Masu (Japanese) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
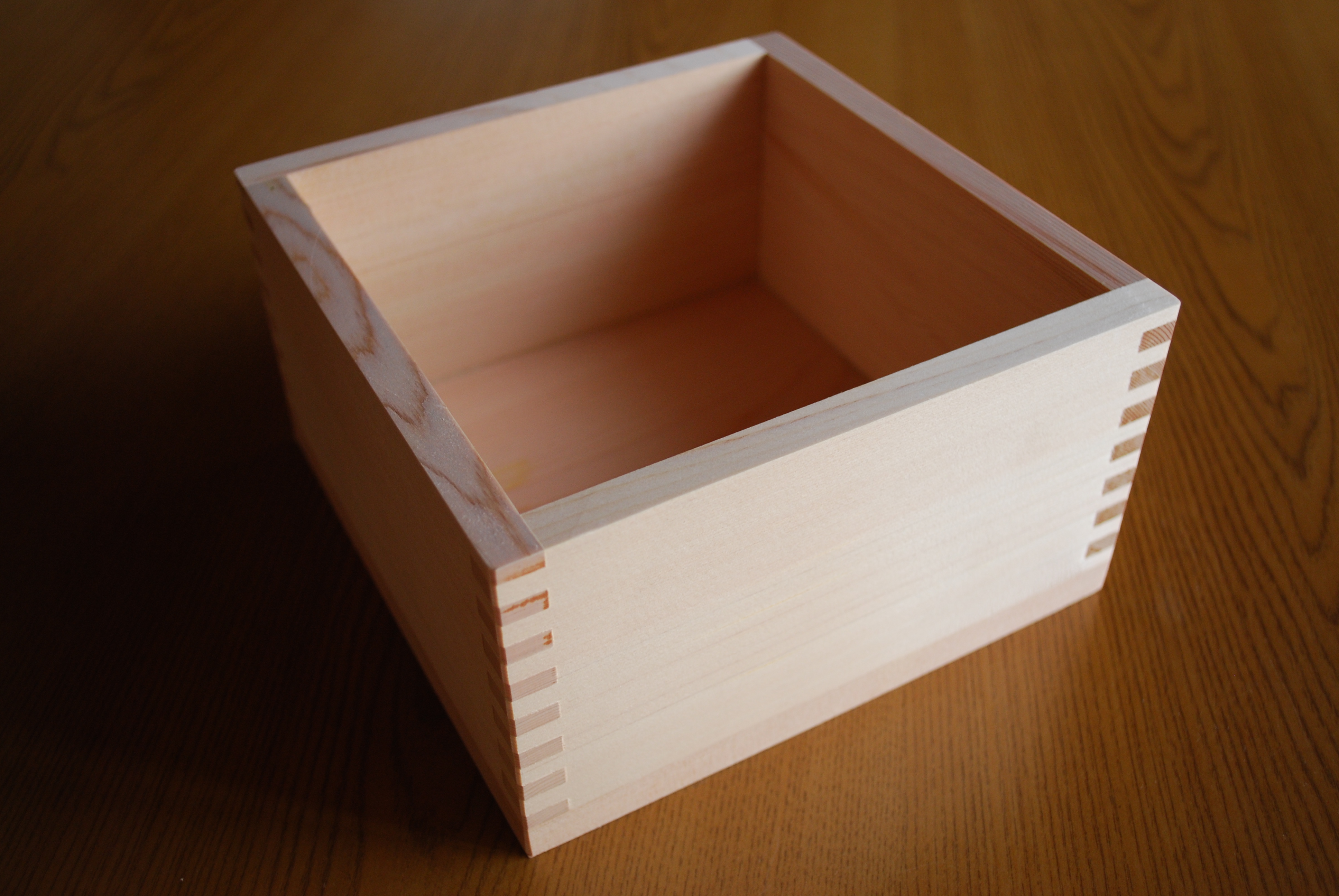 A was originally a square wooden box used to measure rice in
A was originally a square wooden box used to measure rice in
Toasts are poured by stacking a pyramid of the guests' ''masu'' on a towel or cloth, with the toastmaker's ''masu'' on top. It is then overflowed until it fills all the ''masu'' beneath it. This symbolizes the generosity of the toaster to their friends and how they wish to share their happiness and good fortune with them. *''Sanjakumasu'' (measure equal to 3 ''
Sake Traditions
Japanese culture Obsolete units of measurement Units of volume Human-based units of measurement Origami Sake Standards of Japan
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
during the feudal period. In 1885 Japan signed the Convention du Mètre
The Metre Convention (french: link=no, Convention du Mètre), also known as the Treaty of the Metre, is an international treaty that was signed in Paris on 20 May 1875 by representatives of 17 nations (Argentina, Austria-Hungary, Belgium, Brazi ...
and in 1886 converted all of its traditional measures to the metric system.
''Masu'' existed in many sizes, typically covering the range from one to one .
The advent of modern rice cooker
A rice cooker or rice steamer is an automated kitchen appliance designed to boil or steam rice. It consists of a heat source, a cooking bowl, and a thermostat. The thermostat measures the temperature of the cooking bowl and controls the heat. ...
s and a higher calorie diet in Japan has made them impractical for measuring portions of rice.
Today ''masu'' are largely used for drinking sake
Sake, also spelled saké ( ; also referred to as Japanese rice wine), is an alcoholic beverage of Japanese origin made by fermenting rice that has been polished to remove the bran. Despite the name ''Japanese rice wine'', sake, and indee ...
. Drinking vessels are made from ''hinoki
''Chamaecyparis obtusa'' (Japanese cypress, hinoki cypress or hinoki; ja, 檜 or , ) is a species of cypress native to central Japan in East Asia, and widely cultivated in the temperate northern hemisphere for its high-quality timber and orname ...
'' (Japanese Cypress wood), as it imparts a special scent and flavor. The drinker sips from the corner of the box, which pours it into the mouth.Toasts are poured by stacking a pyramid of the guests' ''masu'' on a towel or cloth, with the toastmaker's ''masu'' on top. It is then overflowed until it fills all the ''masu'' beneath it. This symbolizes the generosity of the toaster to their friends and how they wish to share their happiness and good fortune with them. *''Sanjakumasu'' (measure equal to 3 ''
shaku Shaku may refer to:
* Shaku (unit)
* Shaku (ritual baton)
* Buddhist surname
In East Asian Buddhism, monks and nuns usually adopt a Buddhist surname and a Dharma name, which are combined in the surname-first East-Asian naming order. Since the 4th c ...
'' 4ml = Often used in bars to hold a 50ml shotglass, which is then filled to overflowingThis service custom is called ''sosogi-koboshi'' ("overflowing pour") or ''mokkiri zake'' ("generous sake"). Originally the small ''masu'' or a ''sakazuki'' (flat sake saucer) was placed under a ''ochoko'' (sake cup) or shotglass to catch spilt liquor or to use as a coaster. After World War 2 it was used in bars as a bonus to the customer to hustle up business. It then spread to the upper echelons of the hospitality industry. to make up the difference. If the shotglass is used for sake, it is served chilled or at room-temperature. The ''sanjakumasu'' can also be used in the '' san san kudo'' wedding ceremony in the place of the ''sakazuki'' (sake dish).
*''Goshakumasu'' (measure equal to 5 ''shaku'' 0ml = Holds a half ''gō'' measure.
*''Hasshakumasu'' (measure equal to 8 ''shaku'' or 4/5 ''gō'' 44ml = The former standard ''masu'' size, probably because 8 is a lucky number.
*''Ichigōmasu'' (measure equal to 1 ''gō'' 80ml = The modern standard ''masu'' size, equal to a measure of 1 ''gō'' (0.18039 L) or 10 ''shaku''.
*''Nigōhanmasu'' (measure equal to 2.5 ''gō'' 50ml. = Holds a quarter ''shō'' measure.
*''Gogōmasu'' (measure equal to 5 ''gō'' 00ml = Holds a half ''shō'' measure.
*''Isshōmasu'' (measure equal to 1 ''shō'' or 10 ''gō'' .8L = Holds a full ''shō'' measure.
A small , lidded form of ''masu'', is sold for serving pepper, salt, sugar, and other dry condiments at the table.
See also
*Sake set
A consists of the flask and cups used to serve ''sake''. ''Sake'' sets are commonly ceramic, but may be wood, lacquered wood, glass or plastic. The flask and cups may be sold individually or as a set.
Server
The server of a ''sake'' set is ...
* Japanese units of measurement
Traditional Japanese units of measurement or the shakkanhō (, "''shaku–kan'' system") is the traditional system of measurement used by the people of the Japanese archipelago. It is largely based on the Chinese system, which spread to Japan an ...
References
External links
{{Commons cat, Masu (containers), Masu (containers)Sake Traditions
Japanese culture Obsolete units of measurement Units of volume Human-based units of measurement Origami Sake Standards of Japan