Many-to-many (data model) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 In
In
3.7.6.5 hasAndBelongsToMany (HABTM)
{{webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120815165131/http://book.cakephp.org/1.3/view/1044/hasAndBelongsToMany-HABTM , date=2012-08-15 . Cakephp.org
 In
In systems analysis
Systems analysis is "the process of studying a procedure or business to identify its goal and purposes and create systems and procedures that will efficiently achieve them". Another view sees systems analysis as a problem-solving technique that ...
, a many-to-many relationship is a type of cardinality
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thum ...
that refers to the relationship between two entities, say, A and B, where A may contain a parent
A parent is either the progenitor of a child or, in humans, it can refer to a caregiver or legal guardian, generally called an adoptive parent or step-parent. Parents who are progenitors are First-degree relative, first-degree relatives and have ...
instance for which there are many children
A child () is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking ...
in B and vice versa.
Data relationships
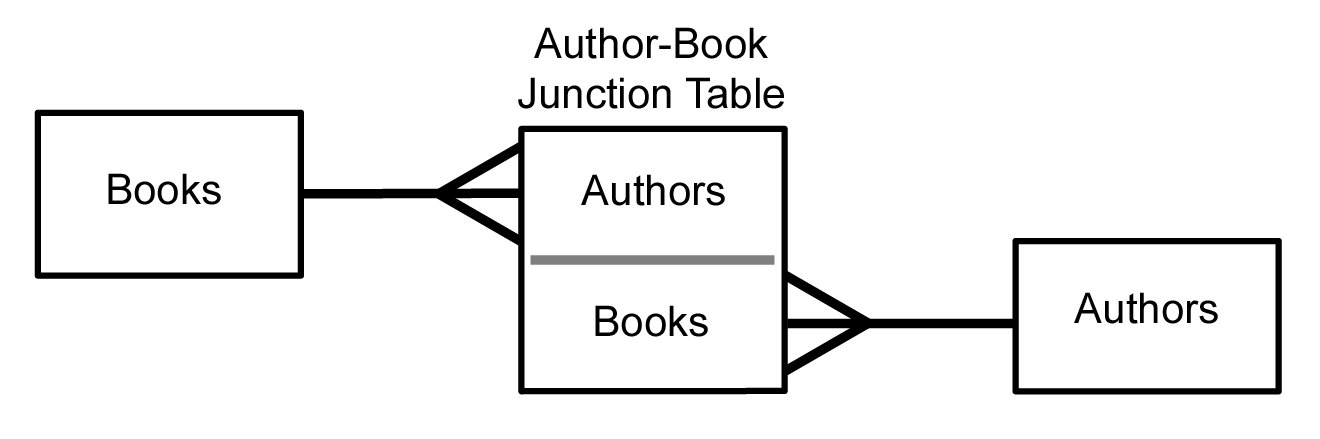
For example, think of A as Authors, and B as Books. An Author can write several Books, and a Book can be written by several Authors. In arelational database management system
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970.
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured for ...
, such relationships are usually implemented by means of an associative table (also known as join table, junction table or ''cross-reference table''), say, AB with two one-to-many relationships and . In this case the logical primary key
In the relational model of databases, a primary key is a designated attribute (column) that can reliably identify and distinguish between each individual record in a table. The database creator can choose an existing unique attribute or combinati ...
for AB is formed from the two foreign key
A foreign key is a set of attributes in a table that refers to the primary key of another table, linking these two tables. In the context of relational databases, a foreign key is subject to an inclusion dependency constraint that the tuples ...
s (i.e. copies of the primary key
In the relational model of databases, a primary key is a designated attribute (column) that can reliably identify and distinguish between each individual record in a table. The database creator can choose an existing unique attribute or combinati ...
s of A and B).
In web application framework
A web framework (WF) or web application framework (WAF) is a software framework that is designed to support the development of web applications including web services, web resources, and web APIs. Web frameworks provide a standard way to build and ...
s such as CakePHP
CakePHP is an open-source web framework. It follows the model–view–controller (MVC) approach and is written in PHP, modeled after the concepts of Ruby on Rails, and distributed under the MIT License.
CakePHP uses well-known software engin ...
and Ruby on Rails
Ruby on Rails (simplified as Rails) is a server-side web application framework written in Ruby under the MIT License. Rails is a model–view–controller (MVC) framework, providing default structures for a database, a web service, and web pa ...
, a many-to-many relationship between entity types represented by logical model database tables is sometimes referred to as a HasAndBelongsToMany (HABTM) relationship.{{webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120815165131/http://book.cakephp.org/1.3/view/1044/hasAndBelongsToMany-HABTM , date=2012-08-15 . Cakephp.org
See also
* Associative entity *One-to-one (data model)
In systems analysis, a one-to-one relationship is a type of cardinality that refers to the relationship between two entities (see also entity–relationship model) A and B in which one element of A may only be linked to one element of B, and vic ...
* One-to-many (data model)
In systems analysis, a one-to-many relationship is a type of cardinality that refers to the relationship between two entities (see also entity–relationship model). For example, take a car and an owner of the car. The car can only be owned by on ...
References