Landlocked Salmon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') is a
 Atlantic salmon are the largest species in their genus, ''Salmo''. After two years at sea, the fish average in length and in weight. But specimens that spend four or more winters feeding at sea can be much larger. An Atlantic salmon netted in 1960 in Scotland, in the estuary of the river Hope, weighed , the heaviest recorded in all available literature. Another netted in 1925 in Norway measured in length, the longest Atlantic salmon on record.Buller F., ''The Domesday Book of Giant Salmon Volume 1 & 2''. Constable (2007) & Constable (2010)
The colouration of young Atlantic salmon does not resemble the adult stage. While they live in fresh water, they have blue and red spots. At maturity, they take on a silver-blue sheen. The easiest way of identifying them as an adult is by the black spots predominantly above the
Atlantic salmon are the largest species in their genus, ''Salmo''. After two years at sea, the fish average in length and in weight. But specimens that spend four or more winters feeding at sea can be much larger. An Atlantic salmon netted in 1960 in Scotland, in the estuary of the river Hope, weighed , the heaviest recorded in all available literature. Another netted in 1925 in Norway measured in length, the longest Atlantic salmon on record.Buller F., ''The Domesday Book of Giant Salmon Volume 1 & 2''. Constable (2007) & Constable (2010)
The colouration of young Atlantic salmon does not resemble the adult stage. While they live in fresh water, they have blue and red spots. At maturity, they take on a silver-blue sheen. The easiest way of identifying them as an adult is by the black spots predominantly above the
 The natural breeding grounds of Atlantic salmon are rivers in Europe and the northeastern coast of North America. In Europe, Atlantic salmon are still found as far south as Spain, and as far north as Russia. Because of sport-fishing, some of the species' southern populations in northern Spain are growing smaller. The species distribution is easily influenced by changes in freshwater habitat and climate. Atlantic salmon are a cold-water fish species and are particularly sensitive to changes in water temperature.
The
The natural breeding grounds of Atlantic salmon are rivers in Europe and the northeastern coast of North America. In Europe, Atlantic salmon are still found as far south as Spain, and as far north as Russia. Because of sport-fishing, some of the species' southern populations in northern Spain are growing smaller. The species distribution is easily influenced by changes in freshwater habitat and climate. Atlantic salmon are a cold-water fish species and are particularly sensitive to changes in water temperature.
The
 Most Atlantic salmon follow an anadromous migration pattern, in that they undergo their greatest feeding and growth in saltwater; however, adults return to
Most Atlantic salmon follow an anadromous migration pattern, in that they undergo their greatest feeding and growth in saltwater; however, adults return to
''Toronto Star'', 9 November 2016, page GT1. In North America, the landlocked strains are frequently known as ''ouananiche''.
File:Salmoneggskils.jpg, Very young fertilized salmon eggs, notice the developing eyes and
 Atlantic salmon breed in the rivers of Western Europe from northern
Atlantic salmon breed in the rivers of Western Europe from northern
 Wood and stone weirs along streams and ponds were used for millennia to harvest salmon in the rivers of New England. European fishermen gillnetted for Atlantic salmon in rivers using hand-made nets for many centuries and gillnetting was also used in early colonial America.
In its natal streams, Atlantic salmon are considered prized recreational fish, pursued by fly anglers during its annual runs. At one time, the species supported an important commercial fishery, but having become endangered throughout its range globally, wild-caught Atlantic salmon are now virtually absent from the market. Instead, nearly all are from
Wood and stone weirs along streams and ponds were used for millennia to harvest salmon in the rivers of New England. European fishermen gillnetted for Atlantic salmon in rivers using hand-made nets for many centuries and gillnetting was also used in early colonial America.
In its natal streams, Atlantic salmon are considered prized recreational fish, pursued by fly anglers during its annual runs. At one time, the species supported an important commercial fishery, but having become endangered throughout its range globally, wild-caught Atlantic salmon are now virtually absent from the market. Instead, nearly all are from
 Adult male and female fish are anaesthetised; their eggs and sperm are "stripped" after the fish are cleaned and cloth dried. Sperm and eggs are mixed, washed, and placed into freshwater. Adults recover in flowing, clean, well-
Adult male and female fish are anaesthetised; their eggs and sperm are "stripped" after the fish are cleaned and cloth dried. Sperm and eggs are mixed, washed, and placed into freshwater. Adults recover in flowing, clean, well-
study
in 2000 demonstrated that the genes of farmed Atlantic salmon intrude wild populations mainly through wild males breeding with farmed females, though farmed specimens showed reduced capacity for breeding success overall compared to their wild counterparts. Further study in 2018 discovered extensive cross-breeding of wild and farmed Atlantic salmon in the Northwest Atlantic, showing that 27.1% of fish in 17 out of 18 rivers examined are artificially stocked or hybrids. Farming of Atlantic salmon in open cages at sea has also been linked, at least in part, to a decline in wild stocks attributed to the passing of parasites from farmed to wild individuals. On the west coast of the United States and Canada, aquaculturists are generally under scrutiny to ensure that non-native Atlantic salmon cannot escape from their open-net pens, however occasional incidents of escape have been documented. During one incident in 2017, for example, up to 300,000 potentially invasive Atlantic salmon escaped a farm among the San Juan Islands in Puget Sound, Washington. Washington went on in 2019 to implement a gradual phase out of salmon farming to be completed by 2025. Despite being the source of considerable controversy, the likelihood of escaped Atlantic salmon establishing an invasive presence in the Pacific Northwest is considered minimal, largely because a number of 20th century efforts aimed at deliberately introducing them to the region were ultimately unsuccessful. From 1905 until 1935, for example, in excess of 8.6 million Atlantic salmon of various life stages (predominantly advanced fry) were intentionally introduced to more than 60 individual
 Beginning around 1990, the rates of Atlantic salmon mortality at sea more than doubled in the western Atlantic. Rivers of the coast of
Beginning around 1990, the rates of Atlantic salmon mortality at sea more than doubled in the western Atlantic. Rivers of the coast of
even disappear
An international effort to study the increased mortality rate was organized by the
 Around the North Atlantic, efforts to restore salmon to their native habitats are underway, with slow progress. Habitat restoration and protection are key to this process, but issues of excessive harvest and competition with farmed and escaped salmon are also primary considerations. In the
Around the North Atlantic, efforts to restore salmon to their native habitats are underway, with slow progress. Habitat restoration and protection are key to this process, but issues of excessive harvest and competition with farmed and escaped salmon are also primary considerations. In the
Rivers Database
showing the stock status of wild Atlantic salmon populations across the species range.
Atlantic salmon
''NOAA FishWatch''. Retrieved 4 November 2012.
official website
of the
official website
of the Atlantic Salmon Trust *Profiles and documents
Species directory: Atlantic salmon
- profile from the
''Salmo salar'' (Atlantic salmon)
- profile in the Nonindigenous Aquatic Species database of the
Maine Atlantic Salmon Commission Documents
archive of documents of the
Invasive Species — Atlantic Salmon (''Salmo salar'')
profile from the
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
of ray-finned fish in the family Salmonidae
Salmonidae is a family of ray-finned fish that constitutes the only currently extant family in the order Salmoniformes . It includes salmon (both Atlantic and Pacific species), trout (both ocean-going and landlocked), chars, freshwater whitefis ...
. It is the third largest of the Salmonidae, behind Siberian taimen and Pacific Chinook salmon
The Chinook salmon (''Oncorhynchus tshawytscha'') is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon in North America, as well as the largest in the genus ''Oncorhynchus''. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other ve ...
, growing up to a meter in length. Atlantic salmon are found in the northern Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
and in rivers that flow into it. Most populations are anadromous
Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or body of water to another. Many types of fish migrate on a regular basis, on time scales ranging from daily to annually or longer, and over distances ranging from a few metres to thousan ...
, hatching in streams and rivers but moving out to sea as they grow where they mature, after which the adults seasonally move upstream again to spawn.
When the mature fish re-enter rivers to spawn, they change in colour and appearance. Some populations of this fish only migrate to large lakes, and are "landlocked", spending their entire lives in freshwater. Such populations are found throughout the range of the species. Unlike Pacific species of salmon, ''S. salar'' is iteroparous
Semelparity and iteroparity are two contrasting reproductive strategies available to living organisms. A species is considered semelparous if it is characterized by a single reproductive episode before death, and iteroparous if it is characteri ...
, which means it can survive spawning and return to sea to repeat the process again in another year. Such individuals can grow to extremely large sizes, although they are rare. The different life stages of the fish are known by many different names in English: alevin
Fish go through various biological life cycle, life stages between fertilization and adulthood. The life of a fish start as spawn (biology), spawned fish egg, eggs which hatch into immotile larvae. These larval hatchlings are not yet capable ...
, fry, parr and smolt.
Atlantic salmon is considered a very healthy food and one of the fish with a more refined taste in many cultures. As such it features in numerous popular traditional cuisines and can fetch a higher price than some other fish. It has thus long been the target of recreational
Recreation is an activity of leisure, leisure being discretionary time. The "need to do something for recreation" is an essential element of human biology and psychology. Recreational activities are often done for enjoyment, amusement, or pleasure ...
and commercial fishing
Commercial fishing is the activity of catching fish and other seafood for commercial profit, mostly from wild fisheries. It provides a large quantity of food to many countries around the world, but those who practice it as an industry must often ...
, and this, as well as habitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
, has impacted the population in some areas. As a result, the species is the subject of conservation efforts in several countries, which appear to have been somewhat successful since the 2000s. Techniques to farm this species using aquacultural methods have also been developed, and at present it is farmed in great numbers in many places around the world. Although this is now a viable alternative to wild-caught fish, farming methods have attracted criticism from environmentalists.
Nomenclature
The Atlantic salmon was given its scientific binomial name by Swedishzoologist
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the Animal, animal kingdom, including the anatomy, structure, embryology, evolution, Biological clas ...
and taxonomist
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given ...
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
in 1758
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Swedish biologist Carl Linnaeus (Carl von Linné) publishes in Stockholm the first volume (''Animalia'') of the 10th edition of Systema Naturae, 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'', the sta ...
. The name, ''Salmo salar'', derives from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''salmo'', meaning salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the ...
, and ''salar'', meaning leaper, according to M. Barton, but more likely meaning "resident of salt water" . Lewis and Short's Latin Dictionary (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1879) translates ''salar'' as a kind of trout from its use in the ''Idylls'' of the poet Ausonius (4th century CE). Later, the differently coloured smolts were found to be the same species.
Other names used for the Atlantic salmon are: bay salmon, black salmon, caplin-scull salmon, fiddler, sebago salmon, silver salmon, outside salmon and winnish. At different points in their maturation and life cycle, they are known as parr, smolt, grilse, grilt, kelt, slink, and spring salmon. Atlantic salmon that do not journey to sea are known as landlocked salmon (or in North America).
Description
 Atlantic salmon are the largest species in their genus, ''Salmo''. After two years at sea, the fish average in length and in weight. But specimens that spend four or more winters feeding at sea can be much larger. An Atlantic salmon netted in 1960 in Scotland, in the estuary of the river Hope, weighed , the heaviest recorded in all available literature. Another netted in 1925 in Norway measured in length, the longest Atlantic salmon on record.Buller F., ''The Domesday Book of Giant Salmon Volume 1 & 2''. Constable (2007) & Constable (2010)
The colouration of young Atlantic salmon does not resemble the adult stage. While they live in fresh water, they have blue and red spots. At maturity, they take on a silver-blue sheen. The easiest way of identifying them as an adult is by the black spots predominantly above the
Atlantic salmon are the largest species in their genus, ''Salmo''. After two years at sea, the fish average in length and in weight. But specimens that spend four or more winters feeding at sea can be much larger. An Atlantic salmon netted in 1960 in Scotland, in the estuary of the river Hope, weighed , the heaviest recorded in all available literature. Another netted in 1925 in Norway measured in length, the longest Atlantic salmon on record.Buller F., ''The Domesday Book of Giant Salmon Volume 1 & 2''. Constable (2007) & Constable (2010)
The colouration of young Atlantic salmon does not resemble the adult stage. While they live in fresh water, they have blue and red spots. At maturity, they take on a silver-blue sheen. The easiest way of identifying them as an adult is by the black spots predominantly above the lateral line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelial ...
, though the caudal fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as se ...
is usually unspotted. When they reproduce, males take on a slight green or red colouration. The salmon has a fusiform
Fusiform means having a spindle-like shape that is wide in the middle and tapers at both ends. It is similar to the lemon-shape, but often implies a focal broadening of a structure that continues from one or both ends, such as an aneurysm on a b ...
body, and well-developed teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
. All fins, except the adipose fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as s ...
, are bordered with black.
Distribution and habitat
 The natural breeding grounds of Atlantic salmon are rivers in Europe and the northeastern coast of North America. In Europe, Atlantic salmon are still found as far south as Spain, and as far north as Russia. Because of sport-fishing, some of the species' southern populations in northern Spain are growing smaller. The species distribution is easily influenced by changes in freshwater habitat and climate. Atlantic salmon are a cold-water fish species and are particularly sensitive to changes in water temperature.
The
The natural breeding grounds of Atlantic salmon are rivers in Europe and the northeastern coast of North America. In Europe, Atlantic salmon are still found as far south as Spain, and as far north as Russia. Because of sport-fishing, some of the species' southern populations in northern Spain are growing smaller. The species distribution is easily influenced by changes in freshwater habitat and climate. Atlantic salmon are a cold-water fish species and are particularly sensitive to changes in water temperature.
The Housatonic River
The Housatonic River ( ) is a river, approximately long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed April 1, 2011 in western Massachusetts and western Connecticut in the United S ...
, and its Naugatuck River
The Naugatuck River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 1, 2011 river in the U.S. state of Connecticut. Its waters carve out the Naugatuck River Valley in the wes ...
tributary, hosted the southernmost Atlantic salmon spawning runs in the United States. However, there is a 1609 account by Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 160 ...
that Atlantic salmon once ran up the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
. In addition, fish scale evidence dating to 10,000 years BP places Atlantic salmon in a coastal New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
pond.
Two publications from 1988 and 1996 questioned the notion that Atlantic salmon were prehistorically plentiful in New England, when the climate was warmer as it is now. This argument was primarily based on a paucity of bone data in archaeological sites relative to other fish species, and the assertion that historical claims of abundance may have been exaggerated. This argument was later challenged in another paper which claimed that lack of archaeological bone fragments could be explained by salmon bones being rare at sites that still have large salmon runs and that salmonid bones in general are poorly recovered relative to other fish species.
Atlantic salmon populations were significantly reduced in the United States following European settlement. The fur trade, timber harvesting, dams and mills and agriculture degraded freshwater habitats and lowered the carrying capacity of most North American streams. Beaver populations were trapped to near-extinction by 1800, and log drives and clear-cutting further exacerbated stream erosion and habitat loss. As timber and fur gave way to agriculture, freshwater Atlantic salmon habitat was further compromised. According to historian D.W. Dunfield (1985) "over half of the historical Atlantic salmon runs had been lost in North America by 1850". As early as 1798, a bill for the preservation of Atlantic Salmon was introduced in Canadian Parliament, to protect populations in Lake Ontario. In the Gulf Region of Nova Scotia it was reported that 31 of the 33 Atlantic salmon streams were blocked off by lumber dams, leading to the extirpation
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, refers to a species (or other taxon) of plant or animal that ceases to exist in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinct ...
of early-run fish in many watersheds. The inshore Atlantic salmon fishery became a major export of the New World, with major fishing operations establishing along the shores of major river systems. The southernmost populations were the first to disappear.
Young salmon spend one to four years in their natal river. When they are large enough (c. ), they smoltify, changing camouflage from stream-adapted with large, gray spots to sea-adapted with shiny sides. They also undergo some endocrinological changes to adapt to osmotic
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of ...
differences between fresh water and seawater habitat. When smoltification is complete, the parr (young fish) now begin to swim with the current instead of against it. With this behavioral change, the fish are now referred to as smolt. When the smolt reach the sea, they follow sea surface currents and feed on plankton or fry from other fish species such as herring. During their time at sea, they can sense the change in the Earth magnetic field through iron in their lateral line.
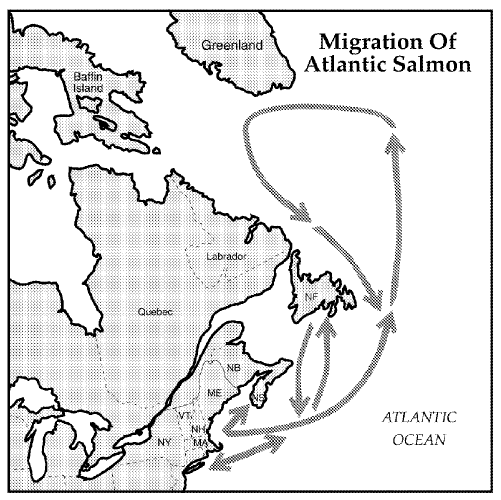
When they have had a year of good growth, they will move to the sea surface currents that transport them back to their natal river. It is a major misconception that salmon swim thousands of kilometres at sea; instead they surf through sea surface currents. It is possible they find their natal river by smell, although this is not confirmed; only 5% of Atlantic salmon go up the wrong river. The range of an individual Atlantic salmon can thus be the river where they are born and the sea surface currents that are connected to that river in a circular path.
Wild salmon continued to disappear from many rivers during the twentieth century due to overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing fish stock), resulting in th ...
and habitat change.
Ecology
Diet
Young salmon begin a feeding response within a few days. After the yolk sac is absorbed by the body, they begin to hunt. Juveniles start with tiny invertebrates, but as they mature, they may occasionally eat small fish. During this time, they hunt both in the substrate and in the current. Some have been known to eat salmon eggs.Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankt ...
such as euphausiid
Krill are small crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, and are found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian word ', meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish.
Krill are consi ...
s are important food for pre-grilse but amphipod
Amphipoda is an order of malacostracan crustaceans with no carapace and generally with laterally compressed bodies. Amphipods range in size from and are mostly detritivores or scavengers. There are more than 9,900 amphipod species so far descr ...
s and decapods are also consumed. The most commonly eaten foods include caddisflies
The caddisflies, or order Trichoptera, are a group of insects with aquatic larvae and terrestrial adults. There are approximately 14,500 described species, most of which can be divided into the suborders Integripalpia and Annulipalpia on the b ...
, blackflies, mayflies
Mayflies (also known as shadflies or fishflies in Canada and the upper Midwestern United States, as Canadian soldiers in the American Great Lakes region, and as up-winged flies in the United Kingdom) are aquatic insects belonging to the orde ...
, stoneflies
Plecoptera is an order of insects, commonly known as stoneflies. Some 3,500 species are described worldwide, with new species still being discovered. Stoneflies are found worldwide, except Antarctica. Stoneflies are believed to be one of the mo ...
, and chironomid
The Chironomidae (informally known as chironomids, nonbiting midges, or lake flies) comprise a family of nematoceran flies with a global distribution. They are closely related to the Ceratopogonidae, Simuliidae, and Thaumaleidae. Many species ...
s, as well as terrestrial insects.
As adults, the salmon prefer capelin
The capelin or caplin (''Mallotus villosus'') is a small forage fish of the smelt family found in the North Atlantic, North Pacific and Arctic oceans. In summer, it grazes on dense swarms of plankton at the edge of the ice shelf. Larger capelin ...
as their meal of choice. Capelin are elongated silvery fish that grow up to long. Other fish consumed include herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, i ...
, alewives
The alewife (''Alosa pseudoharengus'') is an anadromous species of herring found in North America. It is one of the "typical" North American shads, attributed to the subgenus ''Pomolobus'' of the genus ''Alosa''. As an adult it is a marin ...
, smelt
Smelt may refer to:
* Smelting, chemical process
* The common name of various fish:
** Smelt (fish), a family of small fish, Osmeridae
** Australian smelt in the family Retropinnidae and species ''Retropinna semoni''
** Big-scale sand smelt ''At ...
s, scomberids, sand lance
A sand lance or sandlance is a fish belonging to the family Ammodytidae. Several species of sand lances are commonly known as "sand eels", though they are not related to true eels. Another variant name is launce, and all names of the fish are ...
, and small cod
Cod is the common name for the demersal fish genus '' Gadus'', belonging to the family Gadidae. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus ''Gadus'' is commonly not call ...
.
Behavior
Fry and parr have been said to be territorial, but evidence showing them to guard territories is inconclusive. While they may occasionally be aggressive towards each other, thesocial hierarchy
Social stratification refers to a society's categorization of its people into groups based on socioeconomic factors like wealth, income, race, education, ethnicity, gender, occupation, social status, or derived power (social and political). As su ...
is still unclear. Many have been found to school
A school is an educational institution designed to provide learning spaces and learning environments for the teaching of students under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compuls ...
, especially when leaving the estuary.
Adult Atlantic salmon are considered much more aggressive than other salmon, and are more likely to attack other fish than others.
Life stages
 Most Atlantic salmon follow an anadromous migration pattern, in that they undergo their greatest feeding and growth in saltwater; however, adults return to
Most Atlantic salmon follow an anadromous migration pattern, in that they undergo their greatest feeding and growth in saltwater; however, adults return to spawn
Spawn or spawning may refer to:
* Spawn (biology), the eggs and sperm of aquatic animals
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Spawn (character), a fictional character in the comic series of the same name and in the associated franchise
** '' Spawn: ...
in native freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ...
streams where the eggs hatch and juveniles grow through several distinct stages.
Atlantic salmon do not require saltwater. Numerous examples of fully freshwater (i.e., "landlocked") populations of the species exist throughout the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
, including a now extinct population in Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border sp ...
, which have been shown in recent studies to have spent their entire life cycle in watershed of the lake."Study sheds light on extinct Lake Ontario salmon"''Toronto Star'', 9 November 2016, page GT1. In North America, the landlocked strains are frequently known as ''ouananiche''.
Freshwater phase
The freshwater phases of Atlantic salmon vary between two and eight years, according to river location. While the young in southern rivers, such as those to theEnglish Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
, are only one year old when they leave, those further north, such as in Scottish rivers, can be over four years old, and in Ungava Bay
Ungava Bay (french: baie d'Ungava, ; iu, ᐅᖓᕙ ᑲᖏᖅᓗᒃ/) is a bay in northeastern Canada separating Nunavik (far northern Quebec) from Baffin Island. Although not geographically apparent, it is considered to be a marginal sea of the ...
, northern Quebec, smolts as old as eight years have been encountered.
The first phase is the alevin
Fish go through various biological life cycle, life stages between fertilization and adulthood. The life of a fish start as spawn (biology), spawned fish egg, eggs which hatch into immotile larvae. These larval hatchlings are not yet capable ...
stage, when the fish stay in the breeding ground and use the remaining nutrients in their yolk sac
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though ''yolk sac'' is far ...
s. During this developmental stage, their young gills develop and they become active hunters. Next is the fry stage, where the fish grow and subsequently leave the breeding ground in search of food. During this time, they move to areas with higher prey concentration. The final freshwater stage is when they develop into parr, in which they prepare for the trek to the Atlantic Ocean.
During these times, the Atlantic salmon are very susceptible to predation
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the ...
. Nearly 40% are eaten by trout
Trout are species of freshwater fish belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', ''Salmo'' and ''Salvelinus'', all of the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae. The word ''trout'' is also used as part of the name of some non-salmoni ...
alone. Other predators include other fish and birds. Egg and juvenile survival is dependent on habitat quality as Atlantic salmon are sensitive to ecological change.
Saltwater phases
When parr develop into smolt, they begin the trip to the ocean, which predominantly happens between March and June. Migration allowsacclimation
Acclimatization or acclimatisation ( also called acclimation or acclimatation) is the process in which an individual organism adjusts to a change in its environment (such as a change in altitude, temperature, humidity, photoperiod, or pH), a ...
to the changing salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
. Once ready, young smolt leave, preferring an ebb tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables can ...
.
Having left their natal streams, they experience a period of rapid growth during the one to four years they live in the ocean. Typically, Atlantic salmon migrate from their home streams to an area on the continental plate off West Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
. During this time, they face predation from humans, seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
, Greenland shark
The Greenland shark (''Somniosus microcephalus''), also known as the gurry shark, grey shark, or by the Kalaallisut name ''eqalussuaq'', is a large shark of the family Somniosidae ("sleeper sharks"), closely related to the Pacific and souther ...
s, skate
Skate or Skates may refer to: Fish
*Skate (fish), several genera of fish belonging to the family Rajidae
* Pygmy skates, several genera of fish belonging to the family Gurgesiellidae
* Smooth skates or leg skates, several genera of fish belongin ...
, cod
Cod is the common name for the demersal fish genus '' Gadus'', belonging to the family Gadidae. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus ''Gadus'' is commonly not call ...
, and halibut
Halibut is the common name for three flatfish in the genera '' Hippoglossus'' and ''Reinhardtius'' from the family of right-eye flounders and, in some regions, and less commonly, other species of large flatfish.
The word is derived from ''h ...
. Some dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the ...
s have been noticed playing with dead salmon, but it is still unclear whether they consume them.
Once large enough, Atlantic salmon change into the grilse
Salmon () is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus ''Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus ''Oncorhynchus' ...
phase, when they become ready to return to the same freshwater tributary they departed from as smolts. After returning to their natal streams, the salmon will cease eating altogether prior to spawning. Although largely unknown, odor – the exact chemical signature of that stream – may play an important role in how salmon return to the area where they hatched. Once heavier than about 250 g, the fish no longer become prey for birds and many fish, although seals do prey upon them. Grey
Grey (more common in British English) or gray (more common in American English) is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning literally that it is "without color", because it can be composed o ...
and common
Common may refer to:
Places
* Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland
* Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts
* Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts
* Clapham Common, originally com ...
seals commonly eat Atlantic salmon. Survivability to this stage has been estimated at between 14 and 53%.
neural tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural fold become elevated, a ...
File:Salmonlarvakils 2.jpg, Newly hatched alevin feed on their yolk sac
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though ''yolk sac'' is far ...
s
File:Atlantic salmon redd.jpg, When the alevin or sac fry have depleted their yolk sac or "lunch box", they emerge from the gravel habitat of their redd
Redd is a Turkish rock band established in 1996 by tenor opera singer Doğan Duru and guitarist Berke Hatipoğlu under the name ''Ten''. They used to play at bars until they set up their own studio in 2004. Their first album, titled ''"50/50" ...
(nest) to look for food as fry.
File:Atlantic salmon parr.jpg, The fry become parr, and pick home rocks or plants in the streambed from which they dart out to capture insect larvae and other passing food
File:Salmo salar smolts.jpg, When the parr are ready for migration to the ocean, they become smolt
Breeding
 Atlantic salmon breed in the rivers of Western Europe from northern
Atlantic salmon breed in the rivers of Western Europe from northern Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
north to Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
, Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
, and Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
, and the east coast of North America from Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its cap ...
in the United States north to northern Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
and Arctic Canada.
The species constructs a nest or "redd" in the gravel bed of a stream. The female creates a powerful downdraught of water with her tail near the gravel to excavate a depression. After she and a male fish have eggs and milt
Milt is the seminal fluid of fish, mollusks, and certain other water-dwelling animals which reproduce by spraying this fluid, which contains the sperm, onto roe (fish eggs). It can also refer to the sperm sacs or testes that contain the semen.
...
(sperm), respectively, upstream of the depression, the female again uses her tail, this time to shift gravel to cover the eggs and milt which have lodged in the depression.
Unlike the various Pacific salmon species which die after spawning (semelparous
Semelparity and iteroparity are two contrasting reproductive strategies available to living organisms. A species is considered semelparous if it is characterized by a single reproductive episode before death, and iteroparous if it is characteri ...
), the Atlantic salmon is iteroparous
Semelparity and iteroparity are two contrasting reproductive strategies available to living organisms. A species is considered semelparous if it is characterized by a single reproductive episode before death, and iteroparous if it is characteri ...
, which means the fish may recondition themselves and return to the sea to repeat the migration and spawning pattern several times, although most spawn only once or twice. Migration and spawning exact an enormous physiological toll on individuals, such that repeat spawners are the exception rather than the norm. Atlantic salmon show high diversity in age of maturity and may mature as parr, one- to five-sea-winter fish, and in rare instances, at older sea ages. This variety of ages can occur in the same population, constituting a ' bet hedging' strategy against variation in stream flows. So in a drought year, some fish of a given age will not return to spawn, allowing that generation other, wetter years in which to spawn.
Hybridization
When in shared breeding habitats, Atlantic salmon will hybridize withbrown trout
The brown trout (''Salmo trutta'') is a European species of salmonid fish that has been widely introduced into suitable environments globally. It includes purely freshwater populations, referred to as the riverine ecotype, ''Salmo trutta'' morph ...
(''Salmo trutta''). Hybrids between Atlantic salmon and brown trout were detected in two of four watersheds studied in northern Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
. The proportions of hybrids in samples of salmon ranged from 0 to 7-7% but these proportions were not significantly homogeneous among locations, resulting in a mean hybridization rate of 2-3%. This is the highest rate of natural hybridization so far reported and is significantly greater than rates observed elsewhere in Europe.
Beaver impact
The decline in anadromous salmonid species over the last two to three centuries is correlated with the decline in theNorth American beaver
The North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') is one of two Extant taxon, extant beaver species, along with the Eurasian beaver (''Castor fiber''). It is native to North America and introduced in South America (Patagonia) and Europe (primari ...
and European beaver
The Eurasian beaver (''Castor fiber'') or European beaver is a beaver species that was once widespread in Eurasia, but was hunted to near-extinction for both its fur and castoreum. At the turn of the 20th century, only about 1,200 beavers surviv ...
, although some fish and game departments continue to advocate removal of beaver dams as potential barriers to spawning runs. Migration of adult Atlantic salmon may be limited by beaver dams during periods of low stream flows, but the presence of juvenile salmon upstream of the dams suggests they are penetrated by parr. Downstream migration of Atlantic salmon smolts was similarly unaffected by beaver dams, even in periods of low flows.
In a 2003 study, Atlantic salmon and sea-run brown trout
The brown trout (''Salmo trutta'') is a European species of salmonid fish that has been widely introduced into suitable environments globally. It includes purely freshwater populations, referred to as the riverine ecotype, ''Salmo trutta'' morph ...
spawning in the Numedalslågen River and 51 of its tributaries in southeastern Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
was unhindered by beavers. In a restored, third-order stream in northern Nova Scotia, beaver dams generally posed no barrier to Atlantic salmon migration except in the smallest upstream reaches in years of low flow where pools were not deep enough to enable the fish to leap the dam or without a column of water over-topping the dam for the fish to swim up.
The importance of winter habitat to salmonids afforded by beaver ponds may be especially important in streams of northerly latitudes without deep pools where ice cover makes contact with the bottom of shallow streams. In addition, the up to eight-year-long residence time of juveniles in freshwater may make beaver-created permanent summer pools a crucial success factor for Atlantic salmon populations. In fact, two-year-old Atlantic salmon parr in beaver ponds in eastern Canada showed faster summer growth in length and mass and were in better condition than parr upstream or downstream from the pond.
Relationship to humans
Atlantic salmon is a popular fish for human consumption and is commonly sold fresh, canned, or frozen. Wood and stone weirs along streams and ponds were used for millennia to harvest salmon in the rivers of New England. European fishermen gillnetted for Atlantic salmon in rivers using hand-made nets for many centuries and gillnetting was also used in early colonial America.
In its natal streams, Atlantic salmon are considered prized recreational fish, pursued by fly anglers during its annual runs. At one time, the species supported an important commercial fishery, but having become endangered throughout its range globally, wild-caught Atlantic salmon are now virtually absent from the market. Instead, nearly all are from
Wood and stone weirs along streams and ponds were used for millennia to harvest salmon in the rivers of New England. European fishermen gillnetted for Atlantic salmon in rivers using hand-made nets for many centuries and gillnetting was also used in early colonial America.
In its natal streams, Atlantic salmon are considered prized recreational fish, pursued by fly anglers during its annual runs. At one time, the species supported an important commercial fishery, but having become endangered throughout its range globally, wild-caught Atlantic salmon are now virtually absent from the market. Instead, nearly all are from aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lot ...
farms, predominantly in Norway, Chile, Canada, the UK, Ireland, Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway bet ...
, Russia and Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
in Australia.
Aquaculture
 Adult male and female fish are anaesthetised; their eggs and sperm are "stripped" after the fish are cleaned and cloth dried. Sperm and eggs are mixed, washed, and placed into freshwater. Adults recover in flowing, clean, well-
Adult male and female fish are anaesthetised; their eggs and sperm are "stripped" after the fish are cleaned and cloth dried. Sperm and eggs are mixed, washed, and placed into freshwater. Adults recover in flowing, clean, well-aerated
Aeration (also called aerification or aeriation) is the process by which air is circulated through, mixed with or dissolved in a liquid or other substances that act as a fluid (such as soil). Aeration processes create additional surface area in ...
water. Some researchers have even studied cryopreservation
Cryo-preservation or cryo-conservation is a process where Organism, organisms, organelles, cell (biology), cells, Biological tissue, tissues, extracellular matrix, Organ (anatomy), organs, or any other biological constructs susceptible to damage ...
of their eggs.
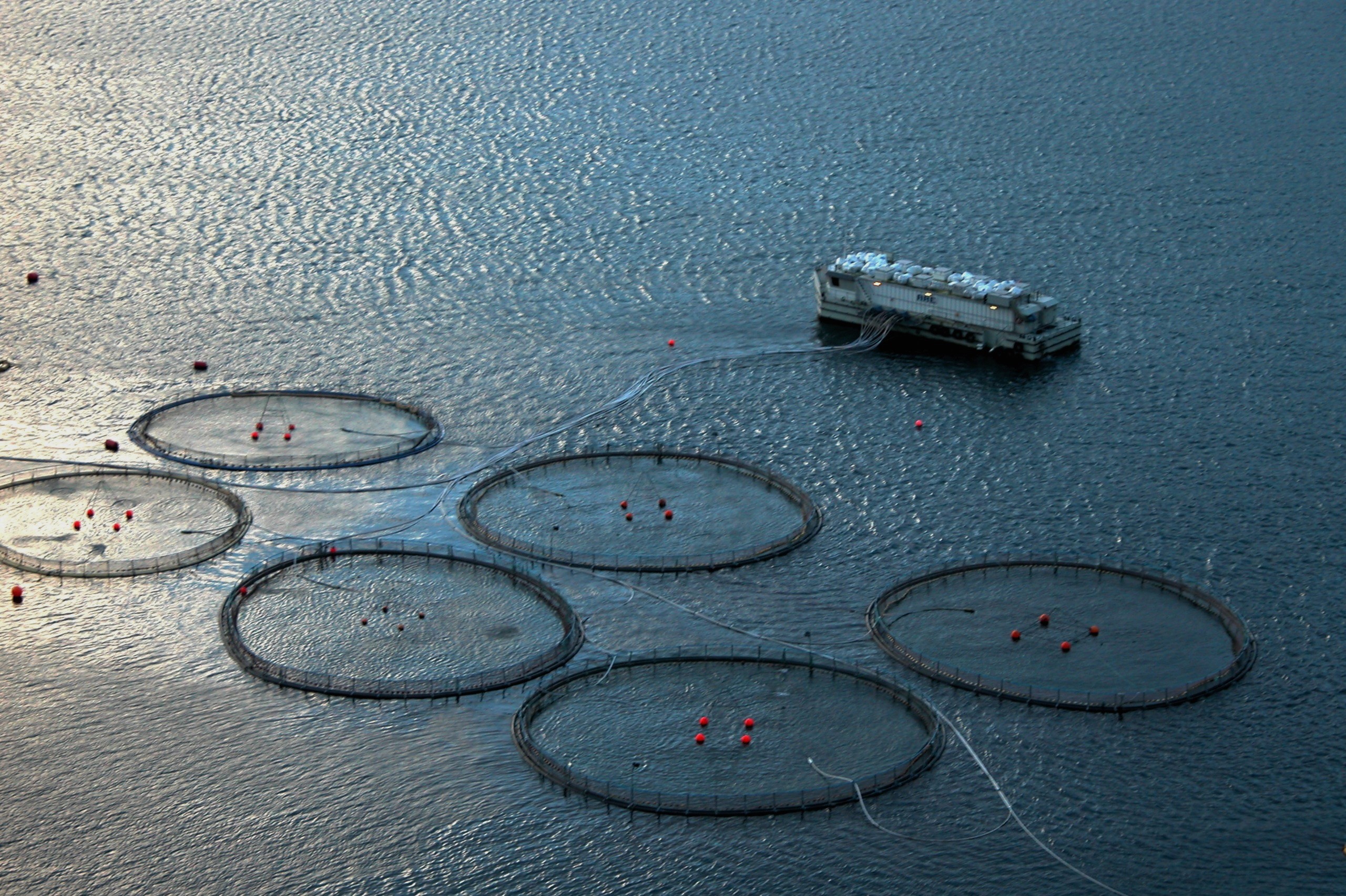
Fry are generally reared in large freshwater tanks for 12 to 20 months. Once the fish have reached the smolt phase, they are taken out to sea, where they are held for up to two years. During this time, the fish grow and mature in large cages off the coasts of Canada, the US, or parts of Europe.
There are many different commercially available cage designs built to operate in a wide variety of aquatic conditions. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) cages are widely used, with HDPE pipes forming a floating collar ring onto which the fish net pen is secured and suspended in the water below.Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. (2015). ''Aquaculture operations in floating HDPE cages - A field handbook''. Retrieved from http://www.fao.org/3/i4508e/i4508e.pdf
Advancements in cage technologies have allowed for reduction in fish escapes, improvement in growing conditions, and maximization of aquaculture production volume per unit area of growing space.
Controversy
Farmed Atlantic salmon are known to occasionally escape from cages and enter the habitat of wild populations. Interbreeding between escaped farm fish and wild fish decreases genetic diversity and introduces "the potential to genetically alter native populations, reduce local adaptation and negatively affect population viability and character".study
in 2000 demonstrated that the genes of farmed Atlantic salmon intrude wild populations mainly through wild males breeding with farmed females, though farmed specimens showed reduced capacity for breeding success overall compared to their wild counterparts. Further study in 2018 discovered extensive cross-breeding of wild and farmed Atlantic salmon in the Northwest Atlantic, showing that 27.1% of fish in 17 out of 18 rivers examined are artificially stocked or hybrids. Farming of Atlantic salmon in open cages at sea has also been linked, at least in part, to a decline in wild stocks attributed to the passing of parasites from farmed to wild individuals. On the west coast of the United States and Canada, aquaculturists are generally under scrutiny to ensure that non-native Atlantic salmon cannot escape from their open-net pens, however occasional incidents of escape have been documented. During one incident in 2017, for example, up to 300,000 potentially invasive Atlantic salmon escaped a farm among the San Juan Islands in Puget Sound, Washington. Washington went on in 2019 to implement a gradual phase out of salmon farming to be completed by 2025. Despite being the source of considerable controversy, the likelihood of escaped Atlantic salmon establishing an invasive presence in the Pacific Northwest is considered minimal, largely because a number of 20th century efforts aimed at deliberately introducing them to the region were ultimately unsuccessful. From 1905 until 1935, for example, in excess of 8.6 million Atlantic salmon of various life stages (predominantly advanced fry) were intentionally introduced to more than 60 individual
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
lakes and streams. Historical records indicate, in a few instances, mature sea-run Atlantic salmon were captured in the Cowichan River
The Cowichan River is a Canadian Heritage River on Vancouver Island, in British Columbia, Canada. Its headwater is Cowichan Lake. The river flows east over Skutz Falls and through Marie Canyon towards its mouth at Cowichan Bay. The river's d ...
; however, a self-sustaining population never materialized. Similarly unsuccessful results were realized after deliberate attempts at introduction by Washington as late as the 1980s. Consequently, environmental assessments by the US National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), the Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife and the BC Environmental Assessment Office have concluded the potential risk of Atlantic salmon colonization in the Pacific Northwest is low.
Future prospects
A study of Næve et al. (2022) estimated the impact of 50 years of genetic selection and tried to predict the impact it could have until 2050. In order to do this, a common garden experiment was used to model and simulate past and future effects for 11 generations of genetic selection of increased growth rate in Atlantic salmon. To model the contribution that breeding has made in the industry from generation 0 (harvested in 1975– 1978) to generation 11 (harvested in 2017 – 2019), and to simulate growth until 2050 (generation 24), the Norwegian salmon aquaculture production between 2016 and 2019 was used as a base case. The simulation of the expected growth until 2050 (generation 24) gave five different scenarios : Historical (H1), Forecast 1 (F1), Forecast 2 (F2), Forecast 3 (F3) and Forecast 4 (F4). Changes in thermal growth coefficient (TGC) per generation were used in the model to simulate the differences in the five scenarios. The genetic data, H1, and the most conservative forecast scenario, F1, simulate what can be expected in 2050 if the trend from generation 0 through 11 is maintained. The following forecast scenarios assume a greater increase in genetic growth with a larger increase in the TGC in the generations to come. In the next two generations, more advanced selection methods such as marker assisted selection (from generation 10) and genomic selection (from generation 11) were implemented. This resulted in increased gain in selection for growth and simulated F2 and F3. The most progressive scenario, F4, aimed at exploring the effect in the industry when the full genetic potential is utilized. This assumes a further development of advanced techniques in the years to come. The authors of the article found that the daily yield of the biomass increased with increasing generations in the historic and forecast scenarios. Further, the production time in seawater to reach the harvest weight of 5100 g is expected to be reduced by 53% in 2050. When production time can be reduced, this will also reduce e.g. time at risk of diseases. In the most progressive scenario, mortality in seawater was expected to be reduced by up to 50%. Further, the authors found that production per license can increase by up to 121%. Additionally, 77% of the new volume needed to achieve five million tonnes in 2050, may be provided by genomic selection. However, one should keep in mind that this article was published by the firm Aquagen, and can possibly be biased and too optimistic.Conservation
TheIUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ...
rates this as a common species with a conservation status of "least concern
A least-concern species is a species that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as evaluated as not being a focus of species conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wild. T ...
", however it has been 25 years since the IUCN has released this status. A more recent regional assessment revealed that the European population of this species is vulnerable, and this might be the same or a similar status globally. Location-specific assessments have shown population declines across parts of the Atlantic Salmon's natural range, with populations along the coast of Maine and the Inner Bay of Fundy now listed as "endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and inva ...
" under the Endangered Species Act, and the Canadian Species at Risk Act, respectively.
Human activities have impacted salmon populations across parts of its range. The major threats are from overfishing and habitat change. Salmon decline in Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border sp ...
goes back to the 18th–19th centuries, due to logging and soil erosion, as well as dam and mill construction. By 1896, the species was declared extirpated from the lake.Harb, M. "Upstream Battle", ''Canadian Geographic Magazine'', June 2008, p. 24
In the 1950s, salmon from rivers in the United States and Canada, as well as from Europe, were discovered to gather in the sea around Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
and the Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway bet ...
. A commercial fishing
Commercial fishing is the activity of catching fish and other seafood for commercial profit, mostly from wild fisheries. It provides a large quantity of food to many countries around the world, but those who practice it as an industry must often ...
industry was established, taking salmon using drift net
Drift netting is a fishing technique where nets, called drift nets, hang vertically in the water column without being anchored to the bottom. The nets are kept vertical in the water by floats attached to a rope along the top of the net and weig ...
s. After an initial series of record annual catches, the numbers crashed; between 1979 and 1990, catches fell from four million to 700,000.
 Beginning around 1990, the rates of Atlantic salmon mortality at sea more than doubled in the western Atlantic. Rivers of the coast of
Beginning around 1990, the rates of Atlantic salmon mortality at sea more than doubled in the western Atlantic. Rivers of the coast of Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and north ...
, southern New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
and much of mainland Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
saw runs drop precipitously, aneven disappear
An international effort to study the increased mortality rate was organized by the
North Atlantic Salmon Conservation Organization
The North Atlantic Salmon Conservation Organization (NASCO) is a specialised regional fishery management organisation established under the Convention for the Conservation of Salmon in the North Atlantic Ocean from 1 October 1983.
The organizat ...
. In 2000 the numbers of Atlantic salmon dropped to very low levels in Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
, Canada. In 2007 at least one sport fishing
Recreational fishing, also called sport fishing or game fishing, is fishing for leisure, exercise or competition. It can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is professional fishing for profit; or subsistence fishing, which is fishing ...
organization from Iceland and Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, ...
blamed less fish caught by recreational anglers on overfishing at sea, and thus created the North Atlantic Salmon Fund to buy commercial quotas in the Atlantic from commercial fishermen in an effort to preserve wild ''Salmo salar'' stocks.
Possibly because of improvements in ocean feeding grounds, returns in 2008 were very positive. On the Penobscot River
The Penobscot River (Abenaki: ''Pαnawάhpskewtəkʷ'') is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed June 22, 2011 river in the U.S. state of Maine. Including the river's We ...
in Maine, returns were about 940 in 2007, and by mid-July 2008, the return was 1,938. Similar stories were reported in rivers from Newfoundland to Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
. In 2011, more than 3,100 salmon returned to the Penobscot, the most since 1986, and nearly 200 ascended the Narraguagus River
The Narraguagus River is a river located in the U.S. state of Maine with its mouth in the Narraguagus Bay of the Gulf of Maine. It flows through the town of Cherryfield, Maine, Cherryfield and was formerly well known for its sport fly fishing for ...
, up from the low two digits just a decade before.
Recreational fishing of Atlantic salmon is now authorized in much of the US and Canada where it occurs in large numbers, but this is subject to regulations in many states or provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
which are designed to maintain the continuity of the species. Strict catch limits, catch and release
Catch and release is a practice within recreational fishing where after capture, often a fast measurement and weighing of the fish is performed, followed by posed photography as proof of the catch, and then the fish are unhooked and returned ...
practices and forced fly fishing
Fly fishing is an angling method that uses a light-weight lure—called an artificial fly—to catch fish. The fly is cast using a fly rod, reel, and specialized weighted line. The light weight requires casting techniques significantly diffe ...
are examples of those regulations. However, catch and release angling can be an additional stressor on Atlantic salmon populations, especially when its impacts are combined with the existing pressures of climate change, overfishing, and predation.
Restoration efforts
 Around the North Atlantic, efforts to restore salmon to their native habitats are underway, with slow progress. Habitat restoration and protection are key to this process, but issues of excessive harvest and competition with farmed and escaped salmon are also primary considerations. In the
Around the North Atlantic, efforts to restore salmon to their native habitats are underway, with slow progress. Habitat restoration and protection are key to this process, but issues of excessive harvest and competition with farmed and escaped salmon are also primary considerations. In the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
, Atlantic salmon have been reintroduced, but the percentage of salmon reproducing naturally is very low. Most areas are re-stocked annually. Since the extirpation of Atlantic salmon from Lake Ontario in the late 19th century, the state of New York has stocked its adjoining rivers and tributaries, and in many cases does not allow active fishing.
The province of Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
started the Atlantic Salmon Restoration Program in 2006, which is one of the largest freshwater conservation programs in North America. It has since stocked Lake Ontario and surrounding tributaries with upwards of 6,000,000 young Atlantic salmon, with efforts growing each year. In New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
, many efforts are underway to restore salmon to the region by knocking down obsolete dams and updating others with fish ladder
A fish ladder, also known as a fishway, fish pass, fish steps, or fish cannon is a structure on or around artificial and natural barriers (such as dams, locks and waterfalls) to facilitate diadromous fishes' natural migration as well as movemen ...
s and other techniques that have proven effective in the West with Pacific salmon
''Oncorhynchus'' is a genus of fish in the family Salmonidae; it contains the Pacific salmon and Pacific trout. The name of the genus is derived from the Greek ὄγκος (ónkos, “lump, bend”) + ῥύγχος (rhúnkhos, “snout”), in r ...
. There is some success thus far, with populations growing in the Penobscot and Connecticut River
The Connecticut River is the longest river in the New England region of the United States, flowing roughly southward for through four states. It rises 300 yards (270 m) south of the U.S. border with Quebec, Canada, and discharges at Long Island ...
s. Lake Champlain
, native_name_lang =
, image = Champlainmap.svg
, caption = Lake Champlain-River Richelieu watershed
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = New York/Vermont in the United States; and Quebec in Canada
, coords =
, type =
, ...
now has Atlantic salmon. The Atlantic Salmon Federation
The Atlantic Salmon Federation (ASF) is an international conservation organization established in 1948.
The Federation is dedicated to the conservation, protection and restoration of wild Atlantic salmon and the ecosystems on which their well bein ...
is involved in restoration efforts along the eastern United States and Canada, where their projects are focused on removing barriers to fish passage and eradicating invasive species.
Recent documented successes in the reintroduction of Atlantic salmon include the following:
* In October 2007, salmon were video-recorded running in Toronto's Humber River by the Old Mill Old Mill may refer to:
Animations
*''The Old Mill'', a 1937 Academy Award-winning ''Silly Symphonies'' cartoon produced by Walt Disney
*'' The Old Mill Pond'', a 1936 Academy Award nominated short film directed by Hugh Harman
Places
Canada
* Old ...
.
* A migrating salmon was observed in Ontario's Credit River
The Credit River is a river in southern Ontario, which flows from headwaters above the Niagara Escarpment near Orangeville and Caledon East to empty into Lake Ontario at Port Credit, Mississauga. It drains an area of approximately . The total le ...
in November 2007.
* As of 2013, there has been some success in establishing Atlantic salmon in Fish Creek, a tributary of Oneida Lake
Oneida Lake is the largest lake entirely within New York state, with a surface area of .
The lake is located northeast of Syracuse and near the Great Lakes. It feeds the Oneida River, a tributary of the Oswego River, which flows into Lake Ontario ...
in central New York.
* In November 2015, salmon nests were observed in Connecticut in the Farmington River
The Farmington River is a river, U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 1, 2011 in length along its main stem, located in northwest Connecticut with major tributaries ex ...
, a tributary of the Connecticut River where Atlantic salmon had not been observed spawning since "probably the Revolutionary War". However, both state and federal experts indicated that this find likely represented a dwindling wave of returning stocked fish from massive salmon restoration efforts that had concluded years earlier in 2012. Significant doubt was cast on fish returning to spawn in meaningful numbers after 2017, when the last generation of stocked salmon would return.
NASCO
TheNorth Atlantic Salmon Conservation Organization
The North Atlantic Salmon Conservation Organization (NASCO) is a specialised regional fishery management organisation established under the Convention for the Conservation of Salmon in the North Atlantic Ocean from 1 October 1983.
The organizat ...
is an international council made up of Canada, the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, Iceland, Norway, the Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, and the United States, with its headquarters in Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
. It was established in 1983 to help protect Atlantic salmon stocks, through the cooperation between nations. They work to restore habitat and promote conservation of the salmon. In December 2021, NASCO published an updated interactive map of theiRivers Database
showing the stock status of wild Atlantic salmon populations across the species range.
Legislation
England and Wales
Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vassal o ...
instituted a penalty for collecting salmon during certain times of the year. His son Edward II
Edward II (25 April 1284 – 21 September 1327), also called Edward of Caernarfon, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1307 until he was deposed in January 1327. The fourth son of Edward I, Edward became the heir apparent to t ...
continued, regulating the construction of weir
A weir or low head dam is a barrier across the width of a river that alters the flow characteristics of water and usually results in a change in the height of the river level. Weirs are also used to control the flow of water for outlets of l ...
s. Enforcement was overseen by those appointed by the justices of the peace
A justice of the peace (JP) is a judicial officer of a lower or ''puisne'' court, elected or appointed by means of a commission ( letters patent) to keep the peace. In past centuries the term commissioner of the peace was often used with the sa ...
. Because of confusing laws and the appointed conservators having little power, most laws were barely enforced.
Based on this, a royal commission was appointed in 1860 to thoroughly investigate the Atlantic salmon and the laws governing the species, resulting in the 1861 Salmon Fisheries Act. The act placed enforcement of the laws under the Home Office's control, but it was later transferred to the Board of Trade
The Board of Trade is a British government body concerned with commerce and industry, currently within the Department for International Trade. Its full title is The Lords of the Committee of the Privy Council appointed for the consideration of ...
, and then later to the Board of Agriculture and Fisheries. Another act passed in 1865 imposed charges to fish and catch limits. It also caused the formation of local boards having jurisdiction over a certain river. The next significant act, passed in 1907, allowed the board to charge 'duties' to catch other freshwater fish, including trout.
Despite legislation, board effects decreased until, in 1948, the River Boards Act gave authority of all freshwater fish and the prevention of pollution to one board per river. In total, it created 32 boards. In 1974, the 32 boards, which by then were integrated into regional river authorities, were reduced to 10 regional water authorities (RWAs). Although only the Northumbrian Water Authority
Northumbrian Water Limited is a water company in the United Kingdom, providing mains water and sewerage services in the English counties of Northumberland, Tyne and Wear, Durham and parts of North Yorkshire, and also supplying water as Essex and ...
, Welsh National Water Development Authority
The Welsh National Water Development Authority (WNWDA) (''Awdurdod Cenedlaethol Datblygu Dwr Cymru'' in Welsh) and later the Welsh Water Authority was one of ten regional water authorities set up in the UK and came into existence on 6 August 19 ...
, Northwest Water Authority and Southwest Water Authority had significant salmon populations, all ten also regulated and conserved trout and freshwater eel
The Anguillidae are a family of ray-finned fish that contains the freshwater eels. Eighteen of the 19 extant species and six subspecies in this family are in the genus ''Anguilla''. They are elongated fish with snake-like bodies, their long dorsa ...
fisheries
The Salmon and Freshwater Fisheries Act was passed in 1975. Among other things, it regulated fishing licences, seasons, and size limits, and banned obstructing the salmon's migratory paths.
Scotland
Salmon was greatly valued inmedieval Scotland
Scotland in the Middle Ages concerns the history of Scotland from the departure of the Romans to the adoption of major aspects of the Renaissance in the early sixteenth century.
From the fifth century northern Britain was divided into a series ...
, and various fishing methods, including the use of weir
A weir or low head dam is a barrier across the width of a river that alters the flow characteristics of water and usually results in a change in the height of the river level. Weirs are also used to control the flow of water for outlets of l ...
s, cruives, and nets, were used to catch the fish. Fishing for salmon was heavily regulated in order to conserve the resource.Kate Buchanan, "Wheeles and Creels: The Physical Representation of the Right to Milling and Fishing in Sixteenth-Century Angus, Scotland" in ''Medieval and Early Modern Representations of Authority in Scotland and the British Isles'' (eds. Kate Buchanan & Lucinda H.S. Dean with Michael Penman: Routledge, 2016), pp. 59–60. In 1318, King Robert I enacted legislation setting a minimum size for cruives, "so that no fry of fish are impeded from ascending and descending..." Laws on catching fish upon royal lands were frequently updated, demonstrating their importance. Because the fish were held in such high regard, poachers
Poaching has been defined as the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights.
Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set a ...
were severely punished; a person twice convicted of poaching salmon on a royal estate could be sentenced to death
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that t ...
. The export of salmon was economically important in Aberdeen
Aberdeen (; sco, Aiberdeen ; gd, Obar Dheathain ; la, Aberdonia) is a city in North East Scotland, and is the third most populous city in the country. Aberdeen is one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas (as Aberdeen City), and ...
; beginning in the 15th century, the fish could be preserved through salting and barreling, allowing them to be exported abroad, including as far away as the Baltic
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10 ...
. The volume of the early Scottish salmon trade is impossible to determine, since surviving custom records date only from the 1420 onward, and since Aberdeen burgess __NOTOC__
Burgess may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Burgess (surname), a list of people and fictional characters
* Burgess (given name), a list of people
Places
* Burgess, Michigan, an unincorporated community
* Burgess, Missouri, U ...
es enjoyed an exemption on salmon customs until the 1530s.
During the 15th century, many laws were passed; many regulated fishing times, and worked to ensure smolts could safely pass downstream. James III even closed a meal
A meal is an eating occasion that takes place at a certain time and includes consumption of food. The names used for specific meals in English vary, depending on the speaker's culture, the time of day, or the size of the meal.
Although they ca ...
mill
Mill may refer to:
Science and technology
*
* Mill (grinding)
* Milling (machining)
* Millwork
* Textile mill
* Steel mill, a factory for the manufacture of steel
* List of types of mill
* Mill, the arithmetic unit of the Analytical Engine early ...
because of its history of killing fish attracted to the wheel.
More recent legislation has established commissioners who manage districts. Furthermore, the Salmon and Freshwater Fisheries Act in 1951 required the Secretary of State be given data about the catches of salmon and trout to help establish catch limits.
United States
Commercial and recreational fishing of wild Atlantic salmon is prohibited in the United States. Several populations of Atlantic salmon are in serious decline, and are listed as endangered under theEndangered Species Act
The Endangered Species Act of 1973 (ESA or "The Act"; 16 U.S.C. § 1531 et seq.) is the primary law in the United States for protecting imperiled species. Designed to protect critically imperiled species from extinction as a "consequence of ec ...
(ESA). Currently, runs of 11 rivers in Maine are on the list – Kennebec, Androscoggin, Penobscot, Sheepscot, Ducktrap, Cove Brook, Pleasant, Narraguagus, Machias, East Machias and Dennys. The Penobscot River
The Penobscot River (Abenaki: ''Pαnawάhpskewtəkʷ'') is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed June 22, 2011 river in the U.S. state of Maine. Including the river's We ...
is the "anchor river" for Atlantic salmon populations in the US. Returning fish in 2008 were around 2,000, more than double the 2007 return of 940.
Section 9 of the ESA makes it illegal to take an endangered species of fish or wildlife. The definition of "take" is to "harass, harm, pursue, hunt, shoot, wound, kill, trap, capture, or collect, or to attempt to engage in any such conduct".
Canada
Thefederal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
has prime responsibility for protecting the Atlantic salmon, but over the last generation, effort has continued to shift management as much as possible to provincial authorities through memoranda of understanding, for example. A new Atlantic salmon policy is in the works, and in the past three years, the government has attempted to pass a new version of the century-old Fisheries Act through Parliament.
Federal legislation regarding at-risk populations is weak. Inner Bay of Fundy
The Bay of Fundy (french: Baie de Fundy) is a bay between the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, with a small portion touching the U.S. state of Maine. It is an arm of the Gulf of Maine. Its extremely high tidal range is the hi ...
Atlantic salmon runs were declared endangered in 2000. A recovery and action plan is in place.
Nongovernmental organizations
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from government. They are typically nonprofit entities, and many of them are active in h ...
, such as the Atlantic Salmon Federation
The Atlantic Salmon Federation (ASF) is an international conservation organization established in 1948.
The Federation is dedicated to the conservation, protection and restoration of wild Atlantic salmon and the ecosystems on which their well bein ...
, constantly demand for improvements in management, and for initiatives to be considered. For example, the ASF and the Nova Scotia Salmon Association desire the use of technology for mitigation of acid rain
Acid rain is rain or any other form of precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). Most water, including drinking water, has a neutral pH that exists between 6.5 and 8.5, but acid ...
-affected rivers such as used in Norway is in 54 Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
rivers and managed to raise the funds to get a project in place in one river.
In Quebec, the daily catch limit for Atlantic salmon is dependent on the individual river. Some rivers are strictly catch and release with a limit of 3 released fish. Each catch must be declared. Some rivers allow you to keep between 1 or 2 grilse (30 cm to 63 cm), while some of the more prolific rivers (mainly on the north coast) will allow you to keep 1 salmon over 63 cm. The annual catch limit is 4 Atlantic salmon of small size and only 1 of those may be bigger than 63 cm.
In Lake Ontario, the historic populations of Atlantic salmon became extinct, and cross-national efforts have been under way to reintroduce the species, with some areas already having restocked naturally reproducing populations.
See also
*AquAdvantage salmon
AquAdvantage salmon is a genetically engineered (GE) fish, a GE Atlantic salmon developed by AquaBounty Technologies in 1989. The typical growth hormone-regulating gene in the Atlantic salmon was replaced with the growth hormone-regulating gen ...
, a genetically modified Atlantic salmon
* Atlantic Salmon Federation
The Atlantic Salmon Federation (ASF) is an international conservation organization established in 1948.
The Federation is dedicated to the conservation, protection and restoration of wild Atlantic salmon and the ecosystems on which their well bein ...
* Salmon as food
Salmon is a common fish as food, food fish classified as an oily fish with a rich content of protein and omega-3 fatty acids. In Norway – a major producer of Aquaculture of salmonids, farmed and Salmon#Wild fisheries, wild salmon – f ...
Notes
References
Atlantic salmon
''NOAA FishWatch''. Retrieved 4 November 2012.
External links
*Groups and initiativesofficial website
of the
Atlantic Salmon Conservation Foundation The Atlantic Salmon Conservation Foundation (ASCF) is a registered charitable organization whose focus is the conservation of wild Atlantic salmon and its habitat in Atlantic Canada and Quebec.
ASCF was established through a one-time grant from the ...
official website
of the Atlantic Salmon Trust *Profiles and documents
Species directory: Atlantic salmon
- profile from the
National Marine Fisheries Service
The National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), informally known as NOAA Fisheries, is a United States federal agency within the U.S. Department of Commerce's National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) that is responsible for the stew ...
of NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditio ...
''Salmo salar'' (Atlantic salmon)
- profile in the Nonindigenous Aquatic Species database of the
U.S. Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and ...
Maine Atlantic Salmon Commission Documents
archive of documents of the
Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and north ...
Atlantic Salmon Commission (which was abolished in 2010)
Invasive Species — Atlantic Salmon (''Salmo salar'')
profile from the
Alaska Department of Fish and Game
The Alaska Department of Fish and Game (ADF&G) is a department within the government of Alaska. ADF&G's mission is to protect, maintain, and improve the fish, game, and aquatic plant resources of the state, and manage their use and development in ...
{{Authority control
Atlantic salmon
The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Salmonidae. It is the third largest of the Salmonidae, behind Siberian taimen and Pacific Chinook salmon, growing up to a meter in length. Atlantic salmon are ...
Atlantic salmon
The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Salmonidae. It is the third largest of the Salmonidae, behind Siberian taimen and Pacific Chinook salmon, growing up to a meter in length. Atlantic salmon are ...
Freshwater fish of the Arctic
Cold water fish
Commercial fish
Freshwater fish of Europe
Fish of the Arctic Ocean
Fish of the North Atlantic
Fish of the Great Lakes
Fish of Greenland
Fauna of Atlantic Canada
Fauna of the Northeastern United States
Atlantic salmon
The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Salmonidae. It is the third largest of the Salmonidae, behind Siberian taimen and Pacific Chinook salmon, growing up to a meter in length. Atlantic salmon are ...
Atlantic salmon
The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Salmonidae. It is the third largest of the Salmonidae, behind Siberian taimen and Pacific Chinook salmon, growing up to a meter in length. Atlantic salmon are ...