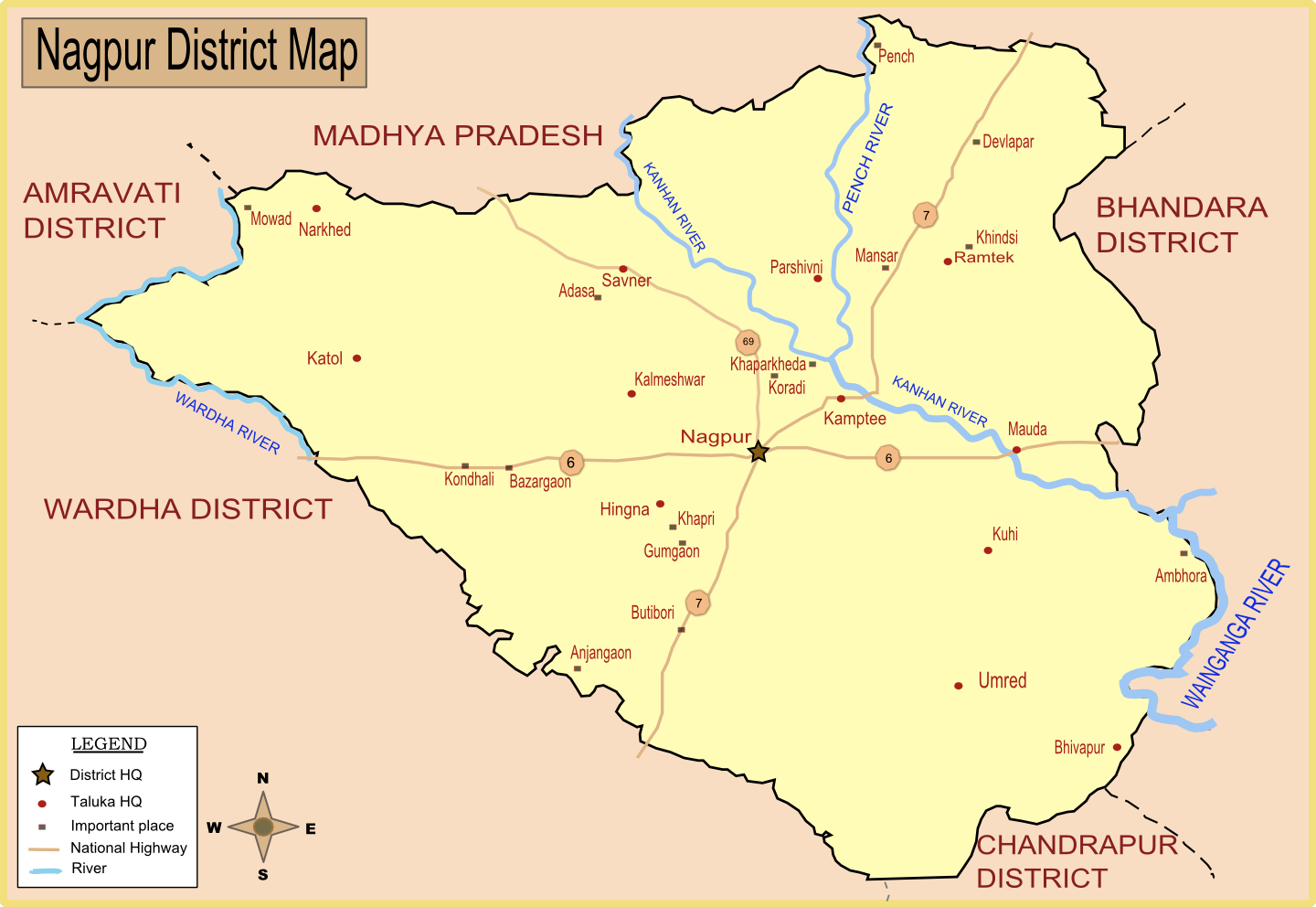
Mansar, India on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mansar is a
 In 1972, an image of a deity, later identified as ''Shiva Vamana'' was found from a hillock in Mansar, locally known as ''Hidimba Tekri''. Important excavations were carried out at the ancient sites of Mansar since 1997-98, under the aegis of the ''Bodhisatva Nagarjun Smarak Samstha Va Anusandhan Kendra'', Nagpur and under the directions of Jagat Pati Joshi and A. K. Sharma. So far 5 sites have been excavated in Mansar, which are designated as MNS 1, MNS 2, MNS 3, MNS 4 and MNS 5.
Exposed Brick Structures containing the Buddhist Monastery, Buddhist Box Pattern Stupa, Small Temples and the Palace Structure. Various Stone images also exposed during the Excavation. Identified as the Capital of Vakatakas. The evidence of Purushamedha and the construction of Sheyna-Chiti is the important point.
These excavations have resulted in the discovery of various shrines (MNS 3, 4, 5) and a palace complex (MNS 2), identified as Pravarapura, the capital of the
In 1972, an image of a deity, later identified as ''Shiva Vamana'' was found from a hillock in Mansar, locally known as ''Hidimba Tekri''. Important excavations were carried out at the ancient sites of Mansar since 1997-98, under the aegis of the ''Bodhisatva Nagarjun Smarak Samstha Va Anusandhan Kendra'', Nagpur and under the directions of Jagat Pati Joshi and A. K. Sharma. So far 5 sites have been excavated in Mansar, which are designated as MNS 1, MNS 2, MNS 3, MNS 4 and MNS 5.
Exposed Brick Structures containing the Buddhist Monastery, Buddhist Box Pattern Stupa, Small Temples and the Palace Structure. Various Stone images also exposed during the Excavation. Identified as the Capital of Vakatakas. The evidence of Purushamedha and the construction of Sheyna-Chiti is the important point.
These excavations have resulted in the discovery of various shrines (MNS 3, 4, 5) and a palace complex (MNS 2), identified as Pravarapura, the capital of the
Mansar Excavations 1998-2004: The Discovery of Pravarapur
Puramanthana 3, 1-26 Cities and towns in Nagpur district Archaeological sites in Maharashtra Tourist attractions in Nagpur
census town
In India and some other countries, a census town is designated as a town that satisfies certain characteristics.
India
In India, a census town is one which is not statutorily notified and administered as a town, but nevertheless whose population ...
in Ramtek tehsil
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluk, or taluka () is a local unit of administrative division in India and Pakistan. It is a subdistrict of the area within a Zila (country subdivision), district including the designated populated place that ser ...
of Nagpur district
Nagpur district (Marathi pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, aːɡpuːɾ is a Districts of Maharashtra, district in the Vidarbha region of Maharashtra state in central India. The city of Nagpur is the district administrative centre. The district ...
in the India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
n state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
of Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
. This town is located 5 km west of Ramtek
Ramtek is a city and municipal council in Nagpur district of Maharashtra, India.
Religious significance
Ramtek hosts a historic temple of Rama. It is believed that Ramtek was the place where Rama, the Hindu god, rested while he was in exile, ...
and 45 km northeast of Nagpur
Nagpur (; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Nāgapura'') is the second capital and third-largest city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is called the heart of India because of its central geographical location. It is the largest and most populated city i ...
city.
Geography
Mansar is located at . It has an average elevation of 471metre
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of ...
s (1545 feet
The foot (: feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is an organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of ...
).

History
Vakataka
The Vakataka dynasty () was an ancient Indian dynasty that originated from the Deccan in the mid-3rd century CE. Their state is believed to have extended from the southern edges of Malwa and Gujarat in the north to the Tungabhadra River in the ...
king Pravarasena II (1st half of 5th century). Adjacent to this palace, on ''Hidimba Tekri'' (MNS 3), an extensive temple complex has been unearthed, identified as ''Pravareśvara''. A 3 m tall lime model of a male human figure in crouching position was found underneath one of the terraces of MNS 3. Significant 5th-century sculptures of Hindu deities, artefacts and some coins have been discovered in the excavations.
The water reservoir around the site and findings of ancient tools and other objects point to the fact that a large population inhabited the area 1600 years ago. The discovery has made Mansar one of the prime archaeological sites in the country
Demographics
Indiacensus
A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given Statistical population, population, usually displayed in the form of stati ...
, Mansar had a population of 6458. Males constitute 50% of the population and females 50%. Mansar has an average literacy rate of 69%, higher than the national average of 59.5%: male literacy is 76%, and female literacy is 61%. In Mansar, 13% of the population is under 6 years of age.
References
{{commons category, MansarFurther reading
*Joshi, Jagadpati; Sharma, A.K. (2005)Mansar Excavations 1998-2004: The Discovery of Pravarapur
Puramanthana 3, 1-26 Cities and towns in Nagpur district Archaeological sites in Maharashtra Tourist attractions in Nagpur