Lynx X-ray Surveyor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Lynx X-ray Observatory (''Lynx'') is a NASA-funded Large Mission Concept Study commissioned as part of the
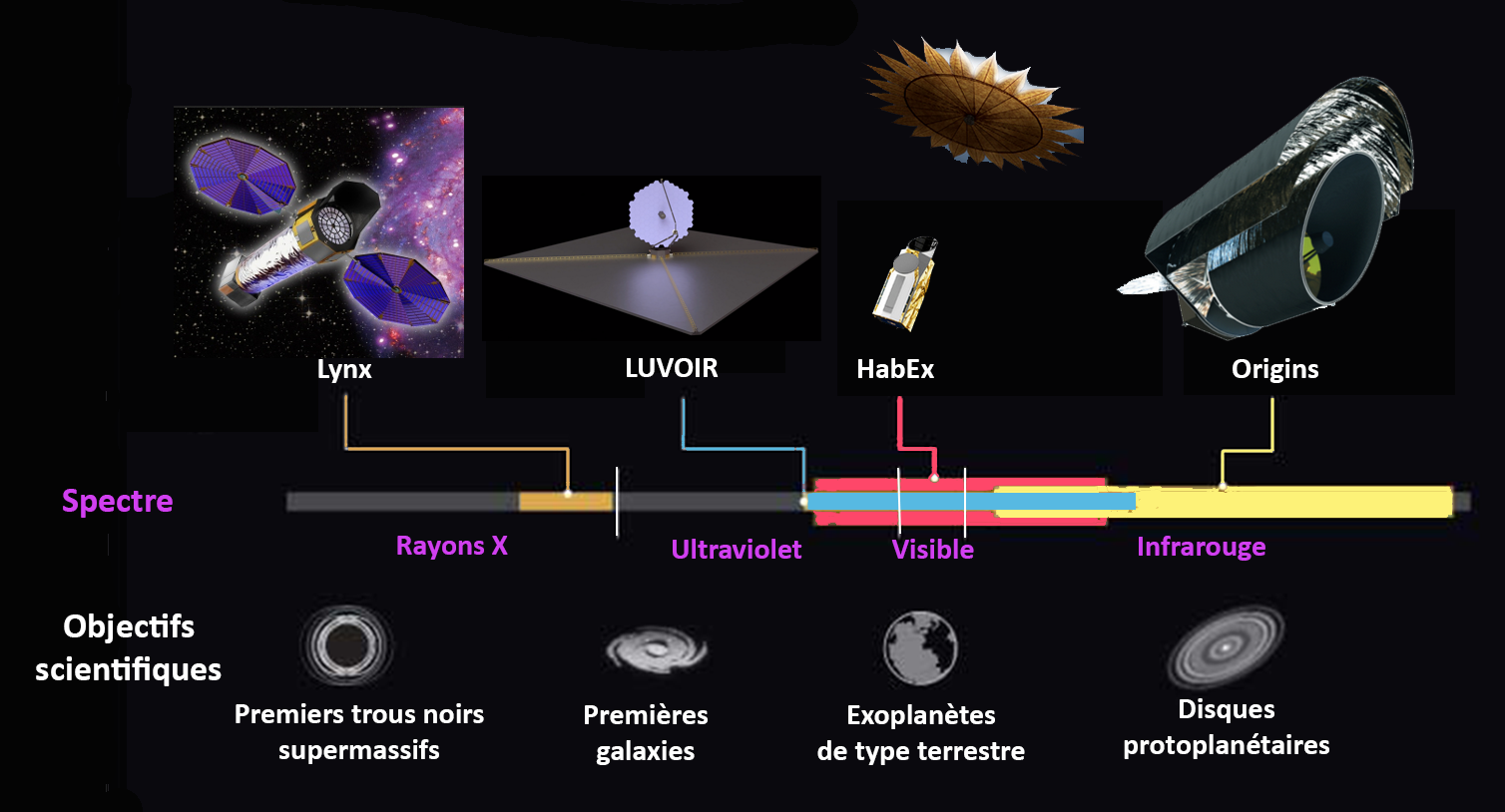 In 2016, following recommendations laid out in the so-called Astrophysics Roadmap of 2013, NASA established four space telescope concept studies for future Large strategic science missions. In addition to ''Lynx'' (originally called X-ray Surveyor in th
In 2016, following recommendations laid out in the so-called Astrophysics Roadmap of 2013, NASA established four space telescope concept studies for future Large strategic science missions. In addition to ''Lynx'' (originally called X-ray Surveyor in th
Roadmap document
'','' they are the Habitable Exoplanet Imaging Mission (HabEx), the Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor (LUVOIR), and the Origins Space Telescope (OST, originally called the Far-Infrared Surveyor). The four team
completed their final reports
in August 2019, and turned them over to both NASA and the
Final Report
the ''Lynx'' Design Reference Mission was intentionally optimized to enable major advances in the following three astrophysical discovery areas: * The dawn of
''Lynx'' Report
* The drivers of galaxy formation and evolution
''Lynx'' Report
Chapter 2) * The energetic properties of stellar evolution and stellar ecosystems
''Lynx'' Report
Chapter 3) Collectively, these serve as three "science pillars" that set the baseline requirements for the observatory. Those requirements include greatly enhanced
''Lynx'' Report
, including multi-messenger astronomy,

Final Report
''Lynx'' is designed as an X-ray observatory with a
 The major advances in sensitivity, spatial, and spectral resolution in the ''Lynx'' Design Reference Mission are enabled by the spacecraft's payload, namely the mirror assembly and suite of three science instruments. The ''Lynx'' Report notes that each of the payload elements features
The major advances in sensitivity, spatial, and spectral resolution in the ''Lynx'' Design Reference Mission are enabled by the spacecraft's payload, namely the mirror assembly and suite of three science instruments. The ''Lynx'' Report notes that each of the payload elements features
Silicon Metashell Optics
(SMO), in which thousands of very thin, highly polished segments of nearly pure silicon are stacked into tightly packed concentric shells. Of the three mirror technologies considered for ''Lynx'', the SMO design is currently the most advanced in terms of demonstrated performance (already approaching what is required for ''Lynx''). The SMO's highly modular design lends itself to parallelized manufacturing and assembly, while also providing high fault tolerance: if some individual mirror segments or even modules are damaged, the impact to schedule and cost is minimal. * The High Definition X-ray Imager (HDXI): The HDXI is the main imager for ''Lynx'', providing high spatial resolution over a wide field of view (FOV) and high sensitivity over the 0.2–10 keV
 The ''Chandra X-ray Observatory'' experience provides the blueprint for developing the systems required to operate ''Lynx'', leading to a significant cost reduction relative to starting from scratch. This starts with a single prime contractor for the science and operations center, staffed by a seamless, integrated team of scientists, engineers, and programmers. Many of the system designs, procedures, processes, and algorithms developed for ''Chandra'' will be directly applicable for ''Lynx'', although all will be recast in a software/hardware environment appropriate for the 2030s and beyond.
The science impact of ''Lynx'' will be maximized by subjecting all of its proposed observations to peer review, including those related to the three science pillars. Time pre-allocation can be considered only for a small number of multi-purpose key programs, such as surveys in pre-selected regions of the sky. Such an open General Observer (GO) program approach has been successfully employed by large missions such as '' Hubble Space Telescope'', '' Chandra X-ray Observatory'', and ''
The ''Chandra X-ray Observatory'' experience provides the blueprint for developing the systems required to operate ''Lynx'', leading to a significant cost reduction relative to starting from scratch. This starts with a single prime contractor for the science and operations center, staffed by a seamless, integrated team of scientists, engineers, and programmers. Many of the system designs, procedures, processes, and algorithms developed for ''Chandra'' will be directly applicable for ''Lynx'', although all will be recast in a software/hardware environment appropriate for the 2030s and beyond.
The science impact of ''Lynx'' will be maximized by subjecting all of its proposed observations to peer review, including those related to the three science pillars. Time pre-allocation can be considered only for a small number of multi-purpose key programs, such as surveys in pre-selected regions of the sky. Such an open General Observer (GO) program approach has been successfully employed by large missions such as '' Hubble Space Telescope'', '' Chandra X-ray Observatory'', and ''
Final Report
the ''Lynx'' team commissioned five independent
Lynx home page
Lynx home page for scientists
at NASA {{Space observatories, show Space telescopes X-ray telescopes Proposed NASA space probes
National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the Nati ...
2020 Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey
The Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey is a review of astronomy and astrophysics literature produced approximately every ten years by the National Research Council of the National Academy of Sciences in the United States. The report surveys ...
. The concept study phase is complete as of August 2019, and the ''Lynx'' final report has been submitted to the Decadal Survey for prioritization. If launched, ''Lynx'' would be the most powerful X-ray astronomy observatory constructed to date, enabling order-of-magnitude advances in capability over the current Chandra X-ray Observatory and XMM-Newton space telescopes.
Background
 In 2016, following recommendations laid out in the so-called Astrophysics Roadmap of 2013, NASA established four space telescope concept studies for future Large strategic science missions. In addition to ''Lynx'' (originally called X-ray Surveyor in th
In 2016, following recommendations laid out in the so-called Astrophysics Roadmap of 2013, NASA established four space telescope concept studies for future Large strategic science missions. In addition to ''Lynx'' (originally called X-ray Surveyor in thRoadmap document
'','' they are the Habitable Exoplanet Imaging Mission (HabEx), the Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor (LUVOIR), and the Origins Space Telescope (OST, originally called the Far-Infrared Surveyor). The four team
completed their final reports
in August 2019, and turned them over to both NASA and the
National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the Nati ...
, whose independent Decadal Survey committee advises NASA on which mission should take top priority. If it receives top prioritization and therefore funding, ''Lynx'' would launch in approximately 2036. It would be placed into a halo orbit around the second Sun–Earth Lagrange point (L2), and would carry enough propellant
A propellant (or propellent) is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or other motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the e ...
for more than twenty years of operation without servicing.
The ''Lynx'' concept study involved more than 200 scientists and engineers across multiple international academic institutions, aerospace, and engineering companies. The ''Lynx'' Science and Technology Definition Team (STDT) was co-chaired by Alexey Vikhlinin
Alexey Vikhlinin (born September 17, 1970) is a Russian-American astrophysicist notable for achievements in the astrophysics of high energy phenomenon, namely galaxy cluster cosmology and the design of space-based X-ray observatories. He is curre ...
and Feryal Özel
Feryal Özel (born May 27, 1975) is a Turkish-American astrophysicist born in Istanbul, Turkey, specializing in the physics of compact objects and high energy astrophysical phenomena. As of 2022, Özel is the Department Chair and a professor at ...
. Jessica Gaskin
Jessica may refer to:
Given name
* Jessica (given name), includes a list of people and fictional characters with this name
* Jessica Folcker, a Swedish singer known by the mononym Jessica
* Jessica Jung, a Korean-American singer known by the m ...
was the NASA Study Scientist, and the Marshall Space Flight Center
The George C. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), located in Redstone Arsenal, Alabama (Huntsville postal address), is the U.S. government's civilian rocketry and spacecraft propulsion research center. As the largest NASA center, MSFC's first ...
managed the ''Lynx'' Study Office jointly with the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory
The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) is a research institute of the Smithsonian Institution, concentrating on astrophysical studies including galactic and extragalactic astronomy, cosmology, solar, earth and planetary sciences, the ...
, which is part of the Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian.
Scientific objectives
According to the concept study'Final Report
the ''Lynx'' Design Reference Mission was intentionally optimized to enable major advances in the following three astrophysical discovery areas: * The dawn of
black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravitation, gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts t ...
s (Chapter 1 of th''Lynx'' Report
* The drivers of galaxy formation and evolution
''Lynx'' Report
Chapter 2) * The energetic properties of stellar evolution and stellar ecosystems
''Lynx'' Report
Chapter 3) Collectively, these serve as three "science pillars" that set the baseline requirements for the observatory. Those requirements include greatly enhanced
sensitivity
Sensitivity may refer to:
Science and technology Natural sciences
* Sensitivity (physiology), the ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli
** Sensory processing sensitivity in humans
* Sensitivity and specificity, statisti ...
, a sub-arcsecond point spread function stable across the telescope's field of view, and very high spectral resolution The spectral resolution of a spectrograph, or, more generally, of a frequency spectrum, is a measure of its ability to resolve features in the electromagnetic spectrum. It is usually denoted by \Delta\lambda, and is closely related to the resolvi ...
for both imaging and gratings spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter wa ...
. These requirements, in turn, enable a broad science case with major contributions across the astrophysical landscape (as summarized in Chapter 4 of th''Lynx'' Report
, including multi-messenger astronomy,
black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravitation, gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts t ...
accretion
Accretion may refer to:
Science
* Accretion (astrophysics), the formation of planets and other bodies by collection of material through gravity
* Accretion (meteorology), the process by which water vapor in clouds forms water droplets around nucl ...
physics, large-scale structure, Solar System science, and even exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
s. The ''Lynx'' team markets the mission's science capabilities as "transformationally powerful, flexible, and long-lived", inspired by the spirit of NASA's Great Observatories program
NASA's series of Great Observatories satellites are four large, powerful space-based astronomical telescopes launched between 1990 and 2003. They were built with different technology to examine specific wavelength/energy regions of the electrom ...
.
Mission design and payload

Spacecraft
As described in Chapters 6-10 of the concept study'Final Report
''Lynx'' is designed as an X-ray observatory with a
grazing incidence The angle of incidence, in geometric optics, is the angle between a ray incident on a surface and the line perpendicular (at 90 degree angle) to the surface at the point of incidence, called the normal. The ray can be formed by any waves, such as o ...
X-ray telescope and detectors that record the position, energy, and arrival time of individual X-ray photons. Post-facto aspect reconstruction leads to modest requirements on pointing precision and stability, while enabling accurate sky locations for detected photons. The design of the ''Lynx'' spacecraft draws heavily on heritage from the '' Chandra X-ray Observatory'', with few moving parts and high technology readiness level
Technology readiness levels (TRLs) are a method for estimating the maturity of technologies during the acquisition phase of a program. TRLs enable consistent and uniform discussions of technical maturity across different types of technology. TR ...
elements. ''Lynx'' will operate in a halo orbit
A halo orbit is a periodic, three-dimensional orbit near one of the L1, L2 or L3 Lagrange points in the three-body problem of orbital mechanics. Although a Lagrange point is just a point in empty space, its peculiar characteristic is that it ca ...
around Sun-Earth L2, enabling high observing efficiency in a stable environment. Its maneuvers and operational procedures on-orbit are nearly identical to ''Chandras, and similar design approaches promote longevity. Without in-space servicing, ''Lynx'' will carry enough consumables to enable continuous operation for at least twenty years. The spacecraft and payload elements are, however, designed to be serviceable, potentially enabling an even longer lifetime.
Payload
 The major advances in sensitivity, spatial, and spectral resolution in the ''Lynx'' Design Reference Mission are enabled by the spacecraft's payload, namely the mirror assembly and suite of three science instruments. The ''Lynx'' Report notes that each of the payload elements features
The major advances in sensitivity, spatial, and spectral resolution in the ''Lynx'' Design Reference Mission are enabled by the spacecraft's payload, namely the mirror assembly and suite of three science instruments. The ''Lynx'' Report notes that each of the payload elements features state-of-the-art
The state of the art (sometimes cutting edge or leading edge) refers to the highest level of general development, as of a device, technique, or scientific field achieved at a particular time. However, in some contexts it can also refer to a level ...
technologies while also representing a natural evolution of existing instrumentation technology development over the last two decades. The key technologies are currently at Technology Readiness Levels (TRL) 3 or 4. The ''Lynx'' Report notes that, with three years of targeted pre-phase A development in early 2020s, three of four key technologies will be matured to TRL 5 and one will reach TRL 4 by start of Phase A, achieving TRL 5 shortly thereafter. The ''Lynx'' payload consists of the following four major elements:
* The ''Lynx'' X-ray Mirror Assembly (LMA): The LMA is the central element of the observatory, enabling the major advances in sensitivity, spectroscopic throughput, survey speed, and greatly improved imaging relative to ''Chandra'' due to greatly improved off-axis performance. The ''Lynx'' design reference mission baselines a new technology calleSilicon Metashell Optics
(SMO), in which thousands of very thin, highly polished segments of nearly pure silicon are stacked into tightly packed concentric shells. Of the three mirror technologies considered for ''Lynx'', the SMO design is currently the most advanced in terms of demonstrated performance (already approaching what is required for ''Lynx''). The SMO's highly modular design lends itself to parallelized manufacturing and assembly, while also providing high fault tolerance: if some individual mirror segments or even modules are damaged, the impact to schedule and cost is minimal. * The High Definition X-ray Imager (HDXI): The HDXI is the main imager for ''Lynx'', providing high spatial resolution over a wide field of view (FOV) and high sensitivity over the 0.2–10 keV
bandpass
A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects (attenuates) frequencies outside that range.
Description
In electronics and signal processing, a filter is usually a two-port ...
. Its 0.3 arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
(0.3′′) pixels will adequately sample the ''Lynx'' mirror point spread function over a 22′ × 22′ FOV. The 21 individual sensors of the HDXI are laid out along the optimal focal surface to improve the off-axis PSF. The ''Lynx'' DRM uses Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSF ...
(CMOS) Active Pixel Sensor (APS) technology, which is projected to have the required capabilities (i.e., high readout rates, high broad-band quantum efficiency
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio of a photosensitive device, or it may refer to the TMR effect of a Magnetic Tunnel Junction.
This article deals with the term as a measurement of ...
, sufficient energy resolution, minimal pixel crosstalk
In electronics, crosstalk is any phenomenon by which a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel of a transmission system creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel. Crosstalk is usually caused by undesired capacitive, induc ...
, and radiation hardness
Radiation hardening is the process of making electronic components and circuits resistant to damage or malfunction caused by high levels of ionizing radiation (particle radiation and high-energy electromagnetic radiation), especially for environ ...
). The ''Lynx'' team has identified three options with comparable TRL ratings (TRL 3) and sound TRL advancement roadmaps: the Monolithic CMOS, Hybrid CMOS, and Digital CCDs with CMOS readout. All are currently funded for technology development.
* The ''Lynx'' X-ray Microcalorimeter (LXM): The LXM is an imaging spectrometer that provides high resolving power (''R'' ~ 2,000) in both the hard and soft X-ray bands, combined with high spatial resolution (down to 0.5′′ scales). To meet the diverse range of ''Lynx'' science requirements, the LXM focal plane includes three arrays that share the same readout technology. Each array is differentiated by its absorber pixel size and thickness, and by how the absorbers are connected to thermal readouts. The total number of pixels exceeds 100,000 — a major leap over past and currently planned X-ray microcalorimeters. This huge improvement does not entail a huge added cost: two of the LXM arrays feature a simple, already proven, “thermal” multiplexing approach where multiple absorbers are connected to a single temperature sensor. This design brings the number of sensors to read out (one of the main power and cost drivers for the X-ray microcalorimeters) to ~7,600. This is only a modest increase over what is planned for the X-IFU instrument on Athena. As of Spring 2019, prototypes of the focal plane have been made that include all three arrays at 2/3 full size. These prototypes demonstrate that arrays with the pixel form factor, size, and wiring density required by Lynx are readily achievable, with high yield. The energy resolution requirements of the different pixel types is also readily achievable. Although the LXM is technically still at TRL 3, there is a clear path for achieving TRL 4 by 2020 and TRL 5 by 2024.
* The X-ray Grating Spectrometer (XGS): The XGS will provide even higher spectral resolution ('' R'' = 5,000 with a goal of 7,500) in the soft X-ray band for point sources. Compared to the current state of the art ('' Chandra''), the XGS provides a factor of > 5 higher spectral resolution and a factor of several hundred higher throughput. These gains are enabled by recent advances in X-ray grating technologies. Two strong technology candidates are: critical angle transmission (used for the ''Lynx'' DRM) and off-plane reflection gratings. Both are fully feasible, currently at TRL 4, and have demonstrated high efficiencies and resolving powers of ∼ 10,000 in recent X-ray tests.
Mission Operations
 The ''Chandra X-ray Observatory'' experience provides the blueprint for developing the systems required to operate ''Lynx'', leading to a significant cost reduction relative to starting from scratch. This starts with a single prime contractor for the science and operations center, staffed by a seamless, integrated team of scientists, engineers, and programmers. Many of the system designs, procedures, processes, and algorithms developed for ''Chandra'' will be directly applicable for ''Lynx'', although all will be recast in a software/hardware environment appropriate for the 2030s and beyond.
The science impact of ''Lynx'' will be maximized by subjecting all of its proposed observations to peer review, including those related to the three science pillars. Time pre-allocation can be considered only for a small number of multi-purpose key programs, such as surveys in pre-selected regions of the sky. Such an open General Observer (GO) program approach has been successfully employed by large missions such as '' Hubble Space Telescope'', '' Chandra X-ray Observatory'', and ''
The ''Chandra X-ray Observatory'' experience provides the blueprint for developing the systems required to operate ''Lynx'', leading to a significant cost reduction relative to starting from scratch. This starts with a single prime contractor for the science and operations center, staffed by a seamless, integrated team of scientists, engineers, and programmers. Many of the system designs, procedures, processes, and algorithms developed for ''Chandra'' will be directly applicable for ''Lynx'', although all will be recast in a software/hardware environment appropriate for the 2030s and beyond.
The science impact of ''Lynx'' will be maximized by subjecting all of its proposed observations to peer review, including those related to the three science pillars. Time pre-allocation can be considered only for a small number of multi-purpose key programs, such as surveys in pre-selected regions of the sky. Such an open General Observer (GO) program approach has been successfully employed by large missions such as '' Hubble Space Telescope'', '' Chandra X-ray Observatory'', and ''Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003. Operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, f ...
'', and is planned for ''James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope which conducts infrared astronomy. As the largest optical telescope in space, its high resolution and sensitivity allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Spa ...
'' and '' Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope''. The ''Lynx'' GO program will have ample exposure time to achieve the objectives of its science pillars, make impacts across the astrophysical landscape, open new directions of inquiry, and produce as yet unimagined discoveries.
Estimated cost
The cost of the ''Lynx X-ray Observatory'' is estimated to be between US$4.8 billion to US$6.2 billion (in FY20 dollars at 40% and 70% confidence levels, respectively). This estimated cost range includes the launch vehicle, cost reserves, and funding for five years of mission operations, while excluding potential foreign contributions (such as participation by theEuropean Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
(ESA)). As described in Section 8.5 of the concept study'Final Report
the ''Lynx'' team commissioned five independent
cost estimates
In production, research, retail, and accounting, a cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something or deliver a service, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which ...
, all of which arrived at similar estimates for the total mission lifecycle cost.
See also
* Advanced Telescope for High Energy Astrophysics * International X-ray Observatory * Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) * List of proposed space observatoriesReferences
External links
Lynx home page
Lynx home page for scientists
at NASA {{Space observatories, show Space telescopes X-ray telescopes Proposed NASA space probes