Levant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean in South-western Asia,Gasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. }, ), meaning "the eastern place, where the Sun rises".
In the 13th and 14th centuries, the term ''levante'' was used for Italian maritime commerce in the Eastern Mediterranean, including Greece,
2
. Typically, it does not include
 The term ''Levant'' appears in English in 1497, and originally meant 'the
The term ''Levant'' appears in English in 1497, and originally meant 'the  In early 19th-century travel writing, the term sometimes incorporated certain Mediterranean provinces of the
In early 19th-century travel writing, the term sometimes incorporated certain Mediterranean provinces of the
UCL Institute of Archaeology, May 2008 the last of which has dated the connection between Cyprus and mainland Levant to the early
 The largest religious group in the Levant are the Muslims and the largest cultural-linguistic group are
The largest religious group in the Levant are the Muslims and the largest cultural-linguistic group are
 Most populations in the Levant speak
Most populations in the Levant speak
Levantine Heritage
site. Includes many oral and scholarly histories, and genealogies for some Levantine Turkish families. * Philip Mansel, ''Levant: Splendour and Catastrophe on the Mediterranean'', London, John Murray, 11 November 2010, hardback, 480 pages, , New Haven, Yale University Press, 24 May 2011, hardback, 470 pages,
''France and the Levant''
{{Authority control Eastern Mediterranean Geography of Cyprus Geography of Hatay Province Geography of Israel Geography of Jordan Geography of Lebanon Geography of Syria Geography of the Middle East Geography of the State of Palestine Historical regions History of Western Asia Near East Regions of Asia Regions of Europe
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
, Syria-Palestine, and Egypt, that is, the lands east of Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
. Eventually the term was restricted to the Muslim countries of Syria-Palestine and Egypt. In 1581, England set up the Levant Company to monopolize commerce with the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. The name ''Levant States'' was used to refer to the French mandate over Syria and Lebanon after World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. This is probably the reason why the term ''Levant'' has come to be used more specifically to refer to modern Syria, Lebanon, Palestine, Israel, Jordan, and Cyprus. Some scholars mistakenly believed that it derives from the name of Lebanon. Today the term is often used in conjunction with prehistoric or ancient historical references. It has the same meaning as "Syria-Palestine" or ''Ash-Shaam
Syria ( Hieroglyphic Luwian: 𔒂𔒠 ''Sura/i''; gr, Συρία) or Sham ( ar, ٱلشَّام, ash-Shām) is the name of a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in Western Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. Other ...
'' ( ar, ٱلشَّام, ), the area that is bounded by the Taurus Mountains of Turkey in the north, the Mediterranean Sea in the west, the north Arabian Desert and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
in the east, and Sinai in the south (which can be fully included or not).Steiner & Killebrew, p2
. Typically, it does not include
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
(also called Asia Minor), the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
Mountains, or any part of the Arabian Peninsula proper. Cilicia (in Asia Minor) and the Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai (now usually ) (, , cop, Ⲥⲓⲛⲁ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is ...
(Asian Egypt) are sometimes included.
As a name for the contemporary region, several dictionaries consider Levant to be archaic today. Both the noun ''Levant'' and the adjective ''Levantine'' are now commonly used to describe the ancient and modern culture area formerly called Syro-Palestinian or Biblical: archaeologists now speak of the Levant and of Levantine archaeology
Levantine archaeology is the archaeological study of the Levant. It is also known as Syro-Palestinian archaeology or Palestinian archaeologyDavis, 2004, p. 146.Dever, 2001, p. 61. (particularly when the area of inquiry centers on ancient Palesti ...
; food scholars speak of Levantine cuisine; and the Latin Christians of the Levant continue to be called Levantine Christians.
The Levant has been described as the "crossroads of Western Asia, the Eastern Mediterranean, and Northeast Africa
Northeast Africa, or ''Northeastern Africa'' or Northern East Africa as it was known in the past, is a geographic regional term used to refer to the countries of Africa situated in and around the Red Sea. The region is intermediate between North ...
", and in geological
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other E ...
( tectonic) terms as the "northwest of the Arabian Plate
The Arabian Plate is a minor tectonic plate in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres.
It is one of the three continental plates (along with the African and the Indian Plates) that have been moving northward in geological history and colliding ...
". The populations of the Levant share not only the geographic position, but cuisine, some customs, and history. They are often referred to as ''Levantines''.
Etymology
 The term ''Levant'' appears in English in 1497, and originally meant 'the
The term ''Levant'' appears in English in 1497, and originally meant 'the East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fac ...
' or 'Mediterranean lands east of Italy'. It is borrowed from the French 'rising', referring to the rising of the sun in the east, or the point where the sun rises. The phrase is ultimately from the Latin word , meaning 'lift, raise'. Similar etymologies are found in Greek ''Anatolē'' (''cf.'' Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
'the direction of sunrise'), in Germanic ''Morgenland'' (), in Italian (as in ''Riviera di Levante'', the portion of the Liguria coast east of Genoa), in Hungarian ''Kelet'' ('east'), in Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
and Catalan ''Levante'' and ''Llevant'', ('the place of rising'), and in Hebrew '' mizraḥ'' ('east'). Most notably, "Orient" and its Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
source ''oriens'' meaning 'east', is literally "rising", deriving from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''orior'' 'rise'.
The notion of the Levant has undergone a dynamic process of historical evolution in usage, meaning, and understanding. While the term "Levantine" originally referred to the European residents of the eastern Mediterranean region, it later came to refer to regional "native" and "minority" groups.
The term became current in English in the 16th century, along with the first English merchant adventurers in the region; English ships appeared in the Mediterranean in the 1570s, and the English merchant company signed its agreement (" capitulations") with the Ottoman Sultan in 1579. The English Levant Company was founded in 1581 to trade with the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, and in 1670 the French Compagnie du Levant was founded for the same purpose. At this time, the Far East was known as the "Upper Levant".
 In early 19th-century travel writing, the term sometimes incorporated certain Mediterranean provinces of the
In early 19th-century travel writing, the term sometimes incorporated certain Mediterranean provinces of the Ottoman empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, as well as independent Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
(and especially the Greek islands). In 19th-century archaeology, it referred to overlapping cultures in this region during and after prehistoric times, intending to reference the place instead of any one culture. The French mandate of Syria and Lebanon
The Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon (french: Mandat pour la Syrie et le Liban; ar, الانتداب الفرنسي على سوريا ولبنان, al-intidāb al-fransi 'ala suriya wa-lubnān) (1923−1946) was a League of Nations mandate fou ...
(1920–1946) was called the Levant states.
Geography and modern-day use of the term
Today, "Levant" is the term typically used by archaeologists and historians with reference to the history of the region. Scholars have adopted the term Levant to identify the region due to its being a "wider, yet relevant, cultural corpus" that does not have the "political overtones" of Syria-Palestine. The term is also used for modern events, peoples, states or parts of states in the same region, namely Cyprus,Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
, Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, Jordan, Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
, Palestine, Syria, and Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
are sometimes considered Levant countries (compare with Near East, Middle East, Eastern Mediterranean and Western Asia). Several researchers include the island of Cyprus in Levantine studies, including the Council for British Research in the Levant The Council for British Research in the Levant (CBRL) is a non-profit organisation that promotes humanities and social science research in the Levant. It consists of two research institutes, the Kenyon Institute in Jerusalem and the British Institu ...
, the UCLA
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the southern branch of the California ...
Near Eastern Languages and Cultures department, '' Journal of Levantine Studies'' and the UCL Institute of Archaeology,The Ancient LevantUCL Institute of Archaeology, May 2008 the last of which has dated the connection between Cyprus and mainland Levant to the early
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
. Archaeologists seeking a neutral orientation that is neither biblical nor national have used terms such as Levantine archaeology
Levantine archaeology is the archaeological study of the Levant. It is also known as Syro-Palestinian archaeology or Palestinian archaeologyDavis, 2004, p. 146.Dever, 2001, p. 61. (particularly when the area of inquiry centers on ancient Palesti ...
and archaeology of the Southern Levant
The Southern Levant is a geographical region encompassing the southern half of the Levant. It corresponds approximately to modern-day Israel, Palestine, and Jordan; some definitions also include southern Lebanon, southern Syria and/or the Sinai P ...
.Dever, William G. "Syro-Palestinian and Biblical Archaeology", pp. 1244-1253.Sharon, Ilan "Biblical archaeology" in ''Encyclopedia of Archaeology'' Elsevier.
While the usage of the term "Levant" in academia has been restricted to the fields of archeology and literature, there is a recent attempt to reclaim the notion of the Levant as a category of analysis in political and social sciences. Two academic journals were launched in the early 2010s using the word: the ''Journal of Levantine Studies'', published by the Van Leer Jerusalem Institute and ''The Levantine Review'', published by Boston College.
The word ''Levant'' has been used in some translations of the term ''ash-Shām'' as used by the organization known as ISIL, ISIS, and other names, though there is disagreement as to whether this translation is accurate.
In archaeology: a definition
In ''The Oxford Handbook of the Archaeology of the Levant: c. 8000–332 BCE'' (OHAL; 2013), the definition of the Levant for the specific purposes of the book is synonymous to that of the Arabic "''bilad al-sham'', 'the land of sham yria", translating in Western parlance to greater Syria. OHAL defines the boundaries of the Levant as follows. * To the north: the Taurus Mountains or the Plain of 'Amuq * To the east: the eastern deserts, i.e. (from north to south) the Euphrates and the Jebel el-Bishrī area for the northern Levant, followed by the Syrian Desert east of the eastern hinterland of theAnti-Lebanon
The Anti-Lebanon Mountains ( ar, جبال لبنان الشرقية, Jibāl Lubnān ash-Sharqiyyah, Eastern Mountains of Lebanon; Lebanese Arabic: , , "Eastern Mountains") are a southwest–northeast-trending mountain range that forms most of ...
range (whose southernmost part is Mount Hermon
Mount Hermon ( ar, جبل الشيخ or جبل حرمون / ALA-LC: ''Jabal al-Shaykh'' ("Mountain of the Sheikh") or ''Jabal Haramun''; he, הַר חֶרְמוֹן, ''Har Hermon'') is a mountain cluster constituting the southern end of th ...
), and Transjordan's highlands and eastern desert (also discussed at Syrian Desert, also known as the Badia region). In other words, Mesopotamia and the North Arabian Desert.
* To the south: Wadi al- Arish in Sinai
* To the west: the Mediterranean Sea
;Subregions
A distinction is made between the main subregions of the Levant, the northern and the southern:
* The Litani River
The Litani River ( ar, نهر الليطاني, Nahr al-Līṭānī), the classical Leontes ( grc-gre, Λέοντες, Léontes, lions), is an important water resource in southern Lebanon. The river rises in the fertile Beqaa Valley, west of B ...
marks the division between the Northern Levant
The Northern Levant is a region in the Eastern Mediterranean, part of the wider region of the Levant, going south as far as the Litani River.
In archaeology, the Northern Levant can be defined as the northern section of what in Arabic is called ...
and the Southern Levant
The Southern Levant is a geographical region encompassing the southern half of the Levant. It corresponds approximately to modern-day Israel, Palestine, and Jordan; some definitions also include southern Lebanon, southern Syria and/or the Sinai P ...
.
The island of Cyprus is also included as a third subregion in the archaeological region of the Levant:
* Cyprus, geographically distinct from the Levant, is included due to its proximity and natural resources (copper in particular), which induced close cultural ties.
History
Demographics and religion
 The largest religious group in the Levant are the Muslims and the largest cultural-linguistic group are
The largest religious group in the Levant are the Muslims and the largest cultural-linguistic group are Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
. Muslim Arabs became the majority due to the Muslim conquest of the Levant in the 7th century and subsequent Arabization of the region. The majority of Muslim Levantines are Sunni with Alawi and Shia minorities. Other large ethnic groups in the Levant include Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, Maronites, Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
, Turkmens, Antiochian Greeks, Assyrians, Yazidi, Kurds, Druze and Armenians.
There are many Levantine Christian groups such as Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, Oriental Orthodox (mainly Syriac Orthodox, Coptic, Georgian, and Maronite), Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
, Nestorian
Nestorianism is a term used in Christian theology and Church history to refer to several mutually related but doctrinarily distinct sets of teachings. The first meaning of the term is related to the original teachings of Christian theologian ...
, and Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
. Armenians mostly belong to the Armenian Apostolic Church
, native_name_lang = hy
, icon = Armenian Apostolic Church logo.svg
, icon_width = 100px
, icon_alt =
, image = Էջմիածնի_Մայր_Տաճար.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, a ...
. There are Levantines or Franco-Levantines who are mostly Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
. There are also Circassians, Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
, Samaritans, and Nawars. There are Assyrian peoples belonging to the Assyrian Church of the East (autonomous) and the Chaldean Catholic Church (Catholic).
In addition, this region has a number of sites that are of religious significance
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, ...
, such as Masjid Al-Aqsa, Antioch in Hatay, the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, and the Western Wall
The Western Wall ( he, הַכּוֹתֶל הַמַּעֲרָבִי, HaKotel HaMa'aravi, the western wall, often shortened to the Kotel or Kosel), known in the West as the Wailing Wall, and in Islam as the Buraq Wall (Arabic: حَائِط � ...
Frishman, Avraham (2004). ''Kum Hisalech Be’aretz'', Jerusalem. in Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
.
Language
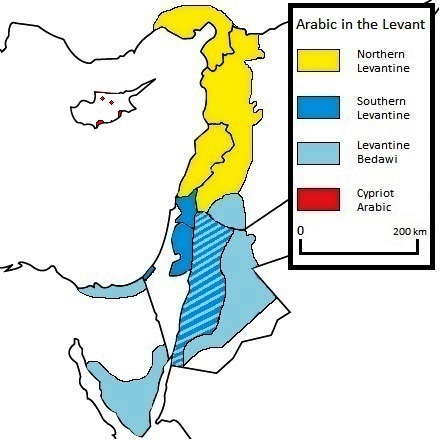
 Most populations in the Levant speak
Most populations in the Levant speak Levantine Arabic
Levantine Arabic, also called Shami ( autonym: or ), is a group of mutually intelligible vernacular Arabic varieties spoken in the Levant, in Syria, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, Israel, and Turkey (historically in Adana, Mersin and Hatay on ...
(, ), usually classified as the varieties North Levantine Arabic in Lebanon, Syria, and parts of Turkey, and South Levantine Arabic
South Levantine Arabic ( ar, اللهجة الشامية الجنوبية), a subdivision of Levantine Arabic, is spoken in the Southern Levant, mostly the Palestinian Territories (the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip) and ...
in Palestine and Jordan. Each of these encompasses a spectrum of regional or urban/rural variations. In addition to the varieties normally grouped together as "Levantine", a number of other varieties and dialects of Arabic are spoken in the Levant area, such as Levantine Bedawi Arabic and Mesopotamian Arabic.
Among the languages of Israel, the official language is Hebrew; Arabic was until July 19, 2018, also an official language. The Arab minority, in 2018 about 21% of the population of Israel, speaks a dialect of Levantine Arabic essentially indistinguishable from the forms spoken in the Palestinian territories.
Of the languages of Cyprus, the majority language is Greek, followed by Turkish (in the north). Two minority languages are recognized: Armenian, and Cypriot Maronite Arabic
Cypriot Arabic ( ar, العربية القبرصية), also known as Cypriot Maronite Arabic or Sanna, is a moribund variety of Arabic spoken by the Maronite community of Cyprus. Formerly speakers were mostly situated in Kormakitis, but follow ...
, a hybrid of mostly medieval Arabic vernaculars with strong influence from contact with Greek, spoken by approximately 1,000 people.
Some communities and populations speak Aramaic, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
, Circassian, French, Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
, or English.
See also
Overlapping regional designations * Fertile Crescent *Mashriq
The Mashriq ( ar, ٱلْمَشْرِق), sometimes spelled Mashreq or Mashrek, is a term used by Arabs to refer to the eastern part of the Arab world, located in Western Asia and eastern North Africa. Poetically the "Place of Sunrise", th ...
* Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
* Middle East
* Near East
* Western Asia
Subregional designations
* Southern Levant
The Southern Levant is a geographical region encompassing the southern half of the Levant. It corresponds approximately to modern-day Israel, Palestine, and Jordan; some definitions also include southern Lebanon, southern Syria and/or the Sinai P ...
Others
* French post offices in the Ottoman Empire
The French post offices in the Ottoman Empire were post offices in various cities of the Ottoman Empire run by France between 1812 and 1923. France was one of a half-dozen European countries, the others being Austria, Russia, Great Britain, Germany ...
("Levant" stamps)
* History of the Levant
* Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (Referred to in current events as ISIL or ISIS)
* Levantine Sea
* Levantines (Latin Christians), Catholic Europeans in the Levant
''Other places in the east of a larger region''
* Levante, Spain
The Levante (; Catalan: ; "Levant, East") is a name used to refer to the eastern region of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Spanish Mediterranean coast. It roughly corresponds to the former Xarq Al-Andalus, but has no modern geopolitical definiti ...
* Riviera di Levante, Italy
Explanatory notes
Citations
General and cited references
* * * * * * * *Further reading
* Julia Chatzipanagioti: Griechenland, Zypern, Balkan und Levante. Eine kommentierte Bibliographie der Reiseliteratur des 18. Jahrhunderts. 2 Vol. Eutin 2006.Levantine Heritage
site. Includes many oral and scholarly histories, and genealogies for some Levantine Turkish families. * Philip Mansel, ''Levant: Splendour and Catastrophe on the Mediterranean'', London, John Murray, 11 November 2010, hardback, 480 pages, , New Haven, Yale University Press, 24 May 2011, hardback, 470 pages,
External links
''France and the Levant''
{{Authority control Eastern Mediterranean Geography of Cyprus Geography of Hatay Province Geography of Israel Geography of Jordan Geography of Lebanon Geography of Syria Geography of the Middle East Geography of the State of Palestine Historical regions History of Western Asia Near East Regions of Asia Regions of Europe