Methylcholanthrene on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Methylcholanthrene is a highly carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon produced by burning organic compounds at very high temperatures. Methylcholanthrene is also known as 3-methylcholanthrene, 20-methylcholanthrene or the IUPAC name 3-methyl-1,2-dyhydrobenzo ceanthrylene. The short notation often used is 3-MC or MCA. This compound forms pale yellow solid crystals when crystallized from benzene and ether. It has a melting point around 180 °C and its boiling point is around 280 °C at a pressure of 80 mmHg. Methylcholanthrene is used in laboratory studies of chemical carcinogenesis. It is an alkylated derivative of benz 'a''nthracene and has a similar UV spectrum. The most common isomer is 3-methylcholanthrene, although the methyl group can occur in other places.
3-Methylcholanthrene, a known carcinogen which builds up in the prostate due to cholesterol breakdown, is implicated in
 First 3-MC was synthesized with the method of reference. Later the synthesis of the compound was improved. The synthesis of 3-MC consists of a few steps, visualized in figure 1; the first step is the key to success for the synthesis. 4-methylindanone (1) reacts in condensation with lithium salt of N,N-diethyl-1-naphthamide (2). At -60 ̊C the reaction of 1 and 2 afforded evenly to the lactone (3), the carbonyl addition product which underwent conversion on treatment with acid. The free acid (4) was obtained when the latter was cleaved reductively with zinc and alkali. Cyclization of the product occurred when treated with ZnCl2 in acetic acid anhydride and gave the compound 6-acetoxy-3-MC (5). Reducing this product with hydriodic acid in propionic acid resulted in 3-MC.
First 3-MC was synthesized with the method of reference. Later the synthesis of the compound was improved. The synthesis of 3-MC consists of a few steps, visualized in figure 1; the first step is the key to success for the synthesis. 4-methylindanone (1) reacts in condensation with lithium salt of N,N-diethyl-1-naphthamide (2). At -60 ̊C the reaction of 1 and 2 afforded evenly to the lactone (3), the carbonyl addition product which underwent conversion on treatment with acid. The free acid (4) was obtained when the latter was cleaved reductively with zinc and alkali. Cyclization of the product occurred when treated with ZnCl2 in acetic acid anhydride and gave the compound 6-acetoxy-3-MC (5). Reducing this product with hydriodic acid in propionic acid resulted in 3-MC.
 3-MC has an inhibitory function in a dimethylnitrosamine demethylase process in rat livers. Inhibition could happen on by interfering in demethylase conformations or by interfering in synthesis and/or degradation of demethylase. Experiments showed that the Km doesn't change after 3-MC treatment. This strongly indicates that enzyme affinity is not influenced by 3-MC. Instead, incubation with 3-MC leads to a decrease in the amount of enzyme activity. These results point towards inhibition of demethylase synthesis and/or induction of demetylase degradation. Unpublished observations of Venkatesan, Argus and Arcos suggest that demethylase synthesis inhibition is most plausible.
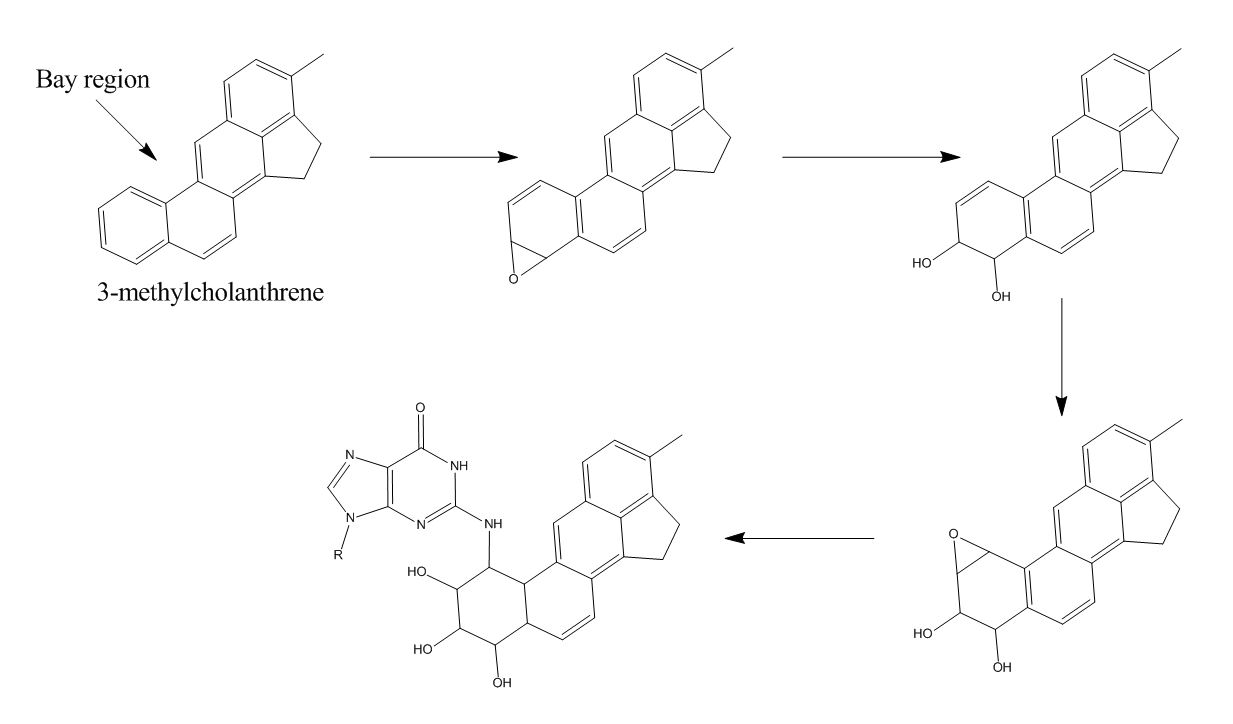
A possible mechanism for this reaction is depicted in figure (2). 3-MC is metabolized, via epoxidation, hydrolysis and another epoxidation, to a very reactive epoxide. Epoxidations are realized by the enzyme
3-MC has an inhibitory function in a dimethylnitrosamine demethylase process in rat livers. Inhibition could happen on by interfering in demethylase conformations or by interfering in synthesis and/or degradation of demethylase. Experiments showed that the Km doesn't change after 3-MC treatment. This strongly indicates that enzyme affinity is not influenced by 3-MC. Instead, incubation with 3-MC leads to a decrease in the amount of enzyme activity. These results point towards inhibition of demethylase synthesis and/or induction of demetylase degradation. Unpublished observations of Venkatesan, Argus and Arcos suggest that demethylase synthesis inhibition is most plausible.
A possible mechanism for this reaction is depicted in figure (2). 3-MC is metabolized, via epoxidation, hydrolysis and another epoxidation, to a very reactive epoxide. Epoxidations are realized by the enzyme
National Pollutant Inventory - Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Fact Sheet
{{Aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulators Carcinogens Hepatotoxins Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that sur ...
. It "readily produces" primary sarcomas in mice.
History
In 1933, the first article about methylcholanthrene was published. Here they described the synthesis of the compound. Not many years later, it became clear that this compound had toxic properties to humans and animals. Therefore, a lot of interest was shown in the compound and it was used often in toxicological research. Methylcholanthrene is often tested on mice and rats to derive information for cancer medicine development. Due to the influence of the compound on the central nervous system, its responses and change in response are compared. It is also known that due to genetic mutations, the compound causes cancer cells to develop. In 1982, the last article appeared on the synthesis of methylcholanthrene. The yield of 93% was reached and therefore no further adjustments were made to the synthesis scheme.Synthesis
: First 3-MC was synthesized with the method of reference. Later the synthesis of the compound was improved. The synthesis of 3-MC consists of a few steps, visualized in figure 1; the first step is the key to success for the synthesis. 4-methylindanone (1) reacts in condensation with lithium salt of N,N-diethyl-1-naphthamide (2). At -60 ̊C the reaction of 1 and 2 afforded evenly to the lactone (3), the carbonyl addition product which underwent conversion on treatment with acid. The free acid (4) was obtained when the latter was cleaved reductively with zinc and alkali. Cyclization of the product occurred when treated with ZnCl2 in acetic acid anhydride and gave the compound 6-acetoxy-3-MC (5). Reducing this product with hydriodic acid in propionic acid resulted in 3-MC.
First 3-MC was synthesized with the method of reference. Later the synthesis of the compound was improved. The synthesis of 3-MC consists of a few steps, visualized in figure 1; the first step is the key to success for the synthesis. 4-methylindanone (1) reacts in condensation with lithium salt of N,N-diethyl-1-naphthamide (2). At -60 ̊C the reaction of 1 and 2 afforded evenly to the lactone (3), the carbonyl addition product which underwent conversion on treatment with acid. The free acid (4) was obtained when the latter was cleaved reductively with zinc and alkali. Cyclization of the product occurred when treated with ZnCl2 in acetic acid anhydride and gave the compound 6-acetoxy-3-MC (5). Reducing this product with hydriodic acid in propionic acid resulted in 3-MC.
Mechanism
cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are ...
. The second epoxide is not hydrolysed immediately because it is localized next to a bay region, which shields the epoxide. This way, the metabolite is able to travel and bind to DNA in figure (2). The mechanism is derived from the binding mechanism of benzo 'a''yrene to DNA. This is likely because it is plausible that two polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are metabolized via the same pathway. Deoxyguanosine is used in the figure, since that base appears to be bound to Benzo yrene far more often than the other bases.
There appears to be an equilibrium in 3-MC-free and 3-MC-bound. It is hard to determine how when the equilibrium is formed due to difficulties with radioactive measurements. A probable saturating dosis is thought to be around 40 mg 3-MC/kg.
Research on the effect of 3-MC in rat uteri concludes that 3-MC acts as an estrogen antagonist. The sexhormone is, like 3-MC, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. 3-MC and estrogen bind to estrogenreceptors competitively, reducing the estrogen expression.
Metabolism
MC is metabolized by rat liver microsomes into oxygenated forms which alkylate DNA. These oxygenated metabolites bind to double-stranded and single-stranded. Empirical data show that MC tends to bind mostly to G-bases8. When injected in lung, kidney or liver tissue of rats, it appears that the liver is able to reverse the MC-binding to DNA. Lung and kidney tissue are not capable of doing this, which may explain why MC is more carcinogenic in lungs and kidneys than in the liver. To be carcinogenic, the MC metabolite has to be covalently bound to DNA. Therefore, it is necessary for MC to be oxygenated in order to carcinogenic. Injected MC does not move away from the injection site. In a rat body MC has a half-life of about 4 weeks. After 8 weeks, 80% of MC is metabolized into water-soluble metabolites. MC and its metabolites mainly exit the body via feces (a ninefold more urine). Three months after injection with MC, 85% of the rats are reported to have tumors. 82% of the tumors is a form of spindle-cell sarcoma.Efficacy
Methylcholanthrene is often used to induce tumors in rodents for carcinogenesis and mutagenesis research. In a study from 1991, lung precancerous and cancerous lesions were induced in Wistar rats by one intrabronchial injection of 3-MC. After 30 days, atypical hyperplasia of bronchiolar epithelium, adenoid hyperplasia or adenomas, and squamous cell carcinoma occurred in 15 (88.2%), 12 (70.6%) and 3 (17.7%) out of 17 rats respectively. After 60 days, the incidences were 15/18 (83.3%), 4/17 (23.5%) and 7/18 (38.9%). All of the precancerous lesions and carcinomas showed positive expression of gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (GGT). Jin et al. (2013) found that the cellular redox balance is altered by acute exposure to 3-MC. This causes the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)-regulated response pathway to induce antioxidant responses.Toxicity
3-MC is a ligand of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), which stimulates transcription directed by xenobiotic response elements. AhR ligands can induce formation of an AhR-estrogen receptor (ER) complex. 3-MC was found to elicit estrogenic activity by this mechanism, and by stimulation of the expression of some endogenous ER target genes. 3-MC may cause respiratory tract irritation, skin irritation or eye irritation.Effects on animals
Effects on human
3-MC is mutagenic to human cells. Curren et al. (1978) were the first to report successfully induced mutations in human cells with 3-MC. Skin epithelial cells are thought to metabolize the compound to mutagenic products. The ability to metabolize mutagens may express genetically regulated differences within a species such as man or mouse, causing environmental chemicals to show a different level of mutagenicity and carcinogenicity to specific individuals.Non-human toxicity studies
The administration of 3-MC to pregnant mice results in the formation of lung tumors in the offspring. Miller et al. (1990) compared the effects of fetal versus adult exposure to 3-MC on both induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase (AHH) activity in lung and dependence of lung tumorigenesis on the Ah genotype. A single ip injection (in inducible fetal lung supernatants) of 100 mg/kg of 3-MC to the mothers resulted in a maximal 50-fold induction of AHH activity by 8 hr, which persisted for 48 hr. The same injections to adult F1 mice revealed only a 4- to 7—fold increase in lung AHH activity, compared to the large fetal induction ratio.References
External links
National Pollutant Inventory - Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Fact Sheet
{{Aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulators Carcinogens Hepatotoxins Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons