Me-262 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Messerschmitt Me 262, nicknamed ''Schwalbe'' (German: " Swallow") in fighter versions, or ''Sturmvogel'' (German: " Storm Bird") in fighter-bomber versions, is a

 The V3 third prototype
The V3 third prototype  Test flights continued over the next year, but engine problems continued to plague the project, the Jumo 004 being only marginally more reliable than the lower-thrust (7.83 kN/1,760 lbf) BMW 003. Early engines were so short-lived that they frequently needed replacement after only a single flight. Airframe modifications were complete by 1942 but, hampered by the lack of engines, serial production did not begin until 1944, and deliveries were low, with 28 Me 262s in June, 59 in July, but only 20 in August.
By mid-1943, the Jumo 004A engine had passed several 100-hour tests, with a time between overhauls of 50 hours being achieved. However, the Jumo 004A engine proved unsuitable for full-scale production because of its considerable weight and its high utilization of
Test flights continued over the next year, but engine problems continued to plague the project, the Jumo 004 being only marginally more reliable than the lower-thrust (7.83 kN/1,760 lbf) BMW 003. Early engines were so short-lived that they frequently needed replacement after only a single flight. Airframe modifications were complete by 1942 but, hampered by the lack of engines, serial production did not begin until 1944, and deliveries were low, with 28 Me 262s in June, 59 in July, but only 20 in August.
By mid-1943, the Jumo 004A engine had passed several 100-hour tests, with a time between overhauls of 50 hours being achieved. However, the Jumo 004A engine proved unsuitable for full-scale production because of its considerable weight and its high utilization of
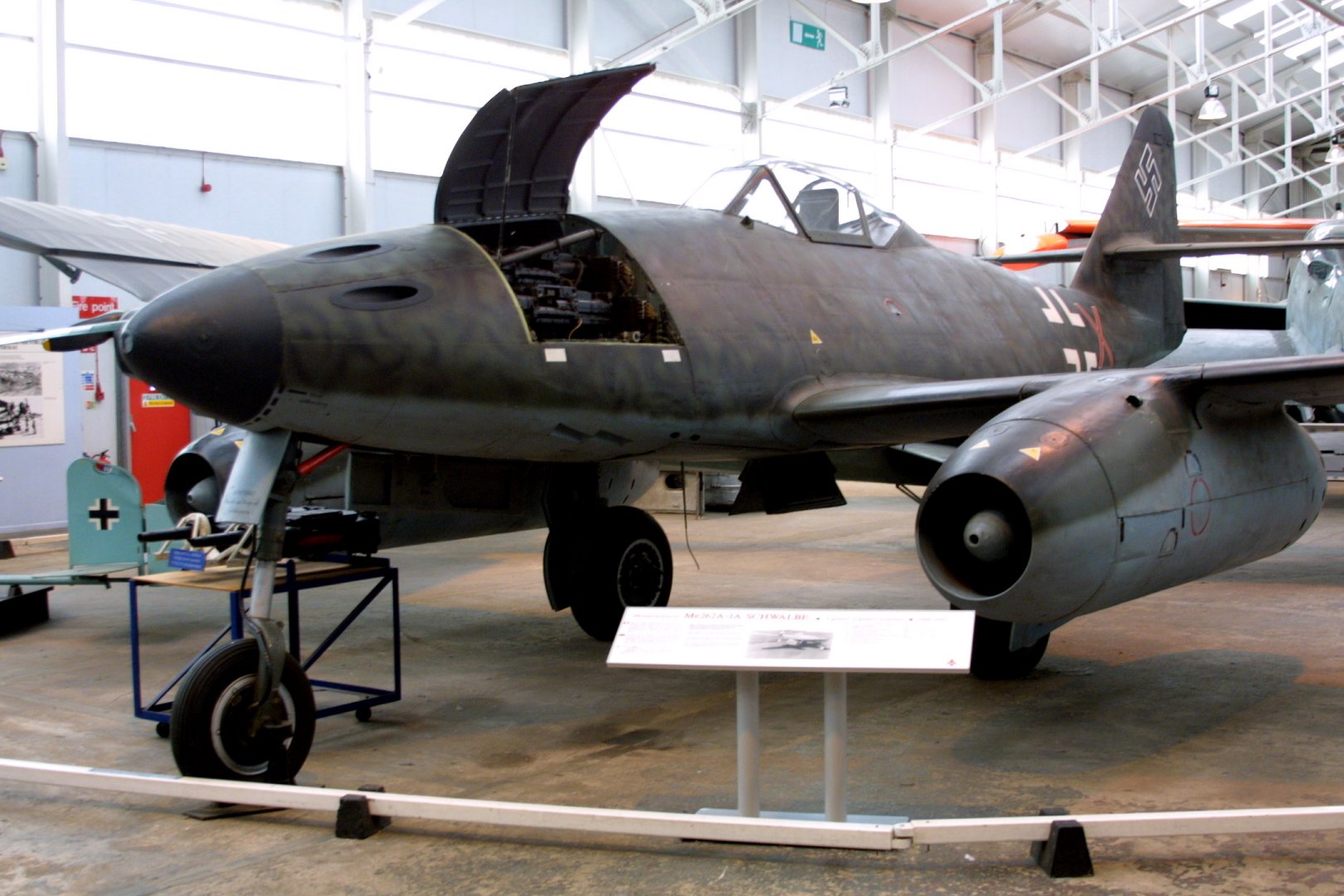 Major Walter Nowotny was assigned as commander after the death of Thierfelder in July 1944, and the unit redesignated '' Kommando Nowotny''. Essentially a trials and development unit, it mounted the world's first jet fighter operations. Trials progressed at a slow pace; it was not until August 1944 that initial operational missions were flown against the Allies; the unit made claims for 19 Allied aircraft in exchange for six Me 262s lost. Despite orders to stay grounded, Nowotny chose to fly a mission against an enemy bomber formation flying some above, on 8 November 1944. He claimed two P-51Ds destroyed before suffering engine failure at high altitude. Then, while diving and trying to restart his engines, he was attacked by other Mustangs, forced to bail out, and died. The ''Kommando'' was then withdrawn for further
Major Walter Nowotny was assigned as commander after the death of Thierfelder in July 1944, and the unit redesignated '' Kommando Nowotny''. Essentially a trials and development unit, it mounted the world's first jet fighter operations. Trials progressed at a slow pace; it was not until August 1944 that initial operational missions were flown against the Allies; the unit made claims for 19 Allied aircraft in exchange for six Me 262s lost. Despite orders to stay grounded, Nowotny chose to fly a mission against an enemy bomber formation flying some above, on 8 November 1944. He claimed two P-51Ds destroyed before suffering engine failure at high altitude. Then, while diving and trying to restart his engines, he was attacked by other Mustangs, forced to bail out, and died. The ''Kommando'' was then withdrawn for further  During March, Me 262 fighter units were able, for the first time, to mount large-scale attacks on Allied bomber formations. On 18 March 1945, thirty-seven Me 262s of JG 7 intercepted a force of 1,221 bombers and 632 escorting fighters. They shot down 12 bombers and one fighter for the loss of three Me 262s. Although a 4:1 ratio was exactly what the Luftwaffe would have needed to make an impact on the war, the absolute scale of their success was minor, as it represented only 1% of the attacking force.
In the last days of the conflict, Me 262s from JG 7 and other units were committed in ground assault missions, in an attempt to support German troops fighting Red Army forces. Just south of Berlin, halfway between Spremberg and the German capital, the Wehrmacht's 9th Army (with elements from the 12 Army and
During March, Me 262 fighter units were able, for the first time, to mount large-scale attacks on Allied bomber formations. On 18 March 1945, thirty-seven Me 262s of JG 7 intercepted a force of 1,221 bombers and 632 escorting fighters. They shot down 12 bombers and one fighter for the loss of three Me 262s. Although a 4:1 ratio was exactly what the Luftwaffe would have needed to make an impact on the war, the absolute scale of their success was minor, as it represented only 1% of the attacking force.
In the last days of the conflict, Me 262s from JG 7 and other units were committed in ground assault missions, in an attempt to support German troops fighting Red Army forces. Just south of Berlin, halfway between Spremberg and the German capital, the Wehrmacht's 9th Army (with elements from the 12 Army and  Several two-seat trainer variants of the Me 262, the Me 262 B-1a, had been adapted through the ''Umrüst-Bausatz 1'' factory refit package as night fighters, complete with on-board FuG 218 ''Neptun'' high-VHF band radar, using ''Hirschgeweih'' ("stag's antlers") antennae with a set of dipole elements shorter than the '' Lichtenstein SN-2'' had used, as the B-1a/U1 version. Serving with 10. ''Staffel'' ''Nachtjagdgeschwader'' 11, near Berlin, these few aircraft (alongside several single-seat examples) accounted for most of the 13 Mosquitoes lost over Berlin in the first three months of 1945. Intercepts were generally or entirely made using ''
Several two-seat trainer variants of the Me 262, the Me 262 B-1a, had been adapted through the ''Umrüst-Bausatz 1'' factory refit package as night fighters, complete with on-board FuG 218 ''Neptun'' high-VHF band radar, using ''Hirschgeweih'' ("stag's antlers") antennae with a set of dipole elements shorter than the '' Lichtenstein SN-2'' had used, as the B-1a/U1 version. Serving with 10. ''Staffel'' ''Nachtjagdgeschwader'' 11, near Berlin, these few aircraft (alongside several single-seat examples) accounted for most of the 13 Mosquitoes lost over Berlin in the first three months of 1945. Intercepts were generally or entirely made using ''
 The Me 262 was so fast that German pilots needed new tactics to attack Allied bombers. In the head-on attack, the combined closing speed of about was too high for accurate shooting with ordnance that could only fire about 650 rounds/min from each cannon, (~44 rounds/sec in total from the quartet of cannon). Even from astern, the closing speed was too great to use the short-ranged quartet of MK 108 cannon to maximum effect. A roller-coaster attack was devised, the Me 262s approached from astern and about than the bombers. From about , they went into a shallow dive that took them through the escort fighters with little risk of interception. When they were about and below the bombers, they pulled up sharply to reduce speed. On levelling off, they were and overtaking the bombers at about , well placed to attack them.
The Me 262 was so fast that German pilots needed new tactics to attack Allied bombers. In the head-on attack, the combined closing speed of about was too high for accurate shooting with ordnance that could only fire about 650 rounds/min from each cannon, (~44 rounds/sec in total from the quartet of cannon). Even from astern, the closing speed was too great to use the short-ranged quartet of MK 108 cannon to maximum effect. A roller-coaster attack was devised, the Me 262s approached from astern and about than the bombers. From about , they went into a shallow dive that took them through the escort fighters with little risk of interception. When they were about and below the bombers, they pulled up sharply to reduce speed. On levelling off, they were and overtaking the bombers at about , well placed to attack them.
 Since the short barrels of the 30 mm MK 108 cannon and low muzzle velocity (only ) rendered it inaccurate beyond ), coupled with the jet's velocity, which required breaking off at to avoid colliding with the target, Me 262 pilots normally commenced firing at . Gunners of Allied bomber aircraft found their electrically powered gun turrets had problems tracking the jets. Aiming was difficult because the jets closed into firing range quickly and remained in firing position only briefly, using their standard attack profile, which proved more effective.
Since the short barrels of the 30 mm MK 108 cannon and low muzzle velocity (only ) rendered it inaccurate beyond ), coupled with the jet's velocity, which required breaking off at to avoid colliding with the target, Me 262 pilots normally commenced firing at . Gunners of Allied bomber aircraft found their electrically powered gun turrets had problems tracking the jets. Aiming was difficult because the jets closed into firing range quickly and remained in firing position only briefly, using their standard attack profile, which proved more effective.
 A prominent Royal Navy test pilot, Captain Eric Brown, chief naval test pilot and commanding officer of the Captured Enemy Aircraft Flight
A prominent Royal Navy test pilot, Captain Eric Brown, chief naval test pilot and commanding officer of the Captured Enemy Aircraft Flight
 The Me 262 was difficult to counter because its high speed and rate of climb made it hard to intercept. However, as with other turbojet engines at the time, the Me 262's engines did not provide sufficient thrust at low airspeeds and throttle response was slow, so that in certain circumstances such as takeoff and landing the aircraft became a vulnerable target. Another disadvantage that pioneering jet aircraft of the World War II era shared, was the high risk of compressor stall and if throttle movements were too rapid, the engine(s) could suffer a flameout. The coarse opening of the throttle would cause fuel surging and lead to excessive jet pipe temperatures. Pilots were instructed to operate the throttle gently and avoid quick changes. German engineers introduced an automatic throttle regulator later in the war but it only partly alleviated the problem.
The plane had, by contemporary standards, a high wing loading (294.0 kg/m2, 60.2 lbs/ft2) that required higher takeoff and landing speeds. Due to poor throttle response, the engines' tendency for airflow disruption that could cause the compressor to stall was ubiquitous. The high speed of the Me 262 also presented problems when engaging enemy aircraft, the high-speed convergence allowing Me 262 pilots little time to line up their targets or acquire the appropriate amount of deflection. This problem faces any aircraft that approaches another from behind at much higher speed, as the slower aircraft in front can always pull a tighter turn, forcing the faster aircraft to overshoot.
Luftwaffe pilots eventually learned how to handle the Me 262's higher speed and the Me 262 soon proved a formidable air superiority fighter, with pilots such as Franz Schall managing to shoot down seventeen enemy fighters in the Me 262, ten of them American
The Me 262 was difficult to counter because its high speed and rate of climb made it hard to intercept. However, as with other turbojet engines at the time, the Me 262's engines did not provide sufficient thrust at low airspeeds and throttle response was slow, so that in certain circumstances such as takeoff and landing the aircraft became a vulnerable target. Another disadvantage that pioneering jet aircraft of the World War II era shared, was the high risk of compressor stall and if throttle movements were too rapid, the engine(s) could suffer a flameout. The coarse opening of the throttle would cause fuel surging and lead to excessive jet pipe temperatures. Pilots were instructed to operate the throttle gently and avoid quick changes. German engineers introduced an automatic throttle regulator later in the war but it only partly alleviated the problem.
The plane had, by contemporary standards, a high wing loading (294.0 kg/m2, 60.2 lbs/ft2) that required higher takeoff and landing speeds. Due to poor throttle response, the engines' tendency for airflow disruption that could cause the compressor to stall was ubiquitous. The high speed of the Me 262 also presented problems when engaging enemy aircraft, the high-speed convergence allowing Me 262 pilots little time to line up their targets or acquire the appropriate amount of deflection. This problem faces any aircraft that approaches another from behind at much higher speed, as the slower aircraft in front can always pull a tighter turn, forcing the faster aircraft to overshoot.
Luftwaffe pilots eventually learned how to handle the Me 262's higher speed and the Me 262 soon proved a formidable air superiority fighter, with pilots such as Franz Schall managing to shoot down seventeen enemy fighters in the Me 262, ten of them American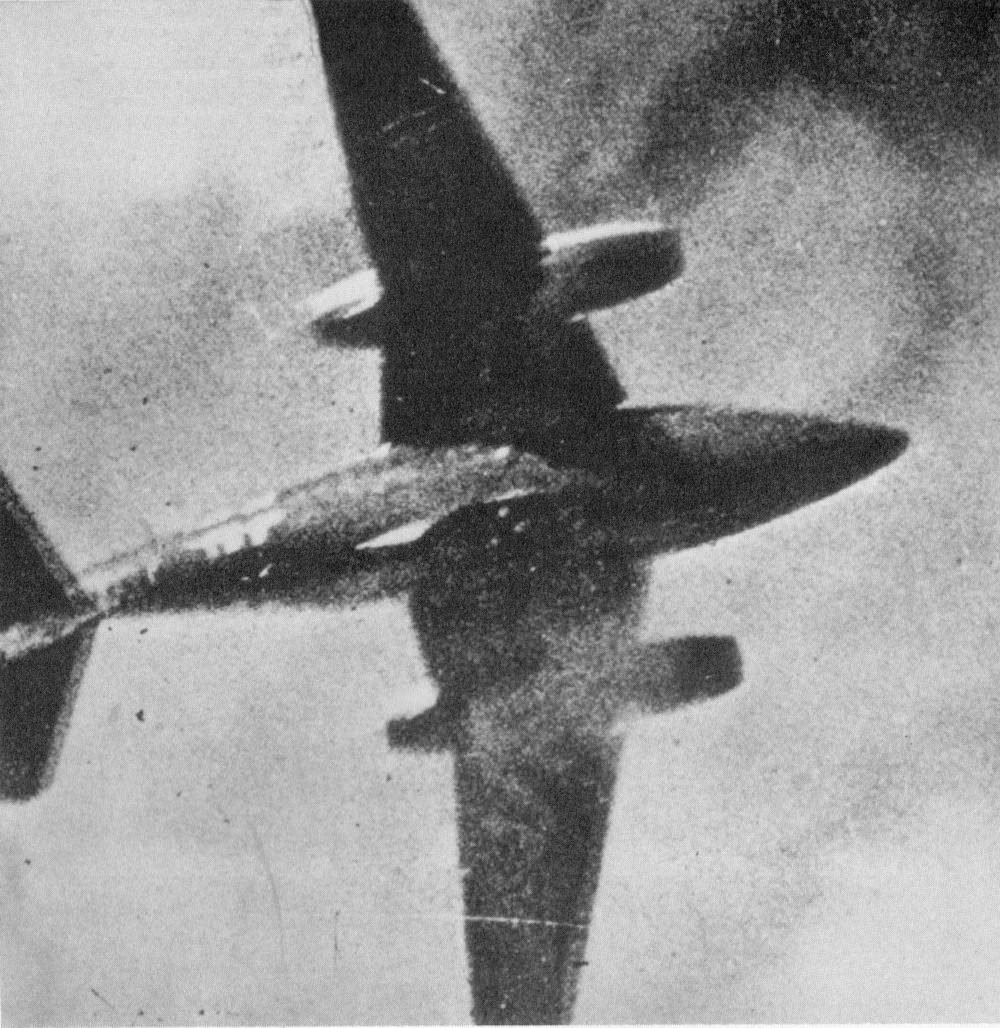  Too fast to catch for the escorting Allied fighters, the Me 262s were almost impossible to head off. As a result, Me 262 pilots were relatively safe from the Allied fighters, as long as they did not allow themselves to get drawn into low-speed turning contests and saved their maneuvering for higher speeds. Combating the Allied fighters could be effectively done the same way as the U.S. fighters fought the more nimble, but slower, Japanese fighters in the Pacific.
Allied pilots soon found that the only reliable way to destroy the jets, as with the even faster Me 163B ''Komet'' rocket fighters, was to attack them on the ground or during takeoff or landing. Luftwaffe airfields identified as jet bases were frequently bombed by medium bombers, and Allied fighters patrolled over the fields to attack jets trying to land. The Luftwaffe countered by installing extensive ''Flak'' alleys of anti-aircraft guns along the approach lines to protect the Me 262s from the ground—and by providing top cover during the jets' takeoff and landing with the most advanced Luftwaffe single-engined fighters, the
Too fast to catch for the escorting Allied fighters, the Me 262s were almost impossible to head off. As a result, Me 262 pilots were relatively safe from the Allied fighters, as long as they did not allow themselves to get drawn into low-speed turning contests and saved their maneuvering for higher speeds. Combating the Allied fighters could be effectively done the same way as the U.S. fighters fought the more nimble, but slower, Japanese fighters in the Pacific.
Allied pilots soon found that the only reliable way to destroy the jets, as with the even faster Me 163B ''Komet'' rocket fighters, was to attack them on the ground or during takeoff or landing. Luftwaffe airfields identified as jet bases were frequently bombed by medium bombers, and Allied fighters patrolled over the fields to attack jets trying to land. The Luftwaffe countered by installing extensive ''Flak'' alleys of anti-aircraft guns along the approach lines to protect the Me 262s from the ground—and by providing top cover during the jets' takeoff and landing with the most advanced Luftwaffe single-engined fighters, the
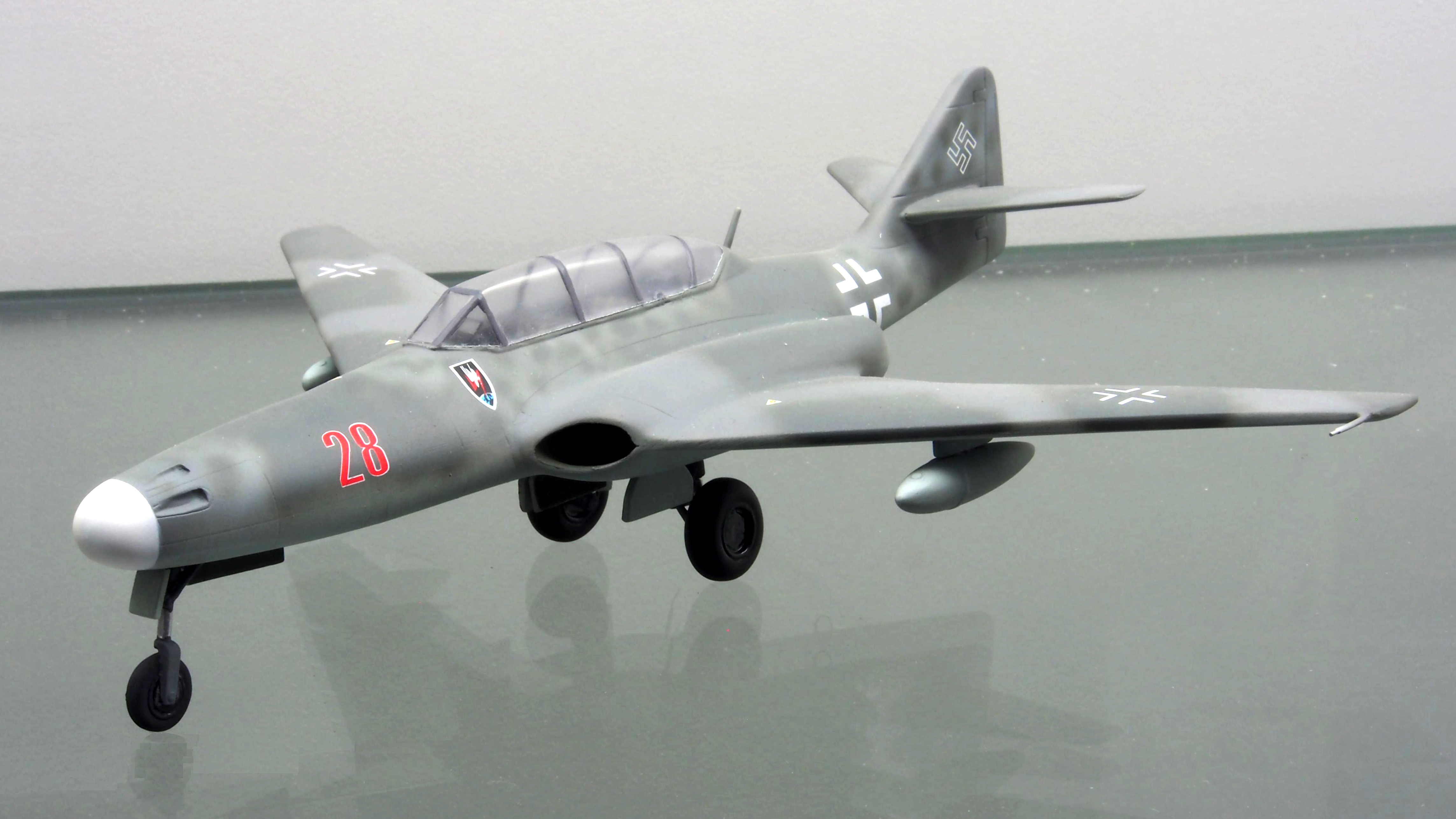

 About 1,400 planes were produced, however, less than a hundred Me 262s were in a combat-ready condition at any one time. According to sources they destroyed from 300 to 450 enemy planes, with the Allies destroying about one hundred Me 262s in the air. While Germany was bombed intensively, production of the Me 262 was dispersed into low-profile production facilities, sometimes little more than clearings in the forests of Germany and occupied countries. From the end of February to the end of March 1945, approximately sixty Me 262s were destroyed in attacks on
About 1,400 planes were produced, however, less than a hundred Me 262s were in a combat-ready condition at any one time. According to sources they destroyed from 300 to 450 enemy planes, with the Allies destroying about one hundred Me 262s in the air. While Germany was bombed intensively, production of the Me 262 was dispersed into low-profile production facilities, sometimes little more than clearings in the forests of Germany and occupied countries. From the end of February to the end of March 1945, approximately sixty Me 262s were destroyed in attacks on
 After the end of the war, the Me 262 and other advanced German technologies were quickly swept up by the Soviets, British and Americans, as part of the USAAF's Operation Lusty. Many Me 262s were found in readily repairable condition and were confiscated. The Soviets, British and Americans wished to evaluate the technology, particularly the engines.
During testing, the Me 262 was found to be faster than the British Gloster Meteor jet fighter, and had better visibility to the sides and rear (mostly due to the canopy frames and the discoloration caused by the plastics used in the Meteor's construction), and was a superior gun platform to the Meteor F.1 which had a tendency to snake at high speed and exhibited "weak" aileron response. The Me 262 had a shorter range than the Meteor and had less reliable engines.
The USAAF compared the Lockheed P-80 Shooting Star and Me 262, concluding that the Me 262 was superior in acceleration and speed, with similar climb performance. The Me 262 appeared to have a higher critical Mach number than any American fighter.
The Americans also tested a Me 262A-1a/U3 unarmed photo reconnaissance version, which was fitted with a fighter nose and a smooth finish. Between May and August 1946, the aircraft completed eight flights, lasting four hours and forty minutes. Testing was discontinued after four engine changes were required during the course of the tests, culminating in two single-engine landings. These aircraft were extensively studied, aiding development of early US, British and Soviet jet fighters. The F-86, designed by engineer Edgar Schmued, used a
After the end of the war, the Me 262 and other advanced German technologies were quickly swept up by the Soviets, British and Americans, as part of the USAAF's Operation Lusty. Many Me 262s were found in readily repairable condition and were confiscated. The Soviets, British and Americans wished to evaluate the technology, particularly the engines.
During testing, the Me 262 was found to be faster than the British Gloster Meteor jet fighter, and had better visibility to the sides and rear (mostly due to the canopy frames and the discoloration caused by the plastics used in the Meteor's construction), and was a superior gun platform to the Meteor F.1 which had a tendency to snake at high speed and exhibited "weak" aileron response. The Me 262 had a shorter range than the Meteor and had less reliable engines.
The USAAF compared the Lockheed P-80 Shooting Star and Me 262, concluding that the Me 262 was superior in acceleration and speed, with similar climb performance. The Me 262 appeared to have a higher critical Mach number than any American fighter.
The Americans also tested a Me 262A-1a/U3 unarmed photo reconnaissance version, which was fitted with a fighter nose and a smooth finish. Between May and August 1946, the aircraft completed eight flights, lasting four hours and forty minutes. Testing was discontinued after four engine changes were required during the course of the tests, culminating in two single-engine landings. These aircraft were extensively studied, aiding development of early US, British and Soviet jet fighters. The F-86, designed by engineer Edgar Schmued, used a
 In January 2003, the American Me 262 Project, based in Everett, Washington, completed flight testing to allow the delivery of partially updated spec reproductions of several versions of the Me 262 including at least two B-1c two-seater variants, one A-1c single-seater and two "convertibles" that could be switched between the A-1c and B-1c configurations. All are powered by General Electric CJ610 engines and feature additional safety features, such as upgraded brakes and strengthened landing gear. The "c" suffix refers to the new CJ610 powerplant and has been informally assigned with the approval of the Messerschmitt Foundation in Germany (the Werknummer of the reproductions picked up where the last wartime produced Me 262 left off – a continuous airframe serial number run with a near 60-year production break).
Flight testing of the first newly manufactured Me 262 A-1c (single-seat) variant (Werknummer 501244) was completed in August 2005. The first of these machines (Werknummer 501241) went to a private owner in the southwestern United States, while the second (Werknummer 501244) was delivered to the Messerschmitt Foundation at Manching, Germany. This aircraft conducted a private test flight in late April 2006 and made its public debut in May at the ILA 2006. The new Me 262 flew during the public flight demonstrations. Me 262 Werknummer 501241 was delivered to the Collings Foundation as White 1 of JG 7; this aircraft offered ride-along flights starting in 2008. The third replica, a non-flyable Me 262 A-1c, was delivered to the Evergreen Aviation & Space Museum in May 2010.
In January 2003, the American Me 262 Project, based in Everett, Washington, completed flight testing to allow the delivery of partially updated spec reproductions of several versions of the Me 262 including at least two B-1c two-seater variants, one A-1c single-seater and two "convertibles" that could be switched between the A-1c and B-1c configurations. All are powered by General Electric CJ610 engines and feature additional safety features, such as upgraded brakes and strengthened landing gear. The "c" suffix refers to the new CJ610 powerplant and has been informally assigned with the approval of the Messerschmitt Foundation in Germany (the Werknummer of the reproductions picked up where the last wartime produced Me 262 left off – a continuous airframe serial number run with a near 60-year production break).
Flight testing of the first newly manufactured Me 262 A-1c (single-seat) variant (Werknummer 501244) was completed in August 2005. The first of these machines (Werknummer 501241) went to a private owner in the southwestern United States, while the second (Werknummer 501244) was delivered to the Messerschmitt Foundation at Manching, Germany. This aircraft conducted a private test flight in late April 2006 and made its public debut in May at the ILA 2006. The new Me 262 flew during the public flight demonstrations. Me 262 Werknummer 501241 was delivered to the Collings Foundation as White 1 of JG 7; this aircraft offered ride-along flights starting in 2008. The third replica, a non-flyable Me 262 A-1c, was delivered to the Evergreen Aviation & Space Museum in May 2010.
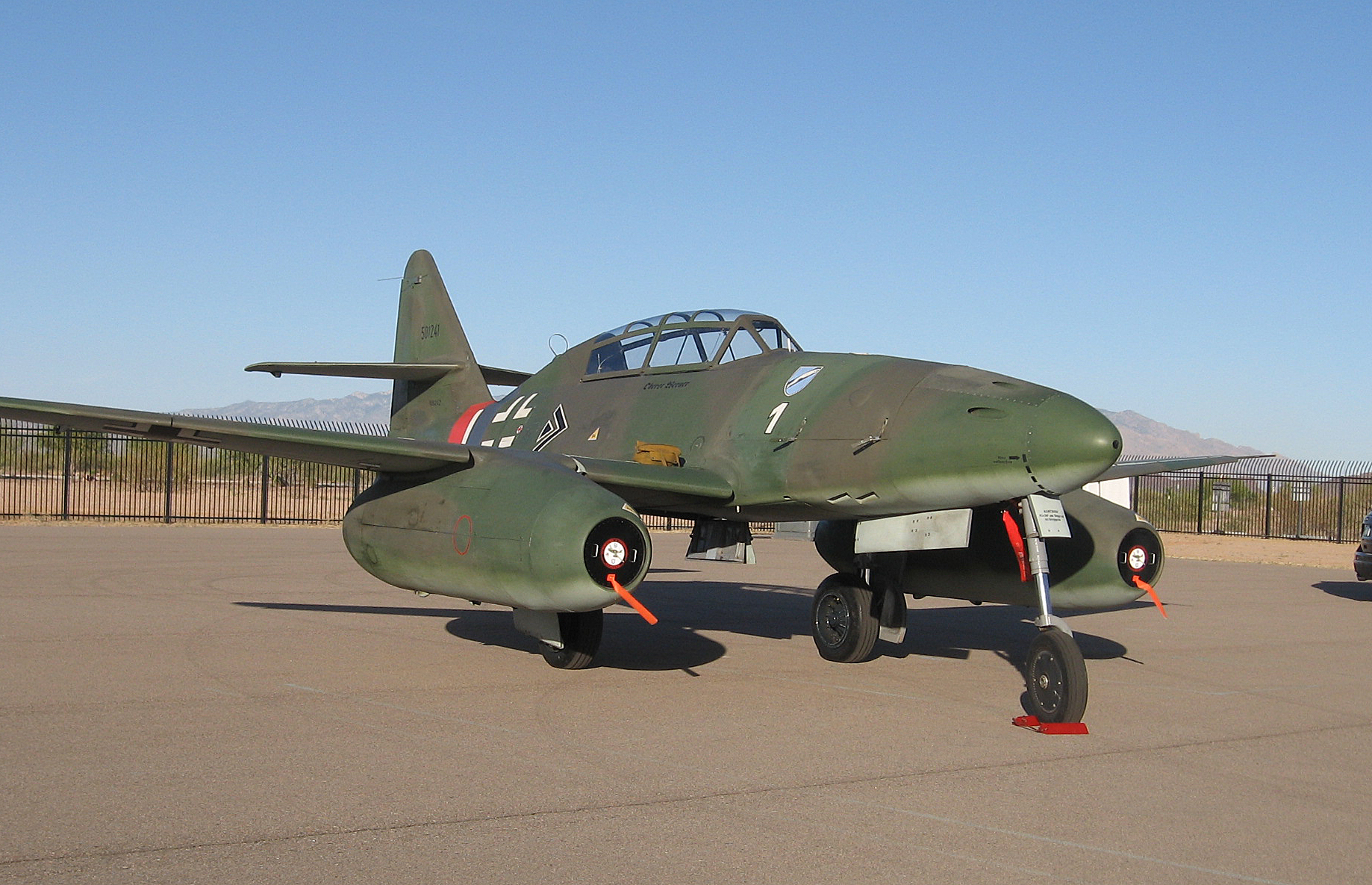

 ''Note:''- U = ''Umrüst-Bausatz'' – conversion kit installed at factory level, denoted as a suffix in the form /U''n''.
; Me 262 A-0
: Pre-production aircraft fitted with two
''Note:''- U = ''Umrüst-Bausatz'' – conversion kit installed at factory level, denoted as a suffix in the form /U''n''.
; Me 262 A-0
: Pre-production aircraft fitted with two
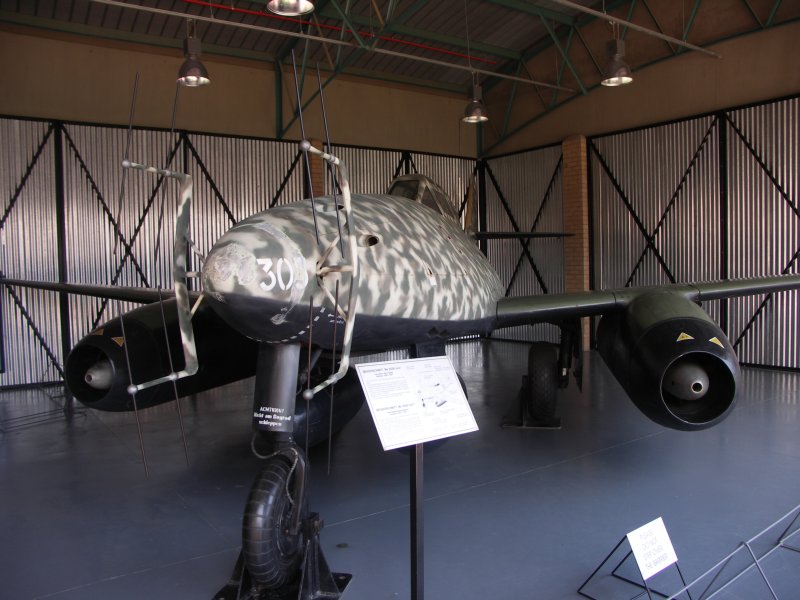



 ; Me 262 A-1a/R7, W.Nr.500071 ''White 3'', III./JG 7
: Deutsches Museum, Munich, Germany. This aircraft, flown by Hans Guido Mutke while a pilot of 9. Staffel/''JG'' 7, was confiscated by Swiss authorities on 25 April 1945 after Mutke made an emergency landing in Switzerland due to lack of fuel (80 litres were remaining, 35 litres were usually burnt in one minute).
; Me 262 A-1a
: Reconstructed from parts of crashed and incomplete Me 262s. Luftwaffenmuseum der Bundeswehr, Germany.
; Me 262 A-1a W.Nr.501232 ''Yellow 5'', 3./KG(J)6
: National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio, US.
; Me 262 A-1a/U3 W.Nr.500453
: Flying Heritage Collection, Everett, Washington, United States, currently undergoing restoration to flying condition. It is intended to fly using its original Jumo 004 engines. The aircraft was bought from the Planes of Fame Air Museum, Chino, California.
; Me 262 A-1a/R7 W.Nr.500491 ''Yellow 7'', II./JG 7
:
; Me 262 A-1a/R7, W.Nr.500071 ''White 3'', III./JG 7
: Deutsches Museum, Munich, Germany. This aircraft, flown by Hans Guido Mutke while a pilot of 9. Staffel/''JG'' 7, was confiscated by Swiss authorities on 25 April 1945 after Mutke made an emergency landing in Switzerland due to lack of fuel (80 litres were remaining, 35 litres were usually burnt in one minute).
; Me 262 A-1a
: Reconstructed from parts of crashed and incomplete Me 262s. Luftwaffenmuseum der Bundeswehr, Germany.
; Me 262 A-1a W.Nr.501232 ''Yellow 5'', 3./KG(J)6
: National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio, US.
; Me 262 A-1a/U3 W.Nr.500453
: Flying Heritage Collection, Everett, Washington, United States, currently undergoing restoration to flying condition. It is intended to fly using its original Jumo 004 engines. The aircraft was bought from the Planes of Fame Air Museum, Chino, California.
; Me 262 A-1a/R7 W.Nr.500491 ''Yellow 7'', II./JG 7
:

Gun camera footage of US 8th Airforce engagements against Me-262s
{{Subject bar , portal1=Aviation , portal2=Military of Germany , portal3=World War II , commons=y Aircraft first flown in 1942 S-092 Cruciform tail aircraft German inventions of the Nazi period Low-wing aircraft Mauthausen concentration camp Me 262 1940s German fighter aircraft Twinjets World War II jet aircraft of Germany
fighter aircraft
Fighter aircraft are fixed-wing military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield ...
and fighter-bomber
A fighter-bomber is a fighter aircraft that has been modified, or used primarily, as a light bomber or attack aircraft. It differs from bomber and attack aircraft primarily in its origins, as a fighter that has been adapted into other roles, wh ...
that was designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt
Messerschmitt AG () was a German share-ownership limited, aircraft manufacturing corporation named after its chief designer Willy Messerschmitt from mid-July 1938 onwards, and known primarily for its World War II fighter aircraft, in partic ...
. It was the world's first operational jet-powered fighter aircraft.
The initial design of what would become the Me 262 started in April 1939, prior to the start of the Second World War. While the aircraft performed its maiden flight on 18 April 1941, this was using piston engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common featu ...
instead of jet propulsion; it was not until 18 July 1942 that the first jet-powered flight was performed. Progress on the project was delayed by problems with engines, metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sc ...
and top-level interference from figures such as Hermann Göring, head of the Luftwaffe, and Adolf Hitler. The latter advocated from the Me 262 to be operated as a ground-attack/ bomber aircraft rather than a defensive interceptor, thus necessitating a redesign. Accordingly, the aircraft was eventually brought into operational status with the Luftwaffe during mid-1944. In its operational configuration, the Me 262 was both faster and more heavily armed than any Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
fighter, including the British jet-powered Gloster Meteor. The Allies countered its effectiveness in the air by frequently attacking the aircraft while on the ground and during takeoff and landing.
Being one of the most advanced aviation designs to attain operational status during the Second World War, the Me 262's roles included light bomber
A light bomber is a relatively small and fast type of military bomber aircraft that was primarily employed before the 1950s. Such aircraft would typically not carry more than one ton of ordnance.
The earliest light bombers were intended to dro ...
, reconnaissance, and experimental night fighter versions. The Me 262 proved to be an effective dogfighter against Allied fighters; German pilots claimed a total of 542 Allied aircraft shot down, although higher claims have sometimes been made. Operations were plagued with reliability issues, which were largely a result of widespread strategic materials
Strategic material is any sort of raw material that is important to an individual's or organization's strategic plan and supply chain management. Lack of supply of strategic materials may leave an organization or government vulnerable to disru ...
shortages as well as design compromises on the Junkers Jumo 004
The Junkers Jumo 004 was the world's first production turbojet engine in operational use, and the first successful axial compressor turbojet engine. Some 8,000 units were manufactured by Junkers in Germany late in World War II, powering the Mess ...
axial-flow turbojet engines that powered it. Attacks by Allied forces on fuel supplies during the deteriorating late-war situation also reduced the effectiveness of the Me 262 as a fighting force. Armament production within Germany was focused on more easily manufactured aircraft. In the end, the Me 262 had a negligible impact on the course of the war as a result of its late introduction and the consequently small numbers that entered operational service.
While German use of the Me 262 ended with the close of the Second World War, a small number were operated by the Czechoslovak Air Force until 1951. Also, Israel was allegedly counted as a user of a handful (between two and eight) of Me 262s, which were supposedly built by Avia and supplied covertly, although there have been no official confirmations of such use.
It also heavily influenced several designs, such as the Sukhoi Su-9 (1946)
The Sukhoi Su-9 (russian: Самолёт K, lit=Aircraft K; USAF/DoD designation: Type 8) was an early jet fighter built in the Soviet Union shortly after World War II. The design began in 1944 and was intended to use Soviet-designed turboj ...
and Nakajima Kikka
The was Japan's first jet aircraft. It was developed late in World War II and the first prototype had only flown once before the end of the conflict. It was also called .
Design and development
After the Japanese military attaché in Germany w ...
. Numerous captured Me 262s were studied and flight-tested by the major powers, and ultimately influenced the designs of post-war aircraft such as the North American F-86 Sabre, MiG-15 and Boeing B-47 Stratojet. Several aircraft have survived on static display in museums, while multiple privately built flying reproductions have also been produced; these are commonly powered by modern General Electric CJ610 engines.
Design and development
Origins
Several years prior to the Second World War, the Germans foresaw the great potential for aircraft powered by thejet engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term ...
constructed by Hans von Ohain in 1936. After the successful test flights of the world's first jet aircraft—the Heinkel He 178—within a week of the invasion of Poland which started the conflict, they adopted the jet engine for an advanced fighter aircraft. As a result, the Me 262 was already under development as ''Projekt'' 1065 (P.1065) before the start of the war. The project had originated with a request by the ''Reichsluftfahrtministerium
The Ministry of Aviation (german: Reichsluftfahrtministerium, abbreviated RLM) was a government department during the period of Nazi Germany (1933–45). It is also the original name of the Detlev-Rohwedder-Haus building on the Wilhelmstrasse ...
'' (RLM, Ministry of Aviation) for a jet aircraft capable of one hour's endurance and a speed of at least . Woldemar Voigt headed the design team, with Messerschmitt's chief of development, Robert Lusser, overseeing.
During April 1939, initial plans were drawn up and, following their submission in June 1939, the original design was very different from the aircraft that eventually entered service. Specifically, it featured wing-root-mounted engines, rather than podded ones. The progression of the original design was delayed greatly by technical problems with the new jet engine. Because the engines were slow to arrive, Messerschmitt moved the engines from the wing roots to underwing pods, allowing them to be changed more readily if needed. That turned out to be important, both for availability and maintenance. Since the BMW 003 jets proved heavier than anticipated, the wing was swept slightly, by 18.5°, to accommodate a change in the center of gravity.
The jet engine program was waylaid by a lack of funding, which was primarily due to a prevailing attitude amongst high-ranking officials that the conflict could be won easily with conventional aircraft. Among these was Hermann Göring, head of the Luftwaffe, who cut the engine development program to just 35 engineers in February 1940 (the month before the first wooden mock-up was completed). The aeronautical engineer Willy Messerschmitt sought to maintain mass production
Mass production, also known as flow production or continuous production, is the production of substantial amounts of standardized products in a constant flow, including and especially on assembly lines. Together with job production and batch ...
of the piston-powered, 1935-origin Bf 109
The Messerschmitt Bf 109 is a German World War II fighter aircraft that was, along with the Focke-Wulf Fw 190, the backbone of the Luftwaffe's fighter force. The Bf 109 first saw operational service in 1937 during the Spanish Civil War an ...
and the projected Me 209
The first Messerschmitt Me 209 was a single-engine racing aircraft which was designed for and succeeded at breaking speed records. This Me 209 was a completely new aircraft whose designation was used by Messerschmitt as a propaganda tool. Alth ...
. Major General Adolf Galland
Adolf Josef Ferdinand Galland (19 March 1912 – 9 February 1996) was a German Luftwaffe general and flying ace who served throughout the Second World War in Europe. He flew 705 combat missions, and fought on the Western Front and in the Defen ...
had supported Messerschmitt through the early development years, flying the Me 262 himself on 22 April 1943. By that time, the problems with engine development had slowed production of the aircraft considerably. One particularly acute problem was the lack of an alloy with a melting point high enough to endure the temperatures involved, a problem that had not been adequately resolved by the end of the war. After a November 1941 flight (with BMW 003s) ended in a double flameout, the aircraft made its first successful flight entirely on jet power on 18 July 1942, propelled by a pair of Jumo 004 engines.

Ludwig Bölkow
Ludwig Bölkow (30 June 1912 – 25 July 2003) was one of the aeronautical pioneers of Germany.
Background
Born in Schwerin, in then north-central Germany, in 1912, Bölkow was the son of a foreman employed by Fokker, one of the leading air ...
was the principal aerodynamicist assigned to work on the design of the Me 262. He initially designed the wing using NACA airfoil
An airfoil (American English) or aerofoil (British English) is the cross-sectional shape of an object whose motion through a gas is capable of generating significant lift, such as a wing, a sail, or the blades of propeller, rotor, or turbine.
...
s modified with an elliptical nose section. Later in the design process, these were changed to AVL derivatives of NACA airfoils, the NACA 00011-0.825-35 being used at the root and the NACA 00009-1.1-40 at the tip. The elliptical nose derivatives of the NACA airfoils were used on the horizontal and vertical tail surfaces. Wings were of single-spar cantilever construction, with stressed skins, varying from skin thickness at the root to at the tip. To expedite construction, save weight, and use fewer strategic material
Strategic material is any sort of raw material that is important to an individual's or organization's strategic plan and supply chain management. Lack of supply of strategic materials may leave an organization or government vulnerable to disru ...
s late in the war, the wing interiors were not painted. The wings were fastened to the fuselage at four points, using a pair of and forty-two bolts.
During mid-1943, Adolf Hitler envisioned the Me 262 as a ground-attack/ bomber aircraft rather than a defensive interceptor. The configuration of a high-speed, light-payload '' Schnellbomber'' ("fast bomber") was intended to penetrate enemy airspace during the expected Allied invasion of France. His edict resulted in the development of (and concentration on) the ''Sturmvogel'' variant. Hitler's interference helped to extend the delay in bringing the ''Schwalbe'' into operation; (other factors contributed too; in particular, there were engine vibration problems which needed attention). In his memoirs, Albert Speer
Berthold Konrad Hermann Albert Speer (; ; 19 March 1905 – 1 September 1981) was a German architect who served as the Minister of Armaments and War Production in Nazi Germany during most of World War II. A close ally of Adolf Hitler, he ...
, then Minister of Armaments and War Production, claimed Hitler originally had blocked mass production of the Me 262, before agreeing in early 1944. Similar criticisms were voiced by Lieutenant General Adolf Galland. Hitler rejected arguments that the aircraft would be more effective as a fighter against the Allied bombers destroying large parts of Germany and wanted it as a bomber for revenge attacks. According to Speer, Hitler felt its superior speed compared to other fighters of the era meant it could not be attacked, and so preferred it for high altitude straight flying.
The Me 262 is often referred to as a "swept wing
A swept wing is a wing that angles either backward or occasionally forward from its root rather than in a straight sideways direction.
Swept wings have been flown since the pioneer days of aviation. Wing sweep at high speeds was first investigate ...
" design as the production aircraft had a small, but significant leading edge sweep of 18.5° which likely provided an advantage by increasing the critical Mach number. Sweep, uncommon at the time, was added after the initial design of the aircraft. The engines proved heavier than originally expected, and the sweep was added primarily to position the center of lift properly relative to the center of mass. (The original 35° sweep, proposed by Adolf Busemann
Adolf Busemann (20 April 1901 – 3 November 1986) was a German aerospace engineer and influential Nazi-era pioneer in aerodynamics, specialising in supersonic airflows. He introduced the concept of swept wings and, after emigrating in 1947 to t ...
, was not adopted.) On 1 March 1940, instead of moving the wing backward on its mount, the outer wing was re-positioned slightly aft; the trailing edge of the midsection of the wing remained unswept. Based on data from the AVA Göttingen and wind tunnel results, the inboard section's leading edge (between the nacelle and wing root) was later swept to the same angle as the outer panels, from the "V6" sixth prototype onward throughout volume production.
Test flights
Testing showed that the Me 262 handled much better than previous fighters, such as the Bf 109 or Fw 190. Handling was so improved over the previous aircraft that a report by Major Ernst Englander stated that any Bf 109 pilot could convert to the Me 262 with only an hour of instruction. According to his report, even bomber pilots who converted to fly the Me 262 only required three instruction flights, and less than 5% had any difficulty retraining. The Me 262 had a gentle stall and gentle landing characteristics compared to previous German fighters. Its handling improved with speed and would lose much less speed during turning. It had a cruising speed of 465 mph, which was faster than the top speed of most other fighters of the day. It also had far better visibility in every direction compared to previous German fighters. Due to lack of engine torque, if a single engine was lost the aircraft remained easily controlled and landed without issue. Its only major deficiency was that brakes could not be used until the nose wheel had touched down, because engaging them before would smash the nose wheel strongly into the runway, potentially destroying the nose wheel and even the aircraft. The quality of the aircraft was high, with only 10% of aircraft returned for minor defects such as wings being out of alignment by under 1 degree. It could reach 515 mph without issue, although because it could reach extreme speeds in dives, components such as bomb racks would sometimes tear off. Test flights began on 18 April 1941, with the Me 262 V1 example, bearing its ''Stammkennzeichen'' radio code letters of PC+UA, but since its intended BMW 003 turbojets were not ready for fitting, a conventionalJunkers Jumo 210
The Jumo 210 was Junkers Motoren's first production inverted V12 gasoline aircraft engine, first produced in the early 1930s. Depending on the version it produced between 610 and 730 PS and can be considered a counterpart of the Rolls-Royce Kest ...
engine was mounted in the V1 prototype's nose, driving a propeller, to test the Me 262 V1 airframe. When the BMW 003 engines were installed, the Jumo was retained for safety, which proved wise as both 003s failed during the first flight and the pilot had to land using the nose-mounted engine alone. The V1 through V4 prototype airframes all possessed what would become an uncharacteristic feature for most later jet aircraft designs, a fully retracting conventional gear setup with a retracting tailwheel—indeed, the very first prospective German "jet fighter" airframe design ever flown, the Heinkel He 280, used a retractable tricycle landing gear from its beginnings and flying on jet power alone as early as the end of March 1941.
 The V3 third prototype
The V3 third prototype airframe
The mechanical structure of an aircraft is known as the airframe. This structure is typically considered to include the fuselage, undercarriage, empennage and wings, and excludes the propulsion system.
Airframe design is a field of aerospa ...
, with the code PC+UC, became a true jet when it flew on 18 July 1942 in Leipheim near Günzburg, Germany, piloted by test pilot Fritz Wendel. This was almost nine months ahead of the British Gloster Meteor's first flight on 5 March 1943. Its retracting conventional tail wheel gear (similar to other contemporary piston-powered propeller aircraft), a feature shared with the first four Me 262 V-series airframes, caused its jet exhaust to deflect off the runway, with the wing's turbulence negating the effects of the elevators, and the first takeoff attempt was cut short.
On the second attempt, Wendel solved the problem by tapping the aircraft's brakes at takeoff speed, lifting the horizontal tail out of the wing's turbulence. The first four prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototyp ...
s (V1-V4) were built with the conventional gear configuration. Changing to a tricycle arrangement—a permanently fixed undercarriage on the fifth prototype (V5, code PC+UE), with the definitive fully retractable nosewheel gear on the V6 (with ''Stammkennzeichen'' code VI+AA, from a new code block) and subsequent aircraft corrected this problem.
 Test flights continued over the next year, but engine problems continued to plague the project, the Jumo 004 being only marginally more reliable than the lower-thrust (7.83 kN/1,760 lbf) BMW 003. Early engines were so short-lived that they frequently needed replacement after only a single flight. Airframe modifications were complete by 1942 but, hampered by the lack of engines, serial production did not begin until 1944, and deliveries were low, with 28 Me 262s in June, 59 in July, but only 20 in August.
By mid-1943, the Jumo 004A engine had passed several 100-hour tests, with a time between overhauls of 50 hours being achieved. However, the Jumo 004A engine proved unsuitable for full-scale production because of its considerable weight and its high utilization of
Test flights continued over the next year, but engine problems continued to plague the project, the Jumo 004 being only marginally more reliable than the lower-thrust (7.83 kN/1,760 lbf) BMW 003. Early engines were so short-lived that they frequently needed replacement after only a single flight. Airframe modifications were complete by 1942 but, hampered by the lack of engines, serial production did not begin until 1944, and deliveries were low, with 28 Me 262s in June, 59 in July, but only 20 in August.
By mid-1943, the Jumo 004A engine had passed several 100-hour tests, with a time between overhauls of 50 hours being achieved. However, the Jumo 004A engine proved unsuitable for full-scale production because of its considerable weight and its high utilization of strategic material
Strategic material is any sort of raw material that is important to an individual's or organization's strategic plan and supply chain management. Lack of supply of strategic materials may leave an organization or government vulnerable to disru ...
(Ni, Co, Mo), which were in short supply. Consequently, the 004B engine was designed to use a minimum amount of strategic materials. All high heat-resistant metal parts, including the combustion chamber, were changed to mild steel (SAE 1010) and were protected only against oxidation by aluminum coating. The total engine represented a design compromise to minimize the use of strategic materials and to simplify manufacture. With the lower-quality steels used in the 004B, the engine required overhaul after just 25 hours for a metallurgical test on the turbine. If it passed the test, the engine was refitted for a further 10 hours of usage, but 35 hours marked the absolute limit for the turbine wheel. While BMW's and Junkers' axial compressor turbojet engines were characterised by a sophisticated design that could offer a considerable advantage – also used in a generalized form for the contemporary American Westinghouse J30 turbojet – the lack of rare materials for the Jumo 004 design put it at a disadvantage compared to the "partly axial-flow" Power Jets W.2/700 turbojet engine which, despite its own largely centrifugal compressor-influenced design, provided (between an operating overhaul interval of 60–65 hours) an operational life span of 125 hours. Frank Whittle concludes in his final assessment over the two engines: "it was in the quality of high temperature materials that the difference between German and British engines was most marked"
Operationally, carrying of fuel in two tanks, one each fore and aft of the cockpit; and a ventral fuselage tank beneath, the Me 262 would have a total flight endurance of 60 to 90 minutes. Fuel was usually J2 (derived
Derive may refer to:
* Derive (computer algebra system), a commercial system made by Texas Instruments
* ''Dérive'' (magazine), an Austrian science magazine on urbanism
*Dérive, a psychogeographical concept
See also
*
*Derivation (disambiguatio ...
from brown coal), with the option of diesel or a mixture of oil and high octane
Octane is a hydrocarbon and an alkane with the chemical formula , and the condensed structural formula . Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the amount and location of branching in the carbon chain. One of these isomers, 2,2,4-Tri ...
B4 aviation petrol. Fuel consumption was double the rate of typical twin-engine fighter aircraft of the era, which led to the installation of a low-fuel warning indicator in the cockpit that notified pilots when remaining fuel fell below .
Unit cost for an Me 262 airframe, less engines, armament, and electronics, was . To build one airframe took around 6,400-man-hours.
Operational history
Introduction
On 19 April 1944, '' Erprobungskommando'' 262 was formed atLechfeld
The Battle of Lechfeld was a series of military engagements over the course of three days from 10–12 August 955 in which the Kingdom of Germany, led by King Otto I the Great, annihilated the Hungarian army led by ''Horka (title), Harka ''Bulcs ...
just south of Augsburg, as a test unit (''Jäger Erprobungskommando Thierfelder'', commanded by '' Hauptmann'' Werner Thierfelder
The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (german: Ritterkreuz des Eisernen Kreuzes) and its variants were the highest awards in the military and paramilitary forces of Nazi Germany during World War II. The decoration was awarded for a wide range of ...
) to introduce the Me 262 into service and train a corps of pilots to fly it. On 26 July 1944, Leutnant Alfred Schreiber
Alfred Schreiber (11 November 1923 – 26 November 1944) was a fighter pilot in the Luftwaffe during World War II. He is noted for claiming the first aerial victory by a Jet aircraft, jet fighter in aviation history.
Biography
Schreiber was born ...
with the 262 A-1a W.Nr. 130 017 damaged a Mosquito reconnaissance aircraft of No. 540 Squadron RAF
No. 540 Squadron RAF was a photoreconnaissance squadron of the Royal Air Force from 1942 to 1956.
History
Formation and World War II
The squadron was formed on 19 October 1942 from 'H' and 'L' flights of No. 1 PRU at RAF Leuchars as a photor ...
PR Squadron, which was allegedly lost in a crash upon landing at an air base in Italy. Other sources state the aircraft was damaged during evasive manoeuvres and escaped.
 Major Walter Nowotny was assigned as commander after the death of Thierfelder in July 1944, and the unit redesignated '' Kommando Nowotny''. Essentially a trials and development unit, it mounted the world's first jet fighter operations. Trials progressed at a slow pace; it was not until August 1944 that initial operational missions were flown against the Allies; the unit made claims for 19 Allied aircraft in exchange for six Me 262s lost. Despite orders to stay grounded, Nowotny chose to fly a mission against an enemy bomber formation flying some above, on 8 November 1944. He claimed two P-51Ds destroyed before suffering engine failure at high altitude. Then, while diving and trying to restart his engines, he was attacked by other Mustangs, forced to bail out, and died. The ''Kommando'' was then withdrawn for further
Major Walter Nowotny was assigned as commander after the death of Thierfelder in July 1944, and the unit redesignated '' Kommando Nowotny''. Essentially a trials and development unit, it mounted the world's first jet fighter operations. Trials progressed at a slow pace; it was not until August 1944 that initial operational missions were flown against the Allies; the unit made claims for 19 Allied aircraft in exchange for six Me 262s lost. Despite orders to stay grounded, Nowotny chose to fly a mission against an enemy bomber formation flying some above, on 8 November 1944. He claimed two P-51Ds destroyed before suffering engine failure at high altitude. Then, while diving and trying to restart his engines, he was attacked by other Mustangs, forced to bail out, and died. The ''Kommando'' was then withdrawn for further flight training
Flight training is a course of study used when learning to pilot an aircraft. The overall purpose of primary and intermediate flight training is the acquisition and honing of basic airmanship skills.
Flight training can be conducted under a str ...
and a revision of combat tactics to optimise the Me 262's strengths.
On 26 November 1944, a Me 262A-2a Sturmvogel of III.''Gruppe''/ KG 51 'Edelweiß' based at Rheine-Hopsten Air Base near Osnabrück was the first confirmed ground-to-air kill of a jet combat aircraft. The Me 262 was shot down by a Bofors gun of B.11 Detachment of 2875 Squadron RAF Regiment
The Royal Air Force Regiment (RAF Regiment) is part of the Royal Air Force and functions as a specialist corps. Founded by royal warrant in 1942, the Corps carries out soldiering tasks relating to the delivery of air power. Examples of such ta ...
at the RAF forward airfield of Helmond, near Eindhoven
Eindhoven () is a city and municipality in the Netherlands, located in the southern province of North Brabant of which it is its largest. With a population of 238,326 on 1 January 2022,Volkel
Volkel (Brabantian: ''Vollekul'') is a village in the Netherlands. It is situated in the north-east corner of the province of North Brabant, south-east of the town of Uden. On 1 January 2021, Volkel had 3,435 inhabitants. It used to be part of th ...
. The final appearance of Me 262s over Volkel was in 1945 when yet another fell to 2809's guns.
By January 1945, ''Jagdgeschwader'' 7 (JG 7) had been formed as a pure jet fighter wing, partly based at Parchim, although it was several weeks before it was operational. In the meantime, a bomber unit—I ''Gruppe'', ''Kampfgeschwader'' 54 (KG(J) 54)—redesignated as such on 1 October 1944 through being re-equipped with, and trained to use the Me 262A-2a fighter-bomber for use in a ground-attack role. However, the unit lost 12 jets in action in two weeks for minimal returns. '' Jagdverband 44'' (JV 44) was another Me 262 fighter unit, of squadron (''Staffel'') size given the low numbers of available personnel, formed in February 1945 by Lieutenant General Adolf Galland
Adolf Josef Ferdinand Galland (19 March 1912 – 9 February 1996) was a German Luftwaffe general and flying ace who served throughout the Second World War in Europe. He flew 705 combat missions, and fought on the Western Front and in the Defen ...
, who had recently been dismissed as Inspector of Fighters
Inspector of Fighters (German language: ''Inspekteur der Jagdflieger'' redesignated to ''General der Jagdflieger'' (General of Fighters)) was not a rank but a leading position within the High Command of the German Luftwaffe in Nazi Germany
...
. Galland was able to draw into the unit many of the most experienced and decorated Luftwaffe fighter pilots from other units grounded by lack of fuel.
 During March, Me 262 fighter units were able, for the first time, to mount large-scale attacks on Allied bomber formations. On 18 March 1945, thirty-seven Me 262s of JG 7 intercepted a force of 1,221 bombers and 632 escorting fighters. They shot down 12 bombers and one fighter for the loss of three Me 262s. Although a 4:1 ratio was exactly what the Luftwaffe would have needed to make an impact on the war, the absolute scale of their success was minor, as it represented only 1% of the attacking force.
In the last days of the conflict, Me 262s from JG 7 and other units were committed in ground assault missions, in an attempt to support German troops fighting Red Army forces. Just south of Berlin, halfway between Spremberg and the German capital, the Wehrmacht's 9th Army (with elements from the 12 Army and
During March, Me 262 fighter units were able, for the first time, to mount large-scale attacks on Allied bomber formations. On 18 March 1945, thirty-seven Me 262s of JG 7 intercepted a force of 1,221 bombers and 632 escorting fighters. They shot down 12 bombers and one fighter for the loss of three Me 262s. Although a 4:1 ratio was exactly what the Luftwaffe would have needed to make an impact on the war, the absolute scale of their success was minor, as it represented only 1% of the attacking force.
In the last days of the conflict, Me 262s from JG 7 and other units were committed in ground assault missions, in an attempt to support German troops fighting Red Army forces. Just south of Berlin, halfway between Spremberg and the German capital, the Wehrmacht's 9th Army (with elements from the 12 Army and 4th Panzer Army
The 4th Panzer Army (german: 4. Panzerarmee) (operating as Panzer Group 4 (german: 4. Panzergruppe) from its formation on 15 February 1941 to 1 January 1942, when it was redesignated as a full army) was a German panzer formation during World War ...
) was assaulting the Red Army's 1st Ukrainian Front
The 1st Ukrainian Front (Russian: Пéрвый Украи́нский фронт), previously the Voronezh Front (Russian: Воронежский Фронт) was a major formation of the Soviet Army during World War II, being equivalent to a ...
. To support this attack, on 24 April, JG 7 dispatched thirty-one Me 262s on a strafing mission in the Cottbus- Bautzen area. Luftwaffe pilots claimed six lorries and seven Soviet aircraft, but three German jets were lost. On the evening of 27 April, thirty-six Me 262s from JG 7, III.KG(J)6 and KJ(J)54 were sent against Soviet forces that were attacking German troops in the forests north-east of Baruth. They succeeded in strafing 65 Soviet lorries, after which the Me 262s intercepted low flying Il-2 Sturmoviks
The Ilyushin Il-2 (Russian: Илью́шин Ил-2) is a ground-attack plane that was produced by the Soviet Union in large numbers during the Second World War. The word ''shturmovík'' ( Cyrillic: штурмовик), the generic Russian term ...
searching for German tanks. The jet pilots claimed six Sturmoviks for the loss of three Messerschmitts. During operations between 28 April and 1 May Soviet fighters and ground fire downed at least ten more Me 262s from JG 7.
However, JG 7 managed to keep its jets operational until the end of the war. And on 8 May, at around 4:00 p.m. ''Oblt.'' Fritz Stehle of 2./JG 7, while flying a Me 262 on the Erzgebirge, attacked a formation of Soviet aircraft. He claimed a Yakovlev Yak-9, but the plane shot down was probably a P-39 Airacobra. Soviet records show that they lost two Airacobras, one of them probably downed by Stehle, who would thus have scored the last Luftwaffe air victory of the war.
 Several two-seat trainer variants of the Me 262, the Me 262 B-1a, had been adapted through the ''Umrüst-Bausatz 1'' factory refit package as night fighters, complete with on-board FuG 218 ''Neptun'' high-VHF band radar, using ''Hirschgeweih'' ("stag's antlers") antennae with a set of dipole elements shorter than the '' Lichtenstein SN-2'' had used, as the B-1a/U1 version. Serving with 10. ''Staffel'' ''Nachtjagdgeschwader'' 11, near Berlin, these few aircraft (alongside several single-seat examples) accounted for most of the 13 Mosquitoes lost over Berlin in the first three months of 1945. Intercepts were generally or entirely made using ''
Several two-seat trainer variants of the Me 262, the Me 262 B-1a, had been adapted through the ''Umrüst-Bausatz 1'' factory refit package as night fighters, complete with on-board FuG 218 ''Neptun'' high-VHF band radar, using ''Hirschgeweih'' ("stag's antlers") antennae with a set of dipole elements shorter than the '' Lichtenstein SN-2'' had used, as the B-1a/U1 version. Serving with 10. ''Staffel'' ''Nachtjagdgeschwader'' 11, near Berlin, these few aircraft (alongside several single-seat examples) accounted for most of the 13 Mosquitoes lost over Berlin in the first three months of 1945. Intercepts were generally or entirely made using ''Wilde Sau
''Wilde Sau'' ( Lit. wild sow; generally known in English as "Wild Boar") was the term given by the ''Luftwaffe'' to the tactic used from 1943 to 1944 during World War II by which British night bombers were engaged by single-seat day-fighter airc ...
'' methods, rather than AI radar-controlled interception. As the two-seat trainer was largely unavailable, many pilots made their first jet flight in a single-seater without an instructor.
Despite its deficiencies, the Me 262 clearly marked the beginning of the end of piston-engined aircraft as effective fighting machines. Once airborne, it could accelerate to speeds over , about faster than any Allied fighter operational in the European Theater of Operations.
The Me 262's top aceFor a list of Luftwaffe jet aces, see List of German World War II jet aces was probably ''Hauptmann'' Franz Schall with 17 kills, including six four-engine bombers and ten P-51 Mustang
The North American Aviation P-51 Mustang is an American long-range, single-seat fighter and fighter-bomber used during World War II and the Korean War, among other conflicts. The Mustang was designed in April 1940 by a team headed by James ...
fighters, although fighter ace ''Oberleutnant'' Kurt Welter
Kurt Welter (25 February 1916 – 7 March 1949) was a German Luftwaffe fighter ace and the most successful ''Jet Expert'' of World War II.For a list of Luftwaffe jet aces see ''List of German World War II jet aces'' A flying ace or fighte ...
claimed 25 Mosquitos and two four-engine bombers shot down by night and two further Mosquitos by day. Most of Welter's claimed night kills were achieved by eye, even though Welter had tested a prototype Me 262 fitted with FuG 218 ''Neptun'' radar. Another candidate for top ace on the aircraft was '' Oberstleutnant'' Heinrich Bär, who is credited with 16 enemy aircraft while flying Me 262s out of his total of 240 aircraft shot down.
Anti-bomber tactics
 The Me 262 was so fast that German pilots needed new tactics to attack Allied bombers. In the head-on attack, the combined closing speed of about was too high for accurate shooting with ordnance that could only fire about 650 rounds/min from each cannon, (~44 rounds/sec in total from the quartet of cannon). Even from astern, the closing speed was too great to use the short-ranged quartet of MK 108 cannon to maximum effect. A roller-coaster attack was devised, the Me 262s approached from astern and about than the bombers. From about , they went into a shallow dive that took them through the escort fighters with little risk of interception. When they were about and below the bombers, they pulled up sharply to reduce speed. On levelling off, they were and overtaking the bombers at about , well placed to attack them.
The Me 262 was so fast that German pilots needed new tactics to attack Allied bombers. In the head-on attack, the combined closing speed of about was too high for accurate shooting with ordnance that could only fire about 650 rounds/min from each cannon, (~44 rounds/sec in total from the quartet of cannon). Even from astern, the closing speed was too great to use the short-ranged quartet of MK 108 cannon to maximum effect. A roller-coaster attack was devised, the Me 262s approached from astern and about than the bombers. From about , they went into a shallow dive that took them through the escort fighters with little risk of interception. When they were about and below the bombers, they pulled up sharply to reduce speed. On levelling off, they were and overtaking the bombers at about , well placed to attack them.
 Since the short barrels of the 30 mm MK 108 cannon and low muzzle velocity (only ) rendered it inaccurate beyond ), coupled with the jet's velocity, which required breaking off at to avoid colliding with the target, Me 262 pilots normally commenced firing at . Gunners of Allied bomber aircraft found their electrically powered gun turrets had problems tracking the jets. Aiming was difficult because the jets closed into firing range quickly and remained in firing position only briefly, using their standard attack profile, which proved more effective.
Since the short barrels of the 30 mm MK 108 cannon and low muzzle velocity (only ) rendered it inaccurate beyond ), coupled with the jet's velocity, which required breaking off at to avoid colliding with the target, Me 262 pilots normally commenced firing at . Gunners of Allied bomber aircraft found their electrically powered gun turrets had problems tracking the jets. Aiming was difficult because the jets closed into firing range quickly and remained in firing position only briefly, using their standard attack profile, which proved more effective.
Royal Aircraft Establishment
The Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE) was a British research establishment, known by several different names during its history, that eventually came under the aegis of the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), UK Ministry of Defence (MoD), bef ...
, who tested the Me 262 noted that:
This was aEventually, German pilots developed new tactics to counter Allied bombers. Me 262s, equipped with up to 24 unguided folding-fin R4M rockets—12 in each of two underwing racks, outboard of the engine nacelles—approached from the side of a bomber formation, where their silhouettes were widest and while still out of range of the bombers' machine guns, fired aBlitzkrieg Blitzkrieg ( , ; from 'lightning' + 'war') is a word used to describe a surprise attack using a rapid, overwhelming force concentration that may consist of armored and motorized or mechanized infantry formations, together with close air su ...aircraft. You whack in at your bomber. It was never meant to be a dogfighter, it was meant to be a destroyer of bombers... The great problem with it was it did not have dive brakes. For example, if you want to fight and destroy a B-17, you come in on a dive. The 30mm cannon were not so accurate beyond . So you normally came in at and would open fire on your B-17. And your closing speed was still high and since you had to break away at to avoid a collision, you only had two seconds firing time. Now, in two seconds, you can't sight. You can fire randomly and hope for the best. If you want to sight and fire, you need to double that time to four seconds. And with dive brakes, you could have done that.
salvo
A salvo is the simultaneous discharge of artillery or firearms including the firing of guns either to hit a target or to perform a salute. As a tactic in warfare, the intent is to cripple an enemy in one blow and prevent them from fighting b ...
of rockets with strongly brisant
In explosives engineering, brisance (; , ) is the shattering capability of a high explosive, determined mainly by its detonation pressure.
Practical uses
Brisance is of practical importance for determining the effectiveness of an explosion in f ...
Hexogen-filled warheads, the same explosive in the shells fired by the Me 262A's MK 108 cannon. One or two of these rockets could shoot down even the famously rugged Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress
The Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress is a four-engined heavy bomber developed in the 1930s for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC). Relatively fast and high-flying for a bomber of its era, the B-17 was used primarily in the European Theater ...
, from the "metal-shattering" brisant effect of the fast-flying rocket's explosive warhead. The much bigger BR 21 large-calibre rockets, fired from their tubular launchers under the nose of the Me 262A (one either side of the nosewheel well) were only as fast as MK 108 rounds.
Though this broadside-attack tactic was effective, it came too late to have a real effect on the war and only small numbers of Me 262s were equipped with the rocket packs; most were Me 262A-1a models, of ''Jagdgeschwader'' 7. This method of attacking bombers became the standard and mass deployment of Ruhrstahl X-4 guided missiles was cancelled. Some nicknamed this tactic the Luftwaffe's Wolf Pack
A pack is a social group of conspecific canines. Packs aren't formed by all canines, especially small sized canines like the Red fox. The number of members in a pack and their social behavior varies from species to species. Social structure is v ...
, as the fighters often made runs in groups of two or three, fired their rockets, then returned to base. On 1 September 1944, USAAF General Carl Spaatz
Carl Andrew Spaatz (born Spatz; June 28, 1891 – July 14, 1974), nicknamed "Tooey", was an American World War II general. As commander of Strategic Air Forces in Europe in 1944, he successfully pressed for the bombing of the enemy's oil product ...
expressed the fear that if greater numbers of German jets appeared, they could inflict losses heavy enough to force cancellation of the Allied bombing offensive by daylight.
Counter-jet tactics
 The Me 262 was difficult to counter because its high speed and rate of climb made it hard to intercept. However, as with other turbojet engines at the time, the Me 262's engines did not provide sufficient thrust at low airspeeds and throttle response was slow, so that in certain circumstances such as takeoff and landing the aircraft became a vulnerable target. Another disadvantage that pioneering jet aircraft of the World War II era shared, was the high risk of compressor stall and if throttle movements were too rapid, the engine(s) could suffer a flameout. The coarse opening of the throttle would cause fuel surging and lead to excessive jet pipe temperatures. Pilots were instructed to operate the throttle gently and avoid quick changes. German engineers introduced an automatic throttle regulator later in the war but it only partly alleviated the problem.
The plane had, by contemporary standards, a high wing loading (294.0 kg/m2, 60.2 lbs/ft2) that required higher takeoff and landing speeds. Due to poor throttle response, the engines' tendency for airflow disruption that could cause the compressor to stall was ubiquitous. The high speed of the Me 262 also presented problems when engaging enemy aircraft, the high-speed convergence allowing Me 262 pilots little time to line up their targets or acquire the appropriate amount of deflection. This problem faces any aircraft that approaches another from behind at much higher speed, as the slower aircraft in front can always pull a tighter turn, forcing the faster aircraft to overshoot.
Luftwaffe pilots eventually learned how to handle the Me 262's higher speed and the Me 262 soon proved a formidable air superiority fighter, with pilots such as Franz Schall managing to shoot down seventeen enemy fighters in the Me 262, ten of them American
The Me 262 was difficult to counter because its high speed and rate of climb made it hard to intercept. However, as with other turbojet engines at the time, the Me 262's engines did not provide sufficient thrust at low airspeeds and throttle response was slow, so that in certain circumstances such as takeoff and landing the aircraft became a vulnerable target. Another disadvantage that pioneering jet aircraft of the World War II era shared, was the high risk of compressor stall and if throttle movements were too rapid, the engine(s) could suffer a flameout. The coarse opening of the throttle would cause fuel surging and lead to excessive jet pipe temperatures. Pilots were instructed to operate the throttle gently and avoid quick changes. German engineers introduced an automatic throttle regulator later in the war but it only partly alleviated the problem.
The plane had, by contemporary standards, a high wing loading (294.0 kg/m2, 60.2 lbs/ft2) that required higher takeoff and landing speeds. Due to poor throttle response, the engines' tendency for airflow disruption that could cause the compressor to stall was ubiquitous. The high speed of the Me 262 also presented problems when engaging enemy aircraft, the high-speed convergence allowing Me 262 pilots little time to line up their targets or acquire the appropriate amount of deflection. This problem faces any aircraft that approaches another from behind at much higher speed, as the slower aircraft in front can always pull a tighter turn, forcing the faster aircraft to overshoot.
Luftwaffe pilots eventually learned how to handle the Me 262's higher speed and the Me 262 soon proved a formidable air superiority fighter, with pilots such as Franz Schall managing to shoot down seventeen enemy fighters in the Me 262, ten of them American P-51 Mustangs
The North American Aviation P-51 Mustang is an American long-range, single-seat fighter and fighter-bomber used during World War II and the Korean War, among other conflicts. The Mustang was designed in April 1940 by a team headed by James H ...
. Other notable Me 262 aces included Georg-Peter Eder, with twelve enemy fighters to his credit (including nine P-51s), Erich Rudorffer also with twelve enemy fighters to his credit, Walther Dahl with eleven (including three Lavochkin La-7s and six P-51s) and Heinz-Helmut Baudach with six (including one Spitfire and two P-51s) amongst many others.
Pilots soon learned that the Me 262 was quite maneuverable despite its high wing loading and lack of low-speed thrust, especially if attention was drawn to its effective maneuvering speeds. The controls were light and effective right up to the maximum permissible speed and perfectly harmonised. The inclusion of full span automatic leading-edge slats
Slats are aerodynamic surfaces on the leading edge of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft which, when deployed, allow the wing to operate at a higher angle of attack. A higher coefficient of lift is produced as a result of angle of attack and speed, ...
, something of a "tradition" on Messerschmitt fighters dating back to the original Bf 109's outer wing slots of a similar type, helped increase the overall lift produced by the wing by as much as 35% in tight turns or at low speeds, greatly improving the aircraft's turn performance as well as its landing and takeoff characteristics. As many pilots soon found out, the Me 262's clean design also meant that it, like all jets, held its speed in tight turns much better than conventional propeller-driven fighters, which was a great potential advantage in a dogfight as it meant better energy retention in manoeuvres.
Focke-Wulf Fw 190
The Focke-Wulf Fw 190, nicknamed ''Würger'' (" Shrike") is a German single-seat, single-engine fighter aircraft designed by Kurt Tank at Focke-Wulf in the late 1930s and widely used during World War II. Along with its well-known counterpart, ...
D and (just becoming available in 1945) Focke-Wulf Ta 152H. Nevertheless, in March–April 1945, Allied fighter patrol patterns over Me 262 airfields resulted in numerous jet losses.
As the Me 262A's pioneering Junkers Jumo 004
The Junkers Jumo 004 was the world's first production turbojet engine in operational use, and the first successful axial compressor turbojet engine. Some 8,000 units were manufactured by Junkers in Germany late in World War II, powering the Mess ...
axial-flow jet engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term ...
s needed careful nursing by their pilots, these jet aircraft were particularly vulnerable during takeoff and landing. Lt. Chuck Yeager of the 357th Fighter Group
The 357th Fighter Group was an air combat unit of the United States Army Air Forces during the Second World War. The 357th operated P-51 Mustang aircraft as part of the U.S. Eighth Air Force and its members were known unofficially as the Yoxfor ...
was one of the first American pilots to shoot down an Me 262, which he caught during its landing approach. On 7 October 1944, Lt. Urban Drew of the 365th Fighter Group 365th may refer to:
*365th Bombardment Squadron, inactive United States Air Force unit
*365th Electronic Warfare Group previously 1st Search Attack Group, United States Army Air Forces unit that served during World War II. 365 EWG was a 'paper' des ...
shot down two Me 262s that were taking off, while on the same day Lt. Col. Hubert Zemke, who had transferred to the Mustang equipped 479th Fighter Group 479th may refer to:
* 479th Antisubmarine Group, inactive United States Air Force unit
* 479th Bombardment Squadron, inactive United States Air Force unit
* 479th Field Artillery Brigade (United States), field artillery brigade of the United States ...
, shot down what he thought was a Bf 109, only to have his gun camera film reveal that it may have been an Me 262. On 25 February 1945, Mustangs of the 55th Fighter Group surprised an entire ''Staffel'' of Me 262As at takeoff and destroyed six jets.
The British Hawker Tempest scored several kills against the new German jets, including the Messerschmitt Me 262. Hubert Lange, a Me 262 pilot, said: "the Messerschmitt Me 262's most dangerous opponent was the British Hawker Tempest—extremely fast at low altitudes, highly manoeuvrable and heavily armed." Some were destroyed with a tactic known to the Tempest-equipped No. 135 Wing RAF
The numero sign or numero symbol, №, (also represented as Nº, No, No. or no.), is a Typography, typographic abbreviation of the word ''number''(''s'') indicating ordinal number, ordinal numeration, especially in names and titles. For exampl ...
as the "Rat Scramble": Tempests on immediate alert took off when an Me 262 was reported airborne. They did not intercept the jet, but instead flew towards the Me 262 and Ar 234
The Arado Ar 234 ''Blitz'' (English: lightning) is a jet-powered bomber designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Arado. It was the world's first operational turbojet-powered bomber, seeing service during the latter half of the ...
base at Hopsten air base. The aim was to attack jets on their landing approach, when they were at their most vulnerable, travelling slowly, with flaps down and incapable of rapid acceleration. The German response was the construction of a "flak lane" of over 150 emplacements of the 20 mm ''Flakvierling'' quadruple autocannon
An autocannon, automatic cannon or machine cannon is a fully automatic gun that is capable of rapid-firing large-caliber ( or more) armour-piercing, explosive or incendiary shells, as opposed to the smaller-caliber kinetic projectiles (bull ...
batteries at Rheine-Hopsten to protect the approaches. After seven Tempests were lost to flak at Hopsten in a week, the "Rat Scramble" was discontinued.
High-speed research
Adolf Busemann
Adolf Busemann (20 April 1901 – 3 November 1986) was a German aerospace engineer and influential Nazi-era pioneer in aerodynamics, specialising in supersonic airflows. He introduced the concept of swept wings and, after emigrating in 1947 to t ...
had proposed swept wings as early as 1935; Messerschmitt researched the topic from 1940. In April 1941, Busemann proposed fitting a 35° swept wing (''Pfeilflügel II'', literally "arrow wing II") to the Me 262, the same wing-sweep angle later used on both the American F-86 Sabre and Soviet Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-15
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-15 (russian: Микоя́н и Гуре́вич МиГ-15; USAF/DoD designation: Type 14; NATO reporting name: Fagot) is a jet fighter aircraft developed by Mikoyan-Gurevich for the Soviet Union. The MiG-15 was one of ...
fighter jets. Though this was not implemented, he continued with the projected HG II and HG III (''Hochgeschwindigkeit'', "high-speed") derivatives in 1944, designed with a 35° and 45° wing sweep, respectively.
Interest in high-speed flight, which led him to initiate work on swept wings starting in 1940, is evident from the advanced developments Messerschmitt had on his drawing board in 1944. While the Me 262 V9 ''Hochgeschwindigkeit I'' (HG I) flight-tested in 1944 had only small changes compared to combat aircraft, most notably a low-profile canopy—tried as the ''Rennkabine'' (literally "racing cabin") on the ninth Me 262 prototype for a short time—to reduce drag, the HG II and HG III designs were far more radical. The projected HG II combined the low-drag canopy with a 35° wing sweep and a V-tail (butterfly tail). The HG III had a conventional tail, but a 45° wing sweep and turbines embedded in the wing roots.
Messerschmitt also conducted a series of flight tests with the series production Me 262. Dive tests determined that the Me 262 went out of control in a dive at Mach
Mach may refer to Mach number, the speed of sound in local conditions. It may also refer to:
Computing
* Mach (kernel), an operating systems kernel technology
* ATI Mach, a 2D GPU chip by ATI
* GNU Mach, the microkernel upon which GNU Hurd is bas ...
0.86, and that higher Mach numbers would cause a nose-down trim that the pilot could not counter. The resulting steepening of the dive would lead to even higher speeds and the airframe would disintegrate from excessive negative g loads.
Messerschmitt believed the HG series of Me 262 derivatives was capable of reaching transonic Mach numbers in level flight, with the top speed of the HG III being projected as Mach 0.96 at altitude. After the war, the Royal Aircraft Establishment
The Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE) was a British research establishment, known by several different names during its history, that eventually came under the aegis of the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), UK Ministry of Defence (MoD), bef ...
, at that time one of the leading institutions in high-speed research, re-tested the Me 262 to help with British attempts at exceeding Mach 1. The RAE achieved speeds of up to Mach 0.84 and confirmed the results from the Messerschmitt dive-tests. The Soviets ran similar tests.
After Willy Messerschmitt's death in 1978, the former Me 262 pilot Hans Guido Mutke claimed to have exceeded Mach 1 on 9 April 1945 in a Me 262 in a "straight-down" 90° dive. This claim relies solely on Mutke's memory of the incident, which recalls effects other Me 262 pilots observed below the speed of sound at high indicated airspeed, but with no altitude reading required to determine the speed. The pitot tube used to measure airspeed in aircraft can give falsely elevated readings as the pressure builds up inside the tube at high speeds. The Me 262 wing had only a slight sweep, incorporated for trim ( center of gravity) reasons and likely would have suffered structural failure due to divergence at high transonic speeds. The Me 262 V9, Werknummer 130 004, with ''Stammkennzeichen'' of VI+AD, was prepared as the HG I test airframe with the low-profile ''Rennkabine'' racing-canopy and may have achieved an unofficial record speed for a turbojet-powered aircraft of , altitude unspecified, even with the recorded wartime airspeed record being set on 6 July 1944, by another Messerschmitt design—the Me 163B V18 rocket fighter setting a record, but landing with a nearly disintegrated rudder surface.
Production
 About 1,400 planes were produced, however, less than a hundred Me 262s were in a combat-ready condition at any one time. According to sources they destroyed from 300 to 450 enemy planes, with the Allies destroying about one hundred Me 262s in the air. While Germany was bombed intensively, production of the Me 262 was dispersed into low-profile production facilities, sometimes little more than clearings in the forests of Germany and occupied countries. From the end of February to the end of March 1945, approximately sixty Me 262s were destroyed in attacks on
About 1,400 planes were produced, however, less than a hundred Me 262s were in a combat-ready condition at any one time. According to sources they destroyed from 300 to 450 enemy planes, with the Allies destroying about one hundred Me 262s in the air. While Germany was bombed intensively, production of the Me 262 was dispersed into low-profile production facilities, sometimes little more than clearings in the forests of Germany and occupied countries. From the end of February to the end of March 1945, approximately sixty Me 262s were destroyed in attacks on Obertraubling
Obertraubling is a Municipalities of Germany, municipality in Bavaria, Upper Palatinate (german: Oberpfalz), in the district of Regensburg.
Geographical Location
Obertraubling is located directly on the southend of the City of Regensburg, the cap ...
and thirty at Leipheim; the Neuburg jet plant itself was bombed on 19 March 1945.
Large, heavily protected underground factories were constructed – as with the partly-buried Weingut I complex for Jumo 004 jet engine production – to take up production of the Me 262, safe from bomb attacks. A disused mine complex under the Walpersberg
The Walpersberg is a sandstone mesa on the west bank of the Saale near Kahla in Thuringia, Germany, formed around 60 million years ago. It is notable for formerly housing the REIMAHG-A aircraft factory, an underground facility for the productio ...
mountain was adapted for the production of complete aircraft. These were hauled to the flat top of the hill where a runway had been cleared and flown out. Between 20 and 30 Me 262s were built here, the underground factory being overrun by Allied troops before it could reach a meaningful output. Wings were produced in Germany's oldest motorway tunnel at Engelberg, to the west of Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; Swabian: ; ) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the ''Stuttgarter Kessel'' (Stuttgart Cauldron) and lies an hour from the ...
. At ''B8 Bergkristall-Esche II'', a vast network of tunnels was excavated beneath St. Georgen/Gusen, Austria, where slave labourers of concentration camp Gusen II produced fully equipped fuselages for the Me 262 at a monthly rate of 450 units on large assembly lines from early 1945. Gusen II was known as one of the harshest concentration camps; the typical life expectancy was six months. An estimated 35,000 to 50,000 people died on the forced labour details for the Me 262.
Postwar history
slat
Slat, slats, or SLAT may refer to:
* Slat (aircraft), aerodynamic surfaces on the leading edge of the wings of fixed-wing aircraft
* a Lath, a narrow strip of straight-grained wood used under roof shingles or tiles
* Vertical or horizontal pieces ...
design based on the Me 262's.
The Czechoslovak aircraft industry continued to produce single-seat (Avia S-92) and two-seat (Avia CS-92) variants of the Me 262 after World War II. From August 1946, a total of nine S-92s and three two-seater CS-92s were completed and test flown. They were introduced in 1947 and in 1950 were supplied to the 5th Fighter Squadron, becoming the first jet fighters to serve in the Czechoslovak Air Force. These were kept flying until 1951, when they were replaced in service by Soviet jet fighters. Both versions are on display at the Prague Aviation museum in Kbely.
Flyable reproductions
 In January 2003, the American Me 262 Project, based in Everett, Washington, completed flight testing to allow the delivery of partially updated spec reproductions of several versions of the Me 262 including at least two B-1c two-seater variants, one A-1c single-seater and two "convertibles" that could be switched between the A-1c and B-1c configurations. All are powered by General Electric CJ610 engines and feature additional safety features, such as upgraded brakes and strengthened landing gear. The "c" suffix refers to the new CJ610 powerplant and has been informally assigned with the approval of the Messerschmitt Foundation in Germany (the Werknummer of the reproductions picked up where the last wartime produced Me 262 left off – a continuous airframe serial number run with a near 60-year production break).
Flight testing of the first newly manufactured Me 262 A-1c (single-seat) variant (Werknummer 501244) was completed in August 2005. The first of these machines (Werknummer 501241) went to a private owner in the southwestern United States, while the second (Werknummer 501244) was delivered to the Messerschmitt Foundation at Manching, Germany. This aircraft conducted a private test flight in late April 2006 and made its public debut in May at the ILA 2006. The new Me 262 flew during the public flight demonstrations. Me 262 Werknummer 501241 was delivered to the Collings Foundation as White 1 of JG 7; this aircraft offered ride-along flights starting in 2008. The third replica, a non-flyable Me 262 A-1c, was delivered to the Evergreen Aviation & Space Museum in May 2010.
In January 2003, the American Me 262 Project, based in Everett, Washington, completed flight testing to allow the delivery of partially updated spec reproductions of several versions of the Me 262 including at least two B-1c two-seater variants, one A-1c single-seater and two "convertibles" that could be switched between the A-1c and B-1c configurations. All are powered by General Electric CJ610 engines and feature additional safety features, such as upgraded brakes and strengthened landing gear. The "c" suffix refers to the new CJ610 powerplant and has been informally assigned with the approval of the Messerschmitt Foundation in Germany (the Werknummer of the reproductions picked up where the last wartime produced Me 262 left off – a continuous airframe serial number run with a near 60-year production break).
Flight testing of the first newly manufactured Me 262 A-1c (single-seat) variant (Werknummer 501244) was completed in August 2005. The first of these machines (Werknummer 501241) went to a private owner in the southwestern United States, while the second (Werknummer 501244) was delivered to the Messerschmitt Foundation at Manching, Germany. This aircraft conducted a private test flight in late April 2006 and made its public debut in May at the ILA 2006. The new Me 262 flew during the public flight demonstrations. Me 262 Werknummer 501241 was delivered to the Collings Foundation as White 1 of JG 7; this aircraft offered ride-along flights starting in 2008. The third replica, a non-flyable Me 262 A-1c, was delivered to the Evergreen Aviation & Space Museum in May 2010.

Variants
 ''Note:''- U = ''Umrüst-Bausatz'' – conversion kit installed at factory level, denoted as a suffix in the form /U''n''.
; Me 262 A-0
: Pre-production aircraft fitted with two
''Note:''- U = ''Umrüst-Bausatz'' – conversion kit installed at factory level, denoted as a suffix in the form /U''n''.
; Me 262 A-0
: Pre-production aircraft fitted with two Jumo 004B
The Junkers Jumo 004 was the world's first production turbojet engine in operational use, and the first successful axial compressor turbojet engine. Some 8,000 units were manufactured by Junkers in Germany late in World War II, powering the Mess ...
turbojet engines, 23 built.
; Me 262 A-1a "''Schwalbe''"
: Primary production version, usable as both fighter (interceptor) and fighter-bomber.
; Me 262 A-1a/U1
: Single prototype with a total of six nose mounted guns, two MG 151/20 cannon, two MK 103 cannon, and two MK 108 cannon.
; Me 262 A-1a/U2
: Single prototype with FuG 220 Lichtenstein SN-2 90 MHz radar transceiver
Bistatic radar is a radar system comprising a transmitter and receiver that are separated by a distance comparable to the expected target distance. Conversely, a conventional radar in which the transmitter and receiver are co-located is called ...
and ''Hirschgeweih'' (stag's antlers) antenna array, for trials as a night-fighter.
; Me 262 A-1a/U3
: Reconnaissance version modified in small numbers, with Rb 20/30 cameras mounted in the nose or alternatively one Rb 20/20 and one Rb 75/30 (Rb – ''Reihenbildner'' – series-picture, topographic camera). Some retained one MK 108 cannon, but most were unarmed.
; Me 262 A-1a/U4
: Bomber destroyer version, two prototypes with an adapted MK 214 (intended armament) or BK 5 (test ordnance only) anti-tank gun in the nose.
; Me 262 A-1a/U5
: Heavy jet fighter with six MK 108 cannon in the nose.
; Me 262 A-1b
: Trio of A-1a evaluation versions, starting with ''Werknummer'' 170 078, re-engined with two BMW 003A turbojets in place of the Jumo 004s, maximum speed .
; Me 262 A-2a "Sturmvogel"
: Definitive bomber version retaining only the two lower MK 108 cannon.
; Me 262 A-2a/U1
: Single prototype with advanced bombsight.
; Me 262 A-2a/U2
: Two prototypes with glazed nose for accommodating a bombardier.
; Me 262 A-3a
: Proposed ground-attack version.
; Me 262 A-4a
: Reconnaissance version.
; Me 262 A-5a
: Definitive reconnaissance version used in small numbers at end of the war.
; Me 262 B-1a
: Two-seat trainer.
; Me 262 B-1a/U1
: Me 262 B-1a trainers converted into provisional night fighters, FuG 218 ''Neptun'' radar, with ''Hirschgeweih'' (eng:antler) eight-dipole antenna array.
; Me 262 B-2
: Proposed night fighter version with stretched fuselage.
; Me 262C
: Proposed development prototypes in four differing designs, meant to augment or replace the Jumo 004 jets with liquid-fueled rocket propulsion, as the "Home Protector" (''Heimatschützer'') series.
; Me 262 C-1a
: Single prototype ade from Me 262A ''Werknummer'' 130 186
Ade, Adé, or ADE may refer to:
Aeronautics
*Ada Air's ICAO code
*Aden International Airport's IATA code
*Aeronautical Development Establishment, a laboratory of the DRDO in India
Medical
* Adverse Drug Event
*Antibody-dependent enhancement
*ADE ...
of rocket-boosted interceptor (''Heimatschützer'' I) with Walter HWK 109-509 liquid-fuelled rocket in the tail, first flown with combined jet/rocket power on 27 February 1945.
; Me 262 C-2b
: Single prototype ade from Me 262A ''Werknummer'' 170 074
Ade, Adé, or ADE may refer to:
Aeronautics
*Ada Air's ICAO code
*Aden International Airport's IATA code
*Aeronautical Development Establishment, a laboratory of the DRDO in India
Medical
* Adverse Drug Event
*Antibody-dependent enhancement
*ADE ...
of rocket-boosted interceptor (''Heimatschützer'' II) with two BMW 003R
The BMW 003 (full RLM designation 109-003) is an early Axial engine, axial turbojet engine produced by BMW, BMW AG in Germany during World War II. The 003 and the Junkers Jumo 004 were the only German turbojet engines to reach production during ...
"combined" powerplants (BMW 003 turbojet, with a single thrust BMW 109-718 liquid-fuelled rocket engine mounted atop the rear of each jet exhaust) for boosted thrust, only flown once with combined jet/rocket power on 26 March 1945.
;Me 262 C-3
: ''Heimatschützer III'' – proposed version with Jumo 004 turbojet engines replaced with Walter HWK RII-211
The Walter HWK 109-509 was a German liquid-fuel bipropellant rocket engine that powered the Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet and Bachem Ba 349 aircraft. It was produced by Hellmuth Walter Kommanditgesellschaft (HWK) commencing in 1943, with license ...
Liquid-fuelled rocket engines.
; Me 262 C-3a
: ''Heimatschützer IV'' - a rocket-boosted interceptor with a Walter HWK 109-509S-2
The Walter HWK 109-509 was a German liquid-fuel bipropellant rocket engine that powered the Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet and Bachem Ba 349 aircraft. It was produced by Hellmuth Walter Kommanditgesellschaft (HWK) commencing in 1943, with licensed p ...
rocket motor housed in a permanent belly pack. Prototypes and initial production aircraft were captured before completion.
; Me 262 D-1
: Proposed variant to carry '' Jagdfaust'' mortars.
; Me 262 E-1
: Proposed variant based on A-1a/U4 with a MK 114 cannon
MK or mk may refer to:
In arts, entertainment and media Fictional characters
* Moon Knight, a Marvel Comics superhero
* M.K., an '' ''Into the Badlands'' (TV series) character
* Mary Katherine "M.K." Bomba, the protagonist in ''Epic'' (2013 fil ...
.
; Me 262 E-2
: Proposed rocket-armed variant carrying up to 48 × R4M rockets.
; Me 262 HG-I
: "High Speed" variant, modified A-1a with new "racing" style cockpit and additional pieces were added to wing roots at the front.Luftwaffe Secret Projects Fighters 1939–1945 by Walter Schick, Ingolf Meyer, Elke Weal, John Weal
; Me 262 HG-II
: Second "High Speed" variant, more heavily modified A-1a with "racing" style cockpit and wings swept at 35-degree angle and engine nacelles were moved closer to fuselage. A new butterfly V-shaped tail was tested but was too unstable in wind tunnel tests, so normal tail was kept.
; Me 262 HG-III
: Proposed Third "High Speed" variant, only progressed to wind tunnel model stage. This was the last and the pinnacle of the Me-262 aerodynamical possibility, which would have been built from the ground up as a new Me-262 instead of modifying older ones. In the Me-262 HG-III, its wings were swept at 45 degrees, it also had the "racing" style cockpit, but the largest change was the moving of the engine nacelles right into the fuselage side and changing the engines to the more powerful Heinkel HeS 011 engines.
; Me 262 S
: Zero-series model for Me 262 A-1a
; Me 262 W-1
: Provisional designation for Me 262 with 2x Argus As 014 pulse jet engines
; Me 262 W-3
: Provisional designation for Me 262 with 2x "square-intake" Argus As 044
Argus is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek word ''Argos (disambiguation), Argos''. It may refer to:
Greek mythology
* See Argus (Greek myth) for mythological characters named Argus
**Argus (king of Argos), son of Zeus (or Phoroneus) and ...
pulse jet engines
; Me 262 Lorin
: Provisional designation for Me 262 with 2x ''Lorin'' ramjet booster engines in "over-wing" mounts, one above each of the Jumo turbojet nacelles.
Rüstsätze (field modification kits)
Rüstsatze may be applied to various sub-types of their respective aircraft type, denoted as a suffix in the form /R''n''. Data from: Messerschmitt Me 262A Schwalbe :/R1: Underfuselage pylon for external fuel tank. :/R2: Ratog installation for two Rheinmetall 109-502 solid rocket engines. :/R3:BMW 003R
The BMW 003 (full RLM designation 109-003) is an early Axial engine, axial turbojet engine produced by BMW, BMW AG in Germany during World War II. The 003 and the Junkers Jumo 004 were the only German turbojet engines to reach production during ...
rocket boosted turbojet installation.
:/R4: Installation of the FuG 350 Zc Naxos
The Naxos radar warning receiver was a World War II German countermeasure to S band microwave radar produced by a cavity magnetron. Introduced in September 1943, it replaced Metox, which was incapable of detecting centimetric radar. Two versions ...
radar warning receiver / detector.
:/R5: The standard 4x MK 108 cannon installation.
:/R6: Jabo (JagdBomber) equipment, such as bombsights and bomb racks.
:/R7: Underwing installation of 12x R4M rockets carried on wooden racks.
:/R8: R110BS R11, R-11, Meaning R11 - Rhyll Anthony, R11.ID
Automobiles
* BMW R 11, a German motorcycle
* R-11 Refueler a military truck of the United States Air Force
* Renault 11, a French family car
Vessels
* , a submarine of the Royal Navy
* , a destro ...
Air to air rocket installation.
:/R9: Ruhrstahl Ru 344 X-4
The Ruhrstahl Ru 344 X-4 or Ruhrstahl-Kramer RK 344 was a wire-guided air-to-air missile designed by Germany during World War II. The X-4 did not see operational service and thus was not proven in combat but inspired considerable post-war work a ...
air-to-air missile installation.
Postwar variants
;Avia
Avia Motors s.r.o. is a Czech automotive manufacturer. It was founded in 1919 as an aircraft maker, and diversified into trucks after 1945. As an aircraft maker it was notable for producing biplane fighter aircraft, especially the B-534. Avia ...
S-92
: Czech-built Me 262 A-1a (fighter)
; Avia CS-92
: Czech-built Me 262 B-1a (fighter trainer, two seats)
Reproductions
A series of reproductions was constructed by American company Legend Flyers (later Me 262 Project) of Everett, Washington. The Jumo 004 engines of the original are replaced by more reliable General Electric CJ610 engines. The first Me 262 reproduction (a two-seater) took off for the first time in December 2002 and the second one in August 2005. This one was delivered to the Messerschmitt Foundation and was presented at the ILA airshow in 2006. :A-1c: American privately built, based on A-1a configuration. :B-1c: American privately built, based on B-1a configuration. :A/B-1c: American privately built, convertible between A-1c and B-1c configuration.Operators
* Luftwaffe * Czechoslovak Air Force (postwar, nine S-92 and three CS-92) * Israel Air Force (allegedly postwar, a number between 2 and 8 S-92, but never officially confirmed - see note 11)Surviving aircraft



 ; Me 262 A-1a/R7, W.Nr.500071 ''White 3'', III./JG 7
: Deutsches Museum, Munich, Germany. This aircraft, flown by Hans Guido Mutke while a pilot of 9. Staffel/''JG'' 7, was confiscated by Swiss authorities on 25 April 1945 after Mutke made an emergency landing in Switzerland due to lack of fuel (80 litres were remaining, 35 litres were usually burnt in one minute).
; Me 262 A-1a
: Reconstructed from parts of crashed and incomplete Me 262s. Luftwaffenmuseum der Bundeswehr, Germany.
; Me 262 A-1a W.Nr.501232 ''Yellow 5'', 3./KG(J)6
: National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio, US.
; Me 262 A-1a/U3 W.Nr.500453
: Flying Heritage Collection, Everett, Washington, United States, currently undergoing restoration to flying condition. It is intended to fly using its original Jumo 004 engines. The aircraft was bought from the Planes of Fame Air Museum, Chino, California.
; Me 262 A-1a/R7 W.Nr.500491 ''Yellow 7'', II./JG 7
:
; Me 262 A-1a/R7, W.Nr.500071 ''White 3'', III./JG 7
: Deutsches Museum, Munich, Germany. This aircraft, flown by Hans Guido Mutke while a pilot of 9. Staffel/''JG'' 7, was confiscated by Swiss authorities on 25 April 1945 after Mutke made an emergency landing in Switzerland due to lack of fuel (80 litres were remaining, 35 litres were usually burnt in one minute).
; Me 262 A-1a
: Reconstructed from parts of crashed and incomplete Me 262s. Luftwaffenmuseum der Bundeswehr, Germany.
; Me 262 A-1a W.Nr.501232 ''Yellow 5'', 3./KG(J)6
: National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio, US.
; Me 262 A-1a/U3 W.Nr.500453
: Flying Heritage Collection, Everett, Washington, United States, currently undergoing restoration to flying condition. It is intended to fly using its original Jumo 004 engines. The aircraft was bought from the Planes of Fame Air Museum, Chino, California.
; Me 262 A-1a/R7 W.Nr.500491 ''Yellow 7'', II./JG 7
: National Air and Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum of the Smithsonian Institution, also called the Air and Space Museum, is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States.
Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, it opened its main building on the Nat ...
, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C., United States. Possesses twin original underwing racks for 24 R4M unguided rockets. Flown by ''Oberfeldwebel'' Heinz Arnold
; Me 262 A-1a W.Nr.112372
: Royal Air Force Museum Cosford RAF Cosford, Cosford, United Kingdom.
; Me 262 A-2a W.Nr.500200 ''Black X 9K+XK'', 2 ''Staffel''./KG 51
: Australian War Memorial
The Australian War Memorial is Australia's national memorial to the members of its armed forces and supporting organisations who have died or participated in wars involving the Commonwealth of Australia and some conflicts involving pe ...
, Canberra, Australia. Built at Regensburg in March 1945, same batch from which the Deutsches Museum ''White 3'' was built. Flown by Fahnenjunker Oberfeldwebel Fröhlich and surrendered at Fassberg. It remains the only Me 262 left in existence wearing original (albeit worn, as seen in the picture) colours. Its markings show both the Unit signatures along with the Air Ministry colours applied at Farnborough Farnborough may refer to:
Australia
* Farnborough, Queensland, a locality in the Shire of Livingstone
United Kingdom
* Farnborough, Hampshire, a town in the Rushmoor district of Hampshire, England
** Farnborough (Main) railway station, a railw ...
, where it was allocated reference ''Air Min 81''. Restoration was completed in 1985 and the aircraft was put up on display. The Australian War Memorial's website states that the aircraft "is the only Me 262 bomber variant to survive, and is the only remaining Me 262 wearing its original paint".
; Me 262 B-1a/U1, W.Nr.110305 ''Red 8''
: South African National Museum of Military History, Johannesburg, South Africa.
; Me 262 B-1a, W.Nr.110639 ''White 35''
: National Museum of Naval Aviation, Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola () is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle, and the county seat and only incorporated city of Escambia County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 54,312. Pensacola is the principal ...
(previously at NAS/JRB Willow Grove, Willow Grove, Pennsylvania, US)
; Avia S-92
: Prague Aviation Museum, Kbely, Prague, Czech Republic.
; Avia CS-92
: Prague Aviation Museum, Kbely, Prague, Czech Republic.
Specifications (Messerschmitt Me 262 A-1a)
Notable appearances in media
See also
References
Notes
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * *External links
Gun camera footage of US 8th Airforce engagements against Me-262s
{{Subject bar , portal1=Aviation , portal2=Military of Germany , portal3=World War II , commons=y Aircraft first flown in 1942 S-092 Cruciform tail aircraft German inventions of the Nazi period Low-wing aircraft Mauthausen concentration camp Me 262 1940s German fighter aircraft Twinjets World War II jet aircraft of Germany