Low German language on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
:
:
:
:
:
(70,000)
(30,000)
(8,000)
, familycolor = Indo-European
, fam2 = Germanic
, fam3 = West Germanic
, fam4 =
 It has been estimated that Low German has approximately 2 to 5 million speakers (depending on the definition of 'native speaker') in Germany, primarily in Northern Germany.
Variants of Low German are spoken in most parts of
It has been estimated that Low German has approximately 2 to 5 million speakers (depending on the definition of 'native speaker') in Germany, primarily in Northern Germany.
Variants of Low German are spoken in most parts of 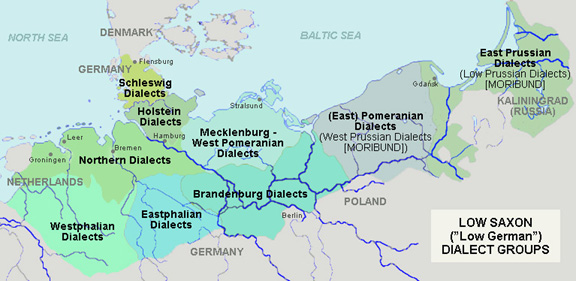
 East Pomeranian is also spoken in parts of
East Pomeranian is also spoken in parts of
* High German is a loanword from Low German
:** The series –, etc. are *** Pronounced ''shepp'' since the 17th century
/ref> However, there is a lot of variation in that respect and some or all of these distinctions may also be absent, so that a single undeclined form of the adjective can occur in all cases, as in English. This is especially common in the neuter. If the adjective is declined, the pattern tends to be as follows: As mentioned above, alternative undeclined forms such as ''dat lütt Land'', ''de lütt Lannen'', ''en stark Kerl'', ''de stark Kerl'', ''stark Kerls'', ''de stark Kerls'' etc. can occur.
Plattmakers dictionary
with more than 20,000 word entries, with translations and interface available in several languages (English too)
Dictionary of the Drents dialect
(Dutch)
Nu is de Welt platt!
International resources in and about Low German
Building Blocks of Low Saxon (Low German)
an introductory grammar in English and German
Niederdeutsch/Plattdeutsch in Westfalen
by Olaf Bordasch
Mönsterlänner Plat
by Klaus-Werner Kahl
IJsselacademie
(Overijssel and Veluwe, the Netherlands)
Staring Instituut
(Achterhoek, the Netherlands)
Stichting Stellingwarver Schrieversronte
(Friesland, the Netherlands)
SONT
(General, the Netherlands)
Oostfreeske Taal
(Eastern Friesland, Germany)
Diesel - dat oostfreeske Bladdje
(Eastern Friesland, Germany)
Institut für niederdeutsche Sprache e.V.
(General, Germany) {{Use dmy dates, date=March 2017 Languages of Germany West Germanic languages German dialects Dutch dialects Danish dialects North Sea Germanic
North Sea Germanic
North Sea Germanic, also known as Ingvaeonic , is a postulated grouping of the northern West Germanic languages that consists of Old Frisian, Old English, and Old Saxon, and their descendants.
Ingvaeonic is named after the Ingaevones, a West G ...
, ancestor = Old Saxon
Old Saxon, also known as Old Low German, was a Germanic language and the earliest recorded form of Low German (spoken nowadays in Northern Germany, the northeastern Netherlands, southern Denmark, the Americas and parts of Eastern Europe). I ...
, ancestor2 = Middle Low German
Middle Low German or Middle Saxon (autonym: ''Sassisch'', i.e. " Saxon", Standard High German: ', Modern Dutch: ') is a developmental stage of Low German. It developed from the Old Saxon language in the Middle Ages and has been documented i ...
, dia1 = West Low German
Low Saxon, also known as West Low German ( nds, Nedersassisch, Nedersaksies; nl, Nedersaksisch) are a group of Low German dialects spoken in parts of the Netherlands, northwestern Germany and southern Denmark (in North Schleswig by parts o ...
, dia2 = East Low German
, iso2 = nds
, iso3 = nds
, iso3comment = (Dutch varieties and Westphalian have separate codes)
, lingua = 52-ACB
, map = Nds Spraakrebeet na1945.svg
, mapcaption = Present day Low German language area in Europe.
, glotto = lowg1239
, glottoname = Low German
, notice = IPA
Low German or Low Saxon (in the language itself: , and other names; german: Plattdeutsch, ) is a West Germanic language variety spoken mainly in Northern Germany
Northern Germany (german: link=no, Norddeutschland) is a linguistic, geographic, socio-cultural and historic region in the northern part of Germany which includes the coastal states of Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Lower Saxony an ...
and the northeastern part of the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite
The Russian Mennonites (german: Russlandmennoniten it. "Russia Mennonites", i.e., Mennonites of or from the Russian Empire occasionally Ukrainian Mennonites) are a group of Mennonites who are descendants of Dutch Anabaptists who settled for abo ...
diaspora worldwide.
Low German is most closely related to Frisian and English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
, with which it forms the North Sea Germanic
North Sea Germanic, also known as Ingvaeonic , is a postulated grouping of the northern West Germanic languages that consists of Old Frisian, Old English, and Old Saxon, and their descendants.
Ingvaeonic is named after the Ingaevones, a West G ...
group of the West Germanic languages. Like Dutch, it is spoken north of the Benrath and Uerdingen isogloss
An isogloss, also called a heterogloss (see Etymology below), is the geographic boundary of a certain linguistic feature, such as the pronunciation of a vowel, the meaning of a word, or the use of some morphological or syntactic feature. Major ...
es, while ( Standard) High German is spoken south of those lines. Like Frisian, English, Dutch and the North Germanic languages
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is also ...
, Low German has not undergone the High German consonant shift
In historical linguistics, the High German consonant shift or second Germanic consonant shift is a phonological development ( sound change) that took place in the southern parts of the West Germanic dialect continuum in several phases. It probabl ...
, as opposed to Standard High German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
, which is based on High German dialects. Low German evolved from Old Saxon (Old Low German), which is most closely related to Old Frisian
Old Frisian was a West Germanic language spoken between the 8th and 16th centuries along the North Sea coast, roughly between the mouths of the Rhine and Weser rivers. The Frisian settlers on the coast of South Jutland (today's Northern Fries ...
and Old English (Anglo-Saxon).
The Low German dialects spoken in the Netherlands are mostly referred to as Low Saxon, those spoken in northwestern Germany (Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
, Westphalia
Westphalia (; german: Westfalen ; nds, Westfalen ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants.
The territory of the regio ...
, Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
, Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
, Bremen
Bremen ( Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state cons ...
, and Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making i ...
west of the Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
) as either Low German or Low Saxon, and those spoken in northeastern Germany (Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV; ; nds, Mäkelborg-Vörpommern), also known by its anglicized name Mecklenburg–Western Pomerania, is a state in the north-east of Germany. Of the country's sixteen states, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern ranks 14th in po ...
, Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 squ ...
, and Saxony-Anhalt east of the Elbe) mostly as Low German. This is because northwestern Germany and the northeastern Netherlands were the area of settlement of the Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
(Old Saxony
"Old Saxony" is the original homeland of the Saxons. It corresponds roughly to the modern German states of Lower Saxony, eastern part of modern North Rhine-Westphalia state (Westphalia), Nordalbingia ( Holstein, southern part of Schleswig-Holstei ...
), while Low German spread to northeastern Germany through eastward migration of Low German speakers into areas with a Slavic-speaking population (Germania Slavica
''Germania Slavica'' is a historiographic term used since the 1950s to denote the landscape of the medieval language border (roughly east of the Elbe-Saale line) zone between Germans and Slavs in Central Europe on the one hand and a 20th-century s ...
).
It has been estimated that Low German has approximately 1.6 million speakers in Germany, primarily Northern Germany, and 2.15 million in the Netherlands.
Geographical extent
Inside Europe
Germany
 It has been estimated that Low German has approximately 2 to 5 million speakers (depending on the definition of 'native speaker') in Germany, primarily in Northern Germany.
Variants of Low German are spoken in most parts of
It has been estimated that Low German has approximately 2 to 5 million speakers (depending on the definition of 'native speaker') in Germany, primarily in Northern Germany.
Variants of Low German are spoken in most parts of Northern Germany
Northern Germany (german: link=no, Norddeutschland) is a linguistic, geographic, socio-cultural and historic region in the northern part of Germany which includes the coastal states of Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Lower Saxony an ...
, for instance in the states of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
, North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia (german: Nordrhein-Westfalen, ; li, Noordrien-Wesfale ; nds, Noordrhien-Westfalen; ksh, Noodrhing-Wäßßfaale), commonly shortened to NRW (), is a state (''Land'') in Western Germany. With more than 18 million inha ...
, Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
, Bremen
Bremen ( Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state cons ...
, Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV; ; nds, Mäkelborg-Vörpommern), also known by its anglicized name Mecklenburg–Western Pomerania, is a state in the north-east of Germany. Of the country's sixteen states, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern ranks 14th in po ...
, Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making i ...
, and Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 squ ...
. Small portions of northern Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are ...
and northern Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt is the capital and lar ...
are traditionally Low Saxon-speaking too.
Historically, Low German was also spoken in formerly German parts of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
as well as in East Prussia and the Baltic provinces (modern Estonia and Latvia). The Baltic Germans spoke a distinct Low German dialect, which has influenced the vocabulary and phonetics of both Estonian and Latvian. The historical Sprachraum of Low German also included contemporary northern Poland, East Prussia (the modern Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia), a part of western Lithuania, and the German communities in Estonia and Latvia, most notably their Hanseatic cities. German speakers in this area fled the Red Army or were forcibly expelled after the border changes at the end of World War II.
The language was also formerly spoken in the outer areas of what is now the city-state of Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ...
, but in the course of urbanisation and national centralisation in that city, the language has vanished (the Berlin dialect itself is a northern outpost of High German, though it has some Low German features).
Today, there are still speakers outside Germany to be found in the coastal areas of present-day Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
(minority of ethnic German
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
East Pomeranian speakers who were not expelled from Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
, as well as the regions around Braniewo
Braniewo () (german: Braunsberg in Ostpreußen, la, Brunsberga, Old Prussian: ''Brus'', lt, Prūsa), is a town in northern Poland, in Warmia, in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, with a population of 16,907 as of June 2021. It is the capital ...
). In the Southern Jutland
Jutland ( da, Jylland ; german: Jütland ; ang, Ēota land ), known anciently as the Cimbric or Cimbrian Peninsula ( la, Cimbricus Chersonesus; da, den Kimbriske Halvø, links=no or ; german: Kimbrische Halbinsel, links=no), is a peninsula of ...
region of Denmark there may still be some Low German speakers in some German minority communities, but the Low German and North Frisian dialects of Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
can be considered moribund at this time.

The Netherlands
Dialects of Low German are spoken in the northeastern area of the Netherlands ( Dutch Low Saxon) and are written there with an unstandardized orthography based on Standard Dutch orthography. The position of the language is, according to UNESCO, vulnerable. Between 1995 and 2011 the numbers of parent speakers dropped from 34% in 1995 to 15% in 2011. Numbers of child speakers dropped from 8% to 2% in the same period. According to a 2005 study 53% speak Low Saxon or Low Saxon and Dutch at home and 71% could speak it in the researched area. The total number of speakers is estimated at 1.7 million speakers.The Other Languages of Europe: Demographic, Sociolinguistic, and Educational Perspectives by Guus Extra, Durk Gorter; Multilingual Matters, 2001 - 454; page 10. There are speakers in the Dutch north and eastern provinces ofGroningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen (province), Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of t ...
, Drenthe
Drenthe () is a province of the Netherlands located in the northeastern part of the country. It is bordered by Overijssel to the south, Friesland to the west, Groningen to the north, and the German state of Lower Saxony to the east. As of Nove ...
, Stellingwerf (part of Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
), Overijssel
Overijssel (, ; nds, Oaveriessel ; german: Oberyssel) is a province of the Netherlands located in the eastern part of the country. The province's name translates to "across the IJssel", from the perspective of the Episcopal principality of U ...
, Gelderland
Gelderland (), also known as Guelders () in English, is a province of the Netherlands, occupying the centre-east of the country. With a total area of of which is water, it is the largest province of the Netherlands by land area, and second by ...
, Utrecht
Utrecht ( , , ) is the fourth-largest city and a municipality of the Netherlands, capital and most populous city of the province of Utrecht. It is located in the eastern corner of the Randstad conurbation, in the very centre of mainland Net ...
and Flevoland
Flevoland () is the twelfth and youngest province of the Netherlands, established in 1986, when the southern and eastern Flevopolders, together with the Noordoostpolder, were merged into one provincial entity. It is in the centre of the countr ...
, in several dialect groups per province.
Outside Europe and the Mennonites
There are also immigrant communities where Low German is spoken in the Western hemisphere, includingCanada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
, Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wa ...
, Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
, Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ...
, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to t ...
and Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
. In some of these countries, the language is part of the Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the R ...
religion and culture. There are Mennonite communities in Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
, Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada, western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on t ...
, Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest T ...
, British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, for ...
, Manitoba
Manitoba ( ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population o ...
, Kansas
Kansas () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its Capital city, capital is Topeka, Kansas, Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita, Kansas, Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebras ...
and Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over t ...
which use Low German in their religious services and communities. These Mennonites are descended from primarily Dutch settlers that had initially settled in the Vistula delta
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
region of Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
in the 16th and 17th centuries before moving to newly acquired Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
n territories in Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, and then to the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
in the 19th and early 20th centuries. The types of Low German spoken in these communities and in the Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
region of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
have diverged since emigration. The survival of the language is tenuous in many places, and has died out in many places where assimilation has occurred. Members and friends of the Historical Society of North German Settlements in Western New York ( Bergholz, NY), a community of Lutherans who trace their immigration from Pomerania in the 1840s, hold quarterly "Plattdeutsch lunch" events, where remaining speakers of the language gather to share and preserve the dialect. Mennonite colonies in Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to t ...
, Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wa ...
, and Chihuahua Chihuahua may refer to:
Places
* Chihuahua (state), a Mexican state
**Chihuahua (dog), a breed of dog named after the state
**Chihuahua cheese, a type of cheese originating in the state
**Chihuahua City, the capital city of the state
**Chihuahua Mu ...
, Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
have made Low German a "co-official language" of the community.
Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
and Southeastern
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sep ...
Brazil, in the latter especially in the state of , being official in five municipalities, and spoken among its ethnically European migrants elsewhere, primarily in the states of Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
and . East Pomeranian-speaking regions of Southern Brazil are often assimilated into the general German Brazilian
German Brazilians (German: ''Deutschbrasilianer'', Hunsrik: ''Deitschbrasiliooner'', pt, teuto-brasileiros) refers to Brazilians of full or partial German ancestry. German Brazilians live mostly in the country's South Region, with a smaller bu ...
population and culture, for example celebrating the , and there can even be a language shift from it to in some areas. In , nevertheless, Pomeranian Brazilians are more often proud of their language, and particular religious traditions and culture, and not uncommonly inheriting the nationalism of their ancestors, being more likely to accept marriages of its members with Brazilians of origins other than a Germanic Central European one than to assimilate with Brazilians of Swiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
*Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
*Swiss, North Carolina
* Swiss, West Virginia
*Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
* Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
* Swiss Internation ...
, Austrian
Austrian may refer to:
* Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent
** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law
* Austrian German dialect
* Something associated with the country Austria, for example: ...
, Czech, and non-East Pomeranian-speaking German and Prussian heritage – that were much more numerous immigrants to both Brazilian regions (and whose language almost faded out in the latter, due to assimilation and internal migration), by themselves less numerous than the Italian ones (with only Venetian communities in areas of highly Venetian presence conserving Talian Talian may refer to:
*Talian dialect
Talian (or Brazilian Venetian, , , but ) is a dialect of the Venetian language, spoken primarily in the Serra Gaúcha region in the northeast of the state of Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil. It is also spoken ...
, and other Italian languages and dialects fading out elsewhere).
Nomenclature
The language grouping of Low German is referred to, in the language itself as well as in its umbrella languages of German and Dutch, in several different ways, ranging from official names such as Niederdeutsche and Nederduits to more general characterisations such as "dialect". The proliferation of names or characterisations is due in part to the grouping stretching mainly across two different countries and to it being a collection of varieties rather than a standardised language. There are different uses of the term "Low German": # A specific name of any West Germanic varieties that neither have taken part in theHigh German consonant shift
In historical linguistics, the High German consonant shift or second Germanic consonant shift is a phonological development ( sound change) that took place in the southern parts of the West Germanic dialect continuum in several phases. It probabl ...
nor classify as Low Franconian
Low Franconian, Low Frankish, NetherlandicSarah Grey Thomason, Terrence Kaufman: ''Language Contact, Creolization, and Genetic Linguistics'', University of California Press, 1991, p. 321. (Calling it "Low Frankish (or Netherlandish)".)Scott Shay ...
or Anglo-Frisian; this is the scope discussed in this article.
# A broader term for the closely related, continental West Germanic languages
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided into ...
unaffected by the High German consonant shift, nor classifying as Anglo-Frisian, and thus including Low Franconian
Low Franconian, Low Frankish, NetherlandicSarah Grey Thomason, Terrence Kaufman: ''Language Contact, Creolization, and Genetic Linguistics'', University of California Press, 1991, p. 321. (Calling it "Low Frankish (or Netherlandish)".)Scott Shay ...
varieties.
In Germany, native speakers of Low German call their language , , , , , (South-Westphalian), (Eastphalian), (Low Prussian), or . In the Netherlands, native speakers refer to their language as , , , or the name of their village, town or district.
Officially, Low German is called or (Nether or Low German language), or (Nether or Low German) in High German by the German authorities, (Nether or Low German language), or (Nether or Low German) in Low German by the German authorities and (Nether or Low Saxon) by the Dutch authorities. , and , are seen in linguistic texts from the German and Dutch linguistic communities respectively.
In Danish it is called , or, rarely, . Mennonite Low German is called .
"Low" refers to the flat plains and coastal area of the northern European lowlands, contrasted with the mountainous areas of central and southern Germany, Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
, and Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, where High German (Highland German) is spoken. Etymologically however, ''Platt'' meant "clear" in the sense of a language the simple people could understand. In Dutch, the word can also mean "improper", "rude" or "too simple" which is why the term is not popular in the Netherlands.
The colloquial term denotes both Low German dialects and any non- standard Western variety of German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
; this use is chiefly found in northern and Western Germany and is not considered to be linguistically
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguis ...
correct.
The ISO 639-2
ISO 639- 2:1998, ''Codes for the representation of names of languages — Part 2: Alpha-3 code'', is the second part of the ISO 639 standard, which lists codes for the representation of the names of languages. The three-letter codes given for ea ...
language code for Low German (Low Saxon
Low Saxon, also known as West Low German ( nds, Nedersassisch, Nedersaksies; nl, Nedersaksisch) are a group of Low German dialects spoken in parts of the Netherlands, northwestern Germany and southern Denmark (in North Schleswig by parts of ...
) has been nds ( or ) since May 2000.
Classification
Low German is a part of the continental West Germanicdialect continuum
A dialect continuum or dialect chain is a series of language varieties spoken across some geographical area such that neighboring varieties are mutually intelligible, but the differences accumulate over distance so that widely separated vari ...
. To the West, it blends into the Low Franconian languages, including Dutch. A distinguishing feature between the Southern Low Franconian varieties and Low German varieties is the plural of the verbs. Low German varieties have a common verbal plural ending, whereas Low Franconian varieties have a different form for the second person plural. This is complicated in that in most Low Franconian varieties, including standard Dutch, the original second-person plural form has replaced the singular. Some dialects, including again standard Dutch, innovated a new second-person plural form in the last few centuries, using the other plural forms as the source.
To the South, Low German blends into the High German dialects of Central German
Central German or Middle German (german: mitteldeutsche Dialekte, mitteldeutsche Mundarten, Mitteldeutsch) is a group of High German dialects spoken from the Rhineland in the west to the former eastern territories of Germany.
Central German d ...
that have been affected by the High German consonant shift
In historical linguistics, the High German consonant shift or second Germanic consonant shift is a phonological development ( sound change) that took place in the southern parts of the West Germanic dialect continuum in several phases. It probabl ...
. The division is usually drawn at the Benrath line
In German linguistics, the Benrath line (german: Benrather Linie) is the ''maken–machen'' isogloss: dialects north of the line have the original in ''maken'' (to make), while those to the south have the innovative (''machen''). The Line runs f ...
that traces the '' – '' isogloss
An isogloss, also called a heterogloss (see Etymology below), is the geographic boundary of a certain linguistic feature, such as the pronunciation of a vowel, the meaning of a word, or the use of some morphological or syntactic feature. Major ...
.
To the East, it abuts the Kashubian language
Kashubian or Cassubian (Kashubian: ', pl, język kaszubski) is a West Slavic language belonging to the Lechitic subgroup along with Polish and Silesian.Stephen Barbour, Cathie Carmichael, ''Language and Nationalism in Europe'', Oxford Univer ...
(the only remnant of the Pomeranian language
), East Low German, East Pomeranian dialect
The Pomeranian language ( Polish: ''pomorszczyzna'' or ''język pomorski'', German: ''Pomoranisch'' or ''die pomoranische Sprache'') is in the Pomeranian group of Lechitic languages ( Polish: ''grupa ...
) and, since the expulsion of nearly all Germans from the Polish part of Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
following the Second World War, also by the Polish language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In ad ...
.
East Pomeranian and Central Pomeranian are dialects of Low German.
To the North and Northwest, it abuts the Danish and the Frisian languages
The Frisian (, ) languages are a closely related group of West Germanic languages, spoken by about 500,000 Frisian people, who live on the southern fringes of the North Sea in the Netherlands and Germany. The Frisian languages are the closest l ...
. Note that in Germany, Low German has replaced the Frisian languages in many regions. Saterland Frisian is the only remnant of East Frisian language and is surrounded by Low German, as are the few remaining North Frisian varieties, and the Low German dialects of those regions have influences from Frisian substrates.
Most linguists classify the dialects of Low German together with English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
and Frisian as the ''North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
Germanic'' or ''Ingvaeonic
North Sea Germanic, also known as Ingvaeonic , is a postulated grouping of the northern West Germanic languages that consists of Old Frisian, Old English, and Old Saxon, and their descendants.
Ingvaeonic is named after the Ingaevones, a West Ge ...
'' languages. However, most exclude Low German from the group often called Anglo-Frisian languages
The Anglo-Frisian languages are the Anglic (English, Scots, and Yola) and Frisian varieties of the West Germanic languages.
The Anglo-Frisian languages are distinct from other West Germanic languages due to several sound changes: besides th ...
because some distinctive features of that group of languages are only partially observed in Low German, for instance the Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law
In historical linguistics, the Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law (also called the Anglo-Frisian or North Sea Germanic nasal spirant law) is a description of a phonological development that occurred in the Ingvaeonic dialects of the West Germanic lan ...
(some dialects have ''us'', for "us" whereas others have , ), and because other distinctive features do not occur in Low German at all, for instance the palatalization of /k/ (compare palatalized forms such as English ''cheese'', Frisian to non-palatalized forms such as Low German or , Dutch , German ).
Language or dialect
The question of whether today's Low German should be considered a separate language or a dialect ofGerman
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
or even Dutch has been a point of contention. Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Ling ...
offers no simple, generally accepted criterion to decide the question.
Scholarly arguments have been put forward for classifying Low German as a German dialect. As stated above, the arguments are not linguistic but rather sociopolitical and revolve mainly around the fact that Low German has no official standard form or use in sophisticated media. The situation of Low German may thus be considered a "pseudo-dialectized abstand language
In sociolinguistics, an abstand language is a variety (linguistics), language variety or cluster of varieties with significant linguistic distance from all others, while an ausbau language is a standard language, standard variety, possibly with re ...
" (""). In contrast, Old Saxon
Old Saxon, also known as Old Low German, was a Germanic language and the earliest recorded form of Low German (spoken nowadays in Northern Germany, the northeastern Netherlands, southern Denmark, the Americas and parts of Eastern Europe). I ...
and Middle Low German
Middle Low German or Middle Saxon (autonym: ''Sassisch'', i.e. " Saxon", Standard High German: ', Modern Dutch: ') is a developmental stage of Low German. It developed from the Old Saxon language in the Middle Ages and has been documented i ...
are generally considered separate languages in their own right. Since Low German has strongly declined since the 18th century, the perceived similarities with High German or Dutch may often be direct adaptations from the dominating standard language, resulting in a growing inability by speakers to speak correctly what was once Low German proper.
Others have argued for the independence of today's Low German dialects, taken as continuous outflow of the Old Saxon and Middle Low German tradition. ''Glottolog'' classifies six varieties of Low German as distinct languages based on a low degree of mutual intelligibility
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. It is sometimes used as ...
. Eastern Low German and Plautdietsch are classified as part of Greater East Low German, while Eastphalian, Westphalic, and the North Low Saxon languages, German Northern Low Saxon and Gronings, are classified as part of West Low German.
Legal status
Low German has been recognized by the Netherlands and by Germany (since 1999) as aregional language
*
A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area.
Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Lan ...
according to the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages
The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML) is a European treaty (CETS 148) adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the Council of Europe to protect and promote historical regional and minority languages in Europe. However, th ...
. Within the official terminology defined in the charter, this status would not be available to a dialect of an official language (as per article 1a), and hence not to Low German in Germany if it were considered a dialect of German. Advocates of the promotion of Low German have expressed considerable hope that this political development will at once lend legitimacy to their claim that Low German is a separate language, and help mitigate the functional limits of the language that may still be cited as objective criteria for a mere dialect (such as the virtually complete absence from legal and administrative contexts, schools, the media, etc.).
At the request of Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
, the German government has declared Low German as a regional language
*
A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area.
Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Lan ...
. German offices in Schleswig-Holstein are obliged to accept and handle applications in Low German on the same footing as Standard High German applications. The ruled in a case that this was even to be done at the patent office in Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and ...
, in a non–Low German region, when the applicant then had to pay the charge for a translator, because applications in Low German are considered not to be written in the German language.
Varieties of Low German
*Low Saxon
Low Saxon, also known as West Low German ( nds, Nedersassisch, Nedersaksies; nl, Nedersaksisch) are a group of Low German dialects spoken in parts of the Netherlands, northwestern Germany and southern Denmark (in North Schleswig by parts of ...
or West Low German ()
** East Frisian Low Saxon
East Frisian Low German or East Frisian Low Saxon is one of the Northern Low Saxon dialects, a West Low German dialect spoken in the East Frisian peninsula of northwestern Lower Saxony. It is used quite frequently in everyday speech there. Ab ...
** Northern Low Saxon
Northern Low Saxon (in High German: ', in Standard Dutch: ') is a subgroup of Low Saxon dialects of Low German. As such, it covers a great part of the West Low German-speaking areas of northern Germany, with the exception of the border regio ...
*** Holsteinian (Holsteinisch)
*** Schleswigian (Schleswigsch)
*** Dithmarsch (Dithmarsisch)
*** North Hanoverian (Nordhannoversch)
*** Emslandish (Emsländisch)
*** Oldenburgish (Oldenburgisch)
*** Gronings and Noord-Drents
**** Hogelandsters
**** Oldambtsters
**** Stadsgronings
**** Veenkoloniaals
**** Westerkwartiers
***** Kollumerpompsters
***** Kollumerlands
***** Middaglands
***** Midden-Westerkwartiers
***** Zuid-Westerkwartiers
**** Westerwolds
** Westphalian ()
*** Westmünsterländisch
*** Münsterländisch
*** South Westphalian ()
*** East Westphalian ()
*** Stellingwerfs
Stellingwarfs ( nl, Stellingwerfs) is a Westphalian and Friso-Saxon dialect spoken in Ooststellingwerf and Weststellingwerf in the Dutch province of Friesland, and also in Steenwijkerland and Westerveld in the Dutch province of Overijssel an ...
*** Drents
**** Midden-Drents
**** Zuid-Drents
*** Twents
Tweants (Tweants pronunciation: ; nl, Twents ) is a group of non-standardised, closely related Westphalian, Dutch Low Saxon dialects, descending from Old Saxon. It is spoken daily by approximately 62% of the population of Twente, a region in t ...
**** Twents-Graafschaps
**** ''Twents''
*** Gelders-Overijssels
**** Achterhoeks
Achterhooks (Dutch Low Saxon: ; nl, Achterhoeks ) is a Westphalian dialect spoken in Gelderland.
Geographic distribution
The Achterhooks language is spoken in the Netherlands in western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Eur ...
**** Sallands
Sallaans ( nl, Sallands; Low Saxon: ''Sallaands'') is a collective term for the Westphalian dialects of the region Salland, in the province of Overijssel, as well as in minor parts of Gelderland and Drenthe in the Eastern Netherlands. In the Ko ...
**** Oost-Veluws (partly classified as Veluws)
**** Urkers
Urkers is the local language of the municipality and former island of Urk, located on the west coast of the Dutch province of Flevoland. Urk was an island until the middle of the 20th century. It was originally located in the Zuiderzee, a bay o ...
*** Veluws
Veluws is a Westphalian dialect which is spoken on the Veluwe, in the northwest of Gelderland, in central Netherlands. The language was recognized by the government of the Netherlands in 1996 (as part of Low Saxon).
Dialects
Veluws is usually ...
**** Oost-Veluws (partly classified as Gelders-Overijssels)
**** West-Veluws
West-Veluws is a Low Saxon dialect of the Dutch province of Gelderland. It is spoken in several Veluwe municipalities and villages including: Nunspeet, Putten, Ermelo (''Armelo''), Harderwijk (''Harderwiek''), Uddel, Nijkerk (''Niekark''), Appel ...
** Eastphalian ()
* East Low German ()
**
**
** Central Pomeranian ()
** East Pomeranian ()
** Low Prussian ()
** (Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the R ...
Low German, used also in many other countries)
History
Old Saxon
Old Saxon (), also known as Old Low German (), is a West Germanic language. It is documented from the 9th century until the 12th century, when it evolved intoMiddle Low German
Middle Low German or Middle Saxon (autonym: ''Sassisch'', i.e. " Saxon", Standard High German: ', Modern Dutch: ') is a developmental stage of Low German. It developed from the Old Saxon language in the Middle Ages and has been documented i ...
. It was spoken on the north-west coast of Germany and in Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
(Schleswig-Holstein) by Saxon people
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
s. It is closely related to Old Anglo-Frisian (Old Frisian
Old Frisian was a West Germanic language spoken between the 8th and 16th centuries along the North Sea coast, roughly between the mouths of the Rhine and Weser rivers. The Frisian settlers on the coast of South Jutland (today's Northern Fries ...
, Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
), partially participating in the Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law
In historical linguistics, the Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law (also called the Anglo-Frisian or North Sea Germanic nasal spirant law) is a description of a phonological development that occurred in the Ingvaeonic dialects of the West Germanic lan ...
.
Only a few texts survive, predominantly in baptismal vows the Saxons were required to perform at the behest of Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
. The only literary texts preserved are '' Heliand'' and the Old Saxon Genesis
''Genesis'' is an Old Saxon Biblical poem recounting the story of the Book of Genesis, dating to the first half of the 9th century, three fragments of which are preserved in a manuscript in the Vatican Library, ''Palatinus Latinus'' 1447. It and th ...
.
Middle Low German
The Middle Low German language () is an ancestor of modern Low German. It was spoken from about 1100 to 1600. The neighbouring languages within thedialect continuum
A dialect continuum or dialect chain is a series of language varieties spoken across some geographical area such that neighboring varieties are mutually intelligible, but the differences accumulate over distance so that widely separated vari ...
of the West Germanic languages
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided into ...
were Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects whose ancestor was Old Dutch. It was spoken and written between 1150 and 1500. Until the advent of Modern Dutch after 1500 or c. 1550, there was no overarc ...
in the West and Middle High German
Middle High German (MHG; german: Mittelhochdeutsch (Mhd.)) is the term for the form of German spoken in the High Middle Ages. It is conventionally dated between 1050 and 1350, developing from Old High German and into Early New High German. Hig ...
in the South, later substituted by Early New High German
Early New High German (ENHG) is a term for the period in the history of the German language generally defined, following Wilhelm Scherer, as the period 1350 to 1650.
The term is the standard translation of the German (Fnhd., Frnhd.), introduc ...
. Middle Low German was the lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
of the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label= Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
, spoken all around the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
and the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
. It had a significant influence on the Scandinavian languages
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is als ...
and other languages around the Baltic Sea. Based on the language of Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the state ...
, a standardized written language was developing, though it was never codified.
Contemporary
There is a distinction between theGerman
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
and the Dutch Low Saxon/Low German situation.
Germany
After mass education inGermany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
in the 19th and 20th centuries, the slow decline which Low German had been experiencing since the end of the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label= Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
turned into a free fall. The decision to exclude Low German in formal education was not without controversy, however. On one hand, proponents of Low German advocated that since it had a strong cultural and historical value and was the native language of students in northern Germany, it had a place in the classroom. On the other hand, High German was considered the language of education, science, and national unity, and since schools promoted these values, High German was seen as the best candidate for the language of instruction.
Initially, regional languages and dialects were thought to limit the intellectual ability of their speakers. When historical linguists illustrated the archaic character of certain features and constructions of Low German, this was seen as a sign of its "backwardness." It wasn't until the efforts of proponents such as Klaus Groth that this impression changed. Groth's publications demonstrated that Low German was a valuable language in its own right, and he was able to convince others that Low German was suitable for literary arts and was a national treasure worth keeping.
Through the works of advocates like Groth, both proponents and opponents of Low German in formal education saw the language's innate value as the cultural and historical language of northern Germany. Nevertheless, opponents claimed that it should simply remain a spoken and informal language to be used on the street and in the home, but not in formal schooling. In their opinion, it simply did not match the nationally unifying power of High German. As a result, while Low German literature was deemed worthy of being taught in school, High German was chosen as the language of scholarly instruction. With High German the language of education and Low German the language of the home and daily life, a stable diglossia developed in Northern Germany. Various Low German dialects are understood by 10 million people, but many fewer are native speakers. Total users of Low German (nds) are approximately 2.5 million, with 300,000 native speakers in Brazil and 1,000 in Germany as of 2016.
The KDE project supports Low German (nds) as a language for its computer desktop environment, as does the GNOME
A gnome is a mythological creature and diminutive spirit in Renaissance magic and alchemy, first introduced by Paracelsus in the 16th century and later adopted by more recent authors including those of modern fantasy literature. Its characte ...
Desktop Project. Open-source software
Open-source software (OSS) is computer software that is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and distribute the software and its source code to anyone and for any purpose. ...
has been translated into Low German; this used to be coordinated via a page on SourceForge, but as of 2015, the most active project is that of KDE.
Netherlands
In the early 20th century, scholars in the Netherlands argued that speaking dialects hindered language acquisition, and it was therefore strongly discouraged. As education improved, and mass communication became more widespread, the Low Saxon dialects further declined, although decline has been greater in urban centres of the Low Saxon regions. When in 1975 dialect folk and rock bands such asNormaal
Normaal is a rock band from the Netherlands, more specifically from the Achterhoek region, who sing in Achterhooks, a local variety of the Low Saxon language group. , who was an arts student at an arts academy, stationed in Amsterdam in the 1 ...
and became successful with their overt disapproval of what they experienced as "misplaced Dutch snobbery" and the Western Dutch contempt for (speakers of) Low Saxon dialects, they gained a following among the more rurally oriented inhabitants, launching Low Saxon as a sub-culture. They inspired contemporary dialect artists and rock bands, such as , , ,
Nonetheless, the position of the language is vulnerable according to UNESCO. Low Saxon is still spoken more widely than in Northern Germany. Efforts are made in Germany and in the Netherlands to protect Low German as a regional language
*
A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area.
Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Lan ...
.
Sound change
As with the Anglo-Frisian andNorth Germanic languages
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is also ...
, Low German has not been influenced by the High German consonant shift
In historical linguistics, the High German consonant shift or second Germanic consonant shift is a phonological development ( sound change) that took place in the southern parts of the West Germanic dialect continuum in several phases. It probabl ...
except for old having shifted to . Therefore, a lot of Low German words sound similar to their English counterparts. One feature that does distinguish Low German from English generally is final devoicing of obstruents, as exemplified by the words 'good' and 'wind' below. This is a characteristic of Dutch and German as well and involves positional neutralization of voicing contrast in the coda position for obstruents (i.e. t = d at the end of a syllable.) This is not used in English except in the Yorkshire dialect
The Yorkshire dialect (also known as Broad Yorkshire, Tyke, Yorkie or Yorkshire English) is a dialect of English, or continuum of dialects, spoken in the Yorkshire region of Northern England. The dialect has roots in Old English and is influen ...
, where there is a process known as '' Yorkshire assimilation''.
For instance: ''water'' , ''later'' , ''bit'' , ''dish'' , ''ship'' , ''pull'' , ''good'' , ''clock'' , ''sail'' , ''he'' , ''storm'' , ''wind'' , ''grass'' , ''hold'' , ''old'' .
The table below shows the relationship between Low German consonants which were unaffected by this chain shift
In historical linguistics, a chain shift is a set of sound changes in which the change in pronunciation of one speech sound (typically, a phoneme) is linked to, and presumably causes, a change in pronunciation of other sounds as well. The soun ...
and their equivalents in other West Germanic languages. Contemporary Swedish and Icelandic shown for comparison; Eastern and Western North Germanic languages, respectively.
''Notes'':
:cognates
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words in different languages that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language. Because language change can have radical eff ...
, not semantic equivalents. The meanings of some of these words have shifted over time. For example, the correct equivalent term for "wife" in modern Dutch, German and Swedish is , and respectively; using , or for a human is considered archaic in Swedish and nowadays derogatory in Dutch and German, comparable to " wicked girl". No cognate to / / has survived in English (compare Old English "lady"; the English word '' frow'' "woman, lady" rather being a borrowing of the Middle Dutch word).
:Grammar
Generally speaking, Low Germangrammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraints, a field that includes doma ...
shows similarities with the grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraints, a field that includes doma ...
s of Dutch, Frisian, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
, and Scots, but the dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that is ...
s of Northern Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
share some features (especially lexical and syntactic
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency) ...
features) with German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
dialects.
Verbs
In Low German verbs are conjugated for person, number, and tense. There are five tenses in Low German:present tense
The present tense ( abbreviated or ) is a grammatical tense whose principal function is to locate a situation or event in the present time. The present tense is used for actions which are happening now. In order to explain and understand present ...
, preterite
The preterite or preterit (; abbreviated or ) is a grammatical tense or verb form serving to denote events that took place or were completed in the past; in some languages, such as Spanish, French, and English, it is equivalent to the simple ...
, perfect, and pluperfect, and in Mennonite Low German the present perfect which signifies a remaining effect from a past finished action. For example, "", "I am come", means that the speaker came and he is still at the place to which he came as a result of his completed action.
Unlike Dutch, High German, and southern Low German, the northern dialects form the past participle without the prefix ''ge-'', like the Scandinavian languages
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is als ...
, Frisian and English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
. Compare northern Low German to the German past participle
In linguistics, a participle () (from Latin ' a "sharing, partaking") is a nonfinite verb form that has some of the characteristics and functions of both verbs and adjectives. More narrowly, ''participle'' has been defined as "a word derived from ...
. This past participle
In linguistics, a participle () (from Latin ' a "sharing, partaking") is a nonfinite verb form that has some of the characteristics and functions of both verbs and adjectives. More narrowly, ''participle'' has been defined as "a word derived from ...
is used with the auxiliary verbs ''hewwen/hebben'' "to have" and ''wesen/sin/sien'' "to be". When the past participle
In linguistics, a participle () (from Latin ' a "sharing, partaking") is a nonfinite verb form that has some of the characteristics and functions of both verbs and adjectives. More narrowly, ''participle'' has been defined as "a word derived from ...
ends with ''-en'' or in a few oft-used words like ''west'' (been).
There is also a progressive form of verbs in present, corresponding to the same in the Dutch language.
It is formed with ''wesen'' (to be), the preposition ''an'' (at) and ''dat'' (the/it).
: 1 Instead of ''wesen, sien'' (to be) Saxon uses ''doon'' (to do) to make to present continuous.
: 2 Many see the ''n'' as an old dative ending of ''dat'' which only occurs when being shortened after prepositions. This is actually the most frequently-used form in colloquial Low German.
: 3 This form is archaic and mostly unknown to Low German speakers. It is the same pattern as in the English example "I am making." The present participle has the same form as the infinitive: ''maken'' is either "to make" or "making".
Adjectives
The forms of Low German's adjectives are distinct from other closely related languages such as German and English. These forms fall somewhere in between these two languages. As in German, the adjectives in Low German may make a distinction between singular and plural to agree with the nouns that they modify, as well as between the three genders, between the nominative and oblique cases and between indefinite (weak) and definite (strong) forms.SASS Plattdeutsche Grammatik 2.5.2. Deklination der Adjektive/ref> However, there is a lot of variation in that respect and some or all of these distinctions may also be absent, so that a single undeclined form of the adjective can occur in all cases, as in English. This is especially common in the neuter. If the adjective is declined, the pattern tends to be as follows: As mentioned above, alternative undeclined forms such as ''dat lütt Land'', ''de lütt Lannen'', ''en stark Kerl'', ''de stark Kerl'', ''stark Kerls'', ''de stark Kerls'' etc. can occur.
Phonology
Consonants
*A common feature of the Low German speaking dialects, is the retraction of / / to . *The sound [] can occur as an allophone of // among dialects. *// and // can have allophones as [] and []. *// can be articulated as uvular [] among Northern dialects and younger speakers. * The sound // can also be realized as fricative or affricate sounds ~ [], in word-initial position.Vowels
* [] and [] can occur as allophones of // and //. *Vowel backness of // to [] may also occur among dialects. * [] can be heard as an allophone of // within diphthongs. *Long phonemes //, //, //, occur mostly in the Geest dialects, while in other dialects, they may be realized as diphthongs.Writing system
Low German is written using theLatin alphabet
The Latin alphabet or Roman alphabet is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered with the exception of extensions (such as diacritics), it used to write English and the ...
. There is no official standard orthography
An orthography is a set of conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalization, word breaks, emphasis, and punctuation.
Most transnational languages in the modern period have a writing system, and ...
, though there are several locally more or less accepted orthographic guidelines. Those in the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
are mostly based on Dutch orthography and may vary per dialect region, and those in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
mostly follow German orthography. To the latter group belongs the orthography devised by Johannes Sass
Johannes Sass (also in German: Saß) born in Hamburg, died ) was a linguist who specialized in the Low German language. He obtained his doctorate in 1926 from the University of Hamburg.
Significance in Low German
Although Low German has no ...
. It is mostly used by modern official publications and internet sites, especially the Low German Wikipedia. This diversity, a result of centuries of official neglect and suppression, has a very fragmenting and thus weakening effect on the language as a whole, since it has created barriers that do not exist on the spoken level.Dieter Stellmacher: ''Niederdeutsche Grammatik - Phonologie und Morphologie''. In: Gerhard Cordes & Dieter Möhn: ''Handbuch zur niederdeutschen Sprach- und Literaturwissenschaft''. Berlin: Erich Schmidt Verlag 1983, p.239. Interregional and international communication is severely hampered by this. Most of these systems aim at representing the phonetic
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that studies how humans produce and perceive sounds, or in the case of sign languages, the equivalent aspects of sign. Linguists who specialize in studying the physical properties of speech are phoneticians. ...
(allophonic
In phonology, an allophone (; from the Greek , , 'other' and , , 'voice, sound') is a set of multiple possible spoken soundsor ''phones''or signs used to pronounce a single phoneme in a particular language. For example, in English, (as in ' ...
) output rather than underlying (phonemic
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-west ...
) representations. An alternative spelling based on etymology
Etymology () The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words ...
was the Algemeyne Schryvwyse developed by Reinhard Franz Hahn, which was designed mostly with Northern Low German dialects in mind. In 2020, a group of Dutch and German Low German Wikipedians took Hahn's principles and used them to create the Nysassiske Skryvwyse (New Saxon Orthography), which is aimed to cover all dialects on both sides of the Dutch-German border. That being as it may, many writers follow guidelines only roughly. This adds numerous idiosyncratic and often inconsistent ways of spelling to the already existing great orthographic diversity.
Notable Low German writers and performers
*Heinrich Bandlow
Heinrich Bandlow (born 14 April 1855 in Tribsees; died 25 August 1933 in Greifswald) was a Pomeranian author, writing in Standard as well as in Low German. For his Low German works he is known as "Pomeranian Reuter", which is a reference to his Me ...
* Hans-Friedrich Blunck
* John Brinckmann
* De fofftig Penns
* Gorch Fock
* Friedrich Wilhelm Grimme (Westphalian: Sauerländisch)
* Klaus Groth (Dithmarsisch)
* August Hermann
Friedrich August Wilhelm Theodor Hermann (14 September 1835 – 20 February 1906) was a German physical education instructor. He, along with Konrad Koch, introduced the game of association football to Germany from England in 1874. He is known ...
* Joachim Mähl
* Johann Meyer (Dithmarsisch)
* Martha Müller-Grählert
* Fritz Reuter (Mecklenburgisch-Vorpommersch)
* Willem Schröder
* Julius Stinde
Julius Stinde (28 August 1841 – 5 August 1905), was a German author born at Kirchnüchel in Holstein, the son of a clergyman.
Having attended the gymnasium at Eutin, he was apprenticed in 1858 to a chemist in Lübeck. He soon tired of the shop ...
* Rudolf Tarnow
* Augustin Wibbelt (Westphalian: Münsterländisch)
* Wilhelm Wieben
Wilhelm Wieben (2 June 1935 – 13 June 2019) was a German journalist, actor and author, best known for presenting the daily news in ''Tagesschau'', the most-watched news program on German television, from 1973 to 1998.
Biography
Wieben was b ...
* Hans-Jürgen Massaquoi
* Normaal
Normaal is a rock band from the Netherlands, more specifically from the Achterhoek region, who sing in Achterhooks, a local variety of the Low Saxon language group. , who was an arts student at an arts academy, stationed in Amsterdam in the 1 ...
* Daniël Lohues
Middle Low German
Middle Low German or Middle Saxon (autonym: ''Sassisch'', i.e. " Saxon", Standard High German: ', Modern Dutch: ') is a developmental stage of Low German. It developed from the Old Saxon language in the Middle Ages and has been documented i ...
authors:
* Eggerik Beninga
Eggerik Beninga (1490–1562), also known as Eggeric(k) Benninga or Benynga, was an East Frisian chronicler and steward of the Leerort Fortress. From 1540 to 1556 he was also counselor to Anna of Oldenburg. He wrote an account of the history of the ...
* Balthasar Russow
* Albert Suho Albert Suho (before 1390 - after 1449) was a cleric and writer. He enjoyed a successful church career in his home town of Osnabrück, and represented the town at the Council of Basel. He wrote a number of theological works in Latin and a world ch ...
Plautdietsch authors:
* Arnold Dyck
* Reuben Epp Reuben Epp (March 1 1920 – June 20, 2009) was an author of works in Plautdietsch (Mennonite Low German).
Early life
Epp's parents were Russian Mennonites who emigrated from Russia to Canada, where Epp was born in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan in 192 ...
* Jack Thiessen
John Peter Thiessen (14 April 1931 – 9 October 2022) was a Canadian Russian Mennonite teacher, translator, and writer from Manitoba. Alongside Arnold Dyck and Reuben Epp, he was an important contributor to the development of Mennonite Low Ge ...
See also
* 1614 Low German Bible *Bible translations into German German language translations of the Bible have existed since the Middle Ages. The most influential is Luther's translation, which established High German as the literary language throughout Germany by the middle of the seventeenth century and which ...
* Friar Rush
''Friar Rush'' (', ', ') is the title of a medieval Low German legend, surviving in a 1488 edition in verse form. During the 16th and 17th centuries, numerous High German, Scandinavian (Danish and Swedish), Dutch and English translations and adapt ...
* Hamborger Veermaster De Hamborger Veermaster (Standard German: Der Hamburger Viermaster, English: Hamburg's four-master) is a famous sea shanty sung in Low German, presumably first published between 1850 and 1890. It is partly in English, an adaptation of the shanty "T ...
* The Juniper Tree (fairy tale)
* Meuse-Rhenish
Meuse-Rhenish (German: ''Rheinmaasländisch'', Dutch: ''Maas-Rijnlands'', and French: ''francique rhéno-mosan'') is the modern term for literature written in the Middle Ages in the greater Meuse-Rhine area, in a literary language that is eff ...
* Moin
* Ohnsorg-Theater
* Masurian dialect
Notes
References
Bibliography
*External links
* http://www.plattmaster.de/ * http://www.platt-online.de/ * http://www.niederdeutschzentrum.de/ * https://www.deutsch-plattdeutsch.de/Online dictionaries
Plattmakers dictionary
with more than 20,000 word entries, with translations and interface available in several languages (English too)
Dictionary of the Drents dialect
(Dutch)
Information
Nu is de Welt platt!
International resources in and about Low German
Building Blocks of Low Saxon (Low German)
an introductory grammar in English and German
Niederdeutsch/Plattdeutsch in Westfalen
by Olaf Bordasch
Mönsterlänner Plat
by Klaus-Werner Kahl
Organisations
IJsselacademie
(Overijssel and Veluwe, the Netherlands)
Staring Instituut
(Achterhoek, the Netherlands)
Stichting Stellingwarver Schrieversronte
(Friesland, the Netherlands)
SONT
(General, the Netherlands)
Oostfreeske Taal
(Eastern Friesland, Germany)
Diesel - dat oostfreeske Bladdje
(Eastern Friesland, Germany)
Institut für niederdeutsche Sprache e.V.
(General, Germany) {{Use dmy dates, date=March 2017 Languages of Germany West Germanic languages German dialects Dutch dialects Danish dialects North Sea Germanic