Los Adaes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
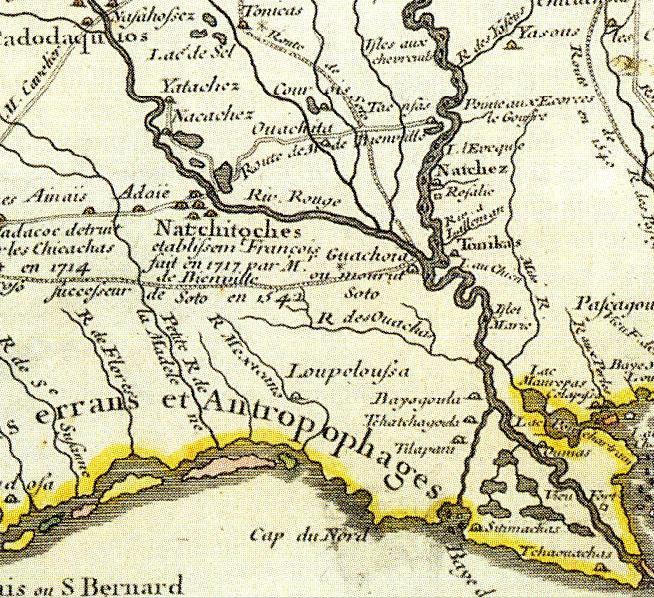 Los Adaes was the capital of Tejas on the northeastern frontier of
Los Adaes was the capital of Tejas on the northeastern frontier of
 Today the site of Los Adaes is th
Today the site of Los Adaes is th
Los Adaes State Historic Site
near the town of
Site Explorer showing the history of Los Adaes
at Louisiana Division of Archaeology
Los Adaes State Historic Site (LA)
- official site
Los Adaes: An 18th-Century Capital of Texas in Northwestern Louisiana
by George Avery, Los Adaes Station Archaeologist.
Cane River National Heritage Area, a National Park Service ''Discover Our Shared Heritage'' Travel Itinerary
{{DEFAULTSORT:Adaes, Los Spanish Texas Colonial forts in Louisiana Spanish forts in the United States Museums in Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana Former colonial and territorial capitals in the United States Archaeological sites on the National Register of Historic Places in Louisiana Forts on the National Register of Historic Places in Louisiana Louisiana State Historic Sites National Historic Landmarks in Louisiana Protected areas of Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana 1729 establishments in Texas 1730s in Texas 1740s in Texas 1750s in Texas National Register of Historic Places in Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana
 Los Adaes was the capital of Tejas on the northeastern frontier of
Los Adaes was the capital of Tejas on the northeastern frontier of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
from 1729 to 1770. It included a mission
Mission (from Latin ''missio'' "the act of sending out") may refer to:
Organised activities Religion
*Christian mission, an organized effort to spread Christianity
*Mission (LDS Church), an administrative area of The Church of Jesus Christ of ...
, San Miguel de Cuellar de los Adaes, and a presidio
A presidio ( en, jail, fortification) was a fortified base established by the Spanish Empire around between 16th century, 16th and 18th century, 18th centuries in areas in condition of their control or influence. The presidios of Captaincy Genera ...
, Nuestra Señora del Pilar de Los Adaes (Our Lady of the Pillar of the Adaes). The name Adaes represents the indigenous Adai people
The Adai (also Adaizan, Adaizi, Adaise, Adahi, Adaes, Adees, Atayos) were a Native American people of northwestern Louisiana and northeastern Texas with a Southeastern culture. The name ''Adai'' is derived from the Caddo word ''hadai'' meaning ' ...
, who were to be served by the mission.
The site, now preserved in the state-run Los Adaes State Historic Site, is located on Louisiana Highway 485
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
in present-day Natchitoches Parish
Natchitoches Parish (french: Paroisse des Natchitoches or ) is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. As of the 2010 census, the population was 39,566. The parish seat is Natchitoches. The parish was formed in 1805.
The Natchito ...
, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
. It was designated a National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
in 1986.
History
Although Spain claimed much of theGulf Coast
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South, is the coast, coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The list of U.S. states and territories by coastline, coastal states that have a shor ...
of North America as part of its colonial territory, it largely ignored the region to the east of the Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico.
The length of the Rio G ...
throughout the 17th century. In 1699, French fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
s were established at Biloxi Bay
Biloxi ( ; ) is a city in and one of two county seats of Harrison County, Mississippi, United States (the other being the adjacent city of Gulfport). The 2010 United States Census recorded the population as 44,054 and in 2019 the estimated popu ...
and on the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
, ending Spain's exclusive control of the Gulf Coast.Weber (1992), p. 158. The Spanish recognized that French encroachment could threaten other Spanish areas, and they ordered the reoccupation of Texas as a buffer between New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
and French settlements in Louisiana.Weber (1992), p. 60.
On April 12, 1716, an expedition led by Domingo Ramon left San Juan Bautista for Tejas, intending to establish four missions and a presidio
A presidio ( en, jail, fortification) was a fortified base established by the Spanish Empire around between 16th century, 16th and 18th century, 18th centuries in areas in condition of their control or influence. The presidios of Captaincy Genera ...
.Chipman (1992), p. 111.Chipman (1992), p. 112. At the same time, the French were building a fort in Natchitoches, having founded the town in 1714. The Spanish countered by founding two more missions just west of Natchitoches, including San Miguel de los Adaes (for a total of six missions in the region).Weber (1992), p. 162. The latter two missions were located in a disputed area; France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
claimed the Sabine River to be the western boundary of colonial Louisiana, while Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
claimed the Red River was the eastern boundary of colonial Texas, leaving an overlap of .
In 1719, European powers embarked on the War of the Quadruple Alliance
The War of the Quadruple Alliance (1718–1720) was caused by Spanish attempts to recover territories in Italy ceded in the 1713 Peace of Utrecht. Largely focused on Sicily, it included minor engagements in North America and Northern Europe as we ...
. In June 1719, 7 Frenchmen from Natchitoches took control of the mission of San Miguel de los Adaes from its sole defender, who did not know that the nations were at war. The French soldiers explained that 100 additional soldiers were coming; the Spanish colonists, missionaries, and remaining soldiers abandoned the area and fled to San Antonio
("Cradle of Freedom")
, image_map =
, mapsize = 220px
, map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = United States
, subdivision_type1= U.S. state, State
, subdivision_name1 = Texas
, s ...
.
The Marquis de San Miguel de Aguayo
A marquess (; french: marquis ), es, marqués, pt, marquês. is a nobleman of high hereditary rank in various European peerages and in those of some of their former colonies. The German language equivalent is Markgraf (margrave). A woman wi ...
volunteered to reconquer Spanish Texas
Spanish Texas was one of the interior provinces of the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1690 until 1821. The term "interior provinces" first appeared in 1712, as an expression meaning "far away" provinces. It was only in 1776 that a lega ...
and raised an army of 500 soldiers.Weber (1992), p. 167. By July 1721 Aguayo reached the Neches River
The Neches River () begins in Van Zandt County west of Rhine Lake and flows for through the piney woods of east Texas, defining the boundaries of 14 counties on its way to its mouth on Sabine Lake near the Rainbow Bridge. Two major reservoirs, ...
. His expedition encountered a French force ''en route'' to attack San Antonio de Bexar
("Cradle of Freedom")
, image_map =
, mapsize = 220px
, map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = United States
, subdivision_type1= State
, subdivision_name1 = Texas
, subdivision_t ...
. The outnumbered Frenchmen agreed to retreat to Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
. Aguayo then ordered the building of a new presidio
A presidio ( en, jail, fortification) was a fortified base established by the Spanish Empire around between 16th century, 16th and 18th century, 18th centuries in areas in condition of their control or influence. The presidios of Captaincy Genera ...
Nuestra Señora del Pilar de Los Adaes, located near present-day Robeline, Louisiana
Robeline is a village in western Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana, United States. The population was 183 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Natchitoches Micropolitan Statistical Area.
History
Robeline was the capital of Texas for 50 years. ...
, only 12 miles (19 km) from Natchitoches. The new fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
became the first capital of Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, and it was guarded by 6 cannon and a garrison of 100 soldiers. All six of the eastern Tejas mission
Mission (from Latin ''missio'' "the act of sending out") may refer to:
Organised activities Religion
*Christian mission, an organized effort to spread Christianity
*Mission (LDS Church), an administrative area of The Church of Jesus Christ of ...
s were reopened, under the protection of the new presidio.
Spain discouraged manufacturing in its colonies and limited trade to Spanish goods handled by Spanish merchants and carried on Spanish vessels. Most of the port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
s, including all of those in Texas, were closed to commercial vessels in the hopes of dissuading smugglers. By law, all goods bound for Texas had to be shipped to Vera Cruz and then transported over the mountains to Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley o ...
before being sent to Texas. This caused the goods to be very expensive in the Texas settlements. Because of the great distance between Los Adaes and the rest of the populated portions of Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, the settlers in the area turned most often to the French colonists in neighboring Natchitoches, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
, for trade. Without many goods to trade, however, the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
missionaries and colonists had little to offer the Indians, who remained loyal to the French traders.
Although the Spanish settlers in the area did not encounter hostile Native Americans, since the local Caddoan
The Caddoan languages are a family of languages native to the Great Plains spoken by tribal groups of the central United States, from present-day North Dakota south to Oklahoma. All Caddoan languages are critically endangered, as the number of ...
-speaking peoples were friendly, the Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related Mendicant orders, mendicant Christianity, Christian Catholic religious order, religious orders within the Catholic Church. Founded in 1209 by Italian Catholic friar Francis of Assisi, these orders include t ...
missionaries were unsuccessful in converting
Converting companies are companies that specialize in modifying or combining raw materials such as polyesters, adhesives, silicone, adhesive tapes, foams, plastics, felts, rubbers, liners and metals, as well as other materials, to create new pro ...
the local people to Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. After many years of frustration in this regard, in 1768 the College of Nuestra Señora de Guadalupe de Zacatecas, which was the sponsor of the missionaries at Los Adaes, recalled their missionaries, and the mission was closed.
On November 3, 1762, as part of the Treaty of Fontainebleau, France ceded the portion of Louisiana west of the Mississippi River to Spain.
With France no longer a threat to Spain's North American interests, the Spanish monarchy
, coatofarms = File:Coat_of_Arms_of_Spanish_Monarch.svg
, coatofarms_article = Coat of arms of the King of Spain
, image = Felipe_VI_in_2020_(cropped).jpg
, incumbent = Felipe VI
, incumbentsince = 19 Ju ...
commissioned the Marquis de Rubi to inspect all of the presidios on the northern frontier of New Spain and make recommendations for the future.Chipman (1992), p. 173. Rubi recommended that eastern Texas be totally abandoned, with all the population moving to San Antonio.Chipman (1992), p. 181. With Louisiana in Spanish control, there was no need for Los Adaes to reside so closely to Natchitoches, especially after the missions had relocated to San Antonio. In August 1768, the acting governor, Juan María Vicencio, Baron de Ripperdá, moved his headquarters and the garrison to San Antonio, and in 1772 San Antonio
("Cradle of Freedom")
, image_map =
, mapsize = 220px
, map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = United States
, subdivision_type1= U.S. state, State
, subdivision_name1 = Texas
, s ...
became the new capital of Tejas.Weber (1992), p. 211.
The settlers who had lived near Los Adaes were forced to resettle in San Antonio, in 1773. In the six years between the inspection and the removal of the settlers, the population of eastern Tejas had increased from 200 settlers of European descent to 500 people, a mixture of Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, French, Indians, and a few blacks
Black is a racialized classification of people, usually a political and skin color-based category for specific populations with a mid to dark brown complexion. Not all people considered "black" have dark skin; in certain countries, often in ...
. The settlers were given only five days to prepare for the move to San Antonio. Many of them perished during the three-month trek and others died soon after arriving.Chipman (1992), p. 186.
After vociferously protesting, the former residents of eastern Tejas were allowed to leave San Antonio the following year (1774); but they were not allowed to locate beyond the Trinity River, 175 miles (282 km) from Natchitoches.Weber (1992), p. 222. In 1779, the Comanche
The Comanche or Nʉmʉnʉʉ ( com, Nʉmʉnʉʉ, "the people") are a Native American tribe from the Southern Plains of the present-day United States. Comanche people today belong to the federally recognized Comanche Nation, headquartered in La ...
s began raiding the new settlement. The former Los Adaes settlers chose to move farther east to the old mission
Mission (from Latin ''missio'' "the act of sending out") may refer to:
Organised activities Religion
*Christian mission, an organized effort to spread Christianity
*Mission (LDS Church), an administrative area of The Church of Jesus Christ of ...
of Nacogdoches, where they founded the town of the same name. The new town quickly became a waystation for contraband.
The site of Los Adaes was declared a National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
in 1986. It is a site on the El Camino Real de los Tejas National Historic Trail
The El Camino Real de los Tejas National Historic Trail is a national historic trail covering the U.S. section of ''El Camino Real de Los Tejas'', a thoroughfare from the 18th-century Spanish colonial era in Spanish Texas, instrumental in the settl ...
.
Present day
 Today the site of Los Adaes is th
Today the site of Los Adaes is thLos Adaes State Historic Site
near the town of
Robeline, Louisiana
Robeline is a village in western Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana, United States. The population was 183 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Natchitoches Micropolitan Statistical Area.
History
Robeline was the capital of Texas for 50 years. ...
. The Los Adaes site has proven to be one of the most important archaeological sites in the US for the study of colonial Spanish culture.
Dr. Hiram F. "Pete" Gregory Jr., an archaeologist at nearby Northwestern State University
Northwestern State University of Louisiana (NSU) is a public university primarily situated in Natchitoches, Louisiana, with a nursing campus in Shreveport and general campuses in Leesville/Fort Polk and Alexandria. It is a part of the Univer ...
, conducted landmark excavations at the historic presidio from the 1960s through the 1980s. In the 1990s, the state appointed Dr. George Avery to the newly created position of station archaeologist of the Los Adaes State Commemorative Area (as it was called at the time). In this capacity, Avery contributed a great deal in his own right. Los Adaes has since lost its station archaeologist position. However, Avery, Gregory, and other archaeologists specializing in the Spanish colonial borderlands continue to advance the knowledge of this frontier outpost. Gregory, in particular, has championed the need for more academic interest in Los Adaes and the colonial history of northern and central Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
in general.
See also
*Adai people
The Adai (also Adaizan, Adaizi, Adaise, Adahi, Adaes, Adees, Atayos) were a Native American people of northwestern Louisiana and northeastern Texas with a Southeastern culture. The name ''Adai'' is derived from the Caddo word ''hadai'' meaning ' ...
*Adai language
Adai (also Adaizan, Adaizi, Adaise, Adahi, Adaes, Adees, Atayos) is an extinct Native American language that was spoken in northwestern Louisiana.
Classification
It was once proposed that there may be a connection between Adai and the nearby Cadd ...
*List of National Historic Landmarks in Louisiana
This is a complete list of National Historic Landmarks in Louisiana,.
The United States National Historic Landmark program is a program of the National Park Service, and recognizes structures, districts, objects, and similar resources according to ...
*Louisiana (New France)
Louisiana (french: La Louisiane; ''La Louisiane Française'') or French Louisiana was an administrative district of New France. Under French control from 1682 to 1769 and 1801 (nominally) to 1803, the area was named in honor of King Louis XIV, ...
*Louisiana (New Spain)
Spanish Louisiana ( es, link=no, la Luisiana) was a governorate and administrative district of the Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1762 to 1801 that consisted of a vast territory in the center of North America encompassing the western basin of t ...
*Spanish missions in Louisiana
The Spanish missions in Louisiana were religious outposts in Spanish Louisiana (''La Luisiana'') region of the Viceroyalty of New Spain, located within the present-day U.S. states of Louisiana and East Texas.
They were established by Spanish mis ...
*Spanish missions in Texas
The Spanish Missions in Texas comprise a series of religious outposts established by Spanish Catholic Dominicans, Jesuits, and Franciscans to spread the Catholic doctrine among area Native Americans, but with
the added benefit of giving Spai ...
*Spanish Texas
Spanish Texas was one of the interior provinces of the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1690 until 1821. The term "interior provinces" first appeared in 1712, as an expression meaning "far away" provinces. It was only in 1776 that a lega ...
*National Register of Historic Places listings in Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana
__NOTOC__
This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana.
This is intended to be a complete list of the properties and districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Natchitoches ...
Footnotes
References
* *External links
*Site Explorer showing the history of Los Adaes
at Louisiana Division of Archaeology
Los Adaes State Historic Site (LA)
- official site
Los Adaes: An 18th-Century Capital of Texas in Northwestern Louisiana
by George Avery, Los Adaes Station Archaeologist.
Cane River National Heritage Area, a National Park Service ''Discover Our Shared Heritage'' Travel Itinerary
{{DEFAULTSORT:Adaes, Los Spanish Texas Colonial forts in Louisiana Spanish forts in the United States Museums in Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana Former colonial and territorial capitals in the United States Archaeological sites on the National Register of Historic Places in Louisiana Forts on the National Register of Historic Places in Louisiana Louisiana State Historic Sites National Historic Landmarks in Louisiana Protected areas of Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana 1729 establishments in Texas 1730s in Texas 1740s in Texas 1750s in Texas National Register of Historic Places in Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana