial drink, which was called ''saka'' on Kosrae and ''sakau'' on Pohnpei.Architecture
The book ''Prehistoric Architecture in Micronesia'' argues that the most prolific pre-colonial Micronesian architecture is: "Palau's monumental sculpted hills, megalithic stone carvings and elaborately decorated structure of wood placed on piers above elevated stone platforms". The archeological traditions of the Yapese people remained relatively unchanged even after the first European contact with the region during Magellan's 1520s circumnavigation of the globe.Art
Micronesia's artistic tradition has developed from theLapita culture
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian people and their material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. They are believed to have originated from the northern Philipp ...
. Among the most prominent works of the region is the megalithic floating city of Nan Madol
Nan Madol is an archaeological site adjacent to the eastern shore of the island of Pohnpei, now part of the Madolenihmw district of Pohnpei state in the Federated States of Micronesia in the western Pacific Ocean. Nan Madol was the capital of t ...
. The city began in 1200 CE and was still being built when European explorers begin to arrive around 1600. The city, however, had declined by around 1800 along with the Saudeleur dynasty and was completely abandoned by the 1820s. During the 19th century, the region was divided between the colonialism, colonial powers, but art continued to thrive. Wood-carving, particularly by men, flourished in the region, resulted in richly decorated ceremonial houses in Belau, stylized bowls, canoe ornaments, ceremonial vessels and sometimes sculptured figures. Women created textiles and ornaments such as bracelets and headbands. Stylistically, traditional Micronesian art is streamlined and of a practical simplicity to its function, but is typically finished to a high standard of quality.
This was mostly to make the best possible use of what few natural materials they had available to them.
The first half of the 20th century saw a downturn in Micronesia's cultural integrity and a strong foreign influence from both western and Japanese Imperialist powers. A number of historical artistic traditions, especially sculpture, ceased to be practiced, although other art forms continued, including traditional architecture and weaving. Independence from colonial powers in the second half of the century resulted in a renewed interest in, and respect for, traditional arts. A notable movement of contemporary art also appeared in Micronesia towards the end of the 20th century.
Cuisine
The cuisine of the Mariana Islands is tropical in nature, including such dishes as Kelaguen as well as many others. Marshallese cuisine comprises the fare and foodways of the Marshall Islands, and includes local foods such as breadfruit, taro root, pandanus and seafood, among others. Palauan cuisine includes local foods such as cassava, taro, yam, potato, fish and pork. Western cuisine is favored among young Palauans.Education
The educational systems in the nations of Micronesia vary depending on the country and there are several higher-level educational institutions. The CariPac consists of institutions of higher education inGuam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
, the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mariånas; cal, Commonwealth Téél Falúw kka Efáng llól Marianas), is an unincorporated territory and commonw ...
, American Samoa, Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
, the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
and Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the ...
. The Agricultural Development in the American Pacific is a partnership of the University of Hawaii, American Samoa Community College, College of Micronesia, Northern Marianas College and the University of Guam.
In the Federated States of Micronesia, education is required for citizens aged 6 to 13, and is important to their economy. The literacy rate for citizens aged 15 to 24 is 98.8%. The College of Micronesia-FSM has a campus in each of the four states with its national campus in the capital city of Palikir, Pohnpei. The COM-FSM system also includes the Fisheries and Maritime Institute (FMI) on the Yap
Yap ( yap, Waqaab) traditionally refers to an island group located in the Caroline Islands of the western Pacific Ocean, a part of Yap State. The name "Yap" in recent years has come to also refer to the state within the Federated States of Micr ...
islands.
The public education in Guam is organized by the Guam Department of Education. Guam also has several educational institutions, such as University of Guam, Pacific Islands University and Guam Community College, There is also the Guam Public Library System and the Umatac Outdoor Library.
Weriyeng is one of the last two schools of traditional navigation found in the central Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the ce ...
in Micronesia, the other being Fanur.
The Northern Marianas College is a two-year community college located in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
Northern Mariana Islands, Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI).
The College of the Marshall Islands is a community college in the Marshall Islands.
Law
''Understanding Law in Micronesia'' notes that The Federated States of Micronesia's laws and legal institutions are "uninterestingly similar to [those of Western countries]". However, it explains that "law in Micronesia is an extraordinary flux and flow of contrasting thought and meaning, inside and outside the legal system". It says that a knee-jerk reaction would be that law is disarrayed in the region and that improvement is required, but argues that the failure is "one endemic to the nature of law or to the ideological views we hold about law". The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands, a United Nations Trusteeship administered by the United States, borrowed heavily from United States law in establishing the Trust Territory Code during the Law and Development movement of the late 1950s and early 1960s. Many of those provisions were adopted by the new Congress of the Federated States of Micronesia when the Federated States of Micronesia became self-governing in 1979.Media
In September 2007, journalists in the region founded the Micronesian Media Association.Music and dance
Micronesian music is influential to those living in the Micronesian islands. Some of the music is based around mythology and ancient Micronesian rituals. It covers a range of styles from traditional songs, handed down through generations, to contemporary music. Traditional beliefs suggest that the music can be presented to people in dreams and altered state of consciousness, trances, rather than being written by composers themselves. Micronesian folk music is, like Music of Polynesia, Polynesian music, primarily vocal-based. In the Marshall Islands, the ''roro (chant), roro'' is a kind of traditional chant, usually about ancient legends and performed to give guidance during navigation and strength for mothers in labour. Modern bands have blended the unique songs of each island in the country with modern music. Though drums (musical instrument), drums are not generally common in Micronesian music, one-sided hourglass-shaped drums are a major part of Marshallese music. There is a traditional Marshallese dance called beet (dance), beet, which is influenced by Spanish folk dances; in it, men and women side-step in parallel lines. There is a kind of Tirere, stick dance performed by the Jobwa, nowadays only for very special occasions. Popular music, both from Micronesia and from other areas of the world, is played on radio stations in Micronesia.Sports
The region is home to the Micronesian Games. This quadrennial international multi-sport event involves all of Micronesia's countries and territories except Wake Island. Nauru has two national sports, Olympic weightlifting, weightlifting and Australian rules football. According to 2007 Australian Football League International Census figures, there are around 180 players in the Nauru senior competition and 500 players in the junior competition, representing an participation rate of over 30% overall for the country.Religion and mythology
The predominant religion in Micronesia is Christianity (93%). Micronesian mythology comprises the traditional belief systems of the people of Micronesia. There is no single belief system in the islands of Micronesia, as each island region has its own mythological creature, mythological beings. There are several significant figures and myths in the Federated States of Micronesia, Nauruan and Kiribati traditions.See also
* Flags of OceaniaReferences
Citations
General bibliography
* * * *Further reading
*External links
History of Micronesia
{{Authority control Micronesia, Asia-Pacific Islands of Oceania Regions of Oceania