Luca Vandi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The last universal common ancestor (LUCA) is the most recent population from which all organisms now living on Earth share
The last universal common ancestor (LUCA) is the most recent population from which all organisms now living on Earth share
 A
A
 The LUCA certainly had genes and a genetic code. Its genetic material was most likely DNA, so that it lived after the RNA world. The DNA was kept double-stranded by an enzyme, DNA polymerase, which recognises the structure and directionality of DNA. The integrity of the DNA was maintained by a group of repair enzymes including
The LUCA certainly had genes and a genetic code. Its genetic material was most likely DNA, so that it lived after the RNA world. The DNA was kept double-stranded by an enzyme, DNA polymerase, which recognises the structure and directionality of DNA. The integrity of the DNA was maintained by a group of repair enzymes including 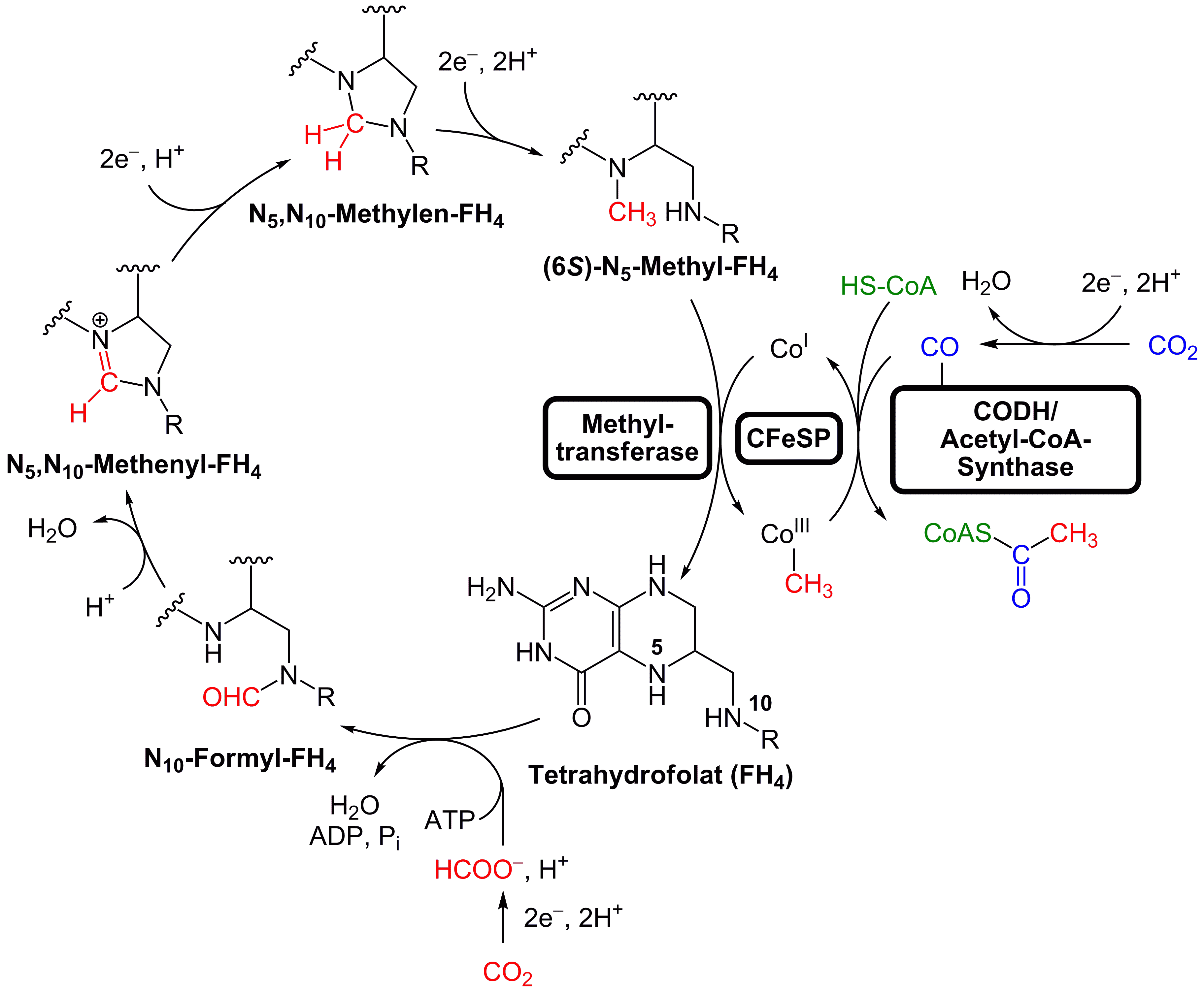 An alternative to the search for "universal" traits is to use genome analysis to identify phylogenetically ancient genes. This gives a picture of a LUCA that could live in a geochemically harsh environment and is like modern prokaryotes. Analysis of biochemical pathways implies the same sort of chemistry as does phylogenetic analysis. Weiss and colleagues write that "Experiments ... demonstrate that ... acetyl-CoA pathway hemicals used in anaerobic respiration
An alternative to the search for "universal" traits is to use genome analysis to identify phylogenetically ancient genes. This gives a picture of a LUCA that could live in a geochemically harsh environment and is like modern prokaryotes. Analysis of biochemical pathways implies the same sort of chemistry as does phylogenetic analysis. Weiss and colleagues write that "Experiments ... demonstrate that ... acetyl-CoA pathway hemicals used in anaerobic respiration
 The most commonly accepted tree of life, based on several molecular studies, has its root between a
The most commonly accepted tree of life, based on several molecular studies, has its root between a
common descent
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. All living beings are in fact descendants of a unique ancestor commonly referred to as the last universal comm ...
—the most recent common ancestor of all current life on Earth. This includes all cellular organisms; the origins of viruses are unclear but they share the same genetic code. LUCA probably harboured a variety of viruses. The LUCA is not the first life on Earth, but rather the latest form ancestral to all existing life.
While there is no specific fossil evidence of the LUCA, the detailed biochemical similarity of all current life confirms its existence. Its characteristics can be inferred from shared features of modern genomes. These genes describe a complex life form with many co-adapted In biology, co-adaptation is the process by which two or more species, genes or phenotypic traits undergo adaptation as a pair or group. This occurs when two or more interacting characteristics undergo natural selection together in response to the s ...
features, including transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
and translation mechanisms to convert information from DNA to RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
to proteins. The LUCA probably lived in the high-temperature water of deep sea vents
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspot ...
near ocean-floor magma flows around 4 billion years ago.
Historical background
 A
A phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spec ...
directly portrays the idea of evolution by descent from a single ancestor. An early tree of life was sketched by Jean-Baptiste Lamarck in his ''Philosophie zoologique
''Philosophie zoologique'' ("Zoological Philosophy, or Exposition with Regard to the Natural History of Animals") is an 1809 book by the French naturalist Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, in which he outlines his pre-Darwinian theory of evolution, part of ...
'' in 1809. Charles Darwin more famously proposed the theory of universal common descent through an evolutionary process in his book '' On the Origin of Species'' in 1859: "Therefore I should infer from analogy that probably all the organic beings which have ever lived on this earth have descended from some one primordial form, into which life was first breathed." The last sentence of the book begins with a restatement of the hypothesis:
: "There is grandeur in this view of life, with its several powers, having been originally breathed into a few forms or into one ..."
The term "last universal common ancestor" or "LUCA" was first used in the 1990s for such a primordial organism.
Inferring LUCA's features
An anaerobic thermophile
In 2016, Madeline C. Weiss and colleagues genetically analyzed 6.1 million protein-coding genes and 286,514 protein clusters from sequenced prokaryotic genomes representing manyphylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spec ...
s, and identified 355 protein clusters that were probably common to the LUCA. The results "depict LUCA as anaerobic, CO2-fixing, H2-dependent with a Wood–Ljungdahl pathway
The Wood–Ljungdahl pathway is a set of biochemical reactions used by some bacteria. It is also known as the reductive acetyl-coenzyme A (Acetyl-CoA) pathway. This pathway enables these organisms to use hydrogen as an electron donor, and carb ...
(the reductive acetyl-coenzyme A pathway), N2-fixing and thermophilic. LUCA's biochemistry was replete with FeS
Fez or Fes (; ar, فاس, fās; zgh, ⴼⵉⵣⴰⵣ, fizaz; french: Fès) is a city in northern inland Morocco and the capital of the Fès-Meknès administrative region. It is the second largest city in Morocco, with a population of 1.11 mi ...
clusters and radical
Radical may refer to:
Politics and ideology Politics
*Radical politics, the political intent of fundamental societal change
*Radicalism (historical), the Radical Movement that began in late 18th century Britain and spread to continental Europe and ...
reaction mechanisms." The cofactors
Cofactor may also refer to:
* Cofactor (biochemistry), a substance that needs to be present in addition to an enzyme for a certain reaction to be catalysed
* A domain parameter in elliptic curve cryptography, defined as the ratio between the order ...
also reveal "dependence upon transition metals, flavins, S-adenosyl methionine, coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a subs ...
, ferredoxin
Ferredoxins (from Latin ''ferrum'': iron + redox, often abbreviated "fd") are iron–sulfur proteins that mediate electron transfer in a range of metabolic reactions. The term "ferredoxin" was coined by D.C. Wharton of the DuPont Co. and applied t ...
, molybdopterin, corrins and selenium. Its genetic code required nucleoside modifications and S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These t ...
s." The results are rather specific: they show that methanogen
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are com ...
ic clostridia was basal, near the root of the phylogenetic tree, in the 355 protein lineages examined, and that the LUCA may therefore have inhabited an anaerobic hydrothermal vent
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspot ...
setting in a geochemically active environment rich in H2, CO2, and iron,
where ocean water interacted with hot magma beneath the ocean floor.
While the gross anatomy of the LUCA can only be reconstructed with much uncertainty, its biochemical mechanisms can be described in some detail, based on the "universal" properties currently shared by all independently living organisms on Earth.
DNA topoisomerase
DNA topoisomerases (or topoisomerases) are enzymes that catalyze changes in the topological state of DNA, interconverting relaxed and supercoiled forms, linked (catenated) and unlinked species, and knotted and unknotted DNA. Topological issues i ...
. If the genetic code was based on dual-stranded DNA, it was expressed by copying the information to single-stranded RNA. The RNA was produced by a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the ...
using nucleotides similar to those of DNA. It had multiple DNA-binding proteins, such as histone-fold proteins. The genetic code was expressed into proteins. These were assembled from 20 free amino acids by translation of a messenger RNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the p ...
via a mechanism of ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to ...
s, transfer RNA
Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes), that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino ac ...
s, and a group of related proteins.
As for the cell's gross structure, it contained a water-based cytoplasm effectively enclosed by a lipid bilayer membrane; it was capable of reproducing by cell division. It tended to exclude sodium and concentrate potassium by means of specific ion transporter
In biology, a transporter is a transmembrane protein that moves ions (or other small molecules) across a biological membrane to accomplish many different biological functions including, cellular communication, maintaining homeostasis, energy produc ...
s (or ion pumps). The cell multiplied by duplicating all its contents followed by cellular division. The cell used chemiosmosis to produce energy. It also reduced CO2 and oxidized H2 (methanogenesis
Methanogenesis or biomethanation is the formation of methane coupled to energy conservation by microbes known as methanogens. Organisms capable of producing methane for energy conservation have been identified only from the domain Archaea, a group ...
or acetogenesis) via acetyl
In organic chemistry, acetyl is a functional group with the chemical formula and the structure . It is sometimes represented by the symbol Ac (not to be confused with the element actinium). In IUPAC nomenclature, acetyl is called ethanoyl, ...
-thioester
In organic chemistry, thioesters are organosulfur compounds with the functional group . They are analogous to carboxylate esters () with the sulfur in the thioester playing the role of the linking oxygen in the carboxylate ester, as implied by t ...
s.
By phylogenetic bracketing, analysis of the presumed LUCA's offspring groups, LUCA appears to have been a small, single-celled organism. It likely had a ring-shaped coil of DNA floating freely within the cell. Morphologically, it would likely not have stood out within a mixed population of small modern-day bacteria. The originator of the three-domain system, Carl Woese, stated that in its genetic machinery, the LUCA would have been a "simpler, more rudimentary entity than the individual ancestors that spawned the three omains(and their descendants)".
 An alternative to the search for "universal" traits is to use genome analysis to identify phylogenetically ancient genes. This gives a picture of a LUCA that could live in a geochemically harsh environment and is like modern prokaryotes. Analysis of biochemical pathways implies the same sort of chemistry as does phylogenetic analysis. Weiss and colleagues write that "Experiments ... demonstrate that ... acetyl-CoA pathway hemicals used in anaerobic respiration
An alternative to the search for "universal" traits is to use genome analysis to identify phylogenetically ancient genes. This gives a picture of a LUCA that could live in a geochemically harsh environment and is like modern prokaryotes. Analysis of biochemical pathways implies the same sort of chemistry as does phylogenetic analysis. Weiss and colleagues write that "Experiments ... demonstrate that ... acetyl-CoA pathway hemicals used in anaerobic respirationformate
Formate (IUPAC name: methanoate) is the conjugate base of formic acid. Formate is an anion () or its derivatives such as ester of formic acid. The salts and esters are generally colorless.Werner Reutemann and Heinz Kieczka "Formic Acid" in ''Ull ...
, methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a ...
, acetyl
In organic chemistry, acetyl is a functional group with the chemical formula and the structure . It is sometimes represented by the symbol Ac (not to be confused with the element actinium). In IUPAC nomenclature, acetyl is called ethanoyl, ...
moieties, and even pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic aci ...
arise spontaneously ... from CO2, native metals, and water", a combination present in hydrothermal vents.
Alternative interpretations
Some other researchers have challenged Weiss et al.'s 2016 conclusions. Sarah Berkemer and Shawn McGlynn argue that Weiss et al. undersampled the families of proteins, so that the phylogenetic trees were not complete and failed to describe the evolution of proteins correctly. A phylogenomic and geochemical analysis of a set of proteins that probably traced to the LUCA show that it had K+-dependent GTPases and the ionic composition and concentration of its intracellular fluid was seemingly high K+/Na+ ratio, , Fe2+, CO2+, Ni2+, Mg2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, pyrophosphate, and which would imply a terrestrial hot spring habitat. It possibly had a phosphate-based metabolism. Further, these proteins were unrelated to autotrophy (the ability of an organism to create its ownorganic matter
Organic matter, organic material, or natural organic matter refers to the large source of carbon-based compounds found within natural and engineered, terrestrial, and aquatic environments. It is matter composed of organic compounds that have c ...
), suggesting that the LUCA had a heterotrophic lifestyle (consuming organic matter) and that its growth was dependent on organic matter produced by the physical environment. Nick Lane argues that Na+/H+ antiporters could readily explain the low concentration of Na+ in the LUCA and its descendants.
The identification of thermophilic genes in the LUCA has also been criticized, as they may instead represent genes that evolved later in archaea or bacteria, then migrated between these via horizontal gene transfers, as in Woese's 1998 hypothesis. Further, the presence of the energy-handling enzymes CODH
In enzymology, carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (CODH) () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
:CO + H2O + A \rightleftharpoons CO2 + AH2
The chemical process catalyzed by carbon monoxide dehydrogenase is similar to the water-gas shif ...
/ acetyl-coenzyme A synthase in LUCA could be compatible not only with being an autotroph but also with life as a mixotroph or heterotroph. Weiss et al. 2018 reply that no enzyme defines a trophic lifestyle, and that heterotrophs evolved from autotrophs.
Age
Studies from 2000 to 2018 have suggested an increasingly ancient time for the LUCA. In 2000, estimates of the LUCA's age ranged from 3.5 to 3.8 billion years ago in the Paleoarchean, a few hundred million years before the earliest fossil evidence of life, for which candidates range in age from 3.48 to 4.28 billion years ago. This placed the LUCA shortly after the Late Heavy Asteroid Bombardment which was thought to have repeatedly sterilized Earth's surface. However, a 2018 study from the University of Bristol, applying a molecular clock model, found that the data (102 species, 29 common protein-coding genes, mostly ribosomal) is compatible only with LUCA as early as within 0.05 billion years of the maximum possible age given by the Earth-sterilizing Moon-forming event about 4.5 billion years ago.Root of the tree of life
monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gro ...
domain
Domain may refer to:
Mathematics
*Domain of a function, the set of input values for which the (total) function is defined
**Domain of definition of a partial function
**Natural domain of a partial function
**Domain of holomorphy of a function
* Do ...
Bacteria and a clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
formed by Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
and Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the ...
. A small minority of studies place the root in the domain bacteria, in the phylum Bacillota, or state that the phylum Chloroflexota
The Chloroflexota are a phylum of bacteria containing isolates with a diversity of phenotypes, including members that are aerobic thermophiles, which use oxygen and grow well in high temperatures; anoxygenic phototrophs, which use light for photo ...
(formerly Chloroflexi) is basal
Basal or basilar is a term meaning ''base'', ''bottom'', or ''minimum''.
Science
* Basal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location for features associated with the base of an organism or structure
* Basal (medicine), a minimal level that is nec ...
to a clade with Archaea and Eukaryotes and the rest of bacteria (as proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith). Recent genomic analyses recover a two-domain system with the domains Archaea and Bacteria; in this view of the tree of life, Eukaryotes are derived from Archaea.
With the later gene pool of the LUCA's descendants, sharing a common framework of the AT/GC rule and the standard twenty amino acids, horizontal gene transfer would have become feasible and could have been common. In 1998, Carl Woese proposed that no individual organism could be considered a LUCA, and that the genetic heritage of all modern organisms derived through horizontal gene transfer among an ancient community of organisms. Other authors concur that there was a "complex collective genome" at the time of the LUCA, and that horizontal gene transfer was important in the evolution of later groups; Nicolas Glansdorff states that "Of course, LUCA was not living alone at that time (as the African Eve
In human genetics, the Mitochondrial Eve (also ''mt-Eve, mt-MRCA'') is the matrilineal most recent common ancestor (MRCA) of all living humans. In other words, she is defined as the most recent woman from whom all living humans descend in an un ...
herself) but among many other organisms that have no descendants today." In 2010, based on "the vast array of molecular sequences now available from all domains of life," a " formal test" of universal common ancestry was published. The formal test favored the existence of a universal common ancestor over a wide class of alternative hypotheses that included horizontal gene transfer. Basic biochemical principles make it overwhelmingly likely that all organisms do have a single common ancestor. While the test overwhelmingly favored the existence of a single LUCA, this does not imply that the LUCA was ever alone: Instead, it was the only cell whose descendants survived beyond the Paleoarchean, outcompeting all others.
LUCA's viruses
Based on how viruses are currently distributed across the bacteria andarchaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
, the LUCA may well have been prey to multiple viruses, ancestral to those that now have those two domains as their hosts. further, extensive virus evolution seems to have preceded the LUCA, since the jelly-roll structure of capsid proteins is shared by RNA and DNA viruses across all three domains of life. LUCA's viruses were probably mainly dsDNA viruses in the groups called '' Duplodnaviria'' and '' Varidnaviria''. Two other single-stranded DNA virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and t ...
groups within the '' Monodnaviria'', the '' Microviridae'' and the ''Tubulavirales
''Tubulavirales'' is an order of viruses.
Taxonomy
The following families are recognized:
* ''Inoviridae
Filamentous bacteriophage is a family of viruses (''Inoviridae'') that infect bacteria. The phages are named for their filamentous sha ...
'', likely infected the last bacterial common ancestor. The last archaeal common ancestor was probably host to spindle-shaped viruses. All of these could well have affected the LUCA, in which case each must since have been lost in the host domain where it is no longer extant.
By contrast, RNA viruses do not appear to have been important parasites of LUCA, even though straightforward thinking might have envisaged viruses as beginning with RNA viruses directly derived from an RNA world. Instead, by the time the LUCA lived, RNA viruses had probably already been out-competed by DNA viruses.
See also
* * *Darwinian threshold
Darwinian threshold or Darwinian transition is a term introduced by Carl Woese to describe a transition period during the evolution of the first Cell (biology), cells when Transmission (genetics), genetic transmission moves from a predominantly hor ...
- Transition period during the evolution of the first cells
*
*
*
*
Notes
References
Further reading
*External links
* {{Organisms et al. Origin of life Evolutionary biology Genetic genealogy Phylogenetics Hypothetical life forms Last common ancestors Events in biological evolution