Maple computer algebra system on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Maple is a symbolic and numeric computing environment as well as a
myfac := proc(n::nonnegint)
local out, i;
out := 1;
for i from 2 to n do
out := out * i
end do;
out
end proc;
Simple functions can also be defined using the "maps to" arrow notation:
myfac := n -> product(i, i = 1..n);
int(cos(x/a), x);
Output:
:
M := Matrix( 1,2,3 ,b,c ,y,z); # example Matrix
:
LinearAlgebra:-Determinant(M);
:
series(tanh(x), x = 0, 15)
:
:
f := x^53-88*x^5-3*x-5 = 0
fsolve(f)
-1.097486315, -.5226535640, 1.099074017
The same command can also solve systems of equations:
f := (cos(x+y))^2 + exp(x)*y+cot(x-y)+cosh(z+x) = 0:
g := x^5 - 8*y = 2:
h := x+3*y-77*z=55;
fsolve( );
plot(x*sin(x), x = -10..10);
plot3d(x^2+y^2, x = -1..1, y = -1..1);
plots:-animate(subs(k = 0.5, f), x=-30..30, t=-10..10, numpoints=200, frames=50, color=red, thickness=3);
 * Animation of functions of three variables
* Animation of functions of three variables
plots:-animate3d(cos(t*x)*sin(3*t*y), x=-Pi..Pi, y=-Pi..Pi, t=1..2);
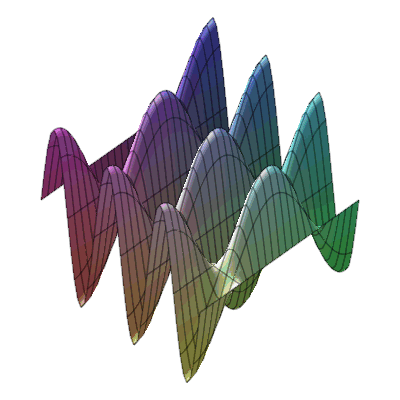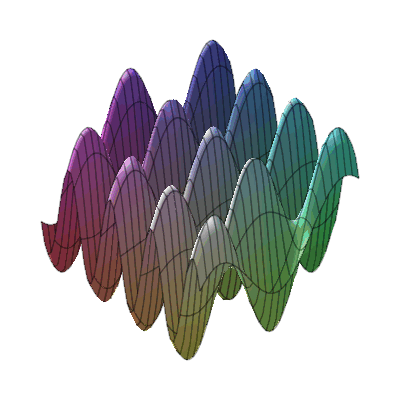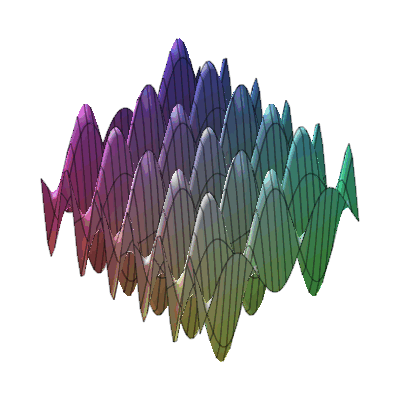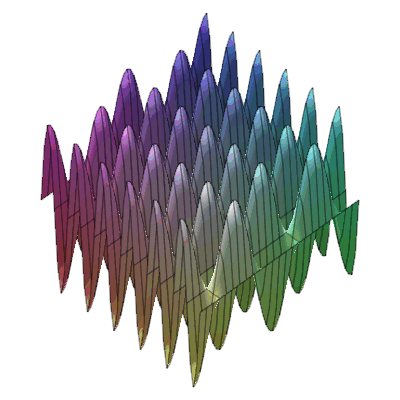 * Fly-through animation of 3-D plots.
* Fly-through animation of 3-D plots.
M := Matrix(

f := (1+A*t+B*t^2)*exp(c*t);
:
inttrans:-laplace(f, t, s);
:
* inverse Laplace transform
inttrans:-invlaplace(1/(s-a), s, x);
:
inttrans:-fourier(sin(x), x, w)
:
eqn:= f(x)-3*Int((x*y+x^2*y^2)*f(y), y=-1..1) = h(x):
intsolve(eqn,f(x));
:
Maplesoft, division of Waterloo Maple, Inc.
– official website {{Authority control C (programming language) software Notebook interface Computer algebra system software for Linux Computer algebra system software for macOS Computer algebra system software for Windows Computer algebra systems Cross-platform software Data mining and machine learning software Data visualization software Data-centric programming languages Econometrics software Functional languages Interactive geometry software IRIX software Linear algebra Maplesoft Mathematical optimization software Mathematical software Numerical analysis software for Linux Numerical analysis software for macOS Numerical analysis software for Windows Numerical programming languages Numerical software Parallel computing Physics software Plotting software Products introduced in 1982 Proprietary commercial software for Linux Proprietary cross-platform software Regression and curve fitting software Simulation programming languages Software modeling language Statistical programming languages Theorem proving software systems Time series software
multi-paradigm programming language
Programming paradigms are a way to classify programming languages based on their features. Languages can be classified into multiple paradigms.
Some paradigms are concerned mainly with implications for the execution model of the language, suc ...
. It covers several areas of technical computing, such as symbolic mathematics, numerical analysis, data processing, visualization, and others. A toolbox, MapleSim
MapleSim is a Modelica-based, multi-domain modeling and simulation tool developed by Maplesoft. MapleSim generates model equations, runs simulations, and performs analyses using the symbolic and numeric mathematical engine of Maple. Models are c ...
, adds functionality for multidomain physical modeling and code generation.
Maple's capacity for symbolic computing include those of a general-purpose computer algebra system
A computer algebra system (CAS) or symbolic algebra system (SAS) is any mathematical software with the ability to manipulate mathematical expressions in a way similar to the traditional manual computations of mathematicians and scientists. The ...
. For instance, it can manipulate mathematical expressions and find symbolic solutions to
certain problems, such as those arising from ordinary and partial differential equations
In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, a ...
.
Maple is developed commercially by the Canadian software company Maplesoft
Waterloo Maple Inc. is a Canadian software company, headquartered in Waterloo, Ontario. It operates under the trade name Maplesoft. It is best known as the manufacturer of the Maple computer algebra system, and MapleSim physical modeling and ...
. The name 'Maple' is a reference to the software's Canadian heritage
The Department of Canadian Heritage, or simply Canadian Heritage (french: Patrimoine canadien), is the department of the Government of Canada that has roles and responsibilities related to initiatives that promote and support "Canadian identity ...
.
Overview
Core functionality
Users can enter mathematics in traditionalmathematical notation
Mathematical notation consists of using symbols for representing operations, unspecified numbers, relations and any other mathematical objects, and assembling them into expressions and formulas. Mathematical notation is widely used in mathe ...
. Custom user interfaces can also be created. There is support for numeric computations, to arbitrary precision, as well as symbolic computation and visualization. Examples of symbolic computations are given below.
Maple incorporates a dynamically typed
In computer programming, a type system is a logical system comprising a set of rules that assigns a property called a type to every "term" (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Usually the terms are various constructs of a computer program ...
imperative-style programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Most programming languages are text-based formal languages, but they may also be graphical. They are a kind of computer language.
The description of a programming l ...
(resembling Pascal), which permits variables of lexical scope
Scope or scopes may refer to:
People with the surname
* Jamie Scope (born 1986), English footballer
* John T. Scopes (1900–1970), central figure in the Scopes Trial regarding the teaching of evolution
Arts, media, and entertainment
* CinemaS ...
. There are also interfaces to other languages ( C, C#, Fortran, Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
, MATLAB
MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementa ...
, and Visual Basic Visual Basic is a name for a family of programming languages from Microsoft. It may refer to:
* Visual Basic .NET (now simply referred to as "Visual Basic"), the current version of Visual Basic launched in 2002 which runs on .NET
* Visual Basic (c ...
), as well as to Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet developed by Microsoft for Windows, macOS, Android and iOS. It features calculation or computation capabilities, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for ...
.
Maple supports MathML
Mathematical Markup Language (MathML) is a mathematical markup language, an application of XML for describing mathematical notations and capturing both its structure and content. It aims at integrating mathematical formulae into World Wide We ...
2.0, which is a W3C
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web. Founded in 1994 and led by Tim Berners-Lee, the consortium is made up of member organizations that maintain full-time staff working t ...
format for representing and interpreting mathematical expressions, including their display in web pages. There is also functionality for converting expressions from traditional mathematical notation to markup suitable for the typesetting system LaTeX
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latexes are found in nature, but synthetic latexes are common as well.
In nature, latex is found as a milky fluid found in 10% of all flowering plants (angiosper ...
.
Architecture
Maple is based on a smallkernel
Kernel may refer to:
Computing
* Kernel (operating system), the central component of most operating systems
* Kernel (image processing), a matrix used for image convolution
* Compute kernel, in GPGPU programming
* Kernel method, in machine lea ...
, written in C, which provides the Maple language. Most functionality is provided by libraries, which come from a variety of sources. Most of the libraries are written in the Maple language; these have viewable source code. Many numerical computations are performed by the NAG Numerical Libraries
The NAG Numerical Library is a software product developed and sold by The Numerical Algorithms Group Ltd. It is a software library of numerical analysis routines, containing more than 1,900 mathematical and statistical algorithms. Areas covered by ...
, ATLAS
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geograp ...
libraries, or GMP libraries.
Different functionality in Maple requires numerical data in different formats. Symbolic expressions are stored in memory as directed acyclic graph
In mathematics, particularly graph theory, and computer science, a directed acyclic graph (DAG) is a directed graph with no directed cycles. That is, it consists of vertices and edges (also called ''arcs''), with each edge directed from one v ...
s. The standard interface and calculator interface are written in Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
.
History
The first concept of Maple arose from a meeting in late 1980 at theUniversity of Waterloo
The University of Waterloo (UWaterloo, UW, or Waterloo) is a public research university with a main campus in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is on of land adjacent to "Uptown" Waterloo and Waterloo Park. The university also operates ...
. Researchers at the university wished to purchase a computer powerful enough to run the Lisp-based computer algebra system Macsyma
Macsyma (; "Project MAC's SYmbolic MAnipulator") is one of the oldest general-purpose computer algebra systems still in wide use. It was originally developed from 1968 to 1982 at MIT's Project MAC.
In 1982, Macsyma was licensed to Symbolics and ...
. Instead, they opted to develop their own computer algebra system, named Maple, that would run on lower cost computers. Aiming for portability, they began writing Maple in programming languages from the BCPL
BCPL ("Basic Combined Programming Language") is a procedural, imperative, and structured programming language. Originally intended for writing compilers for other languages, BCPL is no longer in common use. However, its influence is still ...
family (initially using a subset of B and C, and later on only C). A first limited version appeared after three weeks, and fuller versions entered mainstream use beginning in 1982. By the end of 1983, over 50 universities had copies of Maple installed on their machines.
In 1984, the research group arranged with Watcom Products Inc to license and distribute the first commercially available version, Maple 3.3. In 1988 Waterloo Maple Inc. (Maplesoft) was founded. The company’s original goal was to manage the distribution of the software, but eventually it grew to have its own R&D department, where most of Maple's development takes place today (the remainder being done at various university laboratories).
In 1989, the first graphical user interface for Maple was developed and included with version 4.3 for the Macintosh
The Mac (known as Macintosh until 1999) is a family of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc. Macs are known for their ease of use and minimalist designs, and are popular among students, creative professionals, and software en ...
. X11 and Windows versions of the new interface followed in 1990 with Maple V. In 1992, Maple V Release 2 introduced the Maple "worksheet" that combined text, graphics, and input and typeset output. In 1994 a special issue of a newsletter created by Maple developers called ''MapleTech'' was published.
In 1999, with the release of Maple 6, Maple included some of the NAG Numerical Libraries
The NAG Numerical Library is a software product developed and sold by The Numerical Algorithms Group Ltd. It is a software library of numerical analysis routines, containing more than 1,900 mathematical and statistical algorithms. Areas covered by ...
. In 2003, the current "standard" interface was introduced with Maple 9. This interface is primarily written in Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
(although portions, such as the rules for typesetting mathematical formulae, are written in the Maple language). The Java interface was criticized for being slow; improvements have been made in later versions, although the Maple 11 documentation recommends the previous ("classic") interface for users with less than 500 MB of physical memory.
Between 1995 and 2005 Maple lost significant market share to competitors due to a weaker user interface. With Maple 10 in 2005, Maple introduced a new "document mode" interface, which has since been further developed across several releases.
In September 2009 Maple and Maplesoft were acquired by the Japanese software retailer Cybernet Systems.
Version history
* Maple 1.0: January, 1982 * Maple 1.1: January, 1982 * Maple 2.0: May, 1982 * Maple 2.1: June, 1982 * Maple 2.15: August, 1982 * Maple 2.2: December, 1982 * Maple 3.0: May, 1983 * Maple 3.1: October, 1983 * Maple 3.2: April, 1984 * Maple 3.3: March, 1985 (first public available version) * Maple 4.0: April, 1986 * Maple 4.1: May, 1987 * Maple 4.2: December, 1987 * Maple 4.3: March, 1989 * Maple V: August, 1990 * Maple V R2: November 1992 * Maple V R3: March 15, 1994 * Maple V R4: January, 1996 * Maple V R5: November 1, 1997 * Maple 6: December 6, 1999 * Maple 7: July 1, 2001 * Maple 8: April 16, 2002 * Maple 9: June 30, 2003 * Maple 9.5: April 15, 2004 * Maple 10: May 10, 2005 * Maple 11: February 21, 2007 * Maple 11.01: July, 2007 * Maple 11.02: November, 2007 * Maple 12: May, 2008 * Maple 12.01: October, 2008 * Maple 12.02: December, 2008 * Maple 13: April 28, 2009 * Maple 13.01: July, 2009 * Maple 13.02: October, 2009 * Maple 14: April 29, 2010 * Maple 14.01: October 28, 2010 * Maple 15: April 13, 2011 * Maple 15.01: June 21, 2011 * Maple 16: March 28, 2012 * Maple 16.01: May 16, 2012 * Maple 17: March 13, 2013 * Maple 17.01: July, 2013 * Maple 18: Mar 5, 2014 * Maple 18.01: May, 2014 * Maple 18.01a: July, 2014 * Maple 18.02: Nov, 2014 * Maple 2015.0: Mar 4, 2015 * Maple 2015.1: Nov, 2015 * Maple 2016.0: March 2, 2016 * Maple 2016.1: April 20, 2016 * Maple 2016.1a: April 27, 2016 * Maple 2017.0: May 25, 2017 * Maple 2017.1: June 28, 2017 * Maple 2017.2: August 2, 2017 * Maple 2017.3: October 3, 2017 * Maple 2018.0: March 21, 2018 * Maple 2019.0: March 14, 2019 * Maple 2020.0: March 12, 2020Features
Features of Maple include: * Support for symbolic and numeric computation with arbitrary precision *Elementary
Elementary may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* ''Elementary'' (Cindy Morgan album), 2001
* ''Elementary'' (The End album), 2007
* ''Elementary'', a Melvin "Wah-Wah Watson" Ragin album, 1977
Other uses in arts, entertainment, a ...
and special mathematical function libraries
* Complex number
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the for ...
s and interval arithmetic
* Arithmetic, greatest common divisor
In mathematics, the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two or more integers, which are not all zero, is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers. For two integers ''x'', ''y'', the greatest common divisor of ''x'' and ''y'' i ...
s and factorization
In mathematics, factorization (or factorisation, see English spelling differences) or factoring consists of writing a number or another mathematical object as a product of several ''factors'', usually smaller or simpler objects of the same kind ...
for multivariate polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression consisting of indeterminates (also called variables) and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and positive-integer powers of variables. An exampl ...
s over the rationals, finite field
In mathematics, a finite field or Galois field (so-named in honor of Évariste Galois) is a field that contains a finite number of elements. As with any field, a finite field is a set on which the operations of multiplication, addition, subt ...
s, algebraic number field
In mathematics, an algebraic number field (or simply number field) is an extension field K of the field of rational numbers such that the field extension K / \mathbb has finite degree (and hence is an algebraic field extension).
Thus K is a ...
s, and algebraic function field
In mathematics, an algebraic function field (often abbreviated as function field) of ''n'' variables over a field ''k'' is a finitely generated field extension ''K''/''k'' which has transcendence degree ''n'' over ''k''. Equivalently, an algebra ...
s
* Limits, series and asymptotic expansion In mathematics, an asymptotic expansion, asymptotic series or Poincaré expansion (after Henri Poincaré) is a formal series of functions which has the property that truncating the series after a finite number of terms provides an approximation to ...
s
* Gröbner basis
In mathematics, and more specifically in computer algebra, computational algebraic geometry, and computational commutative algebra, a Gröbner basis is a particular kind of generating set of an ideal in a polynomial ring over a field . A Grö ...
* Differential Algebra
* Matrix manipulation tools including support for sparse array
Sparse is a computer software tool designed to find possible coding faults in the Linux kernel. Unlike other such tools, this static analysis tool was initially designed to only flag constructs that were likely to be of interest to kernel dev ...
s
* Mathematical function graphing
In mathematics, the graph of a function f is the set of ordered pairs (x, y), where f(x) = y. In the common case where x and f(x) are real numbers, these pairs are Cartesian coordinates of points in two-dimensional space and thus form a subset ...
and animation tools
* Solvers for systems of equations
In mathematics, a set of simultaneous equations, also known as a system of equations or an equation system, is a finite set of equations for which common solutions are sought. An equation system is usually classified in the same manner as single ...
, diophantine equation
In mathematics, a Diophantine equation is an equation, typically a polynomial equation in two or more unknowns with integer coefficients, such that the only solutions of interest are the integer ones. A linear Diophantine equation equates to ...
s, ODEs
Odes may refer to:
*The plural of ode, a type of poem
* ''Odes'' (Horace), a collection of poems by the Roman author Horace, circa 23 BCE
* Odes of Solomon, a pseudepigraphic book of the Bible
* Book of Odes (Bible), a Deuterocanonical book of ...
, PDEs, DAEs, DDEs and recurrence relation
In mathematics, a recurrence relation is an equation according to which the nth term of a sequence of numbers is equal to some combination of the previous terms. Often, only k previous terms of the sequence appear in the equation, for a paramete ...
s
* Numeric and symbolic tools for discrete and continuous calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizati ...
including definite and indefinite integration, definite and indefinite sum In discrete calculus the indefinite sum operator (also known as the antidifference operator), denoted by \sum _x or \Delta^ , is the linear operator
In mathematics, and more specifically in linear algebra, a linear map (also called a linear ma ...
mation, automatic differentiation and continuous and discrete integral transform
In mathematics, an integral transform maps a function from its original function space into another function space via integration, where some of the properties of the original function might be more easily characterized and manipulated than i ...
s
* Constrained and unconstrained local and global optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criterion, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfi ...
* Statistics including model fitting, hypothesis testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data at hand sufficiently support a particular hypothesis.
Hypothesis testing allows us to make probabilistic statements about population parameters.
...
, and probability distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomeno ...
s
* Tools for data manipulation, visualization and analysis
* Tools for probability and combinatoric
Combinatorics is an area of mathematics primarily concerned with counting, both as a means and an end in obtaining results, and certain properties of finite structures. It is closely related to many other areas of mathematics and has many appl ...
problems
* Support for time-series and unit based data
* Connection to online collection of financial and economic data
* Tools for financial calculations including bonds, annuities, derivatives, options etc.
* Calculations and simulations on random processes
* Tools for text mining
Text mining, also referred to as ''text data mining'', similar to text analytics, is the process of deriving high-quality information from text. It involves "the discovery by computer of new, previously unknown information, by automatically extract ...
including regular expressions
A regular expression (shortened as regex or regexp; sometimes referred to as rational expression) is a sequence of characters that specifies a search pattern in text. Usually such patterns are used by string-searching algorithms for "find" o ...
* Tools for signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing '' signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, ...
and linear and non-linear control system
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial ...
s
* Discrete math
Discrete mathematics is the study of mathematical structures that can be considered "discrete" (in a way analogous to discrete variables, having a bijection with the set of natural numbers) rather than "continuous" (analogously to continuous ...
tools including number theory
Number theory (or arithmetic or higher arithmetic in older usage) is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and integer-valued functions. German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) said, "Math ...
* Tools for visualizing and analysing directed and undirected graphs
Graph may refer to:
Mathematics
*Graph (discrete mathematics), a structure made of vertices and edges
**Graph theory, the study of such graphs and their properties
* Graph (topology), a topological space resembling a graph in the sense of discr ...
* Group theory including permutation and finitely presented groups
* Symbolic tensor functions
* Import and export filters for data, image, sound, CAD, and document formats
* Technical word processing including formula editing
* Programming language supporting procedural
Procedural may refer to:
* Procedural generation, a term used in computer graphics applications
*Procedural knowledge, the knowledge exercised in the performance of some task
* Procedural law, a legal concept
*Procedural memory, a cognitive scienc ...
, functional
Functional may refer to:
* Movements in architecture:
** Functionalism (architecture)
** Form follows function
* Functional group, combination of atoms within molecules
* Medical conditions without currently visible organic basis:
** Functional s ...
and object-oriented
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of " objects", which can contain data and code. The data is in the form of fields (often known as attributes or ''properties''), and the code is in the form of ...
constructs
* Tools for adding user interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine f ...
s to calculations and applications
* Tools for connecting to SQL, Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
, .NET, C++, Fortran and http
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, ...
* Tools for generating code for C, C#, Fortran, Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
, JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of Website, websites use JavaScript on the Client (computing), client side ...
, Julia
Julia is usually a feminine given name. It is a Latinate feminine form of the name Julio and Julius. (For further details on etymology, see the Wiktionary entry "Julius".) The given name ''Julia'' had been in use throughout Late Antiquity (e ...
, Matlab
MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementa ...
, Perl
Perl is a family of two High-level programming language, high-level, General-purpose programming language, general-purpose, Interpreter (computing), interpreted, dynamic programming languages. "Perl" refers to Perl 5, but from 2000 to 2019 it ...
, Python, R, and Visual Basic Visual Basic is a name for a family of programming languages from Microsoft. It may refer to:
* Visual Basic .NET (now simply referred to as "Visual Basic"), the current version of Visual Basic launched in 2002 which runs on .NET
* Visual Basic (c ...
* Tools for parallel programming
Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different f ...
Examples of Maple code
The following code, which computes the factorial of a nonnegative integer, is an example of animperative programming
In computer science, imperative programming is a programming paradigm of software that uses statements that change a program's state. In much the same way that the imperative mood in natural languages expresses commands, an imperative program co ...
construct within Maple:
Integration
Find :.Determinant
Compute the determinant of a matrix.Series expansion
Solve equations numerically
The following code numerically calculates the roots of a high-order polynomial:Plotting of function of single variable
Plot with ranging from -10 to 10:Plotting of function of two variables
Plot with and ranging from -1 to 1:Animation of functions
* Animation of function of two variables : * Animation of functions of three variables
* Animation of functions of three variables
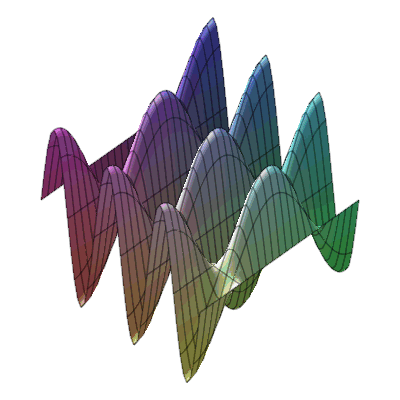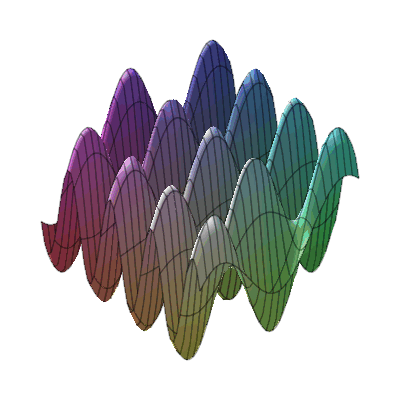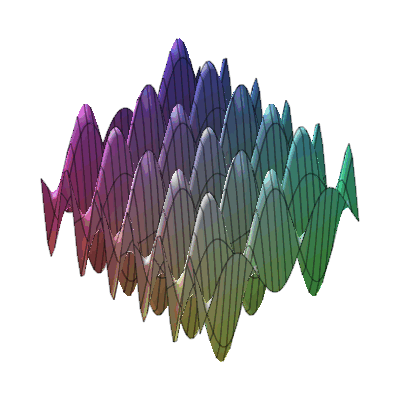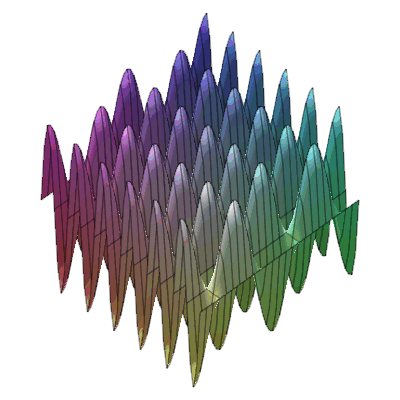 * Fly-through animation of 3-D plots.
* Fly-through animation of 3-D plots.
400,400,200
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures.
In mathematics
Four is the smallest co ...
00,100,-400
This list contains selected positive numbers in increasing order, including counts of things, dimensionless quantities and probabilities. Each number is given a name in the short scale, which is used in English-speaking countries, as well as a ...
,1,1, datatype=float :
plot3d(1, x=0..2*Pi, y=0..Pi, axes=none, coords=spherical, viewpoint= ath=M;

Laplace transform
*Laplace transform
In mathematics, the Laplace transform, named after its discoverer Pierre-Simon Laplace (), is an integral transform that converts a function of a real variable (usually t, in the ''time domain'') to a function of a complex variable s (in the ...
Fourier transform
*Fourier transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed, ...
Integral equations
Find functions that satisfy theintegral equation
In mathematics, integral equations are equations in which an unknown function appears under an integral sign. In mathematical notation, integral equations may thus be expressed as being of the form: f(x_1,x_2,x_3,...,x_n ; u(x_1,x_2,x_3,...,x_n ...
:.
Use of the Maple engine
The Maple engine is used within several other products fromMaplesoft
Waterloo Maple Inc. is a Canadian software company, headquartered in Waterloo, Ontario. It operates under the trade name Maplesoft. It is best known as the manufacturer of the Maple computer algebra system, and MapleSim physical modeling and ...
:
* Moebius, DigitalEd’s online testing suite, uses Maple to algorithmically generate questions and grade student responses.
* MapleNet allows users to create JSP pages and Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
Applets
In computing, an applet is any small application that performs one specific task that runs within the scope of a dedicated widget engine or a larger program, often as a plug-in. The term is frequently used to refer to a Java applet, a program w ...
. MapleNet 12 and above also allow users to upload and work with Maple worksheets containing interactive components.
* MapleSim
MapleSim is a Modelica-based, multi-domain modeling and simulation tool developed by Maplesoft. MapleSim generates model equations, runs simulations, and performs analyses using the symbolic and numeric mathematical engine of Maple. Models are c ...
, an engineering simulation tool.
* Maple Quantum Chemistry Package from RDMChem computes and visualizes the electronic energies and properties of molecules.
Listed below are third-party commercial products that no longer use the Maple engine:
* Versions of Mathcad
Mathcad is computer software for the verification, validation, documentation and re-use of mathematical calculations in engineering and science, notably mechanical, chemical, electrical, and civil engineering. Released in 1986 on DOS, it introduc ...
released between 1994 and 2006 included a Maple-derived algebra engine (MKM, aka Mathsoft Kernel Maple), though subsequent versions use MuPAD
MuPAD is a computer algebra system (CAS). Originally developed by the MuPAD research group at the University of Paderborn, Germany, development was taken over by the company SciFace Software GmbH & Co. KG in cooperation with the MuPAD research gro ...
.
* Symbolic Math Toolbox in MATLAB
MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementa ...
contained a portion of the Maple 10 engine, but now uses MuPAD
MuPAD is a computer algebra system (CAS). Originally developed by the MuPAD research group at the University of Paderborn, Germany, development was taken over by the company SciFace Software GmbH & Co. KG in cooperation with the MuPAD research gro ...
(starting with MATLAB R2007b+ release).
* Older versions of the mathematical editor Scientific Workplace
Scientific WorkPlace (often abbreviated to SWP) is a software package for scientific word processing on Microsoft Windows and OS X.
Although advertised as a WYSIWYG LaTeX-based word processor, it is actually a graphical user interface for editi ...
included Maple as a computational engine, though current versions include MuPAD
MuPAD is a computer algebra system (CAS). Originally developed by the MuPAD research group at the University of Paderborn, Germany, development was taken over by the company SciFace Software GmbH & Co. KG in cooperation with the MuPAD research gro ...
.
See also
*Comparison of computer algebra systems
The following tables provide a comparison of computer algebra systems (CAS). A CAS is a package comprising a set of algorithms for performing symbolic manipulations on algebraic objects, a language to implement them, and an environment in which to ...
* Comparison of numerical-analysis software
The following tables provide a comparison of numerical-analysis software.
Applications
General
Operating system support
The operating systems the software can run on natively (without emulation).
Language features
Colors indicat ...
* Comparison of programming languages
Programming languages are used for controlling the behavior of a machine (often a computer). Like natural languages, programming languages follow the rules for syntax and semantics.
There are thousands of programming languages and new ones are ...
* Comparison of statistical packages
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of statistical analysis packages.
General information
Operating system support
ANOVA
Support for various ANOVA methods
Regression
Support for various regression m ...
* List of computer algebra systems
The following tables provide a comparison of computer algebra systems (CAS). A CAS is a package comprising a set of algorithms for performing symbolic manipulations on algebraic objects, a language to implement them, and an environment in which to ...
* List of computer simulation software
The following is a list of notable computer simulation software.
Free or open-source
* Advanced Simulation Library - open-source hardware accelerated multiphysics simulation software.
* ASCEND - open-source equation-based modelling environmen ...
* List of graphing software
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
* List of numerical-analysis software
Listed here are notable end-user computer applications intended for use with numerical or data analysis:
Numerical-software packages
General-purpose computer algebra systems
Interface-oriented
Language-oriented
Historically significa ...
* Mathematical software Mathematical software is software used to model, analyze or calculate numeric, symbolic or geometric data.
Evolution of mathematical software
Numerical analysis and symbolic computation had been in most important place of the subject, but other ...
* SageMath (an open source algebra program)
References
External links
Maplesoft, division of Waterloo Maple, Inc.
– official website {{Authority control C (programming language) software Notebook interface Computer algebra system software for Linux Computer algebra system software for macOS Computer algebra system software for Windows Computer algebra systems Cross-platform software Data mining and machine learning software Data visualization software Data-centric programming languages Econometrics software Functional languages Interactive geometry software IRIX software Linear algebra Maplesoft Mathematical optimization software Mathematical software Numerical analysis software for Linux Numerical analysis software for macOS Numerical analysis software for Windows Numerical programming languages Numerical software Parallel computing Physics software Plotting software Products introduced in 1982 Proprietary commercial software for Linux Proprietary cross-platform software Regression and curve fitting software Simulation programming languages Software modeling language Statistical programming languages Theorem proving software systems Time series software