Madoc (Brampton) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Madoc ab Owain Gwynedd (also spelled Madog) was, according to folklore, a Welsh prince who sailed to the
Madoc ab Owain Gwynedd (also spelled Madog) was, according to folklore, a Welsh prince who sailed to the
 Madoc's purported father, Owain Gwynedd, was a real king of Gwynedd during the 12th century and is widely considered one of the greatest Welsh rulers of the Middle Ages. His reign was fraught with battles with other Welsh princes and with Henry II of England. At his death in 1170, a bloody dispute broke out between his heir, Hywel the Poet-Prince, and Owain's younger sons, Maelgwn, Rhodri, and led by Dafydd, two the children of the Princess-Dowager Cristen ferch Gronwy and one the child of Gwladus ferch Llywarch. Owain had at least 13 children from his two wives and several more children born out of wedlock but legally acknowledged under Welsh tradition. According to the legend, Madoc and his brother (Rhirid or Rhiryd) were among them, though no contemporary record attests to this.
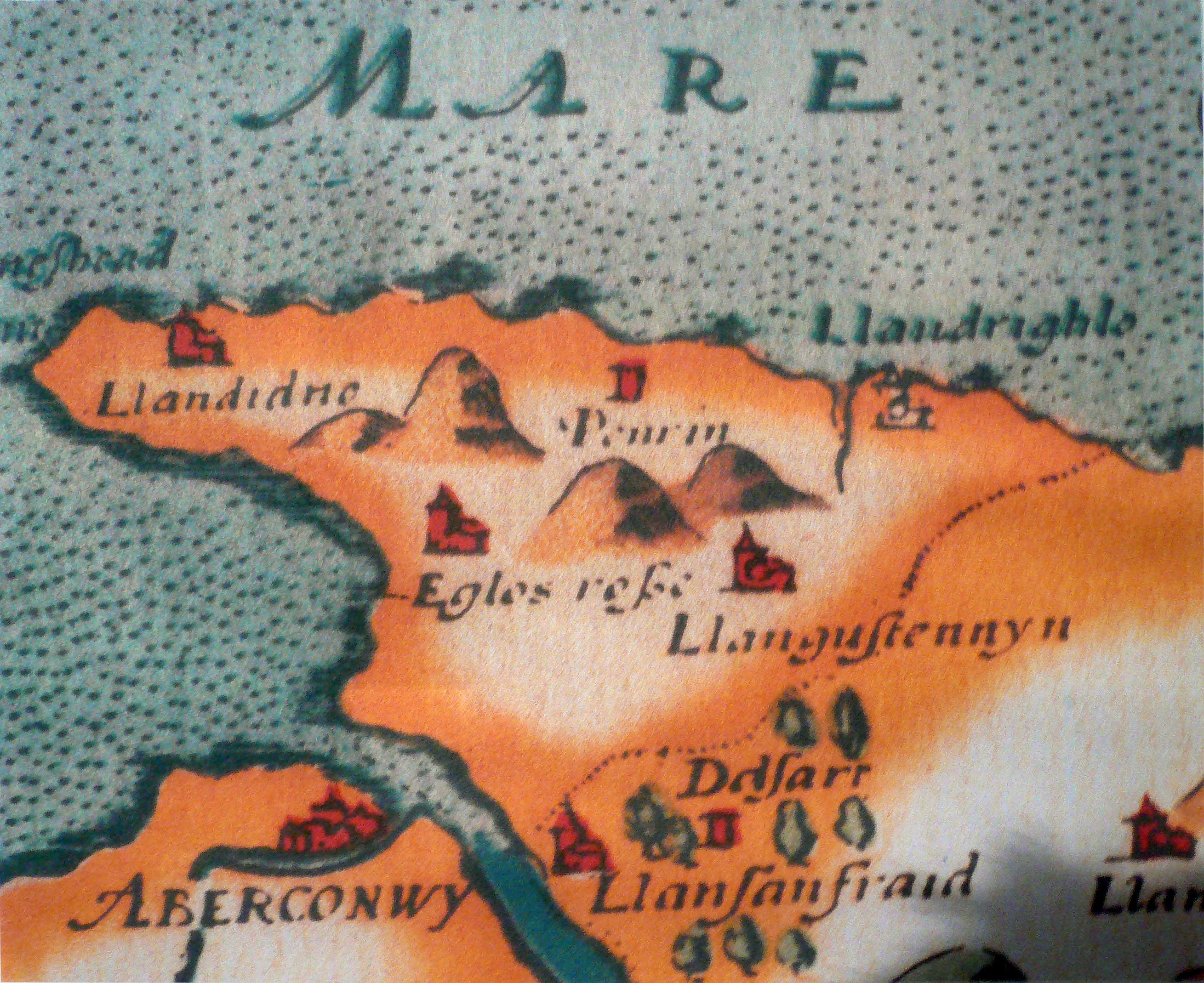
The 1584 ''Historie of Cambria'' by David Powel says that Madoc was disheartened by this family fighting, and that he and Rhirid set sail from Llandrillo ( Rhos-on-Sea) in the
Madoc's purported father, Owain Gwynedd, was a real king of Gwynedd during the 12th century and is widely considered one of the greatest Welsh rulers of the Middle Ages. His reign was fraught with battles with other Welsh princes and with Henry II of England. At his death in 1170, a bloody dispute broke out between his heir, Hywel the Poet-Prince, and Owain's younger sons, Maelgwn, Rhodri, and led by Dafydd, two the children of the Princess-Dowager Cristen ferch Gronwy and one the child of Gwladus ferch Llywarch. Owain had at least 13 children from his two wives and several more children born out of wedlock but legally acknowledged under Welsh tradition. According to the legend, Madoc and his brother (Rhirid or Rhiryd) were among them, though no contemporary record attests to this.
The 1584 ''Historie of Cambria'' by David Powel says that Madoc was disheartened by this family fighting, and that he and Rhirid set sail from Llandrillo ( Rhos-on-Sea) in the
 On 26 November 1608, Peter Wynne, a member of Captain
On 26 November 1608, Peter Wynne, a member of Captain  Folk tradition has long claimed that a site called " Devil's Backbone" at Rose Island, about fourteen miles upstream from Louisville, Kentucky, was once home to a colony of Welsh-speaking Indians. The eighteenth-century Missouri River explorer John Evans of Waunfawr in Wales took up his journey in part to find the Welsh-descended "Padoucas" or "Madogwys" tribes.
In northwest Georgia, legends of the Welsh have become part of the myth surrounding the unknown origin of a mysterious rock formation on Fort Mountain. Historian, Gwyn A. Williams, author of ''Madoc: The Making of a Myth'', suggests that Cherokee tradition concerning that ruin may have been influenced by contemporary European-American legends of the "
Folk tradition has long claimed that a site called " Devil's Backbone" at Rose Island, about fourteen miles upstream from Louisville, Kentucky, was once home to a colony of Welsh-speaking Indians. The eighteenth-century Missouri River explorer John Evans of Waunfawr in Wales took up his journey in part to find the Welsh-descended "Padoucas" or "Madogwys" tribes.
In northwest Georgia, legends of the Welsh have become part of the myth surrounding the unknown origin of a mysterious rock formation on Fort Mountain. Historian, Gwyn A. Williams, author of ''Madoc: The Making of a Myth'', suggests that Cherokee tradition concerning that ruin may have been influenced by contemporary European-American legends of the "

 A plaque at Fort Mountain State Park in Georgia recounts a nineteenth-century interpretation of the ancient stone wall that gives the site its name. The plaque repeats Tennessee governor John Sevier's statement that the Cherokees believed "a people called Welsh" had built a fort on the mountain long ago to repel Indian attacks. The plaque has been changed, leaving no reference to Madoc or the Welsh.
In 1953, the Daughters of the American Revolution (DAR) erected a plaque at Fort Morgan (Alabama), Fort Morgan on the shores of Mobile Bay, Alabama, reading:
The plaque was removed by the Alabama Parks Service, either because of a hurricane or because the site focuses on the period from 1800 to 1945, and put in storage. It is now on display at the DAR headquarters in Mobile, Alabama.
A plaque at Fort Mountain State Park in Georgia recounts a nineteenth-century interpretation of the ancient stone wall that gives the site its name. The plaque repeats Tennessee governor John Sevier's statement that the Cherokees believed "a people called Welsh" had built a fort on the mountain long ago to repel Indian attacks. The plaque has been changed, leaving no reference to Madoc or the Welsh.
In 1953, the Daughters of the American Revolution (DAR) erected a plaque at Fort Morgan (Alabama), Fort Morgan on the shores of Mobile Bay, Alabama, reading:
The plaque was removed by the Alabama Parks Service, either because of a hurricane or because the site focuses on the period from 1800 to 1945, and put in storage. It is now on display at the DAR headquarters in Mobile, Alabama.

 Madoc ab Owain Gwynedd (also spelled Madog) was, according to folklore, a Welsh prince who sailed to the
Madoc ab Owain Gwynedd (also spelled Madog) was, according to folklore, a Welsh prince who sailed to the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
in 1170, over three hundred years before Christopher Columbus's voyage in 1492.
According to the story, he was a son of Owain Gwynedd, and took to the sea to flee internecine violence at home. The "Madoc story" legend evidently evolved out of a medieval tradition about a Welsh hero's sea voyage, to which only allusions survive. However, it attained its greatest prominence during the Elizabethan era, when English and Welsh writers wrote of the claim that Madoc had come to the Americas as an assertion of prior discovery, and hence legal possession, of North America by the Kingdom of England.
The Madoc story remained popular in later centuries, and a later development asserted that Madoc's voyagers had intermarried with local Native Americans, and that their Welsh-speaking descendants still live somewhere in the United States. These "Welsh Indians" were credited with the construction of a number of landmarks throughout the Midwestern United States, and a number of white travelers were inspired to go look for them. The Madoc story has been the subject of much speculation in the context of possible pre-Columbian trans-oceanic contact. No conclusive archaeological proof of such a man or his voyages has been found in the New or Old World; however, speculation abounds connecting him with certain sites, such as Devil's Backbone, located on the Ohio River at Fourteen Mile Creek near Louisville, Kentucky.
Story
 Madoc's purported father, Owain Gwynedd, was a real king of Gwynedd during the 12th century and is widely considered one of the greatest Welsh rulers of the Middle Ages. His reign was fraught with battles with other Welsh princes and with Henry II of England. At his death in 1170, a bloody dispute broke out between his heir, Hywel the Poet-Prince, and Owain's younger sons, Maelgwn, Rhodri, and led by Dafydd, two the children of the Princess-Dowager Cristen ferch Gronwy and one the child of Gwladus ferch Llywarch. Owain had at least 13 children from his two wives and several more children born out of wedlock but legally acknowledged under Welsh tradition. According to the legend, Madoc and his brother (Rhirid or Rhiryd) were among them, though no contemporary record attests to this.
The 1584 ''Historie of Cambria'' by David Powel says that Madoc was disheartened by this family fighting, and that he and Rhirid set sail from Llandrillo ( Rhos-on-Sea) in the
Madoc's purported father, Owain Gwynedd, was a real king of Gwynedd during the 12th century and is widely considered one of the greatest Welsh rulers of the Middle Ages. His reign was fraught with battles with other Welsh princes and with Henry II of England. At his death in 1170, a bloody dispute broke out between his heir, Hywel the Poet-Prince, and Owain's younger sons, Maelgwn, Rhodri, and led by Dafydd, two the children of the Princess-Dowager Cristen ferch Gronwy and one the child of Gwladus ferch Llywarch. Owain had at least 13 children from his two wives and several more children born out of wedlock but legally acknowledged under Welsh tradition. According to the legend, Madoc and his brother (Rhirid or Rhiryd) were among them, though no contemporary record attests to this.
The 1584 ''Historie of Cambria'' by David Powel says that Madoc was disheartened by this family fighting, and that he and Rhirid set sail from Llandrillo ( Rhos-on-Sea) in the cantref
A cantref ( ; ; plural cantrefi or cantrefs; also rendered as ''cantred'') was a medieval Welsh land division, particularly important in the administration of Welsh law.
Description
Land in medieval Wales was divided into ''cantrefi'', which were ...
of Rhos to explore the western ocean. They purportedly discovered a distant and abundant land in 1170 where about one hundred men, women and children disembarked to form a colony. According to Humphrey Llwyd's 1559 '' Cronica Walliae'' and in many other copied sources, Madoc and some others returned to Wales to recruit additional settlers. After gathering eleven ships and 120 men, women and children, the Prince and his recruiters sailed west a second time to "that Westerne countrie" and ported in "Mexico", a fact that too was cited by Reuben T. Durrett
Reuben Thomas Durrett (January 22, 1824 – September 16, 1913) was a lawyer, jurist, linguist, poet, editor, journalist, history writer, and Kentucky bibliographer. In 1871, Durrett founded the failed The Public Library of Kentucky. In 1884, D ...
in his work ''Traditions of the earliest visits of foreigners to north America'', and stated he was never to return to Wales again.
Madoc's landing place has also been suggested to be "Mobile, Alabama; Florida; Newfoundland; Newport, Rhode Island; Yarmouth, Nova Scotia; Virginia; points in the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean including the mouth of the Mississippi River; the Yucatan; the isthmus of Tehuantepec, Panama; the Caribbean coast of South America; various islands in the West Indies and the Bahamas along with Bermuda; and the mouth of the Amazon River". Although the folklore tradition acknowledges that no witness ever returned from the second colonial expedition to report this, the story continues that Madoc's colonists travelled up the vast river systems of North America, raising structures and encountering friendly and unfriendly tribes of Native Americans before finally settling down somewhere in the Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
or the Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
. They are reported to be the founders of various civilisations such as the Aztec, the Maya and the Inca.
Sources
The Madoc story evidently originated in medieval romance. There are allusions to what may have been a sea voyage tale akin to '' The Voyage of Saint Brendan'', but no detailed version of it survives. The earliest certain reference to a seafaring Madoc or Madog appears in a '' cywydd'' by the Welsh poet Maredudd ap Rhys (fl. 1450–1483) of Powys, which mentions a Madog who is a son or descendant of Owain Gwynedd and who voyaged to the sea. The poem is addressed to a local squire, thanking him for a fishing net on a patron's behalf. Madog is referred to as "Splendid Madog ... / Of Owain Gwynedd's line, / He desired not land ... / Or worldy wealth but the sea." A Flemish writer called Willem, in around 1250 to 1255, identifies himself in his poem '' Van den Vos Reinaerde'' as " Willem die Madoc maecte" (Willem, the author of Madoc, known as "Willem the Minstrel"). Though no copies of "Madoc" survive, Gwyn Williams tells us that "In the seventeenth century a fragment of a reputed copy of the work is said to have been found in Poitiers". It provides no topographical details relating to North America, but mentions a sea that may be theSargasso Sea
The Sargasso Sea () is a region of the Atlantic Ocean bounded by four currents forming an ocean gyre. Unlike all other regions called seas, it has no land boundaries. It is distinguished from other parts of the Atlantic Ocean by its charac ...
and says that Madoc (not related to Owain in the fragment according to Gwyn Williams) discovered an island paradise, where he intended "to launch a new kingdom of love and music". There are also claims that the Welsh poet and genealogist Gutun Owain wrote about Madoc before 1492. Gwyn Williams in ''Madoc, the Making of a Myth'', makes it clear that Madoc is not mentioned in any of Owain's surviving manuscripts.
The Madoc legend attained its greatest prominence during the Elizabethan era, when Welsh and English writers used it to bolster British claims in the New World versus those of Spain. The earliest surviving full account of Madoc's voyage, the first to make the claim that Madoc had come to America before Columbus, appears in Humphrey Llwyd's '' Cronica Walliae'' (published in 1559), an English adaptation of the '' Brut y Tywysogion''.
John Dee
John Dee (13 July 1527 – 1608 or 1609) was an English mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, teacher, occultist, and alchemist. He was the court astronomer for, and advisor to, Elizabeth I, and spent much of his time on alchemy, divinatio ...
used Llwyd's manuscript when he submitted the treatise "Title Royal" to Queen Elizabeth in 1580, which stated that "The Lord Madoc, sonne to Owen Gwynned, Prince of Gwynedd
Gwynedd (; ) is a county and preserved county (latter with differing boundaries; includes the Isle of Anglesey) in the north-west of Wales. It shares borders with Powys, Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Anglesey over the Menai Strait, and C ...
, led a Colonie and inhabited in Terra Florida or thereabouts" in 1170. The story was first published by George Peckham
George "Porky" Peckham (born 1942, Blackburn, Lancashire) is an English record engineer, widely recognised as among the most accomplished in the business. He has been responsible for producing the master discs from which many vinyl records have ...
's as ''A True Report of the late Discoveries of the Newfound Landes'' (1583), and like Dee it was used to support English claims to the Americas. It was picked up in David Powel's ''Historie of Cambria'' (1584), and Richard Hakluyt
Richard Hakluyt (; 1553 – 23 November 1616) was an English writer. He is known for promoting the English colonization of North America through his works, notably ''Divers Voyages Touching the Discoverie of America'' (1582) and ''The Pri ...
's ''The Principall Navigations, Voiages and Discoveries of the English Nation'' (1589). Dee went so far as to assert that Brutus of Troy and King Arthur
King Arthur ( cy, Brenin Arthur, kw, Arthur Gernow, br, Roue Arzhur) is a legendary king of Britain, and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
In the earliest traditions, Arthur appears as a ...
as well as Madoc had conquered lands in the Americas and therefore their heir Elizabeth I of England had a priority claim there.
Thomas Herbert popularised the stories told by Dee and Powel, adding more detail from sources unknown, suggesting that Madoc may have landed in Canada, Florida, or even Mexico, and reporting that Mexican sources stated that they used currachs.
The "Welsh Indians" were not claimed until later. Morgan Jones's tract is the first account, and was printed by '' The Gentleman's Magazine'', launching a slew of publications on the subject. There is no genetic or archaeological evidence that the Mandan are related to the Welsh, however, and John Evans and Lewis and Clark reported they had found no Welsh Indians. The Mandan are still alive today; the tribe was decimated by a smallpox epidemic in 1837–1838 and banded with the nearby Hidatsa and Arikara into the Three Affiliated Tribes.
The Welsh Indian legend was revived in the 1840s and 1850s; this time the Zunis, Hopi
The Hopi are a Native American ethnic group who primarily live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona, United States. As of the 2010 census, there are 19,338 Hopi in the country. The Hopi Tribe is a sovereign nation within the Unite ...
s, and Navajo
The Navajo (; British English: Navaho; nv, Diné or ') are a Native American people of the Southwestern United States.
With more than 399,494 enrolled tribal members , the Navajo Nation is the largest federally recognized tribe in the United ...
were claimed to be of Welsh descent by George Ruxton
George Frederick Ruxton (24 July 1821 – 29 August 1848) was a British explorer and travel writer. He was a lieutenant in the British Army, received a medal for gallantry from Queen Isabella II of Spain, was a hunter and explorer and published p ...
(Hopis, 1846), P. G. S. Ten Broeck (Zunis, 1854), and Abbé Emmanuel Domenach (Zunis, 1860), among others. Brigham Young became interested in the supposed Hopi-Welsh connection: in 1858 Young sent a Welshman with Jacob Hamblin to the Hopi mesas to check for Welsh-speakers there. None was found, but in 1863 Hamblin brought three Hopi men to Salt Lake City, where they were "besieged by Welshmen wanting them to utter Celtic words", to no avail.
Llewellyn Harris, a Welsh-American Mormon missionary who visited the Zuni in 1878, wrote that they had many Welsh words in their language, and that they claimed their descent from the "Cambaraga"—white men who had come by sea 300 years before the Spanish. However, Harris's claims have never been independently verified.
Welsh Indians
 On 26 November 1608, Peter Wynne, a member of Captain
On 26 November 1608, Peter Wynne, a member of Captain Christopher Newport
Christopher Newport (1561–1617) was an English seaman and privateer. He is best known as the captain of the ''Susan Constant'', the largest of three ships which carried settlers for the Virginia Company in 1607 on the way to found the settle ...
's exploration party to the villages of the Monacan people, Virginia Siouan
Tutelo, also known as Tutelo–Saponi, is a member of the Virginian branch of Siouan languages that were originally spoken in the territory now known as Virginia and West Virginia in the United States. Some speakers of Tutelo migrated north to es ...
speakers above the falls of the James River
The James River is a river in the U.S. state of Virginia that begins in the Appalachian Mountains and flows U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed April 1, 2011 to Chesapea ...
in Virginia, wrote a letter to John Egerton, informing him that some members of Newport's party believed the pronunciation of the Monacans' language resembled "Welch", which Wynne spoke, and asked Wynne to act as interpreter. The Monacan were among those non-Algonquian tribes collectively referred to by the Algonquians as "Mandoag".
Another early settler to claim an encounter with a Welsh-speaking Indian was the Reverend Morgan Jones, who told Thomas Lloyd, William Penn's deputy, that he had been captured in 1669 in North Carolina by members of a tribe identified as the Doeg, who were said to be a part of the Tuscarora. (However, there is no evidence that the Doeg proper were part of the Tuscarora.) According to Jones, the chief spared his life when he heard Jones speak Welsh, a tongue he understood. Jones' report says that he then lived with the Doeg for several months preaching the Gospel in Welsh and then returned to the British Colonies where he recorded his adventure in 1686. The historian Gwyn A. Williams comments, "This is a complete farrago
Farrago is a Latin word, meaning "mixed cattle fodder", used to refer to a confused variety of miscellaneous things. As a name, it may refer to:
* ''Farrago'' (plant), a genus of plants in the family Poaceae
* ''Farrago'' (magazine), student newsp ...
and may have been intended as a hoax".
 Folk tradition has long claimed that a site called " Devil's Backbone" at Rose Island, about fourteen miles upstream from Louisville, Kentucky, was once home to a colony of Welsh-speaking Indians. The eighteenth-century Missouri River explorer John Evans of Waunfawr in Wales took up his journey in part to find the Welsh-descended "Padoucas" or "Madogwys" tribes.
In northwest Georgia, legends of the Welsh have become part of the myth surrounding the unknown origin of a mysterious rock formation on Fort Mountain. Historian, Gwyn A. Williams, author of ''Madoc: The Making of a Myth'', suggests that Cherokee tradition concerning that ruin may have been influenced by contemporary European-American legends of the "
Folk tradition has long claimed that a site called " Devil's Backbone" at Rose Island, about fourteen miles upstream from Louisville, Kentucky, was once home to a colony of Welsh-speaking Indians. The eighteenth-century Missouri River explorer John Evans of Waunfawr in Wales took up his journey in part to find the Welsh-descended "Padoucas" or "Madogwys" tribes.
In northwest Georgia, legends of the Welsh have become part of the myth surrounding the unknown origin of a mysterious rock formation on Fort Mountain. Historian, Gwyn A. Williams, author of ''Madoc: The Making of a Myth'', suggests that Cherokee tradition concerning that ruin may have been influenced by contemporary European-American legends of the "Welsh Indians
Madoc ab Owain Gwynedd (also spelled Madog) was, according to folklore, a Welsh prince who sailed to America in 1170, over three hundred years before Christopher Columbus's voyage in 1492.
According to the story, he was a son of Owain Gwyned ...
". A newspaper writer in Georgia, Walter Putnam, mentioned the Madoc legend in 2008. The story of Welsh explorers is one of several legends surrounding that site.
In northeastern Alabama, there is a theory that the "Welsh Caves" in DeSoto State Park were built by Madoc's party, since local native tribes were not known to have ever practised such stonework or excavation as was found on the site.
In 1810, John Sevier, the first governor of Tennessee, wrote to his friend Major Amos Stoddard
Amos Stoddard (October 26, 1762 – May 11, 1813) was a career United States Army officer who served in both the American Revolutionary War and the War of 1812, in which he was mortally wounded.
In 1804, Stoddard was the Commandant of the milita ...
about a conversation he had in 1782 with the old Cherokee chief Oconostota concerning ancient fortifications built along the Alabama River
The Alabama River, in the U.S. state of Alabama, is formed by the Tallapoosa and Coosa rivers, which unite about north of Montgomery, near the town of Wetumpka.
The river flows west to Selma, then southwest until, about from Mobile, it un ...
. The chief allegedly told him that the forts were built by a white people called "Welsh", as protection against the ancestors of the Cherokee, who eventually drove them from the region. Sevier had also written in 1799 of the alleged discovery of six skeletons in brass armour bearing the Welsh coat-of-arms. He claims that Madoc and the Welsh were first in Alabama.
In 1824, Thomas S. Hinde
Thomas Spottswood Hinde (April 19, 1785 – February 9, 1846) was an American newspaper editor, opponent of slavery, author, historian, real estate investor, Methodist minister and a founder of the city of Mount Carmel, Illinois. Members of the ...
wrote a letter to John S. Williams, editor of The American Pioneer, regarding the Madoc Tradition. In the letter, Hinde claimed to have gathered testimony from numerous sources that stated Welsh people under Owen Ap Zuinch had come to America in the twelfth century, over three hundred years before Christopher Columbus. Hinde claimed that in 1799, six soldiers had been dug up near Jeffersonville, Indiana
Jeffersonville is a city and the county seat of Clark County, Indiana, Clark County, Indiana, United States, situated along the Ohio River. Locally, the city is often referred to by the abbreviated name Jeff. It lies directly across the Ohio River ...
, on the Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
with breastplates that contained Welsh coats-of-arms.
Encounters with Welsh Indians
Thomas Jefferson had heard of Welsh-speaking Indian tribes. In a letter written toMeriwether Lewis
Meriwether Lewis (August 18, 1774 – October 11, 1809) was an American explorer, soldier, politician, and public administrator, best known for his role as the leader of the Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery, with ...
by Jefferson on 22 January 1804, he speaks of searching for the Welsh Indians "said to be up the Missouri". The historian Stephen E. Ambrose
Stephen Edward Ambrose (January 10, 1936 – October 13, 2002) was an American historian, most noted for his biographies of U.S. Presidents Dwight D. Eisenhower and Richard Nixon. He was a longtime professor of history at the University of New Or ...
writes in his history book ''Undaunted Courage
''Undaunted Courage: Meriwether Lewis, Thomas Jefferson, and the Opening of the American West'' (), written by Stephen Ambrose, is a 1996 biography of Meriwether Lewis of the Lewis and Clark Expedition. The book is based on journals and letters ...
'' that Thomas Jefferson believed the "Madoc story" to be true and instructed the Lewis and Clark Expedition to find the descendants of the Madoc Welsh Indians.
Mandans
In all, at least thirteen real tribes, five unidentified tribes, and three unnamed tribes have been suggested as "Welsh Indians". Eventually, the legend settled on identifying the Welsh Indians with the Mandan people, who were said to differ from their neighbours in culture, language, and appearance. The painter George Catlin suggested the Mandans were descendants of Madoc and his fellow voyagers in ''North American Indians'' (1841); he found the round Mandan Bull Boat similar to the Welsh coracle, and he thought the advanced architecture of Mandan villages must have been learned from Europeans (advanced North American societies such as the Mississippian culture, Mississippian and Hopewell traditions were not well known in Catlin's time). Supporters of this claim have drawn links between Madoc and the Mandan mythological figure "Lone Man", who, according to one tale, protected some villagers from a flooding river with a wooden corral.Later writings
Several attempts to confirm Madoc's historicity have been made, but historians of early America, notably Samuel Eliot Morison, regard the story as a myth. Madoc's legend has been a notable subject for poets, however. The most famous account in English is Robert Southey's long 1805 poem ''Madoc (poem), Madoc'', which uses the story to explore the poet's freethinking and egalitarian ideals. Southey wrote ''Madoc'' to help finance a trip of his own to America, where he and Samuel Taylor Coleridge hoped to establish a Utopian state they called a "Pantisocracy". Southey's poem in turn inspired the twentieth-century poet Paul Muldoon to write ''Madoc: A Mystery'', which won the Geoffrey Faber Memorial Prize in 1992. It explores what may have happened if Southey and Coleridge had succeeded in coming to America to found their "ideal state". In Russian, the noted poet Alexander Pushkin, Alexander S. Pushkin composed a short poem "Madoc in Wales" (Медок в Уаллах, 1829) on the topic. John Smith, historian of Virginia, wrote in 1624 of the ''Chronicles of Wales'' reports Madoc went to the New World in 1170 A.D. (over 300 years before Columbus) with some men and women. Smith says the ''Chronicles'' say Madoc then went back to Wales to get more people and made a second trip back to the New World.
Legacy
The township of Madoc, Ontario (township), Madoc, Ontario, and the nearby village of Madoc, Ontario (town), Madoc are both named in the prince's memory, as are several local guest houses and pubs throughout North America and the United Kingdom. The Welsh town of Porthmadog (meaning "Madoc's Port" in English) and the village of Tremadog ("Madoc's Town") in the county of Gwynedd are actually named after the industrialist and Parliament of the United Kingdom, Member of Parliament William Madocks, William Alexander Madocks, their principal developer, and additionally influenced by the legendary son of Owain Gwynedd, Madoc ab Owain Gwynedd. The ''RV Prince Madog, Prince Madog'', a research vessel owned by the University of Wales and P&O Maritime, entered service in 2001, replacing an earlier research vessel of the same name that first entered service in 1968.In literature
Fiction
* * * * * * * * * *Poetry
* *Juvenile
*Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * *Franklin, Caroline (2003): "The Welsh American Dream: Iolo Morganwg, Robert Southey and the Madoc legend." In ''English romanticism and the Celtic world'', ed. by Gerard Carruthers and Alan Rawes. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 69–84. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*External links
* * * {{authority control American folklore Medieval legends Legendary Welsh people Pre-Columbian trans-oceanic contact Welsh explorers Welsh royalty Origin myths Welsh people of Irish descent