Marc Isambard Brunel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sir Marc Isambard Brunel (, ; 25 April 1769 – 12 December 1849) was a French-British engineer who is most famous for the work he did in Britain. He constructed the
Sir Marc Isambard Brunel (, ; 25 April 1769 – 12 December 1849) was a French-British engineer who is most famous for the work he did in Britain. He constructed the
 During the summer of 1799 Brunel was introduced to
During the summer of 1799 Brunel was introduced to
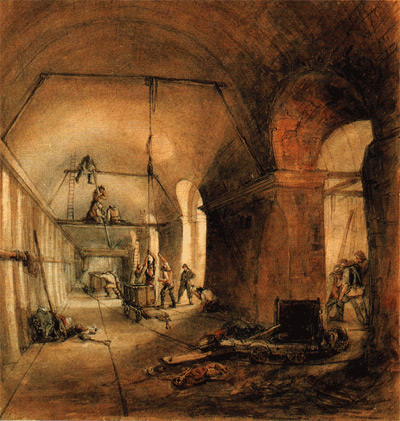 In 1805 the Thames Archway Company was formed with the intention of driving a tunnel beneath the Thames between
In 1805 the Thames Archway Company was formed with the intention of driving a tunnel beneath the Thames between 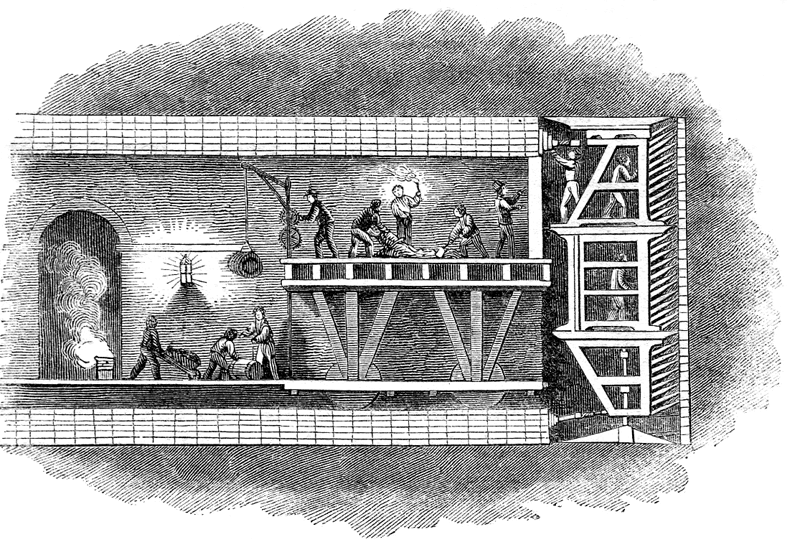 Work began in February 1825, by sinking a diameter vertical shaft on the
Work began in February 1825, by sinking a diameter vertical shaft on the
 After the completion of the Thames Tunnel, his greatest achievement, Brunel was in poor health. He never again accepted major commissions, although he did help his son, Isambard, on various projects. He was proud of his son's achievements, and was present at the launch of the '' SS Great Britain'' in
After the completion of the Thames Tunnel, his greatest achievement, Brunel was in poor health. He never again accepted major commissions, although he did help his son, Isambard, on various projects. He was proud of his son's achievements, and was present at the launch of the '' SS Great Britain'' in
Ancient Places TV: HD Video of Brunel (father and son) and the SS Great BritainThe Brunel Institute
– Collaborative venture between the SS Great Britain Trust and the University of Bristol. Housed alongside the at Bristol it includes the National Brunel Collection.
The Brunel Museum
– Based in Rotherhithe, London the museum is housed in the building that contained the pumps to keep the Thames Tunnel dry. {{DEFAULTSORT:Brunel, Marc Isambard 1769 births 1849 deaths English people of French descent French civil engineers English civil engineers British mechanical engineers British steam engine engineers Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences Fellows of the Royal Society Machine tool builders Members of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences Burials at Kensal Green Cemetery People associated with transport in London English prisoners and detainees English theatre architects Fellows of the Royal Society of Edinburgh French expatriates in England French mechanical engineers People imprisoned for debt 18th-century British engineers 19th-century British engineers Knights Bachelor Family of Isambard Kingdom Brunel People from Eure
 Sir Marc Isambard Brunel (, ; 25 April 1769 – 12 December 1849) was a French-British engineer who is most famous for the work he did in Britain. He constructed the
Sir Marc Isambard Brunel (, ; 25 April 1769 – 12 December 1849) was a French-British engineer who is most famous for the work he did in Britain. He constructed the Thames Tunnel
The Thames Tunnel is a tunnel beneath the River Thames in London, connecting Rotherhithe and Wapping. It measures 35 feet (11 m) wide by 20 feet (6 m) high and is 1,300 feet (396 m) long, running at a depth of 7 ...
and was the father of Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "one ...
.
Born in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, Brunel fled to the United States during the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
. In 1796, he was appointed Chief Engineer of New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the U ...
. He moved to London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
in 1799, where he married Sophia Kingdom. In addition to the construction of the Thames Tunnel, his work as a mechanical engineer included the design of machinery to automate the production of pulley blocks for the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
.
Brunel preferred the given name Isambard, but is generally known to history as Marc to avoid confusion with his more famous son.
Early life in France
Brunel was the second son of Jean Charles Brunel and Marie-Victoire Lefebvre. Jean Charles was a prosperous farmer inHacqueville
Hacqueville () is a commune in the Eure department in north western France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in t ...
, Normandy, and Marc was born on the family farm. It was customary for the first son to inherit the farm and the second son to enter the priesthood. His father therefore started Marc on a classical education, but he showed no liking for Greek or Latin and instead showed himself proficient in drawing and mathematics. He was also very musical from an early age.
At the age of eleven he was sent to a seminary
A seminary, school of theology, theological seminary, or divinity school is an educational institution for educating students (sometimes called ''seminarians'') in scripture, theology, generally to prepare them for ordination to serve as clergy ...
in Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the region of Normandy and the department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of the largest and most prosperous cities of medieval Europe, the population ...
. The superior of the seminary allowed him to learn carpentry, and he soon achieved the standards of a cabinetmaker. He also sketched ships in the local harbour. As he showed no desire to become a priest, his father sent him to stay with relatives in Rouen, where a family friend tutored him on naval matters. In 1786, as a result of this tuition, Marc became a naval cadet on a French frigate and during his service visited the West Indies several times. He made an octant for himself from brass and ivory, and used it during his service.
In 1789, during Brunel's service abroad, the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
began. In January 1792 Brunel's frigate paid off its crew, and Brunel returned to live with his relatives in Rouen. He was a Royalist sympathiser, as were most of the inhabitants of Normandy. In January 1793, whilst visiting Paris during the trial of Louis XVI
Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was e ...
, Brunel unwisely publicly predicted the demise of Robespierre
Maximilien François Marie Isidore de Robespierre (; 6 May 1758 – 28 July 1794) was a French lawyer and statesman who became one of the best-known, influential and controversial figures of the French Revolution. As a member of the Esta ...
, one of the leaders of the Revolution. He was lucky to get out of Paris with his life, and returned to Rouen. However, it was evident that he would have to leave France. During his stay in Rouen, Brunel had met Sophia Kingdom, a young English woman who was an orphan and was working as a governess. He was forced to leave her behind when he fled to Le Havre
Le Havre (, ; nrf, Lé Hâvre ) is a port city in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region of northern France. It is situated on the right bank of the estuary of the river Seine on the Channel southwest of the Pays de Caux, ver ...
and boarded the American ship ''Liberty'', bound for New York.
United States
Brunel arrived in New York on 6 September 1793, and he subsequently travelled toPhiladelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
and Albany. He got involved in a scheme to link the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between Ne ...
by canal with Lake Champlain
, native_name_lang =
, image = Champlainmap.svg
, caption = Lake Champlain-River Richelieu watershed
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = New York/Vermont in the United States; and Quebec in Canada
, coords =
, type =
, ...
, and also submitted a design for the new Capitol building to be built in Washington. The judges were very impressed with the design, but it was not selected.
In 1796, after taking American citizenship, Brunel was appointed Chief Engineer of the city of New York. He designed various houses, docks, commercial buildings, an arsenal, and a cannon factory. No official records exist of the projects that he carried out in New York, as it seems likely that the documents were destroyed in the New York Draft Riots
The New York City draft riots (July 13–16, 1863), sometimes referred to as the Manhattan draft riots and known at the time as Draft Week, were violent disturbances in Lower Manhattan, widely regarded as the culmination of white working-cla ...
of 1863.
In 1798, during a dinner conversation, Brunel learnt of the difficulties that the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
had in obtaining the 100,000 pulley blocks that it needed each year. Each of these was made by hand. Brunel quickly produced an outline design of a set of machines that would automate their production. He decided to sail to England and put his invention before the Admiralty. He sailed for England on 7 February 1799 with a letter of introduction to the Navy Minister, and on 7 March his ship, ''Halifax'', landed at Falmouth.
Britain
Whilst Brunel had been in the United States, Sophia Kingdom had remained in Rouen and during theReign of Terror
The Reign of Terror (french: link=no, la Terreur) was a period of the French Revolution when, following the creation of the First French Republic, First Republic, a series of massacres and numerous public Capital punishment, executions took pl ...
, she was arrested as an English spy and daily expected to be executed. She was only saved by the fall of Robespierre
Maximilien François Marie Isidore de Robespierre (; 6 May 1758 – 28 July 1794) was a French lawyer and statesman who became one of the best-known, influential and controversial figures of the French Revolution. As a member of the Esta ...
in June 1794. In April 1795 Kingdom was able to leave France and travel to London.
When Brunel arrived from the United States, he immediately travelled to London and made contact with Kingdom. They were married on 1 November 1799 at St Andrew, Holborn. In 1801 she gave birth to their first child, a daughter, Sophia;Baptism Register accounts as baptism 27.1.01 in 1804 their second daughter Emma; and in 1806 their son Isambard Kingdom, who became a great engineer. Isambard Kingdom grew up in Lindsey House
Lindsey House is a Grade II* listed villa in Cheyne Walk, Chelsea, London. It is owned by the National Trust but tenanted and only open by special arrangement.
This house should not be confused with the eponymous 1640 house in Lincoln's Inn Fiel ...
in Chelsea, London
Chelsea is an affluent area in west London, England, due south-west of Charing Cross by approximately 2.5 miles. It lies on the north bank of the River Thames and for postal purposes is part of the south-western postal area.
Chelsea histori ...
.
Henry Maudslay
Henry Maudslay ( pronunciation and spelling) (22 August 1771 – 14 February 1831) was an English machine tool innovator, tool and die maker, and inventor. He is considered a founding father of machine tool technology. His inventions were an ...
, a talented engineer who had worked for Joseph Bramah, and had recently started his own business. Maudslay made working models of the machines for making pulley blocks, and Brunel approached Samuel Bentham, the Inspector General of Naval Works. In April 1802 Bentham recommended the installation of Brunel's block-making machinery at Portsmouth Block Mills. Brunel's machine could be operated by unskilled workers, at ten times the previous rate of production. Altogether 45 machines were installed at Portsmouth, and by 1808 the plant was producing 130,000 blocks per year. Unfortunately for Brunel, the Admiralty vacillated over payment, despite the fact that Brunel had spent more than £2,000 of his own money on the project. In August 1808 they agreed to pay £1,000 on account, and two years later they consented to a payment of just over £17,000.
Brunel was a talented mechanical engineer, and did much to develop sawmill machinery, undertaking contracts for the British Government
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal Arms
, date_est ...
at Chatham and Woolwich
Woolwich () is a district in southeast London, England, within the Royal Borough of Greenwich.
The district's location on the River Thames led to its status as an important naval, military and industrial area; a role that was maintained thro ...
dockyards, building on his experience at the Portsmouth Block Mills. He built a sawmill at Battersea
Battersea is a large district in south London, part of the London Borough of Wandsworth, England. It is centred southwest of Charing Cross and extends along the south bank of the River Thames. It includes the Battersea Park.
History
Batte ...
, London (burnt down in 1814 and rebuilt by 1816), which was designed to produce veneers, and he also designed sawmills for entrepreneurs. He also developed machinery for mass-producing soldiers' boots, but before this could reach full production, demand ceased due to the end of the Napoleonic Wars. Brunel was made a Fellow of the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, r ...
in 1814. In 1828, he was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. Brunel was elected a Foreign Honorary Member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, ...
in 1834. In 1845 he was elected an Honorary Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh
The Royal Society of Edinburgh is Scotland's national academy of science and letters. It is a registered charity that operates on a wholly independent and non-partisan basis and provides public benefit throughout Scotland. It was established i ...
.
Debtors' prison
Brunel several times became involved in unprofitable projects. As a consequence, by the beginning of 1821 he was deep in debt, and in May of that year he was tried and committed to the King's Bench Prison, adebtors' prison
A debtors' prison is a prison for people who are unable to pay debt. Until the mid-19th century, debtors' prisons (usually similar in form to locked workhouses) were a common way to deal with unpaid debt in Western Europe
Western Europe is ...
in Southwark
Southwark ( ) is a district of Central London situated on the south bank of the River Thames, forming the north-western part of the wider modern London Borough of Southwark. The district, which is the oldest part of South London, developed ...
. Prisoners in a debtors' prison were allowed to have their family with them, and Sophia accompanied him. Brunel spent 88 days incarcerated. As time passed with no prospect of gaining release, Brunel began to correspond with Alexander I of Russia
Alexander I (; – ) was Emperor of Russia from 1801, the first King of Congress Poland from 1815, and the Grand Duke of Finland from 1809 to his death. He was the eldest son of Emperor Paul I and Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg.
The son of Gra ...
about the possibility of moving with his family to St Petersburg to work for the Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the te ...
. As soon as it was learnt that Britain was likely to lose such an eminent engineer as Brunel, influential figures, such as the Duke of Wellington
Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, (1 May 1769 – 14 September 1852) was an Anglo-Irish soldier and Tory statesman who was one of the leading military and political figures of 19th-century Britain, serving twice as prime minister o ...
, began to press for government intervention. The government granted £5,000 to clear Brunel's debts on condition that he abandon any plans to go to Russia. As a result, Brunel was released from prison in August.
Thames Tunnel
 In 1805 the Thames Archway Company was formed with the intention of driving a tunnel beneath the Thames between
In 1805 the Thames Archway Company was formed with the intention of driving a tunnel beneath the Thames between Rotherhithe
Rotherhithe () is a district of south-east London, England, and part of the London Borough of Southwark. It is on a peninsula on the south bank of the Thames, facing Wapping, Shadwell and Limehouse on the north bank, as well as the Isle of ...
and Limehouse
Limehouse is a district in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in East London. It is east of Charing Cross, on the northern bank of the River Thames. Its proximity to the river has given it a strong maritime character, which it retains throug ...
. Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick (13 April 1771 – 22 April 1833) was a British inventor and mining engineer. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He ...
was engaged by the company to construct the tunnel. He used Cornish miners to work on the tunnel. In 1807 the tunnel encountered quicksand and conditions became difficult and dangerous. Eventually the tunnel was abandoned after more than 1,000 feet had been completed, and expert opinion, led by William Jessop
William Jessop (23 January 1745 – 18 November 1814) was an English civil engineer, best known for his work on canals, harbours and early railways in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.
Early life
Jessop was born in Devonport, Devon, the ...
, was that such a tunnel was impracticable.
Brunel had already drawn up plans for a tunnel under the River Neva in Russia, but this scheme never came to fruition. In 1818 Brunel had patented a tunnelling shield. This was a reinforced shield of cast iron in which miners would work in separate compartments, digging at the tunnel-face. Periodically the shield would be driven forward by large jacks, and the tunnel surface behind it would be lined with brick. It is claimed that Brunel found the inspiration for his tunnelling shield from the shipworm
The shipworms are marine bivalve molluscs in the family Teredinidae: a group of saltwater clams with long, soft, naked bodies. They are notorious for boring into (and commonly eventually destroying) wood that is immersed in sea water, including ...
, ''Teredo navalis
''Teredo navalis'', commonly called the naval shipworm or turu, is a species of saltwater clam, a marine bivalve mollusc in the family '' Teredinidae''. This species is the type species of the genus '' Teredo''. Like other species in this fami ...
'', which has its head protected by a hard shell whilst it bores through ships' timbers. Brunel's invention provided the basis for subsequent tunnelling shields used to build the London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England.
The U ...
system and many other tunnels. Brunel was so convinced that he could use such a tunnelling shield to dig a tunnel under the Thames, that he wrote to every person of influence who might be interested. At last in February 1824 a meeting was held and 2,128 shares at £50 each were subscribed for. In June 1824 the Thames Tunnel Company was incorporated by royal assent. The tunnel was intended for horse-drawn traffic.
 Work began in February 1825, by sinking a diameter vertical shaft on the
Work began in February 1825, by sinking a diameter vertical shaft on the Rotherhithe
Rotherhithe () is a district of south-east London, England, and part of the London Borough of Southwark. It is on a peninsula on the south bank of the Thames, facing Wapping, Shadwell and Limehouse on the north bank, as well as the Isle of ...
bank. This was done by constructing a diameter metal ring, upon which a circular brick tower was built. As the tower rose in height, its weight forced the ring into the ground, and at the same time workmen excavated the earth in the centre of the ring. This vertical shaft was completed in November 1825, and the tunnelling shield, which had been manufactured at Lambeth
Lambeth () is a district in South London, England, in the London Borough of Lambeth, historically in the County of Surrey. It is situated south of Charing Cross. The population of the London Borough of Lambeth was 303,086 in 2011. The area ex ...
by Henry Maudslay
Henry Maudslay ( pronunciation and spelling) (22 August 1771 – 14 February 1831) was an English machine tool innovator, tool and die maker, and inventor. He is considered a founding father of machine tool technology. His inventions were an ...
's company, was then assembled at the bottom. Maudslay also supplied the steam powered pumps for the project. The shield was rectangular in cross section, and consisted of twelve frames, side by side, each of which could be moved forward independently of the others. Each frame contained three compartments, one above the other, each big enough for one man to excavate the tunnel face, and the whole frame accommodated 36 miners. When enough material had been removed from the tunnel face, the frame was moved forward by large jacks. As the shield moved forward, bricklayers followed, lining the walls. The tunnel required over 7,500,000 bricks.
Problems
Brunel was assisted in his work by his son,Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "one ...
, now 18 years old. Brunel had planned the tunnel to pass no more than fourteen feet below the riverbed at its lowest point. This caused problems later. Another problem that hindered Brunel was that William Smith, the chairman of the company, thought that the tunnelling shield was an unnecessary luxury, and that the tunnel could be made more cheaply by traditional methods. He wanted Brunel replaced as Chief Engineer and constantly tried to undermine his position. Fortunately the shield quickly proved its worth. During the tunnelling both Brunel and his assistant engineer suffered ill health and for a while Isambard had to bear the whole burden of the work.
There were several instances of flooding at the tunnel face due to its nearness to the bed of the river, and in May 1827 it was necessary to plug an enormous hole that appeared on the riverbed. Finally the resources of the Thames Tunnel Company were consumed, and despite efforts to raise more money, the tunnel was sealed up in August 1828. Brunel resigned from his position, frustrated by the continued opposition from the chairman. He undertook various civil engineering projects, including helping his son, Isambard, with his design of the Clifton Suspension Bridge
The Clifton Suspension Bridge is a suspension bridge spanning the Avon Gorge and the River Avon, linking Clifton in Bristol to Leigh Woods in North Somerset. Since opening in 1864, it has been a toll bridge, the income from which provide ...
.
In March 1832 William Smith was deposed as chairman of the Thames Tunnel Company. He had been a thorn in Brunel's side throughout the project. In 1834 the government agreed a loan of £246,000 to the Thames Tunnel Company. The old 80-ton tunnelling shield was removed and replaced by a new improved 140-ton shield consisting of 9,000 parts that had to be fitted together underground. Tunnelling was resumed but there were still instances of flooding in which the pumps were overwhelmed. Miners were affected by the constant influx of polluted water, and many fell ill. As the tunnel approached the Wapping shore, work began on sinking a vertical shaft similar to the Rotherhithe one. This began in 1840 and took thirteen months to complete.
On 24 March 1841 Brunel was knighted by the young Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previ ...
. This was at the suggestion of Prince Albert
Prince Albert most commonly refers to:
*Albert, Prince Consort (1819–1861), consort of Queen Victoria
*Albert II, Prince of Monaco (born 1958), present head of state of Monaco
Prince Albert may also refer to:
Royalty
* Albert I of Belgium ...
who had shown keen interest in the progress of the tunnel. The tunnel opened on the Wapping side of the river on 1 August 1842. On 7 November 1842 Brunel suffered a stroke that paralysed his right side for a time. The Thames Tunnel finally officially opened on 25 March 1843 and Brunel, despite ill health, took part in the opening ceremony. Within 15 weeks of opening, 1,000,000 people visited the tunnel. On 26 July 1843 Queen Victoria and Prince Albert visited. Although intended for horse-drawn traffic, the tunnel remained pedestrian only.
Later developments
In 1865 the East London Railway Company purchased the Thames Tunnel for £200,000 and four years later the first trains passed through it. Subsequently, the tunnel became part of theLondon Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England.
The U ...
system, and remains in use today, as part of the East London Line of London Overground
London Overground (also known simply as the Overground) is a suburban rail network serving London and its environs. Established in 2007 to take over Silverlink Metro routes, (via archive.org). it now serves a large part of Greater London as w ...
.
The engine house in Rotherhithe was taken over by a charitable trust in 1975 and transformed into the Brunel Museum in 2006.
Subsequent life
 After the completion of the Thames Tunnel, his greatest achievement, Brunel was in poor health. He never again accepted major commissions, although he did help his son, Isambard, on various projects. He was proud of his son's achievements, and was present at the launch of the '' SS Great Britain'' in
After the completion of the Thames Tunnel, his greatest achievement, Brunel was in poor health. He never again accepted major commissions, although he did help his son, Isambard, on various projects. He was proud of his son's achievements, and was present at the launch of the '' SS Great Britain'' in Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city i ...
on 19 July 1843. In 1845 Brunel suffered another, more severe stroke and was almost totally paralysed on his right side. On 12 December 1849, Brunel died at the age of 80, and his remains were interred in Kensal Green Cemetery
Kensal Green Cemetery is a cemetery in the Kensal Green area of Queens Park in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea in London, England. Inspired by Père Lachaise Cemetery in Paris, it was founded by the barrister George Frederic ...
in London. His wife, Sophia, was subsequently interred in the same plot, followed by their son, Isambard, just 10 years later.
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * *Further reading
* * Reprinted by McGraw-Hill, New York and London, 1926 (); and by Lindsay Publications, Inc., Bradley, Illinois, ().External links
Ancient Places TV: HD Video of Brunel (father and son) and the SS Great Britain
– Collaborative venture between the SS Great Britain Trust and the University of Bristol. Housed alongside the at Bristol it includes the National Brunel Collection.
The Brunel Museum
– Based in Rotherhithe, London the museum is housed in the building that contained the pumps to keep the Thames Tunnel dry. {{DEFAULTSORT:Brunel, Marc Isambard 1769 births 1849 deaths English people of French descent French civil engineers English civil engineers British mechanical engineers British steam engine engineers Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences Fellows of the Royal Society Machine tool builders Members of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences Burials at Kensal Green Cemetery People associated with transport in London English prisoners and detainees English theatre architects Fellows of the Royal Society of Edinburgh French expatriates in England French mechanical engineers People imprisoned for debt 18th-century British engineers 19th-century British engineers Knights Bachelor Family of Isambard Kingdom Brunel People from Eure