Marienfluss Valley on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
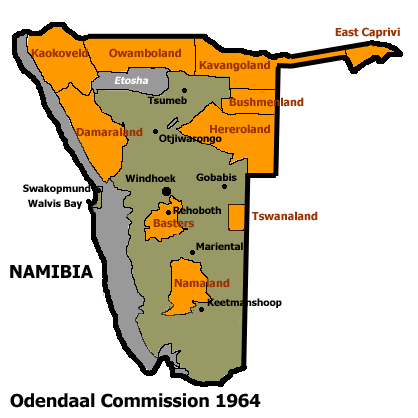 Kaokoland was an administrative unit and a ''
Kaokoland was an administrative unit and a ''
Kaokoland at namibian.org
{{coord, 18, S, 13, E, source:dewiki_region:NA-KU_type:landmark, display=title History of Namibia Kunene Region Bantustans in South West Africa States and territories established in 1964 States and territories disestablished in 1989
 Kaokoland was an administrative unit and a ''
Kaokoland was an administrative unit and a ''bantustan
A Bantustan (also known as Bantu homeland, black homeland, black state or simply homeland; ) was a territory that the National Party administration of South Africa set aside for black inhabitants of South Africa and South West Africa (now N ...
'' in northern South West Africa
South West Africa ( af, Suidwes-Afrika; german: Südwestafrika; nl, Zuidwest-Afrika) was a territory under South African administration from 1915 to 1990, after which it became modern-day Namibia. It bordered Angola (Portuguese colony before 1 ...
(now Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
). Established during the apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
era, it was intended to be a self-governing homeland of the OvaHimba
The Himba (singular: OmuHimba, plural: OvaHimba) are an indigenous people with an estimated population of about 50,000 people living in northern Namibia, in the Kunene Region (formerly Kaokoland) and on the other side of the Kunene River in southe ...
, but an actual government was never established. Like other homelands in South West Africa, the Kaokoland bantustan was abolished in May 1989, at the beginning of the transition of Namibia towards independence. "Kaokoland" remains as an informal name for the geographic area, while the political unit of administration since 1990 is Kunene Region
Kunene is one of the fourteen regions of Namibia. Its capital is Opuwo, its governor is Marius Sheya. The region's name comes from the Kunene River which forms the northern border with Angola. Besides the capital Opuwo, the region contains the ...
. The area is in the Kaokoveld
The Kaokoveld Desert is a coastal desert of northern Namibia and southern Angola.
Setting
The Kaokoveld Desert occupies a coastal strip covering , from 13° to 21°S and is bounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Namibian savanna woodla ...
ecoregion.
The area is one of the wildest and least populated areas in Namibia, with a population density of one person every 2 km² (1/4 of the national average). The most represented ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
is the Himba people
The Himba (singular: OmuHimba, plural: OvaHimba) are an indigenous people with an estimated population of about 50,000 people living in northern Namibia, in the Kunene Region (formerly Kaokoland) and on the other side of the Kunene River in sout ...
, who account for about 5,000 of the overall 16,000 inhabitants of Kaokoland. The main settlement in Kaokoland was the city of Opuwo
Opuwo is the capital of the Kunene Region in north-western Namibia. The town is situated about 720 km north-northwest from the capital Windhoek, and has a population of 20,000. It is the commercial hub of the Kunene Region.
Economy and inf ...
.
Geography
The Kaokoland area extends south-north from theHoanib
The Hoanib is one of the 12 ephemeral seasonal rivers in the west of Namibia, where it was the border between northern Damaraland and Kaokoland. Its length is 270 km. With the low population density, the oasis character of the river valley ...
river to the Kunene river
The Cunene (Portuguese spelling) or Kunene (common Namibian spelling) is a river in Southern Africa. It flows from the Angola highlands south to the border with Namibia. It then flows west along the border until it reaches the Atlantic Ocean. It ...
(that also marks the border between Namibia and Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
). It is largely mountainous, with the northern Baynes Mountains
The Baynes Mountains are a mountain range in Namibia.
Description
The Baynes Mountains form an escarpment plateau in Kunene Region in northwest Namibia, near the border with Angola (formed here by the Kunene River). The mountains range in altitud ...
reaching the maximum elevation at 2039 m. Other notable mountain ranges of Kaokoland include the Otjihipa Mountains (to the north) and the Hartmann Mountains Hartmann is a germanic languages, Germanic and Ashkenazi Jews, Ashkenazi Jewish surname. It is less frequently used as a male given name. The name originates from the Germanic word, "hart", which translates in English to "hardy", "hard", or "tough" ...
(to the east). The land is generally dry and rocky, especially to the south, where it borders on the Namib Desert
The Namib ( ; pt, Namibe) is a coastal desert in Southern Africa. The name is of Khoekhoegowab origin and means "vast place". According to the broadest definition, the Namib stretches for more than along the Atlantic coasts of Angola, Namib ...
; nevertheless, it has several rivers as well as falls. The most notable falls in Kaokoland are the Ruacana Falls
Ruacana Falls is a waterfalls located in Ruacana, Omusati on the Kunene River in Northern Namibia. The waterfall is high and wide in full flood. It is among the largest waterfalls in Africa, both by volume and width.
Description
The Kun ...
(120 m high, 700 m wide) and the Epupa Falls
Epupa Falls (also known as Monte Negro Falls in Angola) is a series of large waterfalls formed by the Cunene River on the border of Angola and Namibia, in the Kaokoland area of the Kunene Region. The river is about wide in this area and drops in ...
, both formed by the Kunene river. The northern part of Kaokoland is greener, with vegetation thriving valleys such as the Marienfluss and Hartmann Valley Hartmann is a Germanic and Ashkenazi Jewish surname. It is less frequently used as a male given name. The name originates from the Germanic word, "hart", which translates in English to "hardy", "hard", or "tough" and "Mann", a suffix meaning "man", ...
.
History
Beforecolonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their relig ...
, Kaokoland was mostly inhabited by the Ovambo Ovambo may refer to:
*Ovambo language
*Ovambo people
* Ovamboland
*Ovambo sparrowhawk
The Ovambo or Ovampo sparrowhawk, also known as Hilgert's sparrowhawk, (''Accipiter ovampensis'') is a species of sub-Saharan African bird of prey in the famil ...
, Nama, and Herero
Herero may refer to:
* Herero people, a people belonging to the Bantu group, with about 240,000 members alive today
* Herero language, a language of the Bantu family (Niger-Congo group)
* Herero and Namaqua Genocide
* Herero chat, a species of b ...
people. In the second half of the 19th century, a group of Herero crossed the Kunene River, migrating north to what is now Angola, joining with the Bushmen
The San peoples (also Saan), or Bushmen, are members of various Khoe, Tuu, or Kxʼa-speaking indigenous hunter-gatherer cultures that are the first cultures of Southern Africa, and whose territories span Botswana, Namibia, Angola, Zambia, ...
in Southern Angola; the modern day Himba people originated from this Angolan Herero group. In 1884, Kaokoland became part of German South West Africa
German South West Africa (german: Deutsch-Südwestafrika) was a colony of the German Empire from 1884 until 1915, though Germany did not officially recognise its loss of this territory until the 1919 Treaty of Versailles. With a total area of ...
, and Namibian Herero changed much of their habits and costumes as a consequence of German rule. After World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, South Africa received the mandate from the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
to administer the territory of Namibia, which became, for all practical purposes, a province of South Africa. South Africa also applied to Namibia the principles of apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
, including the creation of distinct bantustan
A Bantustan (also known as Bantu homeland, black homeland, black state or simply homeland; ) was a territory that the National Party administration of South Africa set aside for black inhabitants of South Africa and South West Africa (now N ...
s (homelands) for different African ethnic groups. Kaokoland was thus established as a bantustan for the Himba people, that in the 1920s had come back from Angola into Namibia. Despite its scarce population, Kaokoland was greatly affected by the struggle for independence of Namibia, and most specifically by the so-called " bush war" that was fought across the border with Angola (i.e., in Kaokoland).
The Himba people
The Himba people are the descendants of a Herero group that got isolated from the others in the 19th century. While the Herero people later experienced German rule and drastically changed their lifestyle as well as their costumes, the Himba retained much of their traditional,nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the popu ...
ic and pastoral habits. In recent times, contacts between Himbas and Western tourists are becoming more and more common, especially in the most easily accessible regions of Kaokoland (e.g., the surroundings of Opuwo). While this has partially affected the Himba culture, Himbas have essentially remained faithful to their tradition.
Fauna
Fauna in Kaokoland suffered from a severe crippling between 1977 and 1982, as well as from poaching throughout the 1970s, but has been recovering afterwards. It includes several desert-dwelling species, most notably a population ofdesert elephants
Desert elephants or desert-adapted elephants are not a distinct species of elephant but are African bush elephants (''Loxodonta africana'') that have made their homes in the Namib and Sahara deserts in Africa. At one time they were classified as ...
that are sometimes classified as a distinct subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
of African elephants because of their shorter legs and specific, desert-adapted behaviour (the only other place in Africa where elephants have adapted to a desert environment is Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
, on the border of the Sahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
desert). Its longer legs, bigger feet, and incredible ability to withstand periods of drought all gave valid reasons to think so. Today, however, it is not considered a different species, rather regarded as only 'desert adapted.' The herds in this area remain separate from other elephant herds in Namibia and only appear to have longer legs and bigger feet because they eat less than elephants living in more food abundant areas such as Etosha National Park, the Caprivi, and Chobe region in Botswana.
The desert elephant claim a three-thousand square kilometre range and regularly travel up to two hundred kilometres in search of water. They only drink every three or four days, compared with elephants in Etosha drinking 100 to 200 L of water a day. They also seem to be more environmentally conscious than other elephants: unlike other elephants, the desert-adapted elephant rarely knock over trees, break branches, or tear away bark.
They are commonly roaming the dry riverbeds of the westward flowing Huab, Hoanib, Hoarusib, and Khumib rivers. It is along these riverbeds the animals find the occasional spring fed waterhole and most of their nutrient rich foods: mopane bark, tamarisk, reeds, and the pods, bark, and leaves of the ana tree. On a typical day, desert elephants travel up to sixty kilometres over rocky, difficult terrain between feeding areas and waterholes. When water is truly scarce, as in times of drought, they dig holes, commonly known as gorras, in the dry riverbeds. Water seeps up from below the surface creating a much needed water source for themselves, and other animals in the area;http://wildsafariafrica.com/destinations/safari-namibia/damaraland-in-namibia/desert-elephant-namibia/ unlike other elephants, which drink daily, desert elephants have been known to survive without water for up to four days.
Black rhinos
Black Rhinos Football Club is a Zimbabwean football club based in Harare. It is a Zimbabwe National Army owned team. They play in the Zimbabwe Premier Soccer League.They are coached by Stanford 'Stix' Mutizwa. Their home stadium is Figaro Stadium ...
were extinguished in the area in 1983, but they have been reintroduced. Other species found in Kaokoland include oryx
''Oryx'' is a genus consisting of four large antelope species called oryxes. Their pelage is pale with contrasting dark markings in the face and on the legs, and their long horns are almost straight. The exception is the scimitar oryx, which l ...
es, kudu
The kudus are two species of antelope of the genus ''Tragelaphus'':
* Lesser kudu, ''Tragelaphus imberbis'', of eastern Africa
* Greater kudu, ''Tragelaphus strepsiceros'', of eastern and southern Africa
The two species look similar, thou ...
s, springbok
The springbok (''Antidorcas marsupialis'') is a medium-sized antelope found mainly in south and southwest Africa. The sole member of the genus ''Antidorcas'', this bovid was first described by the German zoologist Eberhard August Wilhelm v ...
s, ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There are ...
es, giraffes and mountain zebra
The mountain zebra (''Equus zebra'') is a zebra species in the family Equidae, native to southwestern Africa. There are two subspecies, the Cape mountain zebra (''E. z. zebra'') found in South Africa and Hartmann's mountain zebra (''E. z. hartman ...
s.
Tourism and transportation
After the end of the bush war, Kaokoland has become a common tourist destination in Namibia, due its proximity to theEtosha National Park
Etosha National Park is a national park in northwestern Namibia and one of the largest national parks in Africa. It was proclaimed a game reserve in March 1907 in Ordinance 88 by the Governor of German South West Africa, Friedrich von Lindequist. ...
(to the south), the unspoiled nature (with several spots suitable for activities such as rafting
Rafting and whitewater rafting are recreational outdoor activities which use an inflatable raft to navigate a river or other body of water. This is often done on whitewater or different degrees of rough water. Dealing with risk is often a ...
and trekking
Backpacking is the outdoor recreation of carrying gear on one's back, while hiking for more than a day. It is often an extended journey, and may involve camping outdoors. In North America tenting is common, where simple shelters and mountain h ...
), and the opportunity to visit traditional Himba villages. Notable landmarks in the area include the Epupa Falls
Epupa Falls (also known as Monte Negro Falls in Angola) is a series of large waterfalls formed by the Cunene River on the border of Angola and Namibia, in the Kaokoland area of the Kunene Region. The river is about wide in this area and drops in ...
, Sesfontein
Sesfontein is a settlement in the Kunene Region of Namibia, situated from the regional capital Opuwo. It is the district capital of Sesfontein Constituency, its population is 7,358. Sesfontein derives its name from the six fountains which have th ...
, Himba villages, and the Ondurusa Rapids.
Kaokoland is one of the wildest regions of Southern Africa, with very few roads and structures. The only road that is accessible to non-4WD
Four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 ("four by four") or 4WD, refers to a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case ...
vehicles is that connecting Sesfontein and Opuwo
Opuwo is the capital of the Kunene Region in north-western Namibia. The town is situated about 720 km north-northwest from the capital Windhoek, and has a population of 20,000. It is the commercial hub of the Kunene Region.
Economy and inf ...
. Many roads in Kaokoland are often in very bad conditions and may be challenging for 4WDs as well, especially during the rainy season
The rainy season is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs.
Rainy Season may also refer to:
* ''Rainy Season'' (short story), a 1989 short horror story by Stephen King
* "Rainy Season", a 2018 song by Monni
* ''T ...
. Most services such as shops, hospital, garage, and so on are only found in Opuwo.
See also
*Ovamboland
Ovamboland, also referred to as Owamboland, was a Bantustan in South West Africa (present-day Namibia), intended by the apartheid government to be a self-governing homeland for the Ovambo people.
The term originally referred to the parts of ...
*Damaraland
Damaraland was a name given to the north-central part of what later became Namibia, inhabited by the Damara (people), Damaras. It was bounded roughly by Ovamboland in the north, the Namib Desert in the west, the Kalahari Desert in the east, a ...
*Bantustan
A Bantustan (also known as Bantu homeland, black homeland, black state or simply homeland; ) was a territory that the National Party administration of South Africa set aside for black inhabitants of South Africa and South West Africa (now N ...
Notes
References
Kaokoland at namibian.org
{{coord, 18, S, 13, E, source:dewiki_region:NA-KU_type:landmark, display=title History of Namibia Kunene Region Bantustans in South West Africa States and territories established in 1964 States and territories disestablished in 1989