Merino (other) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Merino is a
The Merino is a

 Before the 18th century, the export of Merinos from Spain was a crime punishable by death. In the 18th century, small exportation of Merinos from Spain and local sheep were used as the foundation of Merino flocks in other countries. In 1723, some were exported to Sweden, but the first major consignment of Escurials was sent by
Before the 18th century, the export of Merinos from Spain was a crime punishable by death. In the 18th century, small exportation of Merinos from Spain and local sheep were used as the foundation of Merino flocks in other countries. In 1723, some were exported to Sweden, but the first major consignment of Escurials was sent by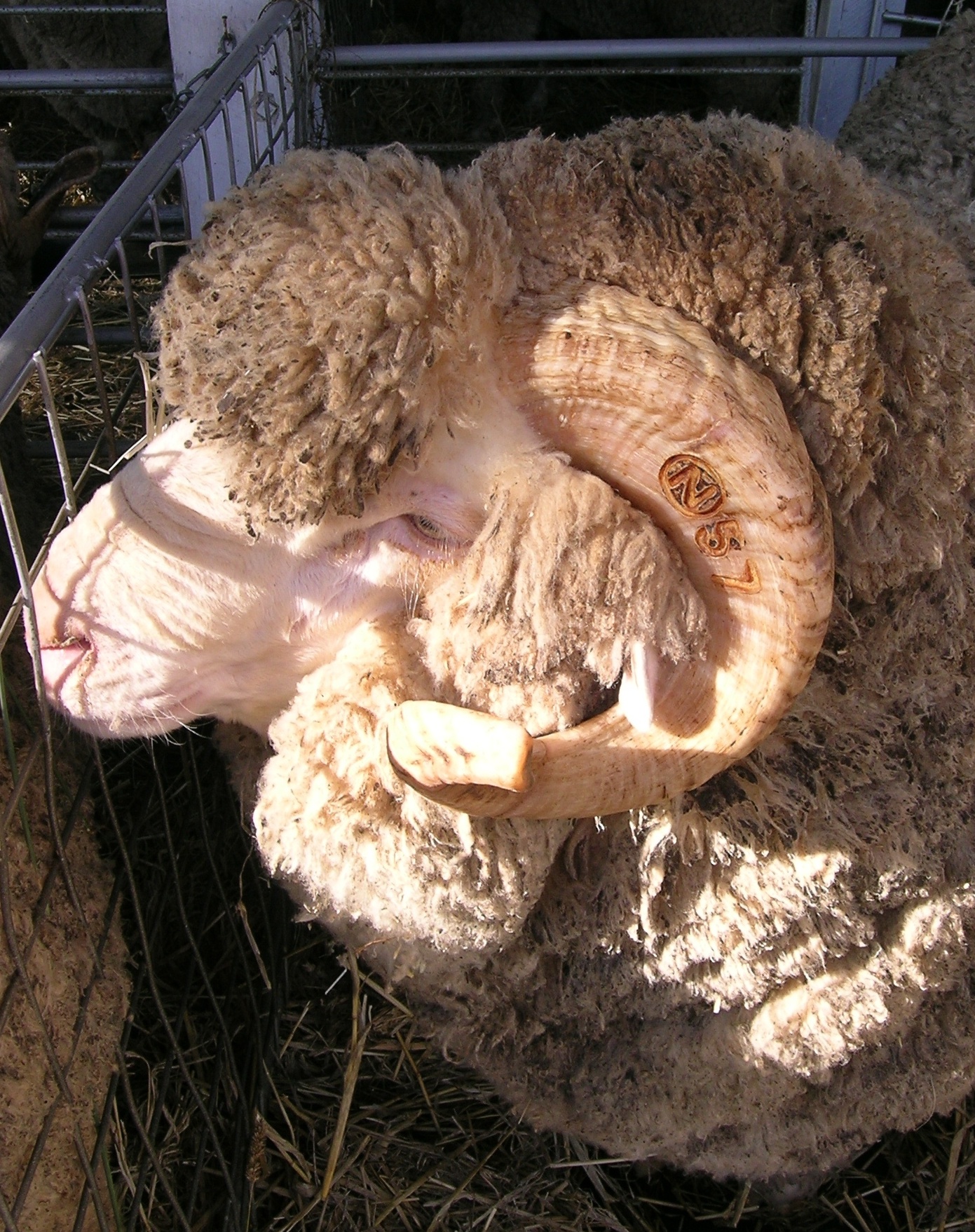  The King of Spain also gave some Escurials to the Dutch government in 1790; these thrived in the Dutch Cape Colony (South Africa). In 1788, John MacArthur, from the Clan Arthur (or MacArthur Clan) introduced Merinos to Australia from South Africa.
From 1765, the Germans in Saxony crossed the Spanish Merino with the Saxon sheep to develop a dense, fine type of Merino (spinning count between 70s and 80s) adapted to its new environment. From 1778, the Saxon breeding center was operated in the Vorwerk Rennersdorf. It was administered from 1796 by Johann Gottfried Nake, who developed scientific crossing methods to further improve the Saxon Merino. By 1802, the region had four million Saxon Merino sheep, and was becoming the centre for stud Merino breeding, and German wool was considered to be the finest in the world.
In 1802, Colonel David Humphreys, United States Ambassador to Spain, introduced the Vermont strain into North America with an importation of 21 rams and 70 ewes from Portugal and a further importation of 100 Infantado Merinos in 1808. The British embargo on wool and wool clothing exports to the U.S. before the 1812 British/U.S. war led to a "Merino Craze", with William Jarvis of the Diplomatic Corps importing at least 3,500
sheep between 1809 and 1811 through Portugal.
The Napoleonic Wars (1793–1813) almost destroyed the Spanish Merino industry. The old ''cabañas'' or flocks were dispersed or slaughtered. From 1810 onwards, the Merino scene shifted to Germany, the United States and Australia. Saxony lifted the export ban on living Merinos after the Napoleonic wars. Highly decorated Saxon sheep breeder Nake from Rennersdorf had established a private sheep farm in Kleindrebnitz in 1811, but ironically after the success of his sheep export to Australia and Russia, failed with his own undertaking.
The King of Spain also gave some Escurials to the Dutch government in 1790; these thrived in the Dutch Cape Colony (South Africa). In 1788, John MacArthur, from the Clan Arthur (or MacArthur Clan) introduced Merinos to Australia from South Africa.
From 1765, the Germans in Saxony crossed the Spanish Merino with the Saxon sheep to develop a dense, fine type of Merino (spinning count between 70s and 80s) adapted to its new environment. From 1778, the Saxon breeding center was operated in the Vorwerk Rennersdorf. It was administered from 1796 by Johann Gottfried Nake, who developed scientific crossing methods to further improve the Saxon Merino. By 1802, the region had four million Saxon Merino sheep, and was becoming the centre for stud Merino breeding, and German wool was considered to be the finest in the world.
In 1802, Colonel David Humphreys, United States Ambassador to Spain, introduced the Vermont strain into North America with an importation of 21 rams and 70 ewes from Portugal and a further importation of 100 Infantado Merinos in 1808. The British embargo on wool and wool clothing exports to the U.S. before the 1812 British/U.S. war led to a "Merino Craze", with William Jarvis of the Diplomatic Corps importing at least 3,500
sheep between 1809 and 1811 through Portugal.
The Napoleonic Wars (1793–1813) almost destroyed the Spanish Merino industry. The old ''cabañas'' or flocks were dispersed or slaughtered. From 1810 onwards, the Merino scene shifted to Germany, the United States and Australia. Saxony lifted the export ban on living Merinos after the Napoleonic wars. Highly decorated Saxon sheep breeder Nake from Rennersdorf had established a private sheep farm in Kleindrebnitz in 1811, but ironically after the success of his sheep export to Australia and Russia, failed with his own undertaking.


 In 1889, while Australian studs were being devastated by the imported Vermont rams, several U.S. Merino breeders formed the Rambouillet Association to prevent the destruction of the Rambouillet line in the U.S. , an estimated 50% of the sheep on the U.S. western ranges are of Rambouillet blood.
The federation drought (1901–1903) reduced the number of Australian sheep from 72 to 53 million and ended the Vermont era. The Peppin and Murray blood strain became dominant in the pastoral and wheat zones of Australia.
In 1889, while Australian studs were being devastated by the imported Vermont rams, several U.S. Merino breeders formed the Rambouillet Association to prevent the destruction of the Rambouillet line in the U.S. , an estimated 50% of the sheep on the U.S. western ranges are of Rambouillet blood.
The federation drought (1901–1903) reduced the number of Australian sheep from 72 to 53 million and ended the Vermont era. The Peppin and Murray blood strain became dominant in the pastoral and wheat zones of Australia.
 The New England Merino Field Days, which display local studs, wool, and sheep, are held during January in even numbered years in and around the Walcha, New South Wales district. The Annual Wool Fashion Awards, which showcase the use of Merino wool by fashion designers, are hosted by the city of Armidale, New South Wales in March each year.
The New England Merino Field Days, which display local studs, wool, and sheep, are held during January in even numbered years in and around the Walcha, New South Wales district. The Annual Wool Fashion Awards, which showcase the use of Merino wool by fashion designers, are hosted by the city of Armidale, New South Wales in March each year.
 Merino is an excellent forager and very adaptable. It is bred predominantly for its wool, and its carcass size is generally smaller than that of sheep bred for meat.
Merino is an excellent forager and very adaptable. It is bred predominantly for its wool, and its carcass size is generally smaller than that of sheep bred for meat.
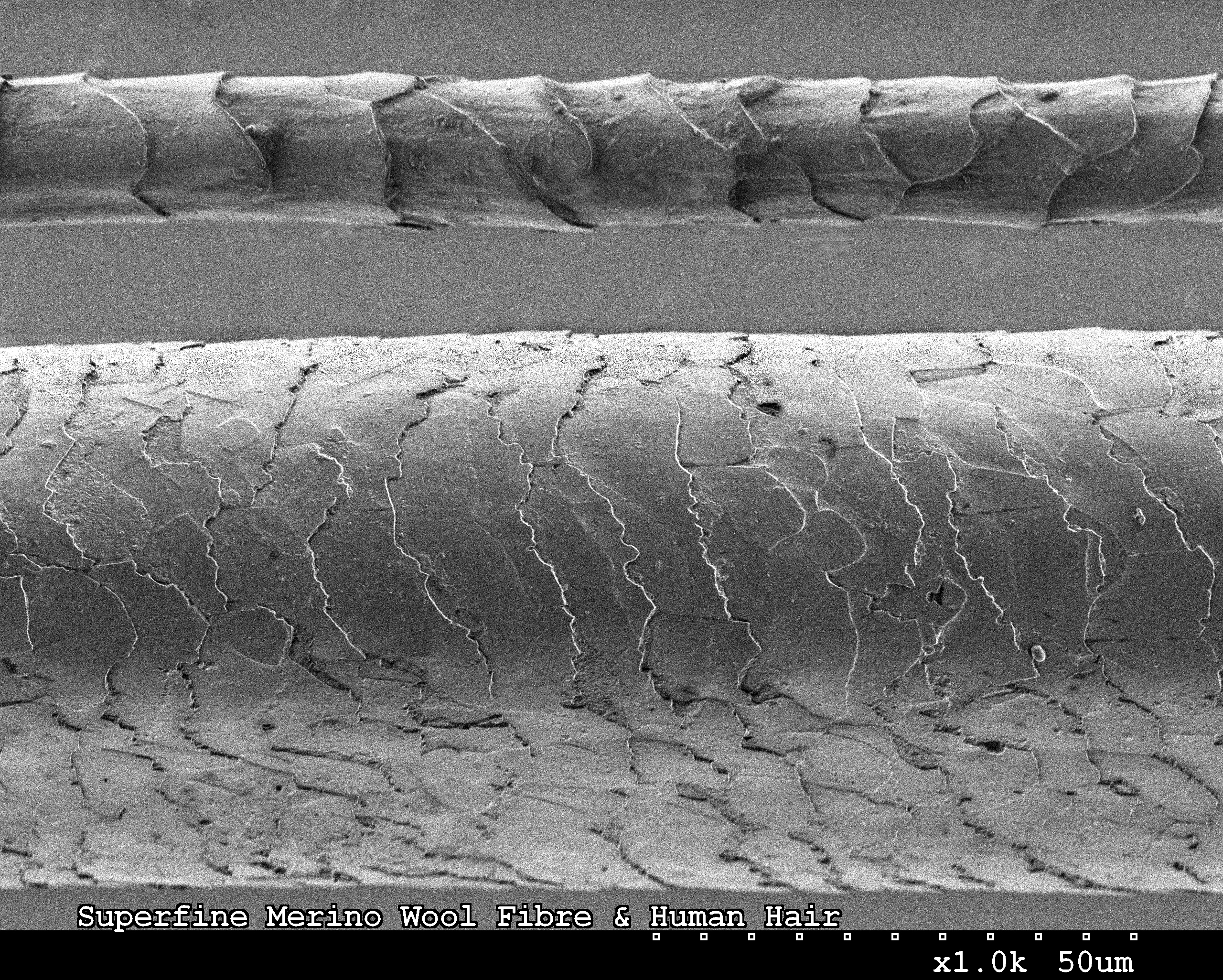
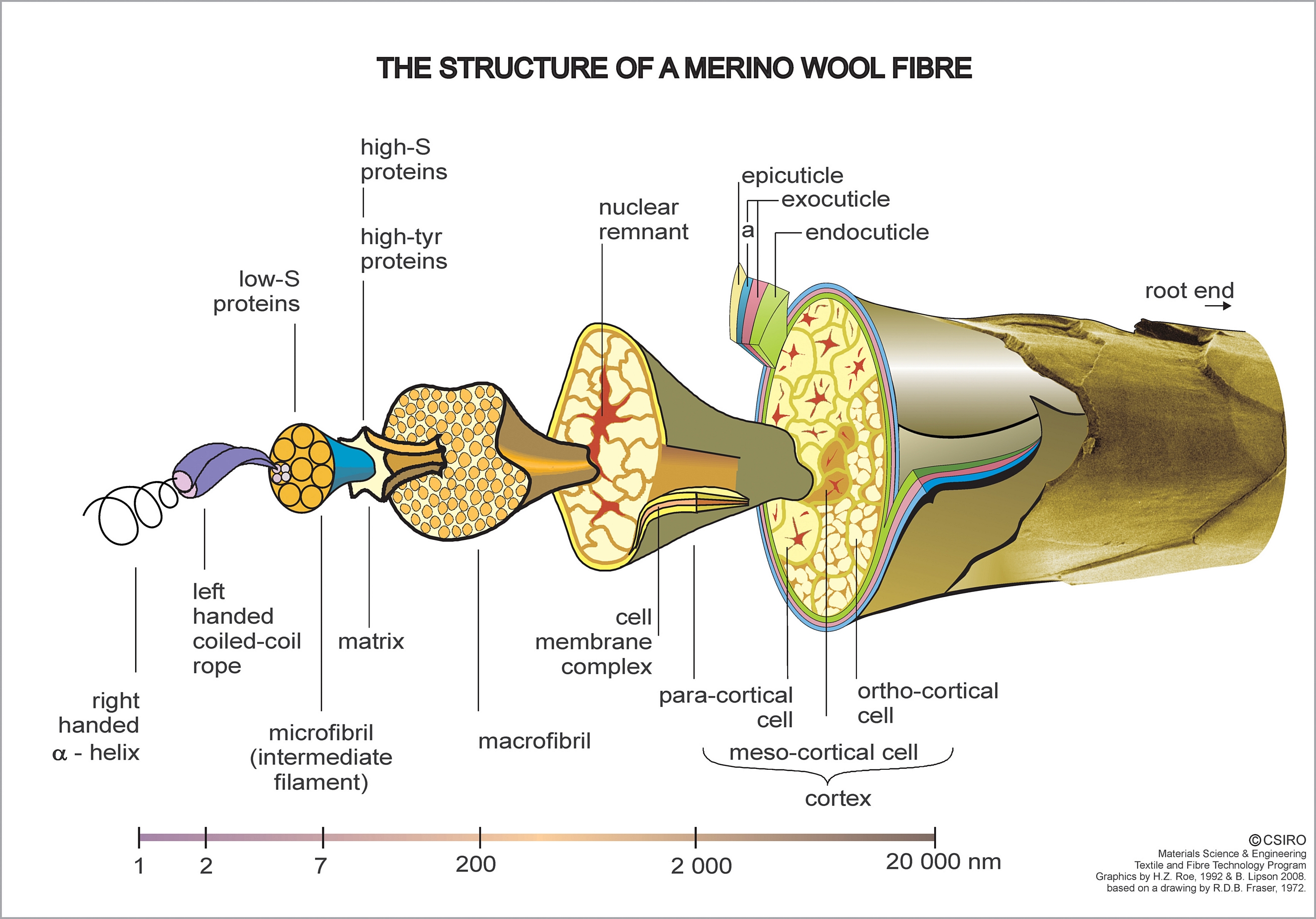 Merino wool is fine and soft. Staples are commonly long. A Saxon Merino produces of greasy wool a year, while a good quality Peppin Merino ram produces up to . Merino wool is generally less than 24 micron (μm) in diameter. Basic Merino types include: strong (broad) wool (23 - 24.5 μm), medium wool (21 - 22.9 μm), fine (18.6 - 20.9 μm), superfine (15 – 18.5 μm) and ultra-fine (11.5 - 15 μm).Australian Wool Classing, Australian Wool Corporation, 1990, p. 26
Merino wool is fine and soft. Staples are commonly long. A Saxon Merino produces of greasy wool a year, while a good quality Peppin Merino ram produces up to . Merino wool is generally less than 24 micron (μm) in diameter. Basic Merino types include: strong (broad) wool (23 - 24.5 μm), medium wool (21 - 22.9 μm), fine (18.6 - 20.9 μm), superfine (15 – 18.5 μm) and ultra-fine (11.5 - 15 μm).Australian Wool Classing, Australian Wool Corporation, 1990, p. 26
The American Delaine & Merino Record AssociationThe American Rambouillet Sheep Breeders AssociationThe Australian Association of Stud Merino BreedersNew Zealand Merino Stud Breeders
{{Authority control Sheep breeds Livestock Sheep breeds originating in Spain
 The Merino is a
The Merino is a breed
A breed is a specific group of domestic animals having homogeneous appearance (phenotype), homogeneous behavior, and/or other characteristics that distinguish it from other organisms of the same species. In literature, there exist several slig ...
or group of breeds of domestic sheep, characterised by very fine soft wool. It was established in Spain near the end of the Middle Ages, and was for several centuries kept as a strict Spanish monopoly; exports of the breed were not allowed, and those who tried risked capital punishment. During the eighteenth century, flocks were sent to the courts of a number of European countries, including France (where they developed into the Rambouillet
Rambouillet (, , ) is a subprefecture of the Yvelines department in the Île-de-France region of France. It is located beyond the outskirts of Paris, southwest of its centre. In 2018, the commune had a population of 26,933.
Rambouillet lies ...
), Hungary, the Netherlands, Prussia, Saxony and Sweden.
The Merino subsequently spread to many parts of the world, including South Africa, Australia, and New Zealand. Numerous recognised breeds, strains and variants have developed from the original type; these include, among others, the American Merino and Delaine Merino in the Americas, the Australian Merino, Booroola Merino and Peppin Merino
The Peppin Merino is a breed of Merino sheep raised for their wool, mostly in Australia. So important is the Peppin Merino that wool producers throughout Australia often classify their sheep simply as being either Peppin, or non-Peppin.
Pepp ...
in Oceania, and the Gentile di Puglia
The Gentile di Puglia is a breed of domestic sheep indigenous to southern Italy. It originates from the Tavoliere di Foggia, a large plain in the northern part of Puglia, and is raised mainly in that region; a few are found in neighbouring reg ...
, Merinolandschaf and Rambouillet in Europe.
The Australian Poll Merino is a polled (hornless) variant. Rams of other Merino breeds have long, spiral horns which grow close to the head, while ewes are usually hornless.
History

Etymology
The name ''merino'' was not documented in Spain until the early 15th century, and its origin is disputed. Two suggested origins for the Spanish word ''merino'' are given in: *It may be an adaptation to the sheep of the name of a Castilian official inspector (''merino'') over a '' merindad'', who may have also inspected sheep pastures. This word is from the medieval Latin ''maiorinus'', a steward or head official of a village, from '' maior'', meaning "greater". However, there is no indication in any of the Leonese or Castilian law codes that this official, either named as ''maiorinus'' or ''merino'' had any duties connected with sheep, and the late date at which ''merino'' was first documented makes any connection with the name of an early medieval magistrate implausible. *It also may be from the name of an Imazighen tribe, the '' Marini'' (or in Spanish, ''Benimerines''), who occupied parts of the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula during the 12th and 13th centuries. This view gains some support from the derivation of many medieval Spanish pastoral terms from Arabic orBerber languages
The Berber languages, also known as the Amazigh languages or Tamazight,, ber, label=Tuareg Tifinagh, ⵜⵎⵣⵗⵜ, ) are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They comprise a group of closely related languages spoken by Berber commun ...
. However, an etymology based on a 12th-century origin for Merino sheep when the Marinids were in Spain is unacceptable; the origin of the breed occurred much later.
Origin
The three theories of the origins of the Merino breed in Spain are: the importation of North African flocks in the 12th century; its origin and improvement in Extremadura in the 12th and 13th centuries; the selective crossbreeding of Spanish ewes with imported rams at several different periods, so that its characteristic fine wool was not fully developed until the 15th century or even later. The first theory accepts that the breed was improved by later importation of North African rams and the second accepts an initial stock of North African sheep related to types from Asia Minor, and both claim an early date and largely North African origin for the Merino breed. Sheep were relatively unimportant in the Islamic Caliphate of Córdoba, and there is no record of extensive transhumance before the caliphate's fall in the 1030s. The Marinids, when a nomadic Zenata Berber tribe, held extensive sheep flocks in what is now Morocco, and its leaders who formed the Marinid Sultanate militarily intervened in southern Spain, supporting the Emirate of Granada several times in the late 13th and early 14th centuries. Although they may possibly have brought new breeds of sheep into Spain, there is no definite evidence that the Marinids did bring extensive flocks to Spain. As the Marinids arrived as an intervening military force, they were hardly in a position to protect extensive flocks and practice selective breeding. The third theory, that the Merino breed was created in Spain over several centuries with a strong Spanish heritage, rather than simply being an existing North African strain that was imported in the 12th century, is supported both by recent genetic studies and the absence of definitive Merino wool before the 15th century. The predominant native sheep breed in Spain from pre-Roman times was the churro, a homogeneous group closely related to European sheep types north of the Pyrenees and bred mainly for meat and milk, with coarse, coloured wool. Churro wool had little value, except where its ewes had been crossed with a fine wool breed from southern Italy in Roman times. Genetic studies have shown that the Merino breed most probably developed by the crossing of churro ewes with a variety of rams of other breeds at different periods, including Italian rams in Roman times, North African rams in the medieval period, and English rams from fine-wool breeds in the 15th century. Although Spain exported wool to England, the Low Countries and Italy in the 13th and 14th centuries, it was only used to make cheap cloth. The earliest evidence of fine Spanish wool exports was to Italy in the 1390s and Flanders in the 1420s, although in both cases fine English wool was preferred. Spain became noted for its fine wool ( spinning count between 60s and 64s) in the late 15th century, and by the mid-16th century its Merino wool was acknowledged to equal that of the finest English wools. The earliest documentary evidence for Merino wools in Italy dates to the 1400s, and in the 1420s and 1430s, Merino wools were being mixed with fine English wool in some towns in the Low Countries to produce high quality cloth. However, it was only in the mid-16th century that the most expensive grades of cloth could be made entirely from Merino wool, after its quality had improved to equal that of the finest English wools, which were in increasingly short supply at that time. Preserved medieval woollen fabrics from the Low Countries show that, before the 16th century, only the best quality English wools had a fineness of staple comparable to modern Merino wool. The wide range of Spanish wools produced in the 13th and early 14th centuries were mostly used domestically for cheap, coarse and light fabrics, and were not Merino wools. Later in the 14th century, similar non-Merino wools were exported from the northern Castilian ports ofSan Sebastián
San Sebastian, officially known as Donostia–San Sebastián (names in both local languages: ''Donostia'' () and ''San Sebastián'' ()) is a city and Municipalities of Spain, municipality located in the Basque Country (autonomous community), B ...
, Santander, and Bilbao to England and the Low Countries to make coarse, cheap cloth. The quality of Spanish wools exported increased markedly in the late 15th century, as did their price, promoted by the efforts of the monarchs Ferdinand and Isabella
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being both ...
to improve quality.
Spain built up a virtual monopoly in fine wool exports in the final decades of the 15th century and in the 16th century, creating a substantial source of income for Castile. In part, this was because most English wool was woven and made into textile goods within England by the 16th century, rather than being exported.
Many of the Castillian Merino flocks were owned by nobility or the church, although Alfonso X realised that granting the urban elites of the towns of Old Castile and León transhumant rights would create an additional source of royal income and counteract the power of the privileged orders. During the late 15th, 16th and early 17th century, two-thirds of the sheep migrating annually were held in flocks of less than 100 sheep and very few flocks exceeded 1,000 sheep. By the 18th century, there were fewer small owners, and several owners held flocks of more than 20,000 sheep, but owners of small to moderately-sized flocks remained, and the Mesta
The ''Mesta'' () was a powerful association protecting livestock owners and their animals in the Crown of Castile that was incorporated in the 13th century and was dissolved in 1836. Although best known for its organisation of the annual migrat ...
was never simply a combination of large owners.
The transhumant sheep grazed the southern Spanish plains in winter and the northern highlands in summer. The annual migrations to and from Castile and León, where the sheep were owned and where they had summer pasturage, was organised and controlled by the Mesta along designated sheep-walks, or ''cañadas reales'' and arranged for suitable grazing, water and rest stops in these routes, and for shearing when the flocks started their return north.
The three Merino strains that founded the world's Merino flocks are the Royal Escurial flocks, the Negretti and the Paula. Among Merino bloodlines stemming from Vermont in the US, three historical studs were highly important: Infantado, Montarcos and Aguires. In recent times, Merino and breeds deriving from Merino stocks have spread worldwide. However, there has been a substantial decline in the numbers of several European Merino breeds, which are now considered to be endangered breeds and are no longer the subject of genetic improvement. In Spain, there are now two populations, the commercial Merino flocks, most common in the province of Extremadura and an "historical" Spanish Merino strain, developed and conserved in a breeding centre near Cordoba. The commercial Merino flocks show considerable genetic diversity, probably because of their cross-breeding with non-Spanish Merino-derived breeds since the 1960s, to create a strain more suitable for meat production. The historical Spanish strain, bred from animals selected from the main traditional Spanish genetic lines to ensure the conservation of a purebred lineage, exhibits signs of inbreeding.
 Before the 18th century, the export of Merinos from Spain was a crime punishable by death. In the 18th century, small exportation of Merinos from Spain and local sheep were used as the foundation of Merino flocks in other countries. In 1723, some were exported to Sweden, but the first major consignment of Escurials was sent by
Before the 18th century, the export of Merinos from Spain was a crime punishable by death. In the 18th century, small exportation of Merinos from Spain and local sheep were used as the foundation of Merino flocks in other countries. In 1723, some were exported to Sweden, but the first major consignment of Escurials was sent by Charles III of Spain
it, Carlo Sebastiano di Borbone e Farnese
, house = Bourbon-Anjou
, father = Philip V of Spain
, mother = Elisabeth Farnese
, birth_date = 20 January 1716
, birth_place = Royal Alcazar of Madrid, Spain
, death_d ...
to his cousin, Prince Xavier the Elector of Saxony, in 1765. Further exportation of Escurials to Saxony occurred in 1774, to Hungary in 1775 and to Prussia in 1786. Later in 1786, Louis XVI of France received 366 sheep selected from 10 different cañadas; these founded the stud at the Royal Farm at Rambouillet
Rambouillet (, , ) is a subprefecture of the Yvelines department in the Île-de-France region of France. It is located beyond the outskirts of Paris, southwest of its centre. In 2018, the commune had a population of 26,933.
Rambouillet lies ...
. In addition to the fine wool breeds mentioned, other breeds derived from Merino stocks were developed to produce mutton, including the French Ile de France and Berrichon du Cher breeds. Merino sheep were also sent to Eastern Europe where their breeding began in Hungary in 1774
The Rambouillet stud enjoyed some undisclosed genetic development with some English long-wool genes contributing to the size and wool-type of the French sheep. Through one ram in particular named Emperor – imported to Australia in 1860 by the Peppin brothers of Wanganella, New South Wales
Wanganella is a village community on the Billabong Creek in New South Wales, Australia. The settlement is on the Cobb Highway, located between Hay (to the north) and Deniliquin (to the south). Wanganella is within the Edward River Council ...
– the Rambouillet stud had an enormous influence on the development of the Australian Merino.
Sir Joseph Banks procured two rams and four ewes in 1787 by way of Portugal, and in 1792 purchased 40 Negrettis for King George III to found the royal flock at Kew. In 1808, 2000 Paulas were imported.
United States Merinos
Merino sheep were introduced to Vermont in 1812. This ultimately resulted in a boom-bust cycle for wool, which reached a price of 57 cents/pound in 1835. By 1837, 1,000,000 sheep were in the state. The price of wool dropped to 25 cents/pound in the late 1840s. The state could not withstand more efficient competition from the other states, and sheep-raising in Vermont collapsed. Many sheep farmers from Vermont migrated with their flocks to other parts of the United States.Australian Merinos
Early history
About 70 native sheep, suitable only for mutton, survived the journey to Australia with theFirst Fleet
The First Fleet was a fleet of 11 ships that brought the first European and African settlers to Australia. It was made up of two Royal Navy vessels, three store ships and six convict transports. On 13 May 1787 the fleet under the command ...
, which arrived in late January 1788. A few months later, the flock had dwindled to just 28 ewes and one lamb.McCosker, Malcolm, Heritage Merino, Owen Edwards Publications, West End, 1988
In 1797, Governor King, Colonel Patterson, Captain Waterhouse and Kent purchased sheep in Cape Town from the widow of Colonel Gordon, commander of the Dutch garrison. When Waterhouse landed in Sydney, he sold his sheep to Captain John MacArthur John MacArthur or Macarthur may refer to:
*J. Roderick MacArthur (1920–1984), American businessman
*John MacArthur (American pastor) (born 1939), American evangelical minister, televangelist, and author
* John Macarthur (priest), 20th-century pro ...
, Samuel Marsden and Captain William Cox. Although the early origin of the Australian Merino breed involved different stocks from Cape Colony, England, Saxony, France and America and although different Merino strains are bred in Australia, the Australian Merino populations are genetically similar and distinct from all other Merino populations, indicating a common history after they arrived in Australia.
John and Elizabeth Macarthur
By 1810, Australia had 33,818 sheep. John MacArthur (who had been sent back from Australia to England following a duel with Colonel Patterson) brought seven rams and one ewe from the first dispersal sale of King George III stud in 1804. The next year, MacArthur and the sheep returned to Australia, Macarthur to reunite with his wife Elizabeth, who had been developing their flock in his absence. Macarthur is considered the father of the Australian Merino industry; in the long term, however, his sheep had very little influence on the development of the Australian Merino. Macarthur pioneered the introduction of Saxon Merinos with importation from the Electoral flock in 1812. The first Australian wool boom occurred in 1813, when theGreat Dividing Range
The Great Dividing Range, also known as the East Australian Cordillera or the Eastern Highlands, is a cordillera system in eastern Australia consisting of an expansive collection of mountain ranges, plateaus and rolling hills, that runs rough ...
was crossed. During the 1820s, interest in Merino sheep increased. MacArthur showed and sold 39 rams in October 1820, grossing £510/16/5. In 1823, at the first sheep show held in Australia, a gold medal was awarded to W. Riley ( 'Raby') for importing the most Saxons; W. Riley also imported cashmere goats
A cashmere goat is a type of goat that produces cashmere wool, the goat's fine, soft, downy, winter undercoat, in commercial quality and quantity. This undercoat grows as the day length shortens and is associated with an outer coat of coarse hair ...
into Australia. 
Eliza and John Furlong
Two of Eliza Furlong's (sometimes spelt Forlong or Forlonge) children had died from consumption, and she was determined to protect her surviving two sons by living in a warm climate and finding them outdoor occupations. Her husband John, a Scottish businessman, had noticed wool from theElectorate of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony (German: or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356–1806. It was centered around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz.
In the Golden Bull of 1356, Emperor Charles ...
sold for much higher prices than wools from New South Wales. The family decided on sheep farming in Australia for their new business. In 1826, Eliza walked over through villages in Saxony and Prussia, selecting fine Saxon Merino sheep. Her sons, Andrew and William, studied sheep breeding and wool classing. The selected 100 sheep were driven (herded) to Hamburg and shipped to Hull. Thence, Eliza and her two sons walked them to Scotland for shipment to Australia. In Scotland, the new Australia Company, which was established in Britain, bought the first shipment, so Eliza repeated the journey twice more. Each time, she gathered a flock for her sons. The sons were sent to New South Wales, but were persuaded to stop in Tasmania with the sheep, where Eliza and her husband joined them.
'' The Age'' in 1908 described Eliza Furlong as someone who had 'notably stimulated and largely helped to mould the prosperity of an entire state and her name deserved to live for all time in our history' (reprinted Wagga Wagga Daily Advertiser 27 January 1989).
John Murray
There were nearly 2 million sheep in Australia by 1830, and by 1836, Australia had won the wool trade war with Germany, mainly because of Germany's preoccupation with fineness. German manufacturers commenced importing Australian wool in 1845. In 1841, at Mount Crawford in South Australia, Murray established a flock of Camden-blood ewes mated to Tasmanian rams. To broaden the wool and give the animals some size, it is thought some English Leicester blood was introduced. The resultant sheep were the foundation of many South Australian strong wool studs. His brother Alexander Borthwick Murray was also a highly successful breeder of Merino sheep.The Peppin brothers
The Peppin brothers took a different approach to producing a hardier, longer-stapled, broader wool sheep. After purchasing Wanganella Station in the Riverina, they selected 200 station-bred ewes that thrived under local conditions and purchased 100 South Australian ewes bred at Cannally that were sired by an imported Rambouillet ram. The Peppin brothers mainly used Saxon and Rambouillet rams, importing four Rambouillet rams in 1860. One of these, Emperor, cut an 11.4 lb (5.1 kg clean) wool clip. They ran some Lincoln ewes, but their introduction into the flock is undocumented. In 1865, George Merriman founded the fine wool Merino Ravensworth Stud, part of which is the Merryville Stud at Yass, New South Wales.Vermont Merinos in Australia
In the 1880s, Vermont rams were imported into Australia from the U.S.; since many Australian stud men believed these sheep would improve wool cuts, their use spread rapidly. Unfortunately, the fleece weight was high, but the clean yield low, the greater grease content increased the risk offly strike
Myiasis is the parasitic infestation of the body of a live animal by fly larvae (maggots) which grow inside the host while feeding on its Biological tissue, tissue. Although flies are most commonly attracted to open wounds and urine- or feces-soa ...
, they had lower uneven wool quality, and lower lambing percentages. Their introduction had a devastating effect on many famous fine-wool studs.
High price records
The world record price for a ram was A$450,000 for JC&S Lustre 53, which sold at the 1988 Merino ram sale atAdelaide, South Australia
Adelaide ( ) is the list of Australian capital cities, capital city of South Australia, the state's largest city and the list of cities in Australia by population, fifth-most populous city in Australia. "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater A ...
. In 2008, an Australian Merino ewe was sold for A$14,000 at the Sheep Show and auction held at Dubbo
Dubbo () is a city in the Orana Region of New South Wales, Australia. It is the largest population centre in the Orana region, with a population of 43,516 at June 2021.
The city is located at the intersection of the Newell, Mitchell, and Gol ...
, New South Wales.
Events
 The New England Merino Field Days, which display local studs, wool, and sheep, are held during January in even numbered years in and around the Walcha, New South Wales district. The Annual Wool Fashion Awards, which showcase the use of Merino wool by fashion designers, are hosted by the city of Armidale, New South Wales in March each year.
The New England Merino Field Days, which display local studs, wool, and sheep, are held during January in even numbered years in and around the Walcha, New South Wales district. The Annual Wool Fashion Awards, which showcase the use of Merino wool by fashion designers, are hosted by the city of Armidale, New South Wales in March each year.
Animal welfare developments
In Australia, mulesing of Merino sheep is a common practice to reduce the incidence offlystrike
Myiasis is the parasitic infestation of the body of a live animal by fly larvae (maggots) which grow inside the host while feeding on its tissue. Although flies are most commonly attracted to open wounds and urine- or feces-soaked fur, some sp ...
. It has been attacked by animal rights and animal welfare
Animal welfare is the well-being of non-human animals. Formal standards of animal welfare vary between contexts, but are debated mostly by animal welfare groups, legislators, and academics. Animal welfare science uses measures such as longevity ...
activists, with PETA
Peta or PETA may refer to:
Acronym
* Pembela Tanah Air, a militia established by the occupying Japanese in Indonesia in 1943
* People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals, an American animal rights organization
* People Eating Tasty Animals, an ...
running a campaign against the practice in 2004. The PETA campaign targeted U.S. consumers by using graphic billboards in New York City. PETA threatened U.S. manufacturers with television advertisements showing their companies' support of mulesing. Fashion retailers including Abercrombie & Fitch Co., Gap Inc
The Gap, Inc., commonly known as Gap Inc. or Gap (stylized as GAP), is an American worldwide clothing and accessories retailer. Gap was founded in 1969 by Donald Fisher and Doris F. Fisher and is headquartered in San Francisco, California. The c ...
and Nordstrom and George (UK) stopped stocking Australian Merino wool products.
New Zealand banned mulesing on 1 October 2018.
Characteristics
 Merino is an excellent forager and very adaptable. It is bred predominantly for its wool, and its carcass size is generally smaller than that of sheep bred for meat.
Merino is an excellent forager and very adaptable. It is bred predominantly for its wool, and its carcass size is generally smaller than that of sheep bred for meat. South African Meat Merino
The South African Meat Merino or SAMM is a wool and meat sheep originating in South Africa, but now found throughout the world.
The SAMM is derived from the German '' Merinofleischschaf'' animals imported into South Africa from Europe in 1932, ...
(SAMM), American Rambouillet and German ''Merinofleischschaf'' have been bred to balance wool production and carcass quality.
Merino has been domesticated and bred in ways that would not allow them to survive well without regular shearing by their owners. They must be shorn at least once a year because their wool does not stop growing. If this is neglected, the overabundance of wool can cause heat stress, mobility issues, and even blindness.
Wool qualities
 Merino wool is fine and soft. Staples are commonly long. A Saxon Merino produces of greasy wool a year, while a good quality Peppin Merino ram produces up to . Merino wool is generally less than 24 micron (μm) in diameter. Basic Merino types include: strong (broad) wool (23 - 24.5 μm), medium wool (21 - 22.9 μm), fine (18.6 - 20.9 μm), superfine (15 – 18.5 μm) and ultra-fine (11.5 - 15 μm).Australian Wool Classing, Australian Wool Corporation, 1990, p. 26
Merino wool is fine and soft. Staples are commonly long. A Saxon Merino produces of greasy wool a year, while a good quality Peppin Merino ram produces up to . Merino wool is generally less than 24 micron (μm) in diameter. Basic Merino types include: strong (broad) wool (23 - 24.5 μm), medium wool (21 - 22.9 μm), fine (18.6 - 20.9 μm), superfine (15 – 18.5 μm) and ultra-fine (11.5 - 15 μm).Australian Wool Classing, Australian Wool Corporation, 1990, p. 26
See also
* Arkhar-Merino * Booroola Merino * Delaine Merino * Jean Chanorier *Peppin Merino
The Peppin Merino is a breed of Merino sheep raised for their wool, mostly in Australia. So important is the Peppin Merino that wool producers throughout Australia often classify their sheep simply as being either Peppin, or non-Peppin.
Pepp ...
* Poll Merino
* Rambouillet sheep
References
Further reading
*External links
The American Delaine & Merino Record Association
{{Authority control Sheep breeds Livestock Sheep breeds originating in Spain