Laminar Organization on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A laminar organization describes the way certain tissues, such as bone membrane,
skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different de ...
, or brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
tissues, are arranged in layers.
Types
Embryo
The earliest forms of laminar organization are shown in thediploblastic
Diploblasty is a condition of the blastula in which there are two primary germ layers: the ectoderm and endoderm.
Diploblastic organisms are organisms which develop from such a blastula, and include cnidaria and ctenophora
Ctenophora (; ...
and triploblastic
Triploblasty is a condition of the gastrula in which there are three primary germ layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Germ cells are set aside in the embryo at the blastula stage, which are incorporated into the gonads during organo ...
formation of the germ layers in the embryo. In the first week of human embryogenesis
Human embryonic development, or human embryogenesis, is the development and formation of the human embryo. It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of de ...
two layers of cells have formed, an external epiblast layer (the primitive ectoderm), and an internal hypoblast layer (primitive endoderm). This gives the early bilaminar disc. In the third week in the stage of gastrulation epiblast cells invaginate to form endoderm, and a third layer of cells known as mesoderm. Cells that remain in the epiblast become ectoderm. This is the trilaminar disc and the epiblast cells have given rise to the three germ layers.
Brain
In the brain a laminar organization is evident in the arrangement of the three meninges, the membranes that cover thebrain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
and spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
. These membranes are the dura mater
In neuroanatomy, dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. ...
, arachnoid mater, and pia mater
Pia mater ( or ),Entry "pia mater"
in
periosteal layer near to the bone of the skull, and a meningeal layer next to the other meninges. The
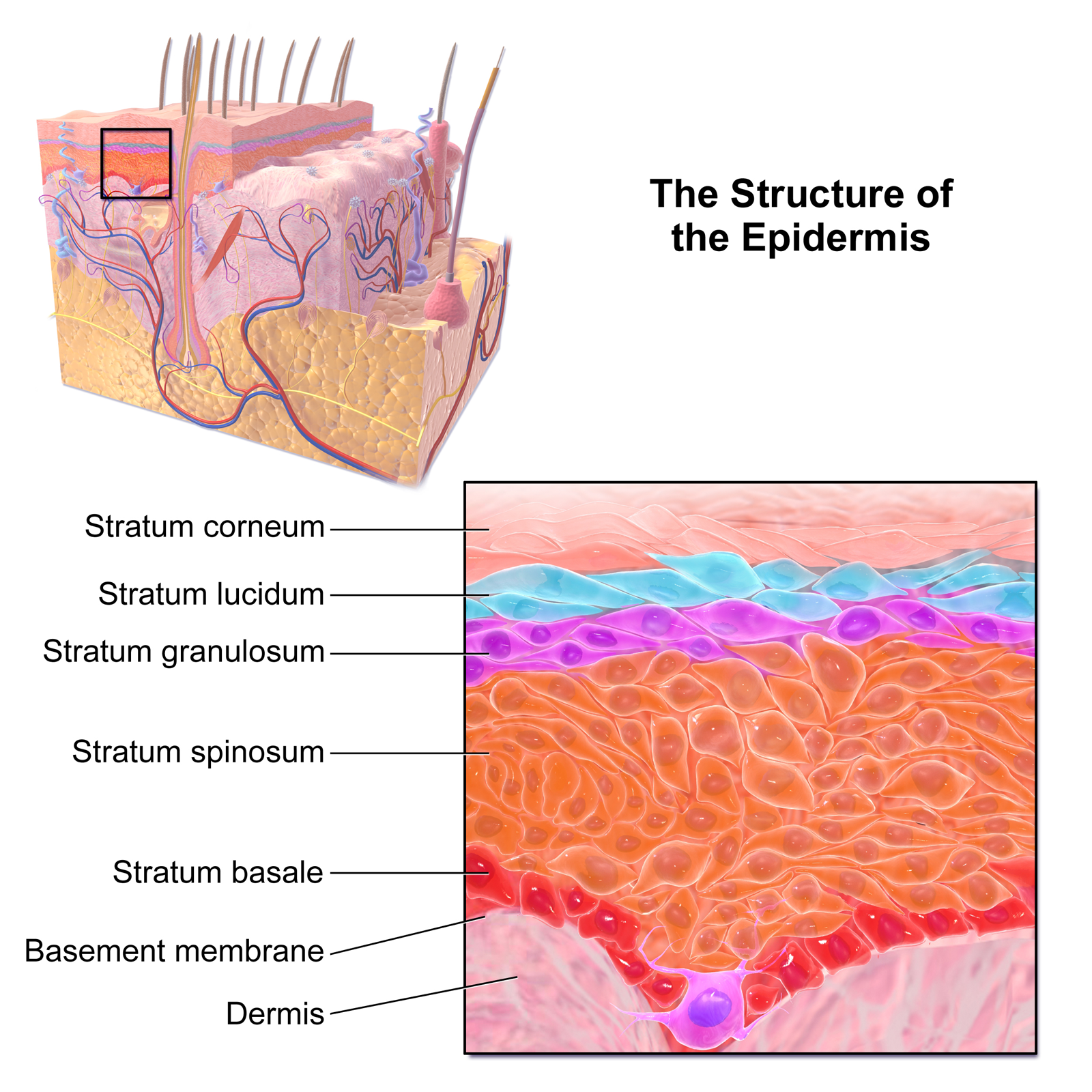 The human skin has a dense laminar organization. The outer epidermis has four or five layers.
The human skin has a dense laminar organization. The outer epidermis has four or five layers.
in
periosteal layer near to the bone of the skull, and a meningeal layer next to the other meninges. The
cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consistin ...
, the outer neural sheet covering the cerebral hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres ...
s can be described by its laminar organization, due to the arrangement of cortical neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. ...
s into six distinct layers.
Eye
The eye in mammals has an extensive laminar organization. There are three main layers – the outer fibrous tunic, the middleuvea
The uvea (; Lat. ''uva'', "grape"), also called the ''uveal layer'', ''uveal coat'', ''uveal tract'', ''vascular tunic'' or ''vascular layer'' is the pigmented middle of the three concentric layers that make up an eye.
History and etymolog ...
, and the inner retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
. These layers have sublayers with the retina having ten ranging from the outer choroid to the inner vitreous humor
The vitreous body (''vitreous'' meaning "glass-like"; , ) is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball (the vitreous chamber) in humans and other vertebrates. It is often referred to as the vitreous humor ...
and including the retinal nerve fiber layer.
Skin
 The human skin has a dense laminar organization. The outer epidermis has four or five layers.
The human skin has a dense laminar organization. The outer epidermis has four or five layers.
References
{{Reflist Tissues (biology)