Media In Ghana on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The mass media in Ghana, includes television, radio, internet publishing and newspapers.
The mass media in Ghana, includes television, radio, internet publishing and newspapers.
''Press Reference''. The paper had several functions: to provide information for civil servants and European
''Government of Ghana''. A new 15-member National Press Commission (later Ghanaian Media Commission) was created that was independent of government, which would uphold the aforementioned responsibilities. Despite these new reforms, President Rawlings and the NDC government remained critical of the private press, calling it "politically irresponsible" and motivated by profit. One government official claimed the private media "tested the limits of the government", while others accused it of portraying Parliament as inferior. A group named Friends of Democracy claimed it had 1,000 signatories protesting against the private media. Editors from the ''Free Press'' and ''New Statesman'' had reported being sent death threats from the NDC for criticising the regime. Valerie Sackey who was an assistant to President Rawlings, noted that the private press had a duty to provide legitimate criticism of the government and to act responsibly, rather than simply portraying that the government was attempting to muzzle them.
'' BBC News''. The media, and broadcast media in particular, were vigorous in their coverage of the
''Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 2012'', Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor, U.S. Department of State, 25 March 2013. Retrieved 14 February 2014. In 2002 the government of Ghana censored Internet media coverage of tribal violence in Northern Ghana.
/ref> The contribution of a large number of state and private newspapers create a diverse media environment in Ghana. State papers such as the '' Daily Graphic'' and ''
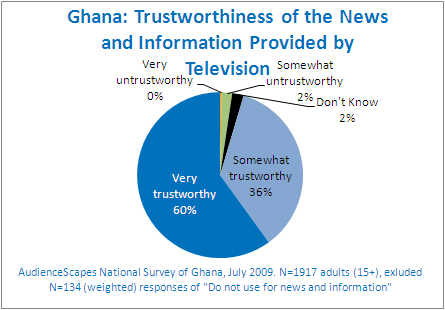
 Television was introduced to Ghana in 1965 and was under State control. The Ghana Broadcasting Corporation held a monopoly on television broadcasting until 1994, following the 1992 constitution of the new democratically elected government. Part of the 1992 constitution established the National Media Commission which held the responsibility to promote and ensure the independence of the media.
Shortly after the 1966 coup of Nkrumah by the National Liberation Council (who held an even tighter State grip on the nation's media), the Ghana Broadcasting Corporation announced a decree to, "broadcast programmes in the field of culture, education, information and entertainment, to reflect national progress and aspirations, and to broadcast in the main Ghanaian languages and in English".
There were seven broadcast stations in 2007.CIA World Factbook - Ghana
Television was introduced to Ghana in 1965 and was under State control. The Ghana Broadcasting Corporation held a monopoly on television broadcasting until 1994, following the 1992 constitution of the new democratically elected government. Part of the 1992 constitution established the National Media Commission which held the responsibility to promote and ensure the independence of the media.
Shortly after the 1966 coup of Nkrumah by the National Liberation Council (who held an even tighter State grip on the nation's media), the Ghana Broadcasting Corporation announced a decree to, "broadcast programmes in the field of culture, education, information and entertainment, to reflect national progress and aspirations, and to broadcast in the main Ghanaian languages and in English".
There were seven broadcast stations in 2007.CIA World Factbook - Ghana
''CIA''. Among the stations, there is the state-run Ghana Broadcasting Corporation and four private channels,
Calculated using penetration rate and population data fro
"Countries and Areas Ranked by Population: 2012"
Population data, International Programs, U.S. Census Bureau, retrieved 26 June 2013."Percentage of Individuals using the Internet 2000-2012"
International Telecommunication Union (Geneva), June 2013, retrieved 22 June 2013. It is unrestricted by the government.
Ghana - 2004 Annual Report
''Reporters Without Borders'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Media Of Ghana Ghana Ghana de:Ghana#Medien
 The mass media in Ghana, includes television, radio, internet publishing and newspapers.
The mass media in Ghana, includes television, radio, internet publishing and newspapers.
History
19th century
The media in the Gold Coast first emerged in the 19th century with the publication of ''The Gold Coast Gazette and Commercial Intelligencer'' in 1822.Ghanaian Media''Press Reference''. The paper had several functions: to provide information for civil servants and European
merchant
A merchant is a person who trades in commodities produced by other people, especially one who trades with foreign countries. Historically, a merchant is anyone who is involved in business or trade. Merchants have operated for as long as indust ...
s; and to help promote literacy rates and rural development among the local population - while encouraging unity with the Gold Coast government. In the mid-19th century, a diverse number of African-owned papers appeared that were largely unrestricted by the colonial government. This led to a surge of independent press, which in part led to the independence of Ghana.
Colonial Governor Sir Arnold Hodson
Sir Arnold Wienholt Hodson (12 February 1881 – 26 May 1944)"Sir Arnold Hodson"
Geni.com. ...
introduced the first radio channel, named Radio ZOY, on 31 July 1935, before it was renamed to the Ghana Broadcasting Corporation upon the country's independence in 1957. Its main use was to spread propaganda to gain support of the colonies
Geni.com. ...
Post-independence
Following the 6 March 1957 declaration of independence by Ghana from the United Kingdom, there were only around four newspapers. LeaderKwame Nkrumah
Kwame Nkrumah (born 21 September 190927 April 1972) was a Ghanaian politician, political theorist, and revolutionary. He was the first Prime Minister and President of Ghana, having led the Gold Coast to independence from Britain in 1957. An in ...
eventually controlled all the press in Ghana and saw it as an instrument of state authority, providing propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded ...
that encouraged national unity and creating a hierarchal system of state apparatus to manage the media. Transfer of the media had changed hands from a civilian to a military government, and a series of arrests and imprisonment of political opponents by Nkrumah had a chilling effect on the media.Anokwa, K. (1997). In ''Press Freedom and Communication in Africa.'' Erbio, F., and W. Jong-Ebot (eds), Africa World Press. . The opposition ''Ashanti Pioneer'', which had operated since the 1930s, was shut down by Nkrumah after being subject to censorship. After Nkrumah's overthrow in a coup, many state outlets changed hands, though still under the control of the ruling party. The National Liberation Council (NLC) imposed stricter controls on domestic private outlets; for example, the Rumours Decree in 1966 that prevented anyone from suing government-owned newspapers.
In 1969, the democratically elected civilian government of Kofi Busia
Kofi Abrefa Busia (born 11 July 1913 – 28 August 1978) was a Ghanaian political leader and academic who was Prime Minister of Ghana from 1969 to 1972. As a nationalist leader and prime minister, he helped to restore civilian government to the ...
that followed the NLC were left with a large number of media outlets under state control. Busia repealed various acts and dismissed the owner of the state-owned '' Daily Graphic'' for opposing Busia, who had appealed for African dialogue with the apartheid government in South Africa. However, when Ignatius Kutu Acheampong overthrew the Busia government, he reinstated strict media control and clamped down on opposition outlets by cutting off foreign exchange. However, a number of opposition media remained unimpeded during the Acheampong regime, and by 1978 had grown in their calls for a multi-party democracy in Ghana.
The regime of Acheampong was overthrown in May 1978 by General Akuffo, who reversed some of his predecessors media policies and released jailed journalists and opposition members. This led to the establishment of two party papers: the ''Star'' of the Popular Front Party
The Popular Front Party (PFP) was the main opposition political party in Ghana during the Third Republic (1979-1981).
In elections held on 18 June 1979, PFP presidential candidate Victor Owusu won 29.9% of the vote and the party won 42 of 140 sea ...
(PFP) and the ''Gong Gong'' of the People's National Party (PNP). The Akuffo regime was short lived, ending in another coup d'état by the Armed Forces Revolutionary Council (AFRC) headed by Jerry Rawlings, who repealed the press laws that were passed by Acheampong. Rawlings replaced the chief editor of the ''Daily Graphic'' who criticised the AFRC executions, though they had no authority to do so as it undermined the Constitution of the Third Republic, which stated they had to be replaced by the Press Commission. After eight months of the AFRC regime, which had promised media reform but in the end did not materialise, power was returned to the democratically elected PNP with Hilla Limann
Hilla Limann, (12 December 1934 – 23 January 1998) was a Ghanaian diplomat and politician who served the President of Ghana from 24 September 1979 to 31 December 1981. He served as a diplomat in Lome, Togo and Geneva, Switzerland.
Education
...
on 24 September 1979. Limann was an advocate of liberal media reform, establishing a 12-member Press Commission on 25 July 1980. In a speech he said:
The Press Commission, as enshrined in law, were to investigate complaints about the press, uphold press freedom
Freedom of the press or freedom of the media is the fundamental principle that communication and expression through various media, including printed and electronic media, especially published materials, should be considered a right to be exerci ...
and provide necessary regulation and licensing to media outlets. During Limann's rule, he respected the new Constitution and accepted criticism from the media. This did not last long however, as John Rawlings, citing "corruption and maladministration", once again seized power under the Provisional National Defence Council on 31 December 1981, and repealed the liberal media reforms instigated by Limann. Under the new government, the Third Constitution, along with the Press Commission, was abolished. Through the state-owned ''Daily Graphic'' on 5 January 1982, he told the press to lead the "Holy War" and direct the revolution. Rawlings passed laws that prevented criticism of the government or its policies, dismissed editors critical of him and passed various laws such as the Preventive Custody Law and Newspaper Licensing Law which allowed indefinite detention without trial of journalists, and stifled private media development respectively. The PNDC Secretary of Information Joyce Aryee in 1983 defended direct government control:
The policies not only affected print media but also the Ghana Broadcasting Corporation, with several dismissals or premature retirement. As a result, some media avoided all discussions of politics altogether and focused on other topics like sport or entertainment instead.
1992-2000
In 1992, Ghana promulgated a new constitution, and returned to democratic rule on 7 January 1993. Rawlings as part of the National Democratic Congress (he retired a Flight Lieutenant of the Ghana Armed Forces) liberalised the media by repealing previous laws the PNDC signed in. The private media, which had previously been silenced under the regime for the past decade, used the new press freedom laws to voice criticism at Rawlings of the years of strict laws and published several accusations of violent authoritarianism and drug abuse. The state media however, maintained a favourable image of Rawlings. Rawlings acknowledged the years of media repression, though he defended the military coup: Furthermore, Rawlings had pledged to uphold Chapter 12 of the Constitution of Ghana, promoting press freedom, responsibility of both private and state outlets and these freedoms to be additional to human rights.Constitution of Ghana''Government of Ghana''. A new 15-member National Press Commission (later Ghanaian Media Commission) was created that was independent of government, which would uphold the aforementioned responsibilities. Despite these new reforms, President Rawlings and the NDC government remained critical of the private press, calling it "politically irresponsible" and motivated by profit. One government official claimed the private media "tested the limits of the government", while others accused it of portraying Parliament as inferior. A group named Friends of Democracy claimed it had 1,000 signatories protesting against the private media. Editors from the ''Free Press'' and ''New Statesman'' had reported being sent death threats from the NDC for criticising the regime. Valerie Sackey who was an assistant to President Rawlings, noted that the private press had a duty to provide legitimate criticism of the government and to act responsibly, rather than simply portraying that the government was attempting to muzzle them.
2000-present
After the election in 2000 of John Kufuor the tensions between the private media and government decreased. Kufuor was a supporter of press freedom and repealed the criminallibel
Defamation is the act of communicating to a third party false statements about a person, place or thing that results in damage to its reputation. It can be spoken (slander) or written (libel). It constitutes a tort or a crime. The legal defini ...
law, though maintained that the media had to act responsibly. The Ghanaian media has been described as "one of the most unfettered" in Africa, operating with little restriction on private media. The private press often carries criticism of government policy.BBC Country Profile: Ghana'' BBC News''. The media, and broadcast media in particular, were vigorous in their coverage of the
2008 Ghanaian presidential election
General elections were held in Ghana on 7 December 2008. Since no candidate received more than 50% of the votes, a run-off election was held on 28 December 2008 between the two candidates who received the most votes, Nana Akufo-Addo of the govern ...
, and the Ghanaian Journalists Association (GJA) praised John Atta Mills on his election, hoping to foster a good media-government relationship. During a 1999 interview, the GJA described how the media has helped promote democracy in the country:
Due to the new freedom of media, the video game industry in Ghana is growing.
Relations with foreign media
The Ghanaian media holds good relations with foreign media, with many international journalists from Western, African and Asian organisations based in the capital,Accra
Accra (; tw, Nkran; dag, Ankara; gaa, Ga or ''Gaga'') is the capital and largest city of Ghana, located on the southern coast at the Gulf of Guinea, which is part of the Atlantic Ocean. As of 2021 census, the Accra Metropolitan District, , ...
. Journalists are not hindered during their work, and information is not censored into or out of the country. The main news agency, ''Ghana News Agency
The Ghana News Agency (GNA) is the official news agency of the country of Ghana. It was founded in 1957 by President Kwame Nkrumah, Mr. Donald Wright, who was seconded by the Reuters News Agency set up the Ghana News Agency and in 1961 President N ...
'', was set up in 1957 by Nkrumah to provide balanced information on local and international news. Reuters helped provide the agency with guidance and technical assistance until 1961. The agency had subscriptions from over 140 organisations and six news agencies in 2000.
Challenges to Ghanaian media
Despite its relative freedom, the media in Ghana does face some challenges. Journalists in Ghana are often poorly paid, under resourced, and often lack training. As a result, journalists in Ghana find themselves susceptible to bribery and self-censorship. The quality of radio and television broadcast media programming is low. With respect to newspapers, the ownership landscape of newspapers is politically polarized with most newspapers supporting either the government or opposition party lines. Only one newspaper, the state-owned '' Daily Graphic'' is truly national in distribution.Freedom of the press
Although the constitution and law provide forfreedom of speech
Freedom of speech is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or a community to articulate their opinions and ideas without fear of retaliation, censorship, or legal sanction. The right to freedom of expression has been recogni ...
and press
Press may refer to:
Media
* Print media or news media, commonly called "the press"
* Printing press, commonly called "the press"
* Press (newspaper), a list of newspapers
* Press TV, an Iranian television network
People
* Press (surname), a famil ...
, the government sometimes restricts those rights. The police arbitrarily arrest and detain journalists. Some journalists practice self-censorship
Self-censorship is the act of censoring or classifying one's own discourse. This is done out of fear of, or deference to, the sensibilities or preferences (actual or perceived) of others and without overt pressure from any specific party or insti ...
. The constitution prohibits arbitrary interference with privacy, family, home, or correspondence, and the government respects these prohibitions in practice."Ghana"''Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 2012'', Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor, U.S. Department of State, 25 March 2013. Retrieved 14 February 2014. In 2002 the government of Ghana censored Internet media coverage of tribal violence in Northern Ghana.
Newspapers
Around 135 newspapers are published in Ghana, including 16 independent newspapers and 9 daily newspapers.Freedom House 2007 report on Ghana/ref> The contribution of a large number of state and private newspapers create a diverse media environment in Ghana. State papers such as the '' Daily Graphic'' and ''
Ghanaian Times
The ''Ghanaian Times'' is a government-owned daily newspaper published in Accra, Ghana. The newspaper was established in 1957. It has a circulation of 80,000 copies and is published six times per week.
History
The newspaper was formerly known as ...
'' tend to promote and encourage support for government policies and follow a conservative line, unlike private press which has exposed lavish styles of government officials and mis-management of government affairs.Hasty, J. (2005). ''The Press and Political Culture in Ghana.'' Indiana University Press. .
The Ghanaian National Media Commission
Ghana has a pluralistic and free media environment with an independent statutory media regulatory body, which is the National Media Commission. The National Media Commission was set up on July 7, 1993 by an act of the Parliament of the Republic of ...
, an independent commission, was set up to monitor and receive complaints about the media.Blankson, I. A., and P. D. Murphy (2007). ''Negotiating Democracy: Media Transformations in Emerging Democracies.'' SUNY Press. . The commission had received 50 complaints in 2002, and in May 2001, forced the ''Ghanaian Chronicle
''The Ghanaian Chronicle'' is an English-language daily newspaper published from Accra, Ghana. It has a circulation of 45,000 copies, making it the biggest private newspaper in Ghana.Kuehnhenrich, Daniel (2012). ''Entwicklung oder Profit? Die staa ...
'' to apologise for publishing "false stories" on individuals without substantial evidence. However, similar rulings have been ignored due to a lack of authority.
Television and radio

 Television was introduced to Ghana in 1965 and was under State control. The Ghana Broadcasting Corporation held a monopoly on television broadcasting until 1994, following the 1992 constitution of the new democratically elected government. Part of the 1992 constitution established the National Media Commission which held the responsibility to promote and ensure the independence of the media.
Shortly after the 1966 coup of Nkrumah by the National Liberation Council (who held an even tighter State grip on the nation's media), the Ghana Broadcasting Corporation announced a decree to, "broadcast programmes in the field of culture, education, information and entertainment, to reflect national progress and aspirations, and to broadcast in the main Ghanaian languages and in English".
There were seven broadcast stations in 2007.CIA World Factbook - Ghana
Television was introduced to Ghana in 1965 and was under State control. The Ghana Broadcasting Corporation held a monopoly on television broadcasting until 1994, following the 1992 constitution of the new democratically elected government. Part of the 1992 constitution established the National Media Commission which held the responsibility to promote and ensure the independence of the media.
Shortly after the 1966 coup of Nkrumah by the National Liberation Council (who held an even tighter State grip on the nation's media), the Ghana Broadcasting Corporation announced a decree to, "broadcast programmes in the field of culture, education, information and entertainment, to reflect national progress and aspirations, and to broadcast in the main Ghanaian languages and in English".
There were seven broadcast stations in 2007.CIA World Factbook - Ghana''CIA''. Among the stations, there is the state-run Ghana Broadcasting Corporation and four private channels,
TV3 Channel 3 or TV 3 may refer to:
Television
*Canal 3 (Burkina Faso), a commercial television channel in Burkina Faso
*Canal 3 (Guatemala), a commercial television channel in Guatemala
*Channel 3 (Algeria), a public Algerian TV channel owned by EPTV ...
, Metro TV Metro TV may refer to:
* Metro TV (Ghana), a television station in Ghana
* Metro TV (Indonesian TV network)
Metro TV is an Indonesian free-to-air television news network based in West Jakarta. It was established on 25 November 2000 and now has ...
, Viasat 1
Viasat 1 was a Ghanaian television channel owned by the Swedish listed media group, Modern Times Group (MTG). It was replaced by '' Kwesé Free Sports'' in 2016.
The channel was awarded a licence from the National Communications Authority of ...
, TV Skyy, and TV Africa, with TV3 and Metro TV going on the air in 1997. Foreign stations such as CNN and BBC are freely accessible.
FM radio began in 1988,Fuller, L. K. (2004), ''National Days/National Ways: Historical, Political, and Religious Celebrations Around the World'', Greenwood Publishing Group. . which allowed foreign radio stations into the country, such as Voice of America, Radio France Internationale and BBC broadcasts on 101.3FM. A public demonstration in 1995 over seizure of equipment from a private station, ''Radio EYE'', forced the government to issue many FM frequencies for other private stations, creating a new era of "broadcast pluralism". Interactive phone-in discussions on local and national issues are very popular on Ghanaian radio. In addition to English-language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the is ...
stations, there are several in local dialect.Ray, D. (1986), ''Ghana: Politics, Economics and Society'', Lynne Reinner Publishers. In 2007, 86 FM and three shortwave stations existed.
Internet
The Internet was used by an estimated 4.2 millionGhanaians
The Ghanaian people are a nation originating in the Gold Coast (region), Ghanaian Gold Coast. Ghanaians predominantly inhabit the Republic of Ghana and are the predominant cultural group and residents of Ghana, numbering 30 million people as of ...
in 2012, roughly 17% of the population. There was no significant improvement in 2014 as reported by Internet World Statistics there were "5,171,993 Internet users on Dec 31, 2014, 19.6% of the population, per IWS.Calculated using penetration rate and population data fro
"Countries and Areas Ranked by Population: 2012"
Population data, International Programs, U.S. Census Bureau, retrieved 26 June 2013."Percentage of Individuals using the Internet 2000-2012"
International Telecommunication Union (Geneva), June 2013, retrieved 22 June 2013. It is unrestricted by the government.
See also
* Telecommunications in Ghana * Telephone numbers in Ghana * New media in Ghana *Ghanaian literature Ghanaian literature is literature produced by authors from Ghana or in the Ghanaian diaspora. The tradition of literature starts with a long oral tradition, was influence heavily by western literature during colonial rule, and became prominent with ...
* News Ghana
News Ghana is a Ghanaian independent news portal. Its one of the most visited website in Ghana, with 200,000 average daily visits.
History
News Ghana formerly known as Spy Ghana started in 2010 as a news blog by Madam Mushura Don-Baare and be ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * *External links
Ghana - 2004 Annual Report
''Reporters Without Borders'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Media Of Ghana Ghana Ghana de:Ghana#Medien