Litmus test (chemistry) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Litmus is a
Litmus is a
 Litmus can be found in different species of
Litmus can be found in different species of
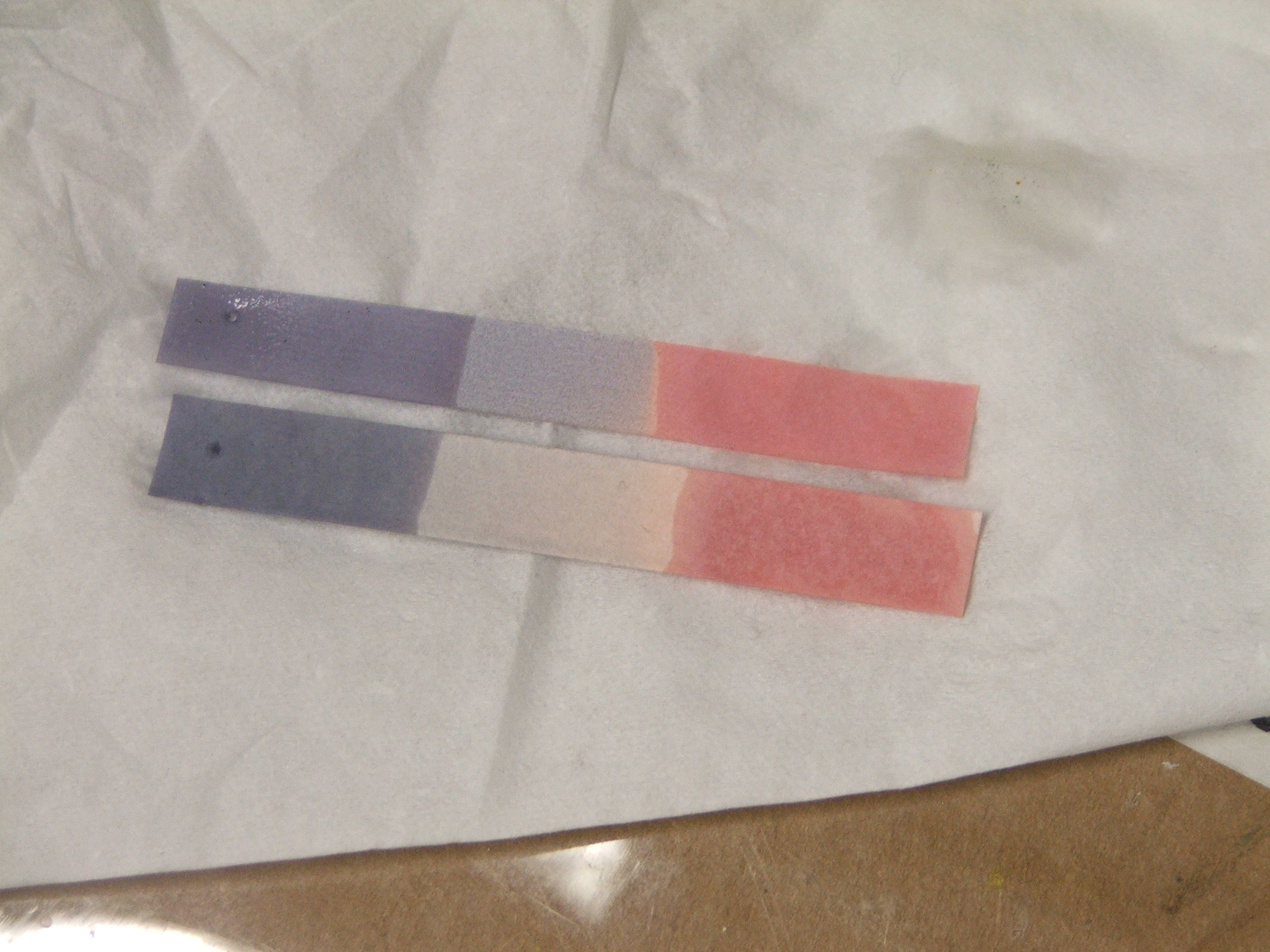 The main use of litmus is to test whether a solution is
The main use of litmus is to test whether a solution is

water-soluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solub ...
mixture of different dyes extracted from lichens. It is often absorbed onto filter paper Filter paper is a semi-permeable paper barrier placed perpendicular to a liquid or air flow. It is used to separate fine solid particles from liquids or gases.
The raw materials are different Pulp (paper), paper pulps. The pulp may be made from soft ...
to produce one of the oldest forms of pH indicator
A pH indicator is a halochromic chemical compound added in small amounts to a solution so the pH (acidity or basicity) of the solution can be determined visually or spectroscopically by changes in absorption and/or emission properties. Hence, ...
, used to test materials for acidity
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a ...
. It is a purple dye that is extracted from a type of algal bloom called ‘lichens’. In an acidic
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
medium, blue litmus paper turns red, and red litmus paper turns blue in a basic or alkaline medium.
History
The word "litmus" comes from an Old Norse word for "pulp". About 1300 theSpanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
physician Arnaldus de Villa Nova
Arnaldus de Villa Nova (also called Arnau de Vilanova in Catalan, his language, Arnaldus Villanovanus, Arnaud de Ville-Neuve or Arnaldo de Villanueva, c. 1240–1311) was a physician and a religious reformer. He was also thought to be an alchem ...
began using litmus to study acids and bases.
From the 16th century onwards, the blue dye was extracted from some lichens, especially in the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
.
Natural sources
 Litmus can be found in different species of
Litmus can be found in different species of lichens
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Roccella tinctoria
''Roccella tinctoria'' is a lichenised species of fungus in the genus ''Roccella'', homotypic synonym of ''Lecanora tinctoria'' (DC.) Czerwiak., 1849. It was first described by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle in 1805. It has the following varietie ...
'' (South American), ''Roccella fuciformis
''Roccella'' is a genus of 23 species of lichens in the family Roccellaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Swiss botanist Augustin Pyramus de Candolle in 1805, with '' Roccella fuciformis'' as the type species.
Species
*'' Roccella albida''
...
'' (Angola and Madagascar), ''Roccella pygmaea
''Roccella'' is a genus of 23 species of lichens in the family Roccellaceae. The genus was circumscription (taxonomy), circumscribed by Swiss botanist Augustin Pyramus de Candolle in 1805, with ''Roccella fuciformis'' as the type species.
Speci ...
'' (Algeria), ''Roccella phycopsis
''Roccella phycopsis'' is a species of lichen in the family Roccellaceae. A study of ''Roccella phycopsis'' in Tunisia revealed that it contains methyl orcellinate, a chemical compound of interest for its anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory is ...
'', '' Lecanora tartarea'' (Norway, Sweden), ''Variolaria dealbata'', ''Ochrolechia parella
''Ochrolechia'' is a genus of crustose lichens in the family Ochrolechiaceae.
Species
, Species Fungorum accepts 38 species of ''Ochrolechia'':
*'' Ochrolechia aegaea''
*'' Ochrolechia africana''
*'' Ochrolechia alaskana''
*'' Ochrolechia a ...
'', ''Parmotrema tinctorum
''Parmotrema tinctorum'' is a lichen which belongs to the ''Parmotrema
''Parmotrema'' is a genus of lichen belonging to the family Parmeliaceae. It is a large genus, containing an estimated 300 species, with a centre of diversity in subtrop ...
'', and ''Parmelia Parmelia may refer to:
* Parmelia (barque), the vessel that in 1829 transported the first settlers of the British colony of Western Australia
* ''Parmelia'' (fungus), a genus of lichens with global distribution
* Parmelia, Western Australia
Pa ...
''. Currently, the main sources are ''Roccella montagnei
''Roccella'' is a genus of 23 species of lichens in the family Roccellaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Swiss botanist Augustin Pyramus de Candolle in 1805, with ''Roccella fuciformis'' as the type species.
Species
*'' Roccella albida''
...
'' (Mozambique) and ''Dendrographa leucophoea
''Dendrographa'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Roccellaceae
The Roccellaceae are a family of fungi in the order Arthoniomycetes. Most taxa are lichenized with green algae, although some are lichenicolous, growing on other ...
'' (California).
Uses
acidic
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a ...
or basic, as blue litmus paper turns red under acidic
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a ...
conditions, and red litmus paper turns blue under basic or alkaline conditions, with the color change occurring over the pH range 4.5–8.3 at . Neutral litmus paper is purple. Wet litmus paper can also be used to test for water-soluble gases that affect acidity
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a ...
or basicity
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G.-F. ...
; the gas dissolves in the water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
and the resulting solution colors the litmus paper. For instance, ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous wa ...
gas, which is alkaline, turns red litmus paper blue. While all litmus paper acts as pH paper, the opposite is not true.
Litmus can also be prepared as an aqueous solution that functions similarly. Under acidic conditions, the solution is red, and under alkaline conditions, the solution is blue.
Chemical reactions other than acid–base can also cause a color change to litmus paper. For instance, chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
gas turns blue litmus paper white; the litmus dye is bleached because hypochlorite ions are present. This reaction is irreversible, so the litmus is not acting as an indicator in this situation.
Chemistry
The litmus mixture has theCAS number
A CAS Registry Number (also referred to as CAS RN or informally CAS Number) is a unique identification number assigned by the Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS), US to every chemical substance described in the open scientific literature. It inclu ...
1393-92-6 and contains 10 to around 15 different dyes. All of the chemical components of litmus are likely to be the same as those of the related mixture known as orcein
Orcein, also archil, orchil, lacmus and C.I. Natural Red 28, are names for dyes extracted from several species of lichen, commonly known as "orchella weeds", found in various parts of the world. A major source is the archil lichen, '' Roccella tinc ...
, but in different proportions. In contrast with orcein, the principal constituent of litmus has an average molecular mass of 3300. Acid-base indicators on litmus owe their properties to a 7-hydroxyphenoxazone chromophore. Some fractions
A fraction (from la, fractus, "broken") represents a part of a whole or, more generally, any number of equal parts. When spoken in everyday English, a fraction describes how many parts of a certain size there are, for example, one-half, eight ...
of litmus were given specific names including erythrolitmin Erythrolitmin (also called erythrolein) is the active ingredient extracted from the Litmus lichen, used in chemistry as a pH indicator. The erythrolitmin molecule is related to the orceins, and consists essentially of several phenoxazone and orcinol ...
(or erythrolein), azolitmin, spaniolitmin, leucoorcein, and leucazolitmin. Azolitmin shows nearly the same effect as litmus.
A recipe to make litmus out of the lichens, as outlined on a UC Santa Barbara
The University of California, Santa Barbara (UC Santa Barbara or UCSB) is a public land-grant research university in Santa Barbara, California with 23,196 undergraduates and 2,983 graduate students enrolled in 2021–2022. It is part of the U ...
website says:
Details are difficult to find because the processes were kept secret.
This summary of a modern manufacturing procedure is from The vanishing lichens, D H S Richardson, London, 1975.
The lichens (preferably Lecanora tartarea and Roccella tinctoria
''Roccella tinctoria'' is a lichenised species of fungus in the genus ''Roccella'', homotypic synonym of ''Lecanora tinctoria'' (DC.) Czerwiak., 1849. It was first described by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle in 1805. It has the following varietie ...
) are ground in a solution of sodium carbonate and ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous wa ...
.
Stir the lichens from time to time and the color changes from red to purple and finally blue after about four weeks. The lichens are then dried and powdered. At this stage the lichens contain partly litmus and partly orcein
Orcein, also archil, orchil, lacmus and C.I. Natural Red 28, are names for dyes extracted from several species of lichen, commonly known as "orchella weeds", found in various parts of the world. A major source is the archil lichen, '' Roccella tinc ...
pigments
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compoun ...
. The orcein is removed by extraction with alcohol, leaving the pure blue litmus. It is marketed as blue lumps, masses, or tablets, after mixing with colorless compounds such as chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Ch ...
and gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywal ...
. Litmus paper is paper impregnated with this substance.
Mechanism
Red litmus contains a weakdiprotic acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
. When it is exposed to a basic compound, the hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
ions react with the added base. The conjugate base formed from the litmus acid has a blue color, so the wet red litmus paper turns blue in alkaline solution.
References
{{reflist PH indicators Paper products