Maputo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Maputo (), formerly named Lourenço Marques until 1976, is the capital, and largest city of

 On the northern bank of Espírito Santo Estuary of
On the northern bank of Espírito Santo Estuary of 
 In the early 20th century, with a well equipped seaport, with piers, quays, landing sheds and electric cranes which enabled large vessels to discharge cargoes direct into the railway trucks, Lourenço Marques developed under Portuguese rule and achieved great importance as a lively cosmopolitan city. It was served by British, Portuguese, and German liners, and the majority of its imported goods were shipped to
In the early 20th century, with a well equipped seaport, with piers, quays, landing sheds and electric cranes which enabled large vessels to discharge cargoes direct into the railway trucks, Lourenço Marques developed under Portuguese rule and achieved great importance as a lively cosmopolitan city. It was served by British, Portuguese, and German liners, and the majority of its imported goods were shipped to
''

 Maputo is located on the west side of
Maputo is located on the west side of
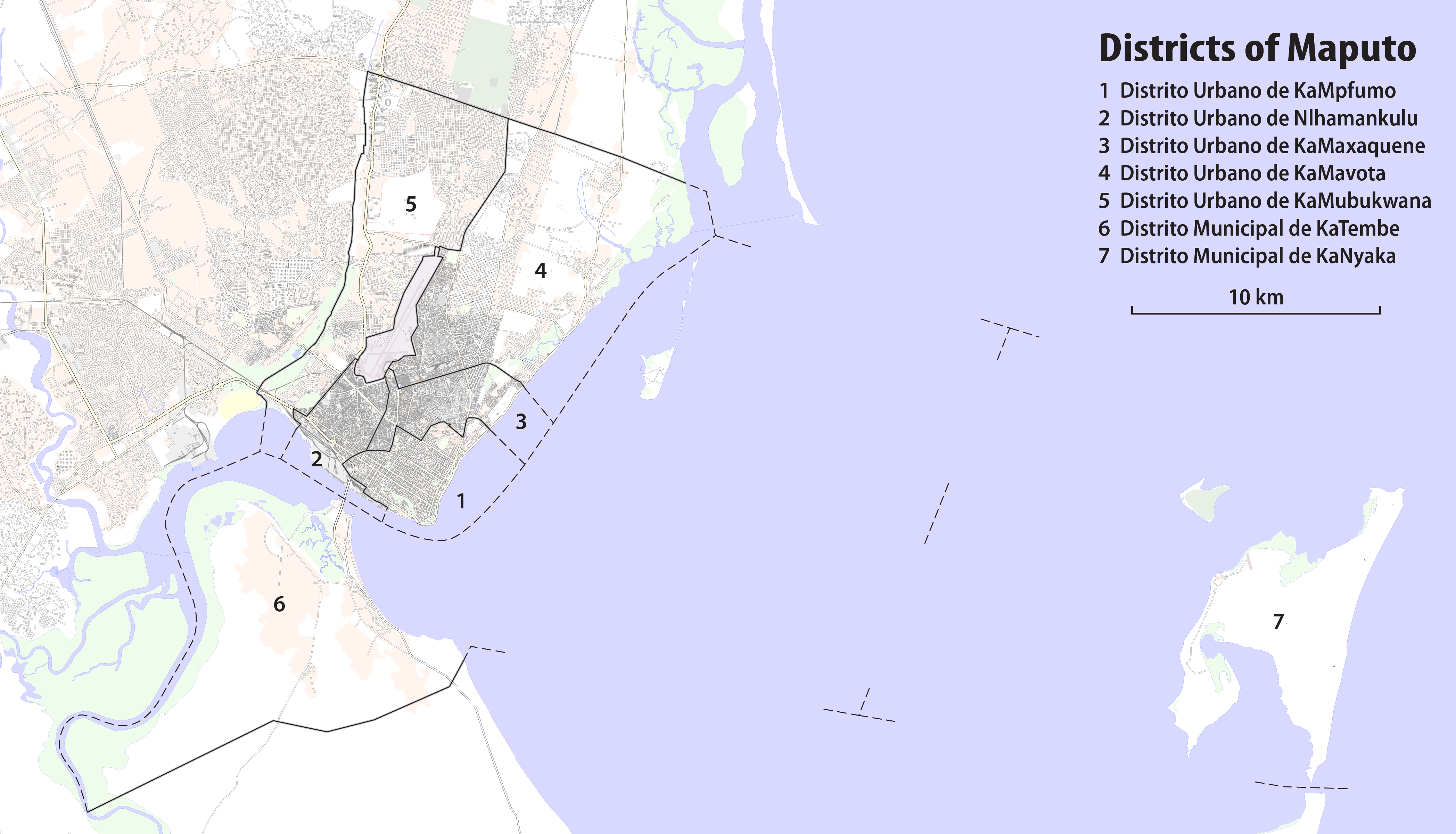 The city is divided into seven main administrative divisions. Each of these consists of several smaller city quarters or ''bairros''.
The city is divided into seven main administrative divisions. Each of these consists of several smaller city quarters or ''bairros''.
 The central area of Maputo corresponds to a planned city with square blocks and wide avenues, with Portuguese traces and their typical architecture of the 1970s. After the
The central area of Maputo corresponds to a planned city with square blocks and wide avenues, with Portuguese traces and their typical architecture of the 1970s. After the
 In 2011, PROMAPUTO2, the second phase of the project began. This phase was to last until 2015 and a total of USD 105 million was spent. The plan called for an IT systems, Integrated Financial Management Information System (IFMIS) together with
In 2011, PROMAPUTO2, the second phase of the project began. This phase was to last until 2015 and a total of USD 105 million was spent. The plan called for an IT systems, Integrated Financial Management Information System (IFMIS) together with
 In spite of its previous instability, Mozambique is experiencing one of the fastest growth rates for a developing country in the world. The projected growth rate for 2011 is expected to be around 7.5%, some of it centered on the construction of several capital intensive projects in Maputo. Some of the more notable developments include Edificio 24, a mixed-use development that will be located at the center of the city along Avenida 24 Julho and Avenida Salvador Allende. The Maputo Business Tower is a modern 19-story building. The Radisson Blu corporation has constructed a 22 story hotel with 256 rooms in one of the city's trendiest spots on the ''marginal'' along the beach. A 15-story building for the second largest telecommunication company in the country,
In spite of its previous instability, Mozambique is experiencing one of the fastest growth rates for a developing country in the world. The projected growth rate for 2011 is expected to be around 7.5%, some of it centered on the construction of several capital intensive projects in Maputo. Some of the more notable developments include Edificio 24, a mixed-use development that will be located at the center of the city along Avenida 24 Julho and Avenida Salvador Allende. The Maputo Business Tower is a modern 19-story building. The Radisson Blu corporation has constructed a 22 story hotel with 256 rooms in one of the city's trendiest spots on the ''marginal'' along the beach. A 15-story building for the second largest telecommunication company in the country,
Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
. Located near the southern end of the country, it is within of the borders with Eswatini
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
. The city has a population of 1,088,449 (as of 2017) distributed over a land area of . The Maputo metropolitan area includes the neighbouring city of Matola
Matola is the largest suburb of the Mozambique capital, Maputo, adjacent to its westernmost side. It is the nation's second most populated city. Matola is the capital of Maputo Province and has had its own elected municipal government since 199 ...
, and has a total population of 2,717,437. Maputo is a port city
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ha ...
, with an economy centered on commerce. It is also noted for its vibrant cultural scene and distinctive, eclectic architecture.
Maputo is situated on a large natural bay on the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
, near where the rivers Tembe, Mbuluzi, Matola and Infulene converge. The city consists of seven administrative divisions, which are each subdivided into quarters or ''bairros''. The city is surrounded by Maputo Province
Maputo Province is a province of Mozambique; the province excludes the city of Maputo (which comprises a separate province). The province has an area of and a population of 1,968,906 (2017 census). Its capital is the city of Matola.
Geography
...
, but is administered as a self-contained, separate province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''Roman province, provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire ...
since 1998. Maputo City is the geographically smallest and most densely populated province in Mozambique. Maputo is a cosmopolitan
Cosmopolitan may refer to:
Food and drink
* Cosmopolitan (cocktail), also known as a "Cosmo"
History
* Rootless cosmopolitan, a Soviet derogatory epithet during Joseph Stalin's anti-Semitic campaign of 1949–1953
Hotels and resorts
* Cosmopoli ...
city, with Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for National ...
, Tsonga
Tsonga may refer to:
* Tsonga language, a Bantu language spoken in southern Africa
* Tsonga people, a large group of people living mainly in southern Mozambique and South Africa.
* Jo-Wilfried Tsonga
Jo-Wilfried Tsonga (; born 17 April 1985) i ...
languages being more common, Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
, and, to a lesser extent, Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
, Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
, and Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
languages and cultures present.
The area on which Maputo stands was first settled as a fishing village
A fishing village is a village, usually located near a fishing ground, with an economy based on catching fish and harvesting seafood. The continents and islands around the world have coastlines totalling around 356,000 kilometres (221,000 ...
by ancient Tsonga people. It was soon named Lourenço Marques, after the navigator of the same name who explored the area in 1544. The modern city traces its origins to a Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
fort established on the site in 1781. A town grew around the fort starting around 1850, and in 1877 it was elevated to city status. In 1898, the colony of Portuguese Mozambique
Portuguese Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique) or Portuguese East Africa (''África Oriental Portuguesa'') were the common terms by which Mozambique was designated during the period in which it was a Portuguese colony. Portuguese Mozambique originally ...
relocated its capital there. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Lourenço Marques grew both in population and economic development as a port city. Upon Mozambican independence in 1975, the city became the national capital and was renamed Maputo. During the Mozambican Civil War
The Mozambican Civil War ( pt, Guerra Civil Moçambicana) was a civil war fought in Mozambique from 1977 to 1992. Like many regional African conflicts during the late twentieth century, the Mozambican Civil War possessed local dynamics but was a ...
, the city's economy was devastated. When the war ended, the FRELIMO
FRELIMO (; from the Portuguese , ) is a democratic socialist political party in Mozambique. It is the dominant party in Mozambique and has won a majority of the seats in the Assembly of the Republic in every election since the country's firs ...
government launched a program to revive the city's economy, and to clean up the city by forcibly removing criminals, squatters, and undocumented residents.
Maputo has a number of landmarks, including Independence Square, City Hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
, Maputo Fortress, the central market Central Market may refer to:
*Central Market, a 2009 album by Tyondai Braxton
Fresh food markets
* Adelaide Central Market, Australia
* Cardiff Central Market, Wales
*Central Market, Hong Kong
* Central Market, Casablanca, Morocco
* Riga Central ...
, Tunduru Gardens
The Tunduru Gardens is public park and garden in downtown Maputo, Mozambique. It was designed in 1885 by British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Oversea ...
, and Maputo Railway Station
The Central Railway Station ( pt, Estação Central dos Caminhos de Ferro) is a historic train station in Maputo, Mozambique. Administered by Mozambique Ports and Railways, it is on the CFM Sul line, which links to South Africa, Eswatini, and Z ...
. Maputo is known as an aesthetically attractive, if dilapidated, city. With wide avenues lined by jacaranda
''Jacaranda'' is a genus of 49 species of flowering plants in the family Bignoniaceae, native to tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas. The generic name is also used as the common name.
The species ''Jacaranda mimosifolia'' has achie ...
and acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as the wattles or acacias, is a large genus of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa and Australasia. The genus na ...
trees, it has earned the nicknames ''City of Acacias'' and the ''Pearl of the Indian Ocean''. The city is known for its distinct, eclectic architecture, with Portuguese colonial Neoclassical and Manueline
The Manueline ( pt, estilo manuelino, ), occasionally known as Portuguese late Gothic, is the sumptuous, composite Portuguese architectural style originating in the 16th century, during the Portuguese Renaissance and Age of Discoveries. Manuel ...
styles alongside modern
Modern may refer to:
History
* Modern history
** Early Modern period
** Late Modern period
*** 18th century
*** 19th century
*** 20th century
** Contemporary history
* Moderns, a faction of Freemasonry that existed in the 18th century
Phil ...
art deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the Unite ...
, bauhaus
The Staatliches Bauhaus (), commonly known as the Bauhaus (), was a German art school operational from 1919 to 1933 that combined crafts and the fine arts.Oxford Dictionary of Art and Artists (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 4th edn., 200 ...
, tropical modernism and Brutalist buildings. The historic ''Baixa de Maputo'' district is the downtown area. Maputo has a vibrant cultural scene, with many restaurants, music and performance venues, and local film industry. Maputo's economy is centered around its port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
, through which much of Mozambique's imports and exports are shipped. The chief exports include cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
, sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
, chromite
Chromite is a crystalline mineral composed primarily of iron(II) oxide and chromium(III) oxide compounds. It can be represented by the chemical formula of FeCr2O4. It is an oxide mineral belonging to the spinel group. The element magnesium can s ...
, sisal
Sisal (, ) (''Agave sisalana'') is a species of flowering plant native to southern Mexico, but widely cultivated and naturalized in many other countries. It yields a stiff fibre used in making rope and various other products. The term sisal ma ...
, copra
Copra (from ) is the dried, white flesh of the coconut from which coconut oil is extracted. Traditionally, the coconuts are sun-dried, especially for export, before the oil, also known as copra oil, is pressed out. The oil extracted from copr ...
, and hardwood
Hardwood is wood from dicot trees. These are usually found in broad-leaved temperate and tropical forests. In temperate and boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostly evergreen. Hardwood (which comes from ...
. In addition to trade, the city has robust manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to a r ...
and service sectors. Several colleges and universities are located in Maputo, including Pedagogical University
The Maputo University ( pt, Universidade Maputo) is one of Mozambique's principal universities. The name of the university is abbreviated to UniMaputo or UM. As a university, it was the first and the only public fully dedicated to teacher educatio ...
, São Tomás University, Catholic University of Mozambique, and Eduardo Mondlane University
, image =
, image_size =
, former_names =
, motto =
, type = Public
, established = 21 August 1962
, rector = Manuel Guilherme Júnior, PhD
, students = 39,078 (2015)
, undergrad = 35,809
, ...
, the oldest in the country.
History

 On the northern bank of Espírito Santo Estuary of
On the northern bank of Espírito Santo Estuary of Delagoa Bay
Maputo Bay ( pt, Baía de Maputo), formerly also known as Delagoa Bay from ''Baía da Lagoa'' in Portuguese, is an inlet of the Indian Ocean on the coast of Mozambique, between 25° 40' and 26° 20' S, with a length from north to south of over 90&n ...
, an inlet of the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
, Lourenço Marques was named after the Portuguese navigator who, with António Caldeira, was sent in 1544 by the governor of Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
on a voyage of exploration. They explored the lower courses of the rivers emptying their waters into Delagoa Bay, notably the Espírito Santo. The forts and trading stations that the Portuguese established, abandoned and reoccupied on the north bank of the river were all named "Lourenço Marques". The existing town dates from about 1850, with the previous settlement having been entirely destroyed by the natives. The town developed around a Portuguese fortress completed in 1787.
On 9 December 1876, Lourenço Marques was elevated to the status of village, and on the 10 November 1887 it became a city. The Luso-British conflict for the possession of Lourenço Marques ended on the 24th of July 1875 with Patrice de MacMahon
Marie Edme Patrice Maurice de MacMahon, marquis de MacMahon, duc de Magenta (; 13 June 1808 – 17 October 1893) was a French general and politician, with the distinction of Marshal of France. He served as Chief of State of France from 1873 to 1 ...
, the French President
The president of France, officially the president of the French Republic (french: Président de la République française), is the executive head of state of France, and the commander-in-chief of the French Armed Forces. As the presidency is ...
, ruling in favour of Portugal.
In 1871, the town was described as a poor place, with narrow streets, fairly good flat-roofed houses, grass huts, decayed forts, and a rusty cannon, enclosed by a recently erected wall high and protected by bastions at intervals. The growing importance of the Transvaal Transvaal is a historical geographic term associated with land north of (''i.e.'', beyond) the Vaal River in South Africa. A number of states and administrative divisions have carried the name Transvaal.
* South African Republic (1856–1902; af, ...
led, however, to greater interest being taken back in Portugal in the development of a port. A commission was sent by the Portuguese government in 1876 to drain the marshy land near the settlement, to plant the blue gum tree
Gum tree is a common name for smooth-barked trees and shrubs in several genera:
* Eucalypteae, particularly:
**''Eucalyptus'', which includes the majority of species of gum trees.
**''Corymbia'', which includes the ghost gums and spotted gums.
**' ...
, and to build a hospital and a church. A city since 1887, it superseded the Island of Mozambique
The Island of Mozambique ( pt, Ilha de Moçambique) lies off northern Mozambique, between the Mozambique Channel and Mossuril Bay, and is part of Nampula Province. Prior to 1898, it was the capital of colonial Portuguese East Africa. With its r ...
as the capital of Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
in 1898. In 1895, the opening of the NZASM railroad to Pretoria
Pretoria () is South Africa's administrative capital, serving as the seat of the Executive (government), executive branch of government, and as the host to all foreign embassies to South Africa.
Pretoria straddles the Apies River and extends ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
, caused the city's population to grow. The Witwatersrand Gold Rush
The Witwatersrand Gold Rush was a gold rush in 1886 that led to the establishment of Johannesburg, South Africa. It was a part of the Mineral Revolution.
Origins
In the modern day province of Mpumalanga, gold miners in the alluvial mines of ...
, which began in 1886, also increased the economic development of the city in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as Lourenço Marques served as the closest seaport for the export of gold from South Africa.

 In the early 20th century, with a well equipped seaport, with piers, quays, landing sheds and electric cranes which enabled large vessels to discharge cargoes direct into the railway trucks, Lourenço Marques developed under Portuguese rule and achieved great importance as a lively cosmopolitan city. It was served by British, Portuguese, and German liners, and the majority of its imported goods were shipped to
In the early 20th century, with a well equipped seaport, with piers, quays, landing sheds and electric cranes which enabled large vessels to discharge cargoes direct into the railway trucks, Lourenço Marques developed under Portuguese rule and achieved great importance as a lively cosmopolitan city. It was served by British, Portuguese, and German liners, and the majority of its imported goods were shipped to Southampton
Southampton () is a port city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also covers Po ...
, Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Grande Lisboa, Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administr ...
, and Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
.
With the continuous growth of the city's population due to its expanding economy centered on the seaport, from the 1940s Portugal's administration built a network of primary and secondary schools, industrial and commercial schools as well as the first university in the region. The University of Lourenço Marques was opened in 1962. Portuguese, Islamic (including Ismailis), Indian (including from Portuguese India
The State of India ( pt, Estado da Índia), also referred as the Portuguese State of India (''Estado Português da Índia'', EPI) or simply Portuguese India (), was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded six years after the discovery of a se ...
) and Chinese (including Macanese) communities — but not the unskilled African majority — achieved great prosperity by developing the industrial and commercial sectors of the city. Urban areas of Mozambique grew quickly in this period due to the lack of restriction on the internal migration of indigenous Mozambicans, a situation that differed from the apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
policies of neighboring South Africa. Before Mozambique's independence in 1975, thousands of tourists from South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
and Rhodesia
Rhodesia (, ), officially from 1970 the Republic of Rhodesia, was an unrecognised state in Southern Africa from 1965 to 1979, equivalent in territory to modern Zimbabwe. Rhodesia was the ''de facto'' successor state to the British colony of S ...
(now Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and Mozam ...
) frequented the city and its scenic beaches, high-quality hotels, restaurants, casinos, and brothels.
The Mozambique Liberation Front, or FRELIMO
FRELIMO (; from the Portuguese , ) is a democratic socialist political party in Mozambique. It is the dominant party in Mozambique and has won a majority of the seats in the Assembly of the Republic in every election since the country's firs ...
, formed in Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and ...
in 1962 and led by Eduardo Mondlane
Eduardo Chivambo Mondlane (20 June 1920 – 3 February 1969) was the President of the Mozambican Liberation Front (FRELIMO) from 1962, the year that FRELIMO was founded in Tanzania, until his assassination in 1969. Born in Mozambique, h ...
, fought for independence from Portuguese rule. The Mozambican War of Independence
The Mozambican War of Independence ( pt, Guerra da Independência de Moçambique, 'War of Independence of Mozambique') was an armed conflict between the guerrilla forces of the Mozambique Liberation Front or FRELIMO () and Portugal. The w ...
lasted over 10 years, ending only in 1974 when the Estado Novo regime was overthrown in Lisbon by a leftist military coup — the Carnation Revolution
The Carnation Revolution ( pt, Revolução dos Cravos), also known as the 25 April ( pt, 25 de Abril, links=no), was a military coup by left-leaning military officers that overthrew the authoritarian Estado Novo regime on 25 April 1974 in Lisbo ...
. The new government of Portugal granted independence to almost all Portuguese overseas territories (except for Timor Leste
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-wes ...
and Macau
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a pop ...
).
The words "Aqui é Portugal" (''Here is Portugal'') were once inscribed on the walkway of its municipal building.
Independence
ThePeople's Republic of Mozambique
The People's Republic of Mozambique (Portuguese: ''República Popular de Moçambique'') was a socialist state that existed in present day Mozambique from 1975 to 1990.
The People's Republic of Mozambique was established when the country gained ...
was proclaimed on 25 June 1975 in accordance with the Lusaka Accord
The Lusaka Accord ( Portuguese: ''Acordo de Lusaka'') was signed in Lusaka, Zambia, on 7 September 1974, between the Front for the Liberation of Mozambique (FRELIMO) and the Portuguese government that had been installed by the Carnation Revolut ...
signed in September 1974. A parade and a state banquet completed the independence festivities in the capital, which was expected to be renamed Can Phumo, or "Place of Phumo", after a Shangaan
Soshangana KaZikode (), born Soshangana Nxumalo, was the Founder and the Monarch of the Gaza Empire, which at the height of its power stretched from the Limpopo river in southern Mozambique up to the Zambezi river in the north. Soshangana rule ...
chief who lived in the area before the Portuguese navigator Lourenço Marques
Maputo (), formerly named Lourenço Marques until 1976, is the capital, and largest city of Mozambique. Located near the southern end of the country, it is within of the borders with Eswatini and South Africa. The city has a population of 1,088 ...
first visited the site in 1545 and gave his name to it."Dismantling the Portuguese Empire"''
Time Magazine
''Time'' (stylized in all caps) is an American news magazine based in New York City. For nearly a century, it was published weekly, but starting in March 2020 it transitioned to every other week. It was first published in New York City on Mar ...
'' (July 7, 1975) However, after independence, the city's name was changed (in February 1976) to Maputo. Maputo's name reputedly has its origin in the Maputo River
The Maputo River (Portuguese ''Rio Maputo''), also called Great Usutu River, Lusutfu River, or Suthu River, is a river in South Africa, Eswatini, and Mozambique. The name ''Suthu'' refers to Basotho people who lived near the source of the river, ...
: in fact, this river, which marks the border with South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
in the far South of Mozambique, had become symbolic during the FRELIMO-led armed struggle against Portuguese sovereignty, after the motto «''Viva Moçambique unido, do Rovuma ao Maputo''», that is, ''Hail Mozambique, united from Rovuma down to Maputo'' (Rovuma
Ruvuma River, formerly also known as the Rovuma River, is a river in the African Great Lakes region. During the greater part of its course, it forms the border between Tanzania and Mozambique (in Mozambique known as ''Rio Rovuma''). The river is ...
is the river which marks the border with Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and ...
in the far North).
After the independence, the statues to Portuguese heroes in the capital city were removed and most were stored at the fortress. Black soldiers carrying Russian rifles replaced Portuguese Army
The Portuguese Army ( pt, Exército Português) is the land component of the Armed Forces of Portugal and is also its largest branch. It is charged with the defence of Portugal, in co-operation with other branches of the Armed Forces. With its ...
soldiers (both black and white) with western arms in city barracks and on the streets. Most of the city's streets, originally named for Portuguese heroes or important dates in Portuguese history
The history of Portugal can be traced from circa 400,000 years ago, when the region of present-day Portugal was inhabited by Homo heidelbergensis.
The Roman invasion in the 3rd century BC lasted several centuries, and developed the Roman provinc ...
, had their names changed to African languages, revolutionary figures of the Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
, or pre-colonial historical names.
After the Carnation Revolution
The Carnation Revolution ( pt, Revolução dos Cravos), also known as the 25 April ( pt, 25 de Abril, links=no), was a military coup by left-leaning military officers that overthrew the authoritarian Estado Novo regime on 25 April 1974 in Lisbo ...
in Lisbon, over 250,000 Portuguese pulled out virtually overnight, leaving Mozambique's economy and administration unmanageable. With the exodus of trained Portuguese personnel, the newly independent country had no time to allocate resources to maintain its well-developed infrastructure. In addition, authoritarian Stalinist policies and bureaucratic central planning made the newly independent country slip into an extremely precarious condition since the beginning, and so the economy plummeted. FRELIMO, now the governing party, turned to the communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a s ...
governments of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
and East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
for help. By the early 1980s the country was bankrupt. Money was worthless and shops were empty. Starting shortly after independence, the country was plagued by the Mozambican Civil War
The Mozambican Civil War ( pt, Guerra Civil Moçambicana) was a civil war fought in Mozambique from 1977 to 1992. Like many regional African conflicts during the late twentieth century, the Mozambican Civil War possessed local dynamics but was a ...
, a long and violent struggle between FRELIMO
FRELIMO (; from the Portuguese , ) is a democratic socialist political party in Mozambique. It is the dominant party in Mozambique and has won a majority of the seats in the Assembly of the Republic in every election since the country's firs ...
and RENAMO
RENAMO (from the Portuguese , ) is a Mozambican political party and militant group. The party was founded with the active sponsorship of the Rhodesian Central Intelligence Organisation (CIO) in May 1977 from anti-communist dissidents oppose ...
, which lasted from 1977 to 1992. The war adversely affected economic activity and political stability in the city. "Operation Production" (''Operação Produção'') was inaugurated in 1983 by the ruling FRELIMO party to deal with the economic crisis. Undocumented residents of Maputo, the "parasitic" urban population, as well as individuals who displayed criminal behavior, were forcibly transferred to state-owned communal farms and villages in the rural north of Mozambique.
Since the peace agreement ending the civil war, which was signed in 1992, the country and the city has returned to its pre-independence levels of political stability. This stability is an encouraging sign that makes Mozambique a promising country for foreign investment.
On 11 July 2003, the Protocol to the African Charter on Human and Peoples’ Rights on the Rights of Women in Africa, better known as the Maputo Protocol
The Protocol to the African Charter on Human and Peoples' Rights on the Rights of Women in Africa, better known as the Maputo Protocol, is an international human rights instrument established by the African Union that went into effect in 2005. I ...
, was adopted in the city by the African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
.
Geography
 Maputo is located on the west side of
Maputo is located on the west side of Maputo Bay
Maputo Bay ( pt, Baía de Maputo), formerly also known as Delagoa Bay from ''Baía da Lagoa'' in Portuguese, is an inlet of the Indian Ocean on the coast of Mozambique, between 25° 40' and 26° 20' S, with a length from north to south of over 90&n ...
, near the Estuário do Espírito Santo where the four rivers Tembe, Umbeluzi
The Mbuluzi River (also known as the iMbuluzi or Umbeluzi) is one of the main rivers of Swaziland, Eswatini, and an important river in Mozambique. On the boundary of these countries, the Mbuluzi cuts through the Lebombo Mountains, Lebombo Range, ...
, Matola
Matola is the largest suburb of the Mozambique capital, Maputo, adjacent to its westernmost side. It is the nation's second most populated city. Matola is the capital of Maputo Province and has had its own elected municipal government since 199 ...
and Infulene drain. The bay is long and wide. At the extreme east of the city and bay is the island of Inhaca
Inhaca is a town, settlement in Mozambique, on the subtropical Inhaca Island ('':pt:Ilha da Inhaca, Ilha da Inhaca'' in Portuguese language, Portuguese) off the East African coast. Inhaca settlement is centered on a Mission (station), mission stat ...
. The total area covered by the municipality of Maputo is and borders the city of Matola
Matola is the largest suburb of the Mozambique capital, Maputo, adjacent to its westernmost side. It is the nation's second most populated city. Matola is the capital of Maputo Province and has had its own elected municipal government since 199 ...
northeast and east, the districts of Marracuene
Marracuene, earlier known as Vila Luísa, is a town in Mozambique's Maputo Province in Marracuene District, located 30 km north of Maputo on the Incomati River. The Parque de Campismo de Marracuene, a popular camping destination, is located ...
to the north; Boane in the east and Matutuíne at the south all of which are part of Maputo Province. The city is from the South African border at Ressano Garcia and from the border with Eswatini
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
near the town of Namaacha
Namaacha or Naamacha is a town in southern Mozambique, lying 80 kilometers west of Maputo on the border with Eswatini. It is located in the Lebombos area. It is known for its colonial church and for its waterfall.
The town of Namaacha lies in ...
.
Administrative subdivisions
 The city is divided into seven main administrative divisions. Each of these consists of several smaller city quarters or ''bairros''.
The city is divided into seven main administrative divisions. Each of these consists of several smaller city quarters or ''bairros''.
Climate
Maputo features atropical savanna climate
Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories ''Aw'' (for a dry winter) and ''As'' (for a dry summer). The driest month has less than of p ...
(''Aw'') bordering on a hot semi-arid climate (''BSh'') under the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
. Maputo is a relatively dry city, averaging of precipitation per year. Precipitation is abundant during summer and only little during winter. The city has a relatively warm climate averaging a mean temperature of . The hottest month is January with a mean temperature of , while the coolest month is July with a mean temperature of .
Situated on the Indian Ocean, Maputo is particularly vulnerable to climate impacts such as cyclones, flooding and sea level rise. Poverty and inequality, which are concentrated in the overpopulated bairro
A ''bairro'' () is a Portuguese language, Portuguese word for a Quarter (urban subdivision), quarter or a neighborhood or, sometimes, a district which is within a city or town. It is commonly used in Portugal, Brazil, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau, ...
s, further exacerbate climate change vulnerabilities in the city.
Infrastructure
 The central area of Maputo corresponds to a planned city with square blocks and wide avenues, with Portuguese traces and their typical architecture of the 1970s. After the
The central area of Maputo corresponds to a planned city with square blocks and wide avenues, with Portuguese traces and their typical architecture of the 1970s. After the Carnation Revolution
The Carnation Revolution ( pt, Revolução dos Cravos), also known as the 25 April ( pt, 25 de Abril, links=no), was a military coup by left-leaning military officers that overthrew the authoritarian Estado Novo regime on 25 April 1974 in Lisbo ...
(1974) military coup in Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Grande Lisboa, Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administr ...
, Portuguese refugees fled in massive numbers close to the date of independence (1975), and the resultant lack of skills and capital, in the context of a fierce civil war and government mismanagement, contributed to its state of dereliction in the years following these events. Nevertheless, the city itself was never damaged, since it was tacitly considered neutral ground during both the colonial and the civil war.
Recovery of the older infrastructure has been slow and most property developers in recent years have decided to invest in the construction of new properties rather than rehabilitating any of the existing ones. The rates for property in the city are high as investment increases, larger numbers of businesses are hoping to locate within easy reach of the airports, banks and other facilities. The infrastructure is expected to spread out across vacant areas of the city hopefully easing property prices within the next couple of years.
Maputo faces many challenges, such as poor transport and drainage infrastructure, which have profound implications on people’s livelihoods, particularly in informal settlements. Inadequate planning regulation and law enforcement, as well as perceived corruption in government processes, lack of communication across government departments and lack of concern or government coordination with respect to building codes are major impediments to progressing the development of Maputo's infrastructure, according to the Climate & Development Knowledge Network
The Climate and Development Knowledge Network (CDKN) works to enhance the quality of life for the poorest and most vulnerable to climate change. CDKN does this by combining research, advisory services and knowledge management in support of local ...
.
As a coastal city, Maputo is particularly vulnerable to the impacts of sea level rise, and population growth is putting increasing pressure on the coastal areas.
Despite its Portuguese heritage, all vehicles are right-hand drive and drive on the left hand side of the road.
Land is not for sale
Another more general impediment is often attributed to land which is legally not for sale in Mozambique. All land is property of the state for which the state grants the rights to use the land. This presupposition combined with historical problems in managing inheritance and documentation have led to complications which discourage investment and expansion of the city. Land, while not sold officially, is actively traded and exchanged on a secondary market leading to the development of unplanned areas and slums in metropolitan areas which the Government, due to the lack of tax money, has no capacity and infrastructure to deal with. The result of such policies is manifested in a crowded CBD, inadequate transport network and crumbling roads.PROMAPUTO
In 2007, the municipality of Maputo began a project to seriously consider rehabilitating the city's infrastructure. PROMAPUTO was a project that began as co-operation between the local city council and theInternational Development Association
The International Development Association (IDA) (french: link=no, Association internationale de développement) is an international financial institution which offers concessional loans and grants to the world's poorest developing countries. Th ...
(IDA) of the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
. The first phase (PROMAPUTO1) took place between 2007 and 2010 and was chiefly concerned with developing the systems, knowledge and planning required to support the gradual overhaul of the infrastructure. The project was broken into several key areas and a budget allocated to each of these, namely: Institutional Development, Financial Sustainability, Urban Planning, Urban Infrastructure Investment and Maintenance, Metropolitan Development (services such as waste collection and disposal). The total financial allocation for this phase was USD 30 million. Little was done, however.
 In 2011, PROMAPUTO2, the second phase of the project began. This phase was to last until 2015 and a total of USD 105 million was spent. The plan called for an IT systems, Integrated Financial Management Information System (IFMIS) together with
In 2011, PROMAPUTO2, the second phase of the project began. This phase was to last until 2015 and a total of USD 105 million was spent. The plan called for an IT systems, Integrated Financial Management Information System (IFMIS) together with Geographic Information System
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing Geographic data and information, geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with Geographic information system software, sof ...
(GIS
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing Geographic data and information, geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with Geographic information system software, sof ...
). These systems would supposedly help the municipality control its budgets and manage tenders, while the GIS
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing Geographic data and information, geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with Geographic information system software, sof ...
would allow for precise information about land location and titling to be kept. Several roads should have been expanded and improved and the Avenida Julius Nyerere finally completed. Financial sustainability for the project was to be guaranteed through the improved collection of property tax (IPRA). The project also coincided with the recent overhaul of the Road Safety and Traffic Regulations (final completion 2020) which was an antiquated system that had not seen changes since the 1950s. Amongst the new regulations, heavy penalties and fines would now apply to many detrimental actions done by automobiles, such as pollution, loud noises, and illegal maneuvers.
Electronic parking meters have now been installed in some areas of the CBD to curb a chronic shortage and wrongful use of parking space.
Building projects
 In spite of its previous instability, Mozambique is experiencing one of the fastest growth rates for a developing country in the world. The projected growth rate for 2011 is expected to be around 7.5%, some of it centered on the construction of several capital intensive projects in Maputo. Some of the more notable developments include Edificio 24, a mixed-use development that will be located at the center of the city along Avenida 24 Julho and Avenida Salvador Allende. The Maputo Business Tower is a modern 19-story building. The Radisson Blu corporation has constructed a 22 story hotel with 256 rooms in one of the city's trendiest spots on the ''marginal'' along the beach. A 15-story building for the second largest telecommunication company in the country,
In spite of its previous instability, Mozambique is experiencing one of the fastest growth rates for a developing country in the world. The projected growth rate for 2011 is expected to be around 7.5%, some of it centered on the construction of several capital intensive projects in Maputo. Some of the more notable developments include Edificio 24, a mixed-use development that will be located at the center of the city along Avenida 24 Julho and Avenida Salvador Allende. The Maputo Business Tower is a modern 19-story building. The Radisson Blu corporation has constructed a 22 story hotel with 256 rooms in one of the city's trendiest spots on the ''marginal'' along the beach. A 15-story building for the second largest telecommunication company in the country, Vodacom
Vodacom Group Limited is a South-Western African mobile communications company, providing voice, messaging, data and converged services to over 55 million customers. From its roots in South Africa, Vodacom has grown its operations to include ...
, was projected to be completed in 2010. The regeneration of the Maputo waterfront is an urban regeneration project that is being developed at site of the former annual industrial fair grounds (FACIM).
Rehabilitation projects
In February 2011, presidentArmando Guebuza
Armando Emílio Guebuza (born 20 January 1943) is a Mozambican politician who was the third President of Mozambique from 2005 to 2015.
Career
Guebuza, born at Murrupula in Nampula Province, joined the Mozambique Liberation Front (FRELIMO) at ...
announced that the Vila Algarve
Vila Algarve is a residential house in the Mozambican capital Maputo. Built in 1934 and later protected as a listed building, the building housed the Portuguese secret police PIDE/DGS until the end of the Portuguese colonial period in Mozambique ...
would be restored to its former condition and the building transformed into a museum for the veterans of the civil war. The Vila Algarve belonged to the International and State Defence Police (PIDE) during colonial rule. It was where political prisoners and others accused of conspiring to harm the regime were taken for interrogation and torture. There are claims that several individuals were executed in the building. No dates have been released on when the renovation is to commence. The building has changed ownership several times and has been an off-on residence for squatters.
Sports facilities
Maputo has a number of stadiums designed for football, which can be modified for other purposes, such as the newEstádio do Zimpeto
Estádio do Zimpeto is a multi-use stadium in Zimpeto - an outlying neighborhood of Maputo, Mozambique, which was inaugurated on 23 April 2011.Estádio do Maxaquene
Estádio do Maxaquene is a multi-purpose stadium in Maputo, Mozambique. It is currently used mostly for football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the wo ...
and the Estádio do Costa do Sol
Estádio do Costa do Sol is a multi-purpose stadium in Maputo, Mozambique. It is currently used mostly for football (soccer), football matches and is the home stadium of Clube de Desportos da Costa do Sol. The stadium holds 10,000 people.
Refe ...
which can seat 32,000, 15,000 and 10,000 people respectively. The largest stadium in the Metropolitan Area is, however, the Estádio da Machava The Estádio da Machava is a multi-purpose stadium in Machava, a mainly residential subdivision of the city of Matola, in the outskirts of Maputo, Mozambique. It is used for football matches and can hold 60,000 spectators.
The stadium was built by ...
(opened as Estádio Salazar), located in neighbouring Matola
Matola is the largest suburb of the Mozambique capital, Maputo, adjacent to its westernmost side. It is the nation's second most populated city. Matola is the capital of Maputo Province and has had its own elected municipal government since 199 ...
municipality. It opened in 1968, in Machava and was at the time the most advanced in the country conforming to standards set by FIFA
FIFA (; stands for ''Fédération Internationale de Football Association'' ( French), meaning International Association Football Federation ) is the international governing body of association football, beach football and futsal. It was found ...
and the Union Cycliste Internationale
The ''Union Cycliste Internationale'' (UCI; ; en, International Cycling Union) is the world governing body for sports cycling and oversees international competitive cycling events. The UCI is based in Aigle, Switzerland.
The UCI issues racing ...
(UCI). The cycling track could be adjusted to allow for 20,000 more seats. It was the site where Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
officially handed over the country to Samora Machel
Samora Moisés Machel (29 September 1933 – 19 October 1986) was a Mozambican military commander and political leader. A socialist in the tradition of Marxism–Leninism, he served as the first President of Mozambique from the country's ...
and FRELIMO
FRELIMO (; from the Portuguese , ) is a democratic socialist political party in Mozambique. It is the dominant party in Mozambique and has won a majority of the seats in the Assembly of the Republic in every election since the country's firs ...
on 25 June 1975. In 2005, the Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the West ...
based reggae
Reggae () is a music genre that originated in Jamaica in the late 1960s. The term also denotes the modern popular music of Jamaica and its diaspora. A 1968 single by Toots and the Maytals, " Do the Reggay" was the first popular song to use ...
group UB40
UB40 are an English reggae and pop band, formed in December 1978 in Birmingham, England. The band has had more than 50 singles in the UK Singles Chart, and has also achieved considerable international success. They have been nominated for the ...
held a one-night-only concert in the stadium filled to maximum capacity. A newer stadium called the Estádio do Zimpeto
Estádio do Zimpeto is a multi-use stadium in Zimpeto - an outlying neighborhood of Maputo, Mozambique, which was inaugurated on 23 April 2011.2011 All-Africa Games with a capacity for 42,000 spectators. A smaller football stadium, Estádio Mahafil, holds 4,000 people.
Beginning in the 1950s, motorsport was introduced to the city. At first race cars would compete in areas around the city, Polana and along the ''marginal'' but as funding and interest increased, a dedicated race track was built in the Costa Do Sol area along and behind the ''marginal'' with the ocean to the east with a length of . The initial surface of the new track, named Autódromo de Lourenço Marques did not provide enough grip and an accident in the late 1960s killed 8 people and injured many more. Therefore, in 1970, the track was renovated and the surface changed to meet the safety requirements that were needed at large events with many spectators. The length then increased to . The city became host to several international and local events beginning with the inauguration on 26 November 1970. The track was abandoned after 1975 and events only occurred sporadically such as in 1981 when the government allowed the sport again. Since 2000, interest has been rekindled by the Automovel & Touring Club de Moçambique (ATCM) and several events including go-carting, drag racing and motocross are planned.
The city's main basketball arena is the Pavilhão do Maxaquene which holds up to 3,500 people. It is home to Ferroviário de Maputo which competes in the


 Ferry boats departing from Maputo to the district of KaTembe are available during the week. A ferry can carry approximately 20 vehicles per trip.
Ferry boats departing from Maputo to the district of KaTembe are available during the week. A ferry can carry approximately 20 vehicles per trip.
Atlassian Confluence. 10 de dezembro de 2018.
 ''A Casa de Ferro'' – The Iron House
Maputo had always been the center of attention during its formative years and this strong artistic spirit was responsible for attracting some of the world's most forward architects at the turn of the 20th century. The city is home to masterpieces of building work by
''A Casa de Ferro'' – The Iron House
Maputo had always been the center of attention during its formative years and this strong artistic spirit was responsible for attracting some of the world's most forward architects at the turn of the 20th century. The city is home to masterpieces of building work by
MozambiqueTraditionalMansion.jpg, Mansion prepared for demolition Av. Kim Il Sung
MansionforDemolitionMaputo.jpg, Mansion prepared for demolition Av. Mao Tse Tung
Additionally, many acacia trees that once lined the footpaths and gave the city its distinct identity have also been removed for unclear reasons. The process gains momentum usually in the winter months between June and August under the guise of pruning overgrown trees. Without proper supervision the pruning work is excessive and destructive leading to the eventual loss of the tree.
Destructive tree cutting in Maputo.jpg, Destructive tree cutting in Maputo
 An important cultural and artists' centre in Maputo is the Associação Núcleo de Arte. It is the oldest collective of artists in Mozambique. Seated in an old villa in the centre of Maputo the Núcleo has played a significant role in metropolitan cultural life for decades. The two best known and most influential contemporary Mozambican artists started their career at Núcleo de Arte, the painter
An important cultural and artists' centre in Maputo is the Associação Núcleo de Arte. It is the oldest collective of artists in Mozambique. Seated in an old villa in the centre of Maputo the Núcleo has played a significant role in metropolitan cultural life for decades. The two best known and most influential contemporary Mozambican artists started their career at Núcleo de Arte, the painter
 * Fortress of Maputo
*
* Fortress of Maputo
*
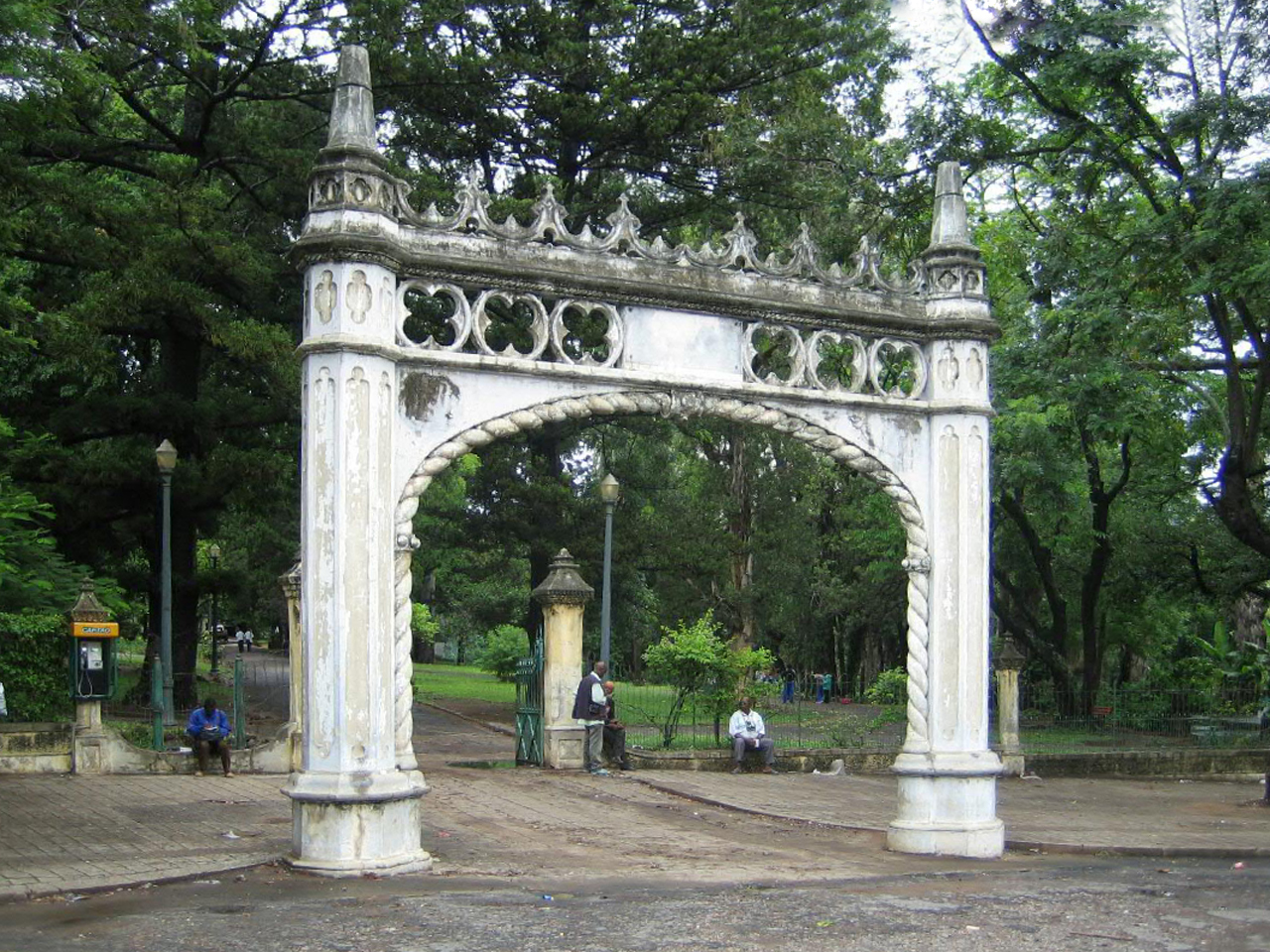
 The city does not yet have a very expansive list of parks and other recreational areas. However, at the center of the city lies the Jardim Tunduru (
The city does not yet have a very expansive list of parks and other recreational areas. However, at the center of the city lies the Jardim Tunduru (
 Maputo has several hospitals and clinics, including the city and country's largest hospital, the Hospital Central de Maputo (Maputo Central Hospital). Other hospitals include the public Hospital Geral José Macamo, and the private Clinica Sommerschield, the Clínica Cruz Azul in ''baixa'' and Hospital Privado located across the Portuguese School.
The construction of Hospital Miguel Bombarda began in 1900. In 1976,
Maputo has several hospitals and clinics, including the city and country's largest hospital, the Hospital Central de Maputo (Maputo Central Hospital). Other hospitals include the public Hospital Geral José Macamo, and the private Clinica Sommerschield, the Clínica Cruz Azul in ''baixa'' and Hospital Privado located across the Portuguese School.
The construction of Hospital Miguel Bombarda began in 1900. In 1976,
Photos and Map of MaputoMaputo Port Development Company
{{Authority control Capitals in Africa Populated coastal places in Mozambique Populated places in Mozambique Provinces of Mozambique Provincial capitals in Mozambique Port cities in Africa Port cities and towns of the Indian Ocean 1782 establishments in the Portuguese Empire Populated places established in 1781
Basketball Africa League
The Basketball Africa League (BAL) is Africa's premier men's basketball league. The league consists of twelve teams, each qualified through their domestic competition, similar to the format of the UEFA Champions League. The league is a joint eff ...
and the Mozambican Basketball League
Mozambican may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Mozambique, a country in southeastern Africa
* A person from Mozambique, or of Mozambican descent:
** Demographics of Mozambique
** Culture of Mozambique
** List of Mozambicans
* Mozambic ...
.
Street names
The street names were changed after independence in 1975. Close ties with theEastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
highly influenced the new names that were chosen as did removal of names referring to colonial era figures.
Transport
Airports

Maputo International Airport
Maputo International Airport , also known as Mavalane International Airport, formerly Lourenço Marques Airport (IATA: LUM), is an airport located northwest of the center of Maputo, the largest city and capital of Mozambique. It is the largest ...
is the main international airport of Mozambique. The new terminal was opened in 2010 with a capacity for 900,000 passengers per year. Work has begun on the construction of a new domestic terminal which will have a capacity for many more passengers at any given time. The construction work will require the current building to be demolished.
Buses
Maputo's transportation needs are mainly served by minibus taxis called ''chapas'', which transport the majority of the city's commuters. In an effort to resolve a public transport crisis in the city, the state-owned company, Transporte de Moçambique (TPM) has recently acquired a new fleet of 270+ buses. There are three major bus terminals in the city: at Baixa (downtown/central), Museu (Museum), and at Junta (regional and national buses).Ferries

 Ferry boats departing from Maputo to the district of KaTembe are available during the week. A ferry can carry approximately 20 vehicles per trip.
Ferry boats departing from Maputo to the district of KaTembe are available during the week. A ferry can carry approximately 20 vehicles per trip.
Rails
The city of Maputo lies at the end of three railway lines:Goba railway
Goba railway, also called Swaziland-Maputo railway and Matsapha-Maputo railway, is a railway that connects the city of Maputo, Mozambique, to the city from Matsapha, in Eswatini. It is 466.8 km long, in a 1067 mm gauge.Limpopo railway
Limpopo Railway, also called Gweru-Maputo railway, is a railway that connects the city of Maputo, Mozambique, to the city from Somabhula, in Zimbabwe. It is 900 km long, in a 1067 mm gauge.
and Pretoria–Maputo railway
Pretoria–Maputo railway, also called Delagoa Bay railway, Iron railway and Eastern railway, is a railway that connects the city of Maputo, Mozambique, to the city of Pretoria, in South Africa. It is 567 km long, in 1067 mm gauge.
.Mozambique Logistics Infrastructure: Mozambique Railway AssessmentAtlassian Confluence. 10 de dezembro de 2018.
Trams
Maputo was home to one of the first electric tramway systems in Africa, commencing in February 1904. At first the lines ran from the Central Railway Station (CFM) to the City Municipality building. It is said that the establishment of the tram system caused some protests from the general public as certain classes had limited access to its use. Trams lost favor in the second half of the 20th century as cars and buses became more common, and they have not been in use at all since 1936, although parts of some of the tracks can still be seen coming up through the tar in certain streets, like Av. 24 de Julho.Ports
The mainport of Maputo
The Port of Maputo, also called the Maputo-Matola port complex, is a Mozambican port located in the cities of Maputo and Matola. They are installed in Maputo Bay, on the north bank of the Espírito Santo estuary, which is separated from the Mozamb ...
handled 17 million tons of cargo in 1971, at its peak. It was part of the trio of Mozambique's main ports for the Nacala-Beira-Maputo route. Today, it is managed by the Maputo Port Development Company (MPDC), a joint venture of Grindrod and DP World. The government has allowed the firm to manage the port until 2030 in order to upgrade much of its infrastructure that has been destroyed after years of stagnation. In 2010, the dredging works in the channel were finished and the Port of Maputo can now handle larger vessels – such as the Panamax vessels – with more cargo. In addition, investments are being made for specific types of terminals such as:
* Bulk liquids
* Granite
* Metals
* Coal
A new terminal for vehicles is also planned which will allow for 57,000 vehicles to be moved per year (Phase 1) with a peak 250,000 under an agreement with Höegh Autoliners as potential trans-shipment route between the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
. Coal will also be exported from the Matola
Matola is the largest suburb of the Mozambique capital, Maputo, adjacent to its westernmost side. It is the nation's second most populated city. Matola is the capital of Maputo Province and has had its own elected municipal government since 199 ...
side at a rate of 10 million tons per year. It is envisaged that by 2020, the port will generate about USD 160 million per year. By 2030, the port will be able to handle up to 25 trains a day and 1,500 trucks for a total of 50 million tons of cargo per year. The total investment will exceed USD 500 million.
Other means
A recent introduction are three-wheelers commonly known as tuk-tuks in some Asian countries. The three-wheeled bikes, called "tchopelas" by the population, are cheaper to own and run and have posed a commercial threat to conventional taxis.Architecture
 ''A Casa de Ferro'' – The Iron House
Maputo had always been the center of attention during its formative years and this strong artistic spirit was responsible for attracting some of the world's most forward architects at the turn of the 20th century. The city is home to masterpieces of building work by
''A Casa de Ferro'' – The Iron House
Maputo had always been the center of attention during its formative years and this strong artistic spirit was responsible for attracting some of the world's most forward architects at the turn of the 20th century. The city is home to masterpieces of building work by Pancho Guedes
Amâncio d'Alpoim Miranda "Pancho" Guedes (Lisbon, Portugal, 13 May 1925 – Graaff-Reinet, South Africa, 7 November 2015) was a Portuguese architect, sculptor and painter an educator.
He is described as one of the earliest post-modernist ar ...
, Herbert Baker
Sir Herbert Baker (9 June 1862 – 4 February 1946) was an English architect remembered as the dominant force in South African architecture for two decades, and a major designer of some of New Delhi's most notable government structures. He wa ...
and Thomas Honney amongst others. The earliest architectural efforts around the city focused on classical European designs such as the Central Train Station (CFM) designed by architects Alfredo Augusto Lisboa de Lima, Mario Veiga and Ferreira da Costa and built between 1913 and 1916 (sometimes mistaken with the work of Gustav Eiffel
Alexandre Gustave Eiffel (born Bonickhausen dit Eiffel; ; ; 15 December 1832 – 27 December 1923) was a French civil engineer. A graduate of École Centrale des Arts et Manufactures, he made his name with various bridges for the French railway ...
), and the Hotel Polana designed by Herbert Baker
Sir Herbert Baker (9 June 1862 – 4 February 1946) was an English architect remembered as the dominant force in South African architecture for two decades, and a major designer of some of New Delhi's most notable government structures. He wa ...
.
As the 1960s and 1970s approached, Maputo was yet again at the center of a new wave of architectural influences made most popular by Pancho Guedes
Amâncio d'Alpoim Miranda "Pancho" Guedes (Lisbon, Portugal, 13 May 1925 – Graaff-Reinet, South Africa, 7 November 2015) was a Portuguese architect, sculptor and painter an educator.
He is described as one of the earliest post-modernist ar ...
. The designs of the 1960s and 1970s were characterized by modernist
Modernism is both a philosophical and arts movement that arose from broad transformations in Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The movement reflected a desire for the creation of new forms of art, philosophy, an ...
movements of clean, straight and functional structures. However, prominent architects such as Pancho Guedes
Amâncio d'Alpoim Miranda "Pancho" Guedes (Lisbon, Portugal, 13 May 1925 – Graaff-Reinet, South Africa, 7 November 2015) was a Portuguese architect, sculptor and painter an educator.
He is described as one of the earliest post-modernist ar ...
fused this with local art schemes giving the city's buildings a unique Mozambican theme. As a result, most of the properties erected during the second construction boom take on these styling cues.
Loss of Heritage
In recent years the influx of capital into the real estate sector from local and international investors has resulted in the demolition of many historically significant buildings. Single homes along Av. Julius Nyerere, Av. 24 de Julho and Av. Mao Tse Tung have been torn down and high rise residential apartments built in their place. The difficulty in legally expanding the city coupled with a limited heritage building protection framework have been the main impediments. The local government, the City Council of Maputo has been unable to bring order to the situation.Culture
Maputo is a melting pot of several cultures. TheBantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for National ...
and Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
cultures dominate, but the influence of Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
n, and Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
cultures is also felt.
Film and cinema
Before television was introduced in 1981, film and cinema had a prominent position as a form of entertainment in the lives of Mozambicans especially in Maputo where there were at least a dozen movie theaters by the time of independence. In the 1950s and 1960s, at the height of racial segregation, most of the movie-goers were either European whites or South Asians – each group having their own designated locale. Black Mozambicans, although more heavily discriminated against, also enjoyed movies in makeshift theatres, often in rooms temporarily converted to handle a projector, screen and chairs. Some of the cinemas can still be seen today, such as the Charlot, Gil Vicente, the Scala, 222 and the Dicca, although not all are still showing movies. The movies screened at the theaters during Portuguese rule were heavily censored. Movies containing sex, violence and themes with a political nature were not allowed but despite these restrictions, it was the first time Mozambicans were able to enjoy entertainment that was prevalent in the rest of the world, thereby greatly increasing cultural affinity. After 1975 and the ensuing mass exodus of European whites, for a time no censorship regulations were in place and Mozambicans could watch content that was previously banned by the dictatorship, and the works of Bruce Lee became immensely popular. However, onceFRELIMO
FRELIMO (; from the Portuguese , ) is a democratic socialist political party in Mozambique. It is the dominant party in Mozambique and has won a majority of the seats in the Assembly of the Republic in every election since the country's firs ...
and the nationalist movement gained momentum, any external influence considered as originating from the "decadent West" was again not allowed. It was at this moment that Mozambique's ruling party FRELIMO realized the immediate potential films could have in delivering propaganda relatively easily.
For much of the late 1970s and 1980s, the local film industry was geared towards creating "home-made" productions depicting Socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the e ...
ideologies which placed great influence on the family unit, the non-commercialized production of agriculture and political autonomy. Maputo has been the setting for many Hollywood blockbuster movies such as ''The Interpreter
''The Interpreter'' is a 2005 political thriller film directed by Sydney Pollack, starring Nicole Kidman, Sean Penn, Catherine Keener, and Jesper Christensen. It was the first film shot inside the United Nations Headquarters, as well as the fin ...
'', '' Blood Diamond'' and ''Ali
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, عَلِيّ بْن أَبِي طَالِب; 600 – 661 CE) was the last of four Rightly Guided Caliphs to rule Islam (r. 656 – 661) immediately after the death of Muhammad, and he was the first Shia Imam ...
''.
Associação Núcleo de Arte
 An important cultural and artists' centre in Maputo is the Associação Núcleo de Arte. It is the oldest collective of artists in Mozambique. Seated in an old villa in the centre of Maputo the Núcleo has played a significant role in metropolitan cultural life for decades. The two best known and most influential contemporary Mozambican artists started their career at Núcleo de Arte, the painter
An important cultural and artists' centre in Maputo is the Associação Núcleo de Arte. It is the oldest collective of artists in Mozambique. Seated in an old villa in the centre of Maputo the Núcleo has played a significant role in metropolitan cultural life for decades. The two best known and most influential contemporary Mozambican artists started their career at Núcleo de Arte, the painter Malangatana Ngwenya
Malangatana Valente Ngwenya (6 June 1936 – 5 January 2011) was a Mozambican painter and poet. He frequently exhibited work under his first name alone, as Malangatana. He died on 5 January 2011 in Matosinhos, Portugal.
Life
Born in Matalana ...
and the sculptor Alberto Chissano
Alberto Mabungulane Chissano (25 January 1935 – 19 February 1994) was a Mozambican sculptor best known for his work using indigenous woods, and sculptures in rock, stone and iron. He is considered to be one of Mozambique's most important and i ...
. Over one hundred painters, sculptors and ceramists are members of the Núcleo, which regularly stages exhibitions on its own premises and over the last few years has actively participated in exchanges with artists from abroad. The Núcleo became well known for their project transforming arms into tools and objects of art. It played an important role for reconciliation after the Mozambican Civil War
The Mozambican Civil War ( pt, Guerra Civil Moçambicana) was a civil war fought in Mozambique from 1977 to 1992. Like many regional African conflicts during the late twentieth century, the Mozambican Civil War possessed local dynamics but was a ...
. The exhibition of art objects such as the Chair of the African King and the Tree of Life
The tree of life is a fundamental archetype in many of the world's mythological, religious, and philosophical traditions. It is closely related to the concept of the sacred tree.Giovino, Mariana (2007). ''The Assyrian Sacred Tree: A History ...
was shown around the world, among others in the British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum ...
in 2006.
Maputo is home to the Dockanema
DOCKANEMA is an annual international documentary film festival held in Maputo, Mozambique. The first edition was held September 2006, and included more than 70 films. The festival is produced by the Mozambican production company Ebano Multimedia, ...
Documentary Film Festival, and international festival showcasing documentary films from around the world.
Landmarks
During its five centuries of Portuguese colonialization, the city has gained several examples of Portuguese architecture. Most of the note-worthy buildings are former colonial administrative buildings or current government buildings. The city's landmarks include: * Fortress of Maputo
*
* Fortress of Maputo
* Maputo Railway Station
The Central Railway Station ( pt, Estação Central dos Caminhos de Ferro) is a historic train station in Maputo, Mozambique. Administered by Mozambique Ports and Railways, it is on the CFM Sul line, which links to South Africa, Eswatini, and Z ...
- ''Caminhos de Ferro de Moçambique (CFM)''
* Independence Square
* Maputo City Hall
Maputo City Hall or Municipal Council Building of Maputo (Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''Edifício do Conselho Municipal de Maputo'') is the seat of the local government of the capital of Mozambique. The Neoclassicism, neoclassical building ...
* Samora Machel Statue
The Samora Machel Statue ( Portuguese: ''A Estátua de Samora Machel'') is a bronze sculpture located in the center of Praça da Independência in Maputo, Mozambique. The statue depicts Samora Machel (1933-1986), military, revolutionary, and the ...
* The Museum of Natural History
* Vila Algarve
Vila Algarve is a residential house in the Mozambican capital Maputo. Built in 1934 and later protected as a listed building, the building housed the Portuguese secret police PIDE/DGS until the end of the Portuguese colonial period in Mozambique ...
– The former location of Portuguese Secret Police (PIDE)
* Hotel Polana
* Tunduru Gardens
The Tunduru Gardens is public park and garden in downtown Maputo, Mozambique. It was designed in 1885 by British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Oversea ...
Places of worship
Among theplaces of worship
A place of worship is a specially designed structure or space where individuals or a group of people such as a congregation come to perform acts of devotion, veneration, or religious study. A building constructed or used for this purpose is somet ...
, they are predominantly Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
churches and temples : Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Maputo (Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
), Reformed Church in Mozambique (World Communion of Reformed Churches
The World Communion of Reformed Churches (WCRC) is the largest association of Calvinist churches in the world. It has 230 member denominations in 108 countries, together claiming an estimated 80 million people, thus being the fourth-largest Chris ...
), Igreja Presbiteriana de Moçambique
Igreja Presbiteriana de Moçambique is one of the largest Protestant denominations of Mozambique.
History
The Presbyterian Church in Mozambique was started by Mozambicans, who heard the gospel in South Africa. Yosefa Mhalamhala converted to the ...
(World Communion of Reformed Churches
The World Communion of Reformed Churches (WCRC) is the largest association of Calvinist churches in the world. It has 230 member denominations in 108 countries, together claiming an estimated 80 million people, thus being the fourth-largest Chris ...
), Convenção Baptista de Moçambique (Baptist World Alliance
The Baptist World Alliance (BWA) is the largest international Baptist organization with an estimated 51 million people in 2022 with 246 member bodies in 128 countries and territories. A voluntary association of Baptist churches, the BWA account ...
), Universal Church of the Kingdom of God
The Universal Church of the Kingdom of God (UCKG; pt, Igreja Universal do Reino de Deus, IURD) is an evangelical charismatic Christian denomination with its headquarters at the Temple of Solomon in São Paulo, Brazil. The church was founded in ...
, Assemblies of God
The Assemblies of God (AG), officially the World Assemblies of God Fellowship, is a group of over 144 autonomous self-governing national groupings of churches that together form the world's largest Pentecostal denomination."Assemblies of God". ...
, Zion Christian Church
The Zion Christian Church (ZCC) is one of the largest African-initiated churches operating across Southern Africa, and is part of the African Zionism movement. The church's headquarters are at Zion City Moria in Limpopo Province (old Northern ...
. There are also Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
mosques.
Parks
 The city does not yet have a very expansive list of parks and other recreational areas. However, at the center of the city lies the Jardim Tunduru (
The city does not yet have a very expansive list of parks and other recreational areas. However, at the center of the city lies the Jardim Tunduru (Tunduru Gardens
The Tunduru Gardens is public park and garden in downtown Maputo, Mozambique. It was designed in 1885 by British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Oversea ...
) which was formerly called the Vasco Da Gama Garden. It was designed in the 1880s by a British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
architect, Thomas Honney. The entrance of the park is designed in the Neo-Manueline
Neo-Manueline is a revival style of architecture which drew from the 16th century Manueline Late Gothic architecture of Portugal. Neo-Manueline constructions have been built across Portugal, Brazil, and the Lusophone world (the former Portuguese ...
style. After independence, the name was changed to the current one and a statue of the country's first president was erected.
Education
Maputo offers several options for education with pre-schools, primary, secondary schools and higher education institutions. The quality of the syllabus is said to differ greatly depending on whether an institution is private or public.Higher education
Mozambique's largest higher education institution is theUniversidade Eduardo Mondlane
The Eduardo Mondlane University ( pt, Universidade Eduardo Mondlane; UEM) is the oldest and largest university in Mozambique. The UEM is located in Maputo and has about 40,000 students enrolled.
History
The institution was set up as a center for ...
which was established in 1968 as the Universidade de Lourenço Marques. Most of the universities faculties and departments are located in the city of Maputo with nearly 8,000 students attending 10 faculties. Some faculties also exist in Beira, Quelimane
Quelimane () is a seaport in Mozambique. It is the administrative capital of the Zambezia Province and the province's largest city, and stands from the mouth of the Rio dos Bons Sinais (or "River of the Good Signs"). The river was named when Va ...
, Nampula and Inhambane.
Since the 1990s there has also been a rapid growth of private education houses offering higher education such as ''Instituto Superior de Ciências e Tecnologias de Moçambique'' (ISCTEM), ''Instituto Superior de Tecnologias e Gestão'' (ISTEG) and ''Instituto Superior de Transportes e Comunicações'' (ISUTC).
Secondary education
In the secondary education market, there is again a strong divergence between private and public schooling. Maputo's private schools include: * Enko Nyamunda International School *Escola Portuguesa de Moçambique
Escola Portuguesa de Moçambique - Centro de Ensino e Língua Portuguesa (EPM-CELP) is a Portuguese international school in Maputo, Mozambique. The school is operated by the Portuguese Ministry of Education and serves from Pre-school up to Grade 1 ...
* French School of Mozambique
* Scuola Italiana Privata "Giovanni Falcone"
* Skandinaviska Skolan Maputo
* American International School of Mozambique
American International School of Mozambique (AISM) is an American international school in Maputo, Mozambique. The school serves grades K-12. The school follows the International Baccalaureate
The International Baccalaureate (IB), formerly kno ...
* The Aga Khan Academy, Maputo
* Princess Cinderella Kindergarten, Primary & High School
* Maputo International School
* Willow International School
* Canadian Montessori Academy
* Maputo International College
*Colégio Kitabu
*Grandeur International School
*Acácias Secondary School
*ISCTEM Secondary School
Some expatriates have chosen to enroll their children in schools in Mbombela
Mbombela (also known as Nelspruit) is a city in northeastern South Africa. It is the capital of the Mpumalanga province. Located on the Crocodile River, Mbombela lies about by road west of the Mozambique border, east of Johannesburg and nort ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
and Waterford Kamhlaba
Waterford Kamhlaba United World College of Southern Africa (WKUWCSA), one of 18 international schools and colleges in the UWC educational movement, is located in Mbabane, Eswatini..
Waterford was the first school in southern Africa open to ch ...
in Mbabane, Eswatini
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
.
Health services
 Maputo has several hospitals and clinics, including the city and country's largest hospital, the Hospital Central de Maputo (Maputo Central Hospital). Other hospitals include the public Hospital Geral José Macamo, and the private Clinica Sommerschield, the Clínica Cruz Azul in ''baixa'' and Hospital Privado located across the Portuguese School.
The construction of Hospital Miguel Bombarda began in 1900. In 1976,
Maputo has several hospitals and clinics, including the city and country's largest hospital, the Hospital Central de Maputo (Maputo Central Hospital). Other hospitals include the public Hospital Geral José Macamo, and the private Clinica Sommerschield, the Clínica Cruz Azul in ''baixa'' and Hospital Privado located across the Portuguese School.
The construction of Hospital Miguel Bombarda began in 1900. In 1976, Samora Machel
Samora Moisés Machel (29 September 1933 – 19 October 1986) was a Mozambican military commander and political leader. A socialist in the tradition of Marxism–Leninism, he served as the first President of Mozambique from the country's ...
renamed the hospital as ''Hospital Central de Maputo'' (HCM). The hospital has 1500 beds for in-patients and has an estimated staff number of 3000. It is made of a multi-block structure with 35 separate buildings spanning an area of 163,800 m2. The hospital has six departments: Medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
, Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
, Pediatrics
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until th ...
, Orthopedics
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternatively spelt orthopaedics), is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal ...
, Gynaecology
Gynaecology or gynecology (see spelling differences) is the area of medicine that involves the treatment of women's diseases, especially those of the reproductive organs. It is often paired with the field of obstetrics, forming the combined are ...
and Obstetrics
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgi ...
. It also has divisions for Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medic ...
and Otolaryngology
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical a ...
and a morgue. The hospital provides services for an average 700 out-patients a day and over of washing is done daily. In the early 1990s, a section of the hospital was divided and turned into a private clinic offering higher quality services for those who could afford it called the ''Clínica Especial de Maputo''. The residence for the head of medicine is on the corner of ''Avenida Eduardo Mondlane'' and ''Avenida Salavador Allende''. It is a historically valuable structure which was completed in 1908 and has since the 1990s been converted into a charming restaurant with colonial themes called ''Restaurante 1908''. The upper floors are still used by the hospital as offices.
Notable people
*Al Bowlly
Albert Allick Bowlly (7 January 1898 – 17 April 1941) was a Mozambican-born South African– British vocalist and jazz guitarist, who was popular during the 1930s in Britain. He recorded more than 1,000 songs.
His most popular songs includ ...
, singer
* Carlos Cardoso, journalist
* Alberto Chissano
Alberto Mabungulane Chissano (25 January 1935 – 19 February 1994) was a Mozambican sculptor best known for his work using indigenous woods, and sculptures in rock, stone and iron. He is considered to be one of Mozambique's most important and i ...
, sculptor
* Moreira Chonguica
Moreira may refer to:
Places
* Moreira (Maia), a parish in Maia Municipality, northern Portugal
* , a parish in Monção Municipality, northern Portugal
* , a parish in Nelas Municipality, central Portugal
People
*Moreira (name) Moreira is a g ...
, musician, composer, social activist
* Gilles Cistac
Gilles Cistac (November 11, 1961 − March 3, 2015) was a French-Mozambican lawyer specialised in constitutional law. He was shot and killed and political motives were suspected. The RENAMO party organised protests.
Biography
Gilles Cistac was b ...
, constitutional lawyer
* Mia Couto
António Emílio Leite Couto, better known as Mia Couto (born 5 July 1955), is a Mozambican writer. He won the Camões Prize in 2013, the most important literary award in the Portuguese language, and the Neustadt International Prize for Liter ...
, writer
* José Craveirinha
José Craveirinha (28 May 1922 – 6 February 2003) was a Mozambican journalist, story writer and poet, who is today considered the greatest poet of Mozambique. His poems, written in Portuguese, address such issues as racism and the Portuguese co ...
, poet
* Eusébio
Eusébio da Silva Ferreira (; 25 January 1942 – 5 January 2014), nicknamed the "Black Panther", the "Black Pearl" or "O Rei" ("The King"), was a Portuguese footballer who played as a striker. He is considered one of the greatest players of ...
, footballer
* Ruth First
Heloise Ruth First (4 May 1925 – 17 August 1982) was a South African anti- apartheid activist and scholar. She was assassinated in Mozambique, where she was working in exile, by a parcel bomb built by South African police.
Family and ed ...
, South African anti-apartheid activist
* Pancho Guedes
Amâncio d'Alpoim Miranda "Pancho" Guedes (Lisbon, Portugal, 13 May 1925 – Graaff-Reinet, South Africa, 7 November 2015) was a Portuguese architect, sculptor and painter an educator.
He is described as one of the earliest post-modernist ar ...
, architect
* Teresa Heinz
Teresa Heinz (born Maria Teresa Thierstein Simões-Ferreira; October 5, 1938), also known as Teresa Heinz Kerry, is a Portuguese-American businesswoman and philanthropist. Heinz is the widow of former U.S. Senator John Heinz and the wife of fo ...
, philanthropist and political figure, widow of John Heinz
Henry John Heinz III (October 23, 1938 – April 4, 1991) was an American businessman and Republican politician from Pennsylvania. Heinz represented the Pittsburgh suburbs in the United States House of Representatives from 1971 to 1977 and ...
and wife of American political figure John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry (born December 11, 1943) is an American attorney, politician and diplomat who currently serves as the first United States special presidential envoy for climate. A member of the Forbes family and the Democratic Party (Unite ...
* Josina Z. Machel
Josina Ziyaya Machel (April 1976) is a human rights activist from Mozambique, who was listed on the BBC's 100 Women list for 2020. Her parents were Samora Machel, the first independent president of Mozambique, and humanitarian and politician Gr ...
, women's rights activist
* Lucas Macie, painter
* Malangatana
Malangatana Valente Ngwenya (6 June 1936 – 5 January 2011) was a Mozambican painter and poet. He frequently exhibited work under his first name alone, as Malangatana. He died on 5 January 2011 in Matosinhos, Portugal.
Life
Born in Matalana ...
, artist
* Henning Mankell
Henning Georg Mankell (; 3February 19485October 2015) was a Swedish crime writer, children's author, and dramatist, best known for a series of mystery novels starring his most noted creation, Inspector Kurt Wallander. He also wrote a number ...
, author, dramatist
* Mariza
Marisa dos Reis Nunes ComIH (born 16 December 1973), known professionally as Mariza (), is a Portuguese fado singer.
Mariza was born in Lourenço Marques, Portuguese Mozambique, to a Portuguese father, José Brandão Nunes, and a Mozambican ...
, fado singer
* Mexer
Edson André Sitoe (born 8 September 1988), known as Mexer, is a Mozambican professional footballer who plays as a centre-back for TFF First League club Bandırmaspor and the Mozambique national team.
Brought to Europe by Sporting CP in 2010 ...
, footballer
* Maria Mutola
Maria de Lurdes Mutola ( ; born 27 October 1972) is a retired female track and field athlete from Mozambique who specialised in the 800 metres running event. She is only the fourth female track and field athlete to compete at six Olympic Games. ...
, runner
* Neyma
Neyma Julio Alfredo (burn 6 May 1978) is a Mozambican singer. She is known for producing songs of the Mozambican genre, such as Marrabenta and Kizomba.
Biography
Neyma began her interest in music at a young age, singing at various events in ...
, singer
* Alexandre Quintanilha
Alexandre Tiedtke Quintanilha, GOSE (born August 9, 1945 in Lourenço Marques (now Maputo), Mozambique) is a Portuguese scientist, former director of the Instituto de Biologia Molecular e Celular (Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology) of the U ...
, scientist
* Ricardo Rangel, photojournalist
Twin towns – sister cities
Maputo is twinned with: *Addis Ababa
Addis Ababa (; am, አዲስ አበባ, , new flower ; also known as , lit. "natural spring" in Oromo), is the capital and largest city of Ethiopia. It is also served as major administrative center of the Oromia Region. In the 2007 census, t ...
, Ethiopia
* Ankara
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the capital of Turkey. Located in the central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center and over 5.7 million in Ankara Province, maki ...
, Turkey
* Bissau, Guinea-Bissau
* Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
, South Africa
* Charles County
Charles County is a county in Southern Maryland. As of the 2020 census, the population was 166,617. The county seat is La Plata. The county was named for Charles Calvert (1637–1715), third Baron Baltimore. Charles County is part of the Wash ...
, United States
* Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; Simplified Chinese characters, simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively Romanization of Chi ...
, China
* Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
, India
* Dili
Dili (Portuguese/Tetum: ''Díli'') is the capital, largest city of East Timor and the second largest city in Timor islands after Kupang (Indonesia). It lies on the northern coast of the island of Timor, in a small area of flat land hemmed in ...
, East Timor
* Durban
Durban ( ) ( zu, eThekwini, from meaning 'the port' also called zu, eZibubulungwini for the mountain range that terminates in the area), nicknamed ''Durbs'',Ishani ChettyCity nicknames in SA and across the worldArticle on ''news24.com'' from ...
, South Africa
* Guarulhos, Brazil
* Harare
Harare (; formerly Salisbury ) is the capital and most populous city of Zimbabwe. The city proper has an area of 940 km2 (371 mi2) and a population of 2.12 million in the 2012 census and an estimated 3.12 million in its metropolitan ...
, Zimbabwe
* Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta ...
, Indonesia
* Lagos
Lagos (Nigerian English: ; ) is the largest city in Nigeria and the List of cities in Africa by population, second most populous city in Africa, with a population of 15.4 million as of 2015 within the city proper. Lagos was the national ca ...
, Nigeria
* Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Grande Lisboa, Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administr ...
, Portugal
* Luanda
Luanda () is the capital and largest city in Angola. It is Angola's primary port, and its major industrial, cultural and urban centre. Located on Angola's northern Atlantic coast, Luanda is Angola's administrative centre, its chief seaport ...
, Angola
* Mbabane, Eswatini
* Port Louis
Port Louis (french: Port-Louis; mfe, label= Mauritian Creole, Polwi or , ) is the capital city of Mauritius. It is mainly located in the Port Louis District, with a small western part in the Black River District. Port Louis is the country's e ...
, Mauritius
* Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
, Brazil
* Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flow ...
, China
Cooperation agreements
Maputo also has a cooperation agreement with: *Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within ci ...
, Spain
See also
*Delagoa Bay
Maputo Bay ( pt, Baía de Maputo), formerly also known as Delagoa Bay from ''Baía da Lagoa'' in Portuguese, is an inlet of the Indian Ocean on the coast of Mozambique, between 25° 40' and 26° 20' S, with a length from north to south of over 90&n ...
*Lourenço Marques (explorer)
Lourenço Marques was a 16th-century Portuguese trader and coloniser.
Biography
Lourenço Marques explored the area that is now Maputo Bay in 1544 and settled permanently in present-day Mozambique, where he spent most of his life with his indi ...
* List of cities in Mozambique by population
*Metropolitan Maputo Metropolitan Maputo is the name for the broader Maputo-Matola area which includes the districts of Marracuene and the city of Matola in the country of Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ...
References
Notes
Bibliography
External links
* *Photos and Map of Maputo
{{Authority control Capitals in Africa Populated coastal places in Mozambique Populated places in Mozambique Provinces of Mozambique Provincial capitals in Mozambique Port cities in Africa Port cities and towns of the Indian Ocean 1782 establishments in the Portuguese Empire Populated places established in 1781