Liver Cancer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Liver cancer (also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy) is
 The most frequent liver cancer, accounting for approximately 75% of all primary liver cancers, is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HCC is a cancer formed by liver cells, known as
The most frequent liver cancer, accounting for approximately 75% of all primary liver cancers, is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HCC is a cancer formed by liver cells, known as
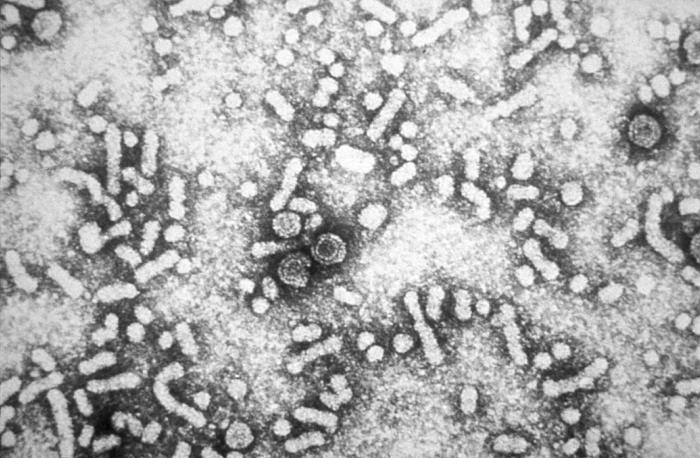 Viral infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) or
Viral infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) or
 In addition to virus-related
In addition to virus-related
 Partial surgical resection is the recommended treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) when patients have sufficient hepatic function reserve. 5-year survival rates after resection have massively improved over the last few decades and can now ranges from 41 to 74%. However, recurrence rates after resection can exceed 70%, whether due to spread of the initial tumor or formation of new tumors . Liver transplantation can also be considered in cases of HCC where this form of treatment can be tolerated and the tumor fits specific criteria (such as the Milan criteria). In general, patients who are being considered for liver transplantation have multiple hepatic lesions, severe underlying liver dysfunction, or both.
Percutaneous ablation is the only non-surgical treatment that can offer cure. There are many forms of percutaneous ablation, which consist of either injecting chemicals into the liver (
Partial surgical resection is the recommended treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) when patients have sufficient hepatic function reserve. 5-year survival rates after resection have massively improved over the last few decades and can now ranges from 41 to 74%. However, recurrence rates after resection can exceed 70%, whether due to spread of the initial tumor or formation of new tumors . Liver transplantation can also be considered in cases of HCC where this form of treatment can be tolerated and the tumor fits specific criteria (such as the Milan criteria). In general, patients who are being considered for liver transplantation have multiple hepatic lesions, severe underlying liver dysfunction, or both.
Percutaneous ablation is the only non-surgical treatment that can offer cure. There are many forms of percutaneous ablation, which consist of either injecting chemicals into the liver (
 Globally, liver cancer is common and increasing. Most recent epidemiological data suggests that liver cancer is in the top 10 for both prevalence and mortality (noted to be the 6th leading cause of cancer and 4th most common cause of death). The Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer Collaboration found that from 1990 to 2015 the new cases of liver cancer per year increased by 75%. Estimates based on most recent data suggest that each year there are 841,000 new liver cancer diagnoses and 782,000 deaths across the globe. Liver cancer is the most common cancer in
Globally, liver cancer is common and increasing. Most recent epidemiological data suggests that liver cancer is in the top 10 for both prevalence and mortality (noted to be the 6th leading cause of cancer and 4th most common cause of death). The Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer Collaboration found that from 1990 to 2015 the new cases of liver cancer per year increased by 75%. Estimates based on most recent data suggest that each year there are 841,000 new liver cancer diagnoses and 782,000 deaths across the globe. Liver cancer is the most common cancer in
EASL Guideline
Liver cancer information
from
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
that starts in the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
. Liver cancer can be primary (starts in liver) or secondary (meaning cancer which has spread from elsewhere to the liver, known as liver metastasis
A liver metastasis is a malignant tumor in the liver that has spread from another organ affected by cancer. The liver is a common site for metastatic disease because of its rich, dual blood supply (the liver receives blood via the hepatic artery a ...
). Liver metastasis
A liver metastasis is a malignant tumor in the liver that has spread from another organ affected by cancer. The liver is a common site for metastatic disease because of its rich, dual blood supply (the liver receives blood via the hepatic artery a ...
is more common than that which starts in the liver. Liver cancer is increasing globally.
Primary liver cancer is globally the sixth-most frequent cancer and the fourth-leading cause of death from cancer. In 2018, it occurred in 841,000 people and resulted in 782,000 deaths globally. Higher rates of liver cancer occur where hepatitis B and C are common, including Asia and sub-Saharan Africa. Males are more often affected with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) than females. Diagnosis is most frequent among those 55 to 65 years old.
The leading cause of liver cancer is cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue rep ...
due to hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.
Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. ...
, hepatitis C or alcohol. Other causes include aflatoxin
Aflatoxins are various poisonous carcinogens and mutagens that are produced by certain molds, particularly ''Aspergillus'' species. The fungi grow in soil, decaying vegetation and various staple foodstuffs and commodities such as hay, sweetcorn ...
, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), also known as metabolic (dysfunction) associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), is excessive fat build-up in the liver without another clear cause such as alcohol use. There are two types; non-alcoholic ...
and liver fluke
Liver fluke is a collective name of a polyphyletic group of parasitic trematodes under the phylum Platyhelminthes.
They are principally parasites of the liver of various mammals, including humans. Capable of moving along the blood circulation, t ...
s. The most common types are HCC, which makes up 80% of cases and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. The diagnosis may be supported by blood tests and medical imaging, with confirmation by tissue biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disea ...
.
Given that there are many different causes of liver cancer, there are many approaches to liver cancer prevention. These efforts include immunization against hepatitis B, hepatitis B treatment, hepatitis C treatment, decreasing alcohol use, decreasing exposure to aflatoxin
Aflatoxins are various poisonous carcinogens and mutagens that are produced by certain molds, particularly ''Aspergillus'' species. The fungi grow in soil, decaying vegetation and various staple foodstuffs and commodities such as hay, sweetcorn ...
in agriculture, and management of obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
and diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
. Screening is recommended in those with chronic liver disease
Chronic liver disease in the clinical context is a disease process of the liver that involves a process of progressive destruction and regeneration of the liver parenchyma leading to fibrosis and cirrhosis. "Chronic liver disease" refers to disease ...
. For example, it is recommended that people with chronic liver disease who are at risk for hepatocellular carcinoma be screened every 6 months using ultrasound imaging.
Because liver cancer is an umbrella term
In linguistics, semantics, general semantics, and ontologies, hyponymy () is a semantic relation between a hyponym denoting a subtype and a hypernym or hyperonym (sometimes called umbrella term or blanket term) denoting a supertype. In other wor ...
for many types of cancer, the signs and symptoms depend on what type of cancer is present. Symptoms can be vague and broad. Cholangiocarcinoma is associated with sweating, jaundice, abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a m ...
, weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat ( adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other co ...
and liver enlargement. Hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with abdominal mass
An abdominal mass is any localized enlargement or swelling in the human abdomen. Depending on its location, the abdominal mass may be caused by an enlarged liver (hepatomegaly), enlarged spleen (splenomegaly), protruding kidney, a pancreatic m ...
, abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a m ...
, emesis
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteriti ...
, anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
, back pain
Back pain is pain felt in the back. It may be classified as neck pain (cervical), middle back pain (thoracic), lower back pain (lumbar) or coccydynia (tailbone or sacral pain) based on the segment affected. The lumbar area is the most common ...
, jaundice, itching
Itch (also known as pruritus) is a Wikt:sensation, sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of Sensory system, sensory experience. Itch has many similarities to pain, ...
, weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat ( adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other co ...
and fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
.
Treatment options may include surgery, targeted therapy
Targeted therapy or molecularly targeted therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment ( pharmacotherapy) for cancer, others being hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medicine, targeted therapy blocks ...
and radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radi ...
. In certain cases, ablation therapy
Ablation ( la, ablatio – removal) is removal or destruction of something from an object by vaporization, chipping, erosive processes or by other means. Examples of ablative materials are described below, and include spacecraft material for a ...
, embolization therapy or liver transplantation may be used.
Classification
Liver cancer can come from the liver parenchyma as well as other structures within the liver such as thebile duct
A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile, and is present in most vertebrates.
Bile is required for the digestion of food and is secreted by the liver into passages that carry bile toward the hepatic duct. It ...
, blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s and immune cells
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
. There are many sub-types of liver cancer, the most common of which are described below.
Hepatocellular carcinoma
 The most frequent liver cancer, accounting for approximately 75% of all primary liver cancers, is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HCC is a cancer formed by liver cells, known as
The most frequent liver cancer, accounting for approximately 75% of all primary liver cancers, is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HCC is a cancer formed by liver cells, known as hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, ...
s, that become malignant. In terms of cancer deaths, worldwide HCC is considered the 3rd most common cause of cancer mortalities.
In terms of HCC diagnosis, it is recommended that people with risk factors (including known chronic liver disease
Chronic liver disease in the clinical context is a disease process of the liver that involves a process of progressive destruction and regeneration of the liver parenchyma leading to fibrosis and cirrhosis. "Chronic liver disease" refers to disease ...
, cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue rep ...
, etc.) should receive screening ultrasounds. If the ultrasound shows a focal area that is larger than 1 centimeter in size, patients should then get a triple-phase contrast-enhanced CT or MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
imaging. HCC can then be diagnosed radiologically using the Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS). There is also a variant type of HCC that consists of both HCC and cholangiocarcinoma.
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Cancer of the bile duct ( cholangiocarcinoma and cholangiocellularcystadenocarcinoma
Cystadenocarcinoma is a malignant form of a cystadenoma and is a cancer derived from glandular epithelium, in which cystic accumulations of retained secretions are formed. The neoplastic cells manifest varying degrees of anaplasia and invasivenes ...
) account for approximately 6% of primary liver cancers. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is an epithelial cancer of the intra-hepatic biliary tree branches. Intrahepatic CCA is the second leading cause of primary liver cancer. It is more common in men and usually is diagnosed in 60-70 year olds. Risk factors for development of intrahepatic CCA include opisthorchus viverrini infection, Clonorchis sinensis
''Clonorchis sinensis'', the Chinese liver fluke, is a liver fluke belonging to the class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes. It infects fish-eating mammals, including humans. In humans, it infects the common bile duct and gall bladder, feeding o ...
infection, sclerosing cholangitis, choledochal cysts, past procedures of the biliary tree, exposure to thorotrast
Thorotrast is a suspension containing particles of the radioactive compound thorium dioxide, ThO2; it was used as a radiocontrast agent in clinical radiography in the 1930s to 1950s. It is no longer used clinically.
Thorium compounds produce ...
and dioxins, and cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue rep ...
. This cancer is usually asymptomatic until the disease has progressed. Symptoms include abdominal pain, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue. Liver markers that can be increased with intrahepatic CCA are carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), CA19-9, and CA-125.
Angiosarcoma and hemangiosarcoma
These are rare and aggressive liver cancers, yet are the third most common primary liver cancer making up 0.1-2.0% of primary liver cancer.Angiosarcoma
Angiosarcoma is a rare and aggressive cancer that starts in the endothelial cells that line the walls of blood vessels or lymphatic vessels. Since they are made from vascular lining, they can appear anywhere and at any age, but older people are ...
and hemangiosarcoma
Hemangiosarcoma is a rapidly growing, highly invasive variety of cancer that occurs almost exclusively in dogs, and only rarely in cats, horses, mice, or humans (vinyl chloride toxicity). It is a sarcoma arising from the lining of blood vessels; ...
of the liver come from the blood vessel's endothelial layer. These tumors have poor outcomes because they grow rapidly and metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then ...
e easily. They are also hard to diagnose but are typically suspected on CT or MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
imaging that shows focal lesions with differing amounts of echogenicity
Echogenicity (misspelled sometimes as echogenecity) or echogeneity is the ability to bounce an echo, e.g. return the signal in ultrasound examinations. In other words, echogenicity is higher when the surface bouncing the sound echo reflects incre ...
(these tumors have a lot of bleeding or hemorrhage and subsequent dying of tissue ( necrosis)). Biopsy with histopathological evaluation yields the definitive diagnosis. While the cause is often never identified (75% are idiopathic
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparent spontaneous origin. From Greek ἴδιος ''idios'' "one's own" and πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", ''idiopathy'' means approximately "a disease of its own kin ...
), they are associated with exposures to substances such as vinyl chloride
Vinyl chloride is an organochloride with the formula H2C=CHCl. It is also called vinyl chloride monomer (VCM) or chloroethene. This colorless compound is an important industrial chemical chiefly used to produce the polymer polyvinyl chloride (PVC ...
, arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, ...
, thorotrast
Thorotrast is a suspension containing particles of the radioactive compound thorium dioxide, ThO2; it was used as a radiocontrast agent in clinical radiography in the 1930s to 1950s. It is no longer used clinically.
Thorium compounds produce ...
(e.g. occupational exposure). Radiation is also a risk factor. In adults, these tumors are more common in males; however, in children they are more common in females.
Even with surgery prognosis is poor with most individuals not living longer than six months after diagnosis. Only 3% of individuals live longer than two years.
Hepatoblastoma
Another type of cancer formed by liver cells ishepatoblastoma
Hepatoblastoma is a malignant liver cancer occurring in infants and children and composed of tissue resembling fetal liver cells, mature liver cells, or bile duct cells. They usually present with an abdominal mass. The disease is most commonly di ...
, which is specifically formed by immature liver cells. It is a rare malignant tumor that primarily develops in children, and accounts for approximately 1% of all cancers in children and 79% of all primary liver cancers under the age of 15. Most hepatoblastomas form in the right lobe.
Metastasis to liver
Many cancers found in the liver are not true liver cancers but are cancers from other sites in the body that have spread to the liver (known asmetastases
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then ...
). Frequently, the site of origin is the gastrointestinal tract, since the liver is close to many of these metabolically active, blood-rich organs near to blood vessels and lymph nodes (such as pancreatic cancer, stomach cancer, colon cancer and carcinoid tumors mainly of the appendix), but also from breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a r ...
, ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous tumor of an ovary. It may originate from the ovary itself or more commonly from communicating nearby structures such as fallopian tubes or the inner lining of the abdomen. The ovary is made up of three different c ...
, lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
, renal cancer
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, is a group of cancers that starts in the kidney. Symptoms may include blood in the urine, lump in the abdomen, or back pain. Fever, weight loss, and tiredness may also occur. Complications can include spr ...
, prostate cancer.
Children
The Children's Oncology Group (COG) has developed a protocol to help diagnose and manage childhood liver tumors.Causes
Viral infection
 Viral infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) or
Viral infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) or Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.
Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. ...
virus (HBV) is the chief cause of liver cancer in the world today, accounting for 80% of HCC. Men with chronic HCV or HBV are more likely to develop HCC than women with chronic HCV or HBV; however, the reasons for this gender difference is unknown. HBV infection is also linked to cholangiocarcinoma. The role of viruses other than HCV or HBV in liver cancer is much less clear, even though there is some evidence that co-infection of HBV and hepatitis D
Hepatitis D is a type of viral hepatitis caused by the hepatitis delta virus (HDV). HDV is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. HDV is considered to be a satellite (a type of subviral agent) because it can propagate only in ...
virus may increase the risk for HCC.
HBV and HCV can lead to HCC, because these viral infections cause massive inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
, fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of perma ...
, and eventual cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue rep ...
occurs within the liver. In addition, many genetic and epigenetic changes are formed in liver cells during HCV and HBV infection, which is a major factor in the production of the liver tumors. The viruses induce malignant changes in cells by altering gene methylation, affecting gene expression, and promoting or repressing cellular signal transduction pathway
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellular ...
s. By doing this, the viruses can prevent cells from undergoing a programmed form of cell death ( apoptosis) and promote viral replication and persistence.
HBV and HCV also induce malignant changes by causing DNA damage and genomic instability
Genome instability (also genetic instability or genomic instability) refers to a high frequency of mutations within the genome of a cellular lineage. These mutations can include changes in nucleic acid sequences, chromosomal rearrangements or aneu ...
. This is by creating reactive oxygen species
In chemistry, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (). Examples of ROS include peroxides, superoxide, hydroxyl radical, singlet oxygen, and alpha-oxygen.
The reduction of molecular oxygen () p ...
, express proteins that interfere with DNA repair enzymes, and HCV causes activation of a mutator enzyme.
Cirrhosis
 In addition to virus-related
In addition to virus-related cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue rep ...
described above, other causes of cirrhosis can lead to HCC. Alcohol intake correlates with risk of HCC, and the risk is far greater in individuals with an alcohol-induced cirrhotic liver. There are a few disorders that are known to cause cirrhosis and lead to cancer, including hereditary hemochromatosis
Iron overload or hemochromatosis (also spelled ''haemochromatosis'' in British English) indicates increased total accumulation of iron in the body from any cause and resulting organ damage. The most important causes are hereditary haemochromatos ...
and primary biliary cirrhosis.
Aflatoxin
Aflatoxin
Aflatoxins are various poisonous carcinogens and mutagens that are produced by certain molds, particularly ''Aspergillus'' species. The fungi grow in soil, decaying vegetation and various staple foodstuffs and commodities such as hay, sweetcorn ...
exposure can lead to the development of HCC. The aflatoxins are a group of chemicals produced by the fungi ''Aspergillus flavus
''Aspergillus flavus'' is a saprotrophic and pathogenic fungus with a cosmopolitan distribution. It is best known for its colonization of cereal grains, legumes, and tree nuts. Postharvest rot typically develops during harvest, storage, and/or ...
'' (the name comes from ''A. flavus'' toxin) and '' A. parasiticus''. Food contamination by the fungi leads to ingestion of the chemicals, which are very toxic to the liver. Common foodstuffs contaminated with the toxins are cereals, peanuts, and other vegetables. The amount (dose) and how long (duration) that a person is in contact with aflatoxin is associated with HCC. Contamination of food is common in Africa, South-East Asia, and China. The mechanism by which aflatoxins cause cancer is through mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
s and epigenetic alteration
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "o ...
s. Aflatoxins induce a spectrum of mutations, including in the p53
p53, also known as Tumor protein P53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thought to be, and often s ...
tumor suppressor
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or re ...
gene, which is a mutation seen in many types of cancers. Mutation in p53, presumably in conjunction with other aflatoxin-induced mutations and epigenetic alterations, is likely a common cause of aflatoxin-induced carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abno ...
.
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and Nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFL)
NASH and NAFL is beginning to be called a risk factor for liver cancer, particularly HCC. In recent years, there has been a noted increase in liver transplantations for HCC that was attributable to NASH. More research is needed in this area and NASH/NAFL.Other risk factors in adults
* High grade dysplastic nodules are precancerous lesions of the liver. Within two years, there is a risk for cancer arising from these nodules of 30–40%. *Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
and metabolic syndrome have emerged as an important risk factor, as they can lead to steatohepatitis
Steatohepatitis is a type of fatty liver disease, characterized by inflammation of the liver with concurrent fat accumulation in liver. Mere deposition of fat in the liver is termed steatosis, and together these constitute fatty liver changes.
...
.
* Diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
increases the risk for HCC.
* Smoking increases the risk for HCC compared to non-smokers and previous smokers.
* There is around 5-10% lifetime risk of cholangiocarcinoma in people with primary sclerosing cholangitis
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a long-term progressive disease of the liver and gallbladder characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, which normally allow bile to drain from the gallbladder. Affected individuals may ha ...
.
* Liver fluke
Liver fluke is a collective name of a polyphyletic group of parasitic trematodes under the phylum Platyhelminthes.
They are principally parasites of the liver of various mammals, including humans. Capable of moving along the blood circulation, t ...
infection increases the risk for cholangiocarcinoma, and this is the reason why Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
has particularly high rates of this cancer.
* Choledochal cysts, Caroli's disease, and congenital hepatic fibrosis are associated with cholangiocarcinoma development.
* Genetic conditions: untreated hereditary hemochromatosis
Hereditary haemochromatosis type 1 (HFE-related Hemochromatosis) is a genetic disorder characterized by excessive intestinal absorption of dietary iron, resulting in a pathological increase in total body iron stores. Humans, like most animals, h ...
, alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, glycogen storage diseases, porphyria cutanea tarda
Porphyria cutanea tarda is the most common subtype of porphyria. The disease is named because it is a porphyria that often presents with skin manifestations later in life. The disorder results from low levels of the enzyme responsible for the fift ...
, Wilson's disease
Wilson's disease is a genetic disorder in which excess copper builds up in the body. Symptoms are typically related to the brain and liver. Liver-related symptoms include vomiting, weakness, fluid build up in the abdomen, swelling of the legs, ...
, tyrosinemia
Tyrosinemia or tyrosinaemia is an error of metabolism, usually inborn, in which the body cannot effectively break down the amino acid tyrosine. Symptoms of untreated tyrosinemia include liver and kidney disturbances. Without treatment, tyrosinemi ...
have all been associated with development of HCC.
* Oral contraceptive pill Oral contraceptives, abbreviated OCPs, also known as birth control pills, are medications taken by mouth for the purpose of birth control.
Female
Two types of female oral contraceptive pill, taken once per day, are widely available:
* The combin ...
: There is insufficient evidence to label oral contraceptives as a risk factor. However, recent studies have found that taking oral contraceptives for longer than 5 years is associated with HCC.
Children
Childhood liver cancer is uncommon. The liver cancer sub-types most commonly seen in children arehepatoblastoma
Hepatoblastoma is a malignant liver cancer occurring in infants and children and composed of tissue resembling fetal liver cells, mature liver cells, or bile duct cells. They usually present with an abdominal mass. The disease is most commonly di ...
, hepatocellular carcinoma, embryomal sarcoma of liver, infantile choriocarcinoma of liver, and biliary rhabdomyosarcoma. Increased risk for liver cancer in children can be caused by Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome (associated with hepatoblastoma), familial adenomatous polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant inherited condition in which numerous adenomatous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon ...
(associated with hepatoblastoma), low birth weight
Low birth weight (LBW) is defined by the World Health Organization as a birth weight of an
infant of or less, regardless of gestational age. Infants born with LBW have added health risks which require close management, often in a neonatal inten ...
(associated with hepatoblastoma), Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (associated with HCC) and Trisomy 18
A trisomy is a type of polysomy in which there are three instances of a particular chromosome, instead of the normal two. A trisomy is a type of aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes).
Description and causes
Most organisms that reprodu ...
(associated with hepatoblastoma).
Diagnosis
Many imaging modalities are used to aid in the diagnosis of liver cancer. For HCC these includemedical ultrasound
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, mu ...
, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). When imaging the liver with ultrasound, large lesions are likely to be HCC (e.g., a mass greater than 2 cm has more than 95% chance of being HCC).Given the blood flow to the liver, HCC would be most visible when the contrast flows through the arteries of the liver (also called the arterial phase) rather than when the contrast flows through the veins (also called the venous phase). Sometimes doctors will get a liver biopsy
Liver biopsy is the biopsy (removal of a small sample of tissue) from the liver. It is a medical test that is done to aid diagnosis of liver disease, to assess the severity of known liver disease, and to monitor the progress of treatment.
Medica ...
, if they are worried about HCC and the imaging studies (CT or MRI) do not have clear results. The majority of cholangiocarcimas occur in the hilar region of the liver, and often present as bile duct obstruction. If the cause of obstruction is suspected to be malignant, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a technique that combines the use of endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat certain problems of the biliary or pancreatic ductal systems. It is primarily performed by highly skille ...
(ERCP), ultrasound, CT, MRI and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is a medical imaging technique. It uses magnetic resonance imaging to visualize the biliary and pancreatic ducts non-invasively. This procedure can be used to determine whether gallstones are ...
(MRCP) are used.
Tumor marker
A tumor marker is a biomarker found in blood, urine, or body tissues that can be elevated by the presence of one or more types of cancer. There are many different tumor markers, each indicative of a particular disease process, and they are used in ...
s, chemicals sometimes found in the blood of people with cancer, can be helpful in diagnosing and monitoring the course of liver cancers. High levels of alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP, α-fetoprotein; also sometimes called alpha-1-fetoprotein, alpha-fetoglobulin, or alpha fetal protein) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AFP'' gene. The ''AFP'' gene is located on the ''q'' arm of chromosome 4 ...
(AFP) in the blood can be found in many cases of HCC and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Of note, AFP is most useful for monitoring if liver cancers come back after treatment rather than for initial diagnosis. Cholangiocarcinoma can be detected with these commonly used tumor markers: carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA 19–9), carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and cancer antigen 125 ( CA125). These tumor markers are found in primary liver cancers, as well as in other cancers and certain other disorders.
Prevention
Prevention of cancers can be separated into primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. Primary prevention preemptively reduces exposure to a risk factor for liver cancer. One of the most successful primary liver cancer preventions is vaccination against hepatitis B. Vaccination against the hepatitis C virus is currently unavailable. Other forms of primary prevention are aimed at limiting transmission of these viruses by promoting safe injection practices, screening blood donation products, and screening high-risk asymptomatic individuals.Aflatoxin
Aflatoxins are various poisonous carcinogens and mutagens that are produced by certain molds, particularly ''Aspergillus'' species. The fungi grow in soil, decaying vegetation and various staple foodstuffs and commodities such as hay, sweetcorn ...
exposure can be avoided by post-harvest intervention to discourage mold, which has been effective in west Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
. Reducing alcohol use disorder, obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
, and diabetes mellitus
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
would also reduce rates of liver cancer. Diet control in hemochromatosis
Iron overload or hemochromatosis (also spelled ''haemochromatosis'' in British English) indicates increased total accumulation of iron in the body from any cause and resulting organ damage. The most important causes are hereditary haemochromatos ...
could decrease the risk of iron overload
Iron overload or hemochromatosis (also spelled ''haemochromatosis'' in British English) indicates increased total accumulation of iron in the body from any cause and resulting organ damage. The most important causes are hereditary haemochromatos ...
, decreasing the risk of cancer.
Secondary prevention includes both cure of the agent involved in the formation of cancer (carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abno ...
) and the prevention of carcinogenesis if this is not possible. Cure of virus-infected individuals is not possible, but treatment with antiviral drugs can decrease the risk of liver cancer. Chlorophyllin may have potential in reducing the effects of aflatoxin.
Tertiary prevention includes treatments to prevent the recurrence of liver cancer. These include the use of surgical interventions, chemotherapy drugs, and antiviral drugs.
Treatment
General considerations
Like many cancers, treatment depends on the specific type of liver cancer as well as stage of the cancer. The main way cancer is staged is based on the TMN staging systems. There are also liver cancer specific staging systems, each of which has treatment options that may result in a non recurrence of cancer, or cure (see Radio Frequency Ablation) For example, for HCC it is common to use the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Staging System. Treatments include surgery, medications, and ablation methods, which are described in the sections below. There are many chemotherapeutic drugs approved for liver cancer including:atezolizumab
Atezolizumab, sold under the brand name Tecentriq, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat urothelial carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), small cell lung cancer (SCLC), hepatocellula ...
, nivolumab
Nivolumab, sold under the brand name Opdivo, is a medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes melanoma, lung cancer, malignant pleural mesothelioma, renal cell carcinoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, head and neck cancer, urotheli ...
, keytruda
Pembrolizumab, sold under the brand name Keytruda, is a humanized antibody used in cancer immunotherapy that treats melanoma, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma, stomach cancer, cervical cancer, and certain types of breast canc ...
, stivarga, etc. Increasingly, immunotherapy
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as ''activation immunotherapies,'' while immunotherap ...
agents (also called targeted cancer therapies or precision medicine
Precision, precise or precisely may refer to:
Science, and technology, and mathematics Mathematics and computing (general)
* Accuracy and precision, measurement deviation from true value and its scatter
* Significant figures, the number of digi ...
) is being used to treat hepatobiliary cancers.
Hepatocellular carcinoma
ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
or acetic acid) or producing extremes of temperature using radio frequency ablation, microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ra ...
s, laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The fi ...
s or cryotherapy
Cryotherapy, sometimes known as cold therapy, is the local or general use of low temperatures in medical therapy. Cryotherapy may be used to treat a variety of tissue lesions. The most prominent use of the term refers to the surgical treatment, s ...
. Of these, radio frequency ablation has one of the best reputations in HCC, but the limitations include inability to treat tumors close to other organs and blood vessels due to heat generation and the heat sink effect, respectively. In addition, long-term of outcomes of percutaneous ablation procedures for HCC have not been well studied. In general, surgery is the preferred treatment modality when possible.
Systemic chemotherapeutics
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherap ...
are not routinely used in HCC, although local chemotherapy may be used in a procedure known as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). In this procedure, drugs that kill cancer cells and interrupt the blood supply are applied to the tumor. Because most systemic drugs have no efficacy in the treatment of HCC, research into the molecular pathways involved in the production of liver cancer produced sorafenib, a targeted therapy
Targeted therapy or molecularly targeted therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment ( pharmacotherapy) for cancer, others being hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medicine, targeted therapy blocks ...
drug that prevents cell proliferation and blood cell growth. Sorafenib obtained FDA approval for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in November 2007. This drug provides a survival benefit for advanced HCC.
Transarterial radioembolization (TRACE) is another option for HCC. In this procedure, radiation treatment is targeted at the tumor. TRACE is still considered an add on treatment rather than the first choice for treatment of HCC, as dual treatments of radiotherapy plus chemoembolization, local chemotherapy, systemic chemotherapy or targeted therapy drugs may show benefit over radiotherapy alone.
Ablation methods (e.g. radiofrequency ablation
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), also called fulguration, is a medical procedure in which part of the electrical conduction system of the heart, tumor or other dysfunctional tissue is ablated using the heat generated from medium frequency alternati ...
or microwave ablation) are also an option for HCC treatment. This method is recommended for small, localized liver tumors as it is recommended that the area treated with radiofrequency ablation should be 2 centimeters or less.

Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Resection is an option in cholangiocarcinoma, but fewer than 30% of cases of cholangiocarcinoma are resectable at diagnosis. The reason the majority of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas are not able to be surgically removed is because there are often multiple focal tumors within the liver. After surgery, recurrence rates are up to 60%. Liver transplant may be used where partial resection is not an option, and adjuvant chemoradiation may benefit some cases. 60% of cholangiocarcinomas form in the perihilar region andphotodynamic therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a form of phototherapy involving light and a photosensitizing chemical substance, used in conjunction with molecular oxygen to elicit cell death (phototoxicity).
PDT is popularly used in treating acne. It is used cl ...
can be used to improve quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
and survival time in these un-resectable cases. Photodynamic therapy is a novel treatment that uses light activated molecules to treat the tumor. The compounds are activated in the tumor region by laser light, which causes the release of toxic reactive oxygen species, killing tumor cells.
Systemic chemotherapies such as gemcitabine
Gemcitabine, with brand names including Gemzar, is a chemotherapy medication. It treats cancers including testicular cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and bladder cancer. It is administered by ...
and cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of cancers. These include testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, ...
are sometimes used in inoperable cases of cholangiocarcinoma.
Radio frequency ablation, transarterial chemoembolization and internal radiotherapy (brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is a form of radiation therapy where a sealed radiation source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment. ''Brachy'' is Greek for short. Brachytherapy is commonly used as an effective treatment for cervical, prost ...
) all show promise in the treatment of cholangiocarcinoma and can sometimes improve bile flow, which can decrease the symptoms a patient experiences.
Radiotherapy may be used in the adjuvant setting or for palliative treatment of cholangiocarcinoma.
Hepatoblastoma
Removing the tumor by either surgical resection orliver transplant
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, al ...
can be used in the treatment of hepatoblastoma. In some cases surgery can offer a cure. Chemotherapy may be used before and after surgery and transplant.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemothe ...
, including cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of cancers. These include testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, ...
, vincristine
Vincristine, also known as leurocristine and marketed under the brand name Oncovin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, Hodgkin's ...
, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used toge ...
are used for the systemic treatment of hepatoblastoma. Out of these drugs, cisplatin seems to be the most effective.
Angiosarcoma and hemangiosarcoma
Many of these tumors end up not being amenable to surgical treatment. Treatment options include surgically removing parts of the liver that are affected. Liver transplantation andchemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemothe ...
are not effective for angiosarcomas and hemangiosarcomas of the liver.
Epidemiology
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, the Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
, Guinea, Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
, Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailan ...
, and Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
. In terms of gender breakdown, globally liver cancer is more common in men than in women.
Given that HCC is the most common type of liver cancer, the areas around the world with the most new cases of HCC each year are Northern and Western Africa as well as Eastern and South-Eastern Asia. China has 50% of HCC cases globally, and more than 80% of total cases occur in sub-Saharan Africa or in East-Asia due to hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.
Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. ...
virus. In these high disease burden areas, evidence indicates the majority of the HBC and HCV infections occur via perinatal transmission (also called mother-to-child transmission). However, it is important to note that the risk factors for HCC varies by geographic region. For example, in China chronic HBV infection and aflatoxin
Aflatoxins are various poisonous carcinogens and mutagens that are produced by certain molds, particularly ''Aspergillus'' species. The fungi grow in soil, decaying vegetation and various staple foodstuffs and commodities such as hay, sweetcorn ...
are the largest risk factors; whereas, in Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
it is a combination of HBV and HCV co-infection and high levels of alcohol use that are driving the high levels of HCC.
In terms of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, we currently do not have sufficient epidemiological data because it is a rare cancer. According to the United States National Cancer Institute, the incidence of cholangiocarcinoma is not known. Cholangiocarcinoma also has a significant geographical distribution, with Thailand showing the highest rates worldwide due to the presence of liver fluke.
In the United States there were 42,810 new cases of liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer in 2020, which represents 2.4% of all new cancer cases in the United States. There are about 89.950 people who have liver and intrahepatic liver cancer in the United States. In terms of mortality, the 5-year survival rate for liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancers in the United States is 19.6%. In the United States there is an estimated 1% chance of getting liver cancer across the lifespan, which makes this cancer relatively rare. Despite the low number of cases, it is one of the top causes of cancer deaths.
References
External links
EASL Guideline
Liver cancer information
from
Cancer Research UK
Cancer Research UK (CRUK) is the world's largest independent cancer research organization. It is registered as a charity in the United Kingdom and Isle of Man, and was formed on 4 February 2002 by the merger of The Cancer Research Campaign and t ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Liver Cancer
Digestive system neoplasia
C
Hepatology
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate