Machine Identification Code on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Printer tracking dots, also known as printer steganography, DocuColor tracking dots, yellow dots, secret dots, or a machine identification code (MIC), is a
Printer tracking dots, also known as printer steganography, DocuColor tracking dots, yellow dots, secret dots, or a machine identification code (MIC), is a
 In 2005, the civil liberties activist group
In 2005, the civil liberties activist group
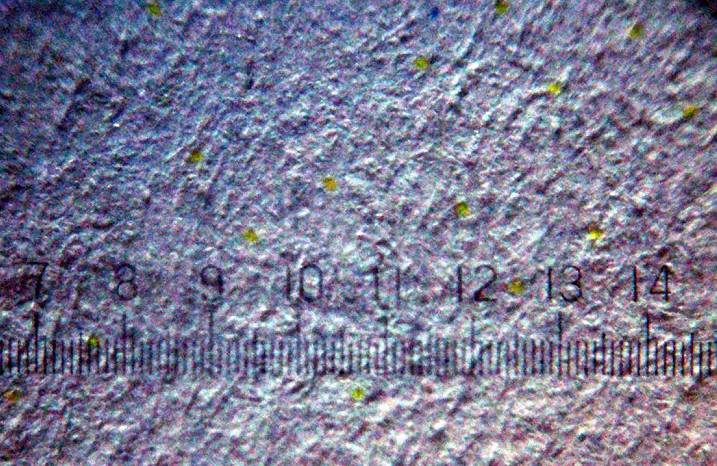
 The pattern consists of a dot-matrix spread of yellow dots, which can barely be seen with the naked eye. The dots have a diameter of and a spacing of about . Their arrangement encodes the serial number of the device, date and time of the printing, and is repeated several times across the printing area in case of errors. For example, if the code consists of 8 × 16 dots in a square or hexagonal pattern, it spreads over a surface of about and appears on a sheet of size A4 paper about 150 times. Thus, it can be analyzed even if only fragments or excerpts are available. Some printers arrange yellow dots in seemingly random point clouds.
According to the
The pattern consists of a dot-matrix spread of yellow dots, which can barely be seen with the naked eye. The dots have a diameter of and a spacing of about . Their arrangement encodes the serial number of the device, date and time of the printing, and is repeated several times across the printing area in case of errors. For example, if the code consists of 8 × 16 dots in a square or hexagonal pattern, it spreads over a surface of about and appears on a sheet of size A4 paper about 150 times. Thus, it can be analyzed even if only fragments or excerpts are available. Some printers arrange yellow dots in seemingly random point clouds.
According to the
 The dots can be made visible by printing or copying a page and subsequently scanning a small section with a high-resolution scanner. The yellow color channel can then be enhanced with an image processing program to make the dots of the identification code clearly visible. Under good lighting conditions, a
The dots can be made visible by printing or copying a page and subsequently scanning a small section with a high-resolution scanner. The yellow color channel can then be enhanced with an image processing program to make the dots of the identification code clearly visible. Under good lighting conditions, a  Using this
Using this
Laudatio der deutschen BigBrotherAwards 2004
Information by the Chaos Computer Club
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170313130611/http://dasalte.ccc.de/colorcopy/ , date=March 13, 2017
Information by the Electronic Frontier FoundationEFF List of Printers Which Do or Do Not Display Tracking Dots
(last updated 2017) Identity documents Printing software Privacy software Steganography Watermarking Computer-related introductions in the 1980s Money forgery Hardware restrictions United States Secret Service Computer forensics
 Printer tracking dots, also known as printer steganography, DocuColor tracking dots, yellow dots, secret dots, or a machine identification code (MIC), is a
Printer tracking dots, also known as printer steganography, DocuColor tracking dots, yellow dots, secret dots, or a machine identification code (MIC), is a digital watermark
A digital watermark is a kind of marker covertly embedded in a noise-tolerant signal such as audio, video or image data.H.T. Sencar, M. Ramkumar and A.N. Akansu: ''Data Hiding Fundamentals and Applications: Content Security in Digital Multimedia'' ...
which many color laser printer
Laser printing is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high-quality text and graphics (and moderate-quality photographs) by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a Electric charge, negatively charged cylinder call ...
s and photocopier
A photocopier (also called copier or copy machine, and formerly Xerox machine, the generic trademark) is a machine that makes copies of documents and other visual images onto paper or plastic film quickly and cheaply. Most modern photocopiers ...
s produce on every printed page that identifies the specific device that was used to print the document. Developed by Xerox
Xerox Holdings Corporation (, ) is an American corporation that sells print and electronic document, digital document products and services in more than 160 countries. Xerox was the pioneer of the photocopier market, beginning with the introduc ...
and Canon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the material accepted as officially written by an author or an ascribed author
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western canon, th ...
in the mid-1980s, the existence of these tracking codes became public only in 2004.
History
In the mid-1980s, Xerox pioneered an encoding mechanism for a unique number represented by tiny dots spread over the entire print area, and first deployed this scheme in its DocuColor line of printers. Xerox developed this surreptitious tracking code "to assuage fears that their color copiers could be used to counterfeit bills" and received U.S. Patent No. 5515451 describing the use of the yellow dots to identify the source of a copied or printed document. The scheme was then widely deployed in other printers, including those made by other manufacturers. The public first became aware of the tracking scheme in October 2004, when Dutch authorities used it to track counterfeiters who had used aCanon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the material accepted as officially written by an author or an ascribed author
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western canon, th ...
color laser printer. In November 2004, ''PC World
''PC World'' (stylized as PCWorld) is a global computer magazine published monthly by IDG. Since 2013, it has been an online-only publication.
It offers advice on various aspects of PCs and related items, the Internet, and other personal tec ...
'' reported the machine identification code had been used for decades in some printers, allowing law enforcement to identify and track counterfeiters. The Central Bank Counterfeit Deterrence Group (CBCDG) has denied that it developed the feature.
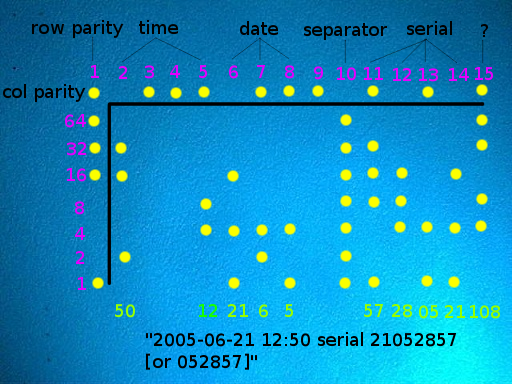
 In 2005, the civil liberties activist group
In 2005, the civil liberties activist group Electronic Frontier Foundation
The Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) is an American international non-profit digital rights group based in San Francisco, California. It was founded in 1990 to promote Internet civil liberties.
It provides funds for legal defense in court, ...
(EFF) encouraged the public to send in sample printouts and subsequently decoded the pattern. The pattern has been demonstrated on a wide range of printers from different manufacturers and models. The EFF stated in 2015 that the documents that they previously received through a Freedom of Information Act Freedom of Information Act may refer to the following legislations in different jurisdictions which mandate the national government to disclose certain data to the general public upon request:
* Freedom of Information Act (United States) of 1966
* F ...
request suggested that all major manufacturers of color laser printers entered a secret agreement with governments to ensure that the output of those printers is forensically traceable.
In 2007, the European Parliament was asked about the question of invasion of privacy.
Technical aspects
 The pattern consists of a dot-matrix spread of yellow dots, which can barely be seen with the naked eye. The dots have a diameter of and a spacing of about . Their arrangement encodes the serial number of the device, date and time of the printing, and is repeated several times across the printing area in case of errors. For example, if the code consists of 8 × 16 dots in a square or hexagonal pattern, it spreads over a surface of about and appears on a sheet of size A4 paper about 150 times. Thus, it can be analyzed even if only fragments or excerpts are available. Some printers arrange yellow dots in seemingly random point clouds.
According to the
The pattern consists of a dot-matrix spread of yellow dots, which can barely be seen with the naked eye. The dots have a diameter of and a spacing of about . Their arrangement encodes the serial number of the device, date and time of the printing, and is repeated several times across the printing area in case of errors. For example, if the code consists of 8 × 16 dots in a square or hexagonal pattern, it spreads over a surface of about and appears on a sheet of size A4 paper about 150 times. Thus, it can be analyzed even if only fragments or excerpts are available. Some printers arrange yellow dots in seemingly random point clouds.
According to the Chaos Computer Club
The Chaos Computer Club (CCC) is Europe's largest association of Hacker (computer security), hackers with 7,700 registered members. Founded in 1981, the association is incorporated as an ''eingetragener Verein'' in Germany, with local chapters ...
in 2005, color printers leave the code in a matrix of 32 × 16 dots and thus can store 64 bytes of data (64×8).
, Xerox
Xerox Holdings Corporation (, ) is an American corporation that sells print and electronic document, digital document products and services in more than 160 countries. Xerox was the pioneer of the photocopier market, beginning with the introduc ...
was one of the few manufacturers to draw attention to the marked pages, stating in a product description, "The digital color printing system is equipped with an anti-counterfeit identification and banknote recognition system according to the requirements of numerous governments. Each copy shall be marked with a label which, if necessary, allows identification of the printing system with which it was created. This code is not visible under normal conditions."
In 2018, scientists at the TU Dresden
TU Dresden (for , abbreviated as TUD), also as the Dresden University of Technology, is a public research university in Dresden, Germany. It is the largest institute of higher education in the city of Dresden, the largest university in Saxony a ...
analyzed the patterns of 106 printer models from 18 manufacturers and found four different encoding schemes.
Visibility
 The dots can be made visible by printing or copying a page and subsequently scanning a small section with a high-resolution scanner. The yellow color channel can then be enhanced with an image processing program to make the dots of the identification code clearly visible. Under good lighting conditions, a
The dots can be made visible by printing or copying a page and subsequently scanning a small section with a high-resolution scanner. The yellow color channel can then be enhanced with an image processing program to make the dots of the identification code clearly visible. Under good lighting conditions, a magnifying glass
A magnifying glass is a convex lens—usually mounted in a frame with a handle—that is used to produce a magnified image of an object. A magnifying glass can also be used to focus light, such as to concentrate the Sun's radiation to create ...
may be enough to see the pattern. Under UV-light, the yellow dots are clearly recognizable.
 Using this
Using this steganographic
Steganography ( ) is the practice of representing information within another message or physical object, in such a manner that the presence of the concealed information would not be evident to an unsuspecting person's examination. In computing/ ...
process, high-quality copies of an original (e.g. a banknote
A banknote or bank notealso called a bill (North American English) or simply a noteis a type of paper money that is made and distributed ("issued") by a bank of issue, payable to the bearer on demand. Banknotes were originally issued by commerc ...
) under blue light can be made identifiable. Using this process, even shredded prints can be identified: the 2011 " Shredder Challenge" initiated by the DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Adva ...
was solved by a team called "All Your Shreds Are Belong To U.S." consisting of Otávio Good
Otávio Good is a Brazilian and American computer programmer and inventor. He is the original author of Word Lens, the first augmented reality translation application that replaces printed text into the desired language in video without connecti ...
and two colleagues.
Practical application
Both journalists and security experts have suggested that ''The Intercept
''The Intercept'' is an American left-wing nonprofit news organization that publishes articles and podcasts online. ''The Intercept'' has published in English since its founding in 2014, and in Portuguese since the 2016 launch of the Brazilia ...
'' handling of the leaks by whistleblower Reality Winner
Reality Leigh Winner (born December 4, 1991) is an American U.S. Air Force veteran and former NSA translator. In 2018, she was given the longest prison sentence ever imposed for an unauthorized release of government information to the media af ...
, which included publishing secret NSA documents unredacted and including the printer tracking dots, was used to identify Winner as the leaker, leading to her arrest in 2017 and conviction.
Protection of privacy and circumvention
Copies or printouts of documents with confidential personal information, for example health care information, account statements, tax declaration or balance sheets, can be traced to the owner of the printer and the inception date of the documents can be revealed. This traceability is unknown to many users and inaccessible, as manufacturers do not publicize the code that produces these patterns. It is unclear which data may be unintentionally passed on with a copy or printout. In particular, there are no mentions of the technique in the support materials of most affected printers. In 2005, theElectronic Frontier Foundation
The Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) is an American international non-profit digital rights group based in San Francisco, California. It was founded in 1990 to promote Internet civil liberties.
It provides funds for legal defense in court, ...
(EFF) sought a decoding method and made available a Python script for analysis.
In 2018, scientists from TU Dresden
TU Dresden (for , abbreviated as TUD), also as the Dresden University of Technology, is a public research university in Dresden, Germany. It is the largest institute of higher education in the city of Dresden, the largest university in Saxony a ...
developed and published a tool to extract and analyze the steganographic codes of a given color printer and subsequently to anonymize prints from that printer. The anonymization works by printing additional yellow dots on top of the printer's tracking dots.DEDA - tracking Dots Extraction, Decoding and Anonymisation toolkit: The scientists made the software available to support whistleblower
Whistleblowing (also whistle-blowing or whistle blowing) is the activity of a person, often an employee, revealing information about activity within a private or public organization that is deemed illegal, immoral, illicit, unsafe, unethical or ...
s in their efforts to publicize grievances.
Comparable processes
Other methods of identification are not as easily recognizable as yellow dots. For example, a modulation of laser intensity and a variation of shades of grey in texts are feasible. , it was unknown whether manufacturers were also using these techniques.See also
*EURion constellation
The EURion constellation (also known as Omron rings or doughnuts) is a pattern of symbols incorporated into a number of secure documents such as banknotes, cheques, and ownership title certificate designs worldwide since about 1996. It is added ...
, a dot matrix spread over a bank note, which stops some printers and color copiers from processing
*
*
References
External links
Laudatio der deutschen BigBrotherAwards 2004
Information by the Chaos Computer Club
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170313130611/http://dasalte.ccc.de/colorcopy/ , date=March 13, 2017
Information by the Electronic Frontier Foundation
(last updated 2017) Identity documents Printing software Privacy software Steganography Watermarking Computer-related introductions in the 1980s Money forgery Hardware restrictions United States Secret Service Computer forensics