Liquid handling robot on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
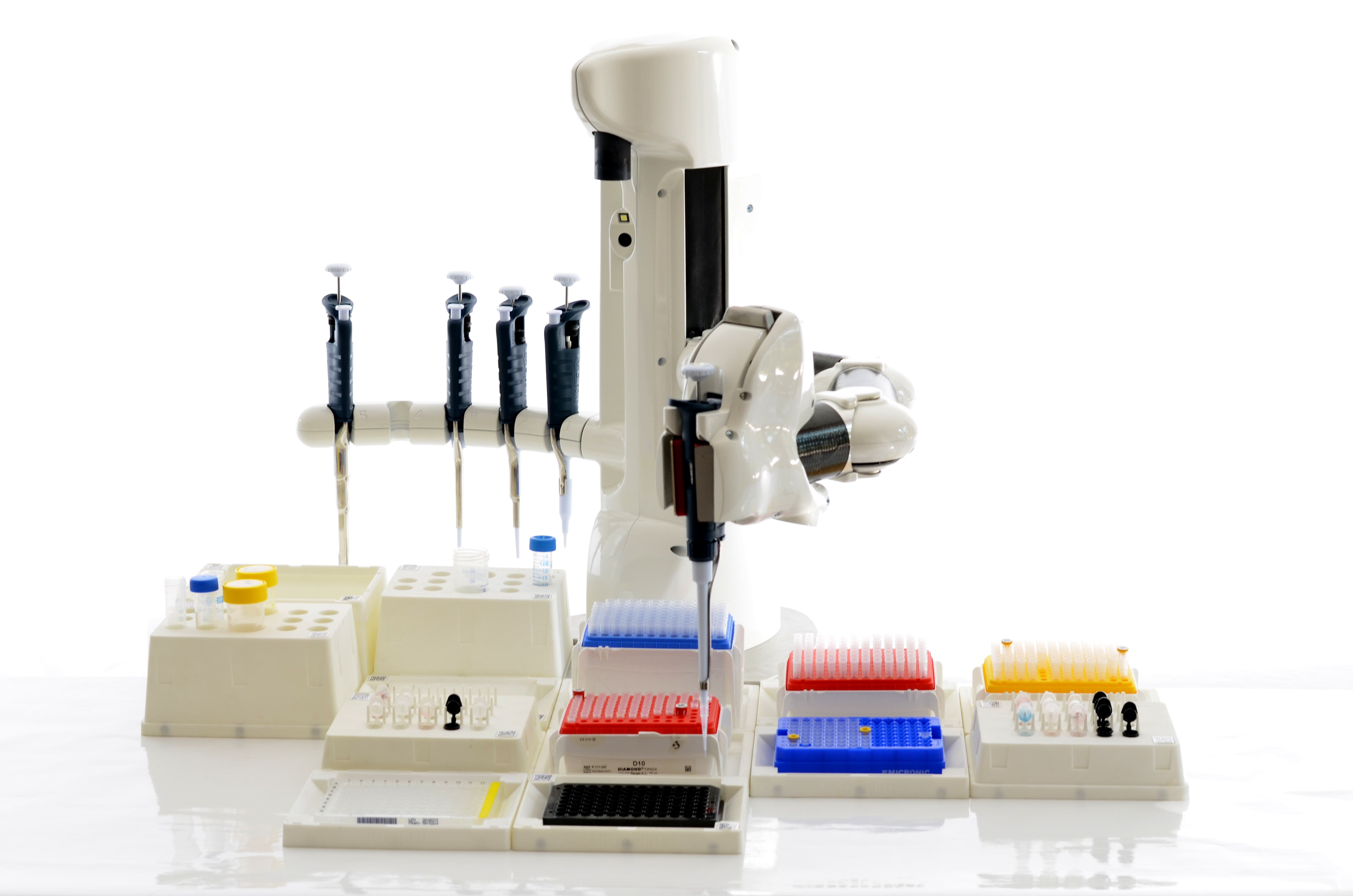

 A liquid handling robot is used to automate workflows in life science laboratories. It is a
A liquid handling robot is used to automate workflows in life science laboratories. It is a
XYZ Triton Robot
from TriContinent Scientific) and/or integrate additional laboratory devices, such as centrifuges, microplate readers, heat sealers, heater/shakers, bar code readers, spectrophotometric devices, storage devices and incubators. More complex liquid handling workstations can perform multiple Laboratory Unit Operations such as sample transport, sample mixing, manipulation and incubation, as well as transporting vessels to/from other workstations. They can range from a specialized bench-top 8-channel DNA PCR processing robot, to a customized-for-process automated liquid handling system, such as the TECAN Freedom EVO (shown on the right), the HighRes Biosolution's PRIME and Janus Automated liquid handlers from


 A liquid handling robot is used to automate workflows in life science laboratories. It is a
A liquid handling robot is used to automate workflows in life science laboratories. It is a robot
A robot is a machine—especially one programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the control may be embedded within. Robots may ...
that dispenses a selected quantity of reagent, samples or other liquid to a designated container.
Introduction
Liquid handling plays a pivotal role in life science laboratories. The sample volumes are usually small, at the micro- or nanoliter level, and the number of transferred samples can be huge. Under these conditions, liquid handling by hand is tedious, time-consuming, and impractical. Consequently, there is a strong demand for automated liquid handling robots.Types of liquid handling robots
The simplest version simply dispenses an allottedvolume
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). Th ...
of liquid from a motorized pipette or syringe; more complicated machines can also manipulate the position of the dispensers and containers (often a Cartesian coordinate robot
A Cartesian coordinate robot (also called linear robot) is an industrial robot whose three principal axes of control are linear (i.e. they move in a straight line rather than rotate) and are at right angles to each other. The three sliding joi ...
, such as thXYZ Triton Robot
from TriContinent Scientific) and/or integrate additional laboratory devices, such as centrifuges, microplate readers, heat sealers, heater/shakers, bar code readers, spectrophotometric devices, storage devices and incubators. More complex liquid handling workstations can perform multiple Laboratory Unit Operations such as sample transport, sample mixing, manipulation and incubation, as well as transporting vessels to/from other workstations. They can range from a specialized bench-top 8-channel DNA PCR processing robot, to a customized-for-process automated liquid handling system, such as the TECAN Freedom EVO (shown on the right), the HighRes Biosolution's PRIME and Janus Automated liquid handlers from
PerkinElmer
PerkinElmer, Inc., previously styled Perkin-Elmer, is an American global corporation focused in the business areas of diagnostics, life science research, food, environmental and industrial testing. Its capabilities include detection, imaging, in ...
. Other liquid handling systems are designed for specific experiments, e.g. the Intavis InsituPro robot for the automation of immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization
''In situ'' hybridization (ISH) is a type of hybridization that uses a labeled complementary DNA, RNA or modified nucleic acids strand (i.e., probe) to localize a specific DNA or RNA sequence in a portion or section of tissue (''in situ'') o ...
on whole-mounts and slides.
An alternative category of liquid handlers mimics the operations of humans, by performing liquid transfers as humans would do. These robots achieve the cartesian, 3-axis movements implemented in larger workstations, by means of an arm. In some cases (like the "Andrew" system or ASSIST PLUS robot shown on the right) they can even use the same pipettes
A pipette (sometimes spelled as pipett) is a laboratory tool commonly used in chemistry, biology and medicine to transport a measured volume of liquid, often as a media dispenser. Pipettes come in several designs for various purposes with diffe ...
and consumables as humans.
Modularity
Liquid handling robots can be customized using different add-on modules such ascentrifuges
A centrifuge is a device that uses centrifugal force to separate various components of a fluid. This is achieved by spinning the fluid at high speed within a container, thereby separating fluids of different densities (e.g. cream from milk) or l ...
, PCR machines, colony pickers, shaking modules, heating modules and others. Some liquid handling robots utilize Acoustic Liquid Handling (also known as acoustic droplet ejection or ADE) which uses sound to move liquids without the traditional pipette or syringe.
Control Software
Control software, either on a connected computer, or integrated into the system itself, allows the user to customize the liquid handling procedures and transfer volumes.Quality Control
One of the challenges in using automated liquid handlers, or liquid handling robots, is in verifying the proper function of the device. Liquid handling operations, performed by these automated systems, can fail due to clogged pipette tips, failed solenoid valves, damaged labware, operator error and many other reasons. A variety of methods exist for performing quality control of liquid dispensing on automated platforms including gravimetric, fluorescent and colorimetric measurements. In addition to manual quality control methods, technologies have been developed which allow for the automated monitoring of quality control of liquid handling robots.References
{{reflist Robotic manipulation