Manx Utilities Authority on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Manx Utilities Authority () is a Statutory Board of the Isle of Man Government which provides utilities for the
 The public utilities on the Isle of Man were the responsibility of a range of organisations; over time they assumed the remit of, or were merged with, or demerged from, other bodies. These historic changes are summarised as follows and are depicted on the diagram.
* The Manx Electricity Authority was established in July 1983 to develop and maintain an efficient and economical system of electricity supply for the Island. Its legal position was established by the Electricity Act 1984.
** The Manx Electricity Authority was constituted by the merger of the Isle of Man Electricity Board (1932–1984) and the Electricity Department of the Douglas Corporation (1921–1983).
** The Manx Electricity Authority only had responsibility for the supply of electricity. These responsibilities were extended in 2003 to include the supply of gas. This was in conjunction with the construction of high pressure natural gas import system from the UK-Ireland gas interconnector. The Gas and Electricity Act 2003 empowered the Manx Electricity Authority to supply gas, and to construct pipes and associated apparatus (Section 1); it also had the duty to supply gas to other organisations such as public gas suppliers (Section2).
* The Isle of Man Water Authority, was established in 1972 by the merger of the Isle of Man Water Board (1946–1972) and the Water Department of Douglas Corporation
** In 1974 it assumed the gas production and distribution functions of the Isle of Man Gas Authority, and was renamed the Isle of Man Water and Gas Authority.
** The IoM Gas Authority (1972–1974) had assumed the responsibilities of the Gas Committee of the Tynwald (1967–1972), which in turn had assumed ownership of the Castletown, Peel and the Port St Mary gas undertakings in 1967. The Douglas and Ramsey gas undertakings were taken over by Calor Gas in 1967.
** In 1985 the gas undertaking was privatised, and the authority reverted to its previous title.
** In 2010 it assumed the sewerage responsibilities of the former Department of Transport and was renamed the Isle of Man Water and Sewerage Authority.
* In 2014 the Manx Electricity Authority merged with the Isle of Man Water and Sewerage Authority to establish the Manx Utilities Authority.
The public utilities on the Isle of Man were the responsibility of a range of organisations; over time they assumed the remit of, or were merged with, or demerged from, other bodies. These historic changes are summarised as follows and are depicted on the diagram.
* The Manx Electricity Authority was established in July 1983 to develop and maintain an efficient and economical system of electricity supply for the Island. Its legal position was established by the Electricity Act 1984.
** The Manx Electricity Authority was constituted by the merger of the Isle of Man Electricity Board (1932–1984) and the Electricity Department of the Douglas Corporation (1921–1983).
** The Manx Electricity Authority only had responsibility for the supply of electricity. These responsibilities were extended in 2003 to include the supply of gas. This was in conjunction with the construction of high pressure natural gas import system from the UK-Ireland gas interconnector. The Gas and Electricity Act 2003 empowered the Manx Electricity Authority to supply gas, and to construct pipes and associated apparatus (Section 1); it also had the duty to supply gas to other organisations such as public gas suppliers (Section2).
* The Isle of Man Water Authority, was established in 1972 by the merger of the Isle of Man Water Board (1946–1972) and the Water Department of Douglas Corporation
** In 1974 it assumed the gas production and distribution functions of the Isle of Man Gas Authority, and was renamed the Isle of Man Water and Gas Authority.
** The IoM Gas Authority (1972–1974) had assumed the responsibilities of the Gas Committee of the Tynwald (1967–1972), which in turn had assumed ownership of the Castletown, Peel and the Port St Mary gas undertakings in 1967. The Douglas and Ramsey gas undertakings were taken over by Calor Gas in 1967.
** In 1985 the gas undertaking was privatised, and the authority reverted to its previous title.
** In 2010 it assumed the sewerage responsibilities of the former Department of Transport and was renamed the Isle of Man Water and Sewerage Authority.
* In 2014 the Manx Electricity Authority merged with the Isle of Man Water and Sewerage Authority to establish the Manx Utilities Authority.
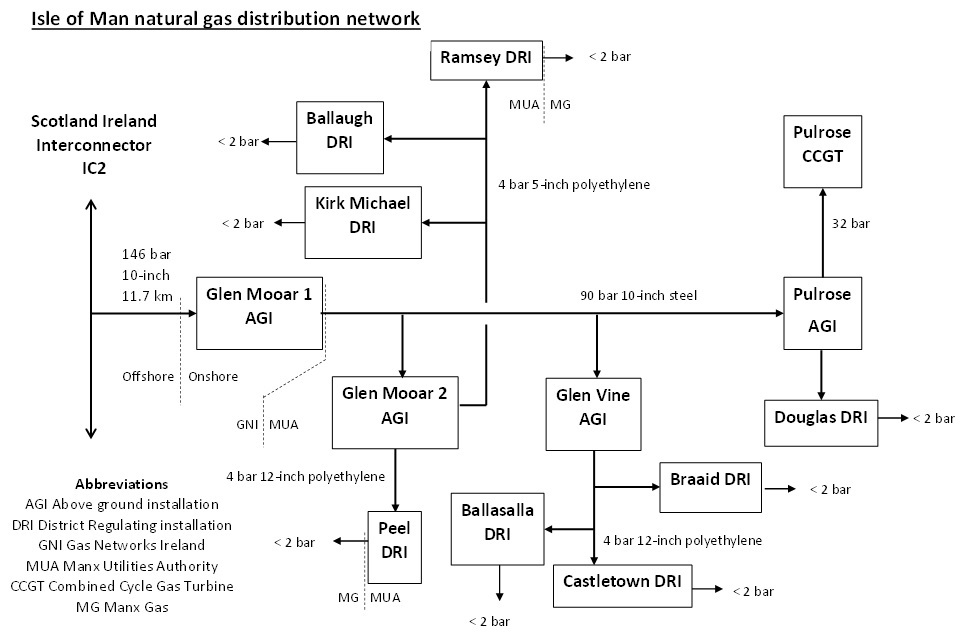 The Authority owns and operates the onshore high pressure
The Authority owns and operates the onshore high pressure
Manx Utilities
{{United Kingdom water industry Electricity authorities Water in the Isle of Man 2014 establishments in the Isle of Man Government of the Isle of Man Organisations based in the Isle of Man Public utilities established in 2014 Energy companies established in 2014 Non-renewable resource companies established in 2014 2014 establishments in the United Kingdom Energy in the Isle of Man
Isle of Man
The Isle of Man ( , also ), or Mann ( ), is a self-governing British Crown Dependency in the Irish Sea, between Great Britain and Ireland. As head of state, Charles III holds the title Lord of Mann and is represented by a Lieutenant Govern ...
. It was created in 2014 by the merging of the Manx Electricity Authority with the Isle of Man Water and Sewerage Authority.
History
 The public utilities on the Isle of Man were the responsibility of a range of organisations; over time they assumed the remit of, or were merged with, or demerged from, other bodies. These historic changes are summarised as follows and are depicted on the diagram.
* The Manx Electricity Authority was established in July 1983 to develop and maintain an efficient and economical system of electricity supply for the Island. Its legal position was established by the Electricity Act 1984.
** The Manx Electricity Authority was constituted by the merger of the Isle of Man Electricity Board (1932–1984) and the Electricity Department of the Douglas Corporation (1921–1983).
** The Manx Electricity Authority only had responsibility for the supply of electricity. These responsibilities were extended in 2003 to include the supply of gas. This was in conjunction with the construction of high pressure natural gas import system from the UK-Ireland gas interconnector. The Gas and Electricity Act 2003 empowered the Manx Electricity Authority to supply gas, and to construct pipes and associated apparatus (Section 1); it also had the duty to supply gas to other organisations such as public gas suppliers (Section2).
* The Isle of Man Water Authority, was established in 1972 by the merger of the Isle of Man Water Board (1946–1972) and the Water Department of Douglas Corporation
** In 1974 it assumed the gas production and distribution functions of the Isle of Man Gas Authority, and was renamed the Isle of Man Water and Gas Authority.
** The IoM Gas Authority (1972–1974) had assumed the responsibilities of the Gas Committee of the Tynwald (1967–1972), which in turn had assumed ownership of the Castletown, Peel and the Port St Mary gas undertakings in 1967. The Douglas and Ramsey gas undertakings were taken over by Calor Gas in 1967.
** In 1985 the gas undertaking was privatised, and the authority reverted to its previous title.
** In 2010 it assumed the sewerage responsibilities of the former Department of Transport and was renamed the Isle of Man Water and Sewerage Authority.
* In 2014 the Manx Electricity Authority merged with the Isle of Man Water and Sewerage Authority to establish the Manx Utilities Authority.
The public utilities on the Isle of Man were the responsibility of a range of organisations; over time they assumed the remit of, or were merged with, or demerged from, other bodies. These historic changes are summarised as follows and are depicted on the diagram.
* The Manx Electricity Authority was established in July 1983 to develop and maintain an efficient and economical system of electricity supply for the Island. Its legal position was established by the Electricity Act 1984.
** The Manx Electricity Authority was constituted by the merger of the Isle of Man Electricity Board (1932–1984) and the Electricity Department of the Douglas Corporation (1921–1983).
** The Manx Electricity Authority only had responsibility for the supply of electricity. These responsibilities were extended in 2003 to include the supply of gas. This was in conjunction with the construction of high pressure natural gas import system from the UK-Ireland gas interconnector. The Gas and Electricity Act 2003 empowered the Manx Electricity Authority to supply gas, and to construct pipes and associated apparatus (Section 1); it also had the duty to supply gas to other organisations such as public gas suppliers (Section2).
* The Isle of Man Water Authority, was established in 1972 by the merger of the Isle of Man Water Board (1946–1972) and the Water Department of Douglas Corporation
** In 1974 it assumed the gas production and distribution functions of the Isle of Man Gas Authority, and was renamed the Isle of Man Water and Gas Authority.
** The IoM Gas Authority (1972–1974) had assumed the responsibilities of the Gas Committee of the Tynwald (1967–1972), which in turn had assumed ownership of the Castletown, Peel and the Port St Mary gas undertakings in 1967. The Douglas and Ramsey gas undertakings were taken over by Calor Gas in 1967.
** In 1985 the gas undertaking was privatised, and the authority reverted to its previous title.
** In 2010 it assumed the sewerage responsibilities of the former Department of Transport and was renamed the Isle of Man Water and Sewerage Authority.
* In 2014 the Manx Electricity Authority merged with the Isle of Man Water and Sewerage Authority to establish the Manx Utilities Authority.
Responsibilities
The Authority is responsible for providing customers with safe, reliable, efficient and economic supplies of electricity, natural gas and clean water; as well as processing waste water. Manx Utilities has two subsidiary businesses on commercial telecommunications and subsea cable management.Electricity
Manx Utilities Authority is responsible for the generation, transmission and distribution of electricity on the island. It also exports electricity to the British National Grid as required through the Isle of Man to England Interconnector. The Authority owns and operates three power stations: * Pulrose power station * Sulby hydroelectric power station * Peel power station The Authority is responsible for 540 km of overhead power lines and 1,380 km of underground cable.Manx Utilities Authority, ''Annual Report 2020/2021'' Key electricity data is summarised in the table:Manx Utilities Authority ''Annual Reports 2015'' to 2021Natural gas
 The Authority owns and operates the onshore high pressure
The Authority owns and operates the onshore high pressure natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
transmission and distribution network from the Scotland to Ireland gas interconnector see diagram. It manages 55 km of gas pipelines, Manx Gas is responsible for the low pressure (<2 bar) local distribution systems.
Key gas data is summarised in the table:
Water
The Utility Authority has the responsibility to provide clear drinking water by collecting, treating, storing and distributing freshpotable water
Drinking water or potable water is water that is safe for ingestion, either when drunk directly in liquid form or consumed indirectly through food preparation. It is often (but not always) supplied through taps, in which case it is also calle ...
.
The Authority's water infrastructure includes:
* 4 impounding reservoir
A reservoir (; ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam, usually built to water storage, store fresh water, often doubling for hydroelectric power generation.
Reservoirs are created by controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of wa ...
s
* 2 water treatment works
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, inc ...
(Sulby and Douglas)
* 20 pumping stations
* 27 service reservoirs
* 1,800 kilometres of water mains
* 55,000 connections
Throughput:
* Annual production 10,000 megalitres of water per year.
* Summer production 35 megalitres of water per day
* Winter production 29 megalitres of water per day
Sewerage
The Utility Authority's responsibility is to manage, maintain and develop the Island'ssewerage
Sewerage (or sewage system) is the infrastructure that conveys sewage or surface runoff ( stormwater, meltwater, rainwater) using sewers. It encompasses components such as receiving drains, manholes, pumping stations, storm overflows, and scr ...
infrastructure and the sewage treatment
Sewage treatment is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable to discharge to the surrounding environment or an intended reuse application, thereby preventing water p ...
and disposal systems.
The Authority's sewerage infrastructure includes:
* Integration and Recycling of the Island's Sewage (IRIS) infrastructure
* Regional Sewage Treatment Strategy (RSTS) infrastructure
* Meary Veg wastewater facility
* 76 pumping stations
* Tanker fleet
* 18 Sewage Treatment Works
* 600 km of sewer
Throughput:
* 10,000 megalitres of waste water (sewage) per year
* 1,000 tonnes of sludge pellets are produced annually
* 1,400 septic tank
A septic tank is an underground chamber made of concrete, fiberglass, or plastic through which domestic wastewater (sewage) flows for basic sewage treatment. Settling and anaerobic digestion processes reduce solids and organics, but the treatment ...
s are emptied annually
Flood risk
The Authority formerly had responsibility for flood risk management. From November 2020 this function was transferred to the Department of Infrastructure (DOI). A Flood Management Division was established, which is responsible for Flood Risk Management.Subsidiaries
Manx Utilities has two subsidiaries * e-llan Communications Limited ** e-llan Communications Ltd provides high bandwidth communication facilities over a fibre optic cable. The cable is buried under the seabed alongside the UK - IOM interconnector power cable. * Manx Cable Company Limited ** Manx Cable Company Limited operates and maintains the 40 MW 90 kV electrical interconnector subsea cable between the Isle of Man and the UK.See also
* List of power stations in the British Crown Dependencies * Isle of Man gas industry * Isle of Man to England InterconnectorReferences
External links
Manx Utilities
{{United Kingdom water industry Electricity authorities Water in the Isle of Man 2014 establishments in the Isle of Man Government of the Isle of Man Organisations based in the Isle of Man Public utilities established in 2014 Energy companies established in 2014 Non-renewable resource companies established in 2014 2014 establishments in the United Kingdom Energy in the Isle of Man