M-M-RVaxPro on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The MMR vaccine is a vaccine against
 Before the widespread use of a vaccine against
Before the widespread use of a vaccine against
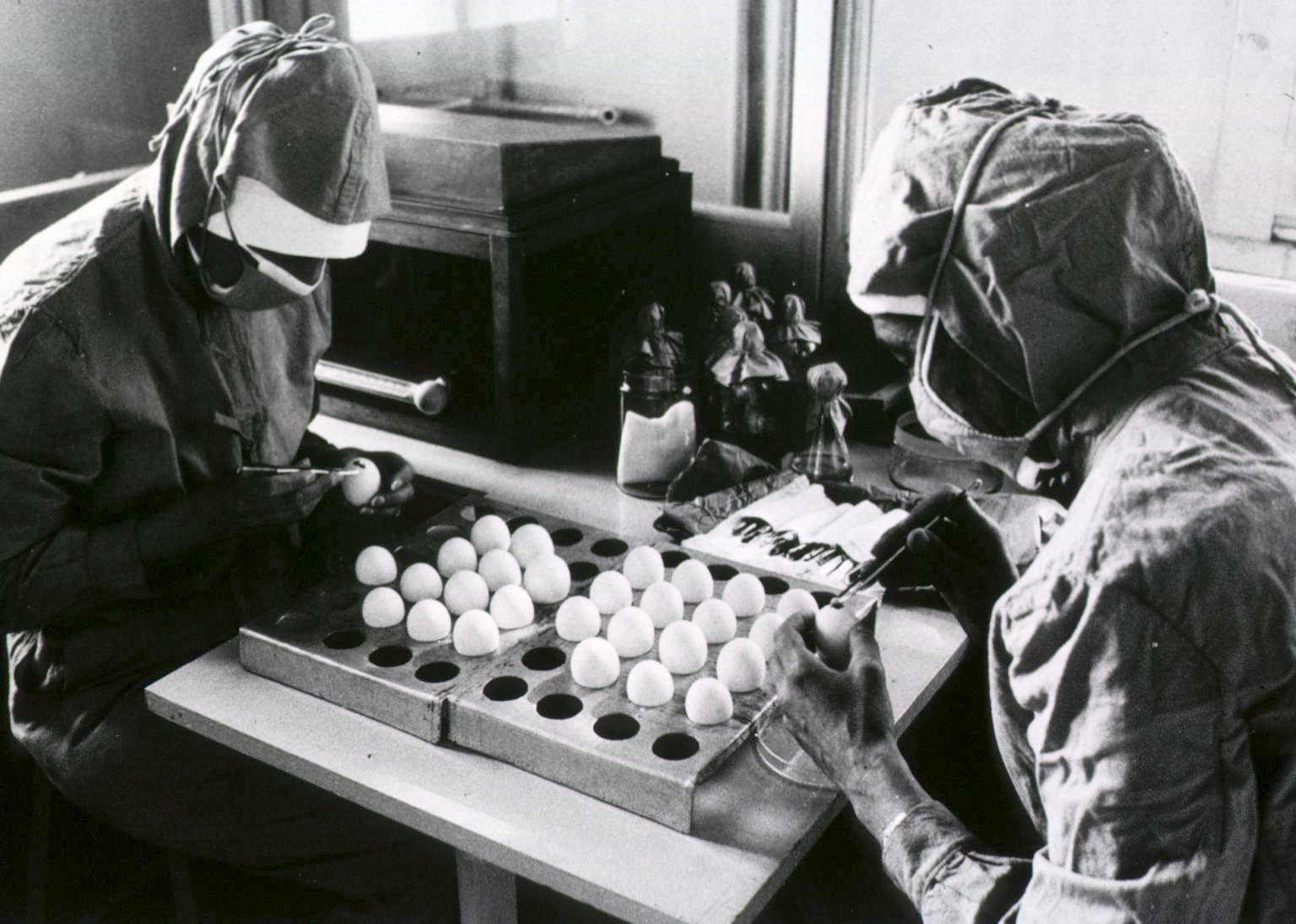

 The component viral strains of MMR vaccine were developed by propagation in animal and human cells as all viruses require a living host cell to replicate.
For example, in the case of mumps and measles viruses, the virus strains were grown in embryonated chicken eggs. This produced strains of virus which were adapted for chicken cells and less well-suited for human cells. These strains are therefore called '' attenuated strains''. They are sometimes referred to as ''neuroattenuated'' because these strains are less virulent to human neurons than the wild strains.
The Rubella component, Meruvax, was developed in 1967, through propagation using the human embryonic lung cell line
The component viral strains of MMR vaccine were developed by propagation in animal and human cells as all viruses require a living host cell to replicate.
For example, in the case of mumps and measles viruses, the virus strains were grown in embryonated chicken eggs. This produced strains of virus which were adapted for chicken cells and less well-suited for human cells. These strains are therefore called '' attenuated strains''. They are sometimes referred to as ''neuroattenuated'' because these strains are less virulent to human neurons than the wild strains.
The Rubella component, Meruvax, was developed in 1967, through propagation using the human embryonic lung cell line
measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
, mumps
MUMPS ("Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System"), or M, is an imperative, high-level programming language with an integrated transaction processing key–value database. It was originally developed at Massachusetts Gener ...
, and rubella
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild, with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and ...
(German measles), abbreviated as ''MMR''. The first dose is generally given to children around 9 months to 15 months of age, with a second dose at 15 months to 6 years of age, with at least four weeks between the doses. After two doses, 97% of people are protected against measles, 88% against mumps, and at least 97% against rubella. The vaccine is also recommended for those who do not have evidence of immunity, those with well-controlled HIV/AIDS, and within 72 hours of exposure to measles among those who are incompletely immunized. It is given by injection.
The MMR vaccine is widely used around the world. Worldwide over 500 million doses were administered between 1999 and 2004, and 575 million doses have been administered since the vaccine's introduction worldwide. Measles resulted in 2.6 million deaths per year before immunization became common. This has decreased to 122,000 deaths per year , mostly in low-income countries. Through vaccination, , rates of measles in North and South America are very low. Rates of disease have been seen to increase in populations that go unvaccinated. Between 2000 and 2018, vaccination decreased measles deaths by 73%.
Side effects of immunization are generally mild and resolve without any specific treatment. These may include fever, as well as pain or redness at the injection site. Severe allergic reaction
Anaphylaxis is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the follow ...
s occur in about one in a million people. Because it contains live viruses, the MMR vaccine is not recommended during pregnancy but may be given while breastfeeding. The vaccine is safe to give at the same time as other vaccines. Being recently immunized does not increase the risk of passing measles, mumps, or rubella on to others. There is no evidence of an association between MMR immunisation and autistic spectrum disorders. The MMR vaccine is a mixture of live weakened viruses of the three diseases.
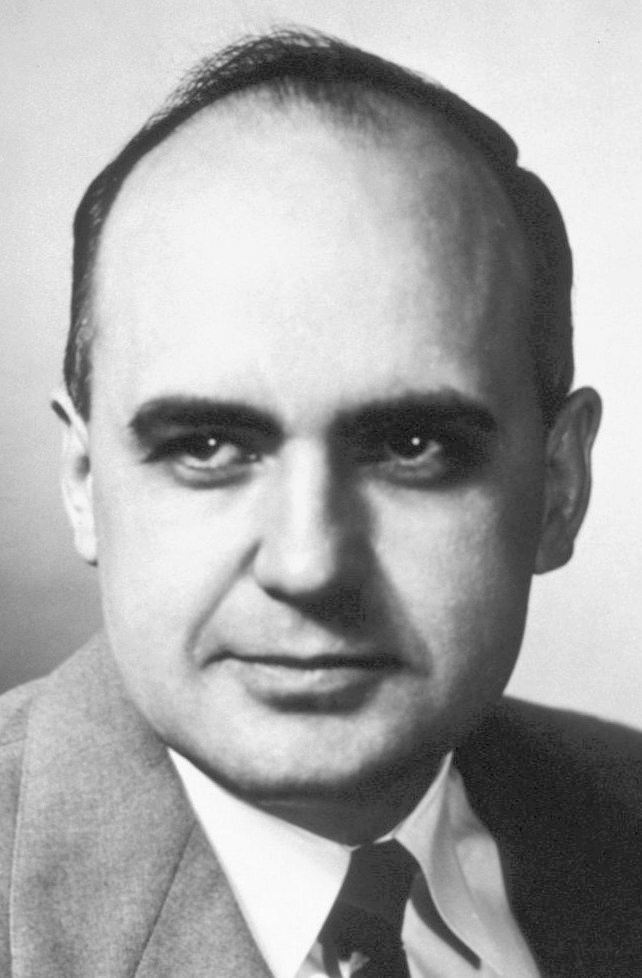
The MMR vaccine was developed by Maurice Hilleman. It was licensed for use in USA by Merck
Merck refers primarily to the German Merck family and three companies founded by the family, including:
* the Merck Group, a German chemical, pharmaceutical and life sciences company founded in 1668
** Merck Serono (known as EMD Serono in the Unite ...
in 1971. Stand-alone measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
, mumps
MUMPS ("Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System"), or M, is an imperative, high-level programming language with an integrated transaction processing key–value database. It was originally developed at Massachusetts Gener ...
, and rubella vaccines had been previously licensed in 1963, 1967, and 1969, respectively. Recommendations for a second dose were introduced in 1989. The MMRV vaccine, which also covers chickenpox
Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab ...
, may be used instead. An MR vaccine, without coverage for mumps, is also occasionally used.
Medical use

Cochrane Cochrane may refer to:
Places Australia
*Cochrane railway station, Sydney, a railway station on the closed Ropes Creek railway line
Canada
* Cochrane, Alberta
* Cochrane Lake, Alberta
* Cochrane District, Ontario
** Cochrane, Ontario, a town wit ...
concluded that the "Existing evidence on the safety and effectiveness of MMR and MMRV vaccine supports current policies of mass immunisation aimed at global measles eradication in order to reduce morbidity and mortality associated with measles mumps rubella and varicella."
The combined MMR vaccine induces immunity less painfully than three separate injections at the same time, and sooner and more efficiently than three injections given on different dates. Public Health England reports that providing a single combined vaccine as of 1988, rather than giving the option to have them also done separately, increased uptake of the vaccine.
Measles
 Before the widespread use of a vaccine against
Before the widespread use of a vaccine against measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
, rates of disease were so high that infection was felt to be "as inevitable as death and taxes." Reported cases of measles in the United States fell from hundreds of thousands to tens of thousands per year following introduction of the vaccine in 1963. Increasing uptake of the vaccine following outbreaks in 1971, and 1977, brought this down to thousands of cases per year in the 1980s. An outbreak of almost 30,000 cases in 1990 led to a renewed push for vaccination and the addition of a second vaccine to the recommended schedule. Fewer than 200 cases have been reported in the US each year between 1997 and 2013, and the disease is no longer considered endemic there.
The benefit of measles vaccination in preventing illness, disability, and death has been well documented. The first 20 years of licensed measles vaccination in the US prevented an estimated 52 million cases of the disease, 17,400 cases of intellectual disability, and 5,200 deaths. During 1999–2004, a strategy led by the World Health Organization and UNICEF led to improvements in measles vaccination coverage that averted an estimated 1.4 million measles deaths worldwide. Between 2000 and 2018, measles vaccination resulted in a 73% decrease in deaths from the disease.
Measles is common
Common may refer to:
Places
* Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland
* Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts
* Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts
* Clapham Common, originally com ...
in many areas of the world. Although it was declared eliminated from the US in 2000, high rates of vaccination and good communication with people who refuse vaccination are needed to prevent outbreaks and sustain the elimination of measles in the US. Of the 66 cases of measles reported in the US in 2005, slightly over half were attributable to one unvaccinated individual who acquired measles during a visit to Romania. This individual returned to a community with many unvaccinated children. The resulting outbreak infected 34 people, mostly children and virtually all unvaccinated; 9% were hospitalized, and the cost of containing the outbreak was estimated at $167,685. A major epidemic was averted due to high rates of vaccination in the surrounding communities.
In 2017, an outbreak of measles occurred among the Somali-American community in Minnesota, where MMR vaccination rates had declined due to the misconception that the vaccine could cause autism. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recorded 65 affected children in the outbreak by April 2017.
Rubella

Rubella
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild, with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and ...
, also known as German measles, was also very common before widespread vaccination. The major risk of rubella is during pregnancy when the baby may contract congenital rubella, which can cause significant congenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
defects.
Mumps
Mumps
MUMPS ("Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System"), or M, is an imperative, high-level programming language with an integrated transaction processing key–value database. It was originally developed at Massachusetts Gener ...
is another viral
Viral means "relating to viruses" (small infectious agents).
Viral may also refer to:
Viral behavior, or virality
Memetic behavior likened that of a virus, for example:
* Viral marketing, the use of existing social networks to spread a marke ...
disease that was once very common, especially during childhood. If mumps is acquired by a male who is past puberty, a possible complication is bilateral orchitis, which can in some cases lead to sterility.
Administration
The MMR vaccine is administered by asubcutaneous injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion.
A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and epidermis, ...
, the first dose typically at twelve months of age. The second dose may be given as early as one month after the first dose. The second dose is a dose to produce immunity in the small number of persons (2–5%) who fail to develop measles immunity after the first dose. In the US it is done before entry to kindergarten because that is a convenient time. Areas where measles is common typically recommend the first dose at nine months of age and the second dose at fifteen months of age.
Safety
Adverse reactions, rarely serious, may occur from each component of the MMR vaccine. Ten percent of children develop fever,malaise
As a medical term, malaise is a feeling of general discomfort, uneasiness or lack of wellbeing and often the first sign of an infection or other disease. The word has existed in French since at least the 12th century.
The term is often used ...
, and a rash 5–21 days after the first vaccination; and 3% develop joint pain lasting 18 days on average. Older women appear to be more at risk of joint pain, acute arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In som ...
, and even (rarely) chronic arthritis. Anaphylaxis is an extremely rare but serious allergic reaction to the vaccine. One cause can be egg allergy. In 2014, the FDA approved two additional possible adverse events on the vaccination label: acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM), and transverse myelitis, with permission to also add "difficulty walking" to the package inserts. A 2012 IOM report found that the measles component of the MMR vaccine can cause measles inclusion body encephalitis in immunocompromised individuals. This report also rejected any connection between the MMR vaccine and autism
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulti ...
. Some versions of the vaccine contain the antibiotic neomycin and therefore should not be used in people allergic to this antibiotic.
The number of reports on neurological disorders is very small, other than evidence for an association between a form of the MMR vaccine containing the Urabe mumps strain and rare adverse events of aseptic meningitis, a form of viral meningitis. The UK National Health Service stopped using the Urabe mumps strain in the early 1990s due to cases of transient mild viral meningitis, and switched to a form using the Jeryl Lynn Jeryl Lynn are strains of mumps virus used in the Mumpsvax mumps vaccine made by Merck. The strains are named after Jeryl Lynn Hilleman. In 1963, Jeryl's father, Maurice Hilleman, was leading efforts to produce a mumps vaccine for Merck. He cult ...
mumps strain instead. The Urabe strain remains in use in a number of countries; MMR with the Urabe strain is much cheaper to manufacture than with the Jeryl Lynn strain, and a strain with higher efficacy
Efficacy is the ability to perform a task to a satisfactory or expected degree. The word comes from the same roots as ''effectiveness'', and it has often been used synonymously, although in pharmacology a pragmatic clinical trial#Efficacy versu ...
along with a somewhat higher rate of mild side effects may still have the advantage of reduced incidence of overall adverse events.
A Cochrane review found that, compared with placebo, MMR vaccine was associated with fewer upper respiratory tract infections, more irritability, and a similar number of other adverse effects.
Naturally acquired measles often occurs with immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP, a purpuric
Purpura () is a condition of red or purple discolored spots on the skin that do not blanch on applying pressure. The spots are caused by bleeding underneath the skin secondary to platelet disorders, vascular disorders, coagulation disorders, ...
rash and an increased tendency to bleed that resolves within two months in children), occurring in 1 to 20,000 cases. Approximately 1 in 40,000 children are thought to acquire ITP in the six weeks following an MMR vaccination. ITP below the age of six years is generally a mild disease, rarely having long-term consequences.
False claims about autism
In 1998 Andrew Wakefield ''et al.'' published a fraudulent paper about twelve children, reportedly with bowel symptoms andautism
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulti ...
or other disorders acquired soon after administration of MMR vaccine, while supporting a competing vaccine. In 2010, Wakefield's research was found by the General Medical Council
The General Medical Council (GMC) is a public body that maintains the official register of medical practitioners within the United Kingdom. Its chief responsibility is to "protect, promote and maintain the health and safety of the public" by c ...
to have been "dishonest", and '' The Lancet'' fully retracted the paper. Three months following ''The Lancet's'' retraction, Wakefield was struck off the UK medical register
The General Medical Council (GMC) is a public body that maintains the official register of medical practitioners within the United Kingdom. Its chief responsibility is to "protect, promote and maintain the health and safety of the public" by c ...
, with a statement identifying deliberate falsification in the research published in ''The Lancet'', and was barred from practising medicine in the UK. The research was declared fraudulent in 2011 by the ''British Medical Journal
''The BMJ'' is a weekly peer-reviewed medical trade journal, published by the trade union the British Medical Association (BMA). ''The BMJ'' has editorial freedom from the BMA. It is one of the world's oldest general medical journals. Origi ...
''.
Since Wakefield's publication, multiple peer-reviewed studies have failed to show any association between the vaccine and autism. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Institute of Medicine
The National Academy of Medicine (NAM), formerly called the Institute of Medicine (IoM) until 2015, is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Medicine is a part of the National Academies of Sciences, E ...
of the US National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the Nati ...
, the UK National Health Service and the Cochrane Library review have all concluded that there is no evidence of a link.
Administering the vaccines in three separate doses does not reduce the chance of adverse effects, and it increases the opportunity for infection by the two diseases not immunized against first. Health experts have criticized media reporting of the MMR-autism controversy for triggering a decline in vaccination rates. Before publication of Wakefield's article, the inoculation rate for MMR in the UK was 92%; after publication, the rate dropped to below 80%. In 1998, there were 56 measles cases in the UK; by 2008, there were 1348 cases, with two confirmed deaths.
In Japan, the MMR triplet is not used. Immunity is achieved by a combination vaccine for measles and rubella, followed up later with a mumps only vaccine. This has had no effect on autism rates in the country, further disproving the MMR autism hypothesis.
History

 The component viral strains of MMR vaccine were developed by propagation in animal and human cells as all viruses require a living host cell to replicate.
For example, in the case of mumps and measles viruses, the virus strains were grown in embryonated chicken eggs. This produced strains of virus which were adapted for chicken cells and less well-suited for human cells. These strains are therefore called '' attenuated strains''. They are sometimes referred to as ''neuroattenuated'' because these strains are less virulent to human neurons than the wild strains.
The Rubella component, Meruvax, was developed in 1967, through propagation using the human embryonic lung cell line
The component viral strains of MMR vaccine were developed by propagation in animal and human cells as all viruses require a living host cell to replicate.
For example, in the case of mumps and measles viruses, the virus strains were grown in embryonated chicken eggs. This produced strains of virus which were adapted for chicken cells and less well-suited for human cells. These strains are therefore called '' attenuated strains''. They are sometimes referred to as ''neuroattenuated'' because these strains are less virulent to human neurons than the wild strains.
The Rubella component, Meruvax, was developed in 1967, through propagation using the human embryonic lung cell line WI-38
WI-38 is a diploid human cell line composed of fibroblasts derived from lung tissue of a 3-month-gestation female fetus. The fetus came from the elective abortion of a Swedish woman in 1963. She was disinterested in the fate of the fetus and its s ...
(named for the Wistar Institute
The Wistar Institute () is an independent, nonprofit research institution in biomedical science, with expertise in oncology, immunology, infectious disease and vaccine research. Located on the campus of the University of Pennsylvania, Wistar was ...
) that was derived six years earlier in 1961.
The term "MPR vaccine" is also used to refer to this vaccine, whereas "P" refer to Parotitis which is caused by mumps.
Merck MMR II is supplied freeze-dried (lyophilized
Freeze drying, also known as lyophilization or cryodesiccation, is a low temperature dehydration process that involves freezing the product and lowering pressure, removing the ice by sublimation. This is in contrast to dehydration by most conve ...
) and contains live viruses. Before injection it is reconstituted with the solvent provided.
According to a review published in 2018, the GlaxoSmithKline
GSK plc, formerly GlaxoSmithKline plc, is a British multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with global headquarters in London, England. Established in 2000 by a merger of Glaxo Wellcome and SmithKline Beecham. GSK is the ten ...
(GSK) MMR vaccine known as Pluserix "contains the Schwarz measles virus, the Jeryl Lynn–like mumps strain, and RA27/3 rubella virus".
Pluserix was introduced in Hungary in 1999. Enders' Edmonston strain has been used since 1999 in Hungary in Merck
Merck refers primarily to the German Merck family and three companies founded by the family, including:
* the Merck Group, a German chemical, pharmaceutical and life sciences company founded in 1668
** Merck Serono (known as EMD Serono in the Unite ...
MMR II product. GSK Priorix vaccine, which uses attenuated Schwarz Measles, was introduced in Hungary in 2003.
MMRV vaccine
The MMRV vaccine, a combined measles, mumps, rubella and varicella (chickenpox) vaccine, has been proposed as a replacement for the MMR vaccine to simplify administration of the vaccines. Preliminary data indicate a rate of febrile seizures of 9 per 10,000 vaccinations with MMRV, as opposed to 4 per 10,000 for separate MMR and varicella shots; US health officials therefore do not express a preference for use of MMRV vaccine over separate injections. In a 2012 study pediatricians and family doctors were sent a survey to gauge their awareness of the increased risk of febrile seizures (fever fits) in the MMRV. 74% of family doctors and 29% of pediatricians were unaware of the increased risk of febrile seizures. After reading an informational statement only 7% of family doctors and 20% of pediatricians would recommend the MMRV for a healthy 12- to 15-month-old child. The factor that was reported as the "most important" deciding factor in recommending the MMRV over the MMR+V was ACIP/ AAFP/ AAP recommendations (pediatricians, 77%; family physicians, 73%).MR vaccine
This is a vaccine that covers measles and rubella but not mumps. As of 2014, it was used in a "few (unidentified) countries".Society and culture
Religious concerns
Some brands of the vaccine usegelatin
Gelatin or gelatine (from la, gelatus meaning "stiff" or "frozen") is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also ...
, derived from pigs, as a stabilizer. This has caused reduced take-up among some communities, despite the fact that alternative vaccines without pig derivatives are approved and available.
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Mmr Vaccine Combination drugs Combination vaccines GSK plc brands Live vaccines Measles Merck & Co. brands Mumps Rubella Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate