Micromoon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A supermoon is a full moon or a
A supermoon is a full moon or a
 In 2011, Nolle added apogees to consideration explaining that he based calculations on 90% of the difference in lunar apsis extremes for the solar year.
In 2011, Nolle added apogees to consideration explaining that he based calculations on 90% of the difference in lunar apsis extremes for the solar year.
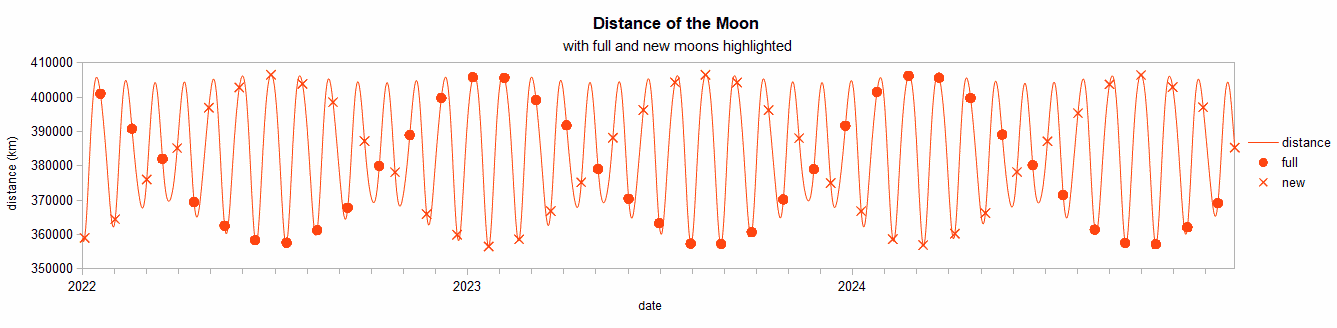 The oscillating nature of the distance to the full or new moon is due to the difference between the synodic and anomalistic months. The period of this oscillation is about 14 synodic months, which is close to 15 anomalistic months. So every 14 lunations there is a Full Moon nearest to perigee.
Occasionally, a supermoon coincides with a
The oscillating nature of the distance to the full or new moon is due to the difference between the synodic and anomalistic months. The period of this oscillation is about 14 synodic months, which is close to 15 anomalistic months. So every 14 lunations there is a Full Moon nearest to perigee.
Occasionally, a supermoon coincides with a
 A full moon at perigee appears roughly 14% larger in diameter than at apogee. Many observers insist that the moon looks bigger to them. This is likely due to observations shortly after sunset when the moon is near the horizon and the moon illusion is at its most apparent.
While the moon's surface
A full moon at perigee appears roughly 14% larger in diameter than at apogee. Many observers insist that the moon looks bigger to them. This is likely due to observations shortly after sunset when the moon is near the horizon and the moon illusion is at its most apparent.
While the moon's surface
Lunar Apogee/Perigee Calculator
Richard Nolle's definition
( Fred Espenak)
Super Blue Blood Moon 2018
, Check123 1 Minute Video {{Authority control Astrology Astronomical events Lunar science Moon Articles containing video clips
 A supermoon is a full moon or a
A supermoon is a full moon or a new moon
In astronomy, the new moon is the first lunar phase, when the Moon and Sun have the same ecliptic longitude. At this phase, the lunar disk is not visible to the naked eye, except when it is silhouetted against the Sun during a solar eclipse.
...
that nearly coincides with perigee—the closest that the Moon comes to the Earth in its elliptic orbit—resulting in a slightly larger-than-usual apparent size of the lunar disk as viewed from Earth. The technical name is a perigee syzygy (of the Earth–Moon–Sun system) or a full (or new) Moon around perigee. Because the term ''supermoon'' is astrological in origin, it has no precise astronomical definition.
The real association of the Moon with both oceanic and crustal tides has led to claims that the supermoon phenomenon may be associated with increased risk of events like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, but no such link has been found.
The opposite phenomenon, an apogee syzygy or a full (or new) Moon around apogee, has been called a micromoon.
Definitions
The term ''supermoon'' is attributed toastrologer
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Dif ...
Richard Nolle ''while reading "Strategic Role Of Perigean spring tides in Nautical History and Coastal flooding"'' published in 1976 by NOAA Hydrologist Fergus Wood''.''' In practice, there is no official or even consistent definition of how near perigee the full Moon must occur to receive the supermoon label, and new moons rarely receive a supermoon label.
Nolle
Nolle described the concept in a 1979 edition ofDell Horoscope
''Dell Horoscope'' was a periodic American magazine published by Penny Publications covering modern astrology, calling itself "the world's leading astrology magazine". It was in circulation between 1935 and 2020.
History
The magazine was first p ...
including both full and new moons, but has never outlined why he chose 90% nor has provided a definitive formula for determining if a given full or new moon is "super". The basic 1979 definition read:
Nolle amended his definition in 2000 specifying the distance of a given full or new moon be judged against 90% of the mean distance of perigees. Nolle (incorrectly) referenced
 In 2011, Nolle added apogees to consideration explaining that he based calculations on 90% of the difference in lunar apsis extremes for the solar year.
In 2011, Nolle added apogees to consideration explaining that he based calculations on 90% of the difference in lunar apsis extremes for the solar year. EarthSky
''Earth & Sky'' was a daily radio series that presented information about science and nature. It began broadcasting in 1991 and ceased operations in 2013. ''EarthSky'' is the ongoing website, serving 21 million users in 2019, according to Google ...
analyzed Nolle's tables and described the updated definition as a full or new moon is considered a supermoon if where is the lunar distance at syzygy, is the lunar distance at apogee, and is the lunar distance at perigee. Nolle based those the mean apsis extremes referencing (incorrectly) the Wikipedia article on the subject arriving at:
Nolle also added the concept of ''extreme supermoon'' in 2000 describing the concept as any new or full moons that are at "100% or greater of the mean perigee".
Espenak
The term ''perigee-syzygy'' or ''perigee full/new moon'' is preferred in the scientific community. Perigee is the point at which the Moon is closest in its orbit to the Earth, and syzygy is when the Earth, the Moon and the Sun are aligned, which happens at everyfull
Full may refer to:
* People with the surname Full, including:
** Mr. Full (given name unknown), acting Governor of German Cameroon, 1913 to 1914
* A property in the mathematical field of topology; see Full set
* A property of functors in the mathe ...
or new moon
In astronomy, the new moon is the first lunar phase, when the Moon and Sun have the same ecliptic longitude. At this phase, the lunar disk is not visible to the naked eye, except when it is silhouetted against the Sun during a solar eclipse.
...
. Astrophysicist Fred Espenak uses Nolle's definition but preferring the label of ''full Moon at perigee on full moons'' occurring "within 90% of its closest approach to Earth in a given orbit" over Nolle's calculations based on the closest of all orbits during the solar year. Wood used the definition of a full or new moon occurring within 24 hours of perigee and also used the label ''perigee-syzygy''.
Other definitions
'' Sky and Telescope'' magazine chose a definition of . TimeandDate.com prefers a definition of . ''EarthSky
''Earth & Sky'' was a daily radio series that presented information about science and nature. It began broadcasting in 1991 and ceased operations in 2013. ''EarthSky'' is the ongoing website, serving 21 million users in 2019, according to Google ...
'' uses Nolle's definition comparing their calculations to tables published by Nolle in 2000.
Wood also coined the less used term ''proxigee'' where perigee and the full or new moon are separated by 10 hours or less.
Occurrence
Of the possible 12 or 13 full (or new) moons each year, usually three or four may be classified as supermoons, as commonly defined. The most recent full supermoon occurred on August 12, 2022, and the next one will be on July 3, 2023. The supermoon of November 14, 2016, was the closest full occurrence since January 26, 1948, and will not be surpassed until November 25, 2034. The closest full supermoon of the 21st century will occur on December 6, 2052. The oscillating nature of the distance to the full or new moon is due to the difference between the synodic and anomalistic months. The period of this oscillation is about 14 synodic months, which is close to 15 anomalistic months. So every 14 lunations there is a Full Moon nearest to perigee.
Occasionally, a supermoon coincides with a
The oscillating nature of the distance to the full or new moon is due to the difference between the synodic and anomalistic months. The period of this oscillation is about 14 synodic months, which is close to 15 anomalistic months. So every 14 lunations there is a Full Moon nearest to perigee.
Occasionally, a supermoon coincides with a total lunar eclipse
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. Such alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to Ecliptic, the plane of t ...
. The most recent occurrence of this by any definition was in May 2022, and the next occurrence will be in October 2032.
Appearance
 A full moon at perigee appears roughly 14% larger in diameter than at apogee. Many observers insist that the moon looks bigger to them. This is likely due to observations shortly after sunset when the moon is near the horizon and the moon illusion is at its most apparent.
While the moon's surface
A full moon at perigee appears roughly 14% larger in diameter than at apogee. Many observers insist that the moon looks bigger to them. This is likely due to observations shortly after sunset when the moon is near the horizon and the moon illusion is at its most apparent.
While the moon's surface luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls withi ...
remains the same, because it is closer to the earth the illuminance is about 30% brighter than at its farthest point, or apogee. This is due to the inverse square law of light which changes the amount of light received on earth in inverse proportion to the distance from the moon. A supermoon directly overhead could provide up to 0.36 lux.
Effects on Earth
Claims that supermoons can cause natural disasters, and the claim of Nolle that supermoons cause "geophysical stress", have been refuted by scientists. Despite lack of scientific evidence, there has been media speculation that natural disasters, such as the2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami
The occurred at 14:46 JST (05:46 UTC) on 11 March. The magnitude 9.0–9.1 (M) undersea megathrust earthquake had an epicenter in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region, and lasted approximately six minutes ...
and the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami
An earthquake and a tsunami, known as the Boxing Day Tsunami and, by the scientific community, the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, occurred at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+7) on 26 December 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Suma ...
, are causally linked with the 1–2-week period surrounding a supermoon. A large, 7.5 magnitude earthquake centred 15 km north-east of Culverden, New Zealand at 00:03 NZDT on November 14, 2016, also coincided with a supermoon.
Tehran earthquake on May 8, 2020, also coincided with a supermoon.
Scientists have confirmed that the combined effect of the Sun and Moon on the Earth's oceans, the tide, is greatest when the Moon is either new
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, ...
or full
Full may refer to:
* People with the surname Full, including:
** Mr. Full (given name unknown), acting Governor of German Cameroon, 1913 to 1914
* A property in the mathematical field of topology; see Full set
* A property of functors in the mathe ...
. and that during lunar perigee, the tidal force is somewhat stronger, resulting in perigean spring tides. However, even at its most powerful, this force is still relatively weak, causing tidal differences of inches at most.
Total lunar eclipses
Total lunar eclipses which fall on supermoon and micromoon days are relatively rare. In the 21st century, there are 87 total lunar eclipses, of which 28 are supermoons and 6 are micromoons. Almost all total lunar eclipses inLunar Saros 129
Saros cycle series 129 for lunar eclipses occurs at the moon's descending node, repeats every 18 years days.
The 129th lunar saros is associated with Solar Saros 136.
Lunar saros 129 contains 71 member events, with ...
are micromoon eclipses. An example of a supermoon lunar eclipse is the September 2015 lunar eclipse
A total lunar eclipse took place between 27 and 28 September 2015. It was seen on Sunday evening, 27 September, in the Americas; while in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, it was seen in the early hours of Monday morning, 28 September. It was ...
.
Annular solar eclipses
Annular solar eclipses occur when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's. Almost all annular solar eclipses between 1880 and 2060 in Solar Saros 144 and almost all annular solar eclipses between 1940 and 2120 in Solar Saros 128 are micromoon annular solar eclipses.See also
* Apsis * Moon illusion *Syzygy (astronomy)
In astronomy, a syzygy ( ; ) is a roughly straight-line configuration of three or more celestial bodies in a gravitational system.
Overview
The word is often used in reference to the Sun, Earth, and either the Moon or a planet, where the latt ...
Notes
References
External links
Lunar Apogee/Perigee Calculator
Richard Nolle's definition
( Fred Espenak)
Super Blue Blood Moon 2018
, Check123 1 Minute Video {{Authority control Astrology Astronomical events Lunar science Moon Articles containing video clips