Messier 94 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Messier 94 (also known as NGC 4736) is a
spiral galaxy
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''northern
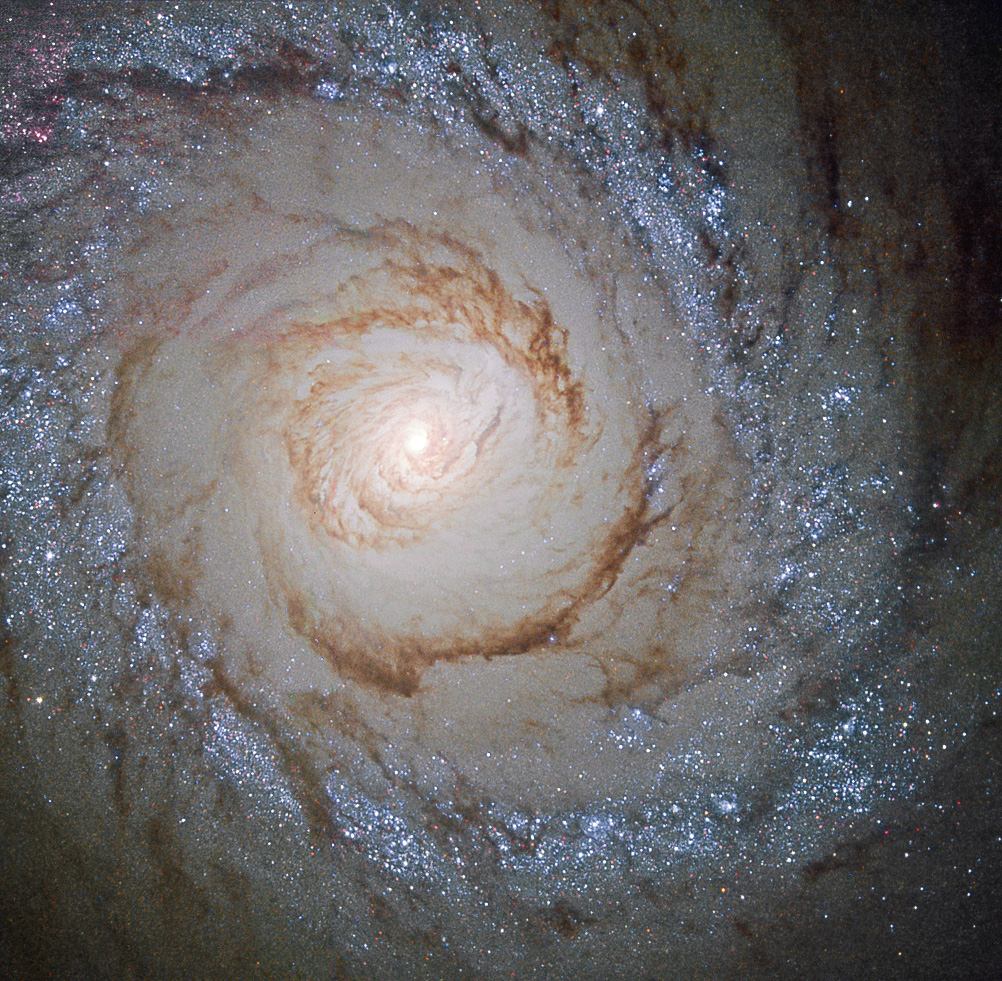 M94 is classified as having a
M94 is classified as having a
constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
Canes Venatici
Canes Venatici () is one of the 88 constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for 'hunting dogs', and ...
. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain
Pierre François André Méchain (; 16 August 1744 – 20 September 1804) was a French astronomer and surveyor who, with Charles Messier, was a major contributor to the early study of deep-sky objects and comets.
Life
Pierre Méchain was born i ...
in 1781,
and catalogued by Charles Messier
Charles Messier (; 26 June 1730 – 12 April 1817) was a French astronomer. He published an astronomical catalogue consisting of 110 nebulae and star clusters, which came to be known as the ''Messier objects''. Messier's purpose f ...
two days later. Although some references describe M94 as a barred spiral galaxy
A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in about two thirds of all spiral galaxies, and generally affect both the motions of stars and interstellar gas within spiral galaxies ...
, the "bar" structure appears to be more oval-shaped.
The galaxy has two ring structures.
Structure
 M94 is classified as having a
M94 is classified as having a low ionization nuclear emission region
A low-ionization nuclear emission-line region (LINER) is a type of galactic nucleus that is defined by its spectral line emission. The spectra typically include line emission from weakly ionized or neutral atoms, such as O, O+, N+, and S+. ...
(LINER) nucleus.
LINERs in general are characterized by optical spectra that reveal that ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
ized gas is present but the gas is only weakly ionized (i.e. the atoms are missing relatively few electrons).
M94 has an inner ring with a diameter of 70 arcseconds (″) (given its distance, about ) and an outer ring with a diameter of 600″ (about ). These rings appear to form at resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillatin ...
points in the disk of the galaxy. The inner ring is the site of strong star formation
Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in The "medium" is present further soon.-->interstellar space
activity and is sometimes referred to as a starburst ring. This star formation is fueled by gas driven dynamically into the ring by the inner oval-shaped bar-like structure.
A 2009 study
conducted by an international team of astrophysicists revealed that the outer ring of M94 is not a closed stellar ring, as historically attributed in the literature, but a complex structure of spiral arms
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''John Kormendy and
Robert Kennicutt
Robert Charles Kennicutt, Jr. FRS is an American astronomer. He is currently a professor at Texas A&M University. He is a former Plumian Professor of Astronomy at the Institute of Astronomy in the University of Cambridge. He was formerly Edit ...
argued that M94 contains a prototypical pseudobulge. A classical spiral galaxy
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''
showing that M94 had very little or no
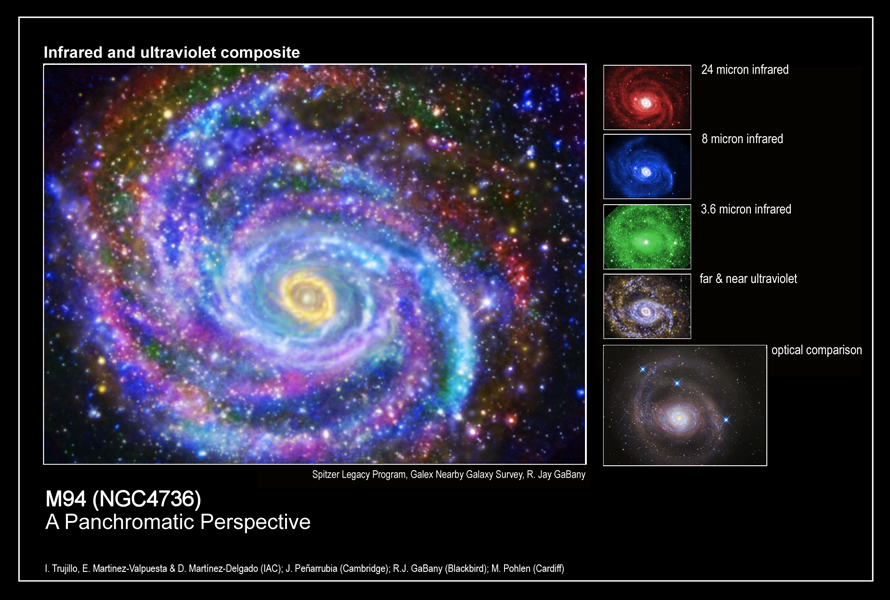 At least two techniques have been used to measure distances to M94. The
At least two techniques have been used to measure distances to M94. The
M94- A Panchromatic Perspective
* * ttp://messier.seds.org/m/m094.html SEDS: Spiral Galaxy M94* {{DEFAULTSORT:Messier 94 Unbarred spiral galaxies Messier 094 Messier 094 Messier 094 094 Messier 094 07996 43495 Astronomical objects discovered in 1781 Discoveries by Pierre Méchain
dark matter
Dark matter is a hypothetical form of matter thought to account for approximately 85% of the matter in the universe. Dark matter is called "dark" because it does not appear to interact with the electromagnetic field, which means it does not a ...
present. The study analyzed the rotation curves of the galaxy's stars and the density of hydrogen gas and found that ordinary luminous matter appeared to account for all of the galaxy's mass. This result was unusual and somewhat controversial, as current models do not indicate how a galaxy could form without a dark matter halo or how a galaxy could lose its dark matter. Other explanations for galactic rotation curves, such as MOND
Modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a hypothesis that proposes a modification of Newton's law of universal gravitation to account for observed properties of galaxies. It is an alternative to the hypothesis of dark matter in terms of explaining ...
, also have difficulty explaining this galaxy.
This result has yet to be confirmed or accepted by other research groups, however, and has not actually been tested against the predictions of standard galaxy formation models.
Location
 At least two techniques have been used to measure distances to M94. The
At least two techniques have been used to measure distances to M94. The surface brightness fluctuation
Surface brightness fluctuation (SBF) is a secondary distance indicator used to estimate distances to galaxies. It is useful to 100 Mpc (parsec). The method measures the variance in a galaxy's light distribution arising from fluctuations in the n ...
s distance measurement technique estimates distances to spiral galaxies based on the graininess of the appearance of their bulges. The distance measured to M94 using this technique is 17.0 ± 1.4 Mly
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
(5.2 ± 0.4 Mpc). However, M94 is close enough that the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versa ...
can be used to resolve and measure the fluxes of the brightest individual stars within the galaxy. These measured fluxes can then be compared to the measured fluxes of similar stars within the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye ...
to measure the distance. The estimated distance to M94 using this technique is 15 ± 2 Mly
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
(4.7 ± 0.6 Mpc). Averaged together, these distance measurements give a distance estimate of 16.0 ± 1.3 Mly
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
(4.9 ± 0.4 Mpc).
M94 is one of the brightest galaxies within the M94 Group, a group of galaxies
A galaxy group or group of galaxies (GrG) is an aggregation of galaxies comprising about 50 or fewer gravitationally bound members, each at least as luminous as the Milky Way (about 1010 times the luminosity of the Sun); collections of galaxies ...
that contains between 16 and 24 galaxies.
This group is one of many that lie within the Virgo Supercluster
The Virgo Supercluster (Virgo SC) or the Local Supercluster (LSC or LS) is a mass concentration of galaxies containing the Virgo Cluster and Local Group, which itself contains the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies, as well as others. At least ...
(i.e. the Local Supercluster). Although a large number of galaxies may be associated with M94, only a few galaxies near M94 appear to form a gravitationally bound system. Most of the other nearby galaxies appear to be moving with the expansion of the universe.
See also
*List of Messier objects
The Messier objects are a set of 110 astronomical objects catalogued by the French astronomer Charles Messier in his ''Catalogue des Nébuleuses et des Amas d'Étoiles'' (''Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters'').
Because Messier was only int ...
* NGC 1512
NGC 1512 is a barred spiral galaxy approximately 38 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation Horologium. The galaxy displays a double ring structure, with a (nuclear) ring around the galactic nucleus and an (inner) further out ...
, a galaxy with a similar double ring.
References
External links
M94- A Panchromatic Perspective
* * ttp://messier.seds.org/m/m094.html SEDS: Spiral Galaxy M94* {{DEFAULTSORT:Messier 94 Unbarred spiral galaxies Messier 094 Messier 094 Messier 094 094 Messier 094 07996 43495 Astronomical objects discovered in 1781 Discoveries by Pierre Méchain