Laryngopharyngeal Reflux on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) is the retrograde flow of gastric contents into the larynx,
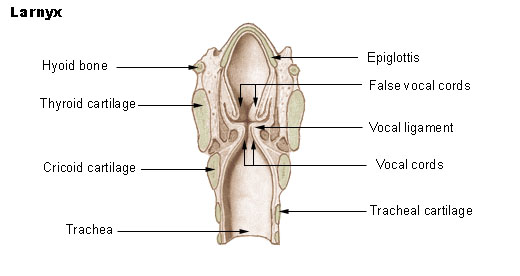 LPR is often regarded as a subtype of GERD that occurs when stomach contents flow upward through the esophagus and reach the level of the larynx and pharynx. However, LPR is associated with a distinct presentation of symptoms. LPR and GERD frequently differ in the relative prevalence of
LPR is often regarded as a subtype of GERD that occurs when stomach contents flow upward through the esophagus and reach the level of the larynx and pharynx. However, LPR is associated with a distinct presentation of symptoms. LPR and GERD frequently differ in the relative prevalence of
oropharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struc ...
and/or the nasopharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
. LPR causes respiratory symptoms such as cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages that can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three ph ...
and wheezing
A wheeze is a continuous, coarse, whistling sound produced in the respiratory airways during breathing. For wheezes to occur, some part of the respiratory tree must be narrowed or obstructed (for example narrowing of the lower respiratory tract ...
and is often associated with head and neck complaints such as dysphonia
A hoarse voice, also known as dysphonia or hoarseness, is when the voice involuntarily sounds breathy, raspy, or strained, or is softer in volume or lower in pitch. A hoarse voice, can be associated with a feeling of unease or scratchiness in the ...
, globus pharyngis
Globus pharyngis or globus sensation is the persistent but painless sensation of having a pill, food bolus, or some other sort of obstruction in the throat when there is none. Swallowing is typically performed normally, so it is not a true case o ...
, and dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liq ...
. LPR may play a role in other diseases, such as sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, head ...
, otitis media
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, ...
, and rhinitis
Rhinitis, also known as coryza, is irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane inside the nose. Common symptoms are a stuffy nose, runny nose, sneezing, and post-nasal drip.
The inflammation is caused by viruses, bacteria, irrita ...
, and can be a comorbidity
In medicine, comorbidity - from Latin morbus ("sickness"), co ("together"), -ity (as if - several sicknesses together) - is the presence of one or more additional conditions often co-occurring (that is, concomitant or concurrent) with a primary ...
of asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, co ...
. While LPR is commonly used interchangeably with gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the upper gastrointestinal chronic diseases where stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/ ...
(GERD), it presents with a different pathophysiology.
LPR reportedly affects approximately 10% of the U.S. population. However, LPR occurs in as many as 50% of individuals with voice disorders.
Signs and symptoms
Extraesophageal symptoms result from exposure of the upper aerodigestive tract to gastric contents. This causes a variety of symptoms, including hoarseness, postnasal drip,sore throat
Sore throat, also known as throat pain, is pain or irritation of the throat. Usually, causes of sore throat include
* viral infections
* group A streptococcal infection (GAS) bacterial infection
* pharyngitis (inflammation of the throat)
* to ...
, difficulty swallowing
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liqui ...
, indigestion
Indigestion, also known as dyspepsia or upset stomach, is a condition of impaired digestion. Symptoms may include upper abdominal fullness, heartburn, nausea, belching, or upper abdominal pain. People may also experience feeling full earlier t ...
, wheezing, globus pharyngeus, and chronic throat-clearing. Some people with LPR have heartburn, while others have little to no heartburn as refluxed stomach contents do not remain in the esophagus long enough to irritate the surrounding tissue. Individuals with more severe forms of LPR may experience abrasion of tooth enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the four major tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many other animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the crown. The other major tissues are dentin, ...
due to intermittent presence of gastric contents in the oral cavity.
Additionally, LPR can cause inflammation in the vocal tract
The vocal tract is the cavity in human bodies and in animals where the sound produced at the sound source ( larynx in mammals; syrinx in birds) is filtered.
In birds it consists of the trachea, the syrinx, the oral cavity, the upper part of th ...
which results in the symptom of dysphonia or hoarseness. Hoarseness is considered to be one of the primary symptoms of LPR and is associated with complaints such as strain, vocal fatigue, musculoskeletal tension, and hard glottal attacks, all of which can reduce a person's ability to communicate effectively. Moreover, LPR patients may try to compensate for their hoarseness by increasing muscular tension in their vocal tract. This hyper-functional technique adopted in response to the inflammation caused by LPR can lead to a condition called muscle tension dysphonia Muscle tension dysphonia (MTD) was originally coined in 1983 by Morrison and describes a dysphonia caused by increased muscle tension of the muscles surrounding the voice box: the laryngeal and paralaryngeal muscles. MTD is a unifying diagnosis for ...
and may persist even after the hoarseness and inflammation has disappeared. A speech-language pathologist will often need to be involved to help resolve this maladaptive, compensatory pattern through the implementation of voice therapy.
LPR presents as a chronic and intermittent disease in children. LPR in children and infants tends to manifest with a unique set of symptoms. Symptoms seen in children with LPR include a cough, hoarseness, stridor, sore throat, asthma, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteri ...
, globus sensation, wheezing, aspiration and recurrent pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
. Common symptoms of LPR in infants include wheezing, stridor, persistent or recurrent cough, apnea, feeding difficulties, aspiration, regurgitation, and failure to thrive
Failure to thrive (FTT), also known as weight faltering or faltering growth, indicates insufficient weight gain or absence of appropriate physical growth in children. FTT is usually defined in terms of weight, and can be evaluated either by a low ...
. Moreover, LPR in children is commonly concomitant with laryngeal disorders such as laryngomalacia
Laryngomalacia (literally, "soft larynx") is the most common cause of chronic stridor in infancy, in which the soft, immature cartilage of the upper larynx collapses inward during inhalation, causing airway obstruction. It can also be seen in o ...
, subglottic stenosis, and laryngeal papillomatosis
Laryngeal papillomatosis, also known as recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP) or glottal papillomatosis, is a rare medical condition in which benign tumors (papilloma) form along the aerodigestive tract. There are two variants based on the ag ...
.
Relationship to GERD
 LPR is often regarded as a subtype of GERD that occurs when stomach contents flow upward through the esophagus and reach the level of the larynx and pharynx. However, LPR is associated with a distinct presentation of symptoms. LPR and GERD frequently differ in the relative prevalence of
LPR is often regarded as a subtype of GERD that occurs when stomach contents flow upward through the esophagus and reach the level of the larynx and pharynx. However, LPR is associated with a distinct presentation of symptoms. LPR and GERD frequently differ in the relative prevalence of heartburn
Heartburn, also known as pyrosis, cardialgia or acid indigestion, is a burning sensation in the central chest or upper central abdomen. Heartburn is usually due to regurgitation of gastric acid (gastric reflux) into the esophagus. It is the m ...
and throat clearing. While heartburn is present in over 80% of GERD cases, it occurs in only 20% of LPR cases. Throat clearing shows the opposite prevalence pattern, occurring in approximately 87% of LPR cases and in fewer than 5% of GERD cases. Unlike GERD, LPR also poses a risk for bronchitis
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) in the lungs that causes coughing. Bronchitis usually begins as an infection in the nose, ears, throat, or sinuses. The infection then makes its way down to the bronchi. ...
or pneumonitis
Pneumonitis describes general inflammation of lung tissue. Possible causative agents include radiation therapy of the chest, exposure to medications used during chemo-therapy, the inhalation of debris (e.g., animal dander), aspiration, herbicide ...
as reflux of stomach acid to the level of the larynx can result in aspiration. LPR is also commonly associated with erythema
Erythema (from the Greek , meaning red) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not asso ...
, or redness, as well as edema in the tissues of the larynx that are exposed to gastric contents. In contrast, most cases of GERD are nonerosive, with no apparent injury to the mucosal lining of the esophageal tissue exposed to the refluxed material.
Differences in the molecular structure of the epithelial tissue lining the laryngopharyngeal region may be partly responsible for the different symptomatic manifestations of LPR in comparison to GERD. In contrast to the resistant stratified squamous epithelium lining the esophagus, the larynx is lined by ciliated respiratory epithelium
Respiratory epithelium, or airway epithelium, is a type of ciliated columnar epithelium found lining most of the respiratory tract as respiratory mucosa, where it serves to moisten and protect the airways. It is not present in the vocal cords o ...
, which is more fragile and susceptible to damage. While the epithelium lining the esophagus is capable of withstanding as many as 50 instances of exposure to gastric contents each day, which is the uppermost estimate considered to be within the range of normal physiologic functioning, injury to laryngeal epithelium can occur following exposure to only small amounts of acidic gastric contents.
Diagnosis
LPR presents withnon-specific symptoms
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showin ...
and signs that make differential diagnosis difficult to achieve. Furthermore, symptoms of the disorder overlap greatly with symptoms of other disorders. Therefore, LPR is under-diagnosed and under-treated. As there are multiple potential etiologies
Cause, also known as etiology () and aetiology, is the reason or origination of something.
The word ''etiology'' is derived from the Greek , ''aitiologia'', "giving a reason for" (, ''aitia'', "cause"; and , ''-logia'').
Description
In medicine, ...
for the respiratory and laryngeal symptoms of LPR, diagnosing LPR based on symptoms alone is unreliable. Laryngoscopic findings such as erythema, edema, laryngeal granulomas, and interarytenoid hypertrophy have been used to establish the diagnosis; however, these findings are nonspecific and have been described in the majority of asymptomatic subjects undergoing laryngoscopy
Laryngoscopy () is endoscopy of the larynx, a part of the throat. It is a medical procedure that is used to obtain a view, for example, of the vocal folds and the glottis. Laryngoscopy may be performed to facilitate tracheal intubation during ...
. Response to acid-suppression therapy has been suggested as a diagnostic tool for confirming diagnosis of LPR, but studies have shown that the response to empirical trials of such therapy (as with proton-pump inhibitors
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase proton pump.
They are the most potent inhibitors ...
) in these patients is often disappointing. Several studies have emphasized the importance of measuring proximal esophageal, or ideally pharyngeal acid exposure, in patients with clinical symptoms of LPR to document reflux as the cause of the symptoms.
Additionally, several potential biomarkers of LPR have been investigated. These include inflammatory cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
s, carbonic anyhydrase, E-cadherin
Cadherin-1 or Epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin), (not to be confused with the APC/C activator protein CDH1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDH1'' gene. Mutations are correlated with gastric, breast, colorectal, thyroid, and ovarian ...
and mucin
Mucins () are a family of high molecular weight, heavily glycosylated proteins (glycoconjugates) produced by epithelial tissues in most animals. Mucins' key characteristic is their ability to form gels; therefore they are a key component in most ...
s; however, their direct implications in LPR are still being established. The presence of pepsin
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, w ...
, an enzyme produced in the stomach, in the hypopharynx has also become an increasingly researched biomarker for LPR. Research suggests that the stomach enzyme pepsin
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, w ...
plays a crucial role in the complex mechanism behind LPR. Once present in the larynx pepsin is active at a low pH, but persists even when inactive. Pepsin can manifest both extracellularly and intracellularly; however, damage is realized differently in these two environments. Intracellularly, pepsin enters the laryngeal tissue through endocytosis and causes damage that accumulates over time. Pepsin has implications on cellular transcription and therefore, gene expression, which subsequently leads to the recruitment of inflammatory cells, but inhibition of protective mechanisms such as growth factors. Structurally, pepsin plays a role in increasing viscosity of the vibratory portion of the vocal folds and decreasing cellular water retention, which reduces the overall thickness of the vocal folds. These morphological changes result in decreased vibratory amplitude, increasing demands for initiating vibration and ultimately, impacting voice quality.
Before a diagnosis can be made, a physician will need to record the patient's medical history and ask for details about the presenting symptoms. Questionnaires such as the Reflux Symptom Index (RSI), Quality-of-Life Index (QLI) for LPR, Glottal Closure/Function Index (GCI) and Voice Handicap Index (VHI) can be administered to gain information about the patient's medical history as well as their symptomatology. A physical examination will then need to be performed with particular concentration around the head and neck. A scope with a specialized camera lens made of fiber optic
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means t ...
strands is gently fed down the throat and feeds back images to a monitor. This provides a clear view of the throat and larynx. Signs of LPR include redness, swelling, and obvious irritation. Other, more invasive tests, such as fibre-optic transnasal laryngoscopy, 24-hour ambulatory dual probe pHmetry, pharyngeal pHmetry, transnasal esophagoscopy (TNE) and biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
may be used. A noninvasive test for diagnosis of LPR is the collection of refluxate where the refluxed material is collected and analyzed. Another noninvasive diagnostic test that can be used is an empirical trial of proton-pump inhibitor
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase proton pump.
They are the most potent inhibitor ...
therapy; however, this test is mostly successful in diagnosing GERD.
There is no agreed-upon assessment technique to identify LPR in children. Of the debated diagnostic tools, multichannel intraluminal impedance with pH monitoring (MII-pH) is used as it recognizes both acid and non-acid reflux. A more common technique that is used is 24-hour dual probe pH monitoring. Both of these tools are expensive and are therefore not widely used.
Treatment
Management of symptoms for patients within this subgroup of theGERD Gerd or GERD may refer to:
* Gerd (given name), a list of people with the given name or nickname
* Gerd (moon), a moon of Saturn
* Gerd Island, South Orkney Islands, Antarctica
* Gastroesophageal reflux disease, a chronic symptom of mucosal damage ...
spectrum is difficult. Once these patients are identified, behavioural and dietary changes are advised. Dietary modifications may include limiting the intake of chocolate, caffeine, acidic food and liquids, gaseous beverages and foods high in fat. Behavioral changes may include weight loss, cessation of smoking, limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding the ingestion of food shortly before bed. Lifestyle changes in children diagnosed with LPR include dietary modifications to avoid foods that will aggravate reflux (e.g., chocolate or acidic and spicy food), altering positioning (e.g., sleeping on your side), modifying the textures of foods (e.g., thickening feeds to heighten awareness of the passing bolus), and eliminating the intake of food before bed.
Proton pump inhibitors
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase proton pump.
They are the most potent inhibitor ...
(PPIs) are the leading pharmaceutical intervention chosen for the relief and reduction of LPR and are typically recommended for ongoing use twice a day for a period of 3–6 months. PPIs have been shown to be ineffective in very young children and are of uncertain efficacy in older children, for whom their use has been discouraged.
While PPIs may provide limited clinical benefits in some adults, there is insufficient evidence to support routine use. Many studies show that PPIs are not more effective than placebo
A placebo ( ) is a substance or treatment which is designed to have no therapeutic value. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
In general, placebos can af ...
s in treating LPR. Alginate products show great promise, as they can form a temporary foam barrier at the LES to block acid and pepsin from refluxing.
When medical management fails, Nissen fundoplication
A Nissen fundoplication, or laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication when performed via laparoscopic surgery, is a surgical procedure to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and hiatal hernia. In GERD, it is usually performed when medical thera ...
can be offered. However, patients should be advised that surgery may not result in complete elimination of LPR symptoms and even with immediate success, recurrence of symptoms later on is still possible.
One way to assess treatment outcomes for LPR is through the use of voice quality measures. Both subjective and objective measures of voice quality can be used to assess treatment outcomes. Subjective measures include scales such as the Grade, Roughness, Breathiness, Asthenia, Strain Scale (GRBAS); the Reflux Symptom Index; the Voice Handicap Index (VHI); and a voice symptom scale. Objective measures often rely on acoustic parameters such as jitter, shimmer, signal-to-noise ratio, and fundamental frequency
The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the ''fundamental'', is defined as the lowest frequency of a periodic waveform. In music, the fundamental is the musical pitch of a note that is perceived as the lowest partial present. I ...
, among others. Aerodynamic measures such as vital capacity
Vital capacity (VC) is the maximum amount of air a person can inhale after a maximum exhalation. It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and expiratory reserve volume. It is approximately equal to Forced Vital Capacity ( ...
and maximum phonation time (MPT) have also been used as an objective measure. However, there is not yet a consensus on how best to use the measures or which measures are best to assess treatment outcomes for LPR.
Procedures
There is tentative evidence from non-controlled trials that oral neuromuscular training may improve symptoms. This has been approved by the UKNational Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the umbrella term for the publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom (UK). Since 1948, they have been funded out of general taxation. There are three systems which are referred to using the " ...
(NHS) for supply on prescription from 1 May 2022.
History
LPR was not discussed as a separate condition from GERD until the 1970s and 1980s. However, at around the same time that GERD was first recognized as a clinical entity in the mid-1930s, a link between gut symptoms and airway disease was suggested. Later, acid-related laryngealulceration
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caused by sloughing o ...
s and granulomas were reported in 1968. Subsequent studies suggested that acid reflux might be a contributory factor in other laryngeal and respiratory conditions. In 1979, the link between these airway symptoms and reflux of gastric contents was first documented. At the same time, treatment of reflux disease results was shown to eliminate these airway symptoms.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Diseases of oesophagus, stomach and duodenum Larynx disorders