Medium Second on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 A neutral second or medium second is an interval wider than a minor second and narrower than a major second. Three distinct intervals may be termed neutral seconds:
* The intermediate neutral second, called the lesser undecimal neutral second , has a ratio between the higher- frequency tone to the lower-frequency tone of 12:11 and is about 150.64 cents wide, while the larger one,
* the greater undecimal neutral second , has a ratio of 11:10 between the two tones and is about 165.00 cents wide. The lesser undecimal neutral second may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the eleventh and twelfth harmonics. The greater undecimal neutral second may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the tenth and eleventh harmonics.
* An ''
A neutral second or medium second is an interval wider than a minor second and narrower than a major second. Three distinct intervals may be termed neutral seconds:
* The intermediate neutral second, called the lesser undecimal neutral second , has a ratio between the higher- frequency tone to the lower-frequency tone of 12:11 and is about 150.64 cents wide, while the larger one,
* the greater undecimal neutral second , has a ratio of 11:10 between the two tones and is about 165.00 cents wide. The lesser undecimal neutral second may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the eleventh and twelfth harmonics. The greater undecimal neutral second may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the tenth and eleventh harmonics.
* An ''
 In
In music theory
Music theory is the study of the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory". The first is the "rudiments", that are needed to understand music notation (ke ...
, a neutral interval is an interval that is neither a major nor minor, but instead in between. For example, in equal temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or tuning system, which approximates just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into equal steps. This means the ratio of the frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same, wh ...
, a major third is 400 cents, a minor third is 300 cents, and a neutral third is 350 cents. A neutral interval inverts to a neutral interval. For example, the inverse of a neutral third is a neutral sixth.
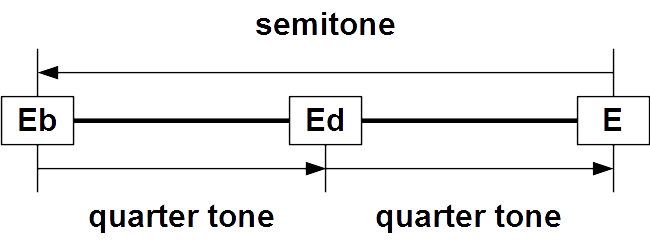
Roughly, neutral intervals are a quarter tone
A quarter tone is a pitch halfway between the usual notes of a chromatic scale or an interval about half as wide (aurally, or logarithmically) as a semitone, which itself is half a whole tone. Quarter tones divide the octave by 50 cents each, a ...
sharp from minor intervals and a quarter tone flat from major intervals. In just intonation, as well as in tunings such as 31-ET, 41-ET, or 72-ET
In music, 72 equal temperament, called twelfth-tone, 72-TET, 72- EDO, or 72-ET, is the tempered scale derived by dividing the octave into twelfth-tones, or in other words 72 equal steps (equal frequency ratios). Each step represents a frequency ...
, which more closely approximate just intonation, the intervals are closer together.
* Neutral second
* Neutral third
*Neutral sixth
A neutral sixth is a musical interval wider than a minor sixth but narrower than a major sixth . Three distinct intervals may be termed neutral sixths:
* The ''undecimal neutral sixth'' has a ratio of 18:11 between the frequencies of the tw ...
*Neutral seventh
In music theory, a neutral interval is an interval that is neither a major nor minor, but instead in between. For example, in equal temperament, a major third is 400 cents, a minor third is 300 cents, and a neutral third is 350 cents. A neutral ...
Second
 A neutral second or medium second is an interval wider than a minor second and narrower than a major second. Three distinct intervals may be termed neutral seconds:
* The intermediate neutral second, called the lesser undecimal neutral second , has a ratio between the higher- frequency tone to the lower-frequency tone of 12:11 and is about 150.64 cents wide, while the larger one,
* the greater undecimal neutral second , has a ratio of 11:10 between the two tones and is about 165.00 cents wide. The lesser undecimal neutral second may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the eleventh and twelfth harmonics. The greater undecimal neutral second may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the tenth and eleventh harmonics.
* An ''
A neutral second or medium second is an interval wider than a minor second and narrower than a major second. Three distinct intervals may be termed neutral seconds:
* The intermediate neutral second, called the lesser undecimal neutral second , has a ratio between the higher- frequency tone to the lower-frequency tone of 12:11 and is about 150.64 cents wide, while the larger one,
* the greater undecimal neutral second , has a ratio of 11:10 between the two tones and is about 165.00 cents wide. The lesser undecimal neutral second may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the eleventh and twelfth harmonics. The greater undecimal neutral second may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the tenth and eleventh harmonics.
* An ''equal-tempered
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or tuning system, which approximates just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into equal steps. This means the ratio of the frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same, w ...
neutral second'' is characterized by a difference in 150 cents between the two tones, a hair smaller than a ratio of frequencies between the two tones of 12:11, and exactly half of an equal-tempered minor third.
The equal-tempered neutral is found in some traditional Arabic music (see also Arab tone system). Because the equal tempered neutral second is essentially a semitone (minor second) plus a quarter-tone, they may be considered three-quarter tone
A quarter tone is a pitch halfway between the usual notes of a chromatic scale or an interval about half as wide (aurally, or logarithmically) as a semitone, which itself is half a whole tone. Quarter tones divide the octave by 50 cents each, a ...
s in the quarter tone scale.
In equal temperament
Approximations to the 12:11 and 11:10 neutral seconds can be found in a number of equally tempered tuning systems. 11:10 is very closely matched by 22-ET, whereas 12:11 is matched by 24-ET, 31-ET and 41-ET.72-ET
In music, 72 equal temperament, called twelfth-tone, 72-TET, 72- EDO, or 72-ET, is the tempered scale derived by dividing the octave into twelfth-tones, or in other words 72 equal steps (equal frequency ratios). Each step represents a frequency ...
matches both intervals closely and is also the smallest widely used equal temperament that uniquely matches both intervals. Tuning systems that temper out the comma
The comma is a punctuation mark that appears in several variants in different languages. It has the same shape as an apostrophe or single closing quotation mark () in many typefaces, but it differs from them in being placed on the baseline ...
of 121:120 do not distinguish between the two intervals. 17-ET has a neutral second between 12:11 and 13:12, and a neutral third between 16:13 and 11:9.
Seventh
A neutral seventh is a musical interval wider than a minor seventh but narrower than a major seventh . Four distinct intervals may be termed neutral sevenths: * A ''septimal neutral seventh'' has a ratio of 64:35 or about 1045 cents. * The just ''undecimal neutral seventh'' has a ratio of 11:6 between thefrequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
of the two tones,Andrew Horner, Lydia Ayres (2002). ''Cooking with Csound: Woodwind and Brass Recipes'', p.131. . or about 1049 cents . Alternately, 13:7 or about 1071.7 cents .
* A ''tridecimal neutral seventh'' has a ratio of 24:13 between the frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
of the two tones, or about 1061 cents. This is the largest neutral seventh, and occurs infrequently in music, as little music utilizes the 13th harmonic
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', the ...
.
* An ''equal-tempered
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or tuning system, which approximates just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into equal steps. This means the ratio of the frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same, w ...
neutral seventh'' is characterized by a difference in 1050 cents between the two tones, a hair larger than the 11:6 ratio, and exactly half of an equal-tempered major thirteenth (octave plus major sixth).
These intervals are all within about 12 cents of each other and are difficult for most people to distinguish.
A neutral seventh can be formed by stacking a neutral third together with a perfect fifth
In music theory, a perfect fifth is the Interval (music), musical interval corresponding to a pair of pitch (music), pitches with a frequency ratio of 3:2, or very nearly so.
In classical music from Western culture, a fifth is the interval fro ...
. Based on its positioning in the harmonic series, the undecimal neutral seventh implies a root one perfect fifth below the lower of the two notes.
See also
*Major fourth and minor fifth
In music, major fourth and minor fifth are interval (music), intervals from the quarter-tone scale, named by Ivan Wyschnegradsky to describe the tones surrounding the tritone (F/G) found in the more familiar twelve-tone scale,Skinner, Miles Lei ...
*Subminor and supermajor
In music, a subminor interval is an interval that is noticeably wider than a diminished interval but noticeably narrower than a minor interval. It is found in between a minor and diminished interval, thus making it below, or subminor to, the min ...
* List of pitch intervals
* Microtonal music
References
{{Intervals Neutral intervals Quarter tones