Microbiome-wide Association Study on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A microbiome-wide association study (MWAS), otherwise known as a metagenome-wide association study (MGWAS), is a statistical methodology used to examine the full metagenome of a defined 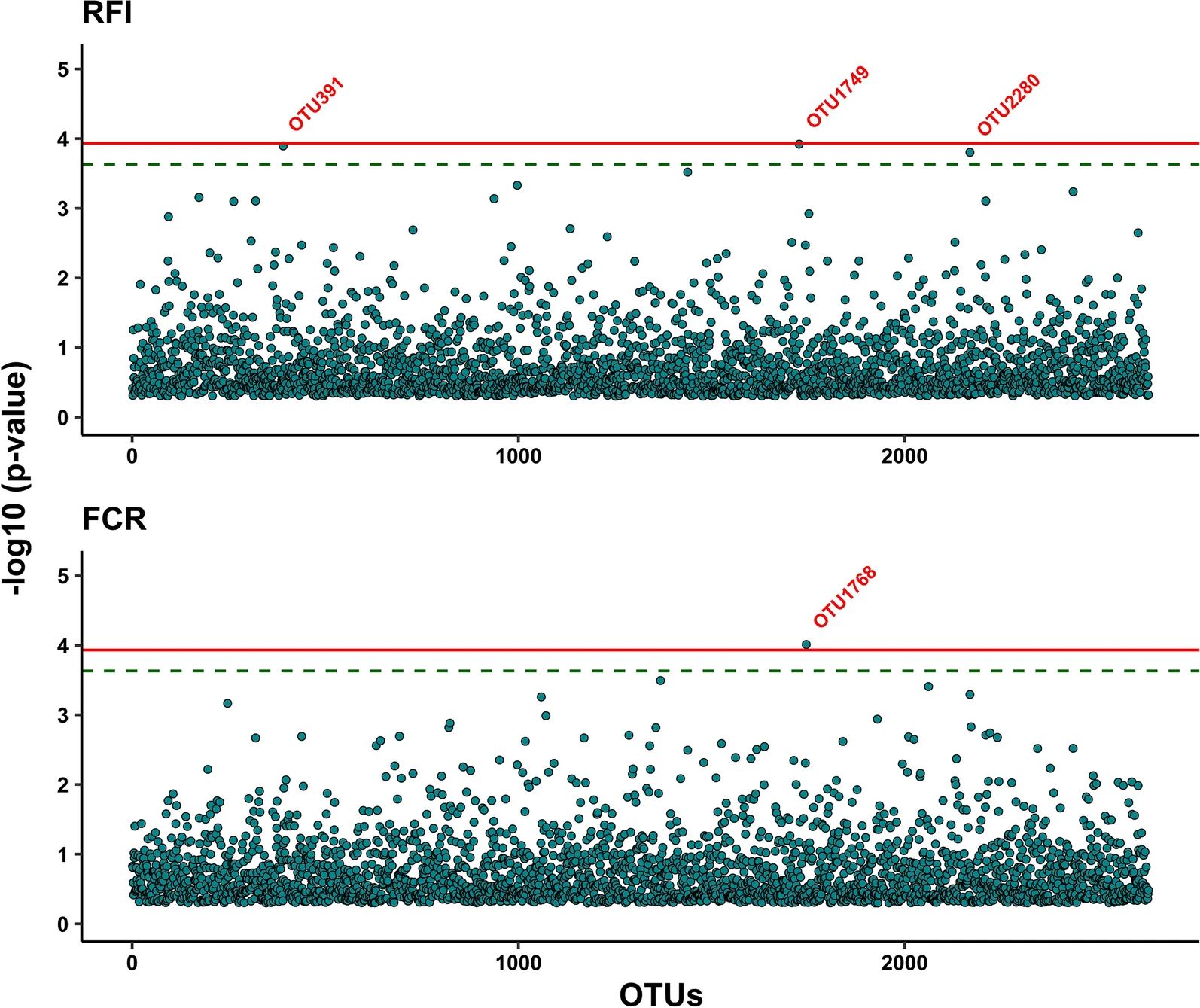 While MWAS is phonetically and conceptually tied to GWAS there are several key differentiations:
* There are roughly 150 times more genes in the microbiome than in the human
While MWAS is phonetically and conceptually tied to GWAS there are several key differentiations:
* There are roughly 150 times more genes in the microbiome than in the human
microbiome
A microbiome () is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps ''et al.'' as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably well ...
in various organisms to determine if some feature (as example, gene or species) of the microbiome is associated with a host
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
* Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
People
*Jim Host (born 1937), American businessman
* Michel Host ...
trait. MWAS has been adopted by the field of metagenomics from the widely used genome-wide association study (GWAS).
 While MWAS is phonetically and conceptually tied to GWAS there are several key differentiations:
* There are roughly 150 times more genes in the microbiome than in the human
While MWAS is phonetically and conceptually tied to GWAS there are several key differentiations:
* There are roughly 150 times more genes in the microbiome than in the human genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
. A GWAS must only find significantly associated genes along the predefined number of chromosomes of the species. On the other hand, the MWAS must analyze however many features are in an undetermined number of microorganisms. As a result, there is a far higher chance of running into the multiple testing problem.
* While host populations contain a relatively similar collection of genes on the genome, the genetic variation of any given microbiome can vary significantly between different hosts and environments. The genome of the microbiome can also vary temporally in a given host while the genome of the host in a GWAS is fixed across their lifespan.
* The realized microbiome datasets are inherently compositional and interactional. The assumption that the genes exist in a Euclidean space
Euclidean space is the fundamental space of geometry, intended to represent physical space. Originally, that is, in Euclid's Elements, Euclid's ''Elements'', it was the three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, but in modern mathematics ther ...
is violated by the non-linear nature of compositional data In statistics, compositional data are quantitative descriptions of the parts of some whole, conveying relative information. Mathematically, compositional data is represented by points on a simplex. Measurements involving probabilities, proportions, ...
.
There are several ways to classify which feature of the microbiome will be used in a MWAS. MWAS can be assessed using a specific taxonomic level (species, genus, phyla, etc.), operational taxonomic unit (OTU) or amplicon sequence variant (ASV), transcriptome
The transcriptome is the set of all RNA transcripts, including coding and non-coding, in an individual or a population of cells. The term can also sometimes be used to refer to all RNAs, or just mRNA, depending on the particular experiment. The t ...
, proteome, and more. The approach used depends upon the research hypothesis as each method will often give differing results.
Often, a taxonomic level or OTU/ASV based approach is used to determine the correlations between the specific microbiome feature and the desired phenotype. Several methods can be employed, such as machine learning approaches like random forest
Random forests or random decision forests is an ensemble learning method for classification, regression and other tasks that operates by constructing a multitude of decision trees at training time. For classification tasks, the output of th ...
s, and deep learning
Deep learning (also known as deep structured learning) is part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on artificial neural networks with representation learning. Learning can be supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised.
De ...
. Feature association can also be established with programs like DESeq2 and ANCOM. However, correlations established by the wide array of tools available may not always translate into causality. Researchers determine causality through sequential testing.
References