List Of Regions In The Human Brain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

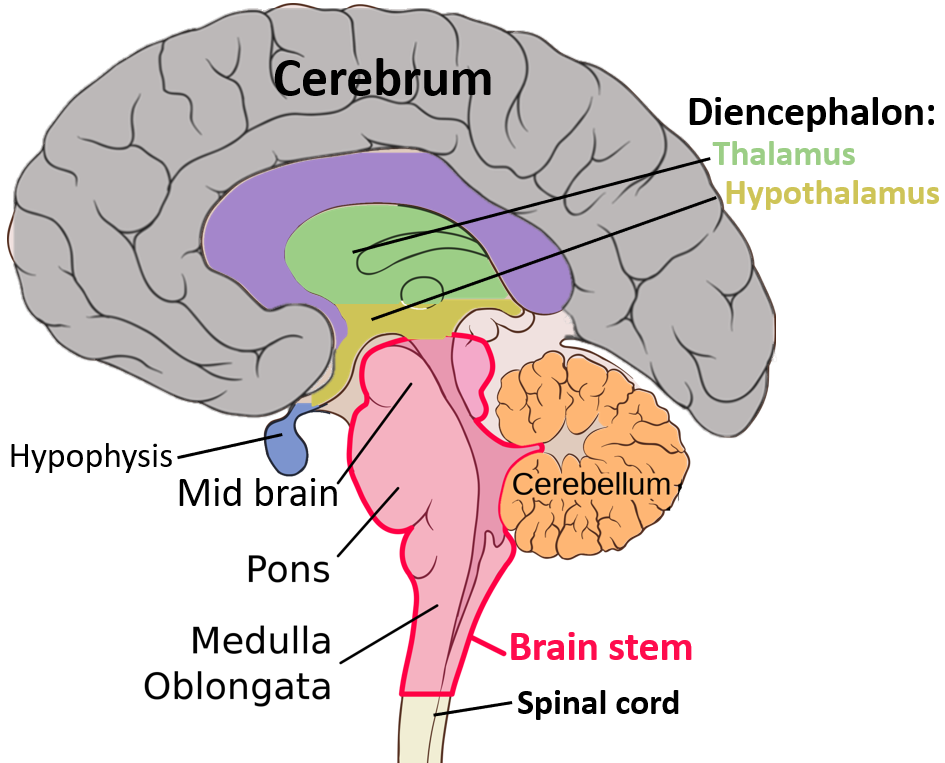 The
The


*
* Pons
** Pontine nuclei
**Pontine cranial nerve nuclei
***''Chief'' or ''pontine'' nucleus of the
 * Tectum
** Corpora quadrigemina
***
* Tectum
** Corpora quadrigemina
***
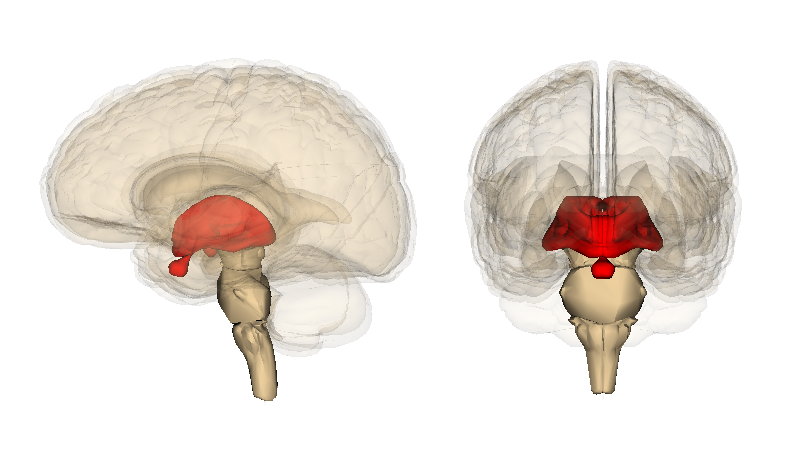
* Pineal body (pineal gland)
* Habenular nuclei
* Stria medullaris
* Taenia thalami
*

* Optic tract
* Optic radiation
*
* Brain stem
** Cranial nerves
*** Terminal (0)
*** Olfactory (I)
*** Optic (II)
*** Oculomotor (III)
*** Trochlear (IV)
*** Trigeminal (V)
*** Abducens (VI)
*** Facial (VII)
*** Vestibulocochlear (VIII)
*** Glossopharyngeal (IX)
*** Vagus (X)
*** Accessory (XI)
*** Hypoglossal (XII)
* Hypothalamic-pituitary hormones
** HPA axis
** HPG axis
** HPT axis
** GHRH - GH
* Hypothalamic–neurohypophyseal system
* Middle cerebral artery
* Posterior cerebral artery
*
* Noradrenaline system
*
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of
High-Resolution Cytoarchitectural Primate Brain Atlases
View information on various brain regions: images, name in seven languages, location, etc.
Medical subject headings: Brain
View tree structures of the brain with the MeSH Tree Structures tab. {{Somatosensory system Brain Cognitive science lists

 The
The human brain
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of ...
anatomical regions are ordered following standard neuroanatomy hierarchies. Functional
Functional may refer to:
* Movements in architecture:
** Functionalism (architecture)
** Form follows function
* Functional group, combination of atoms within molecules
* Medical conditions without currently visible organic basis:
** Functional sy ...
, connective, and developmental regions are listed in parentheses where appropriate.
Hindbrain (rhombencephalon)
Medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (invol ...
**Medullary pyramids
In neuroanatomy, the medullary pyramids are paired white matter structures of the brainstem's medulla oblongata that contain motor fibers of the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts – known together as the pyramidal tracts. The lower limi ...
**Arcuate nucleus
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (also known as ARH, ARC, or infundibular nucleus) is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes seve ...
** Olivary body
*** Inferior olivary nucleus
**Rostral ventrolateral medulla
The rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM), also known as the pressor area of the medulla, is a brain region that is responsible for basal and reflex control of sympathetic activity associated with cardiovascular function. Abnormally elevated sympa ...
**Caudal ventrolateral medulla The ventrolateral medulla, part of the medulla oblongata of the brainstem, plays a major role in regulating arterial blood pressure and breathing. It regulates blood pressure by regulating the activity of the sympathetic nerves
The sympathetic n ...
**Solitary nucleus
In the human brainstem, the solitary nucleus, also called nucleus of the solitary tract, nucleus solitarius, and nucleus tractus solitarii, (SN or NTS) is a series of purely sensory
nuclei (clusters of nerve cell bodies) forming a vertical column ...
(Nucleus of the solitary tract)
**Respiratory center
The respiratory center is located in the medulla oblongata and pons, in the brainstem. The respiratory center is made up of three major respiratory groups of neurons, two in the medulla and one in the pons. In the medulla they are the dorsal ...
- Respiratory groups
*** Dorsal respiratory group
*** Ventral respiratory group or Apneustic centre
****Pre-Bötzinger complex The preBötzinger complex, sometimes written pre-Bötzinger complex (preBötC), is a functionally and anatomically specialized site in the ventral-lateral region of the lower medulla oblongata (i.e., lower brainstem). The preBötC is part of the ve ...
**** Botzinger complex
**** Retrotrapezoid nucleus
**** Nucleus retrofacialis
**** Nucleus retroambiguus
**** Nucleus para-ambiguus
** Paramedian reticular nucleus
** Gigantocellular reticular nucleus
**Parafacial zone
The parafacial zone (PZ) is a brain structure located in the brainstem within the medulla oblongata believed to be heavily responsible for non-rapid eye movement (non-REM) sleep regulation, specifically for inducing slow-wave sleep.
It is one o ...
** Cuneate nucleus
**Gracile nucleus
In neuroanatomy, the dorsal column nuclei are a pair of nuclei in the dorsal columns in the brainstem. The name refers collectively to the cuneate nucleus and gracile nucleus, which are present at the bottom of the medulla oblongata. Both ...
** Perihypoglossal nuclei
*** Intercalated nucleus
*** Prepositus nucleus
*** Sublingual nucleus
** Area postrema
**Medullary cranial nerve nuclei
***Inferior salivatory nucleus
The salivatory nuclei are the superior salivatory nucleus, and the inferior salivatory nucleus that innervate the salivary glands. They are located in the pontine tegmentum in the brainstem. They both are examples of cranial nerve nuclei.
The sup ...
***Nucleus ambiguus
The nucleus ambiguus ("ambiguous nucleus" in English) is a group of large motor neurons, situated deep in the medullary reticular formation named by Jacob Clarke. The nucleus ambiguus contains the cell bodies of neurons that innervate the muscle ...
*** Dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve
*** Hypoglossal nucleus
** Chemoreceptor trigger zone
trigeminal nerve
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve ( lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and che ...
sensory nucleus (V)
*** Motor nucleus for the trigeminal nerve
The trigeminal motor nucleus contains motor neurons that innervate muscles of the first branchial arch, namely the muscles of mastication, the tensor tympani, tensor veli palatini, mylohyoid muscle, mylohyoid, and anterior belly of the digastric. T ...
(V)
*** Abducens nucleus (VI)
*** Facial nerve nucleus (VII)
*** Vestibulocochlear
The vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VIII, or simply CN VIII, is a cranial nerve that transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the br ...
nuclei ( vestibular nuclei and cochlear nuclei
The cochlear nuclear (CN) complex comprises two cranial nerve nuclei in the human brainstem, the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN) and the dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN).
The ventral cochlear nucleus is unlayered whereas the dorsal cochlear nucleus ...
) (VIII)
*** Superior salivatory nucleus
** Pontine tegmentum
*** Pontine micturition center (Barrington's nucleus)
***Locus coeruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system.
The locus coer ...
***Pedunculopontine nucleus
The pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN) or pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus (PPT or PPTg) is a collection of neurons located in the upper pons in the brainstem. It lies caudal to the substantia nigra and adjacent to the superior cerebellar pedunc ...
***Laterodorsal tegmental nucleus
The laterodorsal tegmental nucleus (or lateroposterior tegmental nucleus) is a nucleus situated in the brainstem, spanning the midbrain tegmentum and the pontine tegmentum. Its location is one-third of the way from the pedunculopontine nucleus ...
***Tegmental pontine reticular nucleus
The reticulotegmental nucleus, tegmental pontine reticular nucleus (or pontine reticular nucleus of the tegmentum) is an area within the floor of the pons, in the brain stem. This area is known to affect the cerebellum with its axonal projections.
...
*** Nucleus incertus
**Parabrachial area
The parabrachial nuclei, also known as the parabrachial complex, are a group of nuclei in the dorsolateral pons that surrounds the superior cerebellar peduncle as it enters the brainstem from the cerebellum. They are named from the Latin term for ...
*** Medial parabrachial nucleus
*** Lateral parabrachial nucleus
*** Subparabrachial nucleus (Kölliker-Fuse nucleus)
****Pontine respiratory group
The respiratory center is located in the medulla oblongata and pons, in the brainstem. The respiratory center is made up of three major respiratory groups of neurons, two in the medulla and one in the pons. In the medulla they are the dorsal ...
** Superior olivary complex
***Medial superior olive
The superior olivary complex (SOC) or superior olive is a collection of brainstem nuclei that functions in multiple aspects of hearing and is an important component of the ascending and descending auditory pathways of the auditory system. The SO ...
***Lateral superior olive
The superior olivary complex (SOC) or superior olive is a collection of brainstem nuclei that functions in multiple aspects of hearing and is an important component of the ascending and descending auditory pathways of the auditory system. The SO ...
***Medial nucleus of the trapezoid body
** Paramedian pontine reticular formation
**Parvocellular reticular nucleus
The parvocellular reticular nucleus is part of the brain located dorsolateral to the caudal pontine reticular nucleus.
The dorsal portion of the reticular nucleus has been shown to innervate the mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus and its surroundi ...
** Caudal pontine reticular nucleus
**Cerebellar peduncle
Cerebellar peduncles connect the cerebellum to the brain stem. There are six cerebellar peduncles in total, three on each side:
* Superior cerebellar peduncle is a paired structure of white matter that connects the cerebellum to the mid-brain.
...
s
*** Superior cerebellar peduncle
*** Middle cerebellar peduncle
*** Inferior cerebellar peduncle
* Fourth ventricle
* Cerebellum
** Cerebellar vermis
** Cerebellar hemispheres
***Anterior lobe
The anterior lobe of cerebellum is the portion of the cerebellum responsible for mediating unconscious proprioception. Inputs into the anterior lobe of the cerebellum are mainly from the spinal cord. It is sometimes equated to the "paleocerebellum ...
***Posterior lobe
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebel ...
*** Flocculonodular lobe
** Cerebellar nuclei
*** Fastigial nucleus
*** Interposed nucleus
**** Globose nucleus
**** Emboliform nucleus
*** Dentate nucleus
Midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal ( alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', ...
(mesencephalon)
Inferior colliculi
The inferior colliculus (IC) ( Latin for ''lower hill'') is the principal midbrain nucleus of the auditory pathway and receives input from several peripheral brainstem nuclei in the auditory pathway, as well as inputs from the auditory cortex. Th ...
***Superior colliculi
In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus () is a structure lying on the roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the homologous structure is known as the optic tectum, or optic lobe. The adjective form '' tectal'' is common ...
* Pretectum
*Tegmentum
The tegmentum (from Latin for "covering") is a general area within the brainstem. The tegmentum is the ventral part of the midbrain and the tectum is the dorsal part of the midbrain. It is located between the ventricular system and distinctive ba ...
** Periaqueductal gray
**Rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus
The rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus (riMLF) is a portion of the medial longitudinal fasciculus which controls vertical gaze.
They project to the vestibular nuclei.
External links
* https://uni-tuebingen.de/uni/k ...
** Midbrain reticular formation
** Dorsal raphe nucleus
**Red nucleus
The red nucleus or nucleus ruber is a structure in the rostral midbrain involved in motor coordination. The red nucleus is pale pink, which is believed to be due to the presence of iron in at least two different forms: hemoglobin and ferritin. ...
**Ventral tegmental area
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) (tegmentum is Latin for ''covering''), also known as the ventral tegmental area of Tsai, or simply ventral tegmentum, is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain. The VTA is the ...
*** Parabrachial pigmented nucleus
*** Paranigral nucleus
***Rostromedial tegmental nucleus The rostromedial tegmental nucleus (RMTg), also known as the tail of the ventral tegmental area (tVTA), is a GABAergic nucleus which functions as a "master brake" for the midbrain dopamine system. It is poorly differentiated from the rest of the ve ...
** Caudal linear nucleus
** Rostral linear nucleus of the raphe
** Interfascicular nucleus
**Substantia nigra
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. ''Substantia nigra'' is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra ap ...
*** Pars compacta
*** Pars reticulata
** Interpeduncular nucleus
*Cerebral peduncle
The cerebral peduncles are the two stalks that attach the cerebrum to the brainstem. They are structures at the front of the midbrain which arise from the ventral pons and contain the large ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) nerve tract ...
** Crus cerebri
*Mesencephalic cranial nerve nuclei
** Oculomotor nucleus (III)
** Edinger-Westphal nucleus
** Trochlear nucleus (IV)
*Mesencephalic duct
The cerebral aqueduct (aqueductus mesencephali, mesencephalic duct, sylvian aqueduct or aqueduct of Sylvius) is a conduit for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle of the ventricular system of the brai ...
(cerebral aqueduct, aqueduct of Sylvius)
Forebrain (prosencephalon)

Subcommissural organ
The subcommissural organ (SCO) is one of the circumventricular organs of the brain. It is a small glandular structure that is located in the posterior region of the third ventricle, near the entrance of the cerebral aqueduct. The name of the S ...
* Circumventricular organs (also Fourth ventricle)
Thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all direct ...
*Anterior nuclear group
The anterior nuclei of thalamus (or anterior nuclear group) are a collection of nuclei at the rostral end of the dorsal thalamus. They comprise the anteromedial, anterodorsal, and anteroventral nuclei.
Inputs and outputs
The anterior nuclei recei ...
** Anteroventral nucleus ( ventral anterior nucleus)
** Anterodorsal nucleus
** Anteromedial nucleus
* Medial nuclear group
**Medial dorsal nucleus
The medial dorsal nucleus (or dorsomedial nucleus of thalamus) is a large nucleus in the thalamus.
It is believed to play a role in memory.
Structure
It relays inputs from the amygdala and olfactory cortex and projects to the prefrontal corte ...
** Midline nuclear group
**Paratenial nucleus
The paratenial nucleus, or parataenial nucleus ( la, nucleus parataenialis), is a component of the midline nuclear group in the thalamus. It is sometimes subdivided into the nucleus parataenialis interstitialis and nucleus parataenialis parvocellu ...
**Reuniens nucleus
The nucleus reuniens is a region of the thalamic midline nuclear group. In the human brain, it is located in the interthalamic adhesion (''massa intermedia'').
The nucleus reuniens receives afferent input from a large number of structures, mai ...
**Rhomboidal nucleus
Traditionally, in two-dimensional geometry, a rhomboid is a parallelogram in which adjacent sides are of unequal lengths and angles are non-right angled.
A parallelogram with sides of equal length (equilateral) is a rhombus but not a rhomboid.
...
** Intralaminar nuclear group
** Centromedian nucleus
** Parafascicular nucleus
** Paracentral nucleus
**Central lateral nucleus In the human brain, the central lateral nucleus is a part of the anterior intralaminar nucleus in the thalamus. The intralaminar nuclei project to many different regions of the brain, The thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "cha ...
*Lateral nuclear group
The lateral nuclear group is a collection of nuclei on the lateral side of the thalamus. According to MeSH
A mesh is a barrier made of connected strands of metal, fiber, or other flexible or ductile materials. A mesh is similar to a web or ...
** Lateral dorsal nucleus
** Lateral posterior nucleus
** Pulvinar
* Ventral nuclear group
** Ventral anterior nucleus
**Ventral lateral nucleus
The ventral lateral nucleus (VL) is a nucleus in the ventral nuclear group of the thalamus.
Inputs and outputs
It receives neuronal inputs from the basal ganglia which includes the substantia nigra and the globus pallidus (via the thalamic fascic ...
** Ventral posterior nucleus
***Ventral posterior lateral nucleus
The ventral posterolateral nucleus (VPL) is a nucleus of the thalamus. Together with the ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM), ventral posterior inferior nucleus (VPI) and ventromedial posterior nucleus (VMpo), it constitutes the ventral posterior ...
***Ventral posterior medial nucleus
The ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM) is a Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nucleus of the thalamus.
Inputs and outputs
The VPM contains synapses between second and third order neurons from the Anterior trigeminothalamic tract, anterior (ventral) trigemi ...
* Metathalamus
** Medial geniculate body
**Lateral geniculate body
In neuroanatomy, the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN; also called the lateral geniculate body or lateral geniculate complex) is a structure in the thalamus and a key component of the mammalian visual pathway. It is a small, ovoid, ventral projec ...
* Thalamic reticular nucleus
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus ...
''( limbic system)'' ''( HPA axis)''
*Anterior
**Medial area
***Parts of preoptic area
****Medial preoptic nucleus
***** INAH 1
***** INAH 2
***** INAH 3
***** INAH 4
****Median preoptic nucleus
The median preoptic nucleus is located dorsal to the other three nuclei of the preoptic area of the anterior hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is located just beneath the thalamus, the main sensory relay station of the nervous system, and is consi ...
***Suprachiasmatic nucleus
The suprachiasmatic nucleus or nuclei (SCN) is a tiny region of the brain in the hypothalamus, situated directly above the optic chiasm. It is responsible for controlling circadian rhythms. The neuronal and hormonal activities it generates regu ...
*** Paraventricular nucleus
*** Supraoptic nucleus (mainly)
*** Anterior hypothalamic nucleus
**Lateral area
***Parts of preoptic area
****Lateral preoptic nucleus
***Anterior part of Lateral nucleus
***Part of supraoptic nucleus
**Other nuclei of preoptic area
***Median preoptic nucleus
***Periventricular preoptic nucleus
*Tuberal
**Medial area
*** Dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus
***Ventromedial nucleus
The ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMN, also sometimes referred to as the ventromedial hypothalamus, VMH) is a nucleus of the hypothalamus. "The ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) is a distinct morphological nucleus involved in terminati ...
***Arcuate nucleus
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (also known as ARH, ARC, or infundibular nucleus) is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes seve ...
**Lateral area
***Tuberal part of Lateral nucleus
*** Lateral tuberal nuclei
*Posterior
**Medial area
***Mammillary nuclei (part of mammillary bodies)
*** Posterior nucleus
**Lateral area
***Posterior part of Lateral nucleus
* Surface
** Median eminence
** Mammillary bodies
** Pituitary stalk (infundibulum)
* Optic chiasm
* Subfornical organ
* Periventricular nucleus
*Tuber cinereum
The tuber cinereum is a hollow eminence of the middle–ventral hypothalamus, specifically the arcuate nucleus, situated between the mammillary bodies and the optic chiasm. In addition to the ventral hypothalamus, the tuber cinereum includes ...
**Tuberal nucleus
** Tuberomammillary nucleus
* Tuberal region
* Mammillary nucleus
Subthalamus ''( HPA axis)''
*Subthalamic nucleus
The subthalamic nucleus (STN) is a small lens-shaped nucleus in the brain where it is, from a functional point of view, part of the basal ganglia system. In terms of anatomy, it is the major part of the subthalamus. As suggested by its name, the ...
*Zona incerta
The zona incerta (ZI) is a horizontally elongated region of gray matter in the subthalamus below the thalamus. Its connections project extensively over the brain from the cerebral cortex down into the spinal cord.
Its function is unknown, though ...
Pituitary gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The h ...
''( HPA axis)''
* Neurohypophysis
*Pars intermedia
Pars intermedia is the boundary between the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary. It contains colloid-filled cysts and two types of cells - basophils and chromophobes. The cysts are the remainder of Rathke’s pouch.
In human fetal ...
(Intermediate Lobe)
* Adenohypophysis
Cerebral hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum ( brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemisphere ...
s
White matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribu ...
* Centrum semiovale
* Corona radiata
* Internal capsule
* External capsule
* Extreme capsule
Subcortical
*Hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic syste ...
(Medial Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in p ...
)
** Dentate gyrus
** Cornu ammonis (CA fields)
*** Cornu ammonis area 1 (CA1)
*** Cornu ammonis area 2 (CA2)
*** Cornu ammonis area 3 (CA3)
*** Cornu ammonis area 4 (CA4)
*Amygdala
The amygdala (; plural: amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nuclei located deep and medially within the temporal lobes of the brain's cerebrum in complex ver ...
''( limbic system)'' ''( limbic lobe)''
**Central nucleus
The central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA or aCeN) is a nucleus within the amygdala. It "serves as the major output nucleus of the amygdala and participates in receiving and processing pain information."
CeA "connects with brainstem areas that co ...
''(autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), formerly referred to as the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the peripheral nervous system that supplies internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control system t ...
)''
**Medial nucleus
The medial vestibular nucleus (Schwalbe nucleus) is one of the vestibular nuclei. It is located in the medulla oblongata.
Lateral vestibulo-spinal tract (lateral vestibular nucleus “Deiters”)- via ventrolateral medulla and spinal cord to ven ...
''(accessory olfactory system
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, i ...
)''
** Cortical and basomedial nuclei ''( main olfactory system)''
** Lateral and basolateral nuclei
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (th ...
''( frontotemporal cortical system)''
* Extended amygdala
**Stria terminalis
The stria terminalis (or terminal stria) is a structure in the brain consisting of a band of fibers running along the lateral margin of the ventricular surface of the thalamus. Serving as a major output pathway of the amygdala, the stria term ...
*** Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis
*Claustrum
The claustrum (Latin, meaning "to close" or "to shut") is a thin, bilateral collection of neurons and supporting glial cells, that connects to cortical (e.g., the pre-frontal cortex) and subcortical regions (e.g., the thalamus) of the brain. It ...
*Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG), or basal nuclei, are a group of subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates. In humans, and some primates, there are some differences, mainly in the division of the globus pallidus into an ext ...
**Striatum
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives gluta ...
***Dorsal striatum
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamat ...
(a.k.a. neostriatum)
**** Putamen
****Caudate nucleus
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatum, which is a component of the basal ganglia in the human brain. While the caudate nucleus has long been associated with motor processes due to its role in Parkinson's d ...
*** Ventral striatum
****Nucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for "nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hyp ...
****Olfactory tubercle
The olfactory tubercle (OT), also known as the tuberculum olfactorium, is a multi-sensory processing center that is contained within the olfactory cortex and ventral striatum and plays a role in reward cognition. The OT has also been shown to ...
** Globus pallidus (forms nucleus lentiformis with putamen)
*** Ventral pallidum
**Subthalamic nucleus
The subthalamic nucleus (STN) is a small lens-shaped nucleus in the brain where it is, from a functional point of view, part of the basal ganglia system. In terms of anatomy, it is the major part of the subthalamus. As suggested by its name, the ...
* Basal forebrain
**Anterior perforated substance
The anterior perforated substance is a part of the brain. It is bilateral. It is irregular and quadrilateral. It lies in front of the optic tract and behind the olfactory trigone.
Structure
The anterior perforated substance is bilateral. It ...
**Substantia innominata
The substantia innominata also innominate substance, or substantia innominata of Meynert (Latin for unnamed substance) is a series of layers in the human brain consisting partly of gray and partly of white matter, which lies below the anterior part ...
** Nucleus basalis
** Diagonal band of Broca
**Septal nuclei
The septal area (medial olfactory area), consisting of the lateral septum and medial septum, is an area in the lower, posterior part of the medial surface of the frontal lobe, and refers to the nearby septum pellucidum.
The septal nuclei are loc ...
*** Medial septal nuclei
** Lamina terminalis
***Vascular organ of lamina terminalis
The vascular organ of lamina terminalis (VOLT), organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis (OVLT), or supraoptic crest is one of the four sensory circumventricular organs of the brain, the others being the subfornical organ, the median eminence, ...
Rhinencephalon ''( paleocortex)''
*Olfactory bulb
The olfactory bulb (Latin: ''bulbus olfactorius'') is a neural structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, the sense of smell. It sends olfactory information to be further processed in the amygdala, the orbitofrontal cortex ...
*Olfactory tract
The olfactory tract is a bilateral bundle of afferent nerve fibers from the mitral and tufted cells of the olfactory bulb that connects to several target regions in the brain, including the piriform cortex, amygdala, and entorhinal cortex. It ...
* Anterior olfactory nucleus
* Piriform cortex
*Anterior commissure
The anterior commissure (also known as the precommissure) is a white matter tract (a bundle of axons) connecting the two temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres across the midline, and placed in front of the columns of the fornix. In most exis ...
* Uncus
* Periamygdaloid cortex
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting o ...
''(neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, sp ...
)''
* Frontal lobe
**Cortex
*** Primary motor cortex (Precentral gyrus, M1)
*** Premotor cortex
*** Supplementary motor cortex
***Prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA ...
**** Orbitofrontal cortex
****Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC or DL-PFC) is an area in the prefrontal cortex of the primate brain. It is one of the most recently derived parts of the human brain. It undergoes a prolonged period of maturation which lasts until adult ...
****Ventrolateral prefrontal cortex
The ventrolateral prefrontal cortex (VLPFC) is a section of the prefrontal cortex located on the inferior frontal gyrus, bounded superiorly by the inferior frontal sulcus and inferiorly by the lateral sulcus. It is attributed to the ...
**** Dorsomedial prefrontal cortex
**** Ventromedial prefrontal cortex
**Gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other ...
***Superior frontal gyrus
In neuroanatomy, the superior frontal gyrus (SFG, also marginal gyrus) is a gyrus – a ridge on the brain's cerebral cortex – which makes up about one third of the frontal lobe. It is bounded laterally by the superior frontal sulcus.
The su ...
*** Middle frontal gyrus
*** Inferior frontal gyrus
** Brodmann areas: 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 24, 25, 32, 33, 44, 45, 46, 47
* Parietal lobe
**Cortex
***Primary somatosensory cortex
In neuroanatomy, the primary somatosensory cortex is located in the postcentral gyrus of the brain's parietal lobe, and is part of the somatosensory system. It was initially defined from surface stimulation studies of Wilder Penfield, and pa ...
(S1)
***Secondary somatosensory cortex
The human secondary somatosensory cortex (S2, SII) is a region of cortex in the parietal operculum on the ceiling of the lateral sulcus.
Region S2 was first described by Adrian in 1940, who found that feeling in cats' feet was not only represent ...
(S2)
*** Posterior parietal cortex
**Gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other ...
*** Postcentral gyrus '' (Primary somesthetic area)''
**Other
*** Precuneus
** Brodmann areas 1, 2, 3 '' (Primary somesthetic area)''; 5, 7, 23, 26, 29, 31, 39, 40
* Occipital lobe
**Cortex
*** Primary visual cortex (V1)
*** V2
*** V3
*** V4
***
**Gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other ...
*** Lateral occipital gyrus
**Other
***Cuneus
The cuneus (; plural cunei) is a smaller lobe in the occipital lobe of the brain. The cuneus is bounded anteriorly by the parieto-occipital sulcus and inferiorly by the calcarine sulcus.
Function
The cuneus (Brodmann area 17) receives visu ...
** Brodmann areas 17 ''(V1, primary visual cortex)''; 18, 19
*Temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved i ...
**Cortex
***Primary auditory cortex
The auditory cortex is the part of the temporal lobe that processes auditory information in humans and many other vertebrates. It is a part of the auditory system, performing basic and higher functions in hearing, such as possible relations ...
(A1)
*** Secondary auditory cortex (A2)
*** Inferior temporal cortex
*** V5/MT
*** Posterior inferior temporal cortex
**Gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other ...
***Superior temporal gyrus
The superior temporal gyrus (STG) is one of three (sometimes two) gyri in the temporal lobe of the human brain, which is located laterally to the head, situated somewhat above the external ear.
The superior temporal gyrus is bounded by:
* the l ...
*** Middle temporal gyrus
*** Inferior temporal gyrus
***Entorhinal cortex
The entorhinal cortex (EC) is an area of the brain's allocortex, located in the medial temporal lobe, whose functions include being a widespread network hub for memory, navigation, and the perception of time.Integrating time from experience in th ...
***Perirhinal cortex
The perirhinal cortex is a cortical region in the medial temporal lobe that is made up of Brodmann areas 35 and 36. It receives highly processed sensory information from all sensory regions, and is generally accepted to be an important region ...
***Parahippocampal gyrus
The parahippocampal gyrus (or hippocampal gyrus') is a grey matter cortical region of the brain that surrounds the hippocampus and is part of the limbic system. The region plays an important role in memory encoding and retrieval. It has been in ...
***Fusiform gyrus
The fusiform gyrus, also known as the ''lateral occipitotemporal gyrus'','' ''is part of the temporal lobe and occipital lobe in Brodmann area 37. The fusiform gyrus is located between the lingual gyrus and parahippocampal gyrus above, and the inf ...
** Brodmann areas: 20, 21, 22, 27, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 41, 42
**Other
***Medial superior temporal area The medial superior temporal (MST) area is a part of the cerebral cortex, which lies in the dorsal stream of the visual area of the primate brain. The MST receives most of its inputs from the middle temporal (MT) area, which is involved primarily in ...
(MST)
* Insular cortex
*Cingulate cortex
The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the c ...
**Anterior cingulate
In the human brain, the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is the frontal part of the cingulate cortex that resembles a "collar" surrounding the frontal part of the corpus callosum. It consists of Brodmann areas 24, 32, and 33.
It is involved i ...
** Posterior cingulate
**Retrosplenial cortex
The retrosplenial cortex (RSC) is a cortical area in the brain comprising Brodmann areas 29 and 30. It is secondary association cortex, making connections with numerous other brain regions. The region's name refers to its anatomical location imm ...
** Indusium griseum
**Subgenual area 25
Brodmann area 25 (BA25) is the subgenual area, area subgenualis or subgenual cingulatea area in the cerebral cortex of the brain and delineated based on its cytoarchitectonic characteristics.
It is the 25th "Brodmann area" defined by Korbinian ...
** Brodmann areas 23, 24; 26, 29, 30 '' (retrosplenial areas)''; 31, 32
Neural pathway
In neuroanatomy, a neural pathway is the connection formed by axons that project from neurons to make synapses onto neurons in another location, to enable neurotransmission (the sending of a signal from one region of the nervous system to ...
s
* Superior longitudinal fasciculus
The superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF) is an association tract in the brain that is composed of three separate components. It is present in both hemispheres and can be found lateral to the centrum semiovale and connects the frontal, occipit ...
** Arcuate fasciculus
The arcuate fasciculus (AF) is a bundle of axons that generally connects the Broca's area and the Wernicke's area in the brain. It is an association fiber tract connecting caudal temporal cortex and inferior frontal lobe. ''Fasciculus arcuatus' ...
* Uncinate fasciculus
* Perforant pathway
In the brain, the perforant path or perforant pathway provides a connectional route from the entorhinal cortex to all fields of the hippocampal formation, including the dentate gyrus, all CA fields (including CA1), and the subiculum.
Though it a ...
* Thalamocortical radiations
* Corpus callosum
* Anterior commissure
The anterior commissure (also known as the precommissure) is a white matter tract (a bundle of axons) connecting the two temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres across the midline, and placed in front of the columns of the fornix. In most exis ...
* Amygdalofugal pathway
* Interthalamic adhesion
* Posterior commissure
The posterior commissure (also known as the epithalamic commissure) is a rounded band of white fibers crossing the middle line on the dorsal aspect of the rostral end of the cerebral aqueduct. It is important in the bilateral pupillary light refl ...
* Habenular commissure
* Fornix
* Mammillotegmental fasciculus
The mammillotegmental fasciculus (or mammillotegmental tract, mammillo-tegmental bundle of Gudden, or ''Fasciculus mammillotegmentalis'') is a small bundle of efferent fibers from the hypothalamus running from the mammillary body to the tegmentum.
...
* Incertohypothalamic pathway
* Cerebral peduncle
The cerebral peduncles are the two stalks that attach the cerebrum to the brainstem. They are structures at the front of the midbrain which arise from the ventral pons and contain the large ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) nerve tract ...
* Medial forebrain bundle
* Medial longitudinal fasciculus
* Myoclonic triangle
* Solitary tract
* Major dopaminergic pathways from dopaminergic cell groups
** Mesocortical pathway
** Mesolimbic pathway
The mesolimbic pathway, sometimes referred to as the reward pathway, is a dopaminergic pathway in the brain. The pathway connects the ventral tegmental area in the midbrain to the ventral striatum of the basal ganglia in the forebrain. The ven ...
** Nigrostriatal pathway
** Tuberoinfundibular pathway
* Serotonergic pathways
** Raphe Nuclei
* Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin '' ad ...
Pathways
**Locus coeruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system.
The locus coer ...
and other noradrenergic cell groups
Noradrenergic cell groups refers to collections of neurons in the central nervous system that have been demonstrated by histochemical fluorescence to contain the neurotransmitter norepinephrine (noradrenalin). They are named
* Noradrenergic cell ...
* Epinephrine pathways from adrenergic cell groups
Adrenergic cell groups refers to collections of neurons in the central nervous system that stain for PNMT, the enzyme that converts norepinephrine to epinephrine (adrenaline). Thus, it is postulated that the neurotransmitter they produce may be ep ...
* Glutamate and acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
pathways from mesopontine nuclei
Motor systems / Descending fibers
* Extrapyramidal system * Pyramidal tract **Corticospinal tract
The corticospinal tract is a white matter motor pathway starting at the cerebral cortex that terminates on lower motor neurons and interneurons in the spinal cord, controlling movements of the limbs and trunk. There are more than one million ne ...
or Cerebrospinal fibers
*** Lateral corticospinal tract
*** Anterior corticospinal tract
** Corticopontine fibers
***Frontopontine fibers
The frontopontine fibersKamali A, Kramer LA, Frye RE, Butler IJ, Hasan KM. Diffusion tensor tractography of the human brain cortico-ponto-cerebellar pathways: a quantitative preliminary study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010 Oct;32(4):809-17. doi: 10.10 ...
***Temporopontine fibers
In the human nervous system the temporopontine fibers,Kamali A, Kramer LA, Frye RE, Butler IJ, Hasan KM. Diffusion tensor tractography of the human brain cortico-ponto-cerebellar pathways: a quantitative preliminary study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 201 ...
** Corticobulbar tract
* Corticomesencephalic tract
* Tectospinal tract
* Interstitiospinal tract
* Rubrospinal tract
*Rubro-olivary tract
The rubro-olivary tract (rubroolivary fibers) is a tract which connects the inferior olive and the parvocellular red nucleus.
It is hypothesized that it uses both the corticospinal tract
The corticospinal tract is a white matter motor pathway ...
* Olivocerebellar tract
* Olivospinal tract
* Vestibulospinal tract
** Lateral vestibulospinal tract
**Medial vestibulospinal tract
The medial vestibulospinal tract is one of the descending spinal tracts of the ventromedial funiculus of the spinal cord. It is found only in the cervical spine and above.
The medial part of the vestibulospinal tract is the smaller part, and is pr ...
* Reticulospinal tract
* Lateral raphespinal tract
* Alpha system
* Gamma system
Somatosensory system
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch (haptic perception), as well as temperature (thermoception), body position (proprioception), and pain. It is ...
* Dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway
The dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway (DCML) (also known as the posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway, PCML) is a sensory pathway of the central nervous system that conveys sensations of fine touch, vibration, two-point discrimination, ...
** Gracile fasciculus
Gracility is slenderness, the condition of being gracile, which means slender. It derives from the Latin adjective ''gracilis'' ( masculine or feminine), or ''gracile'' ( neuter), which in either form means slender, and when transferred for exa ...
** Cuneate fasciculus
Cuneate means "wedge-shaped", and can apply to:
* Cuneate leaf
The following is a list of terms which are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple (a single leaf blade or lamina) or compou ...
** Medial lemniscus
* Spinothalamic tract
** Lateral spinothalamic tract
** Anterior spinothalamic tract
** Spinomesencephalic tract
* Spinocerebellar tract
The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum.
Origins of proprioceptive information
Proprioceptive information is obtained by Golgi tendon organs and mu ...
* Spino-olivary tract
The spino-olivary tract (historically Helweg's tract) is located in the anterior funiculus of the spinal cord and provides transmission of unconscious proprioception and is involved in balance. This nerve tract, tract carries proprioception info ...
* Spinoreticular tract
Retinohypothalamic tract
In neuroanatomy, the retinohypothalamic tract (RHT) is a photic neural input pathway involved in the circadian rhythms of mammals. The origin of the retinohypothalamic tract is the intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGC), wh ...
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.
System overview
The outer ear funnels sound vibrations to the eardrum, increasin ...
* Medullary striae of fourth ventricle
* Trapezoid body
* Lateral lemniscus
Anterior cerebral artery
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from ...
*Vertebral artery
The vertebral arteries are major arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline ...
*Basilar artery
The basilar artery () is one of the arteries that supplies the brain with oxygen-rich blood.
The two vertebral arteries and the basilar artery are known as the vertebral basilar system, which supplies blood to the posterior part of the circle of ...
* Circle of Willis (arterial system)
* Blood–brain barrier
* Glymphatic system
* Venous systems
* Circumventricular organs
Dopamine system
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurot ...
* Serotonin system
*Cholinergic system
Cholinergic agents are compounds which mimic the action of acetylcholine and/or butyrylcholine. In general, the word "choline" describes the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the ''N'',''N'',''N''-trimethylethanolammonium cation. F ...
* GABA
* Neuropeptides
** Opioid peptides
*** Endorphins
*** Enkephalin
An enkephalin is a pentapeptide involved in regulating nociception in the body. The enkephalins are termed endogenous ligands, as they are internally derived and bind to the body's opioid receptors. Discovered in 1975, two forms of enkephal ...
s
*** Dynorphins
** Oxytocin
** Substance P
Dural meningeal system
*Cerebrospinal Fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the ...
*Brain-cerebrospinal fluid barrier
* Meningeal coverings
** Dura mater
** Arachnoid mater
** Pia mater
* Epidural space
* Subdural space
* Subarachnoid space
**Arachnoid septum
** Superior cistern
** Cistern of lamina terminalis
** Chiasmatic cistern
** Interpeduncular cistern
** Pontine cistern
** Cisterna magna
** Spinal subarachnoid space
* Ventricular system
** Lateral ventricles
*** Angular bundle
*** Anterior horn
***Body of lateral ventricle
***Inferior horn
*** Posterior horn
**** Calcar avis
*** Subventricular zone
** Third ventricle
** Fourth ventricle
**Foramina
*** Interventricular Foramina
*** Cerebral Aqueduct
*** Foramina of Luschka
***Foramen of Magendie
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (;Entry "foramen"
in
in
brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
structures located on both sides of the thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all direct ...
, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved i ...
of the cerebrum
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. ...
primarily in the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal ( alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', ...
.Schacter, Daniel L. 2012. ''Psychology''.sec. 3.20 The classification of structures as part of the limbic system is historical and originates from the position of the structures at the boundary between two functionally distinct components (hence, the name limbus, meaning border) and the structures' shared roles in emotional processes (see limbic system for more details). Hence, there is overlap of structures in the limbic system and in other classifications of brain structures. The following areas have been considered part of the limbic system.:
*Cortical areas:
** Limbic lobe
** Orbitofrontal cortex: a region in the frontal lobe involved in the process of decision-making
** Piriform cortex: part of the olfactory system
**Entorhinal cortex
The entorhinal cortex (EC) is an area of the brain's allocortex, located in the medial temporal lobe, whose functions include being a widespread network hub for memory, navigation, and the perception of time.Integrating time from experience in th ...
: related to memory and associative components
**Hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic syste ...
and associated structures: play a central role in the consolidation of new memories
** Fornix: a white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribu ...
structure connecting the hippocampus with other brain structures, particularly the mammillary bodies and septal nuclei
The septal area (medial olfactory area), consisting of the lateral septum and medial septum, is an area in the lower, posterior part of the medial surface of the frontal lobe, and refers to the nearby septum pellucidum.
The septal nuclei are loc ...
*Subcortical areas:
**Septal nuclei
The septal area (medial olfactory area), consisting of the lateral septum and medial septum, is an area in the lower, posterior part of the medial surface of the frontal lobe, and refers to the nearby septum pellucidum.
The septal nuclei are loc ...
: a set of structures that lie in front of the lamina terminalis, considered a pleasure zone
**Amygdala
The amygdala (; plural: amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nuclei located deep and medially within the temporal lobes of the brain's cerebrum in complex ver ...
: located deep within the temporal lobes
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in pro ...
and related with a number of emotional processes
**Nucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for "nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hyp ...
: involved in reward, pleasure, and addiction
* Diencephalic structures:
**Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus ...
: a center for the limbic system, connected with the frontal lobes, septal nuclei, and the brain stem reticular formation
The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem. It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain. The neurons of the reticular formatio ...
via the medial forebrain bundle, with the hippocampus via the fornix, and with the thalamus via the mammillothalamic fasciculus
The mammillothalamic tract (mammillothalamic fasciculus, thalamomammillary fasciculus, bundle of Vicq d’Azyr) arises from cells in both the medial and lateral nuclei of the mammillary body and by fibers that are directly continued from the forn ...
; regulates many autonomic processes
** Mammillary bodies: part of the hypothalamus that receives signals from the hippocampus via the fornix and projects them to the thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all direct ...
**Anterior nuclei of thalamus
The anterior nuclei of thalamus (or anterior nuclear group) are a collection of nuclei at the rostral end of the dorsal thalamus. They comprise the anteromedial, anterodorsal, and anteroventral nuclei.
Inputs and outputs
The anterior nuclei rece ...
: receive input from the mammillary bodies and involved in memory processing
Other areas that have been included in the limbic system include the:
* Stria medullaris
* Central gray and dorsal and ventral nuclei of Gudden
Related topics
*Human brain
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of ...
* Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
* Outline of the human nervous system
* List of nerves of the human body
References
External links
High-Resolution Cytoarchitectural Primate Brain Atlases
View information on various brain regions: images, name in seven languages, location, etc.
Medical subject headings: Brain
View tree structures of the brain with the MeSH Tree Structures tab. {{Somatosensory system Brain Cognitive science lists