major calyx on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The renal calyces are chambers of the
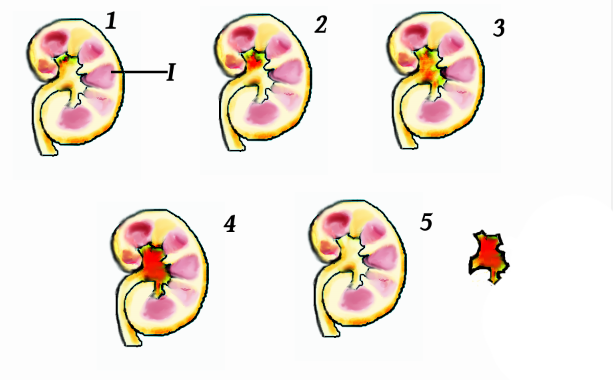 A " staghorn calculus" is a
A " staghorn calculus" is a
Diagram at bway.net
{{kidney Kidney anatomy
kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; bloo ...
through which urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellular ...
passes. The minor calyces surround the apex of the renal pyramids. Urine formed in the kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; bloo ...
passes through a renal papilla at the apex into the minor calyx; two or three minor calyces converge to form a major calyx, through which urine passes before continuing through the renal pelvis into the ureter
The ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In a human adult, the ureters are usually long and around in diameter. The ureter is lined by urothelial cells, a type of transitional e ...
.
Function
Peristalsis of the smooth muscle originating in pace-maker cells originating in the walls of the calyces propels urine through the renal pelvis andureter
The ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In a human adult, the ureters are usually long and around in diameter. The ureter is lined by urothelial cells, a type of transitional e ...
s to the bladder. The initiation is caused by the increase in volume that stretches the walls of the calyces. This causes them to fire impulses which stimulate rhythmical contraction and relaxation, called peristalsis. Parasympathetic innervation enhances the peristalsis while sympathetic innervation inhibits it.
Clinical significance
 A " staghorn calculus" is a
A " staghorn calculus" is a kidney stone
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine ...
that may extend into the renal calyces.
A renal diverticulum is diverticulum of renal calyces.
See also
*Renal medulla
The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the segmental arteries wh ...
* Renal pyramids
References
External links
* - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: Internal Structure of a Kidney" * - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: Internal Structure of a Kidney" * - "Urinary System: neonatal kidney" * ()Diagram at bway.net
{{kidney Kidney anatomy