MPEG Surround on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
MPEG Surround (
 MPEG Surround encoder receives a multichannel audio signal x1 to xN where the number of input channels is ''N''. The most important aspect of the encoding process is that a downmix signal, xt1 and xt2, which is typically stereo, is derived from the multichannel input signal, and it is this downmix signal that is compressed for transmission over the channel rather than the multichannel signal. The encoder may be able to exploit the downmix process so as to be more advantageous. It not only creates a faithful equivalent of the multichannel signal in the mono or stereo downmix, but also creates the best possible multichannel decoding based on the downmix and encoded spatial cues as well. Alternatively, the downmix could be supplied externally (Artistic Downmix in before Diagram Block). The MPEG Surround encoding process could be ignored by the compression algorithm used for the transmitted channels (Audio Encoder and Audio Decoder in before Diagram Block). It could be any type of high-performance compression algorithms such as MPEG-1 Layer III, MPEG-4 AAC or MPEG-4 High Efficiency AAC, or it could even be PCM.
MPEG Surround encoder receives a multichannel audio signal x1 to xN where the number of input channels is ''N''. The most important aspect of the encoding process is that a downmix signal, xt1 and xt2, which is typically stereo, is derived from the multichannel input signal, and it is this downmix signal that is compressed for transmission over the channel rather than the multichannel signal. The encoder may be able to exploit the downmix process so as to be more advantageous. It not only creates a faithful equivalent of the multichannel signal in the mono or stereo downmix, but also creates the best possible multichannel decoding based on the downmix and encoded spatial cues as well. Alternatively, the downmix could be supplied externally (Artistic Downmix in before Diagram Block). The MPEG Surround encoding process could be ignored by the compression algorithm used for the transmitted channels (Audio Encoder and Audio Decoder in before Diagram Block). It could be any type of high-performance compression algorithms such as MPEG-1 Layer III, MPEG-4 AAC or MPEG-4 High Efficiency AAC, or it could even be PCM.
MPEG Surround
Official MPEG web site
RFC 5691
- RTP Payload Format for Elementary Streams with MPEG Surround Multi-Channel Audio {{MPEG, state=collapsed Audio codecs MPEG Open standards covered by patents
ISO
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.
ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance
* Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007
* Iso ...
/IEC
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: ''Commission électrotechnique internationale'') is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and r ...
23003-1 or MPEG-D MPEG-D is a group of standards for audio coding formally known as '' ISO/IEC 23003'' - ''MPEG audio technologies'', published since 2007.
MPEG-D consists of four parts:
* MPEG-D Part 1: MPEG Surround
MPEG Surround (ISO/ IEC 23003-1 or MPEG-D P ...
Part 1), also known as Spatial Audio Coding (SAC) is a lossy
In information technology, lossy compression or irreversible compression is the class of data compression methods that uses inexact approximations and partial data discarding to represent the content. These techniques are used to reduce data size ...
compression
Compression may refer to:
Physical science
*Compression (physics), size reduction due to forces
*Compression member, a structural element such as a column
*Compressibility, susceptibility to compression
* Gas compression
*Compression ratio, of a ...
format for surround sound
Surround sound is a technique for enriching the fidelity and depth of sound reproduction by using multiple audio channels from speakers that surround the listener (surround channels). Its first application was in movie theaters. Prior to s ...
that provides a method for extending mono or stereo audio services to multi-channel audio in a backwards compatible fashion. The total bit rates used for the (mono or stereo) core and the MPEG Surround data are typically only slightly higher than the bit rates used for coding of the (mono or stereo) core.
MPEG Surround adds a side-information stream to the (mono or stereo) core bit stream
A bitstream (or bit stream), also known as binary sequence, is a sequence of bits.
A bytestream is a sequence of bytes. Typically, each byte is an 8-bit quantity, and so the term octet stream is sometimes used interchangeably. An octet may ...
, containing spatial image data. Legacy stereo playback systems will ignore this side-information while players supporting MPEG Surround decoding will output the reconstructed multi-channel audio.
Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) issued a ''call for proposals'' on MPEG Spatial Audio Coding in March 2004. The group decided that the technology that would be the starting point in standardization process, would be a combination of the submissions from two proponents - Fraunhofer IIS / Agere Systems and Coding Technologies / Philips. The MPEG Surround standard was developed by the Moving Picture Experts Group ( ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC29/WG11) and published as ISO/IEC 23003 in 2007. It was the first standard of MPEG-D standards group, formally known as ''ISO/IEC 23003 - MPEG audio technologies''.
MPEG Surround was also defined as one of the MPEG-4 Audio Object Types in 2007. There is also the MPEG-4 No Delay MPEG Surround object type (LD MPEG Surround), which was published in 2010. The Spatial Audio Object Coding (SAOC) was published as MPEG-D Part 2 - ISO/IEC 23003–2 in 2010 and it extends MPEG Surround standard by re-using its spatial rendering capabilities while retaining full compatibility with existing receivers. MPEG SAOC system allows users on the decoding side to interactively control the rendering of each individual audio object (e.g. individual instruments, vocals, human voices). There is also the Unified Speech and Audio Coding (USAC) which will be defined in MPEG-D Part 3 - ISO/IEC 23003-3 and ISO/IEC 14496-3:2009/Amd 3. MPEG-D MPEG Surround parametric coding tools are integrated into the USAC codec.
The (mono or stereo) core could be coded with any (lossy
In information technology, lossy compression or irreversible compression is the class of data compression methods that uses inexact approximations and partial data discarding to represent the content. These techniques are used to reduce data size ...
or lossless
Lossless compression is a class of data compression that allows the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data with no loss of information. Lossless compression is possible because most real-world data exhibits statistic ...
) audio codec
An audio codec is a device or computer program capable of encoding or decoding a digital data stream (a codec) that encodes or decodes audio. In software, an audio codec is a computer program implementing an algorithm that compresses and decompres ...
. Particularly low bitrates (64-96 kbit/s for 5.1 channels) are possible when using HE-AAC v2 as the core codec.
Perception of sounds in space
MPEG Surround coding uses our capacity to perceive sound in the 3D and captures that perception in a compact set of parameters. Spatial perception is primarily attributed to three parameters, or cues, describing how humans localize sound in the horizontal plane:Interaural level difference
Sound localization is a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance.
The sound localization mechanisms of the mammalian auditory system have been extensively studied. The auditory system us ...
(ILD), Interaural time difference
The interaural time difference (or ITD) when concerning humans or animals, is the difference in arrival time of a sound between two ears. It is important in the localization of sounds, as it provides a cue to the direction or angle of the sound s ...
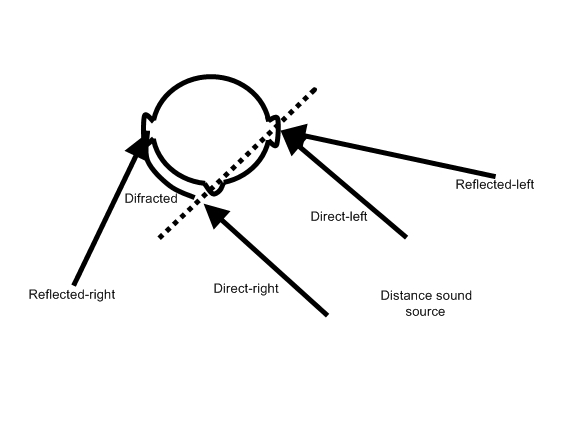
(ITD) and Interaural coherence (IC). This three concepts are illustrated in next image. Direct, or first-arrival, waveforms from the source hit the left ear at time, while direct sound received by the right ear is diffracted around the head, with time delay and level attenuation, associated. These two effects result in ITD and ILD are associated with the main source. At last, in a reverberant environment, reflected sound from the source, or sound from diffuse source, or uncorrelated sound can hit both ears, all of them are related with IC.

Description
MPEG Surround uses interchannel differences in level, phase and coherence equivalent to the ILD, ITD and IC parameters. The spatial image is captured by a multichannel audio signal relative to a transmitted downmix signal. These parameters are encoded in a very compact form so as to decode the parameters and the transmitted signal and to synthesize a high quality multichannel representation. MPEG Surround encoder receives a multichannel audio signal x1 to xN where the number of input channels is ''N''. The most important aspect of the encoding process is that a downmix signal, xt1 and xt2, which is typically stereo, is derived from the multichannel input signal, and it is this downmix signal that is compressed for transmission over the channel rather than the multichannel signal. The encoder may be able to exploit the downmix process so as to be more advantageous. It not only creates a faithful equivalent of the multichannel signal in the mono or stereo downmix, but also creates the best possible multichannel decoding based on the downmix and encoded spatial cues as well. Alternatively, the downmix could be supplied externally (Artistic Downmix in before Diagram Block). The MPEG Surround encoding process could be ignored by the compression algorithm used for the transmitted channels (Audio Encoder and Audio Decoder in before Diagram Block). It could be any type of high-performance compression algorithms such as MPEG-1 Layer III, MPEG-4 AAC or MPEG-4 High Efficiency AAC, or it could even be PCM.
MPEG Surround encoder receives a multichannel audio signal x1 to xN where the number of input channels is ''N''. The most important aspect of the encoding process is that a downmix signal, xt1 and xt2, which is typically stereo, is derived from the multichannel input signal, and it is this downmix signal that is compressed for transmission over the channel rather than the multichannel signal. The encoder may be able to exploit the downmix process so as to be more advantageous. It not only creates a faithful equivalent of the multichannel signal in the mono or stereo downmix, but also creates the best possible multichannel decoding based on the downmix and encoded spatial cues as well. Alternatively, the downmix could be supplied externally (Artistic Downmix in before Diagram Block). The MPEG Surround encoding process could be ignored by the compression algorithm used for the transmitted channels (Audio Encoder and Audio Decoder in before Diagram Block). It could be any type of high-performance compression algorithms such as MPEG-1 Layer III, MPEG-4 AAC or MPEG-4 High Efficiency AAC, or it could even be PCM.
Legacy compatibility
The MPEG Surround technique allows for compatibility with existing and future stereo MPEG decoders by having the transmitted downmix (e.g. stereo) appear to stereo MPEG decoders to be an ordinary stereo version of the multichannel signal. Compatibility with stereo decoders is desirable since stereo presentation will remain pervasive due to the number of applications in which listening is primarily via headphones, such as portable music players. MPEG Surround also supports a mode in which the downmix is compatible with popular matrix surround decoders, such as Dolby Pro-Logic.Applications
Digital Audio Broadcasting
Due to the relatively small channel bandwidth, the relatively large cost of transmission equipment and transmission licenses and the desire to maximize user choices by providing many programs, the majority of existing or planned digital broadcasting systems cannot provide multichannel sound to the users. DRM+ was designed to be fully capable of transmitting MPEG Surround and such broadcasting was also successfully demonstrated. MPEG Surround's backward compatibility and relatively low overhead provides one way to add multichannel sound to DAB without severely reducing audio quality or impacting other services.Digital TV Broadcasting
Currently, the majority of digital TV broadcasts use stereo audio coding. MPEG Surround could be used to extend these established services to surround sound, as with DAB.Music download service
Currently, a number of commercial music download services are available and working with considerable commercial success. Such services could be seamlessly extended to provide multichannel presentations while remaining compatible with stereo players: on computers with 5.1 channel playback systems the compressed sound files are presented in surround sound while on portable players the same files are reproduced in stereo.Streaming music service / Internet radio
Many Internet radios operate with severely constrained transmission bandwidth, such that they can offer only mono or stereo content. MPEG Surround Coding technology could extend this to a multichannel service while still remaining within the permissible operating range of bitrates. Since efficiency is of paramount importance in this application, compression of the transmitted audio signal is vital. Using recent MPEG compression technology (MPEG-4 High Efficiency Profile coding), full MPEG Surround systems have been demonstrated with bitrates as low as 48 kbit/s.See also
*Surround sound
Surround sound is a technique for enriching the fidelity and depth of sound reproduction by using multiple audio channels from speakers that surround the listener (surround channels). Its first application was in movie theaters. Prior to s ...
*Comparison of audio coding formats
The following tables compare general and technical information for a variety of audio coding formats.
For listening tests comparing the perceived audio quality of audio formats and codecs, see the article Codec listening test.
General informati ...
References
External links
MPEG Surround
Official MPEG web site
RFC 5691
- RTP Payload Format for Elementary Streams with MPEG Surround Multi-Channel Audio {{MPEG, state=collapsed Audio codecs MPEG Open standards covered by patents