Liberal Party Of Australia (South Australian Division) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Liberal Party of Australia (South Australian Division), commonly known as the South Australian Liberals, is the
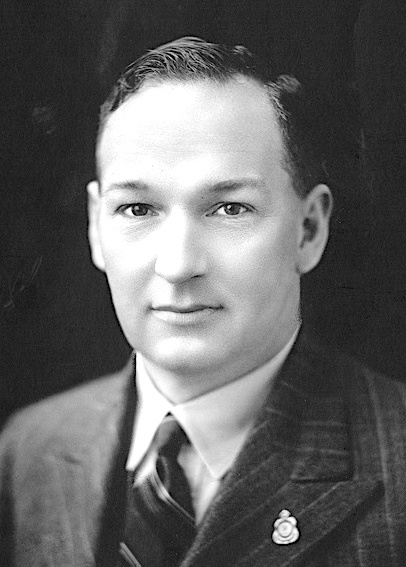 The Butler LCL introduced the electoral
The Butler LCL introduced the electoral
South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
n Division of the Liberal Party of Australia
The Liberal Party of Australia is a centre-right political party in Australia, one of the two major parties in Australian politics, along with the centre-left Australian Labor Party. It was founded in 1944 as the successor to the United Au ...
. It was formed as the Liberal and Country League (LCL) in 1932 and became the South Australian Division of the Liberal Party when the Liberal Party was formed in 1945. It retained its Liberal and Country League name before changing to its current name in 1974. It is one of two major parties in the bicameral Parliament of South Australia, the other being the Australian Labor Party (SA Branch). The party has been led by Leader of the Opposition David Speirs
David James Speirs (born December 15, 1984) is an Australian politician. He has been a Liberal member of the South Australian House of Assembly since the 2014 state election and leader of the Liberal Party since 19 April 2022. He represented ...
since the 2022 state election after a one-term government.
During its 42-year existence as the Liberal and Country League, it spent 34 years in government, mainly due to an electoral malapportionment
Apportionment is the process by which seats in a legislative body are distributed among administrative divisions, such as states or parties, entitled to representation. This page presents the general principles and issues related to apportionmen ...
scheme known as the Playmander
The Playmander was a gerrymandering system, a pro-rural electoral malapportionment in the Australian state of South Australia, which was introduced by the incumbent Liberal and Country League (LCL) government in 1936, and remained in place for 32 ...
. The Playmander was named after LCL leader Sir Tom Playford, who was the Premier of South Australia
The premier of South Australia is the head of government in the state of South Australia, Australia. The Government of South Australia follows the Westminster system, with a Parliament of South Australia acting as the legislature. The premier is ...
for 27 years from 1938 until his election loss in 1965. The Playmander was dismantled through an electoral reform in 1968, with the first election under the new boundaries in 1970
Events
January
* January 1 – Unix time epoch reached at 00:00:00 UTC.
* January 5 – The 7.1 Tonghai earthquake shakes Tonghai County, Yunnan province, China, with a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (''Extreme''). Between 10,000 and ...
. Since the electoral reform, the party has won only 4 of the 17 state elections: 1979
Events
January
* January 1
** United Nations Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim heralds the start of the '' International Year of the Child''. Many musicians donate to the '' Music for UNICEF Concert'' fund, among them ABBA, who write the so ...
, 1993
File:1993 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The Oslo I Accord is signed in an attempt to resolve the Israeli–Palestinian conflict; The Russian White House is shelled during the 1993 Russian constitutional crisis; Czechoslovakia is peacefu ...
, 1997 and 2018
File:2018 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: The 2018 Winter Olympics opening ceremony in PyeongChang, South Korea; Protests erupt following the Assassination of Jamal Khashoggi; March for Our Lives protests take place across the Unit ...
.
History
Formation
The Liberal and Country League had its roots in the Emergency Committee of South Australia, which ran as the main non-Labor party in South Australia at the 1931 federal election landslide. In theHouse of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
, it took an additional two seats to hold six of the state's seven seats. In the bloc-voting winner-take-all Senate, it took the three seats up for election.
Encouraged by this success, the Liberal Federation (the SA branch of the United Australia Party
The United Australia Party (UAP) was an Australian political party that was founded in 1931 and dissolved in 1945. The party won four federal elections in that time, usually governing in coalition with the Country Party. It provided two prim ...
) and the SA Country Party merged to form the LCL on 9 June 1932, with former Liberal Federation leader Richard Layton Butler as its first leader. Liberal Federation itself was preceded by Liberal Union (1910–1923) with the latter created from a tri-merger between the Liberal and Democratic Union (formed 1906), the Farmers and Producers Political Union (formed 1904) and the National Defence League (formed 1891).
In its first electoral test, the 1933 state election, the LCL took advantage of a three-way split in the state Labor government to win a smashing victory, taking 29 seats versus only 13 for the three Labor factions combined. Butler then became the Premier of South Australia
The premier of South Australia is the head of government in the state of South Australia, Australia. The Government of South Australia follows the Westminster system, with a Parliament of South Australia acting as the legislature. The premier is ...
.
Traditionally a socially conservative
Social conservatism is a political philosophy and variety of conservatism which places emphasis on traditional power structures over social pluralism. Social conservatives organize in favor of duty, traditional values and social institution ...
party, the LCL contained relatively distinct factions whose ideologies often conflicted:
* Farmers, graziers and rural property owner
In property law, title is an intangible construct representing a bundle of rights in (to) a piece of property in which a party may own either a legal interest or equitable interest. The rights in the bundle may be separated and held by different ...
s.
* The urban middle class
The urban middle class continued to support the party although they had little say in its running. Indeed, it was not until the election of Robin Millhouse
Robin Rhodes Millhouse, QC (9 December 1929 – 28 April 2017) was, at various times, the 39th Attorney-General of South Australia, the first Australian Democrats parliamentarian, and the Chief Justice of both Kiribati and Nauru and a judge of ...
in 1955 that someone from this third faction was elected to parliament. Millhouse, often considered during his term as the most progressive member of the LCL, continually criticised the conservative wing of the party. He eventually resigned in 1973 and joined the splinter Liberal Movement party.
Playmander period
Early years
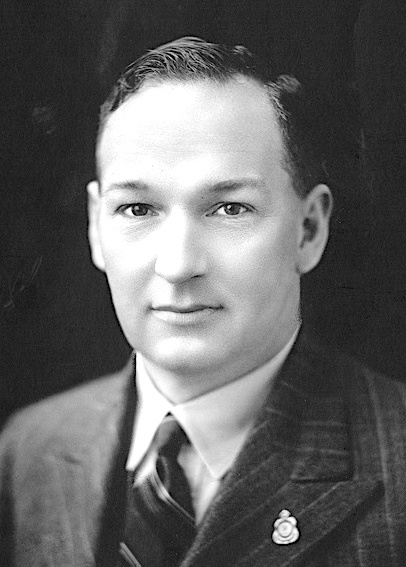 The Butler LCL introduced the electoral
The Butler LCL introduced the electoral malapportionment
Apportionment is the process by which seats in a legislative body are distributed among administrative divisions, such as states or parties, entitled to representation. This page presents the general principles and issues related to apportionmen ...
scheme later known as the Playmander
The Playmander was a gerrymandering system, a pro-rural electoral malapportionment in the Australian state of South Australia, which was introduced by the incumbent Liberal and Country League (LCL) government in 1936, and remained in place for 32 ...
in 1936. The House of Assembly was also reduced from 46 members elected from multi-member
An electoral system or voting system is a set of rules that determine how elections and referendums are conducted and how their results are determined. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political elections ma ...
districts to 39 members elected from single-member electorates. The electorates consisted of rural districts enjoying a 2-to-1 advantage in the state parliament, even though they contained less than half of the population. Two-thirds of seats were to be located in rural areas ("the country"). This arrangement was retained even as Adelaide
Adelaide ( ) is the capital city of South Australia, the state's largest city and the fifth-most populous city in Australia. "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater Adelaide (including the Adelaide Hills) or the Adelaide city centre. The dem ...
, the state capital, grew to two-thirds of the state's population.
Even allowing for a smaller chamber, the LCL suffered heavy losses at the 1938 election, winning just 15 of 39 seats. However, Labor picked up only a small number of additional seats. In an unprecedented result, the crossbench
A crossbencher is an independent or minor party member of some legislatures, such as the British House of Lords and the Parliament of Australia. They take their name from the crossbenches, between and perpendicular to the government and oppositi ...
swelled massively, with no less than 14 independents elected from a combined independent primary vote of 40 percent, higher than either major party (33 percent for the LCL, 26 percent for Labor). Butler and the LCL had to rely on the crossbench for confidence and supply
In a parliamentary democracy based on the Westminster system, confidence and supply are required for a ruling cabinet to retain power in the lower house.
A confidence-and-supply agreement is one whereby a party or independent members of par ...
to remain in government. Only months later, Butler resigned in favour of Tom Playford to make an unsuccessful attempt to enter federal politics. From the 1941 election onward, the Playford LCL would regain and keep a parliamentary majority, albeit narrowly. Additionally, turnout crashed to a record-low 50 percent in 1941, triggering the Playford LCL to introduce compulsory voting from the 1944 election.
In January 1945, the Liberal and Country League became the South Australian division of the newly formed Liberal Party of Australia
The Liberal Party of Australia is a centre-right political party in Australia, one of the two major parties in Australian politics, along with the centre-left Australian Labor Party. It was founded in 1944 as the successor to the United Au ...
. However, the SA division continued to be known as the LCL.
Effects on elections
Under the scheme, a vote in a low-population rural seat had anywhere from double to ten times the value of a vote in a high-population metropolitan seat. For example, at the 1968 election the rural seat ofFrome
Frome ( ) is a town and civil parish in eastern Somerset, England. The town is built on uneven high ground at the eastern end of the Mendip Hills, and centres on the River Frome. The town, about south of Bath, is the largest in the Mendip d ...
had 4,500 formal votes, while the metropolitan seat of Enfield
Enfield may refer to:
Places Australia
* Enfield, New South Wales
* Enfield, South Australia
** Electoral district of Enfield, a state electoral district in South Australia, corresponding to the suburb
** Enfield High School (South Australia)
...
had 42,000 formal votes. The scheme allowed LCL to win sufficient parliamentary seats even when it lost the two-party
A two-party system is a political party system in which two major political parties consistently dominate the political landscape. At any point in time, one of the two parties typically holds a majority in the legislature and is usually referr ...
vote to Labor
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the la ...
opposition by comprehensive margins at several elections: 1944, 1953, 1962
Events January
* January 1 – Western Samoa becomes independent from New Zealand.
* January 3 – Pope John XXIII excommunicates Fidel Castro for preaching communism.
* January 8 – Harmelen train disaster: 93 die in the wor ...
and 1968. For instance, in the 1944 and 1953 elections, Labor took 53 percent of the two-party vote, which would have normally been enough to deliver a solid majority for the Labor leader– Robert Richards in 1944 and Mick O'Halloran in 1953. However, on both occasions, the LCL managed to just barely hold onto power. By the 1950s, a number of Labor figures had despaired of ever winning power. O'Halleran, for instance, felt he needed to maintain a cordial relationship with Playford in hopes of getting Labor-friendly legislation through the House of Assembly.
Playford had become synonymous with the LCL over his record 27-year tenure as Premier of South Australia
The premier of South Australia is the head of government in the state of South Australia, Australia. The Government of South Australia follows the Westminster system, with a Parliament of South Australia acting as the legislature. The premier is ...
. The LCL became so strongly identified with Playford that during election campaigns, it branded itself as "The Playford Liberal and Country League". Playford gave the impression that the LCL membership were there solely to raise money and run election campaigns; his grip on the party was such that he frequently ignored LCL convention decisions. This treatment of rank and file party members continued to cause resentment throughout the party. This split mirrored the dissatisfaction amongst the Establishment faction, which had been steadily losing its power within the party and was appalled at the "nouveau riche
''Nouveau riche'' (; ) is a term used, usually in a derogatory way, to describe those whose wealth has been acquired within their own generation, rather than by familial inheritance. The equivalent English term is the "new rich" or "new money" ( ...
(new money) commoners", such as Millhouse, that had infiltrated the parliamentary wing of the LCL.
Fall from power
The LCL's grip on power began to slip in the 1950s; they would lose seats in every election from 1953 onward. Even at the height of Playford's popularity, the LCL was almost nonexistent in Adelaide, winning almost no seats in the capital outside the wealthy "eastern crescent" and the area around Glenelg and Holdfast Bay. Due to its paper-thin base in the capital, Playford's LCL often won just barely enough seats to govern alone; the party never held more than 23 seats at any time during Playford's tenure. Despite this, the LCL party machine had become moribund as leaders had become lulled into a false sense of security due to the extended run of election wins aided by the Playmander. The LCL was thus caught unawares when O'Halloran's successor as state Labor leader,Frank Walsh
Francis Henry Walsh (6 July 1897 – 18 May 1968) was the 34th Premier of South Australia from 10 March 1965 to 1 June 1967, representing the South Australian Branch of the Australian Labor Party.
Early life
One of eight children, Walsh was b ...
, eschewed a statewide campaign in favour of targeting marginal LCL seats.
Walsh's strategy almost paid off at the 1962 election. Labor won a decisive 54.3 percent of the two-party preferred vote to the LCL's 45.7 percent. In the rest of Australia, this would have been enough for a comprehensive Labor victory. However, due to the Playmander, Labor only picked up a two-seat swing, leaving it one short of a majority. The two independents threw their support to the LCL, allowing Playford to remain in office. This election showed how grossly distorted the Playmander had become; by this time, Adelaide accounted for two-thirds of the state's population, but elected only one-third of the legislature. A year later, the LCL received another jolt with the reformation of a separate Country Party. Although a shadow of its former self, the reformed Country Party served as a wakeup call to Playford that there were problems within the LCL.
Labor finally beat the Playmander against the odds at the 1965 election. Despite winning the same two-party vote as it had three years earlier, the Playmander
The Playmander was a gerrymandering system, a pro-rural electoral malapportionment in the Australian state of South Australia, which was introduced by the incumbent Liberal and Country League (LCL) government in 1936, and remained in place for 32 ...
was strong enough that Labor was only able to win government by two seats. Playford resigned as party leader in 1966 and was succeeded by Steele Hall
Raymond Steele Hall (born 30 November 1928) is a former Australian politician who served as the 36th Premier of South Australia from 1968 to 1970. He also served in the federal Parliament as a senator for South Australia from 1974 to 1977 and ...
.
Dismantling Playmander
At the 1968 election, Labor won a 53.2 percent two-party vote to the LCL's 46.8 percent, but suffered a two-seat swing, resulting in ahung parliament
A hung parliament is a term used in legislatures primarily under the Westminster system to describe a situation in which no single political party or pre-existing coalition (also known as an alliance or bloc) has an absolute majority of legisla ...
. The lone independent in the chamber, Tom Stott, threw his support to the LCL, allowing Hall to form a minority government. Hall was embarrassed that his party was in a position to win power despite having clearly lost the vote. Concerned by the level of publicity and public protest about the issue, Hall committed himself to reducing the rural weighting. Under his watch, the lower house was expanded 39 to 47 seats, 28 of which were located in Adelaide. It fell short of " one vote one value", as Labor had demanded, since rural areas were still over-represented.
Nonetheless, with Adelaide now electing a majority of the legislature, conventional wisdom held that Hall knew he was effectively handing the premiership to Labor leader Don Dunstan
Donald Allan Dunstan (21 September 1926 – 6 February 1999) was an Australian politician who served as the 35th premier of South Australia from 1967 to 1968, and again from 1970 to 1979. He was a member of the House of Assembly (MHA) for th ...
at the next election. That election took place in 1970
Events
January
* January 1 – Unix time epoch reached at 00:00:00 UTC.
* January 5 – The 7.1 Tonghai earthquake shakes Tonghai County, Yunnan province, China, with a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (''Extreme''). Between 10,000 and ...
when Stott crossed the floor to vote against the LCL. As expected, the LCL was defeated. Hall remained as the Leader of the Opposition. One vote one value would later be introduced by Labor following the 1975 election.
The party's problems had already emerged in public spats, most notably the formation of the Liberal Movement, a socially progressive or "small-l liberal" wing of the LCL in 1972. The divisions culminated in the Liberal Movement becoming a separate party in 1973, with Hall and fellow parliamentarians Martin Cameron and Robin Millhouse
Robin Rhodes Millhouse, QC (9 December 1929 – 28 April 2017) was, at various times, the 39th Attorney-General of South Australia, the first Australian Democrats parliamentarian, and the Chief Justice of both Kiribati and Nauru and a judge of ...
resigning from the LCL to join the newly formed party. Hall claimed that the Party had 'lost its idealism ndforgotten...its purpose for existence'.
Bruce Eastick succeeded Hall as LCL leader after Hall's resignation from the party in 1973.
Liberal Party
Renaming to the Liberal Party
During Eastick's leadership, the Liberal and Country League met at the State Council meeting on 22 July 1974 to rename itself to "Liberal Party of Australia (South Australian Division)". The renaming initiative was welcomed by federal Liberal leader and opposition leader Billy Snedden, who was present at the meeting. The party also revised its constitution, adopted a new platform, appointed new young party officials and organisers, modelling after the Victorian Liberals. In July 1975, David Tonkin challenged Eastick for party leadership, and became leader unopposed after Eastick stood aside. This would be the last time that a Liberal leader was elected unopposed until 2013. Hall's Liberal Movement dissolved in 1976 and three of its four state parliamentary members ( Martin Cameron, John Carnie, David Boundy) rejoined the Liberal Party. Hall, who was elected to the Senate in 1974 and 1975 as a Liberal Movement member, also rejoined the Liberal Party and joined the federalLiberal Party
The Liberal Party is any of many political parties around the world. The meaning of ''liberal'' varies around the world, ranging from liberal conservatism on the right to social liberalism on the left.
__TOC__ Active liberal parties
This is a li ...
room. The remaining Liberal Movement state parliamentary member was Millhouse, who refused to rejoin the Liberal Party, founding the New Liberal Movement instead. His new party merged with the Australia Party
The Australia Party was a minor political party established initially in 1966 as the Liberal Reform Group. As the Australia Party, it became influential, particularly in the landmark 1972 federal election when its preferences assisted the Austr ...
a year later in 1977 to become the Australian Democrats
The Australian Democrats is a centrist political party in Australia. Founded in 1977 from a merger of the Australia Party and the New Liberal Movement, both of which were descended from Liberal Party dissenting splinter groups, it was Austral ...
.
One vote one value was introduced by Labor following the 1975 election where the Liberal Party won a 50.8 percent two-party
A two-party system is a political party system in which two major political parties consistently dominate the political landscape. At any point in time, one of the two parties typically holds a majority in the legislature and is usually referr ...
vote but fell one seat short of forming government. Labor would regain their vote and majority at the 1977 election, however Dunstan resigned in the months prior to the 1979 election where the Liberals won government for one term.
Tonkin Government (1979–1982)
At that election, David Tonkin, who succeeded Eastick as party leader in 1975, led the Liberals to victory against a weakened Labor Party. It was the first time in 20 years that the non-Labor side in South Australia had won the most seats while also winning a majority of the vote. However, despite winning 55 percent of the two-party vote, the largest two-party-preferred margin since the end of the Playmander at the time, the Liberals only won 25 of the 47 seats. This was because the "one vote one value" reforms left most of the Liberal vote locked in comfortably safe rural seats. Despite taking six seats off Labor, the Liberals only won 13 seats in Adelaide. As a result, despite winning a margin that would have been large enough for a strong majority government in the rest of Australia, the Liberals won only 25 seats, a bare majority of two. Tonkin survived for only one term before theearly 1980s recession
The early 1980s recession was a severe economic recession that affected much of the world between approximately the start of 1980 and 1983. It is widely considered to have been the most severe recession since World War II. A key event leading to ...
resulted in him narrowly losing the 1982 election to Labor under John Bannon.
Opposition (1982–1993)
John Olsen
John Wayne Olsen, AO (born 7 June 1945) is a former Australian politician, diplomat and football commissioner. He was Premier of South Australia between 28 November 1996 and 22 October 2001. He is now President of the Federal Liberal Party, C ...
succeeded Tonkin as leader in 1982, and led the Liberals to defeats at the 1985
The year 1985 was designated as the International Youth Year by the United Nations.
Events January
* January 1
** The Internet's Domain Name System is created.
** Greenland withdraws from the European Economic Community as a result of a ...
and 1989
File:1989 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The Cypress structure collapses as a result of the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake, killing motorists below; The proposal document for the World Wide Web is submitted; The Exxon Valdez oil tanker runs ...
. In the latter, the Liberals won a bare majority of the two-party vote. However, much of that majority was wasted on landslides in their rural heartland, allowing Labor to eke out a two-seat majority.
Olsen resigned to take up a Senate seat soon afterward, and was succeeded by Dale Baker. By 1992, however, Baker had been unable to gain much ground on Labor despite festering anger over its handling of the collapse of the State Bank of Australia. Baker resigned as leader and called for a spill of all leadership positions. Olsen resigned from the Senate soon afterward, and Baker intended to hand the leadership back to Olsen as soon as Olsen was safely back in the legislature. This gambit backfired, however, former Tonkin minister Dean Brown
Dean may refer to:
People
* Dean (given name)
* Dean (surname), a surname of Anglo-Saxon English origin
* Dean (South Korean singer), a stage name for singer Kwon Hyuk
* Dean Delannoit, a Belgian singer most known by the mononym Dean
Titles
* ...
, returned to politics after a seven-year absence. Olsen, like Baker, was from the conservative wing of the party, while Brown was from the moderate wing. Brown narrowly defeated Olsen in the leadership vote.
Brown and Olsen Governments (1993–2002)
The Liberals went into the 1993 election as unbackable favourites. At that election, Brown won one of the most comprehensive state-level victories since Federation, taking 37 seats on 60.9 percent of the two-party vote and a swing of almost nine percent–in all three cases, the largest on record in South Australia. Along the way, the Liberals won all but nine seats in Adelaide, a city where they had been all but nonexistent even after adopting the Liberal banner. These figures led to talk of a generation of Liberal government in South Australia, much as the 1970s had been considered a "Dunstan Decade." However, Brown was unable to rein in the factional battles in his large party room. By late 1996, the Liberals' poll numbers had tailed off markedly less than a year before a statutory general election. This led two of Brown's fellow moderates, Joan Hall andGraham Ingerson
Graham Alexander Ingerson (born 27 August 1941) is a former Australian politician and 8th Deputy Premier of South Australia from 1996 to 1998. Ingerson was a Liberal Party member of the House of Assembly seat of Bragg between 1983 and 2002.
C ...
, to throw their support to Olsen, which was enough for Olsen to defeat Brown in a leadership spill.
At the 1997 state election, the Liberals withstood a swing slightly larger than the one that swept them to power four years earlier, this time 9.4 percent. However, they only lost 11 seats, allowing Olsen to cling to power with a minority government supported by conservative crossbenchers.
Olsen was forced to resign in 2001 after a finding that he had misled the House about the Motorola affair. He was succeeded by Deputy Premier Rob Kerin
Robert Gerard Kerin (born 4 January 1954) is a former South Australian politician who was the Premier of South Australia from 22 October 2001 to 5 March 2002, representing the South Australian Division of the Liberal Party of Australia. He was ...
.
Opposition (2002–2018)
Kerin only held office for three months before leading the Liberals into a statutory general election in 2002. The Liberals lost two seats to Labor, but won a paper-thin majority of the two-party vote. The balance of power rested with four conservative crossbenchers. They unexpectedly announced their support for Labor, making Labor leaderMike Rann
Michael David Rann, , (born 5 January 1953) is an Australian former politician who was the 44th premier of South Australia from 2002 to 2011. He was later Australian High Commissioner to the United Kingdom from 2013 to 2014, and Australian am ...
premier-designate by one seat. However, Kerin announced that he still had a mandate to govern based on winning the two-party vote. He insisted that he would not resign unless Rann demonstrated he had support on the House floor to govern. Three weeks of deadlock ended in March, when Kerin called a confidence motion in his own government. He lost, and stood down in favour of Rann.
Kerin resigned as leader following a landslide loss in 2006. Factional battles resulted in three leaders in less than three years–Iain Evans
Iain Frederick Evans (born 18 April 1959) is a former Australian politician. He was leader of the South Australian Division of the Liberal Party of Australia from 2006 to 2007.
Early life
Evans attended Heathfield Primary and subsequently He ...
, Martin Hamilton-Smith
Martin Leslie James Hamilton-Smith (born 1 December 1953) is a former Australian politician who represented the South Australian House of Assembly seat of Waite from the 1997 election until his retirement in 2018. First elected as a candidate ...
and the party's first female leader, Isobel Redmond
Isobel Mary Redmond (born 8 April 1953) is a former Australian politician who was the member for the electoral district of Heysen in the House of Assembly from 2002 to 2018. She was the parliamentary leader of the South Australian Division of t ...
.
The last serving parliamentarian from the LCL era, Graham Gunn, retired in 2010; he had been elected in 1970
Events
January
* January 1 – Unix time epoch reached at 00:00:00 UTC.
* January 5 – The 7.1 Tonghai earthquake shakes Tonghai County, Yunnan province, China, with a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (''Extreme''). Between 10,000 and ...
, the next-to-last election that the party fought under the LCL banner.
On 4 February 2013, Steven Marshall was elected unopposed as Liberal leader. Vickie Chapman was elected as deputy leader after a contest with former party leader Iain Evans
Iain Frederick Evans (born 18 April 1959) is a former Australian politician. He was leader of the South Australian Division of the Liberal Party of Australia from 2006 to 2007.
Early life
Evans attended Heathfield Primary and subsequently He ...
.
Marshall Government (2018–2022)
Opposition (2022–present)
Following the election defeat at the 2022 state election, Marshall resigned as leader of the party. In April 2022,David Speirs
David James Speirs (born December 15, 1984) is an Australian politician. He has been a Liberal member of the South Australian House of Assembly since the 2014 state election and leader of the Liberal Party since 19 April 2022. He represented ...
was elected as party leader, securing 18 votes compared to Josh Teague's five and Nick McBride's one. John Gardner was elected as deputy party leader.
Ideology divisions
In the 1990s and 2000s, ongoing division continued based on both ideologies and personalities, with sides forming between the moderate Chapman and conservative Evans family dynasties, complicated further by the moderateBrown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model us ...
and conservative Olsen rifts.
Leader
Since the 1970s, five parliamentary Liberal leaders have served asPremier of South Australia
The premier of South Australia is the head of government in the state of South Australia, Australia. The Government of South Australia follows the Westminster system, with a Parliament of South Australia acting as the legislature. The premier is ...
: David Tonkin (1979–1982), Dean Brown
Dean may refer to:
People
* Dean (given name)
* Dean (surname), a surname of Anglo-Saxon English origin
* Dean (South Korean singer), a stage name for singer Kwon Hyuk
* Dean Delannoit, a Belgian singer most known by the mononym Dean
Titles
* ...
(1993–1996), John Olsen
John Wayne Olsen, AO (born 7 June 1945) is a former Australian politician, diplomat and football commissioner. He was Premier of South Australia between 28 November 1996 and 22 October 2001. He is now President of the Federal Liberal Party, C ...
(1996–2001), Rob Kerin
Robert Gerard Kerin (born 4 January 1954) is a former South Australian politician who was the Premier of South Australia from 22 October 2001 to 5 March 2002, representing the South Australian Division of the Liberal Party of Australia. He was ...
(2001–2002) and Steven Marshall (2018–2022).
All leaders have served as Leader of the Opposition.
List of leaders
Deputy leader
Since the 1970s, seven parliamentary Liberal deputy leaders have served asDeputy Premier of South Australia
Deputy or depute may refer to:
* Steward (office)
* Khalifa, an Arabic title that can signify "deputy"
* Deputy (legislator), a legislator in many countries and regions, including:
** A member of a Chamber of Deputies, for example in Italy, Spain, ...
: Roger Goldsworthy
Sir Roger Tuckfield Goldsworthy (1839 – 6 May 1900) was a British colonial administrator.
Roger Goldsworthy was born in Marylebone, Middlesex in 1839, and educated at Sandhurst, the younger brother of Major-General Walter Tuckfield Goldsw ...
(1979–1982), Stephen Baker (1993–1996), Graham Ingerson
Graham Alexander Ingerson (born 27 August 1941) is a former Australian politician and 8th Deputy Premier of South Australia from 1996 to 1998. Ingerson was a Liberal Party member of the House of Assembly seat of Bragg between 1983 and 2002.
C ...
(1996–1998), Rob Kerin
Robert Gerard Kerin (born 4 January 1954) is a former South Australian politician who was the Premier of South Australia from 22 October 2001 to 5 March 2002, representing the South Australian Division of the Liberal Party of Australia. He was ...
(1998–2001), Dean Brown
Dean may refer to:
People
* Dean (given name)
* Dean (surname), a surname of Anglo-Saxon English origin
* Dean (South Korean singer), a stage name for singer Kwon Hyuk
* Dean Delannoit, a Belgian singer most known by the mononym Dean
Titles
* ...
(2001–2002), Vickie Chapman (2018–2021) and Dan van Holst Pellekaan (2021-2022).
Current federal parliamentarians
Representatives
* Rowan Ramsey –Grey
Grey (more common in British English) or gray (more common in American English) is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning literally that it is "without color", because it can be composed o ...
MP since 2007
* Tony Pasin – Barker MP since 2013
* James Stevens – Sturt MP since 2019
Senators
* Simon Birmingham – Senator since 2008 *David Fawcett
David Julian Fawcett (born 23 October 1963) is an Australian Liberal Party politician who has been a Senator for South Australia since 2011. Fawcett served in the Morrison Government as Assistant Minister for Defence from 2018 to 2019.
Fawcett ...
– Senator since 2011
* Anne Ruston
Anne Sowerby Ruston (born 10 June 1963) is an Australian politician who served as Minister for Families and Social Services in the Morrison Government from 2019 to 2022. She has been a Senator for South Australia since 2012.
Before entering p ...
– Senator since 2012
* Alex Antic – Senator since 2019
* Andrew McLachlan – Senator since 2020
State election results
ThePlaymander
The Playmander was a gerrymandering system, a pro-rural electoral malapportionment in the Australian state of South Australia, which was introduced by the incumbent Liberal and Country League (LCL) government in 1936, and remained in place for 32 ...
began in 1936 and ended after 1968. Compulsory voting was introduced since the 1944 election.
See also
* Members of the South Australian House of Assembly, 2018–2022 * Members of the South Australian Legislative Council, 2018–2022 *Australian Labor Party (South Australian Branch)
The Australian Labor Party (South Australian Branch), commonly known as South Australian Labor, is the South Australian Branch of the Australian Labor Party, originally formed in 1891 as the United Labor Party of South Australia. It is one of two ...
* Playmander
The Playmander was a gerrymandering system, a pro-rural electoral malapportionment in the Australian state of South Australia, which was introduced by the incumbent Liberal and Country League (LCL) government in 1936, and remained in place for 32 ...
, the 1936–1968 electoral malapportionment
* 2018 South Australian state election
The 2018 South Australian state election to elect members to the 54th Parliament of South Australia was held on 17 March 2018. All 47 seats in the House of Assembly or lower house, whose members were elected at the 2014 election, and 11 of 22 se ...
* 2022 South Australian state election
The 2022 South Australian state election was held on 19 March 2022 to elect members to the 55th Parliament of South Australia. All 47 seats in the House of Assembly (the lower house, whose members were elected at the 2018 election), and half t ...
* List of elections in South Australia
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Liberal Party Of Australia (South Australian Division)South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
Political parties in South Australia
1974 establishments in Australia
Political parties established in 1974