Mechanical Power Transmission on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Propulsion transmission is the mode of transmitting and controlling propulsion
Propulsion transmission is the mode of transmitting and controlling propulsion
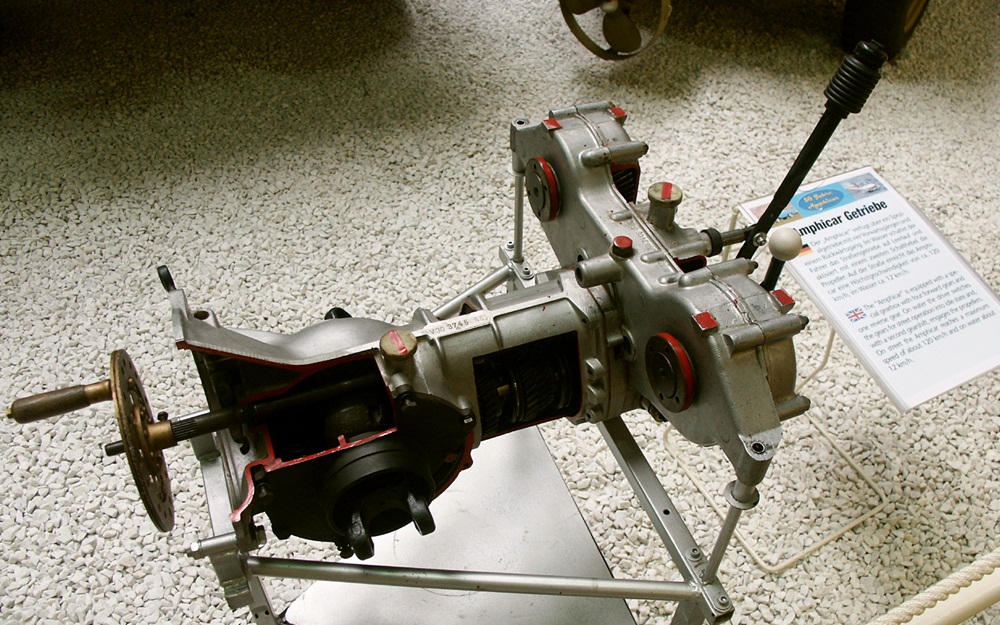
 The gearbox in a
The gearbox in a

 Many applications require the availability of multiple
Many applications require the availability of multiple
 Manual transmissions come in two basic types:
* A simple but rugged sliding-mesh or unsynchronized/non-synchronous system; where straight-cut spur gear sets spin freely and must be synchronized by the operator matching engine revs to road speed, to avoid noisy and damaging clashing of the gears
* The now ubiquitous
Manual transmissions come in two basic types:
* A simple but rugged sliding-mesh or unsynchronized/non-synchronous system; where straight-cut spur gear sets spin freely and must be synchronized by the operator matching engine revs to road speed, to avoid noisy and damaging clashing of the gears
* The now ubiquitous
- YouTube
transmission.
 A sequential manual transmission (like the kind of gearbox used on a fully-manual motorcycle) is a type of multi-speed non-synchronous manual transmission, which only allows the driver to select either the next gear (e.g., shifting from second gear to first gear) or the previous gear (e.g. shifting from second gear to third gear), in a successive order. This restriction avoids accidentally selecting the wrong gear, however, it also prevents the driver from deliberately "skipping" gears. The clutch in a sequential manual transmission is only needed when going from a standstill (i.e., stationary; neutral) into first gear, after which the gears are forced into place by the dogs. This contrasts with a conventional
A sequential manual transmission (like the kind of gearbox used on a fully-manual motorcycle) is a type of multi-speed non-synchronous manual transmission, which only allows the driver to select either the next gear (e.g., shifting from second gear to first gear) or the previous gear (e.g. shifting from second gear to third gear), in a successive order. This restriction avoids accidentally selecting the wrong gear, however, it also prevents the driver from deliberately "skipping" gears. The clutch in a sequential manual transmission is only needed when going from a standstill (i.e., stationary; neutral) into first gear, after which the gears are forced into place by the dogs. This contrasts with a conventional
motor-vehicle transmission
was probably used on the Ferguson '' F-1'' P99 racing car in about 1961. The
 Propulsion transmission is the mode of transmitting and controlling propulsion
Propulsion transmission is the mode of transmitting and controlling propulsion power
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may a ...
of a machine. The term ''transmission'' properly refers to the whole drivetrain
A drivetrain (also frequently spelled as drive train or sometimes drive-train) is the group of components that deliver mechanical power from the prime mover to the driven components. In automotive engineering, the drivetrain is the components o ...
, including clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission, especially from a drive shaft to a driven shaft. In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts). ...
, gearbox, prop shaft (for rear-wheel drive vehicles), differential, and final drive shafts. In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
the term is sometimes used in casual speech to refer more specifically to the gearbox alone, and detailed usage differs. The transmission reduces the higher engine speed to the slower wheel speed, increasing torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of th ...
in the process. Transmissions are also used on pedal bicycle
A bicycle, also called a pedal cycle, bike or cycle, is a human-powered or motor-powered assisted, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, having two wheels attached to a frame, one behind the other. A is called a cyclist, or bicyclist.
Bi ...
s, fixed machines, and where different rotational speeds and torques are adapted.
Often, a transmission has multiple gear ratios (or simply "gears") with the ability to switch between them as the speed varies. This switching may be done manually (by the operator) or automatically (by a control unit). Directional (forward and reverse) control may also be provided. Single-ratio transmissions also exist, which simply change the speed and torque (and sometimes direction) of motor output. Conventional gear/belt transmissions are not the only mechanism for speed/torque adaptation. Alternative mechanisms include torque converter
A torque converter is a type of fluid coupling that transfers rotating power from a prime mover, like an internal combustion engine, to a rotating driven load. In a vehicle with an automatic transmission, the torque converter connects the power ...
s and power transformation (e.g. diesel-electric transmission and hydraulic drive system
Hydraulic machines use liquid fluid power to perform work. Heavy construction vehicles are a common example. In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is pumped to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders throughout the machine and b ...
). Hybrid configurations also exist. Automatic transmissions use a valve body to shift gears using fluid pressures in response to engine RPM, speed, and throttle input.
Often the term ''5-speed transmission'' refers simply to the gearbox, that uses gear
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic pr ...
s and gear train
A gear train is a mechanical system formed by mounting gears on a frame so the teeth of the gears engage.
Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, providing a smooth transmission ...
s to provide speed
In everyday use and in kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a scalar quanti ...
and torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of th ...
block conversions from a rotating power source to another device. The most common use is in motor vehicle
A motor vehicle, also known as motorized vehicle or automotive vehicle, is a self-propelled land vehicle, commonly wheeled, that does not operate on Track (rail transport), rails (such as trains or trams) and is used for the transportation of pe ...
s, where the transmission adapts the output of the internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combus ...
to the drive wheels. Such engines need to operate at a relatively high rotational speed
Rotational frequency (also known as rotational speed or rate of rotation) of an object Rotation around a fixed axis, rotating around an axis is the frequency of rotation of the object. Its unit is revolution per minute (rpm), cycle per second ...
, which is inappropriate for starting, stopping, and slower travel. In motor vehicle
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles (motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles (trains, trams), wa ...
s, the transmission generally is connected to the engine crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting ...
via a flywheel or clutch or fluid coupling, partly because internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combus ...
s cannot run below a particular speed. The output of the transmission is transmitted via the driveshaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power and torque and rotation, usually used to connect ...
to one or more differentials, which drive the wheels. While a differential may also provide gear reduction, its primary purpose is to permit the wheels at either end of an axle to rotate at different speeds (essential to avoid wheel slippage on turns) as it changes the direction of rotation.
Explanation
Early transmissions included the right-angle drives and other gearing inwindmill
A windmill is a structure that converts wind power into rotational energy using vanes called windmill sail, sails or blades, specifically to mill (grinding), mill grain (gristmills), but the term is also extended to windpumps, wind turbines, and ...
s, horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million y ...
-powered devices, and steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
s, in support of pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they u ...
ing, mill
Mill may refer to:
Science and technology
*
* Mill (grinding)
* Milling (machining)
* Millwork
* Textile mill
* Steel mill, a factory for the manufacture of steel
* List of types of mill
* Mill, the arithmetic unit of the Analytical Engine early ...
ing, and hoisting.
Most modern gearboxes are used to increase torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of th ...
while reducing the speed of a prime mover output shaft (e.g. a motor crankshaft). This means that the output shaft of a gearbox rotates at a slower rate than the input shaft, and this reduction in speed produces a mechanical advantage
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. The device trades off input forces against movement to obtain a desired amplification in the output force. The model for t ...
, increasing torque. A gearbox can be set up to do the opposite and provide an increase in shaft speed with a reduction of torque. Some of the simplest gearboxes merely change the physical rotational direction of power transmission.
Many typical automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with Wheel, wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, pe ...
transmissions include the ability to select one of several gear ratio
A gear train is a mechanical system formed by mounting gears on a frame so the teeth of the gears engage.
Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, providing a smooth transmission ...
s. In this case, most of the gear ratios (often simply called "gears") are used to slow down the output speed of the engine and increase torque. However, the highest gears may be "overdrive
Overdrive may refer to:
Organizations
* OverDrive, Inc., a digital distributor of entertainment media
** OverDrive Media Console, a media player developed by OverDrive, Inc.
* Overdrive PC, a subsidiary of Velocity Micro
Technology
* Overdrive ...
" types that increase the output speed.
Uses
Gearboxes have found use in a wide variety of different—oftenstationary
In addition to its common meaning, stationary may have the following specialized scientific meanings:
Mathematics
* Stationary point
* Stationary process
* Stationary state
Meteorology
* A stationary front is a weather front that is not moving ...
—applications, such as wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. ...
s.
Transmissions are also used in agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating Plant, plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of Sedentism, sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of Domestication, domesticated species created food ...
, industrial
Industrial may refer to:
Industry
* Industrial archaeology, the study of the history of the industry
* Industrial engineering, engineering dealing with the optimization of complex industrial processes or systems
* Industrial city, a city dominate ...
, construction
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form objects, systems, or organizations,"Construction" def. 1.a. 1.b. and 1.c. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) Oxford University Press 2009 and com ...
, mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic via ...
and automotive equipment. In addition to ordinary transmission equipped with gears, such equipment makes extensive use of the hydrostatic drive and electrical adjustable-speed drive
Motor drive means a system that includes a motor. An adjustable speed motor drive means a system that includes a motor that has multiple operating speeds. A variable speed motor drive is a system that includes a motor and is continuously variabl ...
s.
Simple
The simplest transmissions, often called gearboxes to reflect their simplicity (although complex systems are also called gearboxes in the vernacular), provide gear reduction (or, more rarely, an increase in speed), sometimes in conjunction with a right-angle change in direction of the shaft (typically inhelicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes ...
s, see picture). These are often used on PTO-powered agricultural equipment, since the axial PTO shaft is at odds with the usual need for the driven shaft, which is either vertical (as with rotary mowers), or horizontally extending from one side of the implement to another (as with manure spreader
A manure spreader or muck spreader or honey wagon is an agricultural machine used to distribute manure over a field as a fertilizer. A typical (modern) manure spreader consists of a trailer towed behind a tractor with a rotating mechanism driven b ...
s, flail mower
A flail mower is a type of powered garden/agricultural equipment which is used to deal with heavier grass/scrub which a normal lawn mower could not cope with. Some smaller models are self-powered, but many are PTO driven implements, which can at ...
s, and forage wagon
A silo (from the Greek σιρός – ''siros'', "pit for holding grain") is a structure for storing bulk materials. Silos are used in agriculture to store fermented feed known as silage, not to be confused with a grain bin, which is used t ...
s). More complex equipment, such as silage
Silage () is a type of fodder made from green foliage crops which have been preserved by fermentation to the point of acidification. It can be fed to cattle, sheep and other such ruminants (cud-chewing animals). The fermentation and storage p ...
choppers and snowblower
A snow blower or snow thrower is a machine for removing snow from an area where it is problematic, such as a driveway, sidewalk, roadway, railroad track, ice rink, or runway. The commonly used term "snow blower" is a misnomer, as the snow is ...
s, have drives with outputs in more than one direction. So too helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes ...
s use a split-torque gearbox where power is taken from the engine in two directions for the different rotors.
 The gearbox in a
The gearbox in a wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. ...
converts the slow, high-torque rotation of the turbine into much faster rotation of the electrical generator
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power (mechanical energy) or fuel-based power (chemical energy) into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas ...
. These are much larger and more complicated than the PTO gearboxes in farm equipment. They weigh several tons and typically contain three stages to achieve an overall gear ratio from 40:1 to over 100:1, depending on the size of the turbine. (For aerodynamic
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dyn ...
and structural reasons, larger turbines have to turn more slowly, but the generators all have to rotate at similar speeds of several thousand rpm
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionl ...
.) The first stage of the gearbox is usually a planetary gear, for compactness, and to distribute the enormous torque of the turbine over more teeth of the low-speed shaft. Durability of these gearboxes has been a serious problem for a long time.
Regardless of where they are used, these simple transmissions all share an important feature: the gear ratio cannot be changed during use. It is fixed at the time the transmission is constructed.
For transmission types that overcome this issue, see Continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission (CVT) is an automatic transmission that can change seamlessly through a continuous range of gear ratios. This contrasts with other transmissions that provide a limited number of gear ratios in fixed steps. T ...
, also known as CVT.
Multi-ratio systems
gear ratio
A gear train is a mechanical system formed by mounting gears on a frame so the teeth of the gears engage.
Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, providing a smooth transmission ...
s. Often, this is to ease the starting and stopping of a mechanical system, though another important need is that of maintaining good fuel efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, wh ...
.
Automotive basics
The need for a transmission in anautomobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with Wheel, wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, pe ...
is a consequence of the characteristics of the internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combus ...
. Engines typically operate over a range of 600 to about 7000 rpm
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionl ...
(though this varies, and is typically less for diesel engines), while the car's wheels rotate between 0 RPM and around 1800 RPM.
Furthermore, the engine provides its highest torque and power outputs unevenly across the rev range resulting in a torque band
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of the ...
and a power band
The power band of an internal combustion engine or electric motor is the range of operating speeds under which the engine or motor is able to output the most power, that is, the maximum energy per unit of time. This usually means that maximum a ...
. Often the greatest torque is required when the vehicle is moving from rest or traveling slowly, while maximum power is needed at high speed. Therefore, a system is required that transforms the engine's output so that it can supply high torque at low speeds, but also operate at highway speeds with the motor still operating within its limits. Transmissions perform this transformation.
The dynamics of a car vary with speed: at low speeds, acceleration is limited by the inertia of vehicular gross mass; while at cruising or maximum speeds wind resistance is the dominant barrier.
Many transmissions and gear
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic pr ...
s used in automotive and truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construction ...
applications are contained in a cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuriti ...
case, though more frequently aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
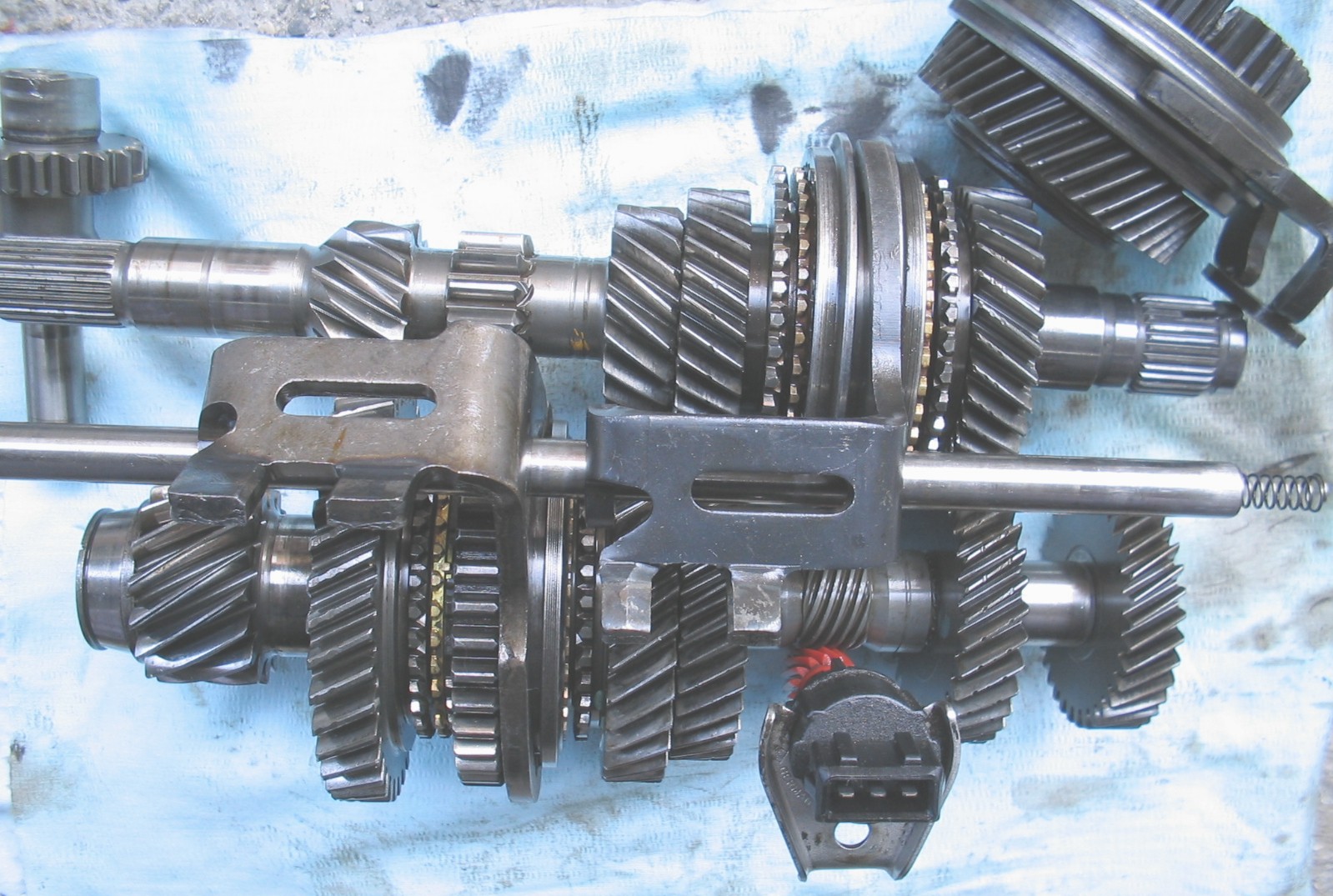
is used for lower weight especially in cars. There are usually three shafts: the main shaft, a countershaft, and an idler shaft.
The main shaft extends outside the case in both directions: the input shaft towards the engine, and the output shaft towards the rear axle (on rear-wheel-drive cars. Front-wheel-drive
Front-wheel drive (FWD) is a form of engine and transmission layout used in motor vehicles, where the engine drives the front wheels only. Most modern front-wheel drive vehicles feature a transverse engine, rather than the conventional lon ...
vehicles generally have the engine and transmission mounted transversely, the differential being part of the transmission assembly.) The shaft is suspended by the main bearings, and is split towards the input end. At the point of the split, a pilot bearing holds the shafts together. The gears and clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission, especially from a drive shaft to a driven shaft. In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts). ...
es ride on the main shaft, the gears being free to turn relative to the mainshaft except when engaged by the clutches.
Manual

 Manual transmissions come in two basic types:
* A simple but rugged sliding-mesh or unsynchronized/non-synchronous system; where straight-cut spur gear sets spin freely and must be synchronized by the operator matching engine revs to road speed, to avoid noisy and damaging clashing of the gears
* The now ubiquitous
Manual transmissions come in two basic types:
* A simple but rugged sliding-mesh or unsynchronized/non-synchronous system; where straight-cut spur gear sets spin freely and must be synchronized by the operator matching engine revs to road speed, to avoid noisy and damaging clashing of the gears
* The now ubiquitous constant-mesh gearbox
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission system, where gear changes ...
es; which can be/include unsynchronized/non-synchronized, or synchronized/synchromesh systems, where typically diagonal-cut helical (or sometimes either straight-cut, or double-helical) gear sets are constantly "meshed" together, and a dog clutch
A dog clutch (also known as a positive clutch or dog gears) is a type of clutch that couples two rotating shafts or other rotating components by engagement of interlocking teeth or dogs rather than by friction. The two parts of the clutch are d ...
is used for changing gears. On synchromesh 'boxes, friction cones or "synchro-rings" are used in addition to the dog clutch to closely match the rotational speeds of the two sides of the (declutched) transmission before making a full mechanical engagement.
The former type was standard in many vintage cars (alongside; e.g., epicyclic and multi-clutch systems) before the development of constant-mesh manuals and hydraulic-epicyclic automatics, older heavy-duty truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construction ...
s, and can still be found in use in some agricultural equipment. The latter is the modern standard for on- and off-road transport manual and automated manual transmission
The automated manual transmission (AMT) is a type of transmission for motor vehicles. It is essentially a conventional manual transmission but uses automatic actuation to operate the clutch and/or shift between gears.
Many early versions of t ...
s, although it may be found in many forms; e.g., non-synchronized straight-cut in a racetrack
A race track (racetrack, racing track or racing circuit) is a facility built for racing of vehicles, athletes, or animals (e.g. horse racing or greyhound racing). A race track also may feature grandstands or concourses. Race tracks are also u ...
or super-heavy-duty applications, non-synchro helical-cut in the majority of heavy-trucks and motorcycles, and in certain classic cars (e.g., the Fiat 500
The Fiat 500 ( it, Cinquecento, ) is a rear-engined, four-seat, small city car that was manufactured and marketed by Fiat Automobiles from 1957 until 1975 over a single generation in two-door saloon and two-door station wagon bodystyles.
Launch ...
), and partly- or fully-synchronized helical in almost all modern manual-shift passenger cars and light trucks.
Manual transmissions are the most common type outside North America and Australia. They are cheaper, lighter, usually give better performance, but the newest automatic transmissions and CVTs give better fuel economy. It is customary for new drivers to learn, and be tested, on a car with a manual gear change. In Malaysia and Denmark all cars used for testing (and because of that, virtually all those used for instruction as well) have a manual transmission. In Japan, the Philippines, Germany, Poland, Italy, Israel, the Netherlands, Belgium, New Zealand, Austria, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon ...
, the UK, Ireland, Sweden, Norway, Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
, France, Spain, Switzerland, the Australian states of Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
, Western Australia and Queensland, Finland, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
and the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
, a test pass using an automatic car does not entitle the driver to use a manual car on the public road; a test with a manual car is required. Manual transmissions are much more common than automatic transmissions in Asia, Africa, South America and Europe.
Manual gearboxes can include both synchromesh engagement and plain tooth to tooth engagement. For example, reverse gear is usually without synchromesh, as the driver is only expected to engage it when the vehicle is at a standstill. Many older (up to 1970s) cars also lacked synchromesh on first gear (for various reasons—cost, typically "shorter" overall gearing, engines typically having more low-end torque), meaning it also could only be used for moving away from a stop unless the driver became adept at double-declutching and had a particular need to regularly downshift into the lowest gear.
Some manual gearboxes have an extremely low ratio for first gear, Referred to in the UK as a ''crawler gear'' but some know it as a ''creeper gear'' or ''granny gear''. Such gears are usually not engaged via a synchromesh mechanism. This feature is used on larger and heavier vehicles (Goods vehicles, coaches or those made for trailer-towing, farming, or construction-site work. During normal on-road use, the truck is usually driven without using the creeper gear at all, and second gear is used from a standing start. Some off-road vehicles, most particularly the Willys Jeep and its descendants, also had transmissions with "granny first's" either as standard or an option, but this function is now more often provided for by a low-range transfer gearbox attached to a normal fully synchromeshed gearbox.
Non-synchronous
Some commercial applications use non-synchronized manual transmissions that require a skilled operator. Depending on the country, many local, regional, and national laws govern the operation of these types of vehicles (''seeCommercial Driver's License
A commercial driver's license (CDL) is a driver's license required in the United States to operate large and heavy vehicles (including trucks, buses, and trailers) or a vehicle of any size that transports hazardous materials or more than 15 p ...
''). This class may include commercial
Commercial may refer to:
* a dose of advertising conveyed through media (such as - for example - radio or television)
** Radio advertisement
** Television advertisement
* (adjective for:) commerce, a system of voluntary exchange of products and s ...
, military, agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating Plant, plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of Sedentism, sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of Domestication, domesticated species created food ...
, or engineering vehicle
Heavy equipment or heavy machinery refers to heavy-duty vehicles specially designed to execute construction tasks, most frequently involving earthwork operations or other large construction tasks. ''Heavy equipment'' usually comprises five e ...
s. Some of these may use combinations of types for multi-purpose functions. An example is a power take-off
A power take-off or power takeoff (PTO) is one of several methods for taking power from a power source, such as a running engine, and transmitting it to an application such as an attached implement or separate machine.
Most commonly, it is a sp ...
(PTO) gear. The non-synchronous transmission type requires an understanding of gear range, torque, engine power, and multi-functional clutch and shifter functions. Sequential manual transmission
A sequential manual transmission, also known as a sequential gearbox, or a sequential transmission, is a type of non-synchronous manual transmission used mostly for motorcycles and racing cars. It produces faster shift times than traditional ...
s, which are commonly used in motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle steered by a handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: long-distance travel, commuting, cruising ...
s and race car
Auto racing (also known as car racing, motor racing, or automobile racing) is a motorsport involving the racing of automobiles for competition.
Auto racing has existed since the invention of the automobile. Races of various sorts were organi ...
s, are a form of non-synchronous manual transmission.
Automatic
Most modern North American and some European and Japanese cars have anautomatic transmission
An automatic transmission (sometimes abbreviated to auto or AT) is a multi-speed transmission used in internal combustion engine-based motor vehicles that does not require any input from the driver to change forward gears under normal driving c ...
that selects an appropriate gear ratio without any operator intervention. They primarily use hydraulics
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counter ...
to select gears, depending on pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and e ...
exerted by fluid within the transmission assembly. Rather than using a clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission, especially from a drive shaft to a driven shaft. In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts). ...
to engage the transmission, a fluid flywheel, or torque converter
A torque converter is a type of fluid coupling that transfers rotating power from a prime mover, like an internal combustion engine, to a rotating driven load. In a vehicle with an automatic transmission, the torque converter connects the power ...
is placed in between the engine and transmission. It is possible for the driver to control the number of gears in use or select reverse, though precise control of which gear is in use may or may not be possible.
Automatic transmissions are easy to use. However, in the past, some automatic transmissions of this type have had a number of problems; they were complex and expensive, sometimes had reliability problems (which sometimes caused more expenses in repair), have often been less fuel-efficient than their manual counterparts (due to "slippage" in the torque converter), and their shift time
Shift time refers to the time interval between gear changes in a transmission. This interval is the time in which power delivery is transferred to the next selected gear, and engine speed is reduced or increased to synchronize the speed of the ne ...
was slower than a manual making them uncompetitive for racing. With the advancement of modern automatic transmissions, this has changed.
Attempts to improve the fuel efficiency of automatic transmissions include the use of torque converter
A torque converter is a type of fluid coupling that transfers rotating power from a prime mover, like an internal combustion engine, to a rotating driven load. In a vehicle with an automatic transmission, the torque converter connects the power ...
s that lock up beyond a certain speed or in higher gear ratios, eliminating power loss, and overdrive gears that automatically actuate above certain speeds. In older transmissions, both technologies could be intrusive, when conditions are such that they repeatedly cut in and out as speed and such load factors as grade or wind vary slightly. Current computerized transmissions possess complex programming that both maximizes fuel efficiency and eliminates intrusiveness. This is due mainly to electronic rather than mechanical advances, though improvements in CVT technology and the use of automatic clutches have also helped. A few cars, including the 2013 Subaru Impreza and the 2012 model of the Honda Jazz sold in the UK, actually claim marginally better fuel consumption for the CVT version than the manual version.
For certain applications, the slippage inherent in automatic transmissions can be advantageous. For instance, in drag racing
Drag racing is a type of motor racing in which automobiles or motorcycles compete, usually two at a time, to be first to cross a set finish line. The race follows a short, straight course from a standing start over a measured distance, most c ...
, the automatic transmission allows the car to stop with the engine at a high rpm (the "stall speed") to allow for a very quick launch when the brakes are released. In fact, a common modification is to increase the stall speed of the transmission. This is even more advantageous for turbocharge
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
d engines, where the turbocharger must be kept spinning at high rpm by a large flow of exhaust to maintain the boost pressure
Boost, boosted or boosting may refer to:
Science, technology and mathematics
* Boost, positive manifold pressure in turbocharged engines
* Boost (C++ libraries), a set of free peer-reviewed portable C++ libraries
* Boost (material), a material ...
and eliminate the turbo lag
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
that occurs when the throttle suddenly opens on an idling engine.
Continuously variable
The continuously variable transmission (CVT) is a transmission in which the ratio of the rotational speeds of two shafts, as the input shaft and output shaft of a vehicle or other machine, can be varied continuously within a given range, providing an infinite number of possible ratios. The CVT allows the driver or a computer to select the relationship between the speed of the engine and the speed of the wheels within a continuous range. This can provide even better fuel economy if the engine constantly runs at a single speed. The transmission is, in theory, capable of better user experience, without the rise and fall in the speed of an engine, and the jerk felt when changing gears poorly. CVTs are increasingly found on small cars and especially high-gas-mileage orhybrid
Hybrid may refer to:
Science
* Hybrid (biology), an offspring resulting from cross-breeding
** Hybrid grape, grape varieties produced by cross-breeding two ''Vitis'' species
** Hybridity, the property of a hybrid plant which is a union of two dif ...
vehicles. On these platforms, the torque is limited because the electric motor
An electric motor is an Electric machine, electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a Electromagneti ...
can provide torque without changing the speed of the engine. By leaving the engine running at the rate that generates the best gas mileage for the given operating conditions, overall mileage can be improved over a system with a smaller number of fixed gears, where the system may be operating at peak efficiency only for a small range of speeds.
CVTs are also found in agricultural equipment; due to the high-torque nature of these vehicles, mechanical gears are integrated to provide tractive force at high speeds. The system is similar to that of a hydrostatic gearbox, and at 'inching speeds' relies entirely on a hydrostatic drive. German tractor manufacturer Fendt
Fendt is a German agricultural machinery manufacturer founded in 1930 by Xaver Fendt in Marktoberdorf, Allgäu region, Germany. Fendt manufactures tractors, combine harvesters, balers, telescopic handlers and row crop planters. It was purchase ...
pioneered the technology, developing its 'Vari- YouTube
transmission.
Electric variable
The Electric Variable Transmission (EVT or e-CVT) are used inhybrid vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is one that uses two or more distinct types of power, such as submarines that use diesel when surfaced and batteries when submerged. Other means to store energy include pressurized fluid in hydraulic hybrids.
The basic princip ...
combines the output of an electric motor and a gasoline engine, and like a CVT, provides continuously varied gear ratios.
In the common implementation, a gasoline engine is connected to a traditional transmission, which is in turn connected to an epicyclic gear
An epicyclic gear train (also known as a planetary gearset) consists of two gears mounted so that the center of one gear revolves around the center of the other. A carrier connects the centers of the two gears and rotates the planet and sun gea ...
system's planet carrier. An electric motor/generator is connected to the central "sun" gear, which is normally un-driven in typical epicyclic systems. Both sources of power can be fed into the transmission's output at the same time, splitting power between them. In common examples, between one-quarter and half of the engine's power can be fed into the sun gear. Depending on the implementation, the transmission in front of the epicyclic system may be greatly simplified or eliminated. EVTs are capable of continuously modulating output/input speed ratios like mechanical CVTs, but offer the distinct benefit of being able to also apply power from two different sources to one output, as well as potentially reducing overall complexity dramatically.
In typical implementations, the gear ratio of the transmission and epicyclic system is set to the ratio of the common driving conditions, say highway speed for a car, or city speeds for a bus. When the driver presses on the gas, the associated electronics interpret the pedal position and immediately set the gasoline engine to the RPM that provides the best gas mileage for that setting. As the gear ratio is normally set far from the maximum torque point, this set-up would normally result in very poor acceleration. Unlike gasoline engines, electric motors offer efficient torque across a wide selection of RPM and are especially effective at low settings where the gasoline engine is inefficient. By varying the electrical load or supply on the motor attached to the sun gear, additional torque can be provided to make up for the low torque output from the engine. As the vehicle accelerates, the power to the motor is reduced and eventually ended, providing the illusion of a CVT.
The canonical example of the e-CVT is Toyota's Hybrid Synergy Drive
Hybrid Synergy Drive (HSD), also known as Toyota Hybrid System II, is the brand name of Toyota Motor Corporation for the hybrid car drive train technology used in vehicles with the Toyota and Lexus marques. First introduced on the Prius, the tec ...
. This implementation has no conventional transmission, and the sun gear always receives 28% of the torque from the engine. This power can be used to operate any electrical loads in the vehicle, recharging the batteries, powering the entertainment system, or running the air conditioning system. Any residual power is then fed back into a second motor that powers the output of the drivetrain directly. At highway speeds, this additional generator/motor pathway is less efficient than simply powering the wheels directly. However, during acceleration, the electrical path is much more efficient than an engine operating so far from its torque point. GM uses a similar system in the Allison Bus hybrid powertrains and the Tahoe and Yukon pick-up trucks, but these use a two-speed transmission in front of the epicyclic system, and the sun gear receives close to half the total power.
Automated manual
Automated manual transmission (AMT) denotes a type of multi-speedmotor vehicle
A motor vehicle, also known as motorized vehicle or automotive vehicle, is a self-propelled land vehicle, commonly wheeled, that does not operate on Track (rail transport), rails (such as trains or trams) and is used for the transportation of pe ...
transmission system that is closely based on the mechanical design and build of a conventional manual transmission
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission (mechanics), transmission ...
, but uses automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines ...
to control either the clutch, and/or the gear shifting.
Modern versions of these systems began to appear on mass-production automobiles in the mid-1990s, and are fully-automatic
An automatic firearm is an auto-loading firearm that continuously chambers and fires rounds when the trigger mechanism is actuated. The action of an automatic firearm is capable of harvesting the excess energy released from a previous discharge ...
in operation. Tradenames include ''Selespeed
Selespeed is the name of an automated manual transmission used in Alfa Romeo cars, developed by Italian company Magneti Marelli and made by Graziano Trasmissioni.
The Selespeed is an automated manual gearbox with an electronic clutch. In its curre ...
'' and ''Easytronic
Easytronic is the Opel tradename for a type of transaxle-based automated manual transmission or gearbox, as used in some Opel/Vauxhall cars.
Easytronic is not a tiptronic gearbox design; it does not have a torque converter. It is fundamental ...
'', and they can control both the clutch operation and the gear shifts automatically, by means of an ECU, therefore requiring no manual intervention or driver input over gear changes.
The usage of modern computer-controlled AMTs in passenger cars increased during the mid-1990s, as a more sporting alternative to the traditional hydraulic automatic transmission
An automatic transmission (sometimes abbreviated to auto or AT) is a multi-speed transmission used in internal combustion engine-based motor vehicles that does not require any input from the driver to change forward gears under normal driving ...
. During the 2010s, AMTs were largely replaced by the increasingly widespread dual-clutch transmission
A dual-clutch transmission (DCT) (sometimes referred to as a twin-clutch transmission) is a type of multi-speed motor vehicle, vehicle Transmission (mechanics), transmission system, that uses two separate clutches for odd and even gear train, g ...
design.
Clutchless manual / Semi-automatic
Semi-automatic transmission denotes a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission where part of its operation isautomated
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines ...
(usually the clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission, especially from a drive shaft to a driven shaft. In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts). ...
actuation), but the driver's input is still required to manually change gear ratios. Most semi-automatic transmissions used in car
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarded as ...
s and motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle steered by a handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: long-distance travel, commuting, cruising ...
s are based on conventional manual transmission
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission (mechanics), transmission ...
s or a sequential manual transmission
A sequential manual transmission, also known as a sequential gearbox, or a sequential transmission, is a type of non-synchronous manual transmission used mostly for motorcycles and racing cars. It produces faster shift times than traditional ...
, but use an automatic clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission, especially from a drive shaft to a driven shaft. In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts). ...
system. Occasionally, however, some semi-automatic transmissions have also been based on standard hydraulic automatic transmissions, with a fluid coupling
A fluid coupling or hydraulic coupling is a hydrodynamic or 'hydrokinetic' device used to transmit rotating mechanical power.
or torque converter
A torque converter is a type of fluid coupling that transfers rotating power from a prime mover, like an internal combustion engine, to a rotating driven load. In a vehicle with an automatic transmission, the torque converter connects the power ...
, and using a planetary gearset
An epicyclic gear train (also known as a planetary gearset) consists of two gears mounted so that the center of one gear revolves around the center of the other. A carrier connects the centers of the two gears and rotates the planet and sun gea ...
.
Names for specific types of semi-automatic transmissions include ''clutchless manual'', ''auto-manual'', ''auto-clutch manual'', and ''paddle-shift'' transmissions. These systems facilitate gear shifts for the driver by operating the clutch system automatically, usually by means, or under control of an actuator
An actuator is a component of a machine that is responsible for moving and controlling a mechanism or system, for example by opening a valve. In simple terms, it is a "mover".
An actuator requires a control device (controlled by control signal) a ...
or servo
Servo may refer to:
Mechanisms
* Servomechanism, or servo, a device used to provide control of a desired operation through the use of feedback
** AI servo, an autofocus mode
** Electrohydraulic servo valve, an electrically operated valve that ...
, and sensor
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
s, while still requiring the driver to manually shift gears
The first usage of semi-automatic transmissions was in automobiles, increasing in popularity in the mid-1930s when they were offered by several American car manufacturers. Less common than traditional (hydraulic) automatic transmission
An automatic transmission (sometimes abbreviated to auto or AT) is a multi-speed transmission used in internal combustion engine-based motor vehicles that does not require any input from the driver to change forward gears under normal driving c ...
s, semi-automatic transmissions have nonetheless been made available on various car and motorcycle models, and currently remain in production. Semi-automatic transmissions with ''paddle-shift'' operation have been used in various racing cars
Auto racing (also known as car racing, motor racing, or automobile racing) is a motorsport involving the racing of automobiles for competition.
Auto racing has existed since the invention of the automobile. Races of various sorts were organise ...
, and were first introduced to control the electro-hydraulic gear shift mechanism of the ''Ferrari 640
The Ferrari 640 (also known as the Ferrari F1-89) was the Formula One racing car with which the Ferrari team competed in the 1989 Formula One World Championship. It was driven by Britain's Nigel Mansell, in his first season with the team, and A ...
'' Formula One
Formula One (also known as Formula 1 or F1) is the highest class of international racing for open-wheel single-seater formula racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The World Drivers' Championship, ...
race car
Auto racing (also known as car racing, motor racing, or automobile racing) is a motorsport involving the racing of automobiles for competition.
Auto racing has existed since the invention of the automobile. Races of various sorts were organi ...
in 1989. These systems are currently used on a variety of top-level racing car classes; including Formula One
Formula One (also known as Formula 1 or F1) is the highest class of international racing for open-wheel single-seater formula racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The World Drivers' Championship, ...
, Indycar
INDYCAR, LLC, is an American-based auto racing sanctioning body for Indy car racing and other disciplines of open wheel car racing. The organization sanctions five racing series: the premier IndyCar Series with its centerpiece the Indianapolis ...
, and Touring car racing
Touring car racing is a motorsport road racing competition with heavily modified road-going cars. It has both similarities to and significant differences from stock car racing, which is popular in the United States.
While the cars do not move ...
. Other applications include motorcycles, trucks, buses, and railway vehicles.
Early semi-automatic systems used a variety of mechanical
Mechanical may refer to:
Machine
* Machine (mechanical), a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement
* Mechanical calculator, a device used to perform the basic operations of ...
, electrical
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by ...
, pneumatic
Pneumatics (from Greek ‘wind, breath’) is a branch of engineering that makes use of gas or pressurized air.
Pneumatic systems used in Industrial sector, industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A central ...
, and hydraulic
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counter ...
systems—including centrifugal clutch
A centrifugal clutch is an automatic clutch that uses centrifugal force to operate. The output shaft is disengaged at low rotational speed and engages more as speed increases. It is often used in mopeds, underbones, lawn mowers, go-karts, chainsaws ...
es, vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often dis ...
-operated clutches, torque converters, electro-pneumatic clutches, electro-mechanical
In engineering, electromechanics combines processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focuses on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems ...
(and even electrostatic
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest (static electricity).
Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber ...
) and servo
Servo may refer to:
Mechanisms
* Servomechanism, or servo, a device used to provide control of a desired operation through the use of feedback
** AI servo, an autofocus mode
** Electrohydraulic servo valve, an electrically operated valve that ...
/solenoid
upright=1.20, An illustration of a solenoid
upright=1.20, Magnetic field created by a seven-loop solenoid (cross-sectional view) described using field lines
A solenoid () is a type of electromagnet formed by a helix, helical coil of wire whose ...
-controlled clutches, and control schemes—automatic clutching when moving the gearshift, pre-selector controls, centrifugal clutches with drum-sequential-shift, requiring the driver to lift the throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle'' ...
for a successful shift, etc.—and some were little more than regular lock-up torque converter automatics with manual gear selection. Semi-automatic transmission systems on motorcycles generally use a centrifugal clutch
A centrifugal clutch is an automatic clutch that uses centrifugal force to operate. The output shaft is disengaged at low rotational speed and engages more as speed increases. It is often used in mopeds, underbones, lawn mowers, go-karts, chainsaws ...
.
An example of this transmission type in automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with Wheel, wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, pe ...
s is the VW Autostick semi-automatic transmission; a conventional 3-speed manual transmission, with a vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often dis ...
-operated automatic clutch, plus a torque converter
A torque converter is a type of fluid coupling that transfers rotating power from a prime mover, like an internal combustion engine, to a rotating driven load. In a vehicle with an automatic transmission, the torque converter connects the power ...
(like in a regular automatic), and a standard gear shifter.
Semi-automatic transmissions on motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle steered by a handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: long-distance travel, commuting, cruising ...
s and ATVs
ATV may refer to:
Broadcasting
* Amateur television
*Analog television
Television stations and companies
* Ràdio i Televisió d'Andorra
* ATV (Armenia)
* ATV (Aruba), NBC affiliate
* ATV (Australian TV station), Melbourne
* ATV (Austria)
* ATV ...
still require the driver to manually shift gears, and generally use a conventional sequential manual foot-shift lever, coupled with an automatic centrifugal clutch
A centrifugal clutch is an automatic clutch that uses centrifugal force to operate. The output shaft is disengaged at low rotational speed and engages more as speed increases. It is often used in mopeds, underbones, lawn mowers, go-karts, chainsaws ...
, so there is no manually-operated clutch lever on the handlebar for the driver to use, as it is a fully-automated clutch system.
Sequential manual
 A sequential manual transmission (like the kind of gearbox used on a fully-manual motorcycle) is a type of multi-speed non-synchronous manual transmission, which only allows the driver to select either the next gear (e.g., shifting from second gear to first gear) or the previous gear (e.g. shifting from second gear to third gear), in a successive order. This restriction avoids accidentally selecting the wrong gear, however, it also prevents the driver from deliberately "skipping" gears. The clutch in a sequential manual transmission is only needed when going from a standstill (i.e., stationary; neutral) into first gear, after which the gears are forced into place by the dogs. This contrasts with a conventional
A sequential manual transmission (like the kind of gearbox used on a fully-manual motorcycle) is a type of multi-speed non-synchronous manual transmission, which only allows the driver to select either the next gear (e.g., shifting from second gear to first gear) or the previous gear (e.g. shifting from second gear to third gear), in a successive order. This restriction avoids accidentally selecting the wrong gear, however, it also prevents the driver from deliberately "skipping" gears. The clutch in a sequential manual transmission is only needed when going from a standstill (i.e., stationary; neutral) into first gear, after which the gears are forced into place by the dogs. This contrasts with a conventional manual transmission
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission (mechanics), transmission ...
, which uses synchromesh for smooth gear shifts. The use of dog-clutches (rather than synchromesh
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission system, where gear changes ...
) results in faster shift speeds than a manual transmission.
Sequential manual transmission
A sequential manual transmission, also known as a sequential gearbox, or a sequential transmission, is a type of non-synchronous manual transmission used mostly for motorcycles and racing cars. It produces faster shift times than traditional ...
s use the rotation of a drum and selector forks to switch gears, like what is used on a fully-manual motorcycle transmission. The shift-drum mechanism is connected and rotated in a fore-and-aft motion by either a mechanical linkage (e.g., shift lever) or via an electro-pneumatic or electro-hydraulic control system, which typically will mechanically connect to the shift forks and dog clutches, and is operated with paddle-shifters, behind the steering wheel. They can also be designed with manual or automatic clutch systems. Semi-automatic sequential transmissions (with automatic clutches) may be found both in automobiles (mainly track and some rally racecars, e.g. paddle-shift), motorcycles (typically light "step-thru" type city utility bikes, e.g.; the ''Honda Super Cub
The Honda Super Cub or Honda Cub is a Honda underbone motorcycle with a four-stroke single-cylinder engine ranging in displacement from .
In continuous manufacture since 1958 with production surpassing 60 million in 2008, 87 million in 2014, an ...
'') and quad bike
An all-terrain vehicle (ATV), also known as a light utility vehicle (LUV), a quad bike, or simply a quad, as defined by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI); is a vehicle that travels on low-pressure tires, with a seat that is strad ...
s (often with a separately engaged reversing gear), the latter two normally using a scooter-style centrifugal clutch.
On a sequential manual transmission, the shift lever operates a ratchet mechanism that converts the fore and aft motion of the shift lever into rotation of a selector drum (sometimes called a barrel) which has three or four tracks machined around its circumference. Selector forks are guided by the tracks, either directly or via selector rods. The tracks deviate around the circumference and as the drum rotates, the selector forks are moved to select the required gear.
Bicycle gearing
Bicycle
A bicycle, also called a pedal cycle, bike or cycle, is a human-powered or motor-powered assisted, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, having two wheels attached to a frame, one behind the other. A is called a cyclist, or bicyclist.
Bic ...
s usually have a system for selecting different gear ratios. There are two main types: derailleur gears
Shimano 600 front derailleur (1980)
A derailleur is a variable-ratio bicycle gearing system consisting of a chain, multiple sprockets of different sizes, and a mechanism to move the chain from one sprocket to another.
Modern front and rear ...
and hub gears
A hub gear, internal-gear hub, internally geared hub or just gear hub is a gear ratio changing system commonly used on bicycles that is implemented with planetary or epicyclic gears. The gears and lubricants are sealed within the shell of the h ...
. The derailleur type is the most common, and the most visible, using sprocket
A sprocket, sprocket-wheel or chainwheel is a profiled wheel with teeth that mesh with a chain, track or other perforated or indented material. The name 'sprocket' applies generally to any wheel upon which radial projections engage a chain passi ...
gears. Typically there are several gears available on the rear sprocket assembly, attached to the rear wheel. A few more sprockets are usually added to the front assembly as well. Multiplying the number of sprocket gears in front by the number to the rear gives the number of gear ratios, often called "speeds".
Several attempts have been made to fit bicycles with an enclosed gearbox, giving obvious advantages for better lubrication, dirt-sealing and shifting. These have usually been in conjunction with a shaft drive, as a gearbox with a traditional chain would (like the hub gear) still have many of the derailleur's disadvantages for an exposed chain. Bicycle gearboxes are enclosed in a box replacing the traditional bottom bracket
The bottom bracket on a bicycle connects the crankset (chainset) to the bicycle and allows the crankset to rotate freely. It contains a spindle to which the crankset attaches, and the bearings that allow the spindle and crankset to rotate. The ch ...
. The requirement for a modified frame has been a serious drawback to their adoption. One of the most recent attempts to provide a gearbox for bicycles is the 18 speed Pinion P1.18. This gives an enclosed gearbox, but still a traditional chain. When fitted to a rear suspension bike, it also retains a derailleur-like jockey cage chain tensioner, although without the derailleur's low ground clearance.
Causes for failure of bicycle gearing include worn teeth, damage caused by a faulty chain, damage due to thermal expansion, broken teeth due to excessive pedaling force, interference by foreign objects, and loss of lubrication due to negligence.
Uncommon types
Dual-clutch transmission
A dual-clutch transmission (DCT) (sometimes referred to as a twin-clutch transmission, or a double-clutch transmission) is a type of multi-speedvehicle
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles (motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles (trains, trams), wa ...
transmission system, that uses two separate clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission, especially from a drive shaft to a driven shaft. In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts). ...
es for odd and even gear sets. The design is often similar to two separate manual transmission
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission (mechanics), transmission ...
s with their respective clutches contained within one housing, and working as one unit. In car and truck applications, the DCT functions as an automatic transmission
An automatic transmission (sometimes abbreviated to auto or AT) is a multi-speed transmission used in internal combustion engine-based motor vehicles that does not require any input from the driver to change forward gears under normal driving c ...
, requiring no driver input to change gears.
A dual-clutch
A dual-clutch transmission (DCT) (sometimes referred to as a twin-clutch transmission) is a type of multi-speed motor vehicle, vehicle Transmission (mechanics), transmission system, that uses two separate clutches for odd and even gear train, g ...
transmission uses two sets of internals, each with its own clutch, so that a "gearchange" actually only consists of one clutch engaging as the other disengages—providing a supposedly "seamless" shift with no break in (or jarring reuptake of) power transmission. Each clutch's attached shaft carries half of the total input gear complement (with a shared output shaft), including synchronized dog clutch systems that pre-select which of its set of ratios is most likely needed at the next shift, under command of a computerized control system. Specific types of this transmission include: ''Direct-Shift Gearbox
A direct-shift gearbox (DSG, german: Direktschaltgetriebe) is an electronically-controlled, dual-clutch, multiple-shaft, automatic gearbox, in either a transaxle or traditional transmission layout (depending on engine/drive configuration), w ...
'' and '' Twin-Clutch SST''.
Infinitely variable
The IVT is a specific type of CVT that includes not only an infinite number of gear ''ratios'', but an "infinite" ''range'' as well. This is a turn of phrase, it actually refers to CVTs that are able to include a "zero ratio", where the input shaft can turn without any motion of the output shaft while remaining in gear. The gear ratio, in that case, is not "infinite" but is instead zero. Most (if not all) IVTs result from the combination of a CVT with an epicyclic gear system with a fixed ratio. The combination of the fixed ratio of the epicyclic gear with a specific matching ratio in the CVT side results in zero output. For instance, consider a transmission with an epicyclic gear set to 1:−1 gear ratio; a 1:1 reverse gear. When the CVT side is set to 1:1 the two ratios add up to zero output. The IVT is always engaged, even during its zero output. When the CVT is set to higher values it operates conventionally, with increasing forward ratios. In practice, the epicyclic gear may be set to the lowest possible ratio of the CVT, if reversing is not needed or is handled through other means. Reversing can be incorporated by setting the epicyclic gear ratio somewhat higher than the lowest ratio of the CVT, providing a range of reverse ratios.Direct-drive mechanism
A direct-drive mechanism is where the transmitting of mechanicalpower
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may a ...
and torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of th ...
from an electric motor
An electric motor is an Electric machine, electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a Electromagneti ...
to the output device (such as the driven wheels of a car) occurs without any gearing reductions.
Several cars from the late 19th century used direct-drive wheel hub motor
The wheel hub motor (also called wheel motor, wheel hub drive, hub motor or in-wheel motor) is an electric motor that is incorporated into the hub of a wheel and drives it directly.
History
* First wheel motor concept: Wellington Adams of ...
s, as did some concept cars in the early 2000s; however, most modern electric car
An electric car, battery electric car, or all-electric car is an automobile that is propelled by one or more electric motors, using only energy stored in batteries. Compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, electric cars are quie ...
s use inboard motor(s), where drive is transferred to the wheels, via the driveshaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power and torque and rotation, usually used to connect ...
or axle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearing ...
s.
Non-direct
Electric
Electric transmissions convert the mechanical power of the engine(s) to electricity withelectric generator
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power (mechanical energy) or fuel-based power (chemical energy) into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas ...
s and convert it back to mechanical power with electric motor
An electric motor is an Electric machine, electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a Electromagneti ...
s. Electrical or electronic adjustable-speed drive
Motor drive means a system that includes a motor. An adjustable speed motor drive means a system that includes a motor that has multiple operating speeds. A variable speed motor drive is a system that includes a motor and is continuously variabl ...
control systems are used to control the speed and torque of the motors. If the generators are driven by turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating e ...
s, such arrangements are called turbo-electric transmission
A turbo-electric transmission uses electric generators to convert the mechanical energy of a turbine (steam or gas) into electric energy, which then powers electric motors and converts back into mechanical energy that power the driveshafts.
Tur ...
. Likewise, installations powered by diesel-engine
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-call ...
s are called diesel-electric.
Diesel-electric arrangements are used on many railway locomotives, ships, large mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic via ...
trucks, and some bulldozers
A bulldozer or dozer (also called a crawler) is a large, motorized machine equipped with a metal #Blade, blade to the front for pushing material: soil, sand, snow, rubble, or rock during construction work. It travels most commonly on continuous ...
. In these cases, each driven wheel is equipped with its own electric motor, which can be fed varying electrical power to provide any required torque or power output for each wheel independently. This produces a much simpler solution for multiple driven wheels in very large vehicles, where driveshafts would be much larger or heavier than the electrical cable that can provide the same amount of power. It also improves the ability to allow different wheels to run at different speeds, which is useful for steered wheels in large construction vehicles.
Hydrostatic
:''See also Continuously variable transmission > Hydrostatic CVTs'' Hydrostatic transmissions transmit all power hydraulically, using the components ofhydraulic machinery
Hydraulic machines use liquid fluid power to perform work. Heavy construction vehicles are a common example. In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is pumped to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders throughout the machine and b ...
. They are similar to electrical transmissions but use the hydraulic fluid as the power distribution system rather than electricity.
The transmission input drive is a central hydraulic pump and the final drive unit(s) is/are a hydraulic motor or hydraulic cylinder (see: ''swashplate
A swashplate, also known as slant disk, was invented by Anthony Michell in 1917. It is a mechanical engineering device used to translate the motion of a rotating shaft into reciprocating motion, or vice versa. The working principle is similar to c ...
''). Both components can be placed physically far apart on the machine, being connected only by flexible hoses. Hydrostatic drive systems are used on excavators, lawn tractors, forklifts, winch drive systems, heavy lift equipment, agricultural machinery, earth-moving equipment, etc. An arrangement fomotor-vehicle transmission
was probably used on the Ferguson '' F-1'' P99 racing car in about 1961. The
Human Friendly Transmission
The Human Friendly Transmission is the marketing name of a proprietary continuously variable transmission (CVT) made by Honda for its motorcycles, including the Honda DN-01 and EVO6 concept motorcycle.
The electronically controlled automatic ...
of the Honda DN-01 is hydrostatic.
Hydrodynamic
If the hydraulic pump or hydraulic motor makes use of thehydrodynamic
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids—liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including ''aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) and ...
effects of the fluid flow, i.e. pressure due to a change in the fluid's momentum as it flows through vanes in a turbine. The pump and motor usually consist of rotating vanes without seals and are typically placed in proximity. The transmission ratio can be made to vary by means of additional rotating vanes, an effect similar to varying the pitch of an airplane propeller
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon ...
.
The torque converter
A torque converter is a type of fluid coupling that transfers rotating power from a prime mover, like an internal combustion engine, to a rotating driven load. In a vehicle with an automatic transmission, the torque converter connects the power ...
in most automotive automatic transmissions is, in itself, a hydrodynamic transmission. Hydrodynamic transmissions are used in many passenger rail vehicles, those that are not using electrical transmissions. In this application, the advantage of smooth power delivery may outweigh the reduced efficiency caused by turbulence energy losses in the fluid.
See also
*Bearing reducer A Bearing reducer in engineering is a bearing that designates the full integration of high-precision reduction gear and high-precision radial-axial bearing in a compact unit. This transmission system allows the utilization of the bearing reducer in ...
*Chain drive
Chain drive is a way of transmitting mechanical power from one place to another. It is often used to convey power to the wheels of a vehicle, particularly bicycles and motorcycles. It is also used in a wide variety of machines besides vehicles. ...
*Clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission, especially from a drive shaft to a driven shaft. In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts). ...
*Driveline shunt
Driveline shunt occurs when a vehicle gives an abrupt jolt while coming on or off overrun or freewheel. It is caused when the gearbox or other transmission linkages do not immediately relay changes in engine output to changes in wheel speed. There ...
*Epicyclic gearing
An epicyclic gear train (also known as a planetary gearset) consists of two gears mounted so that the center of one gear revolves around the center of the other. A carrier connects the centers of the two gears and rotates the planet and sun gea ...
* Hydraulic transmission
*Manual transmission
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission (mechanics), transmission ...
*Motorcycle transmission
A motorcycle transmission is a transmission created specifically for motorcycle applications. They may also be found in use on other light vehicles such as motor tricycles and quadbikes, go-karts, offroad buggies, auto rickshaws, mowers, and oth ...
* Torque converter
A torque converter is a type of fluid coupling that transfers rotating power from a prime mover, like an internal combustion engine, to a rotating driven load. In a vehicle with an automatic transmission, the torque converter connects the power ...
*Transfer case
A transfer case is a part of the drivetrain of four-wheel-drive, all-wheel-drive, and other multiple powered axle vehicles. The transfer case transfers power from the transmission to the front and rear axles by means of drive shafts. It also syn ...
*Idle creep
Idle creep, sometimes called idle speed or just creep is the default speed that a vehicle with an automatic transmission will move either forward or in reverse when the change lever is in D for drive or R for reverse and the foot is taken off the ...
Notes
References
Further reading
*External links
* * WeberAuto 2012-09-23 {{DEFAULTSORT:Transmission (Mechanics) Mechanisms (engineering)