Meteorology is a branch of the
atmospheric science
Atmospheric science is the study of the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere and its various inner-working physical processes. Meteorology includes atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physics with a major focus on weather forecasting. Climat ...
s (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on
weather forecasting
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology forecasting, to predict the conditions of the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia a ...
. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not begin until the 18th century. The 19th century saw modest progress in the field after weather observation networks were formed across broad regions. Prior attempts at
prediction of weather depended on historical data. It was not until after the elucidation of the laws of physics, and more particularly in the latter half of the 20th century the development of the computer (allowing for the automated solution of a great many modelling equations) that significant breakthroughs in weather forecasting were achieved. An important branch of weather forecasting is
marine weather forecasting
Marine weather forecasting is the process by which mariners and meteorological organizations attempt to forecast future weather conditions over the Earth's oceans. Mariners have had rules of thumb regarding the navigation around tropical cyclone ...
as it relates to maritime and coastal safety, in which weather effects also include atmospheric interactions with large bodies of water.
Meteorological phenomena
This glossary of meteorology is a list of terms and concepts relevant to meteorology and atmospheric science, their sub-disciplines, and related fields.
A
...
are observable weather events that are explained by the science of meteorology. Meteorological phenomena are described and quantified by the variables of Earth's atmosphere: temperature, air pressure, water vapour, mass flow, and the variations and interactions of these variables, and how they change over time. Different
spatial scales
Spatial scale is a specific application of the term scale for describing or categorizing (e.g. into orders of magnitude) the size of a space (hence ''spatial''), or the extent of it at which a phenomenon or process occurs.
For instance, in phy ...
are used to describe and predict weather on local, regional, and global levels.
Meteorology,
climatology
Climatology (from Greek , ''klima'', "place, zone"; and , '' -logia'') or climate science is the scientific study of Earth's climate, typically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of at least 30 years. This modern field of stud ...
,
atmospheric physics
Within the atmospheric sciences, atmospheric physics is the application of physics to the study of the atmosphere. Atmospheric physicists attempt to model Earth's atmosphere and the atmospheres of the other planets using fluid flow equations, che ...
, and
atmospheric chemistry
Atmospheric chemistry is a branch of atmospheric science in which the chemistry of the Earth's atmosphere and that of other planets is studied. It is a multidisciplinary approach of research and draws on environmental chemistry, physics, meteoro ...
are sub-disciplines of the
atmospheric sciences
Atmospheric science is the study of the Earth's atmosphere and its various inner-working physical processes. Meteorology includes atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physics with a major focus on weather forecasting. Climatology is the study of ...
. Meteorology and
hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is calle ...
compose the interdisciplinary field of
hydrometeorology
Hydrometeorology is a branch of meteorology and hydrology that studies the transfer of water and energy between the land surface and the lower atmosphere. Hydrologists often use data provided by meteorologists. As an example, a meteorologist might ...
. The interactions between Earth's atmosphere and its oceans are part of a coupled ocean-atmosphere system. Meteorology has application in many diverse fields such as the military, energy production, transport, agriculture, and construction.
The word ''
meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not ...
'' is from the Ancient Greek
μετέωρος ''metéōros'' (''meteor'') and
-λογία ''-logia'' (''
-(o)logy''), meaning "the study of things high in the air."
History
Ancient meteorology up to the time of Aristotle

Early attempts at predicting weather were often related to prophecy and divining, and were sometimes based on astrological ideas.
Ancient religions believed meteorological phenomena to be under the control of the gods.
The ability to predict
rain
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
s and
flood
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrol ...
s based on annual cycles was evidently used by humans at least from the time of agricultural settlement if not earlier. Early approaches to predicting weather were based on
astrology
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of Celestial o ...
and were practiced by priests. The
Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
had
rain-making rituals as early as 3500 BC.
Ancient Indian
Upanishads
The Upanishads (; sa, उपनिषद् ) are late Vedic Sanskrit texts that supplied the basis of later Hindu philosophy.Wendy Doniger (1990), ''Textual Sources for the Study of Hinduism'', 1st Edition, University of Chicago Press, , ...
contain mentions of clouds and
season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and pol ...
s.
The Samaveda mentions sacrifices to be performed when certain phenomena were noticed.
Varāhamihira
Varāhamihira ( 505 – 587), also called Varāha or Mihira, was an ancient Indian astrologer, astronomer, and polymath who lived in Ujjain (Madhya Pradesh, India). He was born at Kapitba in a Brahmin family, in the Avanti region, roughly co ...
's classical work ''Brihatsamhita'', written about 500 AD,
provides evidence of weather observation.
Cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-sha ...
inscriptions on
Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
ian tablets included associations between thunder and rain. The
Chaldeans differentiated the
22° and
46° halo
A 46° halo is a rare atmospheric optical phenomenon that consists of a halo with an apparent radius of approximately 46° around the Sun. At solar elevations of 15–27°, 46° halos are often confused with the less rare and more colourful su ...
s.
The
ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cultu ...
were the first to make theories about the weather. Many
natural philosophers
Natural philosophy or philosophy of nature (from Latin ''philosophia naturalis'') is the philosophical study of physics, that is, nature and the physical universe. It was dominant before the development of modern science.
From the ancient wor ...
studied the weather. However, as
meteorological instruments did not exist, the inquiry was largely qualitative, and could only be judged by more general theoretical speculations.
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known f ...
states that
Thales
Thales of Miletus ( ; grc-gre, Θαλῆς; ) was a Greek mathematician, astronomer, statesman, and pre-Socratic philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. He was one of the Seven Sages of Greece. Many, most notably Aristotle, regarded him ...
predicted the
solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of the Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six month ...
of 585 BC. He studied Babylonian equinox tables. According to Seneca, he gave the explanation that the cause of the
Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered ...
's annual floods was due to northerly winds hindering its descent by the sea.
Anaximander
Anaximander (; grc-gre, Ἀναξίμανδρος ''Anaximandros''; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus,"Anaximander" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 1, p. 403. a city of Ionia (in moder ...
and
Anaximenes thought that thunder and lightning was caused by air smashing against the cloud, thus kindling the flame. Early meteorological theories generally considered that there was a fire-like substance in the atmosphere. Anaximander defined wind as a flowing of air, but this was not generally accepted for centuries. A theory to explain summer hail was first proposed by
Anaxagoras
Anaxagoras (; grc-gre, Ἀναξαγόρας, ''Anaxagóras'', "lord of the assembly"; 500 – 428 BC) was a Pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. Born in Clazomenae at a time when Asia Minor was under the control of the Persian Empire, ...
. He observed that air temperature decreased with increasing height and that clouds contain moisture. He also noted that heat caused objects to rise, and therefore the heat on a summer day would drive clouds to an altitude where the moisture would freeze.
Empledocles theorized on the change of the seasons. He believed that fire and water opposed each other in the atmosphere, and when fire gained the upper hand, the result was summer, and when water did, it was winter.
Democritus
Democritus (; el, Δημόκριτος, ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an atomic theory of the universe. No ...
also wrote about the flooding of the Nile. He said that during the summer solstice, snow in northern parts of the world melted. This would cause vapors to form clouds, which would cause storms when driven to the Nile by northerly winds, thus filling the lakes and the Nile.
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of ...
inquired into the effect of weather on health.
Eudoxus claimed that bad weather followed four-year periods, according to Pliny.
These early observations would form the basis for
Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
's ''
Meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not ...
'', written in 350 BC. Aristotle is considered the founder of meteorology. One of the most impressive achievements described in the ''Meteorology'' is the description of what is now known as the
hydrologic cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly const ...
. His work would remain an authority on metereology for nearly 2,000 years.
The book
De Mundo
''On the Universe'' ( el, Περὶ Κόσμου; la, De Mundo) is a theological and scientific treatise included in the Corpus Aristotelicum but usually regarded as spurious. It was likely published between and the . The work discusses cosmol ...
(composed before 250 BC or between 350 and 200 BC) noted:
:If the flashing body is set on fire and rushes violently to the Earth it is called a thunderbolt; if it is only half of fire, but violent also and massive, it is called a ''meteor''; if it is entirely free from fire, it is called a smoking bolt. They are all called 'swooping bolts' because they swoop down upon the Earth. Lightning is sometimes smoky, and is then called 'smoldering lightning"; sometimes it darts quickly along, and is then said to be ''vivid''. At other times, it travels in crooked lines, and is called ''forked lightning''. When it swoops down upon some object it is called 'swooping lightning'
Meteorology after Aristotle
After Aristotle, progress in meteorology stalled for a long time.
Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; grc-gre, Θεόφραστος ; c. 371c. 287 BC), a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos.Gavin Hardy and Laurence Totelin, ''Ancient Botany'', Routledge ...
compiled a book on weather forecasting, called the ''Book of Signs'', as well as ''On Winds''. He gave hundreds of signs for weather phenomena for a period up to a year. His system was based on dividing the year by the setting and the rising of the Pleiad, halves into solstices and equinoxes, and the continuity of the weather for those periods. He also divided months into the new moon, fourth day, eighth day and full moon, in likelihood of a change in the weather occurring. The day was divided into sunrise, mid-morning, noon, mid-afternoon and sunset, with corresponding divisions of the night, with change being likely at one of these divisions. Applying the divisions and a principle of balance in the yearly weather, he came up with forecasts like that if a lot of rain falls in the winter, the spring is usually dry. Rules based on actions of animals are also present in his work, like that if a dog rolls on the ground, it is a sign of a storm. Shooting stars and the Moon were also considered significant. However, he made no attempt to explain these phenomena, referring only to the Aristotelian method. The work of Theophrastus remained a dominant influence in weather forecasting for nearly 2,000 years.
Speculation on the cause of the flooding of the Nile ended when
Erastothenes, according to
Proclus
Proclus Lycius (; 8 February 412 – 17 April 485), called Proclus the Successor ( grc-gre, Πρόκλος ὁ Διάδοχος, ''Próklos ho Diádokhos''), was a Greek Neoplatonist philosopher, one of the last major classical philosophers ...
, stated that it was known that man had gone to the sources of the Nile and observed the rains, although interest in its implications continued.
During the era of
Roman Greece
Greece in the Roman era describes the Roman conquest of Greece, as well as the period of Greek history when Greece was dominated first by the Roman Republic and then by the Roman Empire.
The Roman era of Greek history began with the Corinthian ...
and Europe, scientific interest in meteorology waned. In the 1st century BC, most natural philosophers claimed that the clouds and winds extended up to 111 miles, but
Posidonius
Posidonius (; grc-gre, wikt:Ποσειδώνιος, Ποσειδώνιος , "of Poseidon") "of Apamea (Syria), Apameia" (ὁ Ἀπαμεύς) or "of Rhodes" (ὁ Ῥόδιος) (), was a Greeks, Greek politician, astronomer, astrologer, geog ...
thought that they reached up to five miles, after which the air is clear, liquid and luminous. He closely followed Aristotle's theories. By the end of the second century BC, the center of science shifted from Athens to
Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria ...
, home to the ancient
Library of Alexandria
The Great Library of Alexandria in Alexandria, Egypt, was one of the largest and most significant libraries of the ancient world. The Library was part of a larger research institution called the Mouseion, which was dedicated to the Muses, th ...
. In the 2nd century AD,
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
's
Almagest
The ''Almagest'' is a 2nd-century Greek-language mathematical and astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Claudius Ptolemy ( ). One of the most influential scientific texts in history, it canoni ...
dealt with meteorology, because it was considered a subset of astronomy. He gave several astrological weather predictions. He constructed a map of the world divided into climactic zones by their illumination, in which the length of the Summer solstice increased by half an hour per zone between the equator and the Arctic. Ptolemy wrote on the
atmospheric refraction
Atmospheric refraction is the deviation of light or other electromagnetic wave from a straight line as it passes through the atmosphere due to the variation in air density as a function of height. This refraction is due to the velocity of light t ...
of light in the context of astronomical observations.
In 25 AD,
Pomponius Mela
Pomponius Mela, who wrote around AD 43, was the earliest Roman geographer. He was born in Tingentera (now Algeciras) and died AD 45.
His short work (''De situ orbis libri III.'') remained in use nearly to the year 1500. It occupies less ...
, a Roman geographer, formalized the climatic zone system. In 63-64 AD,
Seneca
Seneca may refer to:
People and language
* Seneca (name), a list of people with either the given name or surname
* Seneca people, one of the six Iroquois tribes of North America
** Seneca language, the language of the Seneca people
Places Extrat ...
wrote ''
Naturales quaestiones
''Naturales quaestiones'' (''Natural Questions'') is a Latin work of natural philosophy written by Seneca around 65 AD. It is not a systematic encyclopedia like the ''Naturalis Historia'' of Pliny the Elder, though with Pliny's work it represent ...
''. It was a compilation and synthesis of ancient Greek theories. However, theology was of foremost importance to Seneca, and he believed that phenomena such as lightning were tied to fate. The second book(chapter) of
Pliny
Pliny may refer to:
People
* Pliny the Elder (23–79 CE), ancient Roman nobleman, scientist, historian, and author of ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Pliny's Natural History'')
* Pliny the Younger (died 113), ancient Roman statesman, orator, w ...
's
Natural History covers meteorology. He states that more than twenty ancient Greek authors studied meteorology. He didn't make any personal contributions, and the value of his work is in preserving earlier speculation, much like Seneca's work.

From 400 to 1100, scientific learning in Europe was preserved by the clergy.
Isidore of Seville
Isidore of Seville ( la, Isidorus Hispalensis; c. 560 – 4 April 636) was a Spanish scholar, theologian, and archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of 19th-century historian Montalembert, as "the last scholar of ...
devoted a considerable attention to meteorology in ''
Etymologiae
''Etymologiae'' (Latin for "The Etymologies"), also known as the ''Origines'' ("Origins") and usually abbreviated ''Orig.'', is an etymological encyclopedia compiled by Isidore of Seville (c. 560–636) towards the end of his life. Isidore was ...
'', ''De ordine creaturum'' and ''De natura rerum''.
Bede the Venerable
Bede ( ; ang, Bǣda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom ...
was the first Englishman to write about the weather in ''
De Natura Rerum'' in 703. The work was a summary of then extant classical sources. However, Aristotle's works were largely lost until the twelfth century, including ''Meteorologica''. Isidore and Bede were scientifically minded, but
they adhered to the letter of Scripture.
Islamic civilization translated many ancient works into Arabic which were
transmitted and translated in western Europe to Latin.
In the 9th century,
Al-Dinawari
Abū Ḥanīfa Aḥmad ibn Dāwūd Dīnawarī ( fa, ابوحنيفه دينوری; died 895) was a Persian Islamic Golden Age polymath, astronomer, agriculturist, botanist, metallurgist, geographer, mathematician, and historian.
Life
Dinawar ...
wrote the ''Kitab al-Nabat'' (Book of Plants), in which he deals with the application of meteorology to
agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
during the
Arab Agricultural Revolution
The Arab Agricultural Revolution was the transformation in agriculture from the 8th to the 13th century in the Islamic region of the Old World. The agronomic literature of the time, with major books by Ibn Bassal and Abū l-Khayr al-Ishbīlī, ...
. He describes the meteorological character of the sky, the
planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
s and
constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
s, the
sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
and
moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
, the
lunar phase
Concerning the lunar month of ~29.53 days as viewed from Earth, the lunar phase or Moon phase is the shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion, which can be expressed quantitatively using areas or angles, or described qualitatively using the t ...
s indicating
season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and pol ...
s and rain, the ''anwa'' (
heavenly bodies of rain), and atmospheric phenomena such as winds, thunder, lightning, snow, floods, valleys, rivers, lakes.
In 1021,
Alhazen
Ḥasan Ibn al-Haytham, Latinized as Alhazen (; full name ; ), was a medieval mathematician, astronomer, and physicist of the Islamic Golden Age from present-day Iraq.For the description of his main fields, see e.g. ("He is one of the prin ...
showed that atmospheric refraction is also responsible for
twilight
Twilight is light produced by sunlight scattering in the upper atmosphere, when the Sun is below the horizon, which illuminates the lower atmosphere and the Earth's surface. The word twilight can also refer to the periods of time when this il ...
in ''
Opticae thesaurus''; he estimated that twilight begins when the sun is 19 degrees below the
horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This line divides all viewing directions based on whether i ...
, and also used a geometric determination based on this to estimate the maximum possible height of the
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
as 52,000 ''passim'' (about 49 miles, or 79 km).
Adelard of Bath
Adelard of Bath ( la, Adelardus Bathensis; 1080? 1142–1152?) was a 12th-century English natural philosopher. He is known both for his original works and for translating many important Arabic and Greek scientific works of astrology, astronom ...
was one of the early translators of the classics. He also discussed meteorological topics in his ''Quaestiones naturales''. He thought dense air produced propulsion in the form of wind. He explained thunder by saying that it was due to ice colliding in clouds, and in Summer it melted. In the thirteenth century, Aristotelian theories reestablished dominance in meteorology. For the next four centuries, meteorological work by and large was mostly
commentary
Commentary or commentaries may refer to:
Publications
* ''Commentary'' (magazine), a U.S. public affairs journal, founded in 1945 and formerly published by the American Jewish Committee
* Caesar's Commentaries (disambiguation), a number of works ...
. It has been estimated over 156 commentaries on the ''Meteorologica'' were written before 1650.
Experimental evidence was less important than appeal to the classics and authority in medieval thought. In the thirteenth century,
Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon (; la, Rogerus or ', also '' Rogerus''; ), also known by the scholastic accolade ''Doctor Mirabilis'', was a medieval English philosopher and Franciscan friar who placed considerable emphasis on the study of nature through empiri ...
advocated experimentation and the mathematical approach. In his ''
Opus majus
The ''Opus Majus'' (Latin for "Greater Work") is the most important work of Roger Bacon. It was written in Medieval Latin, at the request of Pope Clement IV, to explain the work that Bacon had undertaken. The 878-page treatise ranges over all ...
'', he followed Aristotle's theory on the atmosphere being composed of water, air, and fire, supplemented by optics and geometric proofs. He noted that Ptolemy's climactic zones had to be adjusted for
topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sci ...
.
St. Albert the Great
Albertus Magnus (c. 1200 – 15 November 1280), also known as Saint Albert the Great or Albert of Cologne, was a German Dominican Order, Dominican friar, philosopher, scientist, and Bishop in the Catholic Church, bishop. Later Canonization ...
was the first to propose that each drop of falling rain had the form of a small sphere, and that this form meant that the rainbow was produced by light interacting with each raindrop.
Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon (; la, Rogerus or ', also '' Rogerus''; ), also known by the scholastic accolade ''Doctor Mirabilis'', was a medieval English philosopher and Franciscan friar who placed considerable emphasis on the study of nature through empiri ...
was the first to calculate the angular size of the rainbow. He stated that a rainbow summit can not appear higher than 42 degrees above the horizon.
In the late 13th century and early 14th century,
Kamāl al-Dīn al-Fārisī
Kamal al-Din Hasan ibn Ali ibn Hasan al-Farisi or Abu Hasan Muhammad ibn Hasan (1267– 12 January 1319, long assumed to be 1320)) ( fa, كمالالدين فارسی) was a Persian Muslim scientist. He made two major contributions to scienc ...
and
Theodoric of Freiberg
Theodoric of Freiberg (; – ) was a German member of the Dominican order and a theology, theologian and physicist. He was named Provincial superior, provincial of the Dominican Order in 1293, Albert the Great's old post. He is considered one of t ...
were the first to give the correct explanations for the primary
rainbow
A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon that is caused by reflection, refraction and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a spectrum of light appearing in the sky. It takes the form of a multicoloured circular arc. Rainbows c ...
phenomenon.
Theoderic
Theodoric is a Germanic given name. First attested as a Gothic name in the 5th century, it became widespread in the Germanic-speaking world, not least due to its most famous bearer, Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths.
Overview
The name ...
went further and also explained the secondary rainbow.
By the middle of the sixteenth century, meteorology had developed along two lines: theoretical science based on ''Meteorologica'', and astrological weather forecasting. The pseudoscientific prediction by natural signs became popular and enjoyed protection of the church and princes. This was supported by scientists like
Johannes Muller,
Leonard Digges, and
Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws ...
. However, there were skeptics. In the 14th century,
Nicole Oresme
Nicole Oresme (; c. 1320–1325 – 11 July 1382), also known as Nicolas Oresme, Nicholas Oresme, or Nicolas d'Oresme, was a French philosopher of the later Middle Ages. He wrote influential works on economics, mathematics, physics, astrology an ...
believed that weather forecasting was possible, but that the rules for it were unknown at the time. Astrological influence in meteorology persisted until the eighteenth century.
Gerolamo Cardano
Gerolamo Cardano (; also Girolamo or Geronimo; french: link=no, Jérôme Cardan; la, Hieronymus Cardanus; 24 September 1501– 21 September 1576) was an Italian polymath, whose interests and proficiencies ranged through those of mathematician, ...
's ''De Subilitate'' (1550) was the first work to challenge fundamental aspects of Aristotelian theory. Cardano maintained that there were only three basic elements- earth, air, and water. He discounted fire because it needed material to spread and produced nothing. Cardano thought there were two kinds of air: free air and inclosed air. The former destroyed inanimate things and preserved animate things, while the latter had the opposite effect.
The modern era and scientific meteorology
Rene Descartes's
Discourse on the Method
''Discourse on the Method of Rightly Conducting One's Reason and of Seeking Truth in the Sciences'' (french: Discours de la Méthode Pour bien conduire sa raison, et chercher la vérité dans les sciences) is a philosophical and autobiographical ...
(1637) typifies the beginning of the
scientific revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology (including human anatomy) and chemistry transfo ...
in meteorology. His scientific method had four principles: to never accept anything unless one clearly knew it to be true; to divide every difficult problem into small problems to tackle; to proceed from the simple to the complex, always seeking relationships; to be as complete and thorough as possible with no prejudice.
In the appendix ''Les Meteores'', he applied these principles to meteorology. He discussed terrestrial bodies and vapors which arise from them, proceeding to explain the formation of clouds from drops of water, and winds, clouds then dissolving into rain, hail and snow. He also discussed the effects of light on the rainbow. Descartes hypothesized that all bodies were composed of
small particles of different shapes and interwovenness. All of his theories was based on this hypothesis. He explained the rain as caused by clouds becoming too large for the air to hold, and that clouds became snow if the air was not warm enough to melt them, or hail if they met colder wind. Like his predecessors, Descartes's method was deductive, as
meteorological instruments were not developed and extensively used yet. He introduced the
Cartesian coordinate system
A Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, measured in t ...
to meteorology and stressed the importance of mathematics in natural science. His work established meteorology as a legitimate branch of physics.
Instruments and classification scales

In 1441, Sejong the Great of Joseon, King Sejong's son, Prince Munjong of Korea, invented the first standardized rain gauge. These were sent throughout the Joseon dynasty of Korea as an official tool to assess land taxes based upon a farmer's potential harvest. In 1450, Leone Battista Alberti developed a swinging-plate anemometer, and was known as the first ''anemometer''.
In 1607, Galileo Galilei constructed a Galileo thermometer, thermoscope. In 1611,
Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws ...
wrote the first scientific treatise on snow crystals: "Strena Seu de Nive Sexangula (A New Year's Gift of Hexagonal Snow)." In 1643, Evangelista Torricelli invented the mercury barometer.
In 1662, Sir Christopher Wren invented the mechanical, self-emptying, tipping bucket rain gauge. In 1714, Gabriel Fahrenheit created a reliable scale for measuring temperature with a mercury-type thermometer. In 1742, Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, proposed the "centigrade" temperature scale, the predecessor of the current Celsius scale. In 1783, the first hair hygrometer was demonstrated by Horace-Bénédict de Saussure. In 1802–1803, Luke Howard wrote ''On the Modification of Clouds'', in which he assigns List of cloud types, cloud types Latin names. In 1806, Francis Beaufort introduced his Beaufort scale, system for classifying wind speeds. Near the end of the 19th century the first cloud atlases were published, including the ''International Cloud Atlas'', which has remained in print ever since. The April 1960 launch of the first successful weather satellite, TIROS-1, marked the beginning of the age where weather information became available globally.
Atmospheric composition research
In 1648, Blaise Pascal rediscovered that atmospheric pressure decreases with height, and deduced that there is a vacuum above the atmosphere. In 1738, Daniel Bernoulli published ''Hydrodynamics'', initiating the Kinetic theory of gases and established the basic laws for the theory of gases. In 1761, Joseph Black discovered that ice absorbs heat without changing its temperature when melting. In 1772, Black's student Daniel Rutherford discovered nitrogen, which he called ''phlogisticated air'', and together they developed the phlogiston theory. In 1777, Antoine Lavoisier discovered oxygen and developed an explanation for combustion. In 1783, in Lavoisier's essay "Reflexions sur le phlogistique," he deprecates the phlogiston theory and proposes a caloric theory. In 1804, John Leslie (physicist), John Leslie observed that a matte black surface radiates heat more effectively than a polished surface, suggesting the importance of black-body radiation. In 1808, John Dalton defended caloric theory in ''A New System of Chemistry'' and described how it combines with matter, especially gases; he proposed that the heat capacity of gases varies inversely with atomic weight. In 1824, Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot, Sadi Carnot analyzed the efficiency of steam engines using caloric theory; he developed the notion of a reversible process (thermodynamics), reversible process and, in postulating that no such thing exists in nature, laid the foundation for the second law of thermodynamics. In 1716, Edmund Halley suggested that aurorae are caused by "magnetic effluvia" moving along the Earth's magnetic field lines.
Research into cyclones and air flow

In 1494, Christopher Columbus experienced a tropical cyclone, which led to the first written European account of a hurricane. In 1686, Edmund Halley presented a systematic study of the trade winds and monsoons and identified solar heating as the cause of atmospheric motions. In 1735, an ''ideal'' explanation of Atmospheric circulation, global circulation through study of the trade winds was written by George Hadley. In 1743, when Benjamin Franklin was prevented from seeing a lunar eclipse by a tropical cyclone, hurricane, he decided that cyclones move in a contrary manner to the winds at their periphery.
Understanding the kinematics of how exactly the rotation of the Earth affects airflow was partial at first. Gaspard-Gustave Coriolis published a paper in 1835 on the energy yield of machines with rotating parts, such as waterwheels.
In 1856, William Ferrel proposed the existence of a Ferrel cell, circulation cell in the mid-latitudes, and the air within deflected by the Coriolis force resulting in the prevailing westerly winds. Late in the 19th century, the motion of air masses along isobar (meteorology), isobars was understood to be the result of the large-scale interaction of the pressure gradient force and the deflecting force. By 1912, this deflecting force was named the Coriolis effect. Just after World War I, a group of meteorologists in Norway led by Vilhelm Bjerknes developed the Norwegian cyclone model that explains the generation, intensification and ultimate decay (the life cycle) of extratropical cyclone, mid-latitude cyclones, and introduced the idea of front (meteorology), fronts, that is, sharply defined boundaries between air masses.
The group included Carl-Gustaf Rossby (who was the first to explain the large scale atmospheric flow in terms of fluid dynamics), Tor Bergeron (who first determined how rain forms) and Jacob Bjerknes.
Observation networks and weather forecasting

In the late 16th century and first half of the 17th century a range of meteorological instruments were invented – the thermometer, barometer, hydrometer, as well as wind and rain gauges. In the 1650s natural philosophers started using these instruments to systematically record weather observations. Scientific academies established weather diaries and organised observational networks.
In 1654, Ferdinando II de Medici established the first ''weather observing'' network, that consisted of meteorological stations in Florence, Cutigliano, Vallombrosa, Bologna, Parma, Milan, Innsbruck, Osnabrück, Paris and Warsaw. The collected data were sent to Florence at regular time intervals. In the 1660s Robert Hooke of the Royal Society of London sponsored networks of weather observers.
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of ...
' treatise ''Airs, Waters, and Places'' had linked weather to disease. Thus early meteorologists attempted to correlate weather patterns with epidemic outbreaks, and the climate with public health.
During the Age of Enlightenment meteorology tried to rationalise traditional weather lore, including astrological meteorology. But there were also attempts to establish a theoretical understanding of weather phenomena. Edmond Halley and George Hadley tried to explain trade winds. They reasoned that the rising mass of heated equator air is replaced by an inflow of cooler air from high latitudes. A flow of warm air at high altitude from equator to poles in turn established an early picture of circulation. Frustration with the lack of discipline among weather observers, and the poor quality of the instruments, led the early modern nation states to organise large observation networks. Thus by the end of the 18th century, meteorologists had access to large quantities of reliable weather data.
In 1832, an electromagnetic telegraph was created by Baron Schilling. The arrival of the electrical telegraph in 1837 afforded, for the first time, a practical method for quickly gathering surface weather observations from a wide area.
This data could be used to produce maps of the state of the atmosphere for a region near the Earth's surface and to study how these states evolved through time. To make frequent weather forecasts based on these data required a reliable network of observations, but it was not until 1849 that the Smithsonian Institution began to establish an observation network across the United States under the leadership of Joseph Henry. Similar observation networks were established in Europe at this time. The Reverend William Clement Ley was key in understanding of cirrus clouds and early understandings of Jet Streams. Charles Kenneth Mackinnon Douglas, known as 'CKM' Douglas read Ley's papers after his death and carried on the early study of weather systems.
Nineteenth century researchers in meteorology were drawn from military or medical backgrounds, rather than trained as dedicated scientists. In 1854, the United Kingdom government appointed Robert FitzRoy to the new office of ''Meteorological Statist to the Board of Trade'' with the task of gathering weather observations at sea. FitzRoy's office became the Met Office, United Kingdom Meteorological Office in 1854, the second oldest national meteorological service in the world (the Central Institution for Meteorology and Geodynamics (ZAMG) in Austria was founded in 1851 and is the oldest weather service in the world). The first daily weather forecasts made by FitzRoy's Office were published in ''The Times'' newspaper in 1860. The following year a system was introduced of hoisting storm warning cones at principal ports when a gale was expected.
FitzRoy coined the term "weather forecast", and tried to separate scientific approaches from prophetic ones.
Over the next 50 years, many countries established national meteorological services. The India Meteorological Department (1875) was established to follow tropical cyclone and monsoon. The Finnish Meteorological Central Office (1881) was formed from part of Magnetic Observatory of Helsinki University. Japan's Tokyo Meteorological Observatory, the forerunner of the Japan Meteorological Agency, began constructing surface weather maps in 1883. The United States Weather Bureau (1890) was established under the United States Department of Agriculture. The Bureau of Meteorology, Australian Bureau of Meteorology (1906) was established by a Meteorology Act to unify existing state meteorological services.
Numerical weather prediction

In 1904, Norwegian scientist Vilhelm Bjerknes first argued in his paper ''Weather Forecasting as a Problem in Mechanics and Physics'' that it should be possible to forecast weather from calculations based upon physical law, natural laws.
It was not until later in the 20th century that advances in the understanding of atmospheric physics led to the foundation of modern numerical weather prediction. In 1922, Lewis Fry Richardson published "Weather Prediction By Numerical Process," after finding notes and derivations he worked on as an ambulance driver in World War I. He described how small terms in the prognostic fluid dynamics equations that govern atmospheric flow could be neglected, and a numerical calculation scheme that could be devised to allow predictions. Richardson envisioned a large auditorium of thousands of people performing the calculations. However, the sheer number of calculations required was too large to complete without electronic computers, and the size of the grid and time steps used in the calculations led to unrealistic results. Though numerical analysis later found that this was due to numerical instability.
Starting in the 1950s, number, numerical forecasts with computers became feasible. The first weather forecasts derived this way used barotropic (single-vertical-level) models, and could successfully predict the large-scale movement of midlatitude Rossby waves, that is, the pattern of low-pressure area, atmospheric lows and High-pressure area, highs. In 1959, the UK Meteorological Office received its first computer, a Ferranti Mercury.
In the 1960s, the Chaos theory, chaotic nature of the atmosphere was first observed and mathematically described by Edward Lorenz, founding the field of chaos theory. These advances have led to the current use of ensemble forecasting in most major forecasting centers, to take into account uncertainty arising from the chaotic nature of the atmosphere.
Mathematical models used to predict the long term weather of the Earth (climate models), have been developed that have a resolution today that are as coarse as the older weather prediction models. These climate models are used to investigate long-term climate shifts, such as what effects might be caused by human emission of greenhouse gases.
Meteorologists
Meteorologists are scientists who study and work in the field of meteorology. The American Meteorological Society publishes and continually updates an authoritative electronic ''Meteorology Glossary''. Meteorologists work in Government agency, government agencies, private consulting and research services, industrial enterprises, utilities, radio and television stations, and in education. In the United States, meteorologists held about 10,000 jobs in 2018.
Although weather forecasts and warnings are the best known products of meteorologists for the public, weather presenters on radio and television are not necessarily professional meteorologists. They are most often reporters with little formal meteorological training, using unregulated titles such as ''weather specialist'' or ''weatherman''. The American Meteorological Society and National Weather Association issue "Seals of Approval" to weather broadcasters who meet certain requirements but this is not mandatory to be hired by the media.
Equipment

Each science has its own unique sets of laboratory equipment. In the atmosphere, there are many things or qualities of the atmosphere that can be measured. Rain, which can be observed, or seen anywhere and anytime was one of the first atmospheric qualities measured historically. Also, two other accurately measured qualities are wind and humidity. Neither of these can be seen but can be felt. The devices to measure these three sprang up in the mid-15th century and were respectively the rain gauge, the anemometer, and the hygrometer. Many attempts had been made prior to the 15th century to construct adequate equipment to measure the many atmospheric variables. Many were faulty in some way or were simply not reliable. Even
Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
noted this in some of his work as the difficulty to measure the air.
Sets of surface measurements are important data to meteorologists. They give a snapshot of a variety of weather conditions at one single location and are usually at a weather station, a ship or a weather buoy. The measurements taken at a weather station can include any number of atmospheric observables. Usually, temperature, atmospheric pressure, pressure, wind measurements, and humidity are the variables that are measured by a thermometer, barometer, anemometer, and hygrometer, respectively. Professional stations may also include air quality sensors (carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, dust, and smoke), ceilometer (cloud ceiling), falling precipitation sensor, level sensor, flood sensor, lightning, lightning sensor, microphone (explosions, sonic booms, thunder), pyranometer/pyrheliometer/spectroradiometer (IR/Vis/UV photodiodes), rain gauge/snow gauge, scintillation counter (background radiation, fallout, radon), seismometer (earthquakes and tremors), transmissometer (visibility), and a GPS clock for data logging. Upper air data are of crucial importance for weather forecasting. The most widely used technique is launches of radiosondes. Supplementing the radiosondes a Aircraft Meteorological Data Relay, network of aircraft collection is organized by the World Meteorological Organization.
Remote sensing, as used in meteorology, is the concept of collecting data from remote weather events and subsequently producing weather information. The common types of remote sensing are Radar, Lidar, and satellites (or photogrammetry). Each collects data about the atmosphere from a remote location and, usually, stores the data where the instrument is located. Radar and Lidar are not passive because both use EM radiation to illuminate a specific portion of the atmosphere. Weather satellites along with more general-purpose Earth-observing satellites circling the earth at various altitudes have become an indispensable tool for studying a wide range of phenomena from forest fires to El Niño.
Spatial scales
The study of the atmosphere can be divided into distinct areas that depend on both time and spatial scales. At one extreme of this scale is climatology. In the timescales of hours to days, meteorology separates into micro-, meso-, and synoptic scale meteorology. Respectively, the geospatial size of each of these three scales relates directly with the appropriate timescale.
Other subclassifications are used to describe the unique, local, or broad effects within those subclasses.
Microscale
Microscale meteorology is the study of atmospheric phenomena on a scale of about or less. Individual thunderstorms, clouds, and local turbulence caused by buildings and other obstacles (such as individual hills) are modeled on this scale.
Mesoscale
Mesoscale meteorology is the study of atmospheric phenomena that has horizontal scales ranging from 1 km to 1000 km and a vertical scale that starts at the Earth's surface and includes the atmospheric boundary layer, troposphere, tropopause, and the lower section of the stratosphere. Mesoscale timescales last from less than a day to multiple weeks. The events typically of interest are thunderstorms, squall lines, weather front, fronts, rainbands, precipitation bands in tropical cyclone, tropical and extratropical cyclones, and topographically generated weather systems such as mountain waves and sea breeze, sea and land breezes.
Synoptic scale

Synoptic scale meteorology predicts atmospheric changes at scales up to 1000 km and 10
5 sec (28 days), in time and space. At the synoptic scale, the Coriolis acceleration acting on moving air masses (outside of the tropics) plays a dominant role in predictions. The phenomena typically described by synoptic meteorology include events such as extratropical cyclones, baroclinic troughs and ridges, weather front, frontal zones, and to some extent jet streams. All of these are typically given on weather maps for a specific time. The minimum horizontal scale of synoptic phenomena is limited to the spacing between weather station, surface observation stations.
Global scale
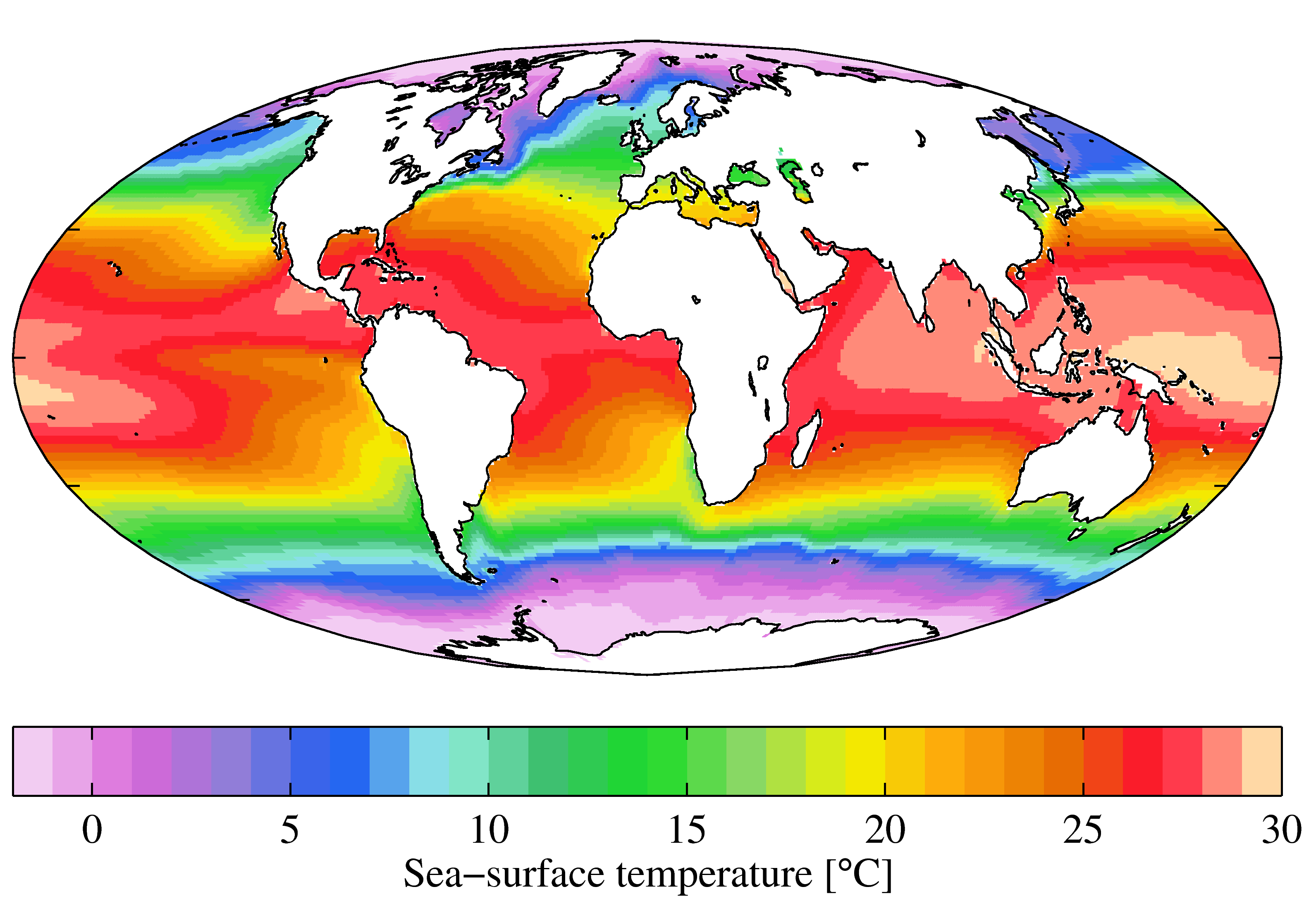
Global scale meteorology is the study of weather patterns related to the transport of heat from the tropics to the Geographical pole, poles. Very large scale oscillations are of importance at this scale. These oscillations have time periods typically on the order of months, such as the Madden–Julian oscillation, or years, such as the El Niño–Southern Oscillation and the Pacific decadal oscillation. Global scale meteorology pushes into the range of climatology. The traditional definition of climate is pushed into larger timescales and with the understanding of the longer time scale global oscillations, their effect on climate and weather disturbances can be included in the synoptic and mesoscale timescales predictions.
Numerical Weather Prediction is a main focus in understanding air–sea interaction, tropical meteorology, atmospheric predictability, and tropospheric/stratospheric processes. The Naval Research Laboratory in Monterey, California, developed a global atmospheric model called Navy Operational Global Atmospheric Prediction System (NOGAPS). NOGAPS is run operationally at Fleet Numerical Meteorology and Oceanography Center for the United States Military. Many other global atmospheric models are run by national meteorological agencies.
Some meteorological principles
Boundary layer meteorology
Boundary layer meteorology is the study of processes in the air layer directly above Earth's surface, known as the Planetary boundary layer, atmospheric boundary layer (ABL). The effects of the surface – heating, cooling, and friction – cause turbulence, turbulent mixing within the air layer. Significant movement of sensible heat, heat, matter, or momentum on time scales of less than a day are caused by turbulent motions. Boundary layer meteorology includes the study of all types of surface–atmosphere boundary, including ocean, lake, urban land and non-urban land for the study of meteorology.
Dynamic meteorology
Dynamic meteorology generally focuses on the fluid dynamics of the atmosphere. The idea of air parcel is used to define the smallest element of the atmosphere, while ignoring the discrete molecular and chemical nature of the atmosphere. An air parcel is defined as a point in the fluid continuum of the atmosphere. The fundamental laws of fluid dynamics, thermodynamics, and motion are used to study the atmosphere. The physical quantities that characterize the state of the atmosphere are temperature, density, pressure, etc. These variables have unique values in the continuum.
Applications
Weather forecasting

Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere at a future time and given location. Humans have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia and formally since at least the 19th century. Weather forecasts are made by collecting quantitative data about the current state of the atmosphere and using scientific understanding of atmospheric processes to project how the atmosphere will evolve.
Once an all-human endeavor based mainly upon changes in Atmospheric pressure, barometric pressure, current weather conditions, and sky condition, numerical weather prediction, forecast models are now used to determine future conditions. Human input is still required to pick the best possible forecast model to base the forecast upon, which involves pattern recognition skills, teleconnections, knowledge of model performance, and knowledge of model biases. The chaos theory, chaotic nature of the atmosphere, the massive computational power required to solve the equations that describe the atmosphere, error involved in measuring the initial conditions, and an incomplete understanding of atmospheric processes mean that forecasts become less accurate as the difference in current time and the time for which the forecast is being made (the ''range'' of the forecast) increases. The use of ensembles and model consensus help narrow the error and pick the most likely outcome.
There are a variety of end uses to weather forecasts. Weather warnings are important forecasts because they are used to protect life and property. Forecasts based on temperature and Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation are important to agriculture, and therefore to commodity traders within stock markets. Temperature forecasts are used by utility companies to estimate demand over coming days. On an everyday basis, people use weather forecasts to determine what to wear. Since outdoor activities are severely curtailed by heavy rain, snow, and wind chill, forecasts can be used to plan activities around these events, and to plan ahead and survive them.
Aviation meteorology
Aviation meteorology deals with the impact of weather on air traffic control, air traffic management. It is important for air crews to understand the implications of weather on their flight plan as well as their aircraft, as noted by the ''Aeronautical Information Manual'':
''The effects of ice on aircraft are cumulative—thrust is reduced, drag increases, lift lessens, and weight increases. The results are an increase in stall speed and a deterioration of aircraft performance. In extreme cases, 2 to 3 inches of ice can form on the leading edge of the airfoil in less than 5 minutes. It takes but 1/2 inch of ice to reduce the lifting power of some aircraft by 50 percent and increases the frictional drag by an equal percentage.''
Agricultural meteorology
Meteorologists, soil science, soil scientists, agricultural hydrologists, and agronomy, agronomists are people concerned with studying the effects of weather and climate on plant distribution, crop yield, water-use efficiency, phenology of plant and animal development, and the energy balance of managed and natural ecosystems. Conversely, they are interested in the role of vegetation on climate and weather.
Hydrometeorology
Hydrometeorology is the branch of meteorology that deals with the hydrologic cycle, the water budget, and the rainfall statistics of storms. A hydrometeorologist prepares and issues forecasts of accumulating (quantitative) precipitation, heavy rain, heavy snow, and highlights areas with the potential for flash flooding. Typically the range of knowledge that is required overlaps with climatology, mesoscale and synoptic meteorology, and other geosciences.
The multidisciplinary nature of the branch can result in technical challenges, since tools and solutions from each of the individual disciplines involved may behave slightly differently, be optimized for different hard- and software platforms and use different data formats. There are some initiatives – such as the DRIHM project – that are trying to address this issue.
Nuclear meteorology
Nuclear meteorology investigates the distribution of radioactive aerosols and gases in the atmosphere.
Maritime meteorology
Maritime meteorology deals with air and wave forecasts for ships operating at sea. Organizations such as the Ocean Prediction Center, Honolulu National Weather Service forecast office, United Kingdom Met Office, Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute, KNMI and Japan Meteorological Agency, JMA prepare high seas forecasts for the world's oceans.
Military meteorology
Military meteorology is the research and application of meteorology for military purposes. In the United States, the United States Navy's Commander, Naval Meteorology and Oceanography Command oversees meteorological efforts for the Navy and United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps while the United States Air Force's Air Force Weather Agency is responsible for the Air Force and United States Army, Army.
Environmental meteorology
Environmental meteorology mainly analyzes industrial pollution dispersion physically and chemically based on meteorological parameters such as temperature, humidity, wind, and various weather conditions.
Renewable energy
Meteorology applications in renewable energy includes basic research, "exploration," and potential mapping of wind power and solar radiation for wind and solar energy.
See also
References
Further reading
*Byers, Horace. General Meteorology. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1994.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Dictionaries and encyclopedias
*
*
*
History
*
External links
''Please see
weather forecasting
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology forecasting, to predict the conditions of the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia a ...
for weather forecast sites.''
Air Quality Meteorology– Online course that introduces the basic concepts of meteorology and air quality necessary to understand meteorological computer models. Written at a bachelor's degree level.
The GLOBE Program– (Global Learning and Observations to Benefit the Environment) An international environmental science and education program that links students, teachers, and the scientific research community in an effort to learn more about the environment through student data collection and observation.
Glossary of Meteorology– From the American Meteorological Society, an excellent reference of nomenclature, equations, and concepts for the more advanced reader.
JetStream – An Online School for Weather– National Weather Service
Learn About Meteorology– Australian Bureau of Meteorology
The Weather Guide– Weather Tutorials and News at About.com
Meteorology Education and Training (MetEd)– The COMET Program
NOAA Central Library– National Oceanic & Atmospheric Administration
The World Weather 2010 Project The University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign
Ogimet – online data from meteorological stations of the world, obtained through NOAA free servicesNational Center for Atmospheric Research Archives, documents the history of meteorologyWeather forecasting and Climate science
– United Kingdom Meteorological Office
Meteorology
BBC Radio 4 discussion with Vladimir Janković, Richard Hambyn and Iba Taub (''In Our Time, 6 March 2003)
Virtual exhibition about meteorology
on the digital library of Paris Observatory
{{Authority control
Meteorology,
Applied and interdisciplinary physics
Oceanography
Physical geography
Greek words and phrases
 Early attempts at predicting weather were often related to prophecy and divining, and were sometimes based on astrological ideas. Ancient religions believed meteorological phenomena to be under the control of the gods. The ability to predict
Early attempts at predicting weather were often related to prophecy and divining, and were sometimes based on astrological ideas. Ancient religions believed meteorological phenomena to be under the control of the gods. The ability to predict  From 400 to 1100, scientific learning in Europe was preserved by the clergy.
From 400 to 1100, scientific learning in Europe was preserved by the clergy.  In 1441, Sejong the Great of Joseon, King Sejong's son, Prince Munjong of Korea, invented the first standardized rain gauge. These were sent throughout the Joseon dynasty of Korea as an official tool to assess land taxes based upon a farmer's potential harvest. In 1450, Leone Battista Alberti developed a swinging-plate anemometer, and was known as the first ''anemometer''. In 1607, Galileo Galilei constructed a Galileo thermometer, thermoscope. In 1611,
In 1441, Sejong the Great of Joseon, King Sejong's son, Prince Munjong of Korea, invented the first standardized rain gauge. These were sent throughout the Joseon dynasty of Korea as an official tool to assess land taxes based upon a farmer's potential harvest. In 1450, Leone Battista Alberti developed a swinging-plate anemometer, and was known as the first ''anemometer''. In 1607, Galileo Galilei constructed a Galileo thermometer, thermoscope. In 1611,  In the late 16th century and first half of the 17th century a range of meteorological instruments were invented – the thermometer, barometer, hydrometer, as well as wind and rain gauges. In the 1650s natural philosophers started using these instruments to systematically record weather observations. Scientific academies established weather diaries and organised observational networks. In 1654, Ferdinando II de Medici established the first ''weather observing'' network, that consisted of meteorological stations in Florence, Cutigliano, Vallombrosa, Bologna, Parma, Milan, Innsbruck, Osnabrück, Paris and Warsaw. The collected data were sent to Florence at regular time intervals. In the 1660s Robert Hooke of the Royal Society of London sponsored networks of weather observers.
In the late 16th century and first half of the 17th century a range of meteorological instruments were invented – the thermometer, barometer, hydrometer, as well as wind and rain gauges. In the 1650s natural philosophers started using these instruments to systematically record weather observations. Scientific academies established weather diaries and organised observational networks. In 1654, Ferdinando II de Medici established the first ''weather observing'' network, that consisted of meteorological stations in Florence, Cutigliano, Vallombrosa, Bologna, Parma, Milan, Innsbruck, Osnabrück, Paris and Warsaw. The collected data were sent to Florence at regular time intervals. In the 1660s Robert Hooke of the Royal Society of London sponsored networks of weather observers.  In 1904, Norwegian scientist Vilhelm Bjerknes first argued in his paper ''Weather Forecasting as a Problem in Mechanics and Physics'' that it should be possible to forecast weather from calculations based upon physical law, natural laws.
It was not until later in the 20th century that advances in the understanding of atmospheric physics led to the foundation of modern numerical weather prediction. In 1922, Lewis Fry Richardson published "Weather Prediction By Numerical Process," after finding notes and derivations he worked on as an ambulance driver in World War I. He described how small terms in the prognostic fluid dynamics equations that govern atmospheric flow could be neglected, and a numerical calculation scheme that could be devised to allow predictions. Richardson envisioned a large auditorium of thousands of people performing the calculations. However, the sheer number of calculations required was too large to complete without electronic computers, and the size of the grid and time steps used in the calculations led to unrealistic results. Though numerical analysis later found that this was due to numerical instability.
Starting in the 1950s, number, numerical forecasts with computers became feasible. The first weather forecasts derived this way used barotropic (single-vertical-level) models, and could successfully predict the large-scale movement of midlatitude Rossby waves, that is, the pattern of low-pressure area, atmospheric lows and High-pressure area, highs. In 1959, the UK Meteorological Office received its first computer, a Ferranti Mercury.
In the 1960s, the Chaos theory, chaotic nature of the atmosphere was first observed and mathematically described by Edward Lorenz, founding the field of chaos theory. These advances have led to the current use of ensemble forecasting in most major forecasting centers, to take into account uncertainty arising from the chaotic nature of the atmosphere. Mathematical models used to predict the long term weather of the Earth (climate models), have been developed that have a resolution today that are as coarse as the older weather prediction models. These climate models are used to investigate long-term climate shifts, such as what effects might be caused by human emission of greenhouse gases.
In 1904, Norwegian scientist Vilhelm Bjerknes first argued in his paper ''Weather Forecasting as a Problem in Mechanics and Physics'' that it should be possible to forecast weather from calculations based upon physical law, natural laws.
It was not until later in the 20th century that advances in the understanding of atmospheric physics led to the foundation of modern numerical weather prediction. In 1922, Lewis Fry Richardson published "Weather Prediction By Numerical Process," after finding notes and derivations he worked on as an ambulance driver in World War I. He described how small terms in the prognostic fluid dynamics equations that govern atmospheric flow could be neglected, and a numerical calculation scheme that could be devised to allow predictions. Richardson envisioned a large auditorium of thousands of people performing the calculations. However, the sheer number of calculations required was too large to complete without electronic computers, and the size of the grid and time steps used in the calculations led to unrealistic results. Though numerical analysis later found that this was due to numerical instability.
Starting in the 1950s, number, numerical forecasts with computers became feasible. The first weather forecasts derived this way used barotropic (single-vertical-level) models, and could successfully predict the large-scale movement of midlatitude Rossby waves, that is, the pattern of low-pressure area, atmospheric lows and High-pressure area, highs. In 1959, the UK Meteorological Office received its first computer, a Ferranti Mercury.
In the 1960s, the Chaos theory, chaotic nature of the atmosphere was first observed and mathematically described by Edward Lorenz, founding the field of chaos theory. These advances have led to the current use of ensemble forecasting in most major forecasting centers, to take into account uncertainty arising from the chaotic nature of the atmosphere. Mathematical models used to predict the long term weather of the Earth (climate models), have been developed that have a resolution today that are as coarse as the older weather prediction models. These climate models are used to investigate long-term climate shifts, such as what effects might be caused by human emission of greenhouse gases.
 Each science has its own unique sets of laboratory equipment. In the atmosphere, there are many things or qualities of the atmosphere that can be measured. Rain, which can be observed, or seen anywhere and anytime was one of the first atmospheric qualities measured historically. Also, two other accurately measured qualities are wind and humidity. Neither of these can be seen but can be felt. The devices to measure these three sprang up in the mid-15th century and were respectively the rain gauge, the anemometer, and the hygrometer. Many attempts had been made prior to the 15th century to construct adequate equipment to measure the many atmospheric variables. Many were faulty in some way or were simply not reliable. Even
Each science has its own unique sets of laboratory equipment. In the atmosphere, there are many things or qualities of the atmosphere that can be measured. Rain, which can be observed, or seen anywhere and anytime was one of the first atmospheric qualities measured historically. Also, two other accurately measured qualities are wind and humidity. Neither of these can be seen but can be felt. The devices to measure these three sprang up in the mid-15th century and were respectively the rain gauge, the anemometer, and the hygrometer. Many attempts had been made prior to the 15th century to construct adequate equipment to measure the many atmospheric variables. Many were faulty in some way or were simply not reliable. Even  Synoptic scale meteorology predicts atmospheric changes at scales up to 1000 km and 105 sec (28 days), in time and space. At the synoptic scale, the Coriolis acceleration acting on moving air masses (outside of the tropics) plays a dominant role in predictions. The phenomena typically described by synoptic meteorology include events such as extratropical cyclones, baroclinic troughs and ridges, weather front, frontal zones, and to some extent jet streams. All of these are typically given on weather maps for a specific time. The minimum horizontal scale of synoptic phenomena is limited to the spacing between weather station, surface observation stations.
Synoptic scale meteorology predicts atmospheric changes at scales up to 1000 km and 105 sec (28 days), in time and space. At the synoptic scale, the Coriolis acceleration acting on moving air masses (outside of the tropics) plays a dominant role in predictions. The phenomena typically described by synoptic meteorology include events such as extratropical cyclones, baroclinic troughs and ridges, weather front, frontal zones, and to some extent jet streams. All of these are typically given on weather maps for a specific time. The minimum horizontal scale of synoptic phenomena is limited to the spacing between weather station, surface observation stations.
 Global scale meteorology is the study of weather patterns related to the transport of heat from the tropics to the Geographical pole, poles. Very large scale oscillations are of importance at this scale. These oscillations have time periods typically on the order of months, such as the Madden–Julian oscillation, or years, such as the El Niño–Southern Oscillation and the Pacific decadal oscillation. Global scale meteorology pushes into the range of climatology. The traditional definition of climate is pushed into larger timescales and with the understanding of the longer time scale global oscillations, their effect on climate and weather disturbances can be included in the synoptic and mesoscale timescales predictions.
Numerical Weather Prediction is a main focus in understanding air–sea interaction, tropical meteorology, atmospheric predictability, and tropospheric/stratospheric processes. The Naval Research Laboratory in Monterey, California, developed a global atmospheric model called Navy Operational Global Atmospheric Prediction System (NOGAPS). NOGAPS is run operationally at Fleet Numerical Meteorology and Oceanography Center for the United States Military. Many other global atmospheric models are run by national meteorological agencies.
Global scale meteorology is the study of weather patterns related to the transport of heat from the tropics to the Geographical pole, poles. Very large scale oscillations are of importance at this scale. These oscillations have time periods typically on the order of months, such as the Madden–Julian oscillation, or years, such as the El Niño–Southern Oscillation and the Pacific decadal oscillation. Global scale meteorology pushes into the range of climatology. The traditional definition of climate is pushed into larger timescales and with the understanding of the longer time scale global oscillations, their effect on climate and weather disturbances can be included in the synoptic and mesoscale timescales predictions.
Numerical Weather Prediction is a main focus in understanding air–sea interaction, tropical meteorology, atmospheric predictability, and tropospheric/stratospheric processes. The Naval Research Laboratory in Monterey, California, developed a global atmospheric model called Navy Operational Global Atmospheric Prediction System (NOGAPS). NOGAPS is run operationally at Fleet Numerical Meteorology and Oceanography Center for the United States Military. Many other global atmospheric models are run by national meteorological agencies.
 Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere at a future time and given location. Humans have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia and formally since at least the 19th century. Weather forecasts are made by collecting quantitative data about the current state of the atmosphere and using scientific understanding of atmospheric processes to project how the atmosphere will evolve.
Once an all-human endeavor based mainly upon changes in Atmospheric pressure, barometric pressure, current weather conditions, and sky condition, numerical weather prediction, forecast models are now used to determine future conditions. Human input is still required to pick the best possible forecast model to base the forecast upon, which involves pattern recognition skills, teleconnections, knowledge of model performance, and knowledge of model biases. The chaos theory, chaotic nature of the atmosphere, the massive computational power required to solve the equations that describe the atmosphere, error involved in measuring the initial conditions, and an incomplete understanding of atmospheric processes mean that forecasts become less accurate as the difference in current time and the time for which the forecast is being made (the ''range'' of the forecast) increases. The use of ensembles and model consensus help narrow the error and pick the most likely outcome.
There are a variety of end uses to weather forecasts. Weather warnings are important forecasts because they are used to protect life and property. Forecasts based on temperature and Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation are important to agriculture, and therefore to commodity traders within stock markets. Temperature forecasts are used by utility companies to estimate demand over coming days. On an everyday basis, people use weather forecasts to determine what to wear. Since outdoor activities are severely curtailed by heavy rain, snow, and wind chill, forecasts can be used to plan activities around these events, and to plan ahead and survive them.
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere at a future time and given location. Humans have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia and formally since at least the 19th century. Weather forecasts are made by collecting quantitative data about the current state of the atmosphere and using scientific understanding of atmospheric processes to project how the atmosphere will evolve.
Once an all-human endeavor based mainly upon changes in Atmospheric pressure, barometric pressure, current weather conditions, and sky condition, numerical weather prediction, forecast models are now used to determine future conditions. Human input is still required to pick the best possible forecast model to base the forecast upon, which involves pattern recognition skills, teleconnections, knowledge of model performance, and knowledge of model biases. The chaos theory, chaotic nature of the atmosphere, the massive computational power required to solve the equations that describe the atmosphere, error involved in measuring the initial conditions, and an incomplete understanding of atmospheric processes mean that forecasts become less accurate as the difference in current time and the time for which the forecast is being made (the ''range'' of the forecast) increases. The use of ensembles and model consensus help narrow the error and pick the most likely outcome.
There are a variety of end uses to weather forecasts. Weather warnings are important forecasts because they are used to protect life and property. Forecasts based on temperature and Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation are important to agriculture, and therefore to commodity traders within stock markets. Temperature forecasts are used by utility companies to estimate demand over coming days. On an everyday basis, people use weather forecasts to determine what to wear. Since outdoor activities are severely curtailed by heavy rain, snow, and wind chill, forecasts can be used to plan activities around these events, and to plan ahead and survive them.