Mensur Akgun on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Academic fencing (german: link=no, akademisches Fechten) or is the traditional kind of fencing practiced by some student corporations () in Germany, Austria,

 Modern academic fencing, the ''Mensur'', is neither a
Modern academic fencing, the ''Mensur'', is neither a



 Starting in Spain at the end of the 15th century, the dueling sword ( rapier) became a regular part of the attire of noblemen throughout Europe. In the Holy Roman Empire, this became usual among students, as well. Brawling and fighting were regular occupations of students in the German-speaking areas during the early modern period. In line with developments in the aristocracy and the military, regulated duels were introduced to the academic environment, as well. The basis of this was the conviction that being a student meant being something different from the rest of the population. Students wore special clothes, developed special kinds of festivities, sang student songs, and fought duels, sometimes spontaneously (so-called ''rencontre'', French "meeting" or "combat"), sometimes according to strict regulations called ''comment'' (French "how"). The weapons used were the same as those employed in civilian dueling, being at first the rapier and later the smallsword (court sword, dress sword, French ''l'ÃĐpÃĐe de cour'', German ''KostÞmdegen'', ''Galanteriedegen''), which was seen as part of the dress and always at hand as a side arm.
Student life was quite unsafe in these years, especially in the 16th and 17th centuries during the Reformation wars and the Thirty Years' War (1618â1648), when a major part of the German population was killed. Public life was brutal and students killing each other in the street was not uncommon.
A major step towards civilization was the introduction of the "regulated"
Starting in Spain at the end of the 15th century, the dueling sword ( rapier) became a regular part of the attire of noblemen throughout Europe. In the Holy Roman Empire, this became usual among students, as well. Brawling and fighting were regular occupations of students in the German-speaking areas during the early modern period. In line with developments in the aristocracy and the military, regulated duels were introduced to the academic environment, as well. The basis of this was the conviction that being a student meant being something different from the rest of the population. Students wore special clothes, developed special kinds of festivities, sang student songs, and fought duels, sometimes spontaneously (so-called ''rencontre'', French "meeting" or "combat"), sometimes according to strict regulations called ''comment'' (French "how"). The weapons used were the same as those employed in civilian dueling, being at first the rapier and later the smallsword (court sword, dress sword, French ''l'ÃĐpÃĐe de cour'', German ''KostÞmdegen'', ''Galanteriedegen''), which was seen as part of the dress and always at hand as a side arm.
Student life was quite unsafe in these years, especially in the 16th and 17th centuries during the Reformation wars and the Thirty Years' War (1618â1648), when a major part of the German population was killed. Public life was brutal and students killing each other in the street was not uncommon.
A major step towards civilization was the introduction of the "regulated" 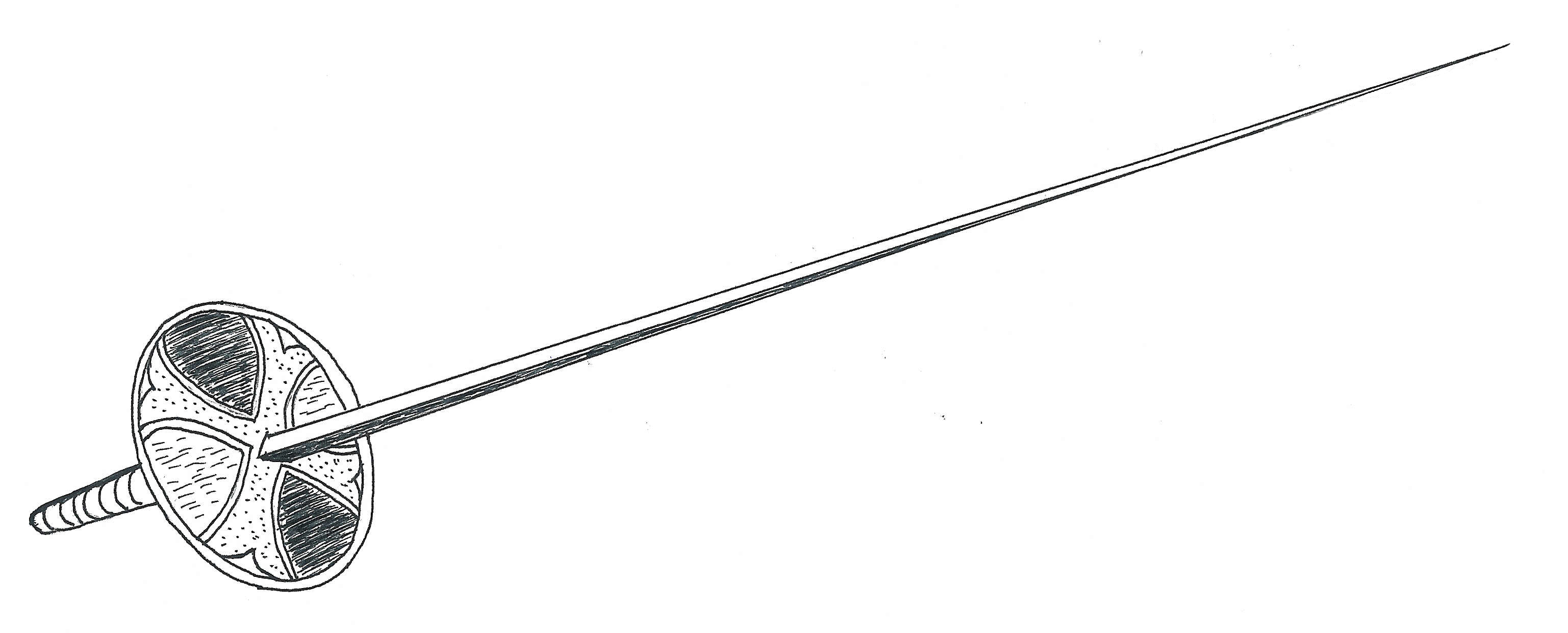 The foil was invented in France as a training weapon in the middle of the 18th century to practice fast and elegant thrust fencing. Fencers blunted the point by wrapping a foil around the blade or fastening a knob on the point ("blossom", French ''fleuret''). In addition to practising, some fencers took away the protection and used the sharp foil for duels. German students took up that practice and developed the ''Pariser'' ("Parisian") thrusting small sword for the ''StoÃmensur'' ("thrusting mensur"). After the dress sword was abolished, the ''Pariser'' became the only weapon for academic thrust fencing in Germany.
Since fencing on thrust with a sharp point is quite dangerous, many students died from their lungs being pierced (''Lungenfuchser''), which made breathing difficult or impossible. However, the counter-movement had already started in GÃķttingen in the 1760s. Here the ''GÃķttinger Hieber'' was invented, the predecessor of the modern ''KorbschlÃĪger'', a new weapon for cut fencing. In the following years, the ''GlockenschlÃĪger'' was invented in east German universities for cut fencing as well.
Thrust fencing (using ''Pariser'') and cut fencing (using '' KorbschlÃĪger'' or '' GlockenschlÃĪger'') existed in parallel in Germany during the first decades of the 19th centuryâwith local preferences. Thrust fencing was especially popular in Jena, Erlangen, WÞrzburg, and Ingolstadt/
The foil was invented in France as a training weapon in the middle of the 18th century to practice fast and elegant thrust fencing. Fencers blunted the point by wrapping a foil around the blade or fastening a knob on the point ("blossom", French ''fleuret''). In addition to practising, some fencers took away the protection and used the sharp foil for duels. German students took up that practice and developed the ''Pariser'' ("Parisian") thrusting small sword for the ''StoÃmensur'' ("thrusting mensur"). After the dress sword was abolished, the ''Pariser'' became the only weapon for academic thrust fencing in Germany.
Since fencing on thrust with a sharp point is quite dangerous, many students died from their lungs being pierced (''Lungenfuchser''), which made breathing difficult or impossible. However, the counter-movement had already started in GÃķttingen in the 1760s. Here the ''GÃķttinger Hieber'' was invented, the predecessor of the modern ''KorbschlÃĪger'', a new weapon for cut fencing. In the following years, the ''GlockenschlÃĪger'' was invented in east German universities for cut fencing as well.
Thrust fencing (using ''Pariser'') and cut fencing (using '' KorbschlÃĪger'' or '' GlockenschlÃĪger'') existed in parallel in Germany during the first decades of the 19th centuryâwith local preferences. Thrust fencing was especially popular in Jena, Erlangen, WÞrzburg, and Ingolstadt/
 American traveller
American traveller
The Secret History of the Sword
{{DEFAULTSORT:Academic Fencing Fencing Historical fencing Student societies in Germany Student sport Blood sports
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, NeuchÃĒtel ...
, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, LeÅĢmÅ), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, LeÅĢmÅ VabÄmÅ, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, Estonia, and, to a minor extent, in Belgium, Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
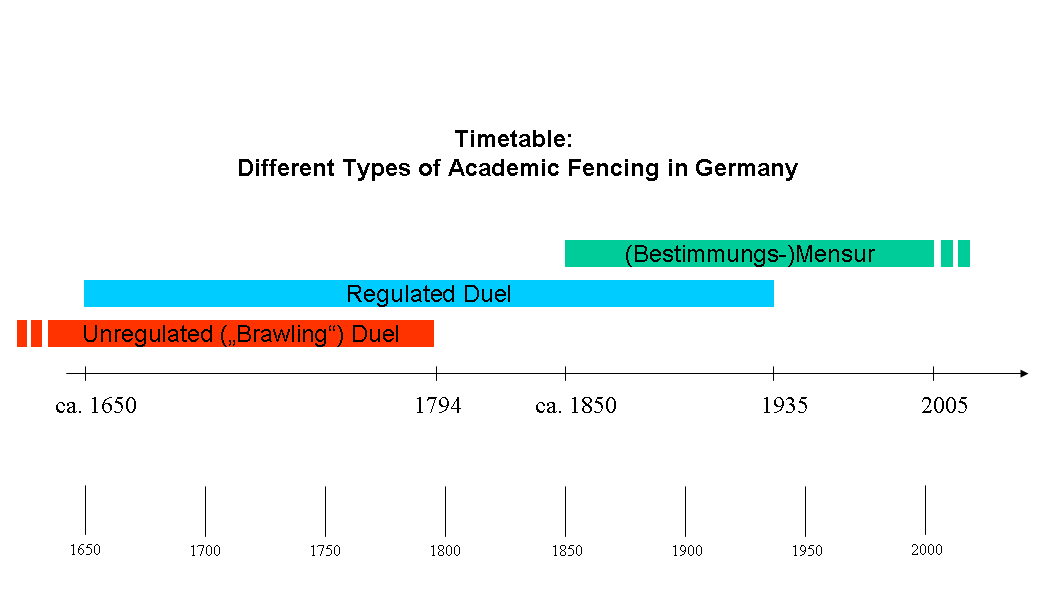
, and Poland. It is a traditional, strictly regulated ÃĐpÃĐe fight between two male members of different fraternities with sharp weapons. The German technical term (from Latin meaning 'dimension') in the 16th century referred to the specified distance between each of the fencers.
Technique

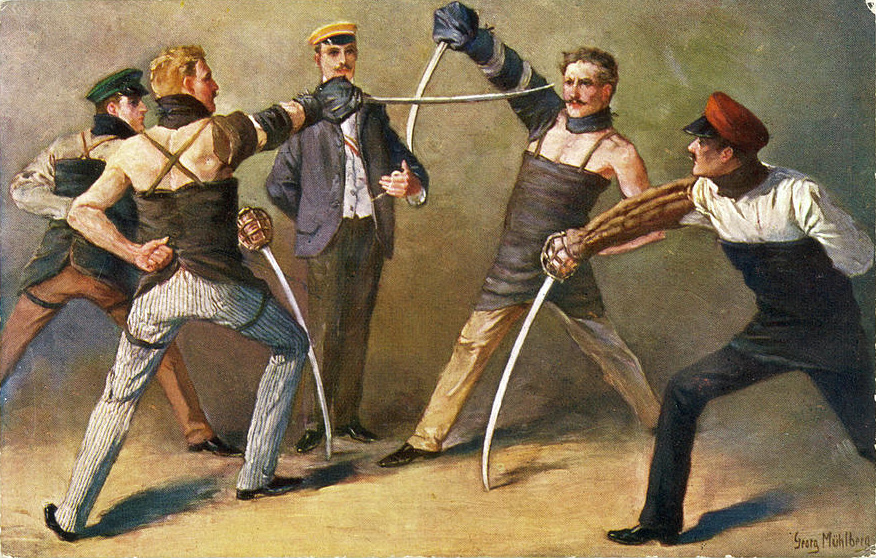
 Modern academic fencing, the ''Mensur'', is neither a
Modern academic fencing, the ''Mensur'', is neither a duel
A duel is an arranged engagement in combat between two people, with matched weapons, in accordance with agreed-upon Code duello, rules.
During the 17th and 18th centuries (and earlier), duels were mostly single combats fought with swords (the r ...
nor a sport. It is a traditional way of training and educating character and personality; thus, in a mensur bout, there is neither winner nor loser. In contrast to sports fencing, the participants stand their ground at a fixed distance. At the beginning of the tradition, duelers wore only their normal clothing (as duels sometimes would arise spontaneously) or light-cloth armor on the arm, torso, and throat. In recent years, fencers are protected by mail or padding for the body, fencing arm, fencing hand (gauntlet
Gauntlet or the gauntlet may refer to:
Common uses
*Gauntlet (glove), protective gloves used as a form of armor
*Running the gauntlet, a form of physical punishment
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional characters
*Gauntlet (comics), a Marvel ...
) and the throat, completed by steel goggles with a nose guard. In Austria and Switzerland, a nose guard is uncommon. Opponents fence at arm's length and stand more or less in one place, while attempting to hit the unprotected areas of their opponent's face and head. Flinching or dodging is not allowed, the goal being less to avoid injury than to endure it stoically. Two physicians are present (one for each opponent) to attend to injuries and stop the fight if necessary.
The participants, or ''Paukanten'', use specially developed swords. The so-called ''MensurschlÃĪger'' (or simply ''SchlÃĪger''), exists in two versions. The most common weapon is the ''KorbschlÃĪger'' with a basket-type guard. Some universities use the so-called ''GlockenschlÃĪger'', which is equipped with a bell-shaped guard. These universities are Leipzig, Berlin, Greifswald, Dresden, Tharandt (in the Forestry College, which is now part of Technische UniversitÃĪt Dresden), Halle on the Saale, Frankfurt-an-der-Oder, and Freiberg. In Jena, both ''KorbschlÃĪger'' and ''GlockenschlÃĪger'' are used. ''Studentenverbindungen'' from some western cities use ''GlockenschlÃĪger'' because their tradition had its origin in one of the eastern universities but moved to West Germany after World War II.
The scar resulting from a hit is called a "smite" (German ''Schmiss''), and was seen as a badge of honour, especially in the second half of the 19th century and the first half of the 20th. Nowadays the presence of scars usually indicates a mistake and therefore are no longer considered especially dignified. Today, it is not easy for an outsider to identify Mensur scars due to better medical treatment. Also, the number of mandatory Mensuren was reduced in the second half of the 20th century. Most Mensur scars are located on the left temple of the forehead. Scars on the cheek and chin are rather uncommon today and sometimes due to accidents.
History




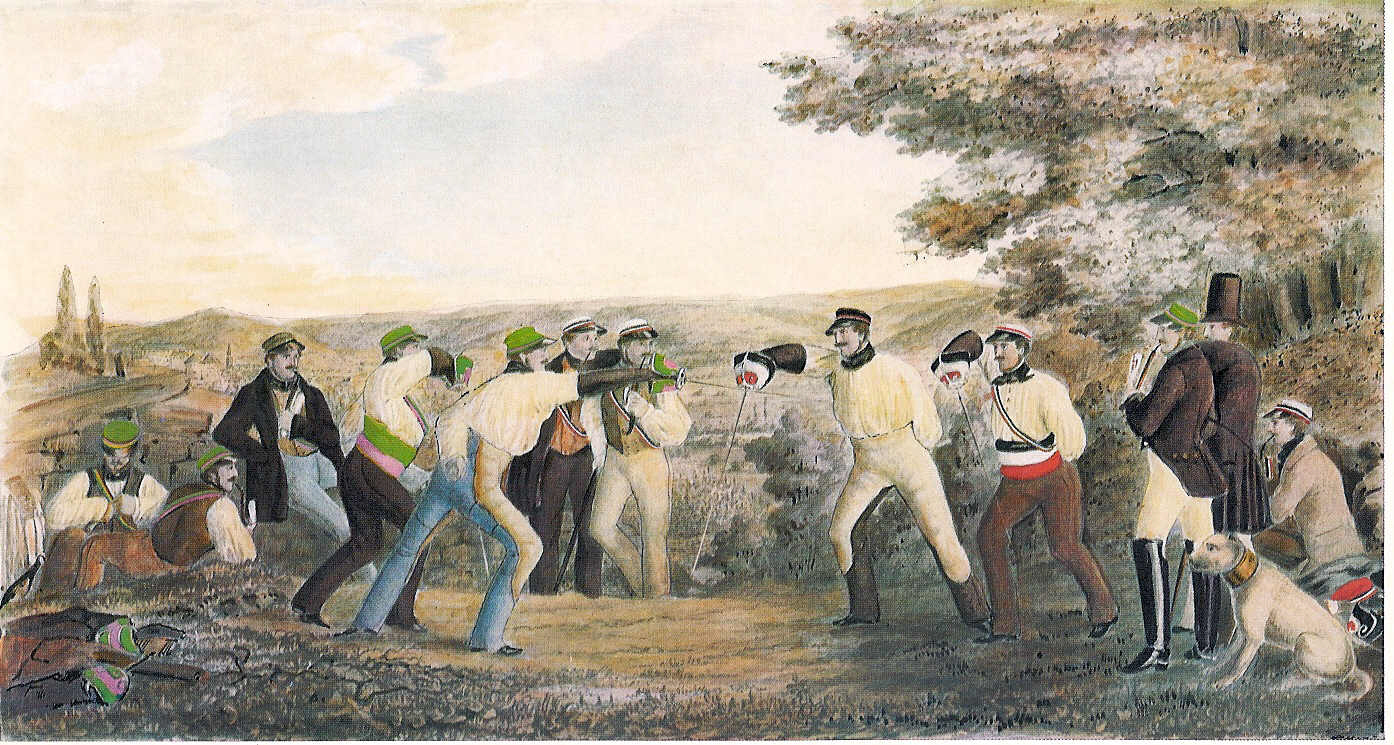
 Starting in Spain at the end of the 15th century, the dueling sword ( rapier) became a regular part of the attire of noblemen throughout Europe. In the Holy Roman Empire, this became usual among students, as well. Brawling and fighting were regular occupations of students in the German-speaking areas during the early modern period. In line with developments in the aristocracy and the military, regulated duels were introduced to the academic environment, as well. The basis of this was the conviction that being a student meant being something different from the rest of the population. Students wore special clothes, developed special kinds of festivities, sang student songs, and fought duels, sometimes spontaneously (so-called ''rencontre'', French "meeting" or "combat"), sometimes according to strict regulations called ''comment'' (French "how"). The weapons used were the same as those employed in civilian dueling, being at first the rapier and later the smallsword (court sword, dress sword, French ''l'ÃĐpÃĐe de cour'', German ''KostÞmdegen'', ''Galanteriedegen''), which was seen as part of the dress and always at hand as a side arm.
Student life was quite unsafe in these years, especially in the 16th and 17th centuries during the Reformation wars and the Thirty Years' War (1618â1648), when a major part of the German population was killed. Public life was brutal and students killing each other in the street was not uncommon.
A major step towards civilization was the introduction of the "regulated"
Starting in Spain at the end of the 15th century, the dueling sword ( rapier) became a regular part of the attire of noblemen throughout Europe. In the Holy Roman Empire, this became usual among students, as well. Brawling and fighting were regular occupations of students in the German-speaking areas during the early modern period. In line with developments in the aristocracy and the military, regulated duels were introduced to the academic environment, as well. The basis of this was the conviction that being a student meant being something different from the rest of the population. Students wore special clothes, developed special kinds of festivities, sang student songs, and fought duels, sometimes spontaneously (so-called ''rencontre'', French "meeting" or "combat"), sometimes according to strict regulations called ''comment'' (French "how"). The weapons used were the same as those employed in civilian dueling, being at first the rapier and later the smallsword (court sword, dress sword, French ''l'ÃĐpÃĐe de cour'', German ''KostÞmdegen'', ''Galanteriedegen''), which was seen as part of the dress and always at hand as a side arm.
Student life was quite unsafe in these years, especially in the 16th and 17th centuries during the Reformation wars and the Thirty Years' War (1618â1648), when a major part of the German population was killed. Public life was brutal and students killing each other in the street was not uncommon.
A major step towards civilization was the introduction of the "regulated" duel
A duel is an arranged engagement in combat between two people, with matched weapons, in accordance with agreed-upon Code duello, rules.
During the 17th and 18th centuries (and earlier), duels were mostly single combats fought with swords (the r ...
, of which the first recordings exist from the 17th century. The fight was not decided on the spot, but the time and location were appointed and negotiations were done by officials. A so-called ''KartelltrÃĪger'' did the arrangements and a "second" represented the interests of the fighter during the duel and could even give physical protection from illegal actions. A kind of referee was present to make decisions, and eventually, the practice of having an attending doctor became normal so as to give medical help in case of an injury.
At the end of the 18th century (after the French Revolution), wearing weapons in everyday life fell out of fashion and was more and more forbidden, even for students. This certainly reduced the number of spontaneous duels dramatically. The regulated duel remained in use, though still forbidden.
 The foil was invented in France as a training weapon in the middle of the 18th century to practice fast and elegant thrust fencing. Fencers blunted the point by wrapping a foil around the blade or fastening a knob on the point ("blossom", French ''fleuret''). In addition to practising, some fencers took away the protection and used the sharp foil for duels. German students took up that practice and developed the ''Pariser'' ("Parisian") thrusting small sword for the ''StoÃmensur'' ("thrusting mensur"). After the dress sword was abolished, the ''Pariser'' became the only weapon for academic thrust fencing in Germany.
Since fencing on thrust with a sharp point is quite dangerous, many students died from their lungs being pierced (''Lungenfuchser''), which made breathing difficult or impossible. However, the counter-movement had already started in GÃķttingen in the 1760s. Here the ''GÃķttinger Hieber'' was invented, the predecessor of the modern ''KorbschlÃĪger'', a new weapon for cut fencing. In the following years, the ''GlockenschlÃĪger'' was invented in east German universities for cut fencing as well.
Thrust fencing (using ''Pariser'') and cut fencing (using '' KorbschlÃĪger'' or '' GlockenschlÃĪger'') existed in parallel in Germany during the first decades of the 19th centuryâwith local preferences. Thrust fencing was especially popular in Jena, Erlangen, WÞrzburg, and Ingolstadt/
The foil was invented in France as a training weapon in the middle of the 18th century to practice fast and elegant thrust fencing. Fencers blunted the point by wrapping a foil around the blade or fastening a knob on the point ("blossom", French ''fleuret''). In addition to practising, some fencers took away the protection and used the sharp foil for duels. German students took up that practice and developed the ''Pariser'' ("Parisian") thrusting small sword for the ''StoÃmensur'' ("thrusting mensur"). After the dress sword was abolished, the ''Pariser'' became the only weapon for academic thrust fencing in Germany.
Since fencing on thrust with a sharp point is quite dangerous, many students died from their lungs being pierced (''Lungenfuchser''), which made breathing difficult or impossible. However, the counter-movement had already started in GÃķttingen in the 1760s. Here the ''GÃķttinger Hieber'' was invented, the predecessor of the modern ''KorbschlÃĪger'', a new weapon for cut fencing. In the following years, the ''GlockenschlÃĪger'' was invented in east German universities for cut fencing as well.
Thrust fencing (using ''Pariser'') and cut fencing (using '' KorbschlÃĪger'' or '' GlockenschlÃĪger'') existed in parallel in Germany during the first decades of the 19th centuryâwith local preferences. Thrust fencing was especially popular in Jena, Erlangen, WÞrzburg, and Ingolstadt/Landshut
Landshut (; bar, Landshuad) is a town in Bavaria in the south-east of Germany. Situated on the banks of the River Isar, Landshut is the capital of Lower Bavaria, one of the seven administrative regions of the Free State of Bavaria. It is also t ...
, two towns where the predecessors of Munich University were located. The last thrust ''Mensur'' is recorded to have taken place in WÞrzburg in 1860.
Until the first half of the 19th century, all types of academic fencing can be seen as duels, since all fencing with sharp weapons was about honour. No combat with sharp blades took place without a formal insult. Compared to pistol duels, these events were relatively harmless. The fight regularly ended when a contestant received a wound at least one inch long that produced at least one drop of blood. It was not uncommon for students to have fought approximately 10 to 30 duels of that kind during their university years. The German student Fritz Bacmeister is the 19th-century record holder, due to his estimated 100 mensur bouts fought in GÃķttingen, Jena, and WÞrzburg between 1860 and 1866.
In the 20th and 21st century it was Alexander Kliesch (Landsmannschaft Brandenburg Berlin) with 70.
For duels with nonstudents, e.g., military officers, the "academic sabre" became usual, apparently derived from the military sabre. It was a heavy weapon with a curved blade and a hilt similar to the ''KorbschlÃĪger''.
During the first half of the 19th century and some of the 18th century, students believed the character of a person could easily be judged by watching him fight with sharp blades under strict regulations. Academic fencing was more and more seen as a kind of personality training by showing countenance and fairness even in dangerous situations. Student corporations demanded their members fight at least one duel with sharp blades during their university time. The problem was that some peaceful students had nobody to offend them. The solution was a kind of formal insult that did not actually infringe honour, but was just seen as a challenge for fencing. The standard wording was ''dummer Junge'' (German for "stupid boy.")
In the long term, this solution was unsatisfying. Around 1850, the ''Bestimmungsmensur'' (German ''bestimmen'' means "ascertain", "define" or "determine") was developed and introduced throughout Germany. This meant the opponents of a ''Mensur'' were determined by the fencing official of their corporations. These officials were regularly vice-chairmen (''Consenior'') and responsible for arranging ''Mensur'' bouts in cooperation with their colleagues from other corporations. Their objective was to find opponents of equal physical and fencing capabilities to make the event challenging for both participants. That is the way it is still done today and is the concept of the ''Mensur'' in the modern sense of the word.
Before the Communist revolution in Russia and before World War II, academic fencing was known in most countries of Eastern Europe, as well.
Modern Mensur
By the end of the 19th century, the dueling form evolved into the modern Mensur. In 1884, the British '' Saturday Review'' described the dueling as follows:In the German SchlÃĪger combat the position is the same as in back-swording, save that the left arm is kept, as in sabre play, behind the body; commonly the waistband of the trousers is grasped by the left hand. The weapon is a long, narrow blade, like a pointless rapier, but much more flexible. It is sharpened for a length of twenty centimetres (say eight inches) on the true edge, and five on the false edge. For practice and instruction blunt and rather stouter blades are used. The mask is like an English single-stick mask, but stronger and heavier. A padded leather vest, coming almost down to the knees, covers the body, and the right arm is encased in a sleeve attached to a gauntlet, which may be compared to an elongated Rugby football. In the actual duel, there is an even more elaborate system of defense; the right wrist is guarded with a ring of mail, and the arm with folds of silk, which, like the turban of the East, are enough to stop an ordinary cut. Practically, though not according to strict rules, the body is altogether covered. The eyes are protected by iron spectacles, with a strong wire net instead of glasses.During the times of the Third Reich, the national socialist leadership chose to forbid academic fencing. They had recognized that Mensur fencing was an integral part of the internal strength of the last still-existing independent Studentenverbindung fraternities during the later 1930s. As Nazi pressure increased and fraternities were forced to officially suspend their activities, so-called comradeships were founded. These provided means for practicing and organizing the Mensur among former fraternities while remaining undetected to the Nazi secret police. One such example was the SC-Comradeship '' Hermann LÃķns'' initiated by members of the
Corps Hubertia Freiburg
The Corps Hubertia Freiburg is a fraternity (''Studentenverbindung'') in Freiburg, Germany. It was founded on October 29, 1868 and is one of 162 German Student Corps in Europe today. The Corps is a member of the KÃķsener Senioren-Convents-Verban ...
and other fraternities in Freiburg, Germany. There, fencing Mensur "duels" continued and even intensified from 1941 on, with over 100 of such duels happening during World War II in Freiburg alone. Following the war, most of the formerly suspended fraternities were reactivated and resumed the traditions of Mensur fencing if they had not continued throughout the time of Nazi occupation.
Today, the Mensur is practiced by about 400 traditional ''Studentenverbindung'' fraternities in Germany, several of the Corps, Burschenschaften, Landsmannschaften, Turnerschaften and SÃĪngerschaften. Menzura, as the Mensur is known in Poland, and is still practised, although its popularity has declined since the end of World War II. It is also still known in a few other European countries, though there, protective equipment use is extensive and dueling scars are almost unheard of.
In literature
 American traveller
American traveller Mark Twain
Samuel Langhorne Clemens (November 30, 1835 â April 21, 1910), known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American writer, humorist, entrepreneur, publisher, and lecturer. He was praised as the "greatest humorist the United States has p ...
devoted several chapters of '' A Tramp Abroad'' (1880) to Heidelberg students' fencing.
In ''Three Men on the Bummel
''Three Men on the Bummel'' (also known as ''Three Men on Wheels'') is a humorous novel by Jerome K. Jerome. It was published in 1900, eleven years after his most famous work, '' Three Men in a Boat (To Say Nothing of the Dog)''.
The sequel bri ...
'' (1900), Jerome K. Jerome devoted a chapter to German student life, and describes the "German Mensur" in detail. While much of the book has a tone of admiration for the German people, he expressed extreme disapproval for this tradition.
In George MacDonald Fraser's '' Royal Flash'' (1970), the protagonist Harry Flashman
Sir Harry Paget Flashman is a fictional character created by Thomas Hughes (1822â1896) in the semi-autobiographical ''Tom Brown's School Days'' (1857) and later developed by George MacDonald Fraser (1925â2008). Harry Flashman appears in a ...
is scarred with a ''SchlÃĪger'' as part of his disguise as a Danish prince.
Mensur is featured in Heinrich Mann's novel ''Man of Straw'' ('' Der Untertan'').
Mensur scars are repeatedly noted and described as a sign of beauty and manliness by German characters in Katherine Anne Porter's novel ''Ship of Fools''.
Mensur scars are mentioned in passing in Robert Heinlein's ''Starship Troopers
''Starship Troopers'' is a military science fiction novel by American writer Robert A. Heinlein. Written in a few weeks in reaction to the US suspending nuclear tests, the story was first published as a two-part serial in ''The Magazine of F ...
'' when two German recruits are asked at the beginning of boot camp where they got their scars. The drill sergeant even uses the term ''Korpsbruder'' (as spelled in modern German). E. C. Gordon, the hero of Heinlein's '' Glory Road'', mentions his desire for a degree from Heidelberg and the dueling scars to go with it.
The opening scene of "The Mystery of the Spanish Chest," in season three of '' Agatha Christie's Poirot'', features two men fighting in the mensur style. The episode's dialogue implies that the fencers are English, rather than German, and that one fencer has challenged the other to a duel over a woman.
In the James Bond books by Ian Fleming
Ian Lancaster Fleming (28 May 1908 â 12 August 1964) was a British writer who is best known for his postwar ''James Bond'' series of spy novels. Fleming came from a wealthy family connected to the merchant bank Robert Fleming & Co., a ...
, the supervillain
A supervillain or supercriminal is a variant of the villainous stock character that is commonly found in American comic books, usually possessing superhuman abilities. A supervillain is the antithesis of a superhero.
Supervillains are oft ...
Ernst Stavro Blofeld has a dueling scar below his eye.
In film
The Mensur is featured in a number ofGerman film
The film industry in Germany can be traced back to the late 19th century. German cinema made major technical and artistic contributions to early film, broadcasting and television technology. Babelsberg became a household synonym for the early 20 ...
s, notably:
* ''Hans Westmar
''Hans Westmar'' (full title: ' "Hans Westmar. One of many. A German Fate from the Year 1929") was the last of an unofficial trilogy of films produced by the Nazis shortly after coming to power in January 1933, celebrating their '' Kampfzeit'' â ...
- Einer von Vielen'' ("Hans Westmar - One of Many"), 1933
*'' Der Untertan'', 1951
and less commonly in films outside Germany, such as
*'' The Life and Death of Colonel Blimp'', 1943
*'' Royal Flash'', 1975
In television
* "The Mystery of the Spanish Chest" in series 3 of '' Agatha Christie's Poirot'' begins with a mensur. * In episode 77 of Roald Dahl's '' Tales of the Unexpected'', "The Vorpal Blade", the story revolves around duelling of this kind * In ''Freud
Sigmund Freud ( , ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 â 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating pathologies explained as originating in conflicts in ...
'', dueling is shown and many characters have scars from dueling.
See also
''A more detailed article (in German) with multiple illustrations can be found on the German Wikipedia:'' Mensur (Studentenverbindung) * Dueling scars * FencingReferences
References (in German)
* Hermann Rink: ''Die Mensur, ein wesentliches Merkmal des Verbandes.'' In: Rolf-Joachim Baum (Hrsg.): ''âWir wollen MÃĪnner, wir wollen Taten!â Deutsche Corpsstudenten 1848 bis heute.'' Siedler, Berlin 1998. pages 383-402 * Hermann Rink: ''Vom studentischen Fechten bis zur Mensur.'' In: ''Handbuch des KÃķsener Corpsstudenten.'' Verband Alter Corpsstudenten e.V. Volume I. WÞrzburg 1985 (6. edition), pages 151-171 * Martin Biastoch: ''Duell und Mensur im Kaiserreich (am Beispiel der TÞbinger Corps Franconia, Rhenania, Suevia und Borussia zwischen 1871 und 1895).'' SH-Verlag, Vierow 1995. * Wilhelm Fabricius: ''Die Deutschen Corps. Eine historische Darstellung mit besonderer BerÞcksichtigung des Mensurwesens''. Berlin 1898 (2. edition 1926)External links
The Secret History of the Sword
{{DEFAULTSORT:Academic Fencing Fencing Historical fencing Student societies in Germany Student sport Blood sports