Manatee County Courthouses (other) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Manatees ( family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing three of the four living species in the order Sirenia: the
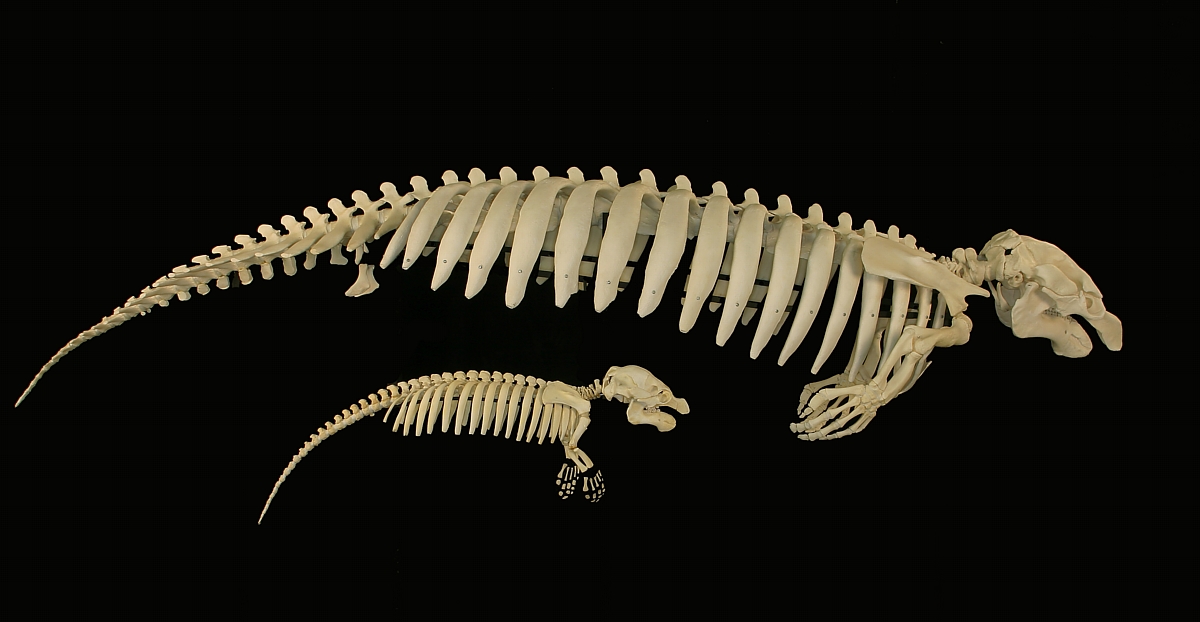
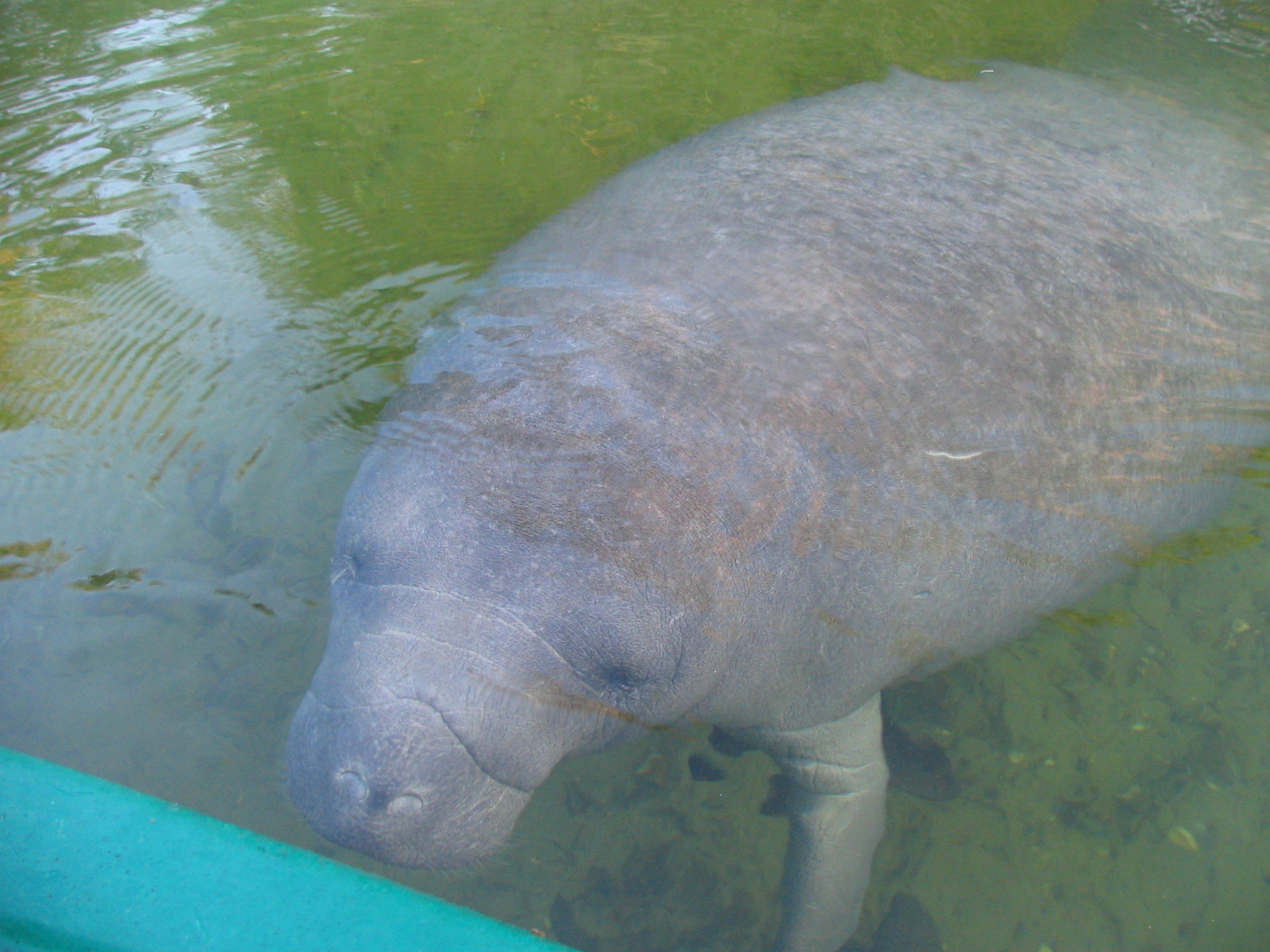
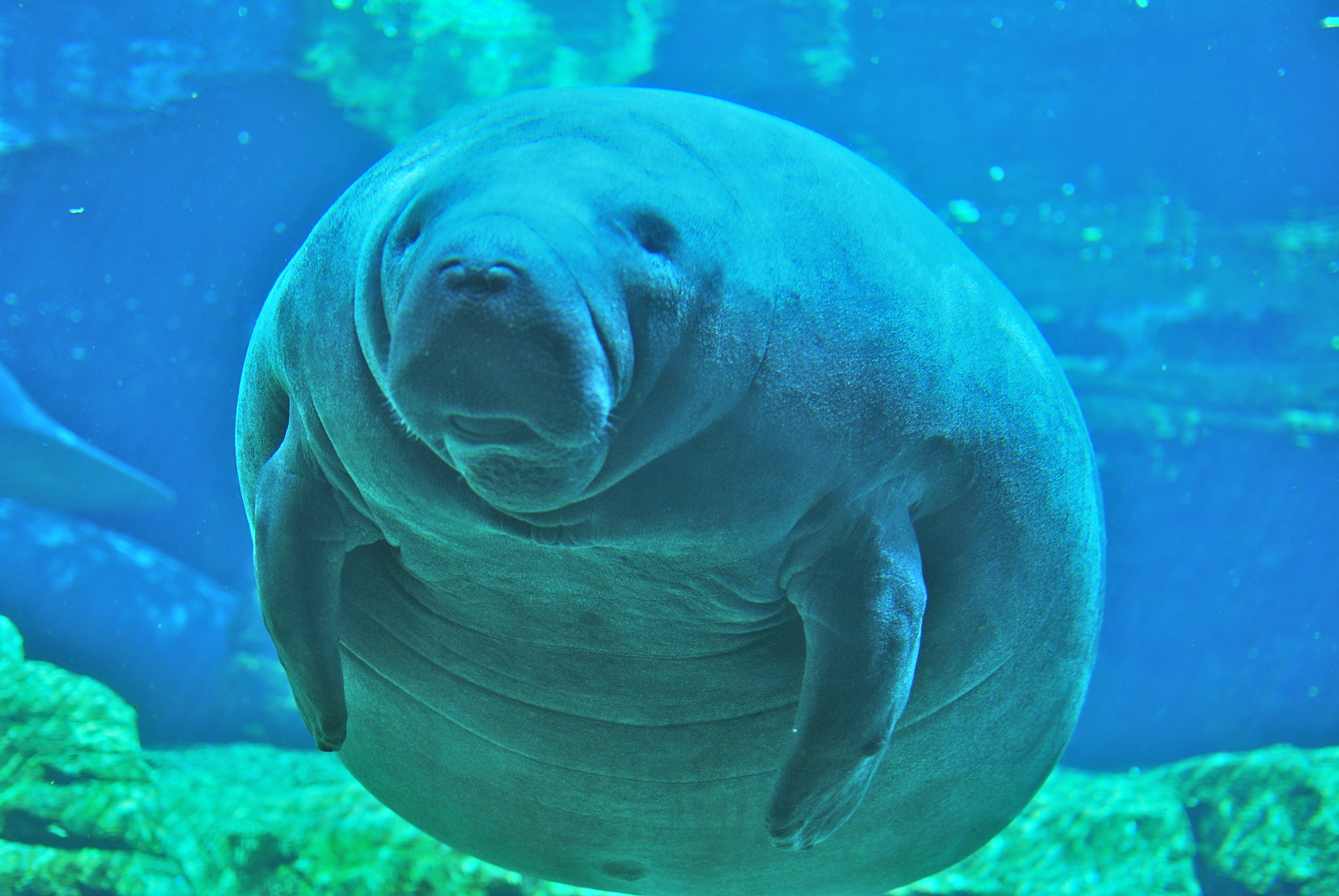
 Manatees weigh , and average in length, sometimes growing to and and females tend to be larger and heavier than males. At birth, baby manatees weigh about each. The female manatee has two teats, one under each flipper, a characteristic that was used to make early links between the manatee and elephants.
The lids of manatees' small, widely spaced eyes close in a circular manner. The manatee has a large, flexible, prehensile upper lip, used to gather food and eat and for social interaction and communication. Manatees have shorter snouts than their fellow sirenians, the dugongs.
Manatee adults have no incisor or
Manatees weigh , and average in length, sometimes growing to and and females tend to be larger and heavier than males. At birth, baby manatees weigh about each. The female manatee has two teats, one under each flipper, a characteristic that was used to make early links between the manatee and elephants.
The lids of manatees' small, widely spaced eyes close in a circular manner. The manatee has a large, flexible, prehensile upper lip, used to gather food and eat and for social interaction and communication. Manatees have shorter snouts than their fellow sirenians, the dugongs.
Manatee adults have no incisor or
 Apart from mothers with their young, or males following a receptive female, manatees are generally solitary animals. Manatees spend approximately 50% of the day sleeping submerged, surfacing for air regularly at intervals of less than 20 minutes. The remainder of the time is mostly spent grazing in shallow waters at depths of . The Florida subspecies (''T. m. latirostris'') has been known to live up to 60 years.
Apart from mothers with their young, or males following a receptive female, manatees are generally solitary animals. Manatees spend approximately 50% of the day sleeping submerged, surfacing for air regularly at intervals of less than 20 minutes. The remainder of the time is mostly spent grazing in shallow waters at depths of . The Florida subspecies (''T. m. latirostris'') has been known to live up to 60 years.
 Manatees are capable of understanding discrimination tasks and show signs of complex associative learning. They also have good long-term memory. They demonstrate discrimination and task-learning abilities similar to dolphins and pinnipeds in acoustic and visual studies.(Marine Mammal Medicine, 2001, Leslie Dierauf & Frances Gulland, CRC Press) Social interactions between manatees are highly complex and intricate, which may indicate higher intelligence than previously thought, although they remain poorly understood by science.
Manatees are capable of understanding discrimination tasks and show signs of complex associative learning. They also have good long-term memory. They demonstrate discrimination and task-learning abilities similar to dolphins and pinnipeds in acoustic and visual studies.(Marine Mammal Medicine, 2001, Leslie Dierauf & Frances Gulland, CRC Press) Social interactions between manatees are highly complex and intricate, which may indicate higher intelligence than previously thought, although they remain poorly understood by science.
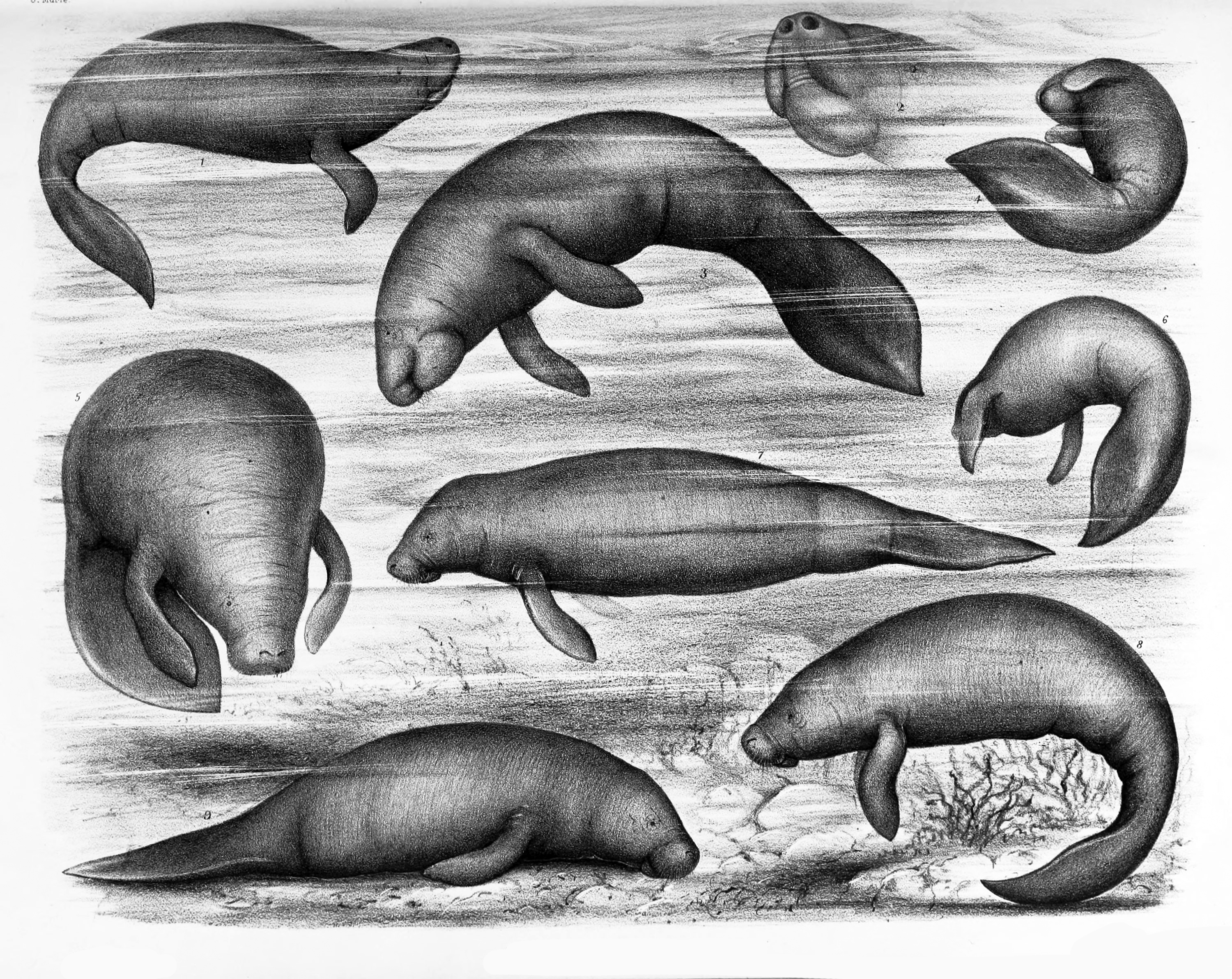
 Manatees use their flippers to "walk" along the bottom whilst they dig for plants and roots in the substrate. When plants are detected, the flippers are used to scoop the vegetation toward the manatee's lips. The manatee has prehensile lips; the upper lip pad is split into left and right sides which can move independently. The lips use seven muscles to manipulate and tear at plants. Manatees use their lips and front flippers to move the plants into the mouth. The manatee does not have front teeth, however, behind the lips, on the roof of the mouth, there are dense, ridged pads. These horny ridges, and the manatee's lower jaw, tear through ingested plant material.
Manatees use their flippers to "walk" along the bottom whilst they dig for plants and roots in the substrate. When plants are detected, the flippers are used to scoop the vegetation toward the manatee's lips. The manatee has prehensile lips; the upper lip pad is split into left and right sides which can move independently. The lips use seven muscles to manipulate and tear at plants. Manatees use their lips and front flippers to move the plants into the mouth. The manatee does not have front teeth, however, behind the lips, on the roof of the mouth, there are dense, ridged pads. These horny ridges, and the manatee's lower jaw, tear through ingested plant material.

 Manatees inhabit the shallow, marshy coastal areas and rivers of the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico (''T. manatus'', West Indian manatee), the
Manatees inhabit the shallow, marshy coastal areas and rivers of the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico (''T. manatus'', West Indian manatee), the


 These veterinarians go on to state:
One quarter of annual manatee deaths in Florida are caused by boat collisions with manatees. In 2009, of the 429 Florida manatees recorded dead, 97 were killed by commercial and recreational vessels, which broke the earlier record number of 95 set in 2002.
These veterinarians go on to state:
One quarter of annual manatee deaths in Florida are caused by boat collisions with manatees. In 2009, of the 429 Florida manatees recorded dead, 97 were killed by commercial and recreational vessels, which broke the earlier record number of 95 set in 2002.
 There are a number of manatee rehabilitation centers in the United States. These include three government-run critical care facilities in Florida at Lowry Park Zoo, Miami Seaquarium, and SeaWorld Orlando. After initial treatment at these facilities, the manatees are transferred to rehabilitation facilities before release. These include the
There are a number of manatee rehabilitation centers in the United States. These include three government-run critical care facilities in Florida at Lowry Park Zoo, Miami Seaquarium, and SeaWorld Orlando. After initial treatment at these facilities, the manatees are transferred to rehabilitation facilities before release. These include the
Save the Manatee
Murie, James ''On the Form and Structure of the Manatee'' (''Manatus americanus''), (1872) London, Zoological Society of London Year
Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission
Reuters: Florida manatees may lose endangered status
''Bibliography and Index of the Sirenia and Desmostylia'' – Dr. Domning's authoritative manatee research bibliography
{{Authority control Sirenians Mammal families Extant Pleistocene first appearances Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Taxa named by Theodore Gill
Amazonian manatee
The Amazonian manatee (''Trichechus inunguis'') is a species of manatee that lives in the Amazon Basin in Brazil, Peru, Colombia and Ecuador. It has thin, wrinkled brownish or gray colored skin, with fine hairs scattered over its body and a whit ...
(''Trichechus inunguis''), the West Indian manatee (''Trichechus manatus''), and the West African manatee (''Trichechus senegalensis''). They measure up to long, weigh as much as , and have paddle-like tails.
Manatees are herbivores and eat over 60 different freshwater and saltwater plants. Manatees inhabit the shallow, marshy coastal areas and rivers of the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico, the Amazon basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivi ...
, and West Africa.
The main causes of death for manatees are human-related issues, such as habitat destruction and human objects. Their slow-moving, curious nature has led to violent collisions with propeller-driven boats and ships. Some manatees have been found with over 50 scars on them from propeller blades. Natural causes of death include adverse temperatures, predation by crocodiles on young, and disease.
Etymology
The etymology of the name is unclear, with connections having been made to Latin "hand" and to pre-Columbian Taíno ''manati'' "breast". The term ''sea cow'' is a reference to the species' slow, peaceful, herbivorous nature, reminiscent of that of bovines.Taxonomy
Manatees are three of the four living species in the order Sirenia. The fourth is theEastern Hemisphere
The Eastern Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth which is east of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and west of the antimeridian (which crosses the Pacific Ocean and relatively little land from pole to pol ...
's dugong. The Sirenia are thought to have evolved from four-legged land mammals more than 60 million years ago, with the closest living relatives being the Proboscidea
The Proboscidea (; , ) are a taxonomic order of afrotherian mammals containing one living family (Elephantidae) and several extinct families. First described by J. Illiger in 1811, it encompasses the elephants and their close relatives. From ...
( elephants) and Hyracoidea (hyrax
Hyraxes (), also called dassies, are small, thickset, herbivorous mammals in the order Hyracoidea. Hyraxes are well-furred, rotund animals with short tails. Typically, they measure between long and weigh between . They are superficially simil ...
es).
Description

 Manatees weigh , and average in length, sometimes growing to and and females tend to be larger and heavier than males. At birth, baby manatees weigh about each. The female manatee has two teats, one under each flipper, a characteristic that was used to make early links between the manatee and elephants.
The lids of manatees' small, widely spaced eyes close in a circular manner. The manatee has a large, flexible, prehensile upper lip, used to gather food and eat and for social interaction and communication. Manatees have shorter snouts than their fellow sirenians, the dugongs.
Manatee adults have no incisor or
Manatees weigh , and average in length, sometimes growing to and and females tend to be larger and heavier than males. At birth, baby manatees weigh about each. The female manatee has two teats, one under each flipper, a characteristic that was used to make early links between the manatee and elephants.
The lids of manatees' small, widely spaced eyes close in a circular manner. The manatee has a large, flexible, prehensile upper lip, used to gather food and eat and for social interaction and communication. Manatees have shorter snouts than their fellow sirenians, the dugongs.
Manatee adults have no incisor or canine
Canine may refer to:
Zoology and anatomy
* a dog-like Canid animal in the subfamily Caninae
** '' Canis'', a genus including dogs, wolves, coyotes, and jackals
** Dog, the domestic dog
* Canine tooth, in mammalian oral anatomy
People with the ...
teeth, just a set of cheek teeth, which are not clearly differentiated into molars and premolar
The premolars, also called premolar teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant in the permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth ...
s. These teeth are repeatedly replaced throughout life, with new teeth growing at the rear as older teeth fall out from farther forward in the mouth, somewhat as elephants' teeth do. At any time, a manatee typically has no more than six teeth in each jaw of its mouth.
The manatee's tail is paddle-shaped, and is the clearest visible difference between manatees and dugongs; a dugong tail is fluked, similar in shape to that of a whale.
The manatee is unusual among mammals in having just six cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In ...
, a number that may be due to mutations in the homeotic genes In evolutionary developmental biology, homeotic genes are genes which regulate the development of anatomical structures in various organisms such as echinoderms, insects, mammals, and plants. Homeotic genes often encode transcription factors, transc ...
. All other mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, other than the two-toed and three-toed sloths.
Like the horse, the manatee has a simple stomach, but a large cecum, in which it can digest tough plant matter. Generally, the intestines are about 45 meters, unusually long for an animal of the manatee's size.
Evolution
Fossil remains of manatee ancestors - also known as sirenians - date back to theEarly Eocene
In the geologic timescale the Ypresian is the oldest age or lowest stratigraphic stage of the Eocene. It spans the time between , is preceded by the Thanetian Age (part of the Paleocene) and is followed by the Eocene Lutetian Age. The Ypresian i ...
. It is thought that they reached the isolated area of the South American continent and became known as Trichechidae. In the Late Miocene
The Late Miocene (also known as Upper Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made up of two faunal stage, stages. The Tortonian and Messinian stages comprise the Late Miocene sub-epoch, which lasted from 11.63 Ma (million ye ...
, trichechids were likely restricted in South American coastal rivers and they fed on many freshwater plants. Dugongs inhabited the West Atlantic and Caribbean waters and fed on seagrass meadows instead. As the sea grasses began to grow, manatees adapted to the changing environment by growing supernumerary molars. Sea levels lowered and increased erosion and silt runoff was caused by glaciation. This increased the tooth wear of the bottom-feeding manatees.
Behavior
 Apart from mothers with their young, or males following a receptive female, manatees are generally solitary animals. Manatees spend approximately 50% of the day sleeping submerged, surfacing for air regularly at intervals of less than 20 minutes. The remainder of the time is mostly spent grazing in shallow waters at depths of . The Florida subspecies (''T. m. latirostris'') has been known to live up to 60 years.
Apart from mothers with their young, or males following a receptive female, manatees are generally solitary animals. Manatees spend approximately 50% of the day sleeping submerged, surfacing for air regularly at intervals of less than 20 minutes. The remainder of the time is mostly spent grazing in shallow waters at depths of . The Florida subspecies (''T. m. latirostris'') has been known to live up to 60 years.
Locomotion
Generally, manatees swim at about . However, they have been known to swim at up to in short bursts.Intelligence and learning
 Manatees are capable of understanding discrimination tasks and show signs of complex associative learning. They also have good long-term memory. They demonstrate discrimination and task-learning abilities similar to dolphins and pinnipeds in acoustic and visual studies.(Marine Mammal Medicine, 2001, Leslie Dierauf & Frances Gulland, CRC Press) Social interactions between manatees are highly complex and intricate, which may indicate higher intelligence than previously thought, although they remain poorly understood by science.
Manatees are capable of understanding discrimination tasks and show signs of complex associative learning. They also have good long-term memory. They demonstrate discrimination and task-learning abilities similar to dolphins and pinnipeds in acoustic and visual studies.(Marine Mammal Medicine, 2001, Leslie Dierauf & Frances Gulland, CRC Press) Social interactions between manatees are highly complex and intricate, which may indicate higher intelligence than previously thought, although they remain poorly understood by science.
Reproduction
Manatees typically breed once every two years; generally only a single calf is born.Gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregna ...
lasts about 12 months and to wean the calf takes a further 12 to 18 months, although females may have more than one estrous cycle per year.
Communication
Manatees emit a wide range of sounds used in communication, especially between cows and their calves. Their ears are large internally but the external openings are small, and they are located four inches behind each eye. Adults communicate to maintain contact and during sexual and play behaviors. Taste and smell, in addition to sight, sound, and touch, may also be forms of communication.Diet
Manatees are herbivores and eat over 60 different freshwater (e.g., floating hyacinth, pickerel weed, alligator weed, water lettuce, hydrilla, water celery, musk grass, mangrove leaves) and saltwater plants (e.g., sea grasses, shoal grass, manatee grass,turtle grass
''Thalassia testudinum'', commonly known as turtlegrass, is a species of Marine (ocean), marine seagrass. It forms meadows in shallow sandy or muddy locations in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. Turtle grass and other seagrasses form sea ...
, widgeon grass, sea clover, and marine algae). Using their divided upper lip, an adult manatee will commonly eat up to 10%–15% of their body weight (about 50 kg) per day. Consuming such an amount requires the manatee to graze for up to seven hours a day. To be able to cope with the high levels of cellulose in their plant based diet, manatees utilize hindgut fermentation to help with the digestion process. Manatees have been known to eat small numbers of fish from nets.
Feeding behavior
 Manatees use their flippers to "walk" along the bottom whilst they dig for plants and roots in the substrate. When plants are detected, the flippers are used to scoop the vegetation toward the manatee's lips. The manatee has prehensile lips; the upper lip pad is split into left and right sides which can move independently. The lips use seven muscles to manipulate and tear at plants. Manatees use their lips and front flippers to move the plants into the mouth. The manatee does not have front teeth, however, behind the lips, on the roof of the mouth, there are dense, ridged pads. These horny ridges, and the manatee's lower jaw, tear through ingested plant material.
Manatees use their flippers to "walk" along the bottom whilst they dig for plants and roots in the substrate. When plants are detected, the flippers are used to scoop the vegetation toward the manatee's lips. The manatee has prehensile lips; the upper lip pad is split into left and right sides which can move independently. The lips use seven muscles to manipulate and tear at plants. Manatees use their lips and front flippers to move the plants into the mouth. The manatee does not have front teeth, however, behind the lips, on the roof of the mouth, there are dense, ridged pads. These horny ridges, and the manatee's lower jaw, tear through ingested plant material.
Dentition
Manatees have four rows of teeth. There are 6 to 8 high-crowned, open-rooted molars located along each side of the upper and lower jaw giving a total of 24 to 32 flat, rough-textured teeth. Eating gritty vegetation abrades the teeth, particularly the enamel crown; however, research indicates that the enamel structure in manatee molars is weak. To compensate for this, manatee teeth are continually replaced. When anterior molars wear down, they are shed. Posterior molars erupt at the back of the row and slowly move forward to replace these like enamel crowns on a conveyor belt, similarly to elephants. This process continues throughout the manatee's lifetime. The rate at which the teeth migrate forward depends on how quickly the anterior teeth abrade. Some studies indicate that the rate is about 1 cm/month although other studies indicate 0.1 cm/month.Ecology
Range and habitat

 Manatees inhabit the shallow, marshy coastal areas and rivers of the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico (''T. manatus'', West Indian manatee), the
Manatees inhabit the shallow, marshy coastal areas and rivers of the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico (''T. manatus'', West Indian manatee), the Amazon basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivi ...
(''T. inunguis'', Amazonian manatee
The Amazonian manatee (''Trichechus inunguis'') is a species of manatee that lives in the Amazon Basin in Brazil, Peru, Colombia and Ecuador. It has thin, wrinkled brownish or gray colored skin, with fine hairs scattered over its body and a whit ...
), and West Africa (''T. senegalensis'', West African manatee).
West Indian manatees prefer warmer temperatures and are known to congregate in shallow waters. They frequently migrate through brackish water estuaries to freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ...
springs
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a he ...
. They cannot survive below 15 °C (60 °F). Their natural source for warmth during winter is warm, spring-fed rivers.
West Indian
The coast of the state of Georgia is usually the northernmost range of the West Indian manatees because their low metabolic rate does not protect them in cold water. Prolonged exposure to water below 20 °C (68 °F) can cause "cold stress syndrome" and death. Florida manatees can move freely between fresh water and salt water. Manatees have been seen as far north as Cape Cod, and in 1995 and again in 2006, one was seen in New York City and Rhode Island's Narragansett Bay. A manatee was spotted in the Wolf River harbor near the Mississippi River in downtown Memphis in 2006, and was later found dead downriver in McKellar Lake. Another manatee was found dead on a New Jersey beach in February 2020, considered especially unusual given the time of year. At the time of the manatee's discovery, the water temperature in the area was below 6.5 °C (43.7 °F). The West Indian manatee migrates into Florida rivers—such as the Crystal, the Homosassa, and the Chassahowitzka rivers, whose headsprings are 22 °C (72 °F) all year. Between November and March each year, about 600 West Indian manatees gather in the rivers inCitrus County, Florida
Citrus County is a county located on the west central coast of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 153,843. Its county seat is Inverness, and its largest community is Homosassa Springs.
Citrus County comprise ...
such as the Crystal River National Wildlife Refuge.
In winter, manatees often gather near the warm-water outflows of power plants along the Florida coast, instead of migrating south as they once did. Some conservationists are concerned that these manatees have become too reliant on these artificially warmed areas. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service is trying to find a new way to heat the water for manatees that depended on plants that have closed.
Studies suggest that Florida manatees need access to fresh water for proper regulation of water and salts in their bodies.
Accurate population estimates of the Florida manatee (''T. manatus'') are difficult. They have been called scientifically weak because they vary widely from year to year, some areas showing increases, others decreases, and little strong evidence of increases except in two areas. Manatee counts are highly variable without an accurate way to estimate numbers: In Florida in 1996, a winter survey found 2,639 manatees; in 1997, a January survey found 2,229, and a February survey found 1,706. A statewide synoptic survey in January 2010 found 5,067 manatees living in Florida, the highest number recorded to that time.
As of January 2016, the USFWS estimates the range-wide manatee population to be at least 13,000; as of January 2018, at least 6,100 are estimated to be in Florida.
Population viability
Population viability analysis (PVA) is a species-specific method of risk assessment frequently used in conservation biology.
It is traditionally defined as the process that determines the probability that a population will go extinct within a given ...
studies conducted in 1997 found that decreasing adult survival and eventual extinction were a probable future outcome for Florida manatees unless they got more protection. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service proposed downgrading the manatee's status from endangered to threatened in January 2016 after more than 40 years of the manatee's being classified as on the endangered.
Amazonian
The freshwater Amazonian manatee (''T. inunguis'') inhabits the Central Amazon Basin in Brazil, easternPerú
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy fo ...
, southeastern Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
, but not Ecuador. It is the only exclusively freshwater manatee, and is also the smallest. Since they are unable to reduce peripheral heat loss, it is found primarily in tropical waters.
West African
They are found in coastal marine and estuarine habitats, and in freshwater river systems along the west coast of Africa from theSenegal River
,french: Fleuve Sénégal)
, name_etymology =
, image = Senegal River Saint Louis.jpg
, image_size =
, image_caption = Fishermen on the bank of the Senegal River estuary at the outskirts of Saint-Louis, Senegal ...
south to the Cuanza River in Angola. They live as far upriver on the Niger River as Koulikoro in Mali, from the coast.
Predation
In relation to the threat posed by humans, predation does not present a significant threat to manatees. When threatened, the manatee's response is to dive as deeply as it can, suggesting that threats have most frequently come from land dwellers such as humans rather than from other water-dwelling creatures such as caimans or sharks.Relation to humans

Threats
The main causes of death for manatees are human-related issues, such as habitat destruction and human objects. Natural causes of death include adverse temperatures, predation by crocodiles on young, and disease.Ship strikes
Their slow-moving, curious nature, coupled with dense coastal development, has led to many violent collisions with propeller-driven boats and ships, leading frequently to maiming, disfigurement, and even death. As a result, a large proportion of manatees exhibit spiral cutting propeller scars on their backs, usually caused by larger vessels that do not have skegs in front of the propellers like the smaller outboard and inboard-outboard recreational boats have. They are now even identified by humans based on their scar patterns. Many manatees have been cut in two by large vessels like ships and tug boats, even in the highly populated lower St. Johns River's narrow channels. Some are concerned that the current situation is inhumane, with upwards of 50 scars and disfigurements from vessel strikes on a single manatee. Often, the lacerations lead to infections, which can prove fatal. Internal injuries stemming from being trapped between hulls and docks and impacts have also been fatal. Recent testing shows that manatees may be able to hear speed boats and other watercraft approaching, due to the frequency the boat makes. However, a manatee may not be able to hear the approaching boats when they are performing day-to-day activities or distractions. The manatee has a tested frequency range of 8 to 32 kilohertz. Manatees hear on a higher frequency than would be expected for such large marine mammals. Many large boats emit very low frequencies, which confuse the manatee and explain their lack of awareness around boats. The Lloyd's mirror effect results in low frequency propeller sounds not being discernible near the surface, where most accidents occur. Research indicates that when a boat has a higher frequency the manatees rapidly swim away from danger. In 2003, a population model was released by the United States Geological Survey that predicted an extremely grave situation confronting the manatee in both the Southwest and Atlantic regions where the vast majority of manatees are found. It states, According to marine mammal veterinarians: These veterinarians go on to state:
One quarter of annual manatee deaths in Florida are caused by boat collisions with manatees. In 2009, of the 429 Florida manatees recorded dead, 97 were killed by commercial and recreational vessels, which broke the earlier record number of 95 set in 2002.
These veterinarians go on to state:
One quarter of annual manatee deaths in Florida are caused by boat collisions with manatees. In 2009, of the 429 Florida manatees recorded dead, 97 were killed by commercial and recreational vessels, which broke the earlier record number of 95 set in 2002.
Red tide
Another cause of manatee deaths are red tides, a term used for the proliferation, or "blooms", of the microscopic marine algae ''Karenia brevis
''Karenia brevis'' is a microscopic, single-celled, photosynthetic organism in the genus '' Karenia''. It is a marine dinoflagellate commonly found in the waters of the Gulf of Mexico. It is the organism responsible for the "Florida red tides" t ...
''. This dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are ...
produces brevetoxins that can have toxic effects on the central nervous system of animals.
In 1996, a red tide was responsible for 151 manatee deaths in Florida. The bloom was present from early March to the end of April and killed approximately 15% of the known population of manatees along South Florida's western coast.
Other blooms in 1982 and 2005 resulted in 37 and 44 deaths, respectively.
Starvation
In 2021 a massive die-off of seagrass along the Atlantic coast of Florida left manatees without enough food to eat. As a result of this ecological disaster Florida's manatees began dying at an alarming rate, largely fromstarvation
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, dea ...
. In early 2022 the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service began a feeding program to address the situation by distributing 3,000 pounds (1,361 kg) of lettuce per day to save the malnourished animals.
Additional threats
Manatees can also be crushed and isolated in water control structures (navigation locks, floodgates, etc.) and are occasionally killed by entanglement in fishing gear, such as crab pot float lines, box traps, and shark nets. While humans are allowed to swim with manatees in one area of Florida, there have been numerous charges of people harassing and disturbing the manatees. According to the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, approximately 99 manatee deaths each year are related to human activities. In January 2016, there were 43 manatee deaths in Florida alone.Conservation
All three species of manatee are listed by the World Conservation Union as vulnerable to extinction. However, The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS) does not consider the West Indian manatee to be "endangered" anymore, having downgraded its status to "threatened" as of March 2017. They cite improvements to habitat conditions, population growth and reductions of threats as reasoning for the change. The reclassification was met with controversy, with Florida congressman Vern Buchanan and groups such as the Save the Manatee Club and the Center for Biological Diversity expressing concerns that the change would have a detrimental effect on conservation efforts. The new classification will not affect current federal protections. West Indian manatees were originally classified as endangered with the 1967 class of endangered species. Manatee population in the United States reached a low in the 1970s, during which only a few hundred individuals lived in the nation. As of February 2016, 6,250 manatees were reported swimming in Florida's springs. It is illegal under federal and Florida law to injure or harm a manatee. There are many conservation programs that have been created to help manatees.Save the Manatee Club
Save the Manatee (SMC) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit group and membership organization dedicated to the conservation of manatees. The organization was founded in 1981 by singer and songwriter Jimmy Buffett, and Governor of Florida (and later U.S. Sen ...
is a non-profit group and membership organization that works to protect manatees and their aquatic ecosystems. Founded by Bob Graham
Daniel Robert "Bob" Graham (born November 9, 1936) is an American lawyer, author, and politician who served as the 38th governor of Florida from 1979 to 1987 and a United States senator from Florida from 1987 to 2005. He is a member of the Dem ...
, former Florida governor, and singer/songwriter Jimmy Buffett
James William Buffett (born December 25, 1946) is an American singer-songwriter, musician, author, and businessman. He is best known for his music, which often portrays an "island escapism" lifestyle. Together with his Coral Reefer Band, Buffet ...
, this is today's leading manatee conservation club.
The MV ''Freedom Star'' and MV ''Liberty Star'', ships used by NASA to tow Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Boosters back to Kennedy Space Center, were propelled only by water jets to protect the endangered manatee population that inhabits regions of the Banana River where the ships are based.
Brazil outlawed hunting in 1973 in an effort to preserve the species. Deaths by boat strikes are still common. Although countries are protecting Amazonian manatees in the locations where they are endangered, as of 1994 there were no enforced laws, and the manatees were still being captured throughout their range.
Captivity
Cincinnati Zoo and Botanical Garden
The Cincinnati Zoo & Botanical Garden is the sixth oldest zoo in the United States, founded in 1873 and officially opening in 1875. It is located in the Avondale neighborhood of Cincinnati, Ohio. It originally began with in the middle of the c ...
, Columbus Zoo and Aquarium, Epcot's The Seas, South Florida Museum, and Homosassa Springs Wildlife State Park.
The Columbus Zoo was a founding member of the Manatee Rehabilitation Partnership in 2001. Since 1999, the zoo's Manatee Bay facility has helped rehabilitate 20 manatees. The Cincinnati Zoo has rehabilitated and released more than a dozen manatees since 1999.
Manatees can also be viewed in a number of European zoos, such as the Tierpark Berlin and the Nuremberg Zoo in Germany, in ZooParc de Beauval in France, the Aquarium of Genoa in Italy and the Royal Burgers' Zoo in Arnhem, the Netherlands, where manatees have parented offspring. The River Safari at Singapore features seven of them.
The oldest manatee in captivity was Snooty
Snooty (July 21, 1948 – July 23, 2017) was a male Florida manatee that resided at the Bishop Museum of Science and Nature's Parker Manatee Aquarium in Bradenton, Florida. He was one of the first recorded captive manatee births, and at age 69, ...
, at the South Florida Museum's Parker Manatee Aquarium in Bradenton, Florida
Bradenton ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Manatee County, Florida, Manatee County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, the city's population is 55,698.
History
Late 18th and early 19th centuries ...
. Born at the Miami Aquarium and Tackle Company on July 21, 1948, Snooty was one of the first recorded captive manatee births. Raised entirely in captivity, Snooty was never to be released into the wild. As such he was the only manatee at the aquarium, and one of only a few captive manatees in the United States that was allowed to interact with human handlers. That made him uniquely suitable for manatee research and education.
Snooty died suddenly two days after his 69th birthday, July 23, 2017, when he was found in an underwater area only used to access plumbing for the exhibit life support system. The South Florida Museum's initial press release stated, “Early indications are that an access panel door that is normally bolted shut had somehow been knocked loose and that Snooty was able to swim in.”Guyana
Since the 19th century,Georgetown, Guyana
Georgetown is the capital (political), capital and largest city of Guyana. It is situated in Demerara-Mahaica, region 4, on the Atlantic Ocean coast, at the mouth of the Demerara River. It is nicknamed the "Garden City of the Caribbean." It is t ...
has kept West Indian manatees in its botanical garden, and later, its national park.
In the 1910s and again in the 1950s, sugar estate
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double s ...
s in Guyana used manatees to keep their irrigation canals weed-free.
Between the 1950s and 1970s, the Georgetown water treatment plant
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, includ ...
used manatees in their storage canals for the same purpose.
Culture
The manatee has been linked to folklore on mermaids. In West African folklore, they were considered sacred and thought to have been once human. Killing one was taboo and required penance. In the novel '' Moby-Dick'', Herman Melville distinguishes manatees ("Lamatins", cf. '' lamatins'') from small whales; stating, "I am aware that down to the present time, the fish styled Lamatins and Dugongs (Pig-fish and Sow-fish of the Coffins of Nantucket) are included by many naturalists among the whales. But as these pig-fish are a noisy, contemptible set, mostly lurking in the mouths of rivers, and feeding on wet hay, and especially as they do not spout, I deny their credentials as whales; and have presented them with their passports to quit the Kingdom of Cetology." A manatee called Wardell appears in the Animal Crossing: New Horizons video game. He is part of a paid downloadable content expansion, managing and selling furniture to the player.See also
* Dwarf manatee *Manatee of Helena
The Manatee of Helena is a creature believed to have once inhabited the coast of Saint Helena, an island supposed to be largely populated by manatee
Manatees (family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herb ...
References
Further reading
*External links
Save the Manatee
Murie, James ''On the Form and Structure of the Manatee'' (''Manatus americanus''), (1872) London, Zoological Society of London Year
Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission
Reuters: Florida manatees may lose endangered status
''Bibliography and Index of the Sirenia and Desmostylia'' – Dr. Domning's authoritative manatee research bibliography
{{Authority control Sirenians Mammal families Extant Pleistocene first appearances Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Taxa named by Theodore Gill