Martinique At The 2022 Central American And Caribbean Beach Games on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=
INSEE One of the
 Because there were few
Because there were few
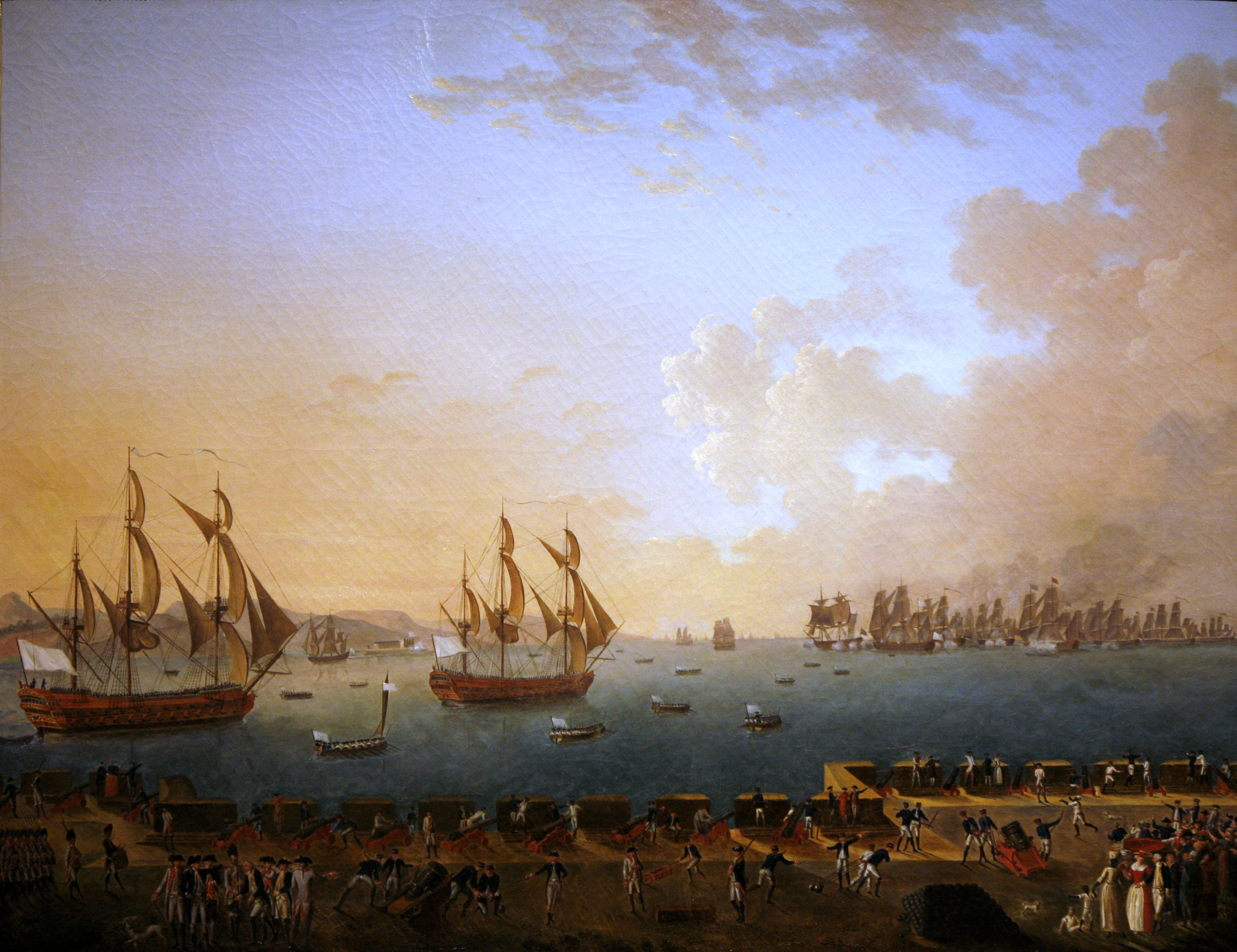 Martinique was attacked or occupied several times by the British, in 1693,
Martinique was attacked or occupied several times by the British, in 1693,
Martinican Creole
Antillean Creole (Antillean French Creole, Kreyol, Kwéyòl, Patois) is a French-based creole that is primarily spoken in the Lesser Antilles. Its grammar and vocabulary include elements of Carib, English, and African languages.
Antillean Creol ...
, Matinik or ; Kalinago
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated language ...
: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity
A single territorial collectivity (french: collectivité territoriale unique) is a chartered subdivision of France that exercises the powers of both a region and a department. This subdivision was introduced in Mayotte in 2011, in French Guian ...
of France. An integral part of the French Republic
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, Martinique is located in the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc betwe ...
of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
. It has a land area of and a population of 364,508 inhabitants as of January 2019.Populations légales 2019: 972 MartiniqueINSEE One of the
Windward Islands
french: Îles du Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Windward Islands. Clockwise: Dominica, Martinique, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Grenada.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean SeaNorth ...
, it is directly north of Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerindian ...
, northwest of Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate). ...
and south of Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically ...
. Martinique is an Outermost Region and a special territory of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
; the currency in use is the euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
. Virtually the entire population speaks both French (the sole official language) and Martinican Creole
Antillean Creole (Antillean French Creole, Kreyol, Kwéyòl, Patois) is a French-based creole that is primarily spoken in the Lesser Antilles. Its grammar and vocabulary include elements of Carib, English, and African languages.
Antillean Creol ...
.

Etymology
It is thought that Martinique is a corruption of theTaíno
The Taíno were a historic Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the ...
name for the island (/, meaning 'island of flowers', or , 'island of women'), as relayed to Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
when he visited the island in 1502. According to historian Sydney Daney, the island was called or by the Caribs
“Carib” may refer to:
People and languages
*Kalina people, or Caribs, an indigenous people of South America
**Carib language, also known as Kalina, the language of the South American Caribs
*Kalinago people, or Island Caribs, an indigenous pe ...
, which means 'the island of iguanas'.
History
Pre-European contact and early colonial periods
The island was occupied first byArawaks
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, wh ...
, then by Caribs
“Carib” may refer to:
People and languages
*Kalina people, or Caribs, an indigenous people of South America
**Carib language, also known as Kalina, the language of the South American Caribs
*Kalinago people, or Island Caribs, an indigenous pe ...
. The Arawaks were described as gentle timorous Indians and the Caribs as ferocious cannibal warriors. The Arawaks came from Central America in the 1st century AD and the Caribs came from the Venezuelan coast around the 11th century.
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
charted Martinique (without landing) in 1493, during his first voyage, but Spain had little interest in the territory. Columbus landed during a later voyage, on 15 June 1502, after a 21-day trade wind
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisph ...
passage
Passage, The Passage or Le Passage may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Films
* ''Passage'' (2008 film), a documentary about Arctic explorers
* ''Passage'' (2009 film), a short movie about three sisters
* ''The Passage'' (1979 film), starring ...
, his fastest ocean voyage. He spent three days there refilling his water casks, bathing and washing laundry.
The indigenous people Columbus encountered called Martinique ‘Matinino’. He was told by indigenous people of
San Salvador that ‘the island of Matinino was entirely populated by women on whom the Caribs descended at certain seasons of the year; and if these women bore sons they were entrusted to the father to bring up.’
On 15 September 1635, Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc
Pierre Belain, sieur d'Esnambuc (; 1585–1636) was a French trader and adventurer in the Caribbean, who established the first permanent French colony, Saint-Pierre, on the island of Martinique in 1635.
Biography Youth
Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc wa ...
, French governor of the island of St. Kitts, landed in the harbour of St. Pierre with 80-150 French settlers after being driven off St. Kitts by the English. D'Esnambuc claimed Martinique for the French king Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crown ...
and the French "Compagnie des Îles de l'Amérique The Company of the American Islands (french: Compagnie des Îles de l'Amérique) was a French chartered company that in 1635 took over the administration of the French portion of ''Saint-Christophe island'' (Saint Kitts) from the Compagnie de Saint- ...
" (Company of the American Islands), and established the first European settlement at Fort Saint-Pierre (now St. Pierre). D'Esnambuc died in 1636, leaving the company and Martinique in the hands of his nephew, Jacques Dyel du Parquet
Jacques Dyel du Parquet (1606 – 3 January 1658) was a French soldier who was one of the first governors of Martinique.
He was appointed governor of the island for the Compagnie des Îles de l'Amérique in 1636, a year after the first French se ...
, who in 1637 became governor of the island.
In 1636, in the first of many skirmishes, the indigenous Caribs rose against the settlers to drive them off the island. The French successfully repelled the natives and forced them to retreat to the eastern part of the island, on the Caravelle Peninsula in the region then known as the Capesterre. When the Caribs revolted against French rule in 1658, the governor Charles Houël du Petit Pré Charles Houël du Petit Pré (1616—22 April 1682) was a French governor of Guadeloupe from 1643 to 1664. He was also knight and lord.
He became, by a royal proclamation dated August 1645, the first of the island judicial officer. He is named Marq ...
retaliated with war against them. Many were killed, and those who survived were taken captive and expelled from the island. Some Caribs fled to Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically ...
or St. Vincent
Saint Vincent may refer to:
People Saints
* Vincent of Saragossa (died 304), a.k.a. Vincent the Deacon, deacon and martyr
* Saint Vincenca, 3rd century Roman martyress, whose relics are in Blato, Croatia
* Vincent, Orontius, and Victor (died 305) ...
, where the French agreed to leave them at peace.
After the death of du Parquet in 1658, his widow Marie Bonnard du Parquet
Marie Bonnard du Parquet (died 1659) was the wife of Jacques Dyel du Parquet, one of the first governors of Martinique, who purchased the island in 1650.
When her husband died she tried to act as governor in the name of her children, but was force ...
tried to govern Martinique, but dislike of her rule led King Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
to take over the sovereignty of the island. In 1654, Dutch Jews expelled from Portuguese Brazil introduced sugar plantations worked by large numbers of enslaved Africans.
In 1667, the Second Anglo-Dutch War
The Second Anglo-Dutch War or the Second Dutch War (4 March 1665 – 31 July 1667; nl, Tweede Engelse Oorlog "Second English War") was a conflict between Kingdom of England, England and the Dutch Republic partly for control over the seas a ...
spilled out into the Caribbean, with Britain attacking the pro-Dutch French fleet in Martinique, virtually destroying it and further cementing British preeminence in the region. In 1674, the Dutch attempted to conquer the island, but were repulsed.
 Because there were few
Because there were few Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
priests in the French Antilles, many of the earliest French settlers were Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss politica ...
who sought religious freedom. Others were transported there as a punishment for refusing to convert to Catholicism, many of them dying en route. Those who survived were quite industrious and over time prospered, though the less fortunate were reduced to the status of indentured servants. Although edicts from King Louis XIV's court regularly came to the islands to suppress the Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
"heretics", these were mostly ignored by island authorities until Louis XIV's Edict of Revocation in 1685.
As many of the planters on Martinique were Huguenots suffering under the harsh strictures of the Revocation, they began plotting to emigrate from Martinique with many of their recently arrived brethren. Many of them were encouraged by the Catholics, who looked forward to their departure and the opportunities for seizing their property. By 1688, nearly all of Martinique's French Protestant population had escaped to the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
American colonies or Protestant countries in Europe. The policy decimated the population of Martinique and the rest of the French Antilles and set back their colonisation by decades, causing the French king to relax his policies in the region, which left the islands susceptible to British occupation over the next century.
Post-1688 period
Under governor of the AntillesCharles de Courbon, comte de Blénac
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was " ...
, Martinique served as a home port for French pirates, including Captain Crapeau, Étienne de Montauban
Étienne de Montauban ( fl. 1691-1695) was a French ''flibustier'' (buccaneer), privateer, and pirate active in the Caribbean and off the west African coast. Frequently referred to as Sieur de Montauban (last name occasionally Montauband), he wro ...
, and Mathurin Desmarestz
Mathurin Desmarestz (1653-1700, last name also Demarais) was a French pirate and buccaneer active in the Caribbean, the Pacific, and the Indian Ocean.
History
Born Isaac Veyret (or Vereil) in 1653, son of Isaac Veyret and Esther Pennaud, Mathuri ...
. French language original, as reprinted in ''Le Diable Volant: Une histoire de la flibuste: de la mer des Antilles à l'océan Indien (1688–1700)'' / (''The Flying Devil: A History of the Filibusters: From the Antilles to the Indian Ocean (1688–1700)''). In later years, pirate Bartholomew Roberts
)
, type=Pirate
, birth_place = Casnewydd Bach, near Puncheston, Pembrokeshire, Wales, Kingdom of England
, death_place = At sea off of Cape Lopez, Gabon
, allegiance=
, serviceyears=1719–1722
, base of operations= Off the coast of the Americas ...
styled his jolly roger
Jolly Roger is the traditional English name for the flags flown to identify a pirate ship preceding or during an attack, during the early 18th century (the later part of the Golden Age of Piracy).
The flag most commonly identified as the Jolly ...
as a black flag depicting a pirate standing on two skulls labeled "ABH" and "AMH" for "A Barbadian's Head" and "A Martinican's Head" after governors of those two islands sent warships to capture Roberts.
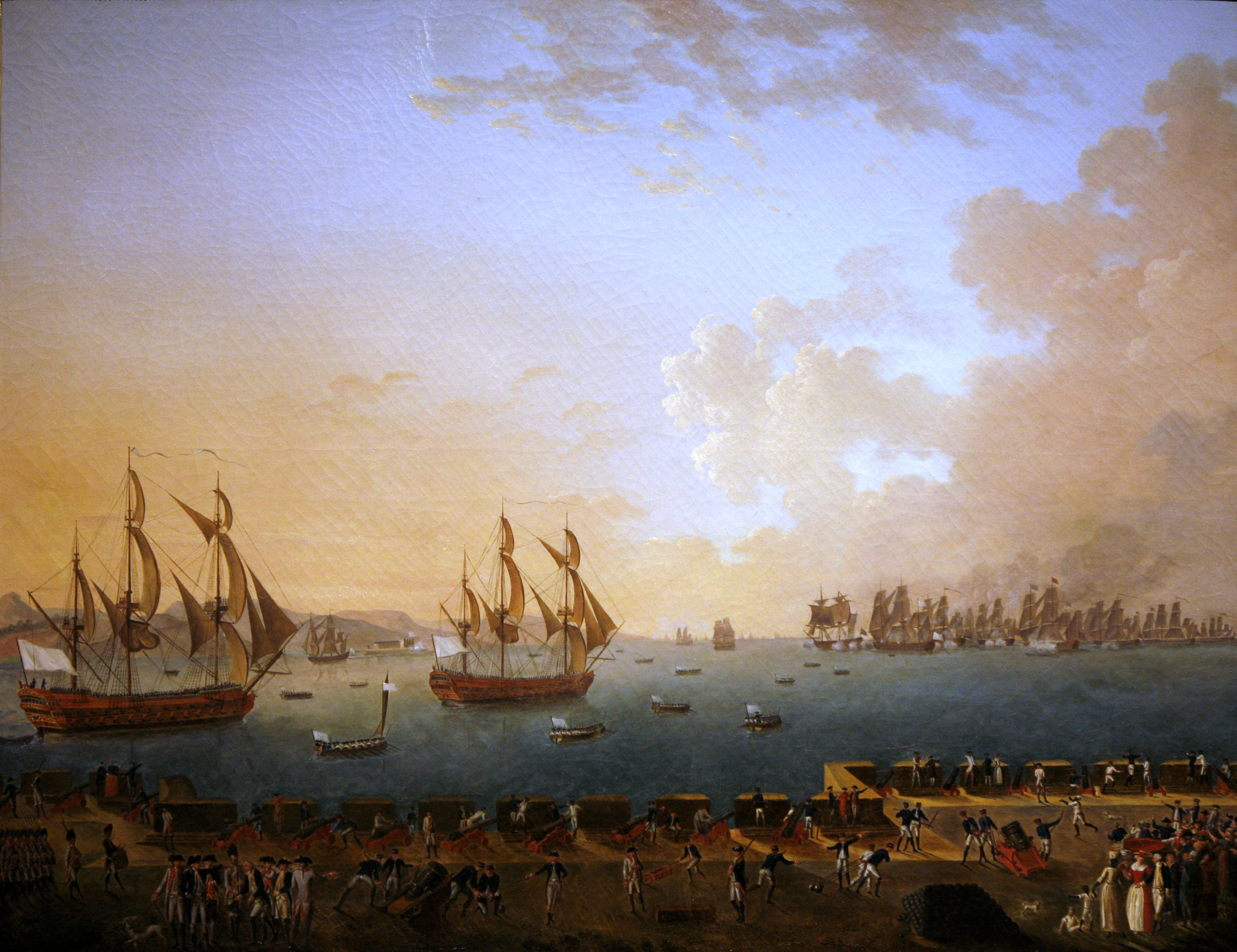 Martinique was attacked or occupied several times by the British, in 1693,
Martinique was attacked or occupied several times by the British, in 1693, 1759
In Great Britain, this year was known as the ''Annus Mirabilis'', because of British victories in the Seven Years' War.
Events
January–March
* January 6 – George Washington marries Martha Dandridge Custis.
* January 11 &ndas ...
, 1762
Events
January–March
* January 4 – Britain enters the Seven Years' War against Spain and Naples.
* January 5 – Empress Elisabeth of Russia dies, and is succeeded by her nephew Peter III. Peter, an admirer of Frederick t ...
and 1779
Events
January–March
* January 11 – British troops surrender to the Marathas in Wadgaon, India, and are forced to return all territories acquired since 1773.
* January 11 – Ching-Thang Khomba is crowned King of Manip ...
. Excepting a period from 1802 to 1809 following signing of the Treaty of Amiens
The Treaty of Amiens (french: la paix d'Amiens, ) temporarily ended hostilities between France and the United Kingdom at the end of the War of the Second Coalition
The War of the Second Coalition (1798/9 – 1801/2, depending on perio ...
, Britain controlled the island for most of the time from 1794 to 1815, when it was traded back to France at the conclusion of the Napoleonic Wars. Martinique has remained a French possession since then.
Despite the introduction of successful coffee plantations in the 1720s to Martinique, the first coffee-growing area in the Western hemisphere, as sugar prices declined in the early 1800s, the planter class lost political influence. Slave rebellions in 1789, 1815 and 1822, plus the campaigns of abolitionists such as Cyrille Bissette
Cyrille Bissette (1795–1858) was a French abolitionist, politician and publisher. A free person of color (''homme de couleur'') from Martinique, his radical activities and publications galvanized the abolition movement in France and its colonies. ...
and Victor Schœlcher
Victor Schœlcher (; 22 July 1804 – 25 December 1893) was a French abolitionist, writer, politician and journalist, best known for his leading role in the abolition of slavery in France in 1848, during the Second Republic.
Early life
Schœlche ...
, persuaded the French government to end slavery in the French West Indies in 1848. As a result, some plantation owners imported workers from India and China. Despite the abolition of slavery, life scarcely improved for most Martinicans; class and racial tensions exploded into rioting in southern Martinique in 1870 following the arrest of Léopold Lubin, a trader of African ancestry who retaliated after he was beaten by a Frenchman. After several deaths, the revolt was crushed by French militia.
20th–21st centuries
On 8 May 1902,Mont Pelée
Mont may refer to:
Places
* Mont., an abbreviation for Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to ...
erupted and completely destroyed St. Pierre, killing 30,000 people. Refugees from Martinique travelled by boat to the southern villages of Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically ...
, and some of them remained permanently on the island. The only survivor in the town of Saint-Pierre, Auguste Cyparis, was saved by the thick walls of his prison cell. Shortly thereafter, the capital shifted to Fort-de-France
Fort-de-France (, , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Fodfwans) is a Communes of France, commune and the capital city of Martinique, an overseas department and region of France located in the Caribbean. It is also one of the major cities in the ...
, where it remains today.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the pro-Nazi Vichy government
Vichy France (french: Régime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its terr ...
controlled Martinique under Admiral Georges Robert. German U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare role ...
s used Martinique for refuelling and re-supply during the Battle of the Caribbean
The Battle of the Caribbean refers to a naval campaign waged during World War II that was part of the Battle of the Atlantic, from 1941 to 1945. German U-boats and Italian submarines attempted to disrupt the Allied supply of oil and other mate ...
. In 1942, 182 ships were sunk in the Caribbean, dropping to 45 in 1943, and five in 1944. Free French
Free France (french: France Libre) was a political entity that claimed to be the legitimate government of France following the dissolution of the Third Republic. Led by French general , Free France was established as a government-in-exile ...
forces took over on the island on Bastille Day
Bastille Day is the common name given in English-speaking countries to the national day of France, which is celebrated on 14 July each year. In French, it is formally called the (; "French National Celebration"); legally it is known as (; "t ...
, 14 July 1943.
In 1946, the French National Assembly
The National Assembly (french: link=no, italics=set, Assemblée nationale; ) is the lower house of the bicameral French Parliament under the Fifth Republic, the upper house being the Senate (). The National Assembly's legislators are known a ...
voted unanimously to transform the colony into an Overseas Department of France. Meanwhile, the post-war period saw a growing campaign for full independence; a notable proponent of this was the author Aimé Césaire
Aimé Fernand David Césaire (; ; 26 June 1913 – 17 April 2008) was a French poet, author, and politician. He was "one of the founders of the Négritude movement in Francophone literature" and coined the word in French. He founded the Par ...
, who founded the