List Of Galaxies on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The following is a list of notable
The following is a list of notable
Lab scientists revoke status of space object
* BR1202-0725 LAE, discovered in 1998 at z=5.64 does not appear on the list because it was not definitively pinned. BR1202-0725 ( QSO 1202-07) refers to a quasar that the Lyman alpha emitting galaxy is near. The quasar itself lies at z=4.6947 * BR2237-0607 LA1 and BR2237-0607 LA2 were found at z=4.55 while investigating around the quasar BR2237-0607 in 1996. Neither of these appear on the list because they were not definitively pinned down at the time. The quasar itself lies at z=4.558 * Two absorption dropouts in the spectrum of quasar BR 1202-07 ( QSO 1202-0725, BRI 1202-0725, BRI1202-07) were found, one in early 1996, another later in 1996. Neither of these appear on the list because they were not definitively pinned down at the time. The early one was at z=4.38, the later one at z=4.687, the quasar itself lies at z=4.695 * In 1986, a gravitationally lensed galaxy forming a blue arc was found lensed by galaxy cluster CL 2224-02 (C12224 in some references). However, its redshift was only determined in 1991, at z=2.237, by which time, it would no longer be the most distant galaxy known. * An absorption drop was discovered in 1985 in the light spectrum of quasar PKS 1614+051 at z=3.21 This does not appear on the list because it was not definitively fixed down. At the time, it was claimed to be the first non-QSO galaxy found beyond redshift 3. The quasar itself is at z=3.197 * In 1975, 3C 123 was incorrectly determined to lie at z=0.637 (actually z=0.218). * From 1964 to 1997, the title of most distant object in the universe was held by a succession of quasars. That list is available at

Brightest Galaxies
* 1956 Catalogue of Galaxy Redshifts
Redshifts and magnitudes of extragalactic nebulae
by Milton L. Humason, Nicholas U. Mayall,
The Apparent Radial Velocities of 100 Extra-Galactic Nebulae
by Milton L. Humason * 1925 Catalogue of Galaxy Redshifts: by
Nebulae
by
Deep Space Map
{{Portal bar, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System, Science * *
galaxies
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. ...
.
There are about 51 galaxies in the Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way.
It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of .
It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form ...
(see list of nearest galaxies
This is a list of known Galaxy, galaxies within 3.8 Parsec, megaparsecs (12.4 million light-years) of the Solar System, in ascending order of heliocentric distance, or the distance to the Sun.
This encompasses about 50 major Local Group galaxies, ...
for a complete list), on the order of 100,000 in the Local Supercluster
The Virgo Supercluster (Virgo SC) or the Local Supercluster (LSC or LS) is a mass concentration of galaxies containing the Virgo Cluster and Local Group, which itself contains the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies, as well as others. At least ...
, and an estimated 100 billion in all of the observable universe
The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time, because the electromagnetic radiation from these obj ...
.
The discovery of the nature of galaxies as distinct from other nebula
A nebula ('cloud' or 'fog' in Latin; pl. nebulae, nebul├” or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regio ...
e (interstellar cloud
An interstellar cloud is generally an accumulation of gas, plasma, and dust in our and other galaxies. Put differently, an interstellar cloud is a denser-than-average region of the interstellar medium, the matter and radiation that exists in t ...
s) was made in the 1920s. The first attempts at systematic catalogues of galaxies were made in the 1960s, with the Catalogue of Galaxies and Clusters of Galaxies
The Catalogue of Galaxies and of Clusters of Galaxies (or CGCG) was compiled by Fritz Zwicky in 1961ŌĆō68. It contains 29,418 galaxies and 9,134 galaxy clusters.
Gallery
File:I Zwicky 18a.jpg, I Zwicky 18
File:Galaxy I Zwicky 32.jpeg, I Zwicky 3 ...
listing 29,418 galaxies and galaxy clusters, and with the Morphological Catalogue of Galaxies
The Morphological Catalogue of Galaxies (MCG) or Morfologiceskij Katalog Galaktik, is a Russian catalogue of 30,642 galaxies compiled by Boris Vorontsov-Velyaminov
Boris Aleksandrovich Vorontsov-Velyaminov (russian: ąæąŠčĆąĖčü ąÉą╗ąĄą║čüą░ąĮą┤č ...
, a putatively complete list of galaxies with photographic magnitude
Photographic magnitude ( or ) is a measure of the relative brightness of a star or other astronomical object as imaged on a photographic film emulsion with a camera attached to a telescope. An object's apparent photographic magnitude depends on i ...
above 15, listing 30,642. In the 1980s, the Lyons Groups of Galaxies Lyons Groups of Galaxies (or LGG) is an astronomical catalog of nearby groups of galaxies complete to a limiting apparent magnitude B0=14.0 with a recession velocity smaller than 5,500 km/s. The catalogue was obtained from the Lyon-Meudon Ext ...
listed 485 galaxy groups with 3,933 member galaxies. Galaxy Zoo
Galaxy Zoo is a crowdsourced astronomy project which invites people to assist in the morphological classification of large numbers of galaxies. It is an example of citizen science as it enlists the help of members of the public to help in scien ...
is a project aiming at a more comprehensive list: launched in July 2007, it has classified over one million galaxy images from The Sloan Digital Sky Survey, The Hubble Space Telescope and the Cosmic Assembly Near-Infrared Deep Extragalactic Legacy Survey.
There is no universal naming convention for galaxies, as they are mostly catalogued before it is established whether the object is or isn't a galaxy. Mostly they are identified by their celestial coordinates together with the name of the observing project ( HUDF, SDSS, 3C, CFHQS, NGC/IC, etc.)
__TOC__
Named galaxies
This is a list of galaxies that are well known by something other than an entry in a catalog or list, or a set of coordinates, or a systematic designation.Naked-eye galaxies
This is a list of galaxies that are visible to the naked eye, for at the very least, keen-eyed observers in a very dark-sky environment that is high in altitude, during clear and stable weather. *Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy
The Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy (Sgr dSph), also known as the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy (Sgr dE or Sag DEG), is an elliptical loop-shaped satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. It contains four globular clusters in ...
is not listed, because it is not discernible as being a separate galaxy in the sky.
Observational firsts
Prototypes
This is a list of galaxies that became prototypes for a class of galaxies.Closest and most distant-known galaxies by type
Closest galaxies
Most distant galaxies
Timeline notes
*MACS0647-JD
__NOTOC__
MACS0647-JD is a galaxy with a redshift of about ''z'' = 10.7, equivalent to a light travel distance of 13.26 billion light-years (4 billion parsecs). If the distance estimate is correct, it formed about 427 million years after the Big B ...
, discovered in 2012, with z=10.7, does not appear on this list because it has not been confirmed with a spectroscopic redshift.
* UDFy-38135539
UDFy-38135539 (also known as "HUDF.YD3") is the Hubble Ultra Deep Field (UDF) identifier for a galaxy which was calculated to have a light travel time of 13.1 billion years with a present proper distance of around 30 billion light-years.
...
, discovered in 2009, with z=8.6, does not appear on this list because its claimed redshift is disputed. Follow-up observations have failed to replicate the cited redshift measurement.
* A1689-zD1
A1689-zD1 is a galaxy in the Virgo constellation. It was a candidate for the most distant and therefore earliest-observed galaxy discovered , based on a photometric redshift.
If the redshift, z~7.6, is correct, it would explain why the galax ...
, discovered in 2008, with z=7.6, does not appear on this list because it has not been confirmed with a spectroscopic redshift.
* Abell 68 c1 and Abell 2219 c1, discovered in 2007, with z=9, do not appear on this list because they have not been confirmed.
* IOK4 and IOK5, discovered in 2007, with z=7, do not appear on this list because they have not been confirmed with a spectroscopic redshift.
* Abell 1835 IR1916
Abell 1835 IR1916 (also known as Abell 1835, Galaxy Abell 1835, Galaxy Abell 1835 IR1916, or simply The Abell) was a candidate for being the most distant galaxy ever observed, although that claim has not been verified by additional observations. ...
, discovered in 2004, with z=10.0, does not appear on this list because its claimed redshift is disputed. Some follow-up observations have failed to find the object at all.
* STIS 123627+621755, discovered in 1999, with z=6.68, does not appear on this list because its redshift was based on an erroneous interpretation of an oxygen emission line as a hydrogen emission line.Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is a federal research facility in Livermore, California, United States. The lab was originally established as the University of California Radiation Laboratory, Livermore Branch in 1952 in response ...
Lab scientists revoke status of space object
* BR1202-0725 LAE, discovered in 1998 at z=5.64 does not appear on the list because it was not definitively pinned. BR1202-0725 ( QSO 1202-07) refers to a quasar that the Lyman alpha emitting galaxy is near. The quasar itself lies at z=4.6947 * BR2237-0607 LA1 and BR2237-0607 LA2 were found at z=4.55 while investigating around the quasar BR2237-0607 in 1996. Neither of these appear on the list because they were not definitively pinned down at the time. The quasar itself lies at z=4.558 * Two absorption dropouts in the spectrum of quasar BR 1202-07 ( QSO 1202-0725, BRI 1202-0725, BRI1202-07) were found, one in early 1996, another later in 1996. Neither of these appear on the list because they were not definitively pinned down at the time. The early one was at z=4.38, the later one at z=4.687, the quasar itself lies at z=4.695 * In 1986, a gravitationally lensed galaxy forming a blue arc was found lensed by galaxy cluster CL 2224-02 (C12224 in some references). However, its redshift was only determined in 1991, at z=2.237, by which time, it would no longer be the most distant galaxy known. * An absorption drop was discovered in 1985 in the light spectrum of quasar PKS 1614+051 at z=3.21 This does not appear on the list because it was not definitively fixed down. At the time, it was claimed to be the first non-QSO galaxy found beyond redshift 3. The quasar itself is at z=3.197 * In 1975, 3C 123 was incorrectly determined to lie at z=0.637 (actually z=0.218). * From 1964 to 1997, the title of most distant object in the universe was held by a succession of quasars. That list is available at
list of quasars
This article contains lists of quasars. More than a million quasars have been observed, so any list on Wikipedia is necessarily a selection of them.
Proper naming of quasars are by Catalogue Entry, Qxxxx┬▒yy using B1950 coordinates, or QSO Jxxxx┬ ...
.
* In 1958, clusters Cl 0024+1654 and Cl 1447+2619 were estimated to have redshifts of z=0.29 and z=0.35, respectively. However, no galaxy was spectroscopically determined.
Galaxies by brightness and power
Galaxies by mass and density
Galaxies by size
Field galaxies
A field galaxy is a galaxy that does not belong to a larger cluster of galaxies and hence is gravitationally alone.Interacting galaxies
Galaxy mergers
Galaxies with some other notable feature

See also
*Galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. ...
* Galaxy groups and clusters
Galaxy groups and clusters are the largest known gravitationally bound objects to have arisen thus far in the process of cosmic structure formation. They form the densest part of the large-scale structure of the Universe. In models for the gravit ...
* Illustris project
The Illustris project was a series of astrophysical simulations run by an international collaboration of scientists. The aim was to study the processes of galaxy formation and evolution in the universe with a comprehensive physical model. Early r ...
* List of galaxy groups and clusters
This article lists some galaxy groups and galaxy clusters.
Defining the limits of galaxy clusters is imprecise as many clusters are still forming. In particular, clusters close to the Milky Way tend to be classified as galaxy clusters even whe ...
* List of galaxy superclusters
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn ...
* Lists of astronomical objects
This is a list of lists, grouped by type of astronomical object.
Solar System
* List of Solar System objects
* List of gravitationally rounded objects of the Solar System
* List of Solar System objects most distant from the Sun
* List of So ...
* Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way.
It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of .
It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form ...
* Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye ...
Galaxy
* Supercluster
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn ...
* Virgo Supercluster
The Virgo Supercluster (Virgo SC) or the Local Supercluster (LSC or LS) is a mass concentration of galaxies containing the Virgo Cluster and Local Group, which itself contains the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies, as well as others. At least ...
Lists of galaxies
*Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way.
It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of .
It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form ...
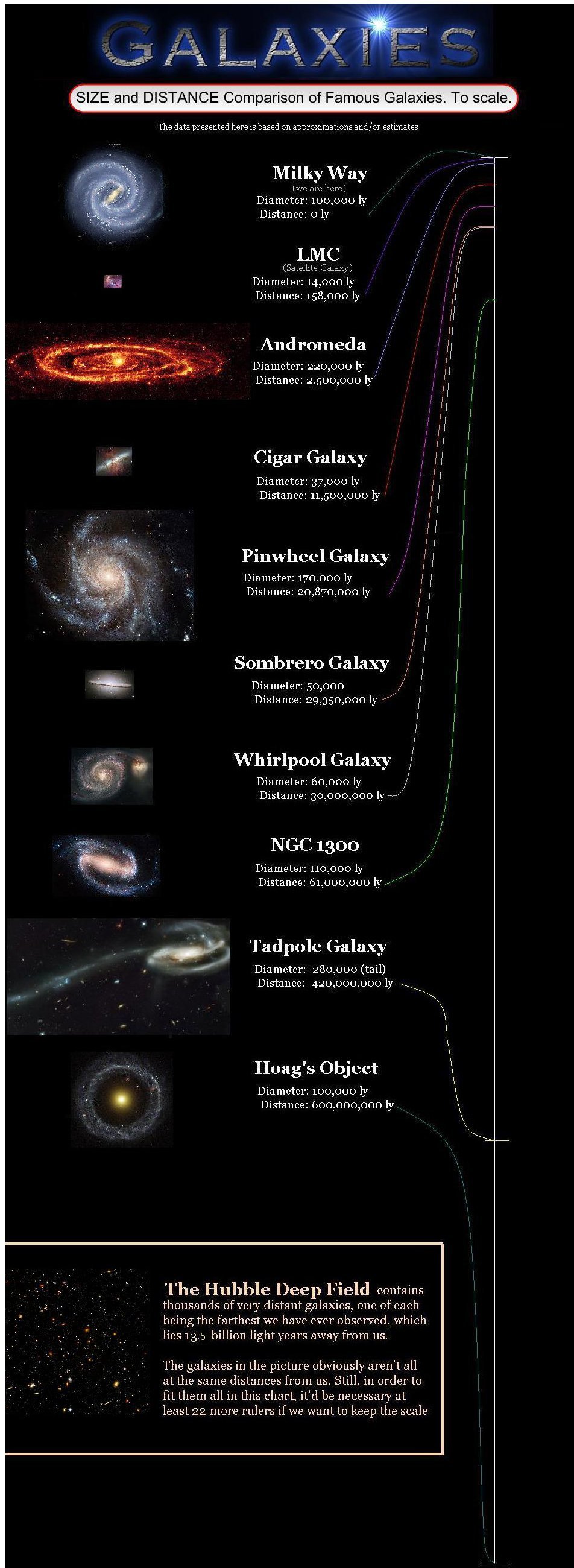
* List of largest galaxies
This is a list of largest galaxies known, sorted by order of increasing major axis diameters. The unit of measurement used is the light-year (approximately 9.46 kilometers).
Overview
Galaxies are vast collections of stars, planets, nebulae ...
* List of nearest galaxies
This is a list of known Galaxy, galaxies within 3.8 Parsec, megaparsecs (12.4 million light-years) of the Solar System, in ascending order of heliocentric distance, or the distance to the Sun.
This encompasses about 50 major Local Group galaxies, ...
* List of polar-ring galaxies
* List of spiral galaxies
A spiral galaxy is a type of galaxy characterized by a central bulge of old Population II stars surrounded by a rotating disc of younger Population I stars. A spiral galaxy maintains its spirals arms due to density wave theory.
__TOC__
Spiral g ...
* List of ring galaxies
* List of quasars
This article contains lists of quasars. More than a million quasars have been observed, so any list on Wikipedia is necessarily a selection of them.
Proper naming of quasars are by Catalogue Entry, Qxxxx┬▒yy using B1950 coordinates, or QSO Jxxxx┬ ...
Notes
References
External links
*Wolfram Research
Wolfram Research, Inc. ( ) is an American multinational company that creates computational technology. Wolfram's flagship product is the technical computing program Wolfram Mathematica, first released on June 23, 1988. Other products include Wo ...
: Scientific Astronomer Documentations ŌĆBrightest Galaxies
* 1956 Catalogue of Galaxy Redshifts
Redshifts and magnitudes of extragalactic nebulae
by Milton L. Humason, Nicholas U. Mayall,
Allan Sandage
Allan Rex Sandage (June 18, 1926 – November 13, 2010) was an American astronomer. He was Staff Member Emeritus with the Carnegie Observatories in Pasadena, California. He determined the first reasonably accurate values for the Hubble con ...
* 1936 Catalogue of Galaxy RedshiftsThe Apparent Radial Velocities of 100 Extra-Galactic Nebulae
by Milton L. Humason * 1925 Catalogue of Galaxy Redshifts: by
Vesto Slipher
Vesto Melvin Slipher (; November 11, 1875 ŌĆō November 8, 1969) was an American astronomer who performed the first measurements of radial velocities for galaxies. He was the first to discover that distant galaxies are redshifted, thus providing th ...
* (1917) First Catalogue of Galaxy RedshiftsNebulae
by
Vesto Slipher
Vesto Melvin Slipher (; November 11, 1875 ŌĆō November 8, 1969) was an American astronomer who performed the first measurements of radial velocities for galaxies. He was the first to discover that distant galaxies are redshifted, thus providing th ...
* Interactive Map of the Visible Universe with GalaxiesDeep Space Map
{{Portal bar, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System, Science * *